Comparison on the Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Ti6Al4V Alloys Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Casting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
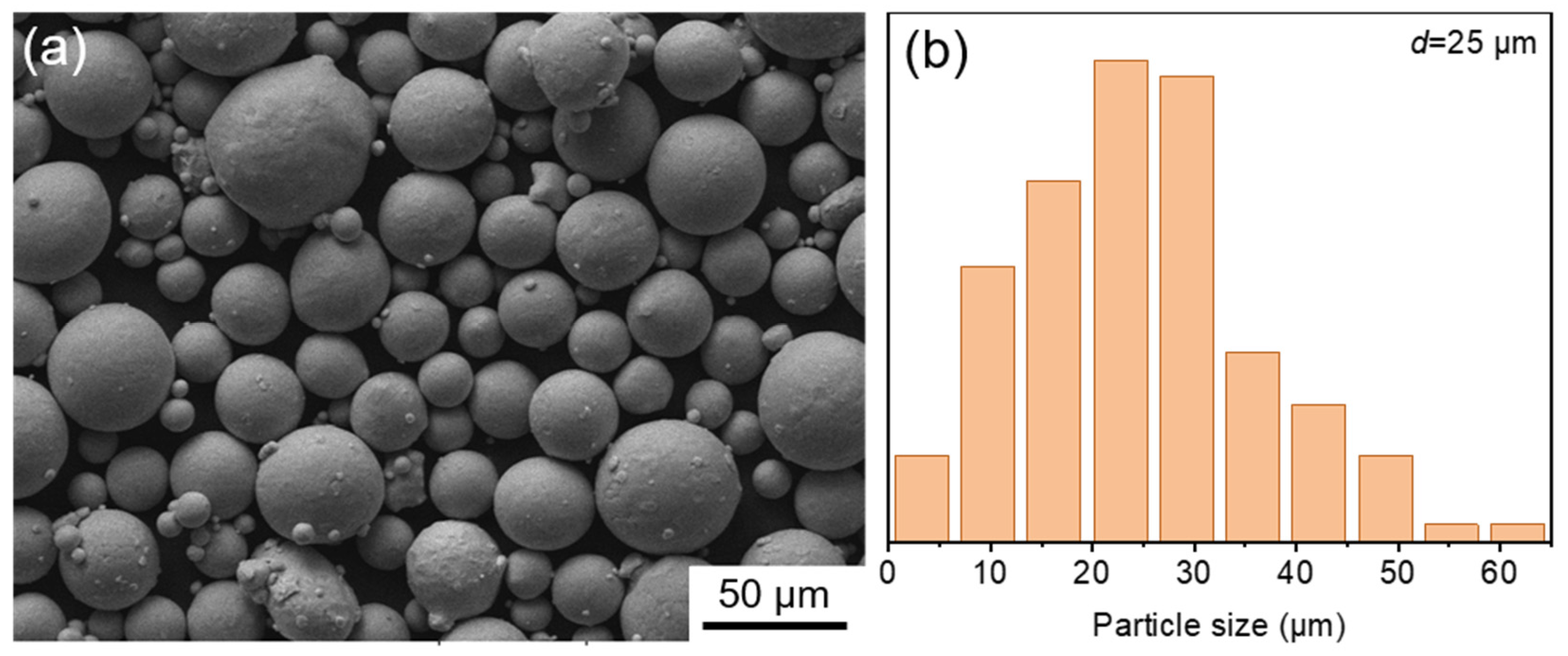
2.1. Materials and LPBF Processing
2.2. Microstructural Characterizations
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
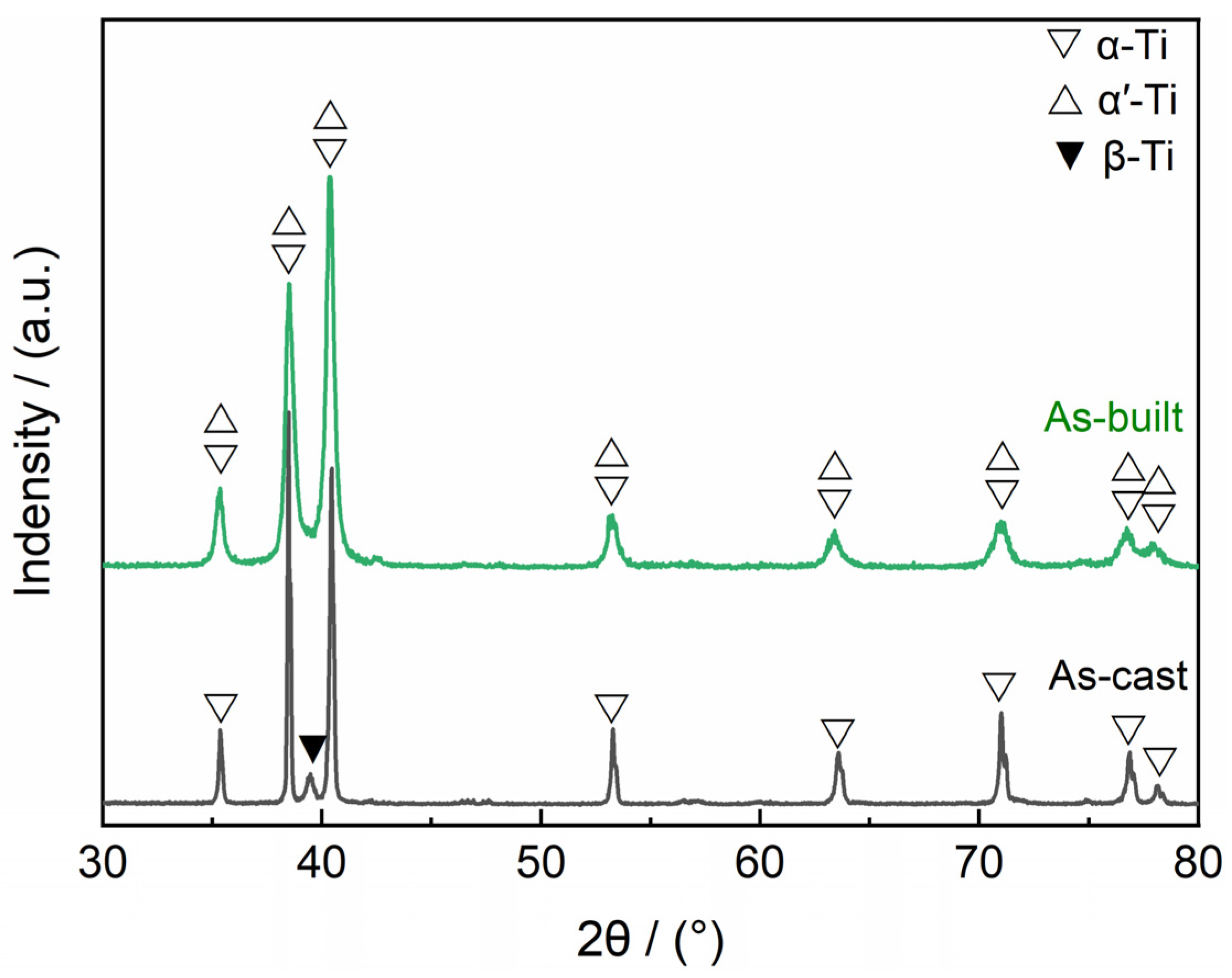
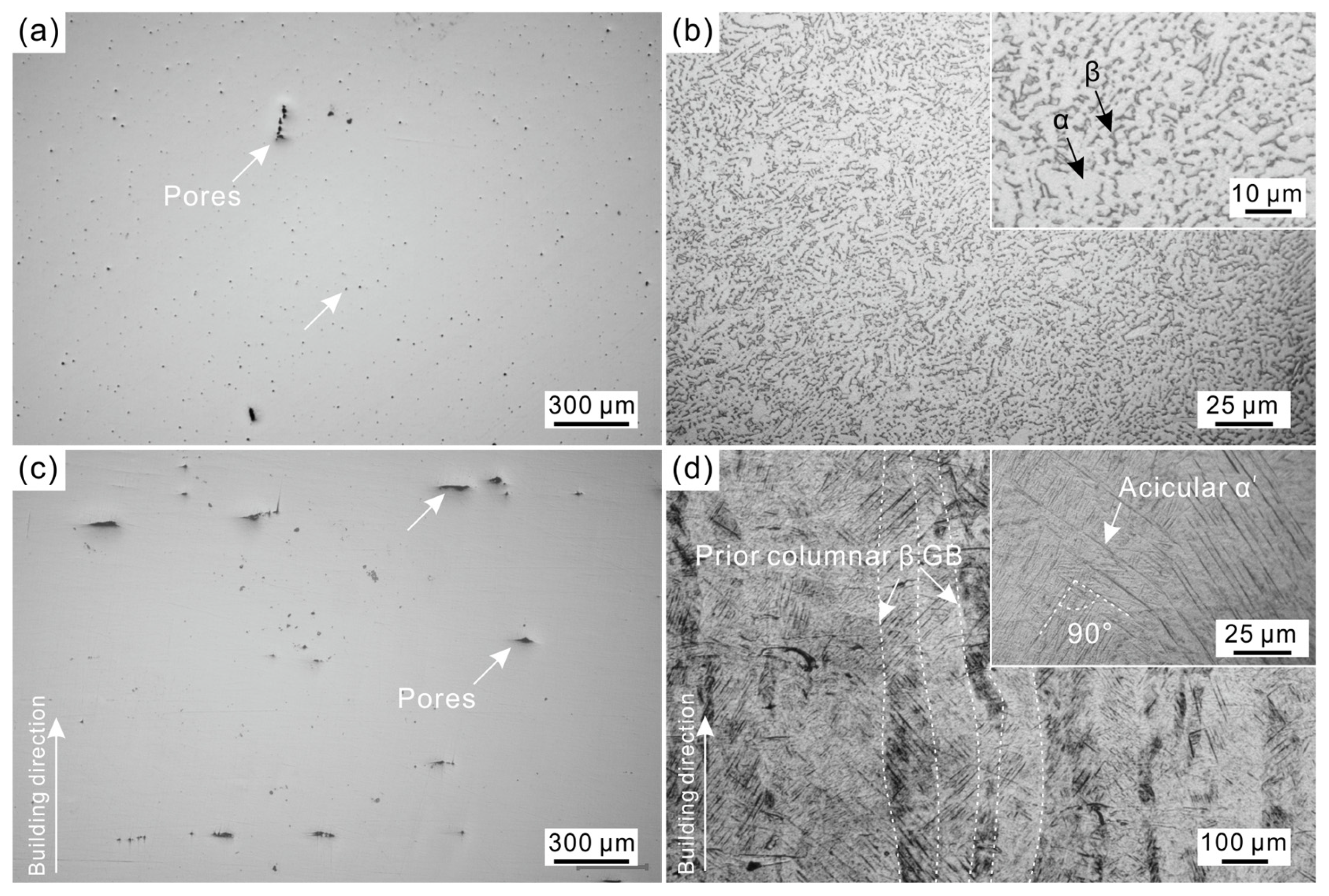
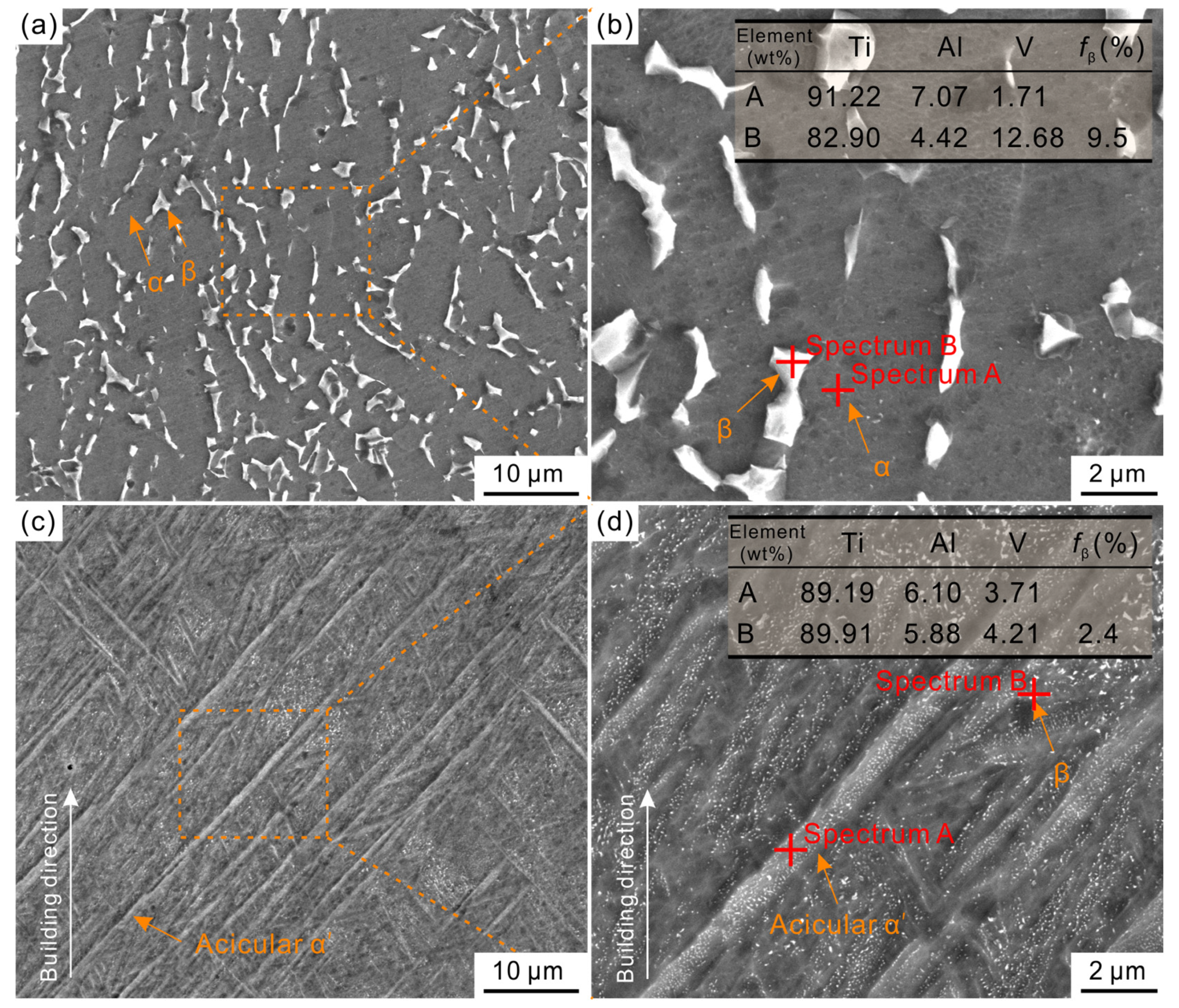
3.1. Microstructural Analysis of As-Cast and As-Built Ti6Al4V Alloys
3.2. Potentiodynamic Polarization Test Results of As-Cast and As-Built Ti6Al4V Alloys
3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of As-Cast and As-Built Ti6Al4V Alloys
3.4. Discussion on Corrosion Behavior for As-Cast and As-Built Ti6Al4V Alloys
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The LPBF-processed Ti6Al4V alloy dominates by acicular α′ martensite along with only a small amount of β-Ti phase, while the cast Ti6Al4V alloy exhibits an α + β dual-phase structure. Furthermore, LPBF-processed Ti6Al4V alloy possesses a higher porosity than cast Ti6Al4V alloy.
- (2)
- Compared to the as-cast Ti6Al4V alloy, LPBF-processed Ti6Al4V alloy has worse corrosion resistance, especially the pitting corrosion resistance. The passive film of LPBF-processed Ti6Al4V alloy is thinner (2.02 nm) and unstable, the passivation current density is about ten times that of the as-cast sample and the value of Rf and Rct are also smaller than that of the as-cast Ti6Al4V alloy.
