An Innovative Design to Enhance Osteoinductive Efficacy and Biomechanical Behavior of a Titanium Dental Implant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Implants Preparation
2.2. Experimental Groups
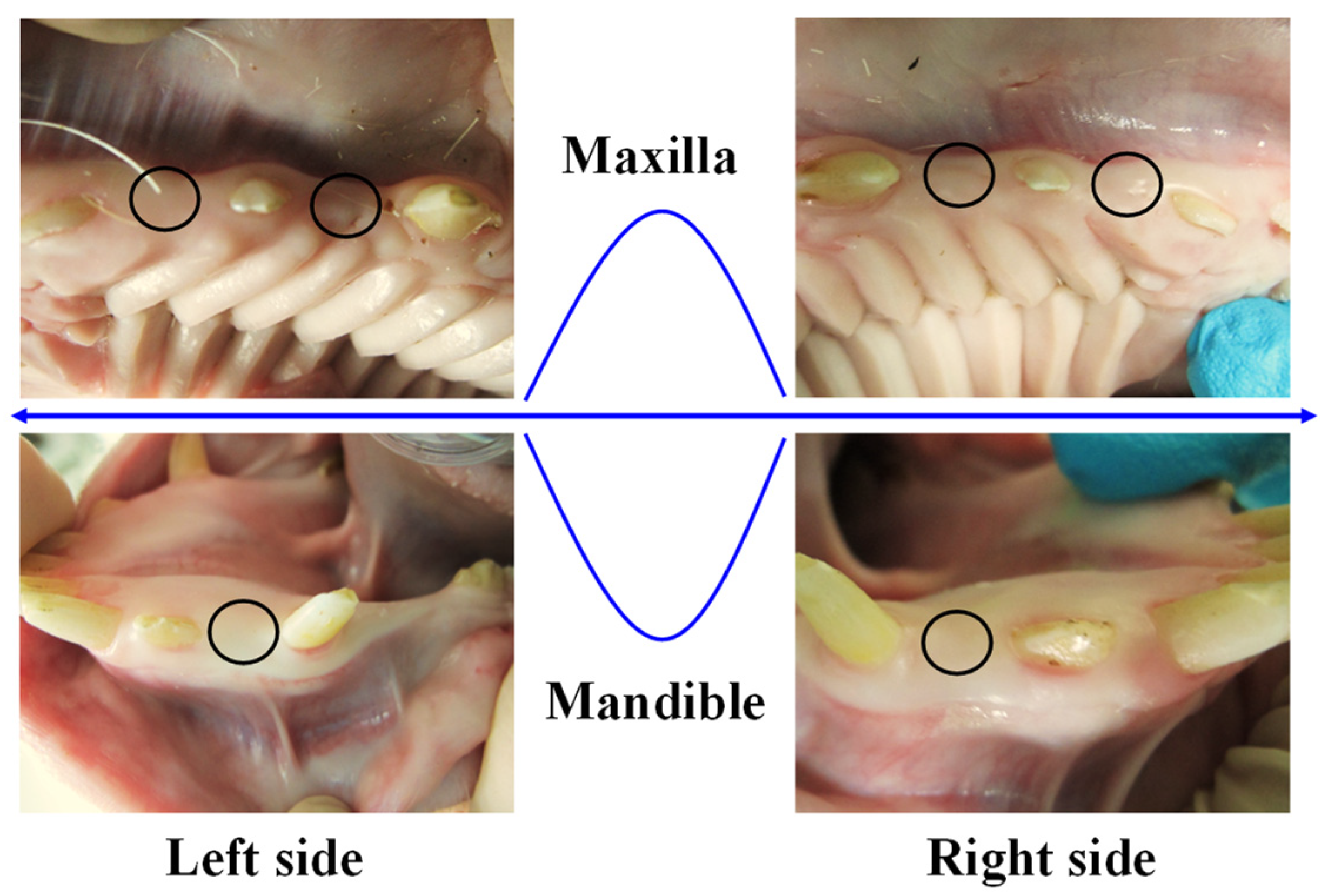
2.3. Experimental Animal Model
2.4. Evaluation of Bone Tissue Regeneration
2.5. Removal Torque Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
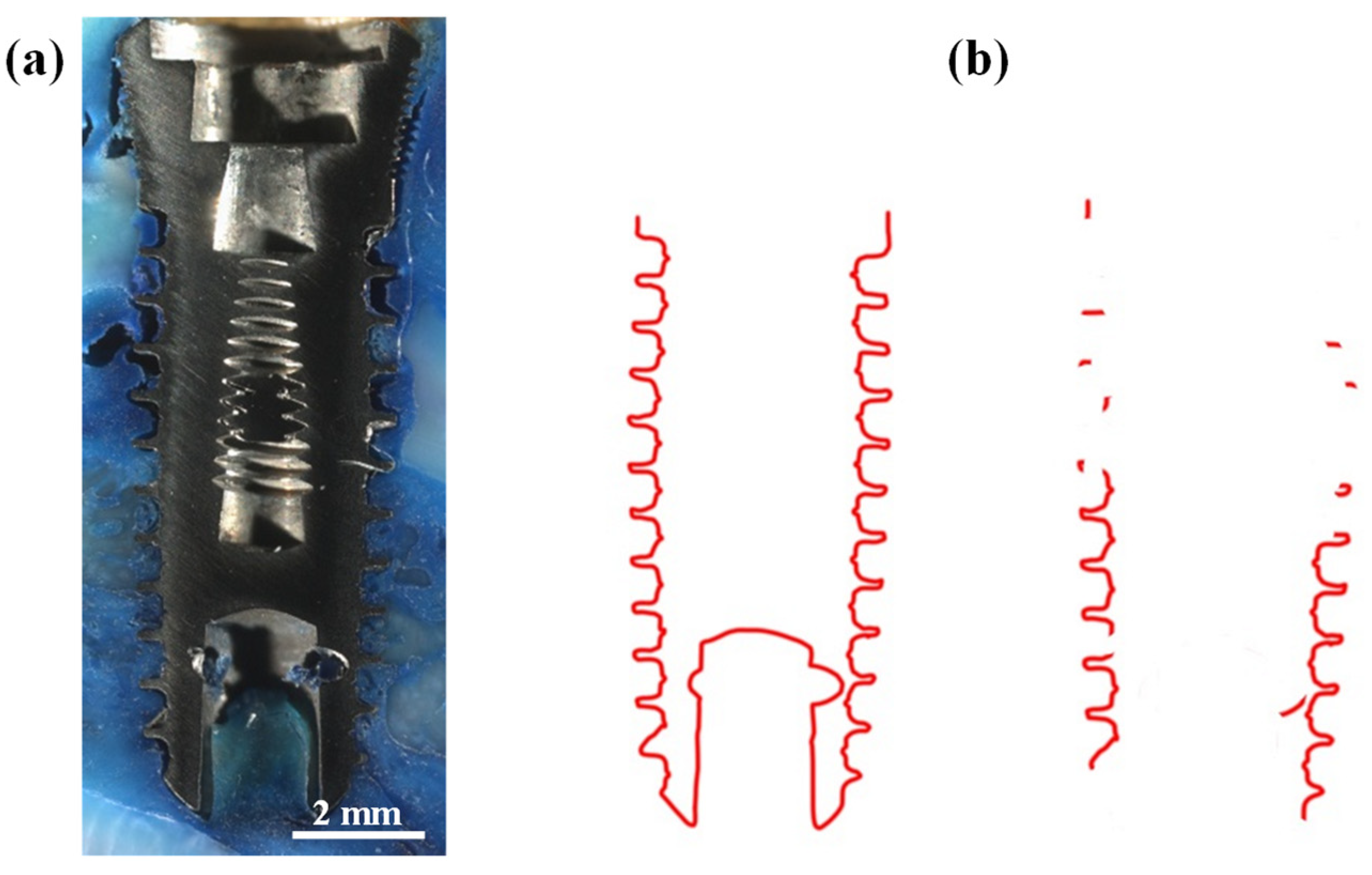
3.1. Implant Features
3.2. Radiograph Observation
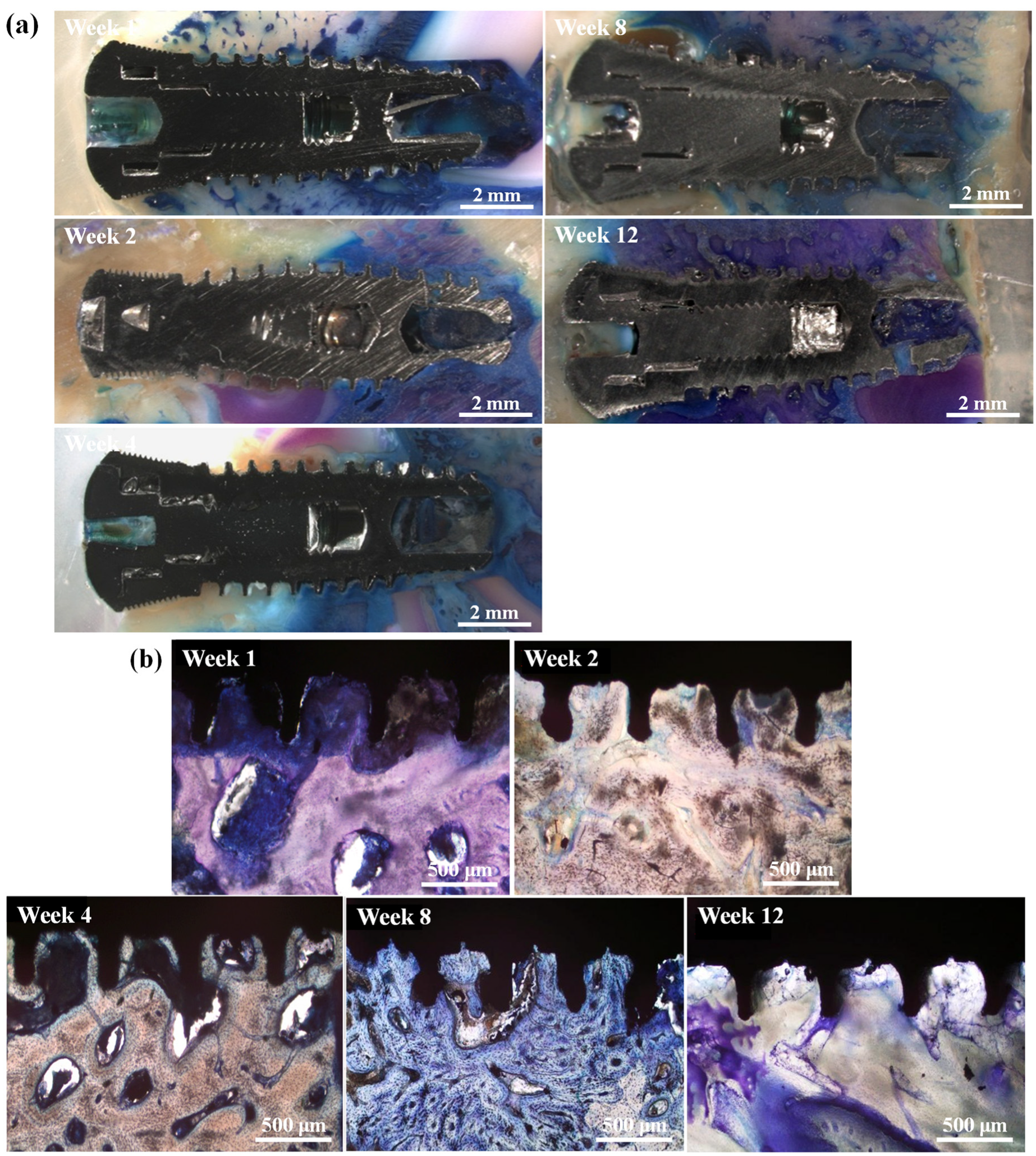
3.3. Histological Analysis
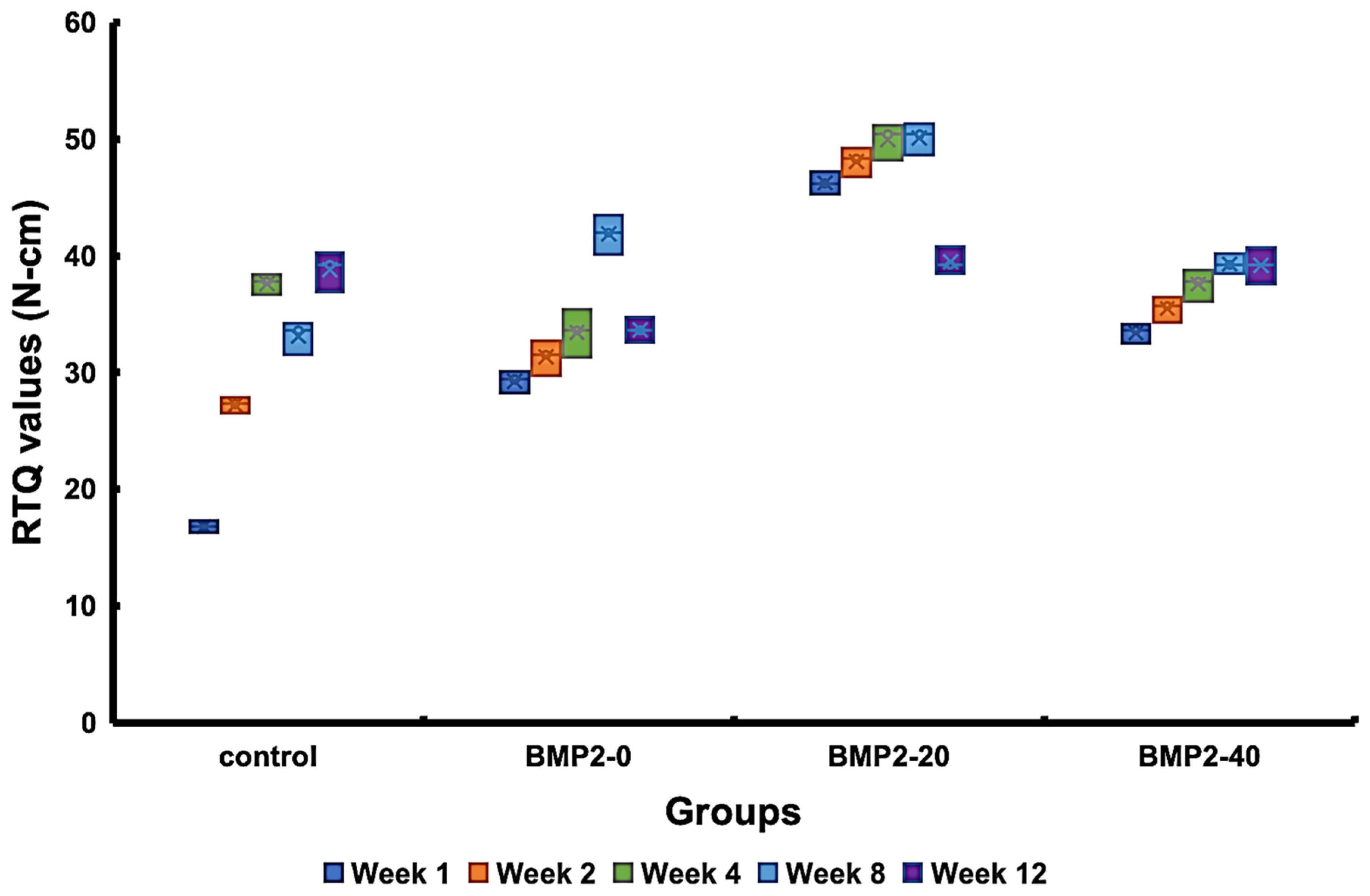
3.4. New Bone Formation and Biomechanical Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smeets, R.; Stadlinger, B.; Schwarz, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Jung, O.; Precht, C.; Kloss, F.; Gröbe, A.; Heiland, M.; Ebker, T. Impact of dental implant surface modifications on osseointegration. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6285620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, I.A.-W.; Ibrahim, W.; Iskandar, S.M.; AbdelNabi, N. Prognosis of dental implants in patients with low bone density: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-W.; Hahn, B.-D.; Kang, T.Y.; Lee, M.-J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, S.-G. Hydroxyapatite and collagen combination-coated dental implants display better bone formation in the peri-implant area than the same combination plus bone morphogenetic protein-2–coated implants, hydroxyapatite only coated implants, and uncoated implants. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.-C.; Chang, F.-M.; Yang, T.-S.; Ou, K.-L.; Lin, C.-T.; Peng, P.