Electromagnetic Characterization of EAC-1A and JSC-2A Lunar Regolith Simulants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurements Methods
OECP and Transmission Line Methods
3. Results and Discussion
Comparison of Dielectric Properties
4. Other Studies
4.1. Drying Lunar Simulants
4.2. Study on Variations in Density
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ISRU | In situ resource utilization |
| OECP | Open-Ended Coaxial Probe |
| ISR | In situ resource |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| JSC | Johnson Space Center |
| DAK | Dielectric Assessment Kit |
| EuCAP | European Conference on Antennas and Propagation |
| CLEP | China Lunar Exploration Program |
| CAEM-Lab | Computational and Applied Electromagnetism Laboratory |
| SAR | Synthetic aperture radar |
References
- Shaw, M.G.; Humbert, M.S.; Brooks, G.A.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Duffy, A.R.; Pownceby, M.I. Metal and Oxide Sublimation from Lunar Regolith: A Kinetics Study. Minerals 2023, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korniejenko, K.; Pławecka, K.; Kozub, B. An Overview for Modern Energy-Efficient Solutions for Lunar and Martian Habitats Made Based on Geopolymers Composites and 3D Printing Technology. Energies 2022, 15, 9322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, J.J.; Woyciechowski, P.; Kalinowski, M. Rheological Properties of Lunar Mortars. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damięcka-Suchocka, M.; Katzer, J. Terrestrial Laser Scanning of Lunar Soil Simulants. Materials 2022, 15, 8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlüter, L.; Cowley, A. Review of Techniques for In-Situ Oxygen Extraction on the Moon. Planet. Space Sci. 2019, 181, 104753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethridge, E.; William, K. Microwave Extraction of Water from Lunar Regolith Simulant. Am. Inst. Phys. 2007, 880, 830–837. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kochar, I.M.; Pandey, D.K.; Das, A.; Putrevu, D.; Kumar, R.; Panigrahi, R.K. Dielectric Constant Estimation of Lunar Surface Using Mini-RF and Chandrayaan-2 SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdashelt, M.; Bustin, R.; Gibson, E. Hydrogen Extraction from Lunar Soil: Methods Applicable to a Lunar Processing Facility. Lunar Planet. Inst. 1989, 20, 424. [Google Scholar]
- Faierson, E.; Logan, K. Potential ISRU of Lunar Regolith for Planetary Habitation Applications. In Moon: Prospective Energy and Material Resources; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 201–234. [Google Scholar]
- Alpay, A.; Ertl, F.; Marechal, M.; Makaya, A.; Schwentenwein, M. Additive manufacturing of lunar regolith structures. Open Ceram. 2021, 5, 100058. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.A.; Meek, T.T. Microwave Sintering of Lunar Soil: Properties, Theory, and Practice. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2005, 18, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Lim, S.; Anand, M. Microwave processing of lunar soil for supporting longer-term surface exploration on the Moon. Space Policy 2016, 37, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toklu, Y.C.; Akpınar, P. Lunar Soil Simulants—An Assessment. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST), Istanbul, Turkey, 11–14 June 2019; pp. 635–638. [Google Scholar]
- Barmatz, M.; Steinfeld, D.; Winterhalter, D.; Rickman, R.; Gustafson, D.B.; Weinstein, M. Microwave permittivity and permeability measurements on lunar simulants. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Woodlands, TX, USA, 19–23 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, T.; Filbert, J.; Ghasr, M.T.; Zoughi, R. Wideband Microwave Dielectric Properties of Martian and Lunar Regolith Simulants. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16–19 May 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Heggy, E.; Palmer, E.; Kofman, W.; Clifford, S.; Righter, K.; Hérique, A. Radar properties of comets: Parametric dielectric modeling of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Icarus 2012, 221, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelschiøn, V.S.; Eriksson, S.R.; Cowley, A.; Fateri, M.; Meurisse, A.; Kueppers, U.; Sperl, M. EAC-1A: A novel large-volume lunar regolith simulant. Nat. Res. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zocca, A.; Fateri, M.; AlSabbagh, D.; Günstera, J. Investigation of the sintering and melting of JSC-2A lunar regolith simulant. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 14097–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Chen, S.; Du, X.; Osei Jnr, E.M.; Lu, P.; Wang, Z. Influence of temperature and frequency on microwave dielectric properties of lunar regolith simulant. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, D.S.; Carter, J.L.; Boles, W.W.; Allen, C.C.; Alton, J.H. JSC-1: A new lunar soil simulant. In Engineering Construction and Operations in Space IV; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1994; pp. 857–866. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Wang, J.; Polansky, J. Measurement of Dust Charging on a Lunar Regolith Simulant Surface. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2013, 41, 3498–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethridge, E.C.; Kaukler, W. Microwave processing of planetary surfaces for the extraction of volatiles. In Proceedings of the 49th Aerospace Sciences Meeting (AIAA), Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2011; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Exolith Lab—Regolith Simulants. Available online: https://exolithsimulants.com/collections/regolith-simulants/products/lhs-1-lunar-highlands-simulant (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Exolith Lab—Regolith Simulants. Available online: https://exolithsimulants.com/collections/regolith-simulants/products/lms-1-lunar-mare-simulant (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Feng, J. CAS-1 lunar soil simulant. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussey, H.E. Microwave dielectric measurements of lunar soil with a coaxial line resonator method. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Institute (NASA Astrophysics Data System), Houston, TX, USA, 19–23 March 1979; pp. 2175–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Bassett, H.L.; Shackelford, R.G. (NASA-CR-115571) Complex Permittivity Measurements of Lunar Samples at Microwave and Milimeter Wavelengths; Engineering Expertiment Station Special Techniques Division: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- 14163—Bulk Soil Sample 7776 Grams. Available online: https://curator.jsc.nasa.gov/lunar/lsc/14163.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Su, Y.; Wang, R.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhouand, J.; Xiao, Z.; Ding, C.; Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Ren, X.; et al. Hyperfine structure of regolith unveiled by chang’e-5 lunar regolith penetrating radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, M.T.; Zaka ur Rehman, M.; Khan, A.M.; Khan, M.T.; Ali, S.M. A brief review of measuring techniques for characterization of dielectric materials. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Electr. Eng. 2012, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Jarvis, J.; Janezic, M.D.; Degroot, D.C. A brief review of measuring techniques for characterization of dielectric materials. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2010, 13, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivo, E.; Hernandez, D.; Garranzo, D.; Barandiaran, J.; Reina, M. New Environmental Testing Capabilities at INTA. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Spacecraft Structures, Materials and Environmental Testing, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 20–23 March 2012; Volume 691. [Google Scholar]
- Shull, P.J. Nondestructive Evaluation Theory, Techniques, and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- López-Rodríguez, P.; Escot-Bocanegra, D.; Poyatos-Martínez, D.; Weinmann, F. Comparison of Metal-Backed Free-Space and Open-Ended Coaxial Probe Techniques for the Dielectric Characterization of Aeronautical Composites. Sensors 2016, 16, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Professional Handbook V2.0. Schmid & Partner Engineering AG. Available online: https://speag.swiss/ (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Sabouroux, P.; Boschi, P. Epsimu: A new microwave materials measurement kit. Rev. Electr. Electron. 2005, 10, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Basics of Measuring the Dielectric Properties of Materials, Application Note 5989-2589; Keysight Technologies: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2012.
