Effect of Modifiers on Self-Healing and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dynamic Shear Rheometer Test
2.2. Multiple-Stress Creep Recovery Test
2.3. Healing Test
- G0 is the initial dynamic shear modulus during the first loading;
- Ga is the dynamic shear modulus at the end of the first loading;
- Gb is the dynamic shear modulus before the second loading.
3. Results and Discussion
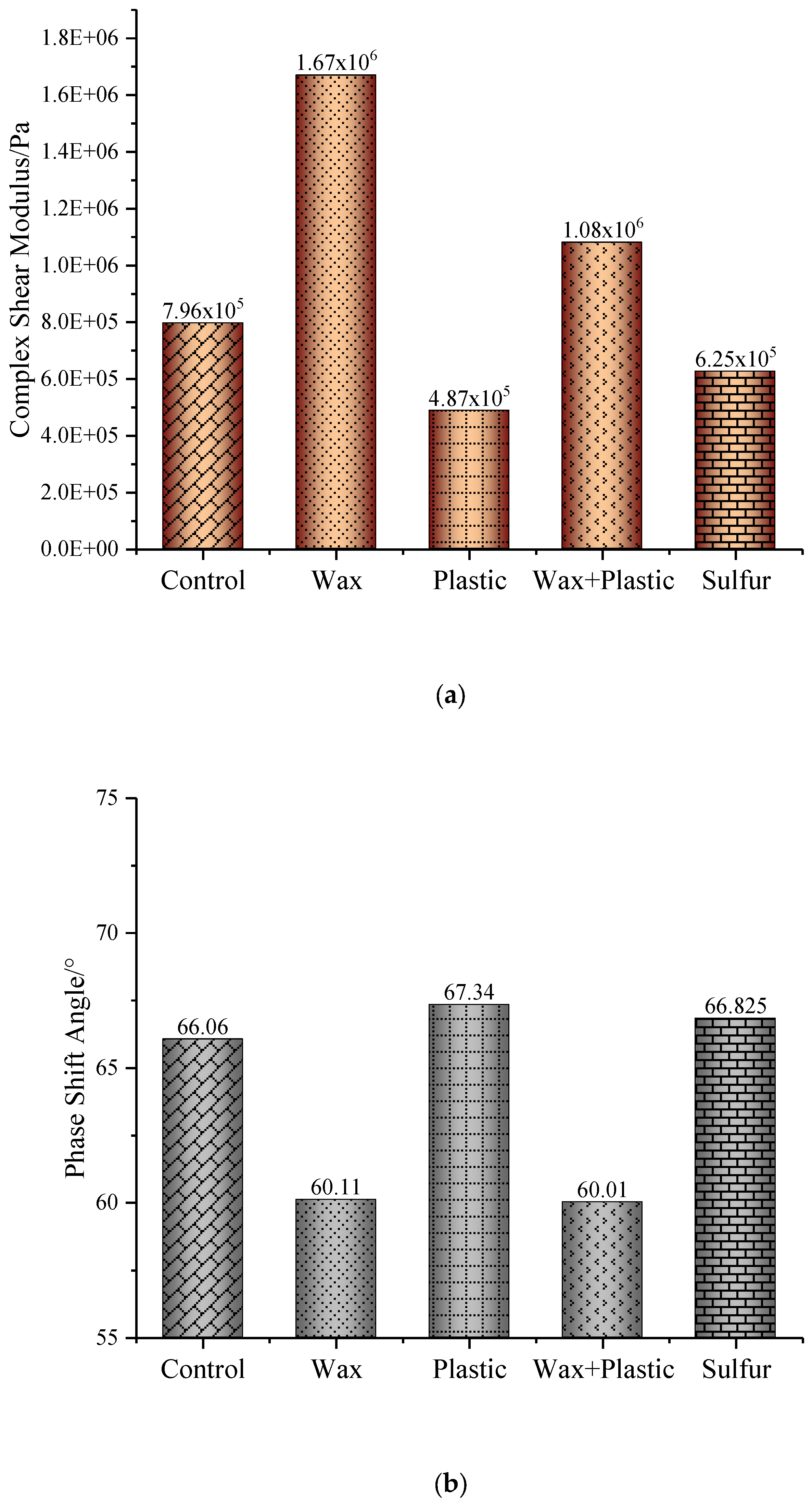
3.1. Rheological Properties of Binders
3.2. Elastic Response Property of Binders
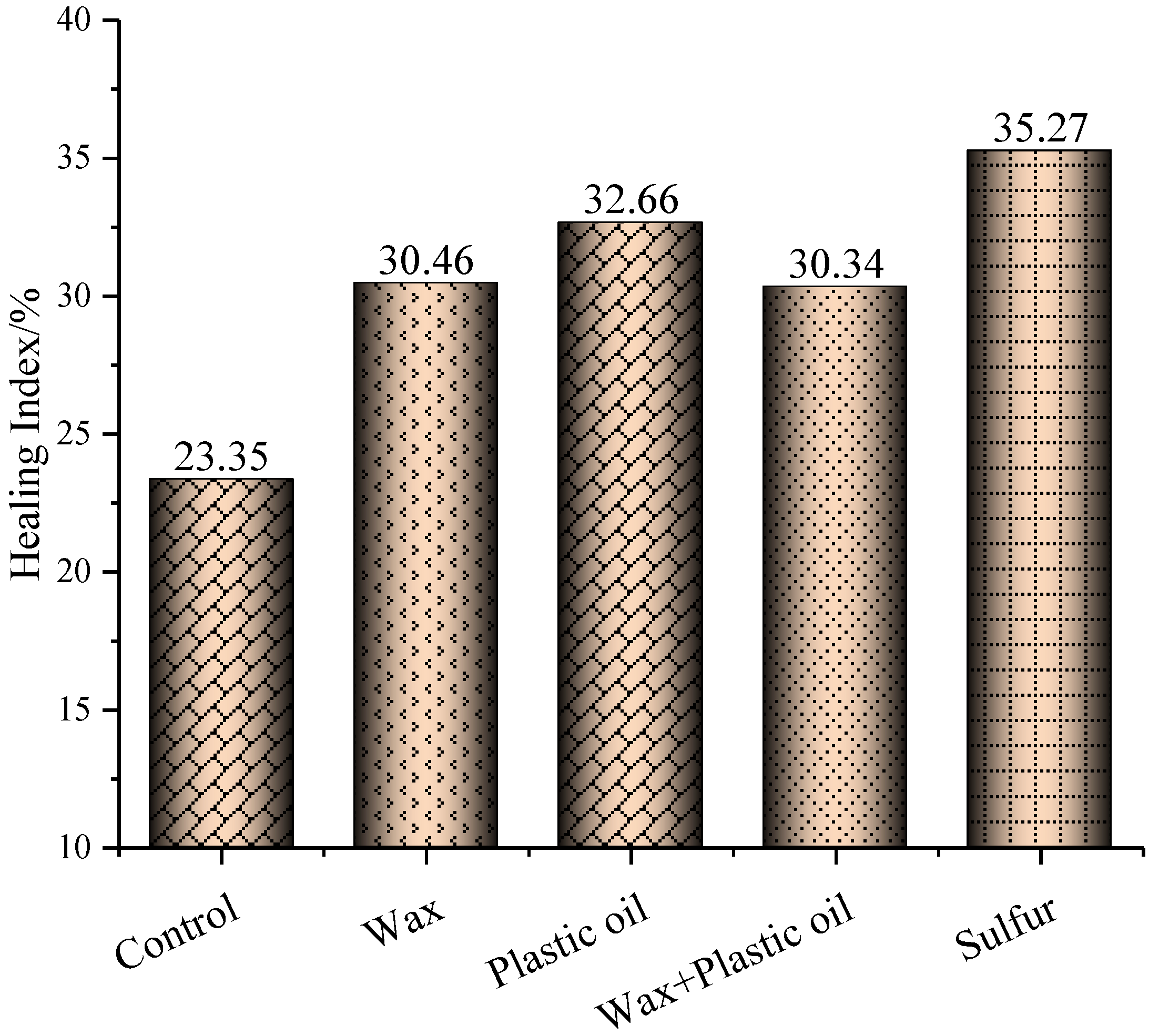
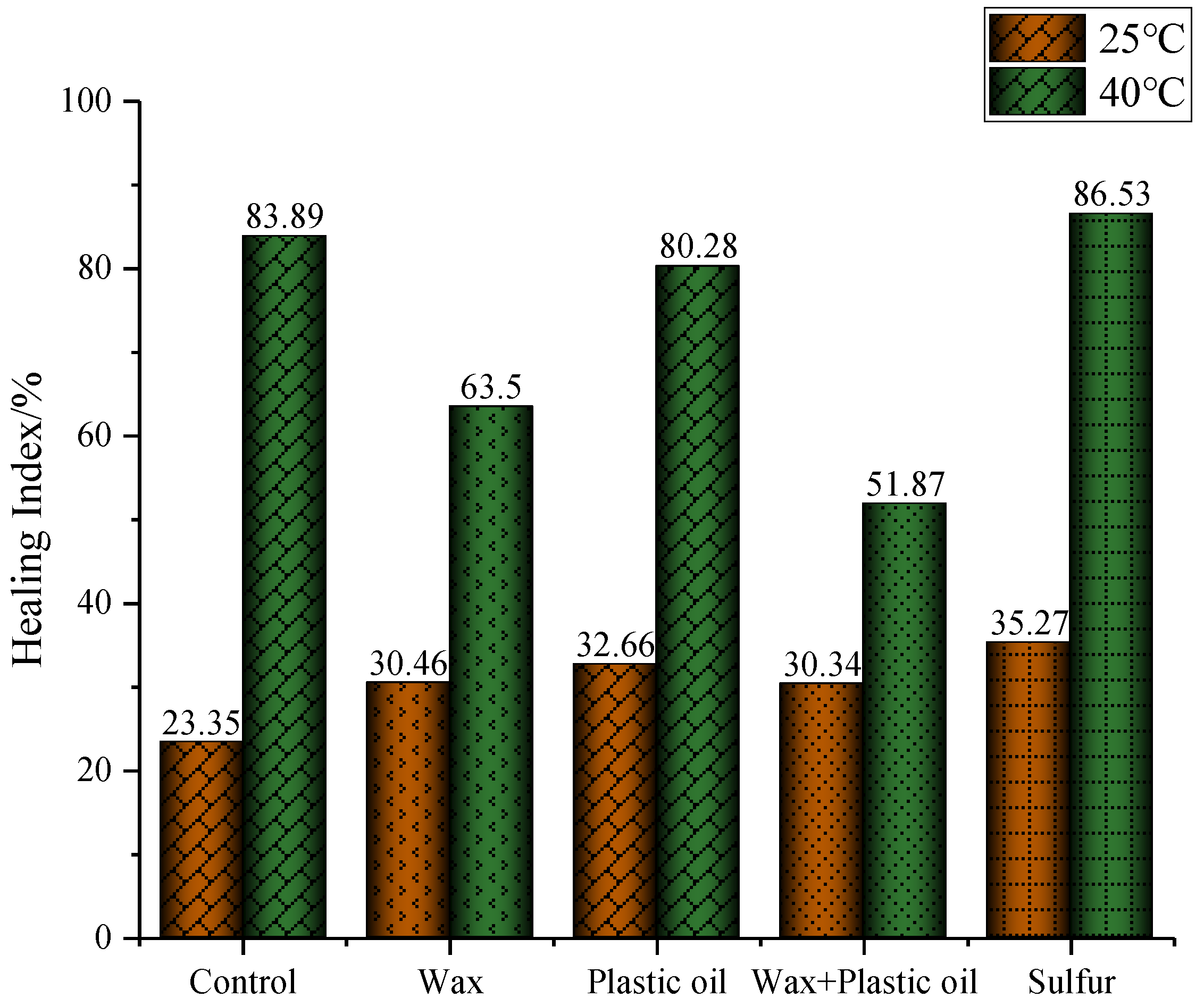
3.3. Self-Healing Property of Binders
4. Conclusions
- Adding each of the modifiers to asphalt binder increased its healing capacity at 25 °C. Among the four modifiers, sulfur provided the greatest improvement in healing capacity, followed by plastic oil, wax with plastic oil, and wax. Sulfur’s performance was attributed to sulfur’s plasticizing effect, which facilitates the self-diffusion of asphalt binder molecules.