-W. Oxygen-implanted induced formation of oxide layer enhances blood compatibility on titanium for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asri, R.; Harun, W.; Samykano, M.; Lah, N.; Ghani, S.; Tarlochan, F.; Raza, M. Corrosion and surface modification on biocompatible metals: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, F.; Liang, L.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Scheideler, L.; Hüttig, F. Surface characteristics of dental implants: A review. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puleo, D.; Nanci, A. Understanding and controlling the bone–implant interface. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.; Kossenko, A.; Zinigrad, M.; Danchuk, V.; Sobolev, A. Cleaning Strategies of Synthesized Bioactive Coatings by PEO on Ti-6Al-4V Alloys of Organic Contaminations. Materials 2023, 16, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.; Seo, Y.-K.; Lee, J.-H. Effects of the combination of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and nano-hydroxyapatite on the osseointegration of dental implants. jkaoms 2021, 47, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Chen, P.; Zhao, Y.; Hang, R.; Yao, X.; Tang, B.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Hang, R. A micro/nano-biomimetic coating on titanium orchestrates osteo/angio-genesis and osteoimmunomodulation for advanced osseointegration. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öncü, E.; Bayram, B.; Kantarcı, A.; Gülsever, S.; Alaaddinoğlu, E.-E. Posıtıve effect of platelet rich fibrin on osseointegration. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Y Cir. Bucal 2016, 21, e601. [Google Scholar]