- (3)
- The poor corrosion resistance of LPBF-processed Ti6Al4V alloy should be attributed to a large number of pores, less β and a large number of acicular α′ martensite. The presence of pores disrupts the integrity of the passive film, while the presence of the acicular α′ martensite phase accelerates the dissolution of the passive film.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N. Microstructural evolution, mechanical and tribological properties of TiC/Ti6Al4V composites with unique microstructure prepared by SLM. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 814, 141187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Qiao, L.; Yan, Y. Anisotropy of wear and tribocorrosion properties of L-PBF Ti6Al4V. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 2690–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Qin, P.; Liu, Y.J.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhang, L.C. Advances in additively manufactured titanium alloys by powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition: Microstructure, defects, and mechanical behavior. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 183, 32–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Shi, X.; Poprawe, R.; Bourell, D.L.; Setchi, R.; Zhu, J. Material-structure-performance integrated laser-metal additive manufacturing. Science 2021, 372, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Hutchinson, C.; Ramamurty, U. Mesostructure engineering in additive manufacturing of alloys. Scr. Mater. 2023, 230, 115429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.X.Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhan, S.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Cao, S.C. Biomedical applications of the powder-based 3D printed titanium alloys: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 125, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijs, L.; Verhaeghe, F.; Craeghs, T.; Humbeeck, J.V.; Kruth, J.-P. A study of the microstructural evolution during selective laser melting of Ti–6Al–4V. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3303–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, G.P.; Song, L.; Mazumder, J. Fabrication of Ti-6Al-4V Scaffolds by Direct Metal Deposition. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2914–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, P.; Huang, W. Distinction in electrochemical behaviour of Ti6Al4V alloy produced by direct energy deposition and forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 860, 157912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, E.; Ghio, E.; Bolelli, G. Effect of surface roughness and industrial heat treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion in different built orientations. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 851, 143635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, X. Corrosion Behavior of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy in NaCl Solution. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 3583–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shi, S. Electrochemical properties and dissolved behavior of laser solid formed Ti6Al4V alloy in NaCl solution with different current densities. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, N.; Zhang, L.-C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, M. Corrosion behavior of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4 V alloy in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Xu, H.; Zhong, Q. The influence of process parameters on corrosion behavior of Ti6Al4V alloy processed by selective laser melting. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 032010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Sanchez, H.; Collado-Vian, M.; Mohedano, M.; Arrabal, R.; Matykina, E. Corrosion of an Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V Alloy in Saline and Acidic Media. Materials 2024, 17, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toptan, F.; Alves, A.C.; Carvalho, Ó.; Bartolomeu, F.; Pinto, A.M.P.; Silva, F.; Miranda, G. Corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviour of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting and hot pressing in comparison with the commercial alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 266, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Brandt, M.; Sun, S.; Elambasseril, J.; Liu, Q.; Latham, K.; Xia, K.; Qian, M. Additive manufacturing of strong and ductile Ti–6Al–4V by selective laser melting via in situ martensite decomposition. Acta Mater. 2015, 85, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.; Bolot, R.; Lupoi, R.; Kuang, M.; Ma, W.; Coddet, C.; Liao, H.; et al. Effect of heat treatment on the phase transformation and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Lin, F. A study of the microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V fabricated by SLM under vacuum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 724, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, B.; Wei, Q.; Bourell, D.; Shi, Y. A review of selective laser melting of aluminum alloys: Processing, microstructure, property and developing trends. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, C.; Le Guen, E.; Lacoste, E.; Arvieu, C. Main defects observed in aluminum alloy parts produced by SLM: From causes to consequences. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Gu, D. Molten pool behaviour and its physical mechanism during selective laser melting of TiC/AlSi10Mg nanocomposites: Simulation and experiments. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 035303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Xu, A.; Dong, C.; Mao, F.; Xiao, K.; Li, X.; Macdonald, D.D. Electrochemical investigation and ab initio computation of passive film properties on copper in anaerobic sulphide solutions. Corros. Sci. 2017, 116, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J. Is niobium more corrosion-resistant than commercially pure titanium in fluoride-containing artificial saliva? Electrochim. Acta 2017, 233, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, J.X.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.S.; Chen, B. Study on corrosion resistance of artificially aged 7075 aluminium alloy by using Cs-corrected STEM. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 2828–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Nickchi, T.; Attar, M.M.; Alfantazi, A. EIS study of potentiostatically formed passive film on 304 stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta. 2011, 56, 8727–8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, É.; Azzi, M.; Salishchev, G.A.; Szpunar, J. Influence of microstructure and texture on the corrosion and tribocorrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Prasad, A.; Bermingham, M.J.; Todaro, C.J.; Benoit, M.J.; Patel, M.N.; Qiu, D.; Stjohn, D.H.; Qian, M.; Easton, M.A. Grain refinement of alloys in fusion-based additive manufacturing processes. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 4341–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gu, D. Parametric analysis of thermal behavior during selective laser melting additive manufacturing of aluminum alloy powder. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-R.; Tsai, W.-T. In situ corrosion monitoring of Ti–6Al–4V alloy in H2SO4/HCl mixed solution using electrochemical AFM. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
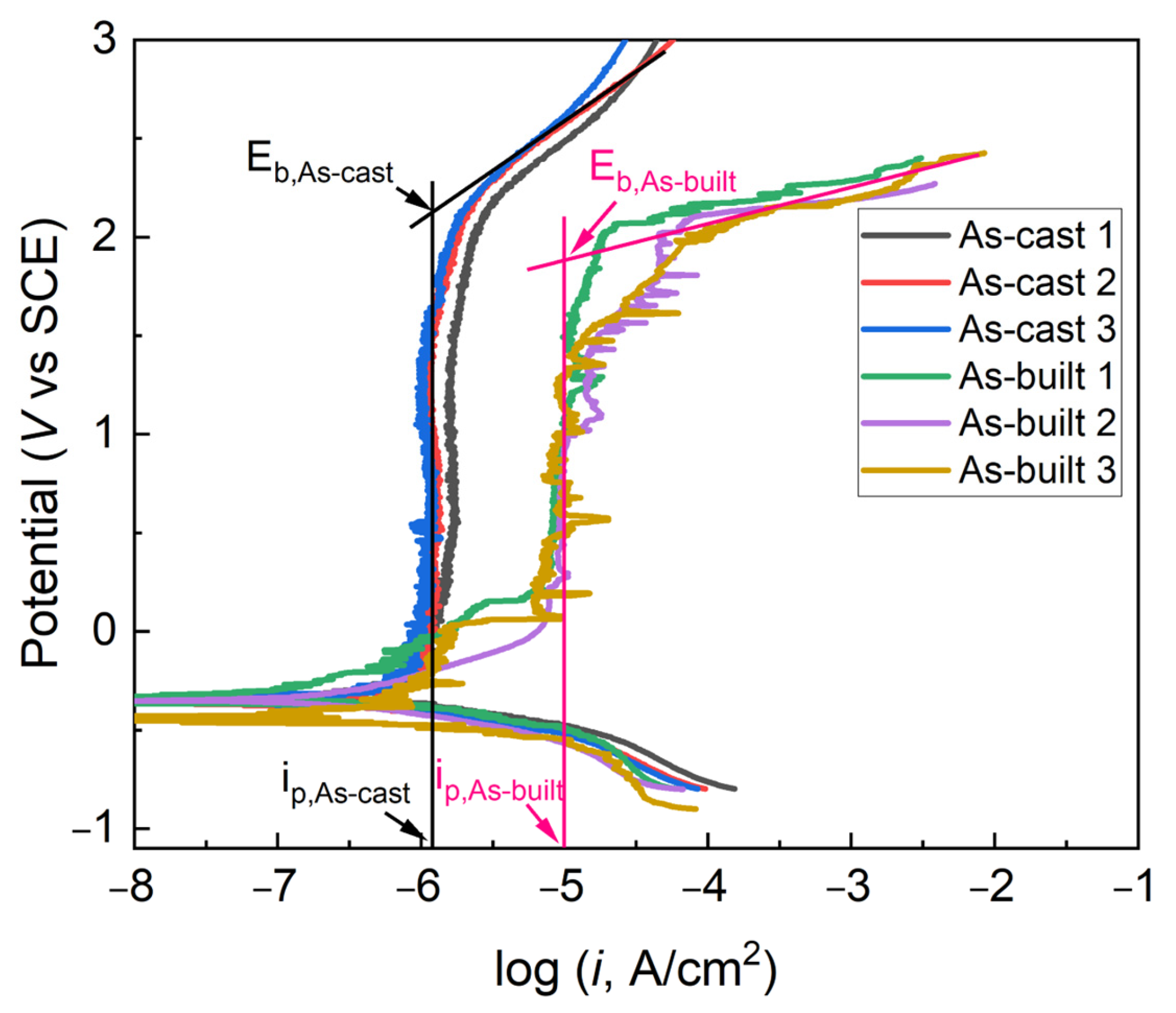
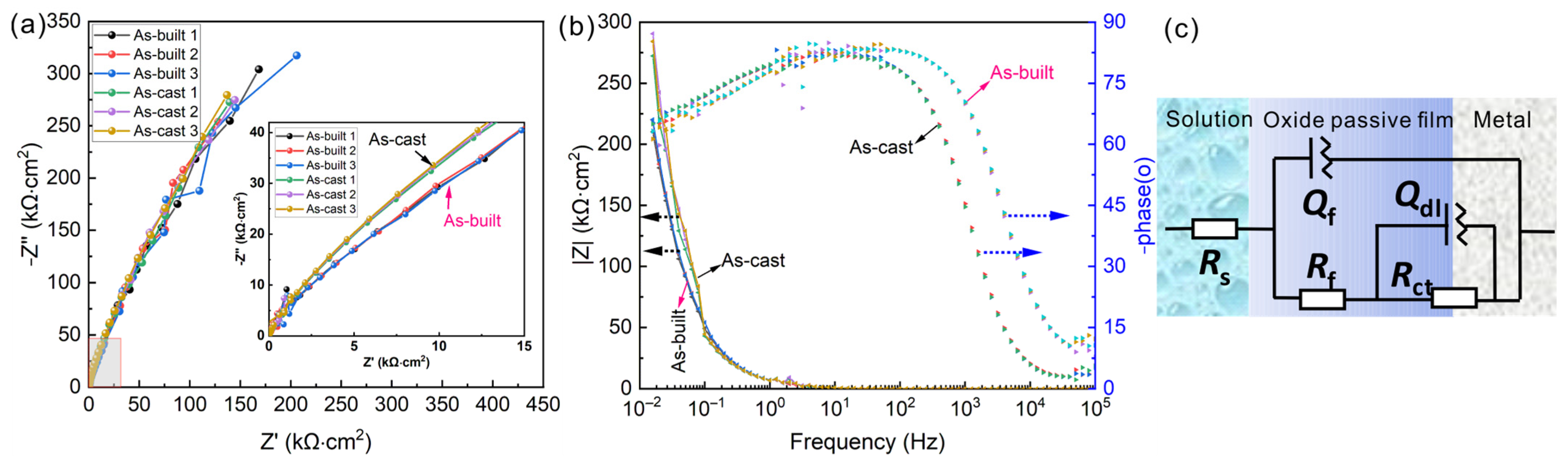
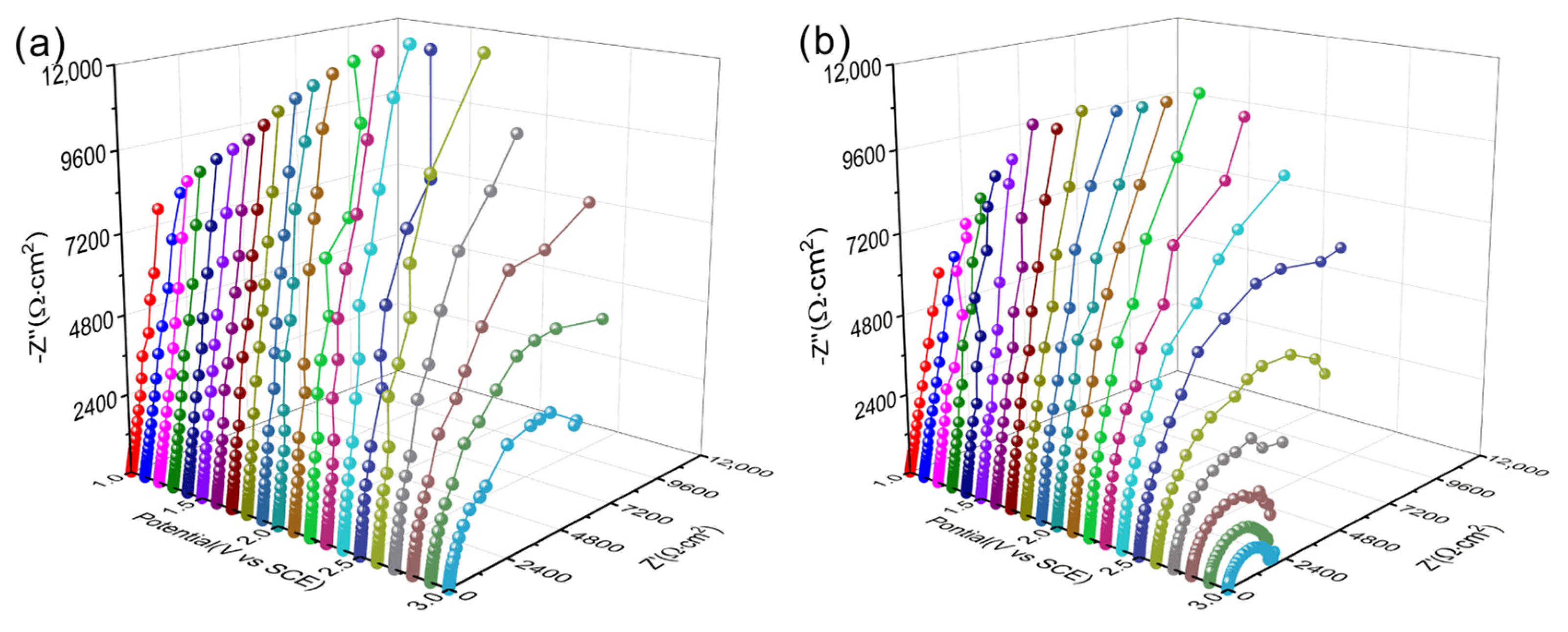
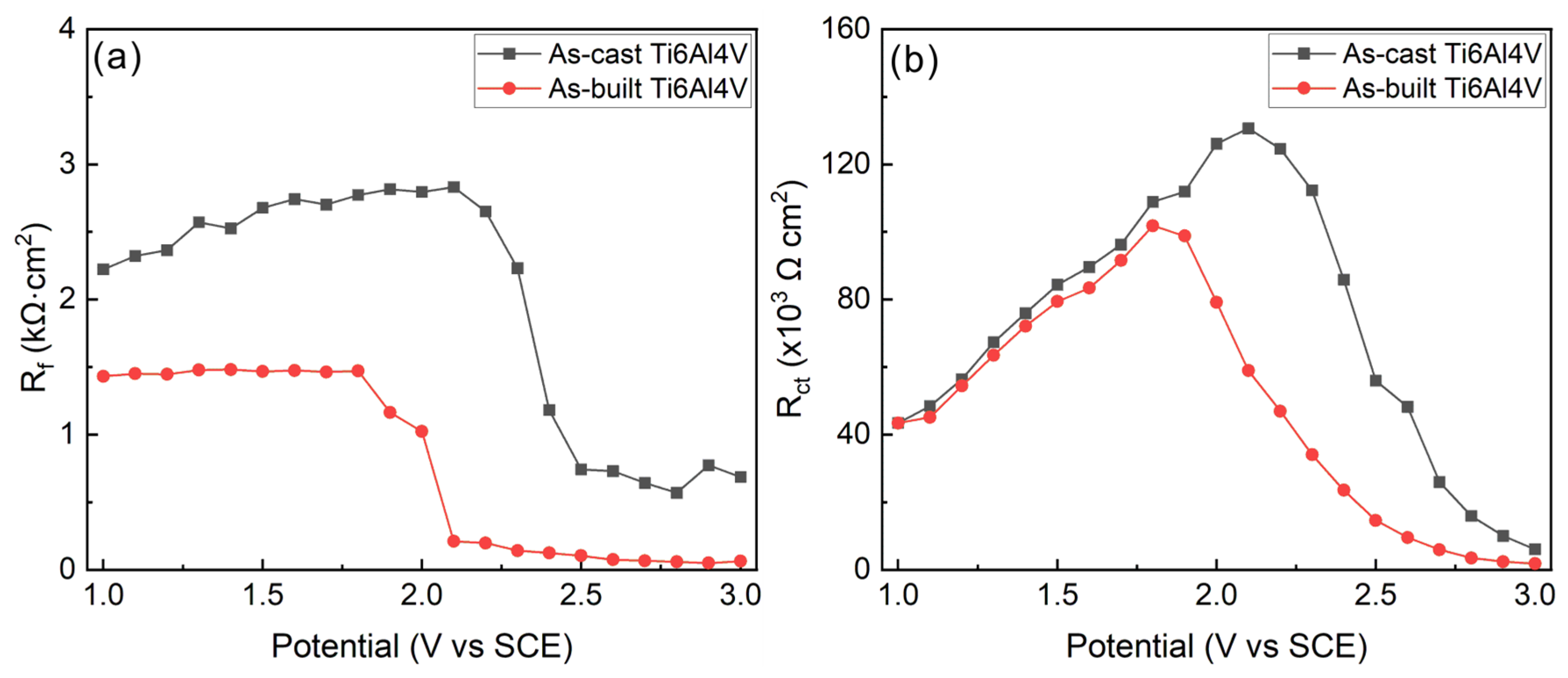

| Sample | Ecorr/V | icorr/μA∙cm−2 | Eb/V | ip/μA∙cm−2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast | −0.341 ± 0.018 | 0.92 ± 0.06 | 2.054 ± 0.089 | 1.28 ± 0.34 |
| As-built | −0.389 ± 0.046 | 1.11 ± 0.24 | 1.979 ± 0.094 | 11.21 ± 1.15 |
| Sample | Rf (kΩ·cm2) | Qf × 10−5 (Ω−1·Sn·cm−2) | nf | Rct (MΩ·cm2) | Qdl × 10−5 (Ω−1·Sn·cm−2) | ndl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast | 36.72 ± 2.90 | 1.792 ± 0.089 | 0.980 ±0.004 | 1.679 ± 0.200 | 1.275 ± 0.009 | 0.991 ± 0.004 |
| As-built | 33.17 ± 1.33 | 2.128 ± 0.035 | 0.951 ± 0.003 | 1.469 ± 0.020 | 1.386 ± 0.625 | 0.661 ± 0.033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Ge, Y.; Du, N. Comparison on the Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Ti6Al4V Alloys Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Casting. Materials 2024, 17, 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133322
Zhan Z, Zhang Q, Wang S, Liu X, Zhang H, Sun Z, Ge Y, Du N. Comparison on the Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Ti6Al4V Alloys Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Casting. Materials. 2024; 17(13):3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133322
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Zhongwei, Qi Zhang, Shuaixing Wang, Xiaohui Liu, Hao Zhang, Zhihua Sun, Yulin Ge, and Nan Du. 2024. "Comparison on the Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Ti6Al4V Alloys Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Casting" Materials 17, no. 13: 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133322
APA StyleZhan, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, S., Liu, X., Zhang, H., Sun, Z., Ge, Y., & Du, N. (2024). Comparison on the Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Ti6Al4V Alloys Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Casting. Materials, 17(13), 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133322







