Comparative Analysis of Microabrasive Film Finishing Effects across Various Process Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
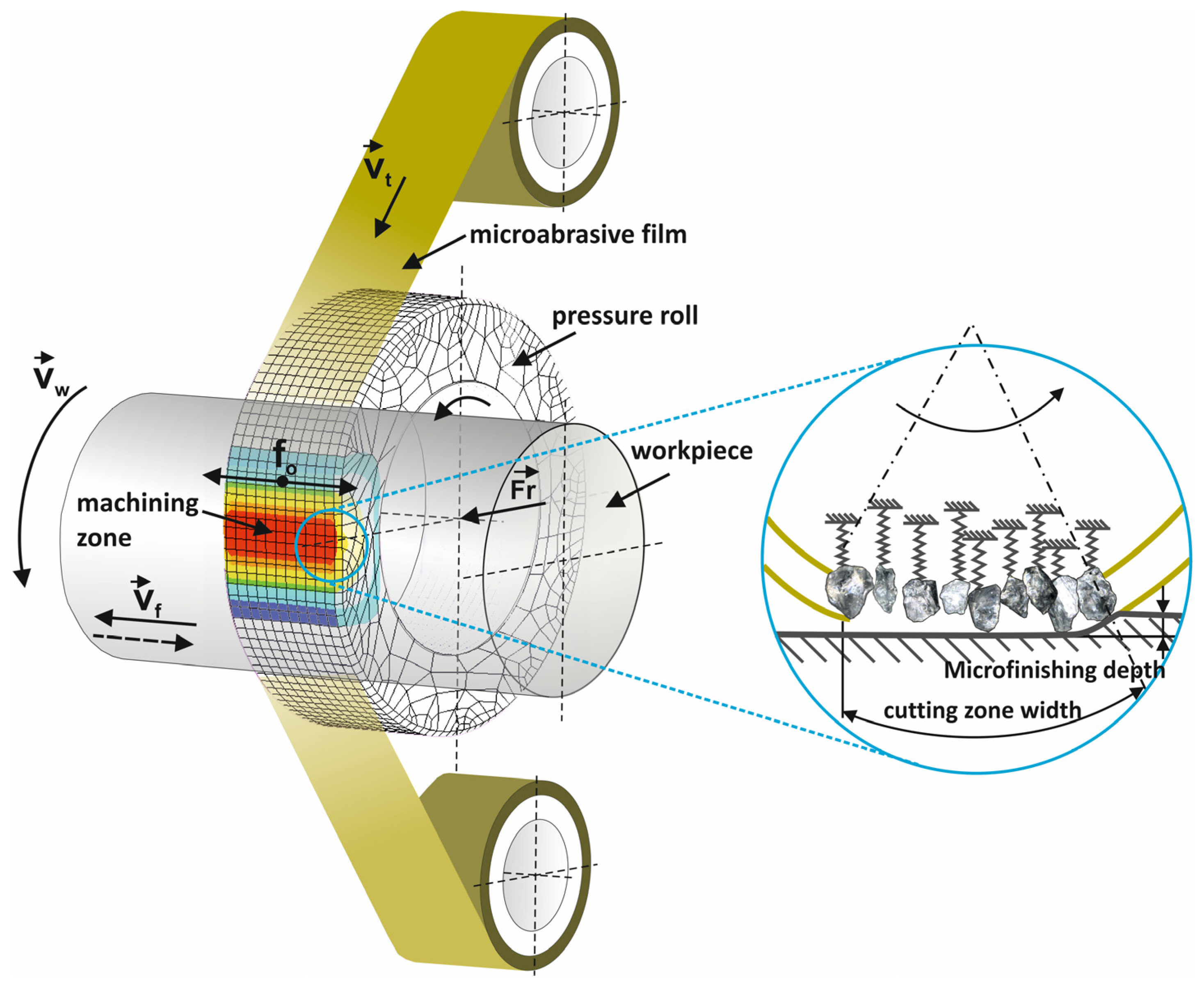
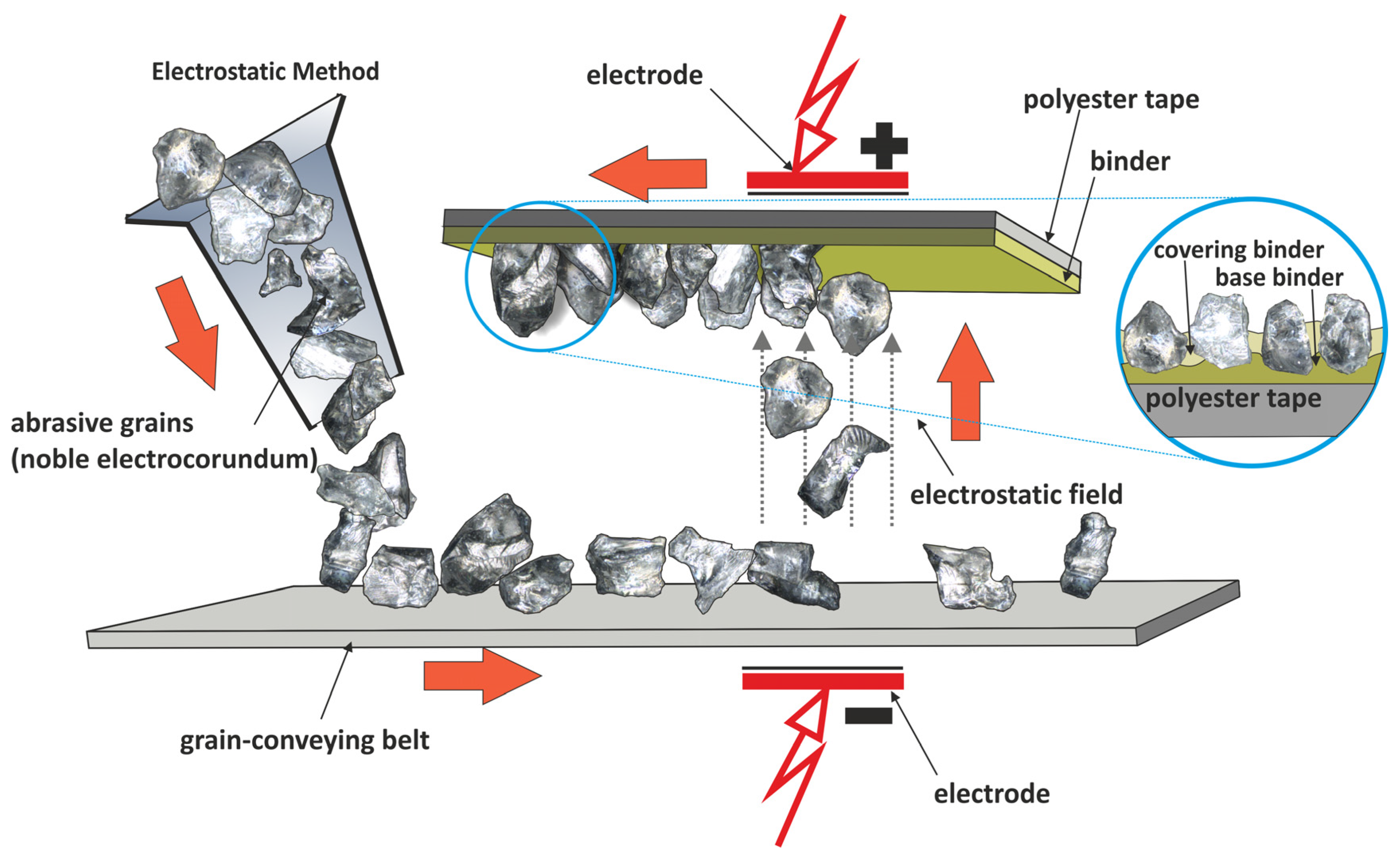
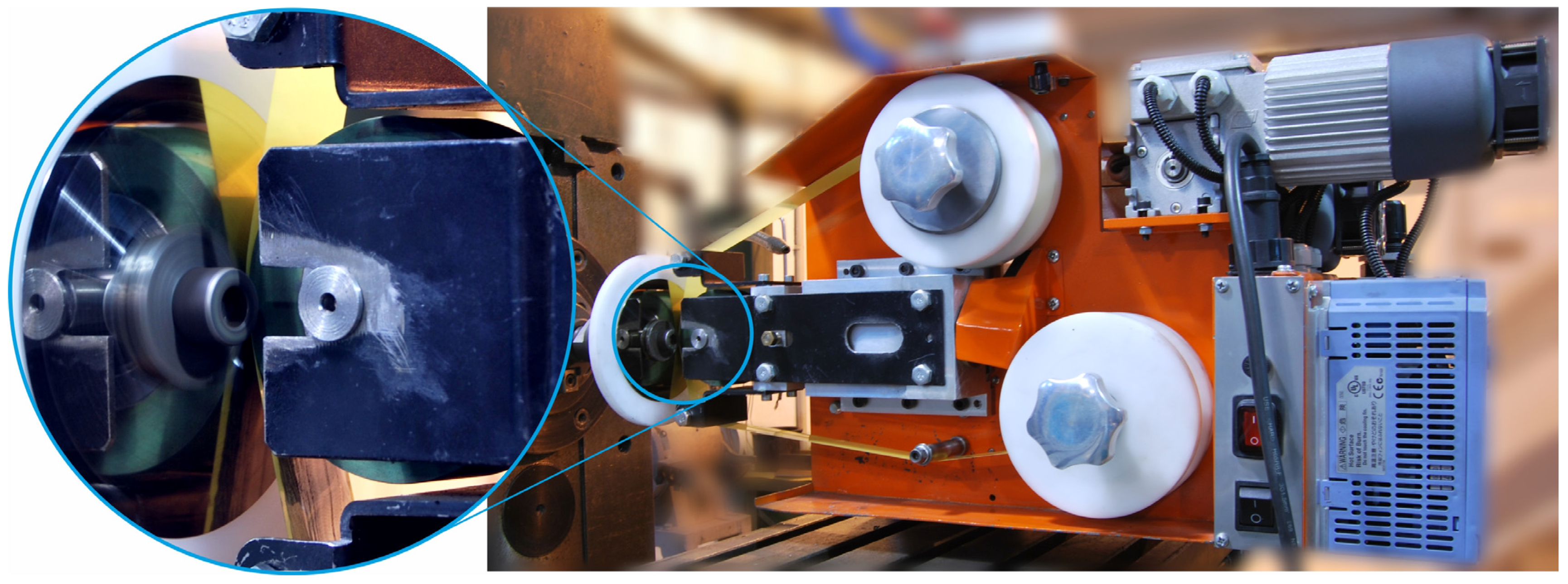
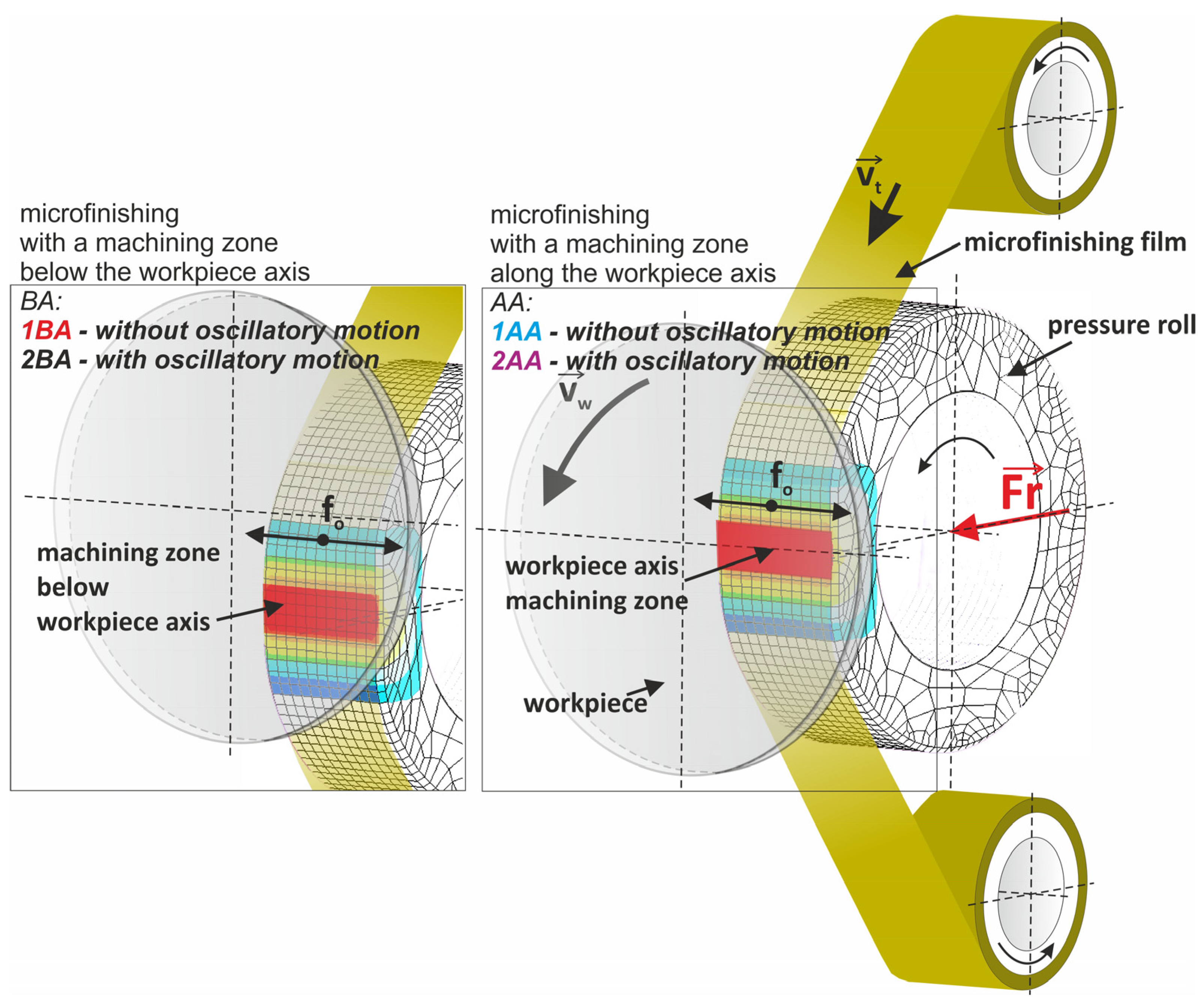
2.1. Microfinishing Process