- Sulfur modifier can improve the healing performance, but the other three modifiers (especially wax) weakened the healing performance of asphalt binder at 40 °C. In terms of percent recoverable strain, wax showed the highest percent, while the other additives did not show significant changes relevant to control asphalt binder.
- The wax-modified asphalt binder had the highest complex shear modulus compared to the other three modified binders and control binder. And its phase angle was lower than that of plastic oil-, sulfur-modified asphalt binder, and control binder. The latter improvement is attributed to wax crystallization, which aligns with the findings of prior studies.
- The significantly higher complex modulus of the asphalt binder modified with wax compared to modifying with plastic oil is attributed to the crystallizing ability of the wax’s alkane molecules. The alkanes in plastic oil range from C13 to C20 molecules; the alkanes in wax are C50 molecules, which are more prone to crystallization at typical service temperatures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Polaczyk, P.; Park, H.; Jiang, X.; Hu, W.; Huang, B. Performance evaluation of temperature effect on hot in-place recycling asphalt mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, M.T.; Shbeeb, L. The use of polyethylene in hot asphalt mixtures. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 4, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; Mi, X. Combined modification of asphalt with polyethylene packaging waste and organophilic montmorillonite. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isacsson, U.L.F.; Lu, X. Characterization of bitumens modified with SEBS, EVA and EBA polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 3737–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Morales, M.; Partal, P.; Navarro, F.J.; Gallegos, C. Effect of waste polymeraddition on the rheology of modified bitumen. Fuel 2006, 85, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Morales, M.; Partal, P.; Navarro, F.J.; Martínez-Boza, F.; Gallegos, C.; Gonzalez, N.; Gonzlez, O.; Mufoz, M.E. Viscous properties and microstructure of recycled eva modified bitumen. Fuel 2004, 83, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samieadel, A.; Schimmel, K.; Fini, E.H. Comparative life cycle assessment (LCA) of bio-modified binder and conventional asphalt binder. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Poulikakos, L.; Frank, R. Influence of six rejuvenators on the performance properties of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) binder and 100% recycled asphalt mixtures. Construct. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmae, K.A.; Abdullah, M.E.; Nda, M.; Usman, N.; Hassan, N.A. Effect of Bio based rejuvenator on Permanent Deformation of Aged Asphalt. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2018, 10, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zargar, M.; Ahmadinia, E.; Asli, H.; Karim, M.R. Investigation of the possibility of using waste cooking oil as a rejuvenating agent for aged asphalt. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asli, H.; Karim, M.R. Effect of waste cooking oil as a rejuvenating agent for aged bituminous pavement. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Geotechnical and Transportation Engineering, Stirling, UK, 19–21 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhri, M.; Bahmai, B.B.; Javadi, S.; Sharafi, M. An evaluation of the mechanical and self-healing properties of warm mix asphalt containing scrap metal additives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnaure, F.P.; Huibers, A.H.J.J.; Boonders, A. A laboratory investigation of the influence of rest periods on the fatigue characteristics of bituminous mixes (with discussion). In Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists Proceedings; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; Volume 51. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, M.; Sánchez, J.A. Fatigue and healing of asphalt mixtures: Discriminate analysis of fatigue curves. J. Transp. Eng. 2006, 132, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, H.U.; Zhai, H.; Bonnetti, K.; Kose, S. Non-linear viscoelastic and fatigue properties of asphalt binders. J. Assoc. Asphalt Paving Technol. 