- Eawsakul, K.; Tancharoen, S.; Nasongkla, N. Combination of dip coating of BMP-2 and spray coating of PLGA on dental implants for osseointegration. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Zhang, W.; Shi, B.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced bone regeneration around dental implant with bone morphogenetic protein 2 gene and vascular endothelial growth factor protein delivery. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelić, D.; Finšgar, M. The role of growth factors in bioactive coatings. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, M.; Mundy, G.R. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors 2004, 22, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczewski, C.J.; Saul, J.M. Biomaterials for the delivery of growth factors and other therapeutic agents in tissue engineering approaches to bone regeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogisu, K.; Fujio, M.; Tsuchiya, S.; Tsuboi, M.; Qi, C.; Toyama, N.; Kamio, H.; Hibi, H. Conditioned media from mesenchymal stromal cells and periodontal ligament fibroblasts under cyclic stretch stimulation promote bone healing in mouse calvarial defects. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Karl, M.; Pendrys, D.; Shafer, D.; Freilich, M.; Kuhn, L. An evaluation of BMP-2 delivery from scaffolds with miniaturized dental implants in a novel rat mandible model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 97, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, M.; Li, R.; Friess, W. Collagen sponges for bone regeneration with rhBMP-2. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, R.; Park, J.; Felszeghy, E.; Wiltfang, J.; Nkenke, E.; Schlegel, K.A. Bone regeneration after topical BMP-2-gene delivery in circumferential peri-implant bone defects. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, D.; Geissler, U.; Hempel, U.; Bierbaum, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Worch, H.; Wenzel, K.W. Proliferation and differentiation of rat calvarial osteoblasts on type I collagen-coated titanium alloy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2002, 59, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begam, H.; Nandi, S.K.; Kundu, B.; Chanda, A. Strategies for delivering bone morphogenetic protein for bone healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Duan, Z.; Hui, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, D.; Fan, D.; Shang, L.; Chen, F. Newly designed human-like collagen to maximize sensitive release of BMP-2 for remarkable repairing of bone defects. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouxsein, M.; Turek, T.; Blake, C.; D’Augusta, D.; Li, X.; Stevens, M.; Seeherman, H.; Wozney, J. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 accelerates healing in a rabbit ulnar osteotomy model. JBJS 2001, 83, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Lee, C.; Fang, Y.; Choi, B.H. Immediate nonfunctional loading of implants placed simultaneously using computer-guided flapless maxillary crestal sinus augmentation with bone morphogenetic protein-2/collagen matrix. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zechner, W.; Tangl, S.; Fürst, G.; Tepper, G.; Thams, U.; Mailath, G.; Watzek, G. Osseous healing characteristics of three different implant types: A histologic and histomorphometric study in mini-pigs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumcuoglu Guvenc, D.; Fahmy-Garcia, S.; Ridwan, Y.; Nickel, J.; Farrell, E.; Kluijtmans, S.; van Osch, G. Injectable BMP-2 delivery system based on collagen-derived microspheres and alginate induced bone formation in a time-and dose-dependent manner. Eur. Cells Mater. 