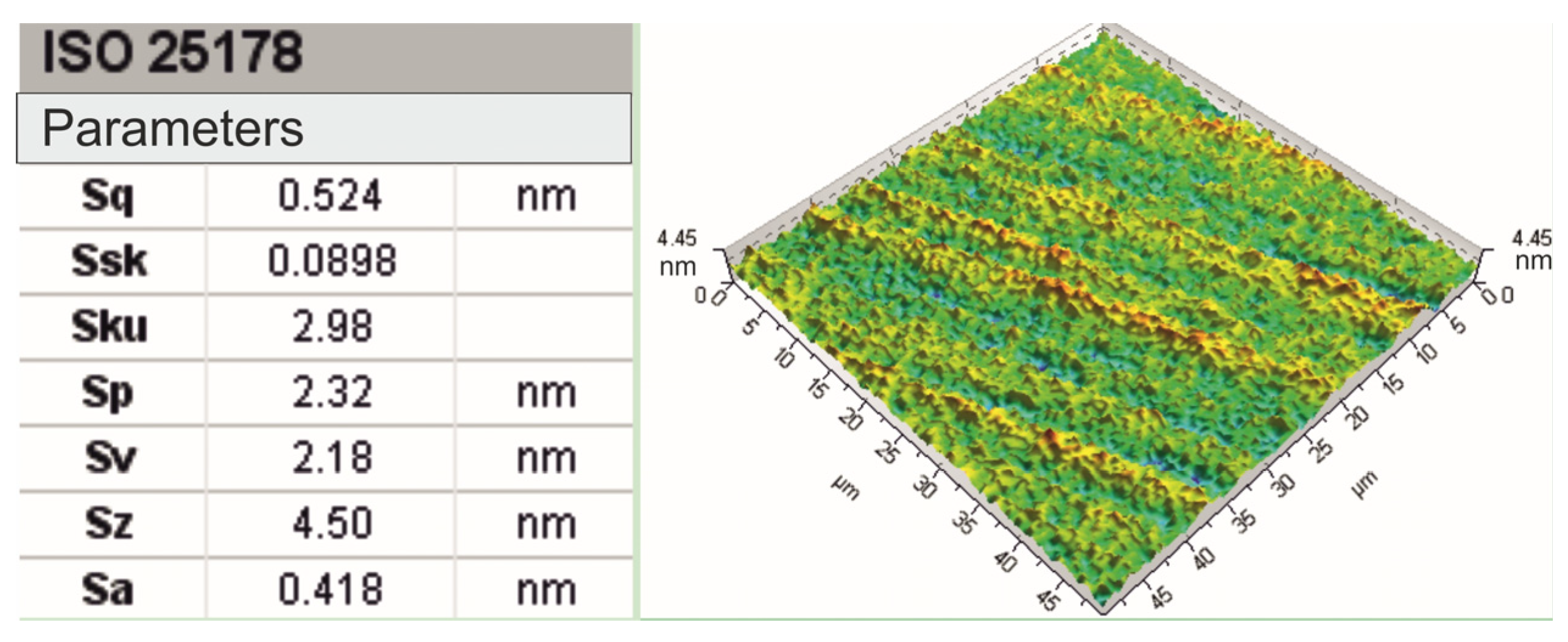
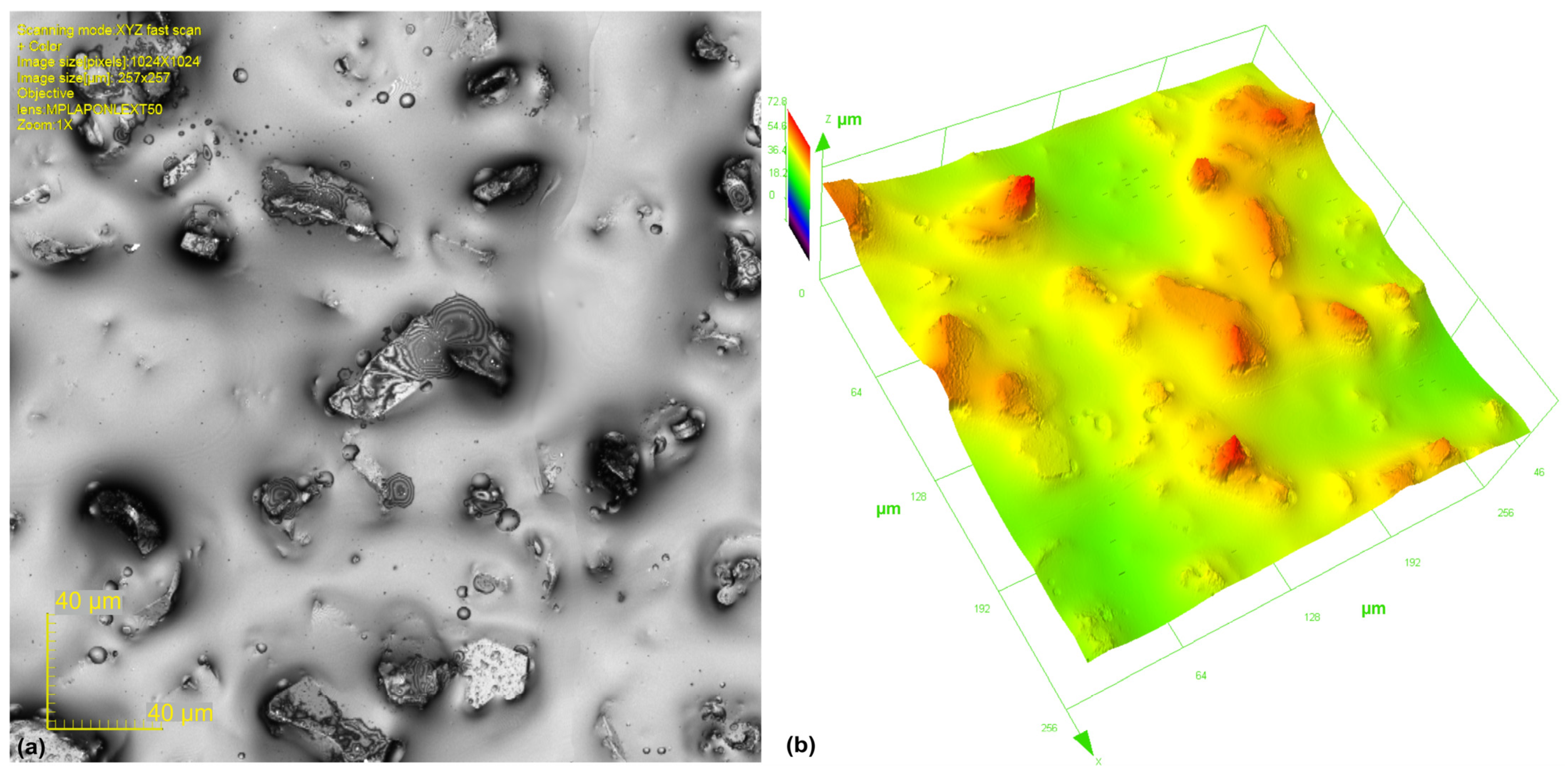
2.2. Assessment of the Level of Surface Smoothness Being Processed
3. Results and Discussion
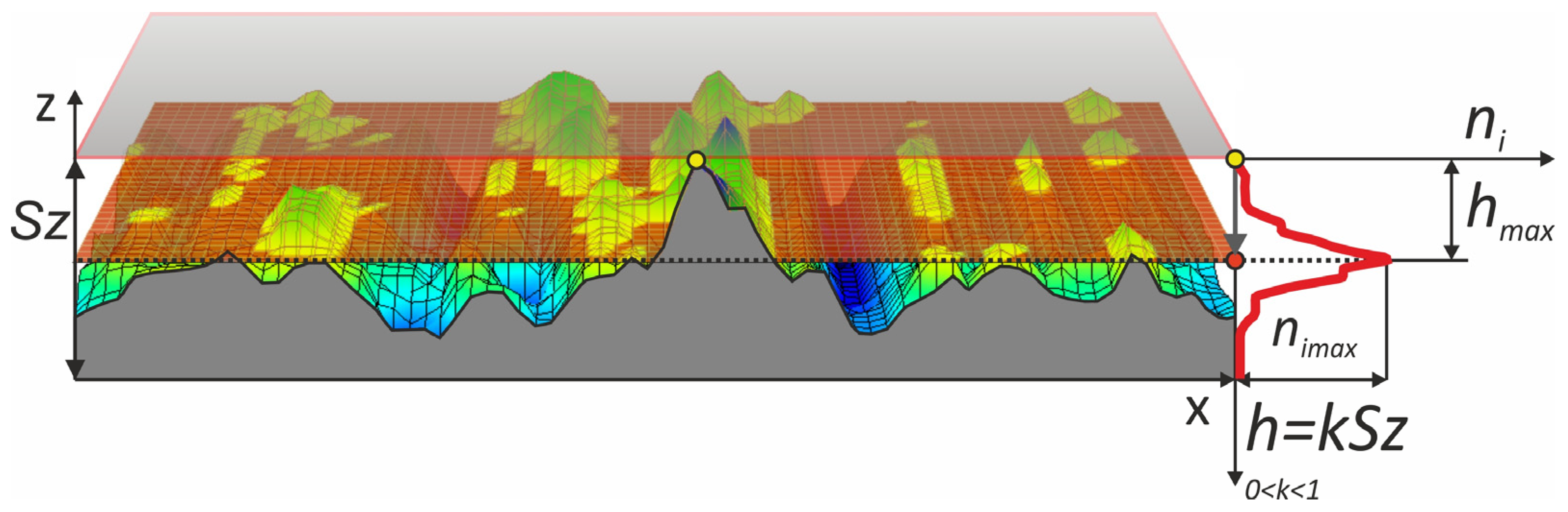
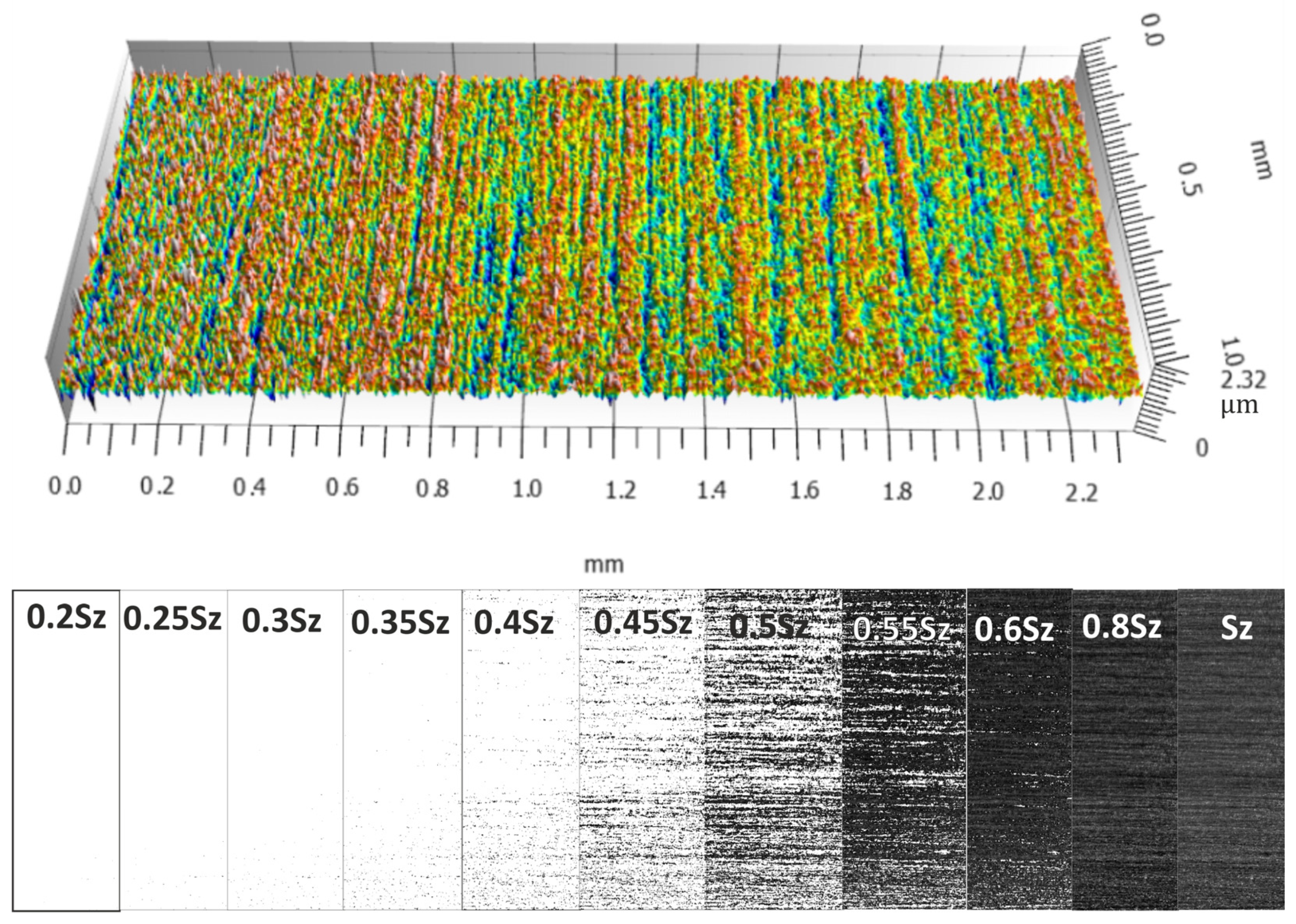
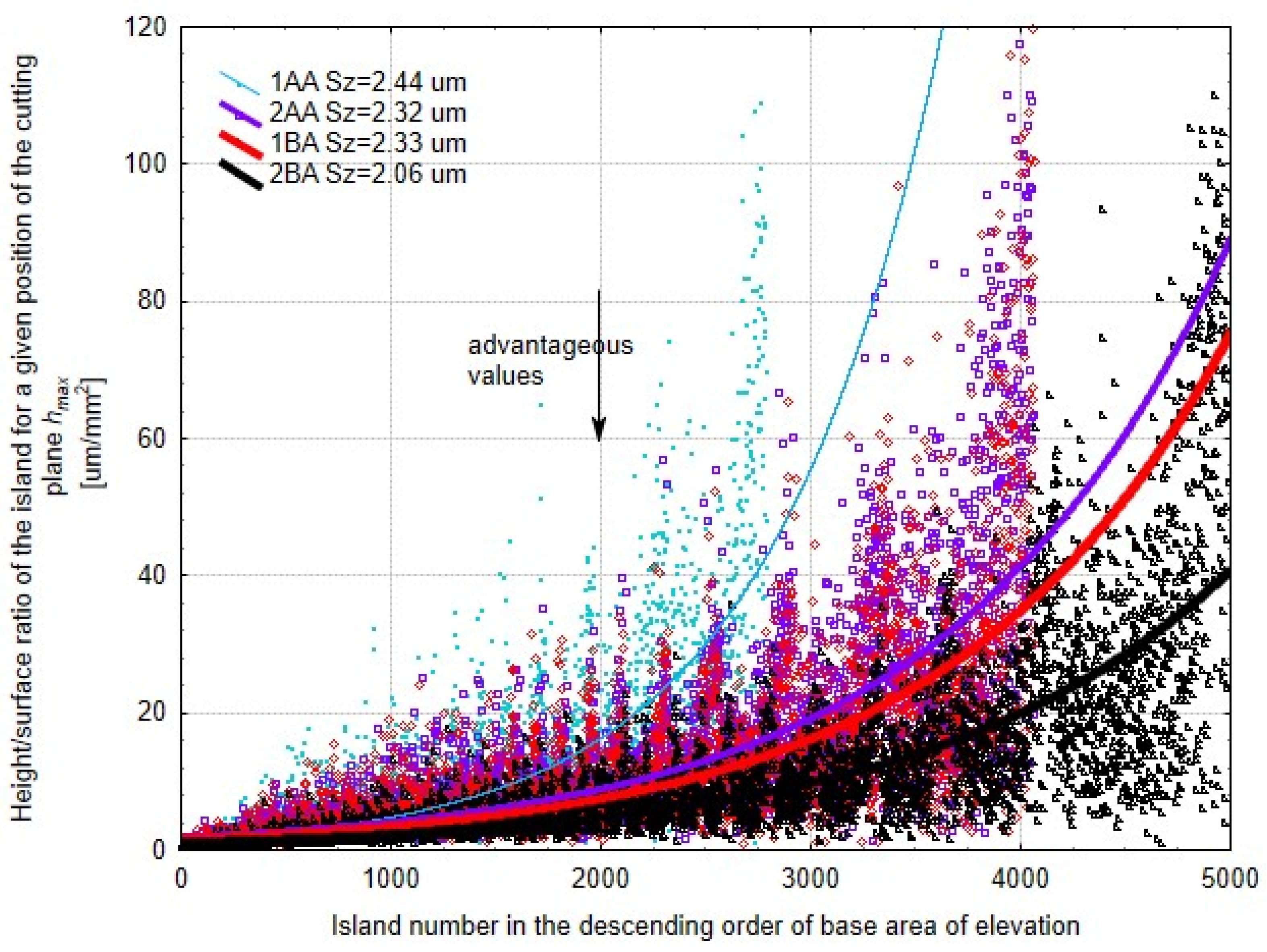
