A Complementary Fusion-Based Multimodal Non-Destructive Testing and Evaluation Using Phased-Array Ultrasonic and Pulsed Thermography on a Composite Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Material Description and Inspection Details
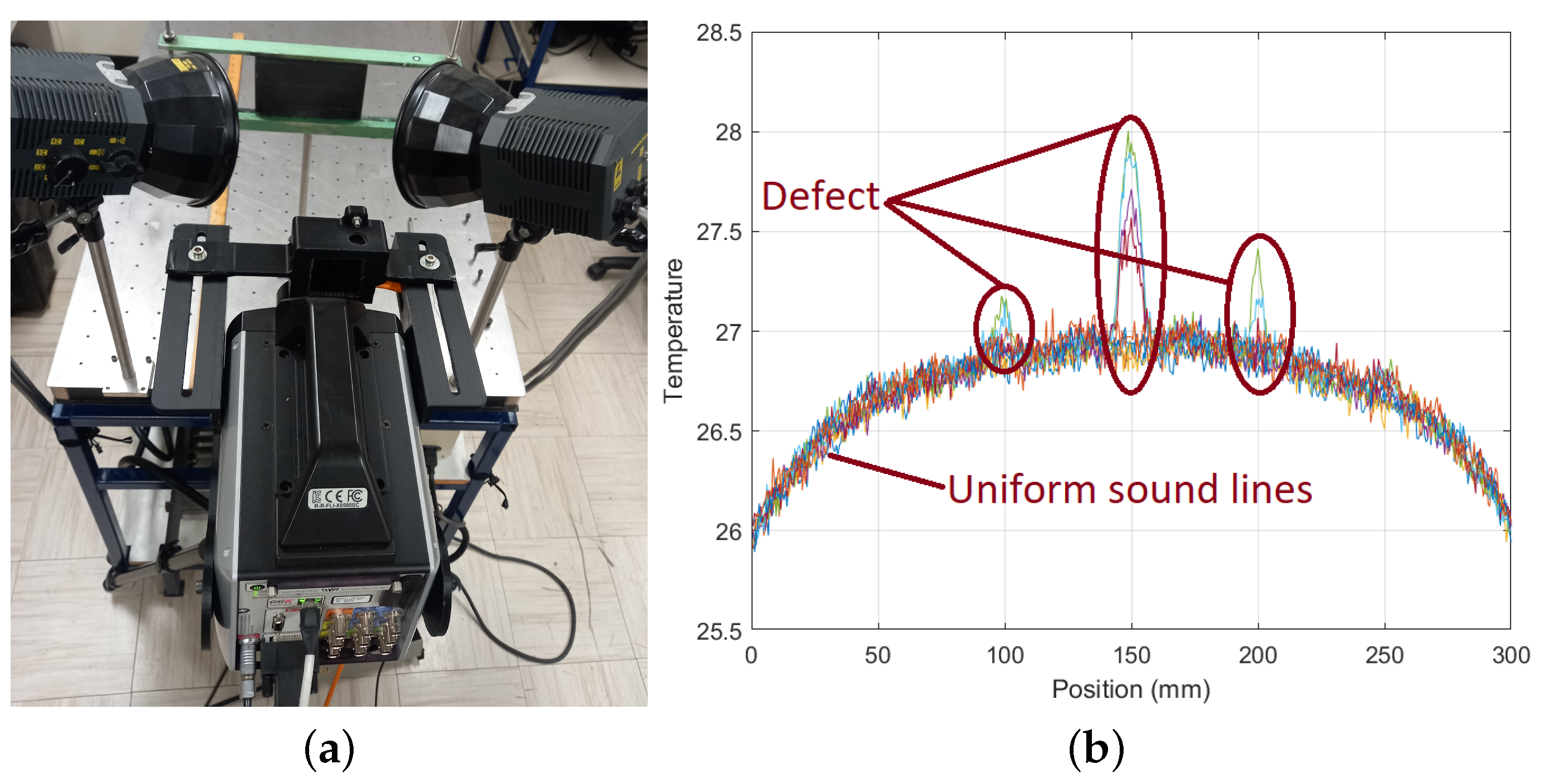
2.2. Experimental Details of PAUT
2.3. Experimental Details of PT
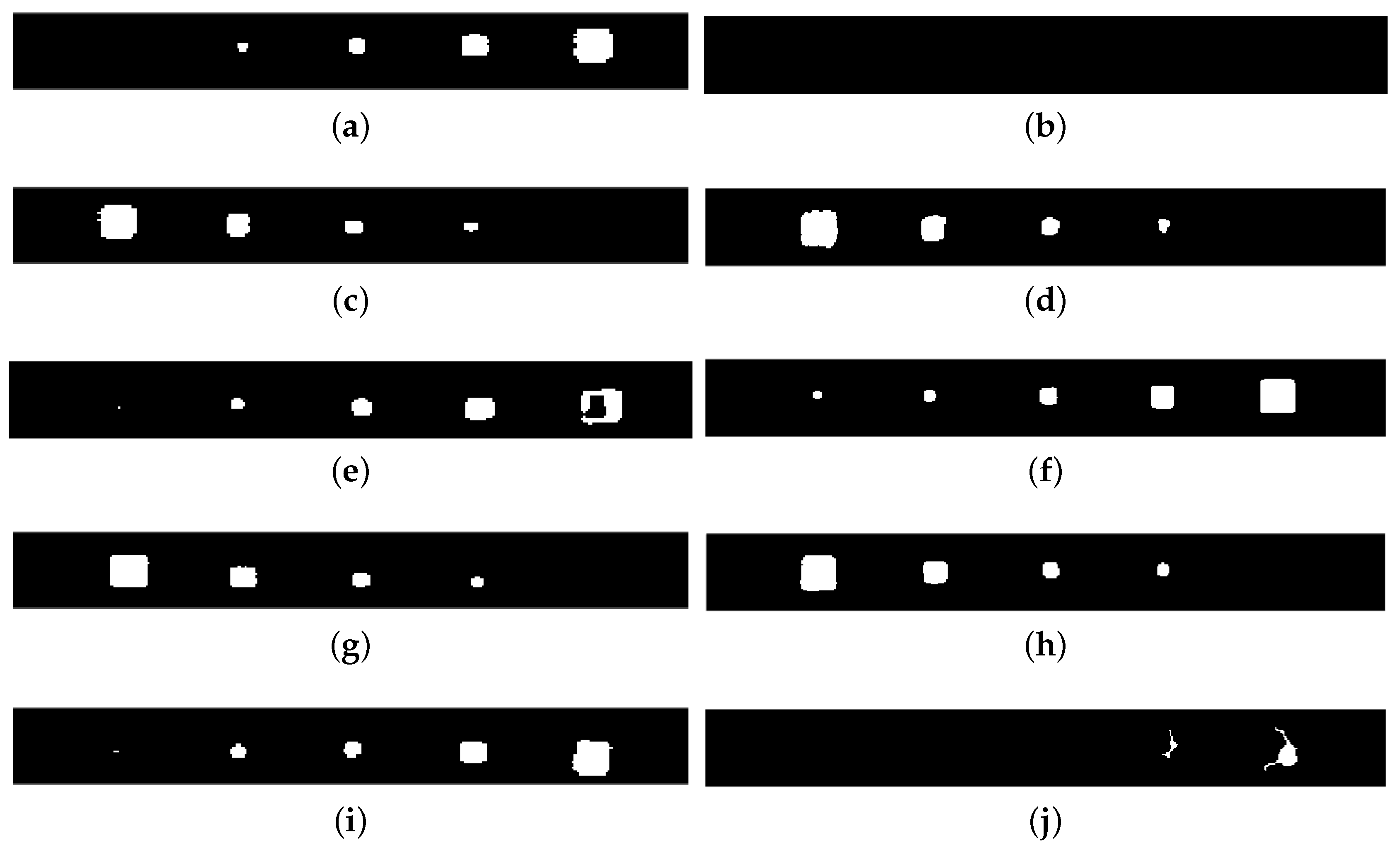
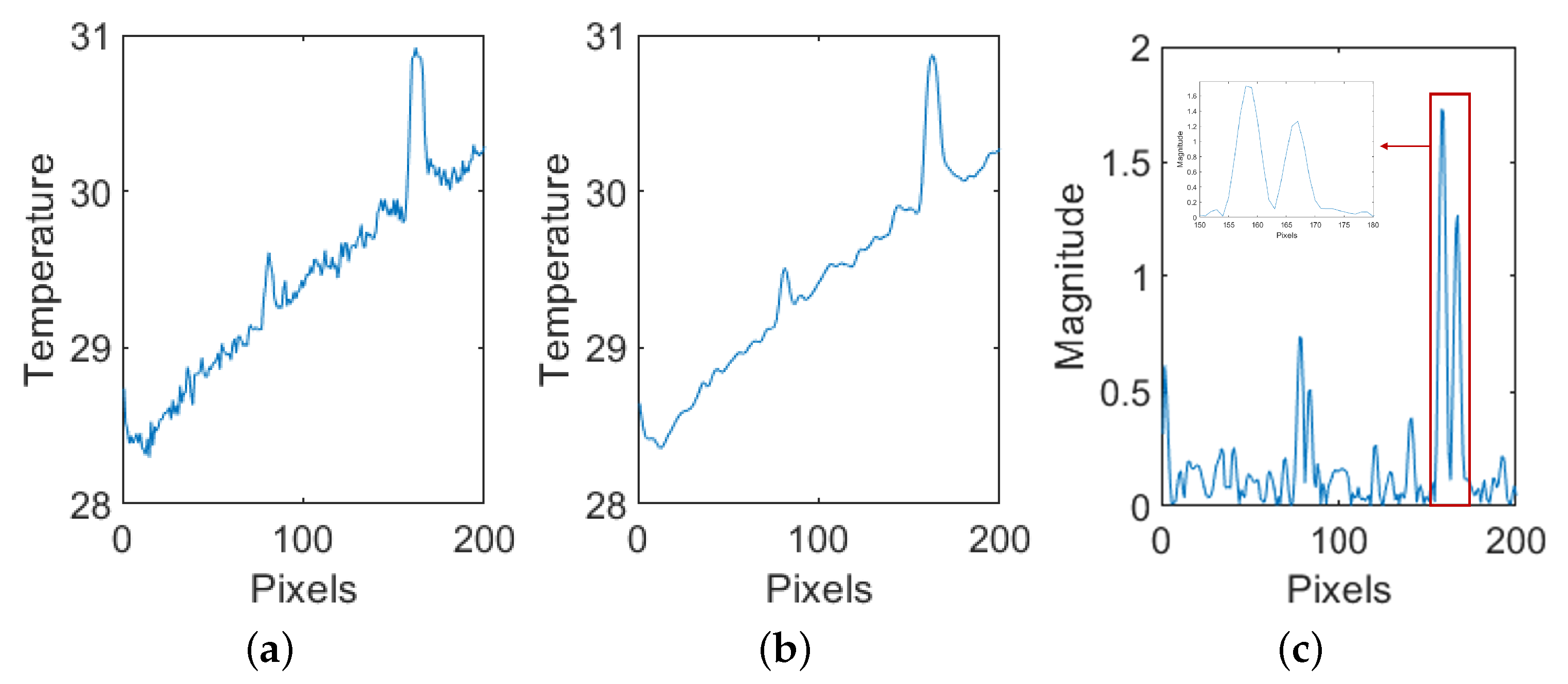
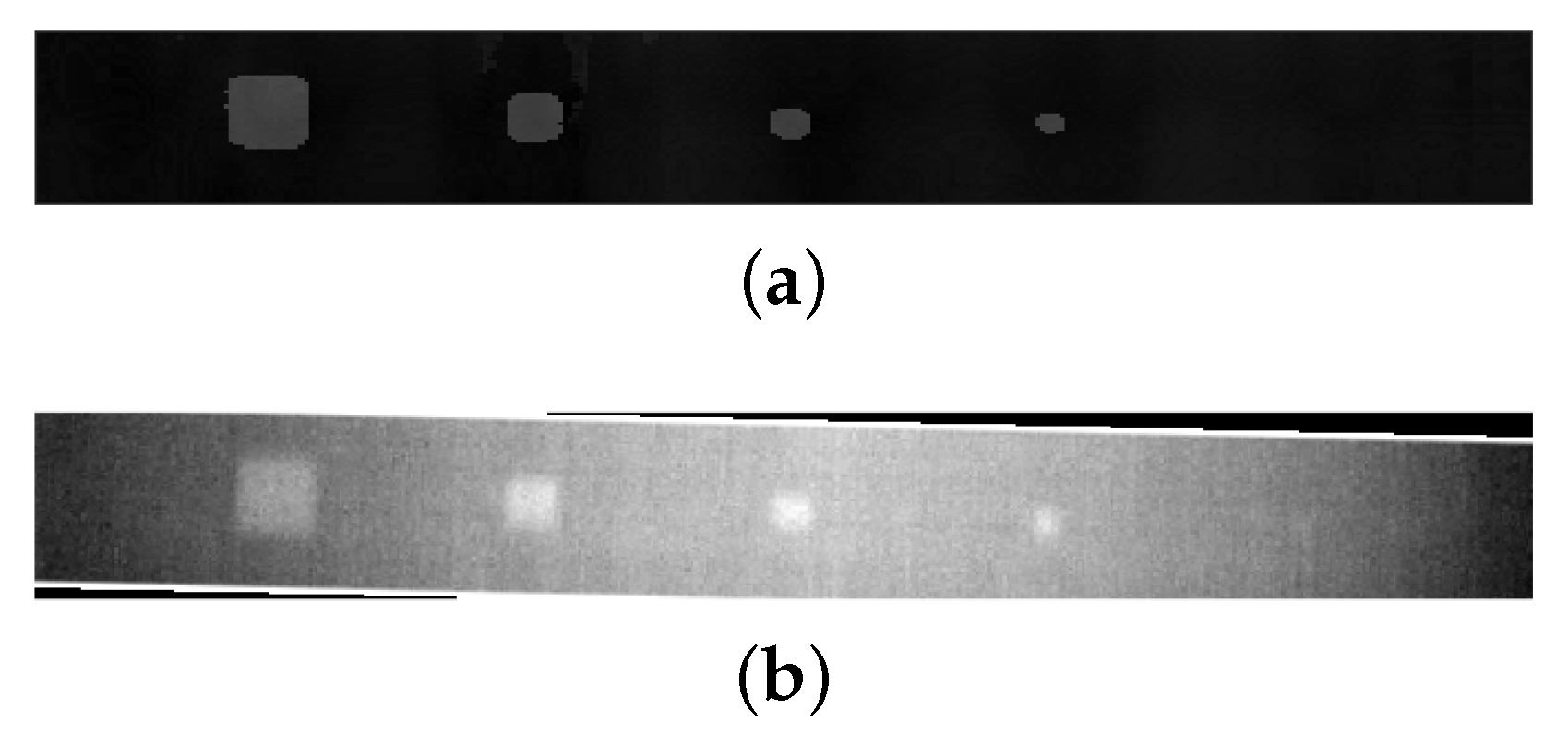
2.4. Image Binarization
2.5. Details of Registration Procedure
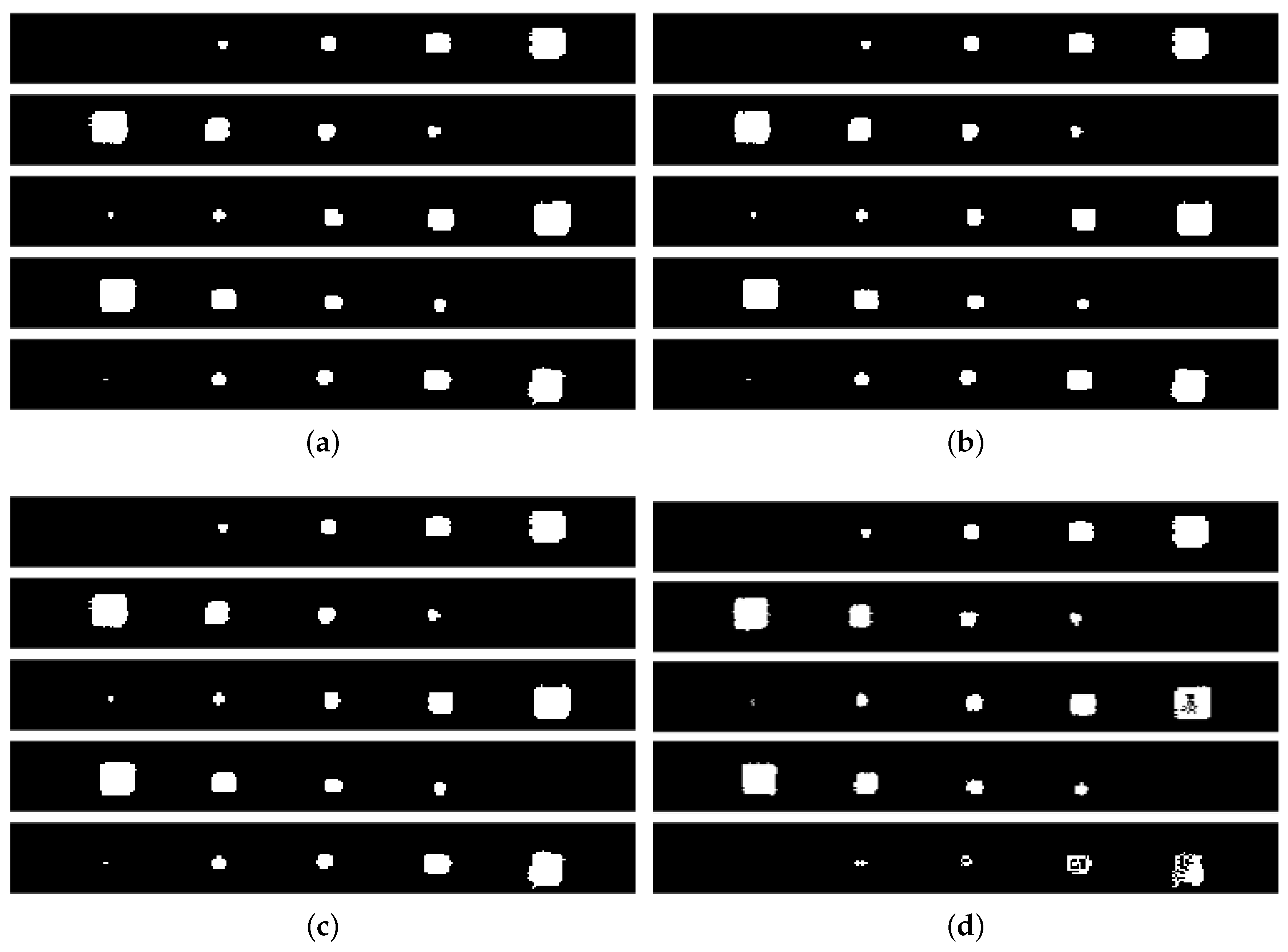
2.6. Fusion Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Image Registration
3.2. Defect Detection
3.3. Fusion
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFRP | carbon fiber-reinforced polymer |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DDC | depth-driven combination |
| GFRP | glass fiber-reinforced polymer; |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| MMIR | multimodal image registration |
| NDT&E | non-destructive testing and evaluation |
| PA | phased array |
| PAUT | phased-array ultrasonic inspection |
| PI | pattern intensity |
| PT | pulsed thermography |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| SSD | sum of squared differences |
References
- Taheri, H.; Hassen, A. Nondestructive Ultrasonic Inspection of Composite Materials: A Comparative Advantage of Phased Array Ultrasonic. Appl. Sci 2019, 9, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Krenek, R.; Taheri, H.; Dababneh, F. Ultrasonic Phased Array Technique for Defect Detection and Sizing in Heavy-Walled Cast Components. In Proceedings of the ASME 2020 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Virtual-Online, 16–19 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xiangbo, X.; Bo, R.; Nan, J.; Lei, X.; Pan, H.; Xianwei, Z.; Zhe, L. A systematic review of ultrasonic techniques for defects detection in construction and building materials. Measurement 2024, 226, 114181. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, G.; Mateus, J.; Li, J.; Pachha, R.; Walia, P.; Deng, Y.; Chakrapani, S.K. Phased array ultrasonic imaging and characterization of adhesive bonding between thermoplastic composites aided by machine learning. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2023, 38, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, Q.; Cui, F.; Malcolm, A.A.; Su, Z.; Liu, M. Ultrasonic detection and characterization of delamination and rich resin in thick composites with waviness. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 189, 108016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhani, R.; Zanotti Fragonara, L.; Padiyar, M.J.; Petrunin, I.; Raposo, J.; Tsour-dos, A.; Gray, I. Improving Depth Resolution of Ultrasonic Phased Array Imaging to Inspect Aerospace Composite Structures. Sensors 2020, 20, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Q. Phased array ultrasonic inspection and automated identification of wrinkles in laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 2022, 300, 116170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, J.; Guo, W.; Guan, X. Three-dimensional damage quantification of low velocity impact damage in thin composite plates using phased-array ultrasound. Ultrasonics 2021, 110, 106264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbali, M.E.; Alhammad, M.; Zolotas, A.; Avdelidis, N.P.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Maldague, X.P.V. Enhanced defect identification by image fusion of infrared thermography and ultrasonic phased array inspection techniques. In Proceedings of the SPIE 12536, Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XLV, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 April–5 May 2023; Volume 125360. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.B.; Santos, J.; Sousa, J.P.; Santos, T.G.; Quintino, L. Phased Array Ultrasonic Inspection of Metal Additive Manufacturing Parts. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2019, 38, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, A.; Laroche, N.; Carcreff, E.; Rauch, M.; Hascoet, J.Y. Towards defect monitoring for metallic additive manufacturing components using phased array ultrasonic testing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.I.; Park, J.; Kim, H.J.; Song, S.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Kang, S.S. Performance Comparison of Ultrasonic Focusing Techniques for Phased Array Ultrasonic Inspection of Dissimilar Metal Welds. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, M.; Dubé, N.; Labbé, S.; Ginzel, E. Review of Ultrasonic Phased Arrays for Pressure Vessel and Pipeline Weld Inspections. ASME J. Press. Vessel Technol. 2005, 127, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Kim, Y.L.; Cho, S.; Park, I.K. Ultrasonic Inspection for Welds with Irregular Curvature Geometry Using Flexible Phased Array Probes and Semi-Auto Scanners: A Feasibility Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.R. Automated data evaluation in phased-array ultrasonic testing based on A-scan and feature training. NDT E Int. 2024, 141, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, R.; Zhang, D.; Gachagan, A.; Dobie, G. Modelling and characterisation ultrasonic phased array transducers for pipe inspections. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 200, 104808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, E.; Ozevin, D.; Li, H. Phased acoustic emission sensor array for localizing radial and axial positions of defects in hollow structures. Measurement 2020, 151, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Seo, M.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, S.; Kim, K. Development of phased array ultrasonic system for detecting rail cracks. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 311, 112086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzeroual, H.; Khamlichi, A.; Zakriti, A. Inspection of transverse flaws for railways using phased array ultrasonic technique. Int. Rev. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2021, 12, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetstone, G.; Liu, T.; Fudlailah, P.; Droddy, C.V.; Allen, D.H. Experimental Evaluation of Crack Evolution in Rails Using a Phased Array. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2023, 42, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Wirdelius, H.; Rosell, A. Experimental validation of a phased array probe model in ultrasonic inspection. Ultrasonics 2020, 108, 106217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont-Marillia, F.; Jahazi, M.; Lafreniere, S.; Belanger, P. Design and optimisation of a phased array transducer for ultrasonic inspection of large forged steel ingots. NDT E Int. 2019, 103, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Shin, H.J.; Jang, Y.H. Development of an ultra sonic phased array system for nondestructive tests of nuclear power plant components. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2002, 214, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, W. Latest Advances in Common Signal Processing of Pulsed Thermography for Enhanced Detectability: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.J.; Jenkins, R.J.; Butler, C.P.; Abbott, G.L. Flash Method of Determining Thermal Diffusivity, Heat Capacity, and Thermal Conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdelidis, N.P.; Almond, D.P.; Dobbinson, A.; Hawtin, B.C.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Maldague, X. Aircraft composites assessment by means of transient thermal NDT. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2004, 40, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostroun, T.; Dvořák, M. Application of the Pulse Infrared Thermography Method for Nondestructive Evaluation of Composite Aircraft Adhesive Joints. Materials 2021, 14, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, B.; Yang, C.; Fang, D.; Xu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Wan, C. Pulse-heating infrared thermography inspection of bonding defects on carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panella, F.W.; Pirinu, A. Application of Pulsed Thermography and Post-processing Techniques for CFRP Industrial Components. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2021, 40, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovchenko, A.I.; Vavilov, V.P.; Bernegger, R.; Maierhofer, C.; Chulkov, A.O. Detecting Delaminations in Semitransparent Glass Fiber Composite by Using Pulsed Infrared Thermography. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2020, 39, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhang, D. Accurate depth determination of defects in composite materials using pulsed thermography. Compos. Struct. 2021, 267, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, B.C.; Marció, B.S.; Flesch, R.C. Enhanced damage measurement in a metal specimen through the image fu- sion of tone-burst vibro-acoustography and pulse-echo ultrasound data. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 167, 108445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdelidis, N.; Gan, T.H.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Maldague, X. Infrared thermography as a nondestructive tool for materials characterisation and assessment. In Proceedings of the Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XXXIII, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–28 April 2011; Volume 8013, pp. 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Servais, P.; Klein, M.; Boulanger, T.; Kinard, A.; Hoffait, S.; Maldague, X.P. Detection and characterization of artificial porosity and impact damage in aerospace carbon fiber composites by pulsed and line scan thermography. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Tang, T.; Zhu, B.; Yang, C.; Li, B.; Hao, S. A Multiscale Framework with Unsu- pervised Learning for Remote Sensing Image Registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5622215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, G.; Ma, M. TD-Net: Unsupervised medical image registration network based on Transformer and CNN. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 18201–18209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ma, J.; Xiao, G.; Shao, Z.; Guo, X. A review of multimodal image matching: Methods and applications. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 22–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamal, F.; Elmogy, M.; Atwan, A. Current trends in medical image registration and fusion. Egypt. Inform. J. 2016, 17, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Williams, J.P.; Sun, Y.; Blum, R.S.; Xu, C. A robust hybrid method for nonrigid image registration. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekaya, I.B.; Kaftandjian, V.; Buyens, F.; Sevestre, S.; Legoupil, S. Registration-Based Geometric Calibration of Industrial X-ray Tomography System. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 3937–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennessier, C.; Clackdoyle, R.; Noo, F. Direct determination of geometric align- ment parameters for cone-beam scanners. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, F.; Hu, J. A calibration method for misaligned scanner geometry in cone-beam computed tomography. NDT E Int. 2006, 39, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Smekal, L.; Kachelrieß, M.; Stepina, E.; Kalender, W.A. Geometric misalignment and calibration in cone-beam tomography. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 3242–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.A.; Payne, G.S. Radiotherapy planning using MRI. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, R323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erazo-Aux, J.; Loaiza-Correa, H.; Restrepo-Giron, A.D.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Maldague, X. Thermal imaging dataset from composite material academic samples inspected by pulsed thermography. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Li, Y. A method of lane edge detection based on Canny algorithm. In Proceedings of the Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 2120–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Ge, F.; Liu, T. Evaluating edge detection through boundary detection. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2006, 2006, 76278. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, F.; Zou, L.; Song, B. Edge feature extraction based on digital image processing techniques. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Qingdao, China, 1–3 September 2008; pp. 2320–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digit. Image Process; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Xie, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Gubanski, S.M. Ultrasonic phased array detection of internal defects in composite insulators. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Chang, Y.S.; Yao, Y. Defect detection in CFRP structures using pulsed thermographic data enhanced by penalized least squares methods. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 79, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.; Rendahl, B.; Annergren, I. The use of infrared thermography in the corrosion science area. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Avdelidis, N.P.; Grinzato, E.G.; Bison, P.G.; Marinetti, S.; Chen, L.; Maldague, X. Quantitative inspection of non-planar composite specimens by pulsed phase thermography. Quant. Infrared Thermogr. J. 2006, 3, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Specimen | Defect Material | Defect Sizes | Number of Plies | Thickness (mm) | Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial delamination specimen | Artificial Teflon inclusions | 3, 5, 7, 10, and 15 mm square inclusions (depths and locations indicated in Figure 1) | 10 | 2 | 300 × 300 |