2018, 35, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Miyaji, H.; Ishizuka, R.; Tokunaga, K.; Inoue, K.; Kosen, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Sugaya, T.; Tanaka, S.; Sakagami, R. Combination of root surface modification with BMP-2 and collagen hydrogel scaffold implantation for periodontal healing in beagle dogs. Open Dent. J. 2015, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Enggist, L.; Kuffer, A.F.; Buser, D.; Hunziker, E.B. The influence of BMP-2 and its mode of delivery on the osteoconductivity of implant surfaces during the early phase of osseointegration. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, C.A.; Verri, F.R.; de Oliveira Neto, O.B.; Cruz, R.S.; Gomes, J.M.L.; da Silva Casado, B.G.; Pellizzer, E.P. Clinical effect of the high insertion torque on dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisi, P.; Perfetti, G.; Baldoni, E.; Berardi, D.; Colagiovanni, M.; Scogna, G. Implant micromotion is related to peak insertion torque and bone density. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eini, E.; Yousefimanesh, H.; Ashtiani, A.H.; Saki-Malehi, A.; Olapour, A.; Rahim, F. Comparing success of immediate versus delay loading of implants in fresh sockets: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 26, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Group | rhBMP-2 Concentration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 | Without collagen sponge and BMP-2 |
| BMP2-0 | 0 | Without BMP-2 |
| BMP2-20 | 20 μg/collagen sponge | 20 μg of BMP-2 infiltrating into the collagen sponge |
| BMP2-40 | 40 μg/collagen sponge | 40 μg of BMP-2 infiltrating into the collagen sponge |
| Ti | Si | O | C | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bal. | 1.23 ± 0.12 | 0.83 ± 0.23 | 0.21 ± 0.1 | <0.01 |