3.1. Analysis of Surface Smoothness Using the Analysis of Islands Technique
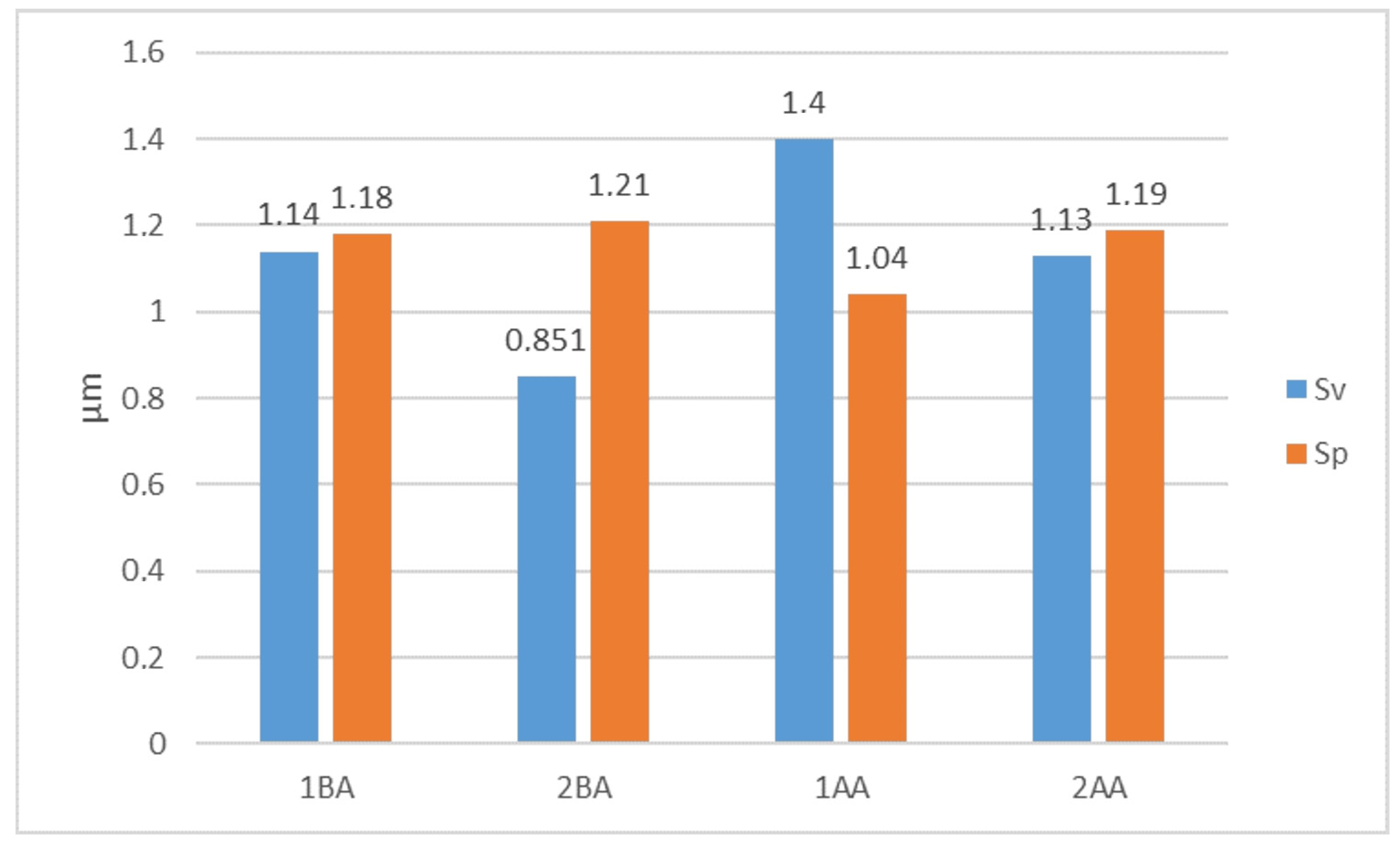
3.2. Analysis of Machined Surface Roughness
4. Summary and Conclusions
- The method of machining below the workpiece axis with oscillatory motion turned out to be the most effective from the viewpoint of improving the smoothness of a surface—in this case, it resulted in the largest density of protrusions and lowest values of roughness.
- Methods not using oscillatory motion but having the machining zone below the workpiece axis were equally good. This may imply that the relocation of the machining zone can substitute for lack of oscillation, hence making the process easier without sacrificing quality.
- The technique of “analysis of islands” showed that the method with machining below the axis by oscillatory motion ensures an excellent structure of a surface with a high concentration of islands at optimal cut-off levels.