| Transformation Type | Identity | Scaling | Translation | Rotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affine Matrix, A | ||||
| Coordinate Equations | ||||
| Example Shape |  | 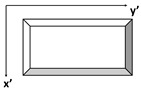 | 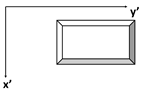 |  |
| Methods for Line Detection | Line1 | Line 2 | Line 3 | Line 4 | Line 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources | PA | 0.0113 | 0.0115 | 0.0209 | 0.0112 | 0.0131 |
| PT | - | 0.0109 | 0.0062 | 0.0301 | 0.0421 | |
| Fusion Rules | Maximum | 0.0113 | 0.0093 | 0.0098 | 0.0083 | 0.0134 |
| DDC | 0.0113 | 0.0099 | 0.0090 | 0.0085 | 0.0134 | |
| Weighted Averaging | 0.0113 | 0.0109 | 0.0097 | 0.0112 | 0.0131 | |
| Wavelet Decomposition | 0.0369 | 0.0230 | 0.0310 | 0.0210 | 0.0355 |
| Detection Errors (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detected by | Defect 1 | Defect 2 | Defect 3 | Defect 4 | Defect 5 | ||
| Line 1 | Sources | PA | ND | −33.33 | −11.90 | 7.65 | 6.40 |
| PT | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| Fusion Rules | Maximum | ND | −33.33 | −11.90 | 7.65 | 6.40 | |
| DDC | ND | −33.33 | −11.90 | 7.65 | 6.40 | ||
| Weighted Average | ND | −33.33 | −11.90 | 7.65 | 6.40 | ||
| Wavelet (Daubechies) | ND | −33.33 | −11.90 | 7.65 | 6.40 | ||
| Line 2 | Sources | PA | 3.74 | 0.00 | −7.14 | −20.00 | ND |
| PT | 13.33 | 16.47 | 14.29 | −13.33 | ND | ||
| Fusion Rules | Maximum | 14.94 | 27.65 | 19.05 | −2.22 | ND | |
| DDC | 14.94 | 27.65 | 19.05 | −2.22 | ND | ||
| Weighted Average | 3.73 | 0.00 | −7.14 | −20.22 | ND | ||
| Wavelet (Daubechies) | 8.53 | 8.24 | 3.57 | −17.78 | ND | ||
| Line 3 | Sources | PA | −94.00 | −13.33 | 17.86 | 18.24 | −20.27 |
| PT | 13.33 | −2.22 | 21.43 | 8.24 | 13.07 | ||
| Fusion Rules | Maximum | 13.33 | 26.67 | 30.95 | 30.59 | 21.87 | |
| DDC | 13.33 | 2.22 | 21.43 | 20.00 | 21.87 | ||
| Weighted Average | 13.33 | −2.22 | 21.43 | 8.24 | 13.07 | ||
| Wavelet (Daubechies) | −40.00 | −6.67 | 19.05 | 12.94 | −3.74 | ||