| Group | Histomorphometric Evaluation (n) | Biomechanical Analysis (n) | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1 | 2 | 7.5 |
| BMP2-0 | 0 | 4 | 10 |
| BMP2-20 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| BMP2-40 | 0 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Total | 2 | 10 | 7.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.-C.; Peng, P.-W.; Ou, Y.-S.; Liu, C.-M.; Huang, B.-H.; Lan, W.-C.; Kuo, H.-H.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Chen, B.; Huang, M.-S.; et al. An Innovative Design to Enhance Osteoinductive Efficacy and Biomechanical Behavior of a Titanium Dental Implant. Materials 2024, 17, 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102276
Cho Y-C, Peng P-W, Ou Y-S, Liu C-M, Huang B-H, Lan W-C, Kuo H-H, Hsieh C-C, Chen B, Huang M-S, et al. An Innovative Design to Enhance Osteoinductive Efficacy and Biomechanical Behavior of a Titanium Dental Implant. Materials. 2024; 17(10):2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102276
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Yung-Chieh, Pei-Wen Peng, Yu-Sin Ou, Chung-Ming Liu, Bai-Hung Huang, Wen-Chien Lan, Hsin-Hui Kuo, Chia-Chien Hsieh, Brian Chen, Mao-Suan Huang, and et al. 2024. "An Innovative Design to Enhance Osteoinductive Efficacy and Biomechanical Behavior of a Titanium Dental Implant" Materials 17, no. 10: 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102276
APA StyleCho, Y.-C., Peng, P.-W., Ou, Y.-S., Liu, C.-M., Huang, B.-H., Lan, W.-C., Kuo, H.-H., Hsieh, C.-C., Chen, B., Huang, M.-S., & Nakano, H. (2024). An Innovative Design to Enhance Osteoinductive Efficacy and Biomechanical Behavior of a Titanium Dental Implant. Materials, 17(10), 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102276