- The best microfinishing technique indicated from the findings is the below-axis machining with oscillatory motion. However, the non-oscillatory techniques also offer some very promising alternatives, which bring flexibility to process optimization and quite likely reduce the complexity of equipment, hence the operational costs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mezghani, S.; El Mansori, M.; Zahouani, H. New criterion of grain size choice for optimal surface texture and tolerance in belt finishing production. Wear 2009, 266, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, S.; El Mansori, M.; Sura, E. Wear mechanism maps for the belt finishing of steel and cast iron. Wear 2009, 267, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigerelle, M.; Hagege, B.; El Mansori, M. Mechanical modelling of micro-scale abrasion in superfinish belt grinding. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpin, K.; Mezghani, S.; El Mansori, M. Wear study of structured coated belts in advanced abrasive belt finishing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 284, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, S.; El Mansori, M.; Massaq, A.; Ghidossi, P. Correlation between surface topography and tribological mechanisms of the belt-finishing process using multiscale finishing process signature. Comptes Rendus-Mec. 2008, 336, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandecka, K.; Kacalak, W.; Rypina, Ł.; Wiliński, M.; Wieczorowski, M.; Mathia, T.G. Effects of Pressure Rollers with Variable Compliance in the Microfinishing Process Utilizing Abrasive Films. Materials 2024, 17, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandecka, K.; Kacalak, W.; Szafraniec, F.; Wieczorowski, M.; Mathia, T.G. Evaluation of the Surface Topography of Microfinishing Abrasive Films in Relation to Their Machining Capability of Nimonic 80A Superalloy. Materials 2024, 17, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorciapino, M.A.; Fantauzzi, M.; Crobu, M.; Navarra, G.; Elsener, B.; Rossi, A. Nanostructure of Surface Films on Ni18P Alloy in Sulfate Solutions by the Maximum Entropy Method. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7790–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łosiewicz, B.; Dercz, G.; Popczyk, M. Amorphous Ni-P electrode materials. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 228, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Jian, Z.; Hai, R.; Chang, F. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of amorphous electroless nickel-phosphorus alloy plating. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Jian, Z.; Hai, R. Preparation and properties of thick nickel-phosphorus amorphous plating on SiCp/Al composite by double zincate pretreatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; Qin, W.; Li, Y. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of electroless Ni-P on sprayed Al-Ce coating of 3003 aluminum alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 281, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchuk, O.; Sknar, Y.; Sknar, I.; Cheremysinova, A.; Kozlov, Y. Examining the effect of electrosynthesis conditions on the Ni-P alloy composition. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2017, 4, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Bian, C.; Hu, L. Exploration of the Corrosion Behavior of Electroless Plated Ni-P Amorphous Alloys via X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Molecules 2023, 28, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandecka, K.; Kacalak, W.; Wiliński, M.; Wieczorowski, M.; Mathia, T.G. Morphology of Microchips in the Surface Finishing Process Utilizing Abrasive Films. Materials 2024, 17, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Dai, Y.; Hu, H.; Tie, G.; Guan, C.; Chen, X. Research on deterministic figuring of ultra-precision shaft parts based on analysis and control of figuring ability. Materials 2020, 13, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaborski, S.; Pszczołowski, W. Selected problems in evaluating topography of coated abrasives. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2006, 6, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courbon, C.; Valiorgue, F.; Claudin, C.; Jacquier, M.; Dumont, F.; Rech, J. Influence of Some Superfinishing Processes on Surface Integrity in Automotive Industry. Procedia CIRP 2016, 45, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, W.; Rech, J.; Wanat, T. Surface finish on hardened bearing steel parts produced by superhard and abrasive tools. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermouche, G.; Rech, J.; Hamdi, H.; Bergheau, J.M. On the residual stress field induced by a scratching round abrasive grain. Wear 2010, 269, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Peng, X.; Sun, Z.; Hu, H.; Dai, Y.; Lai, T. Modeling and Experimental Verification of Time-Controlled Grinding Removal Function for Optical Components. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Dai, Y.; Hu, H.; Tie, G.; Guan, C. Research on high precision and deterministic figuring for shaft parts based on abrasive belt polishing. Materials 2019, 12, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourani, A.; Dursapt, M.; Hamdi, H.; Rech, J.; Zahouani, H. Effect of the belt grinding on the surface texture: Modeling of the contact and abrasive wear. Wear 2005, 259, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Jiang, F.; Li, C. A review of surface quality control technology for robotic abrasive belt grinding of aero-engine blades. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2023, 220, 113381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutowska, M.; Łukianowicz, C.; Szada-Borzyszkowska, M. Sequential Smoothing Treatment of Glass Workpieces Cut by Abrasive Water Jet. Materials 2022, 15, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilger, M.; Kipp, M.; Schumann, S.; Dereli, T.T.; Biermann, D. Structuring surfaces by microfinishing using defined abrasive belts. Inventions 2017, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Xiao, G.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y. A new force-depth model for robotic abrasive belt grinding and confirmation by grinding of the Inconel 718 alloy. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2023, 80, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Xiao, G. Prediction of surface roughness of abrasive belt grinding of superalloy material based on rlsom-rbf. Materials 2021, 14, 5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanettes, F.; Cherguy, O.; Courbon, C.; Giovenco, A.; Han, S.; Rech, J. Towards the prediction of surface roughness induced by the belt finishing process: Influence of the workmaterial on the roughness reduction rate. Procedia CIRP 2020, 87, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherguy, O.; Cabanettes, F.; Han, S.; Rech, J. Modeling surface roughness profiles generated by the belt finishing process of a 27MnCr5 carburized steel. Precis. Eng. 2024, 88, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Xiao, G.; Chen, S.; Li, S. Analysis of thermal-mechanical causes of abrasive belt grinding for titanium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 3241–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Salvatore, F.; Rech, J.; Li, J. Investigating adhesion wear on belt and its effects on dry belt finishing. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, J.; Kermouche, G.; Claudin, C.; Khellouki, A.; Grzesik, W. Modelling of the residual stresses induced by belt finishing on a AISI52100 hardened steel. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khellouki, A.; Rech, J.; Zahouani, H. The effect of lubrication conditions on belt finishing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigerelle, M.; Gautier, A.; Hagege, B.; Favergeon, J.; Bounichane, B. Roughness characteristic length scales of belt finished surface. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 6103–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrol, A.; Hoffmann, M.; Lisek, M.; Bozek, J. The Quality of Surgical Instrument Surfaces Machined with Robotic Belt Grinding. Materials 2023, 16, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandecka, K.; Kacalak, W.; Wiliński, M.; Wieczorowski, M.; Mathia, T.G. Superfinishing with Abrasive Films Featuring Discontinuous Surfaces. Materials 2024, 17, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacalak, W.; Lipiński, D.; Szafraniec, F.; Zawada-Tomkiewicz, A.; Tandecka, K.; Królczyk, G. Metrological basis for assessing the state of the active surface of abrasive tools based on parameters characterizing their machining potential. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2020, 165, 108068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopytowski, A.; Świercz, R.; Oniszczuk-Świercz, D.; Zawora, J.; Kuczak, J.; Żrodowski, Ł. Effects of a New Type of Grinding Wheel with Multi-Granular Abrasive Grains on Surface Topography Properties after Grinding of Inconel 625. Materials 2023, 16, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacalak, W.; Tandecka, K.; Mathia, T.G. A method and new parameters for assessing the active surface topography of diamond abrasive films. J. Mach. Eng. 2016, 16, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Deja, M.; Zieliński, D. A Pilot Study on Machining Difficult-to-Cut Materials with the Use of Tools Fabricated by SLS Technology. Materials 2021, 14, 5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiński, D.; Banaszek, K.; Rypina, Ł. Analysis of the Cutting Abilities of the Multilayer Grinding Wheels—Case of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Grinding. Materials 2022, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiński, D.; Bałasz, B.; Rypina, Ł. Modelling of surface roughness and grinding forces using artificial neural networks with assessment of the ability to data generalisation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpin, K.; Mezghani, S.; El Mansori, M. Multiscale assessment of structured coated abrasive grits in belt finishing process. Wear 2015, 332–333, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, S.; Xiao, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, K. A high-precision prediction model for surface topography of abrasive belt grinding considering elastic contact. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandecka, K.; Kacalak, W.; Wieczorowski, M.; Rokosz, K.; Chapon, P.; Mathia, T.G. Ultrathin Carbon Textures Produced on Machined Surfaces in an Integrated Finishing Process Using Microabrasive Films. Materials 2024, 17, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Ruan, X.; Li, L.; Xie, M. Multiscale characterization and contact performance analysis of machining surfaces. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 25178-2:2021; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS): Surface Texture: Areal—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.