| Line 4 | Sources | PA | 11.47 | 4.12 | −1.19 | −11.11 | ND |
| PT | 10.40 | 1.18 | 1.19 | 11.11 | ND | ||
| Fusion Rules | Maximum | 20.27 | 17.06 | 11.90 | 20.00 | ND | |
| DDC | 20.27 | 17.06 | 11.90 | 20.00 | ND | ||
| Weighted Average | 12.27 | 2.94 | 0.00 | 13.33 | ND | ||
| Wavelet (Daubechies) | 11.47 | 4.12 | -1.19 | 0.00 | ND | ||
| Line 5 | Sources | PA | −86.67 | 28.89 | −10.71 | 7.09 | −0.27 |
| PT | ND | ND | ND | −80.00 | −66.93 | ||
| Fusion Rules | Maximum | -86.67 | 28.89 | −10.71 | 8.24 | 1.33 | |
| DDC | −86.67 | 28.89 | −10.71 | 8.24 | 1.33 | ||
| Weighted Average | −86.67 | 28.89 | −10.71 | 7.09 | −0.27 | ||
| Wavelet (Daubechies) | −93.33 | −35.56 | −55.95 | −36.47 | −33.60 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torbali, M.E.; Zolotas, A.; Avdelidis, N.P.; Alhammad, M.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Maldague, X.P. A Complementary Fusion-Based Multimodal Non-Destructive Testing and Evaluation Using Phased-Array Ultrasonic and Pulsed Thermography on a Composite Structure. Materials 2024, 17, 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143435
Torbali ME, Zolotas A, Avdelidis NP, Alhammad M, Ibarra-Castanedo C, Maldague XP. A Complementary Fusion-Based Multimodal Non-Destructive Testing and Evaluation Using Phased-Array Ultrasonic and Pulsed Thermography on a Composite Structure. Materials. 2024; 17(14):3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143435
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorbali, Muhammet E., Argyrios Zolotas, Nicolas P. Avdelidis, Muflih Alhammad, Clemente Ibarra-Castanedo, and Xavier P. Maldague. 2024. "A Complementary Fusion-Based Multimodal Non-Destructive Testing and Evaluation Using Phased-Array Ultrasonic and Pulsed Thermography on a Composite Structure" Materials 17, no. 14: 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143435
APA StyleTorbali, M. E., Zolotas, A., Avdelidis, N. P., Alhammad, M., Ibarra-Castanedo, C., & Maldague, X. P. (2024). A Complementary Fusion-Based Multimodal Non-Destructive Testing and Evaluation Using Phased-Array Ultrasonic and Pulsed Thermography on a Composite Structure. Materials, 17(14), 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143435