1998, 68, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Little, D.N.; Lytton, R.L.; Williams, D.; Chen, C.W. Microdamage Healing in Asphalt and Asphalt Concrete, Volume 1: Microdamage and Microdamage Healing, Project Summary Report; Rep. No. FHWARD-98-141; Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bhasin, A.; Little, D.N.; Bommavaram, R.; Vasconcelos, K.L. A framework to quantify the effect of healing in bituminous materials using material properties. Int. J. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2008, 8, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tabaković, A.; Liu, X.; Schlangen, E. Calcium alginate capsules encapsulating rejuvenator as healing system for asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daquan, S.; Qi, P.; Xingyi, Z.; Yang, T.; Tong, L.; Yang, Y. Enhanced Self-Healing Process of Sustainable Asphalt Materials Containing Microcapsules. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9881–9893. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Han, N.X.; Yang, P.; Han, S. Experimental investigation and mechanism analysis of novel multi-self-healing behaviors of asphalt using microcapsules containing rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Tam, A.B.; Kim, J.; Park, D.-W. Evaluation of rejuvenators based on the healing and mechanistic performance of recycled asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.F.; Schlangen, E.; Wang, Y.Y. Investigation the self-healing mechanism of aged asphalt using microcapsules containing rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 85, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.M.; Mousavi, M.; Fini, E.H. Implication of wax on hindering self-healing processes in asphalt. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 523, 146–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM-D7405–15; Standard Test Method for Multiple Stress Creep and Recovery (MSCR) of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ASTM-D7552-09; Standard Test Method for Determining the Complex Shear Modulus (G*) of Bituminous Mixtures Using Dynamic Shear Rheometer. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Chen, L.X.; Xiang, H.; He, Z.Y.; Wang, D.M.; Xu, X.X. Analysis of self-healing evaluation index of asphalt cement based on DSR. J. Build. Mater. 2019, 22, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Mannan, U.; Ahmad, A.M.; Tarefder, R.A. Influence of moisture conditioning on healing of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Q.; Lin, T.F. Influence of Modifiers on Asphalt Self-healing Property. Highway 2015, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlavan, F.; Mousavi, M.; Hung, A.; Fini, E.H. Investigating molecular interactions and surface morphology of wax-doped asphaltenes. J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 8840–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Lv, Q.; Xiao, F. Investigation of using binder bond strength test to evaluate adhesion and self-healing properties of modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, A.; Bommavaram, R.; Greenfield, M.L.; Little, D.N. Use of Molecular Dynamics to Investigate Self-Healing Mechanisms in Asphalt Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.K.; Burnham, N.A.; Tao, M.J. Surface microstructure of bitumen characterized by atomic force microscopy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 218, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.M.; Fini, E.H. AFM study of asphalt binder “bee” structures: Origin, mechanical fracture, topological evolution, and experimental artifacts. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 96972–96982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, M. Effect of Modifiers on Self-Healing and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder. Materials 2024, 17, 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133304
Zhu Q, Liu C, Wang Y, Su Y, Li M. Effect of Modifiers on Self-Healing and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder. Materials. 2024; 17(13):3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133304
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Qipeng, Cuiran Liu, Yanhong Wang, Yanzhen Su, and Mingxia Li. 2024. "Effect of Modifiers on Self-Healing and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder" Materials 17, no. 13: 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133304
APA StyleZhu, Q., Liu, C., Wang, Y., Su, Y., & Li, M. (2024). Effect of Modifiers on Self-Healing and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder. Materials, 17(13), 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133304