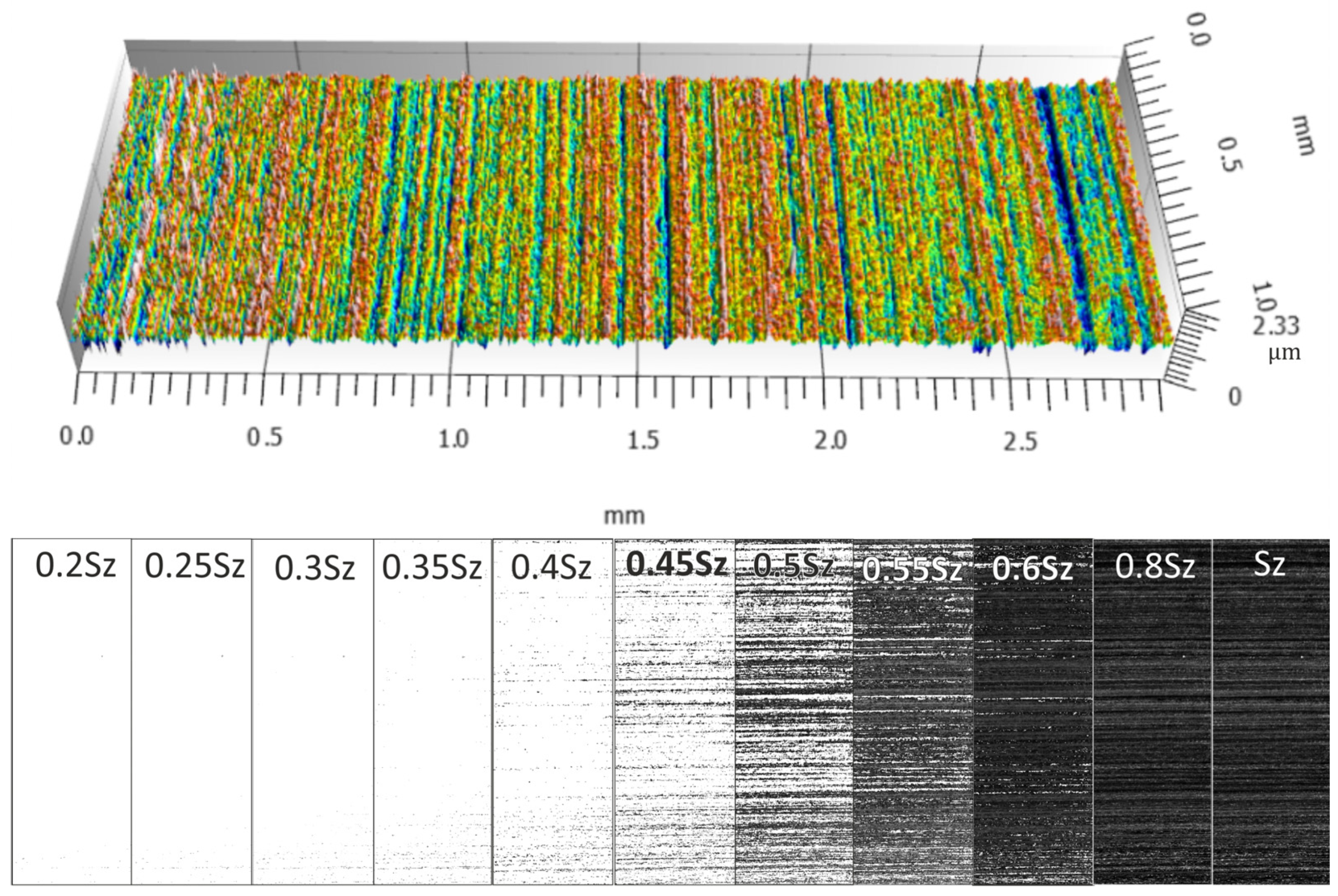
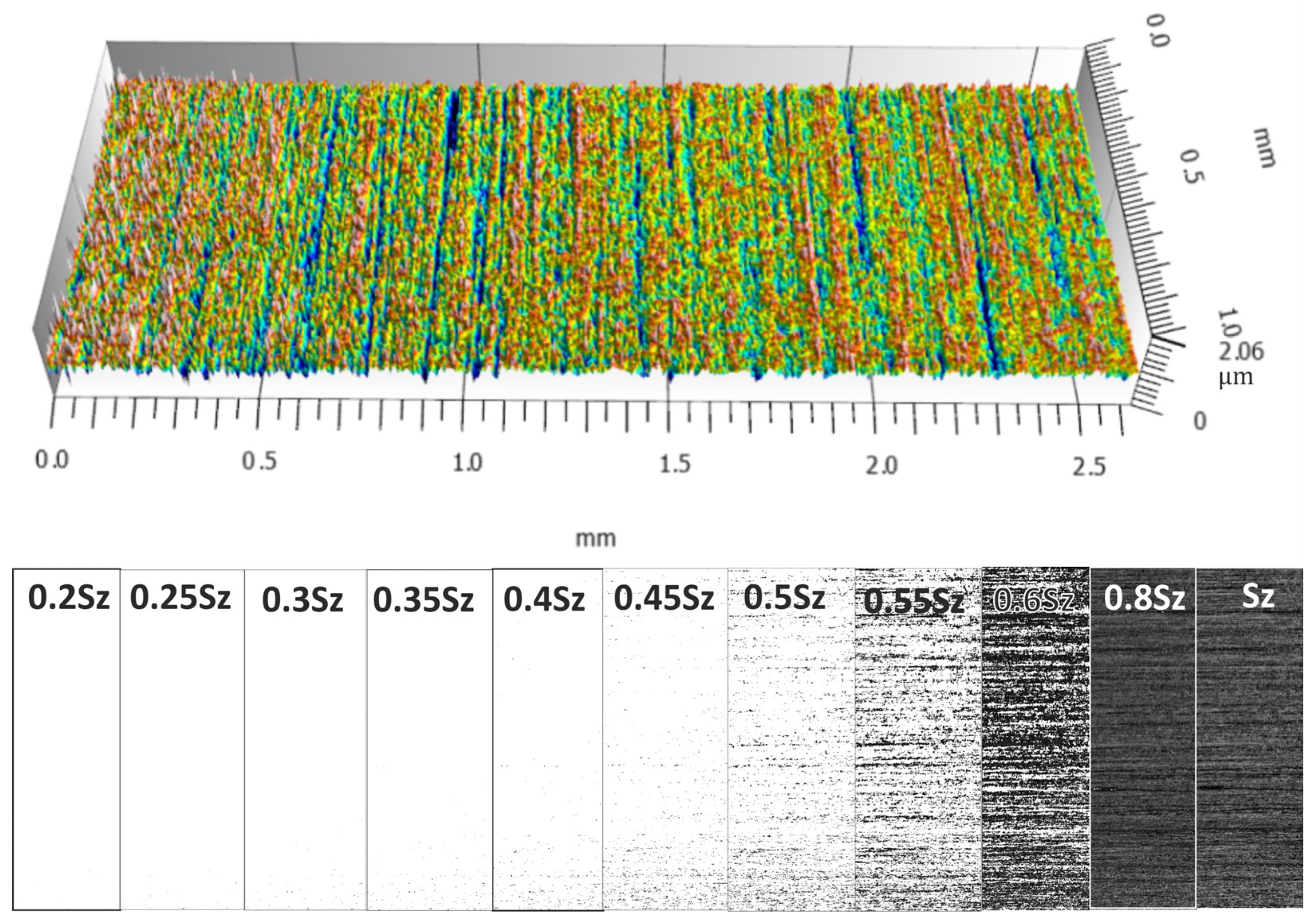
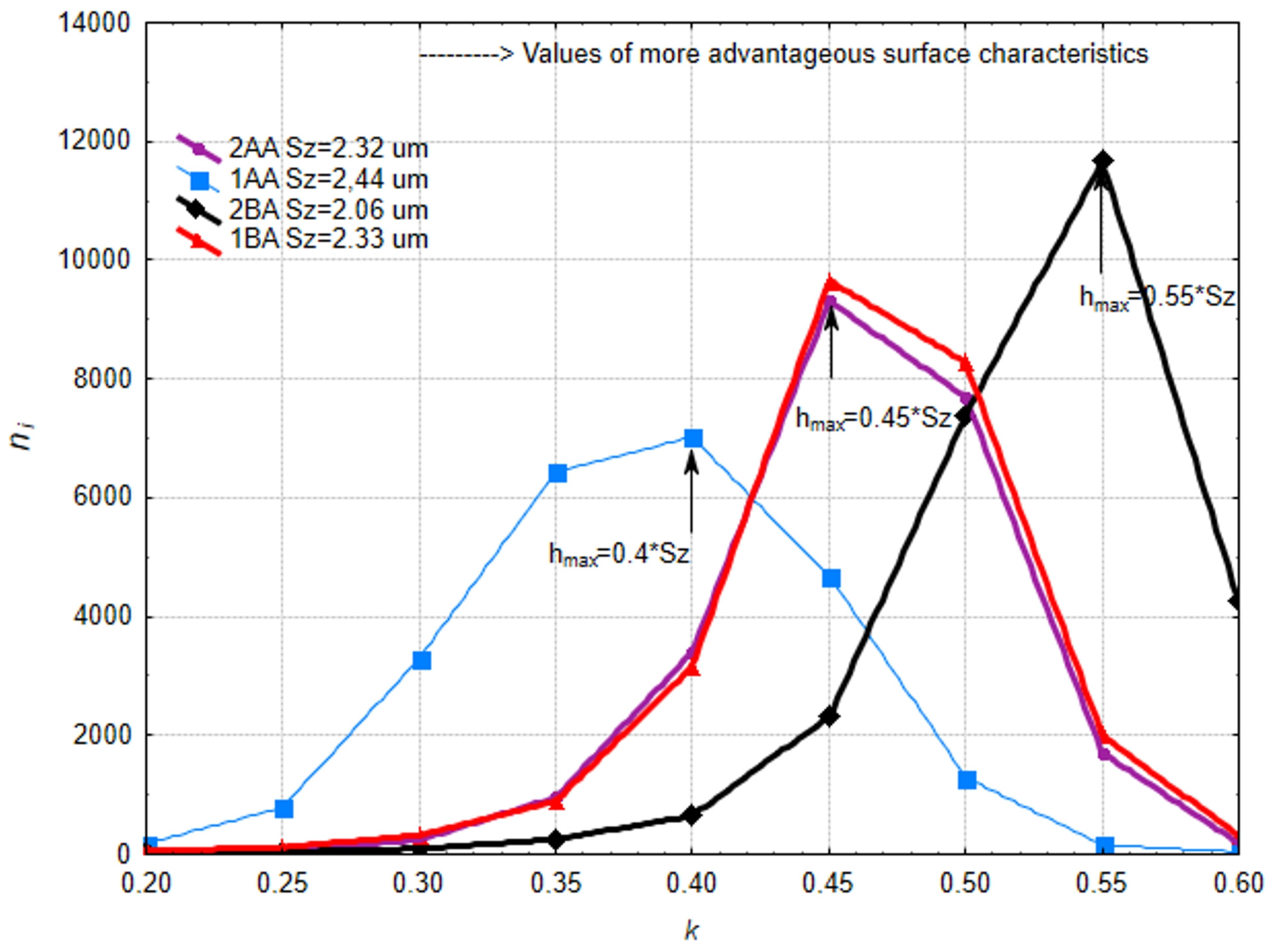
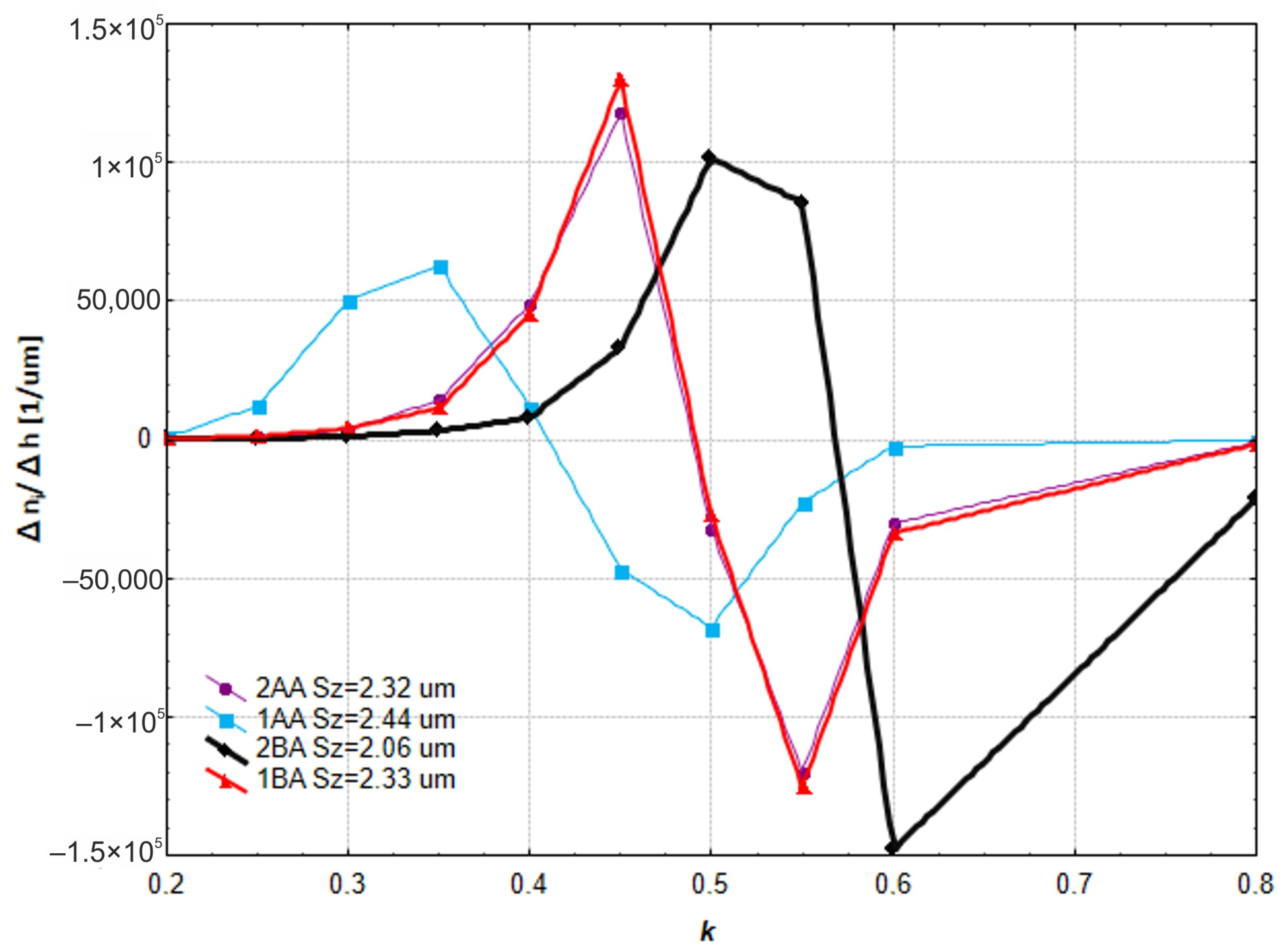


| Machining Variant | ce | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2AA | 9310 | 0.45 | 4189.5 |
| 1AA | 7023 | 0.4 | 2809.2 |
| 2BA | 11,664 | 0.55 | 6415.2 |
| 1BA | 9652 | 0.45 | 4343.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tandecka, K.; Kacalak, W.; Mathia, T.G. Comparative Analysis of Microabrasive Film Finishing Effects across Various Process Variants. Materials 2024, 17, 3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143582
Tandecka K, Kacalak W, Mathia TG. Comparative Analysis of Microabrasive Film Finishing Effects across Various Process Variants. Materials. 2024; 17(14):3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143582
Chicago/Turabian StyleTandecka, Katarzyna, Wojciech Kacalak, and Thomas G. Mathia. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Microabrasive Film Finishing Effects across Various Process Variants" Materials 17, no. 14: 3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143582
APA StyleTandecka, K., Kacalak, W., & Mathia, T. G. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Microabrasive Film Finishing Effects across Various Process Variants. Materials, 17(14), 3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143582