- Estévez Cidrás, J.; Ramos Somolinos, D.; Plaza Gallardo, B.; Stepanyan Stepanyan, N.; Cowley, A.; Poyatos Martínez, D. Electromagnetic Characterization of Lunar Dust Simulants. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Madrid, Spain, 27 March–1 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ginés-Palomares, J.C.; Fateri, M.; Schubert, T.; de Peindray d’Ambelle, L.; Simon, S.; Gluth, G.J.; Günster, J.; Zocca, A. Material aspects of sintering of EAC-1A lunar regolith simulant. Nat. Res. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 23053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, M.; Wilson, S.A. Apparatus and Method for Producing a Lunar Agglutinate Simulant. U.S. Patent 8,610,024, 17 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bassett, H.L.; Shackelford, R.G. Dielectric properties of apollo 14 lunar samples at microwave and millimeter wavelengths. In Proceedings of the Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 10–13 January 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Oghbaei, M.; Mirzaee, O. Microwave versus conventional sintering: A review of fundamentals, advantages and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 494, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadoji, P.; Peelamedu, R.; Agrawal, D.; Roy, R. Microwave sintering of Ni–Zn ferrites: Comparison with conventional sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2003, 98, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, S.; Zhang, X.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.R.; Cui, B.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, J. Hybrid microwave sintering of a lunar soil simulant: Effects of processing parameters on microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2022, 220, 110878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
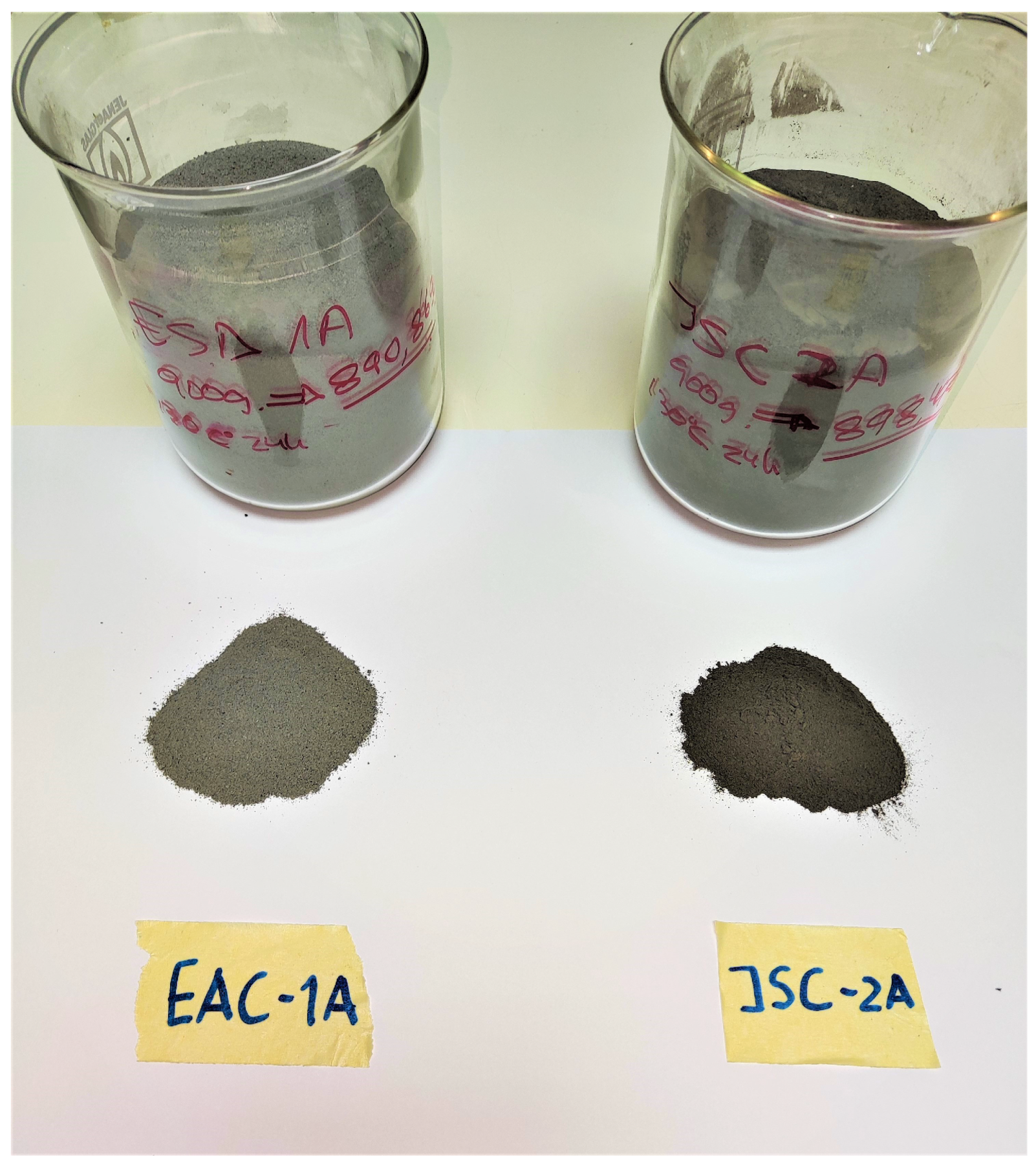

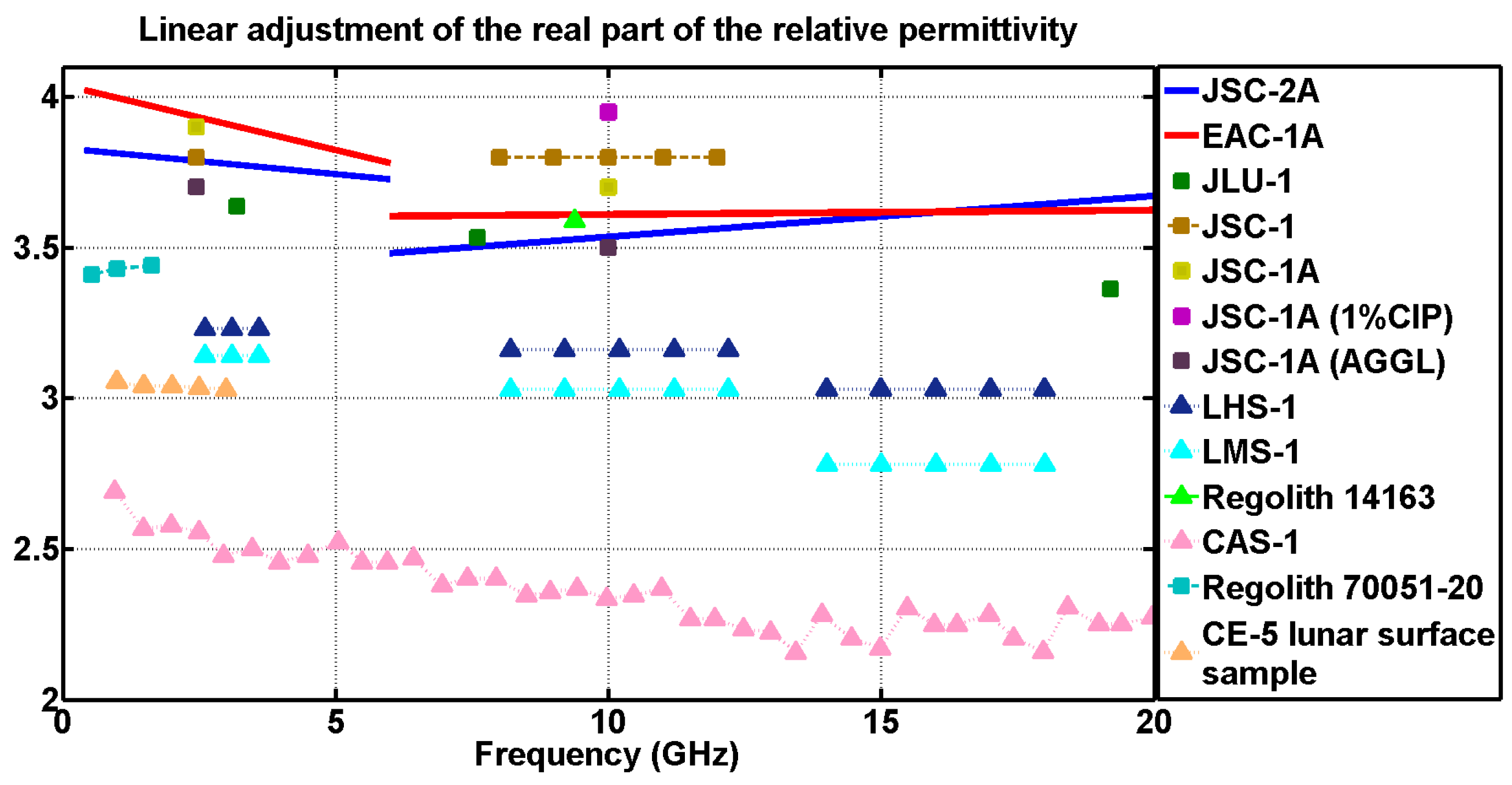


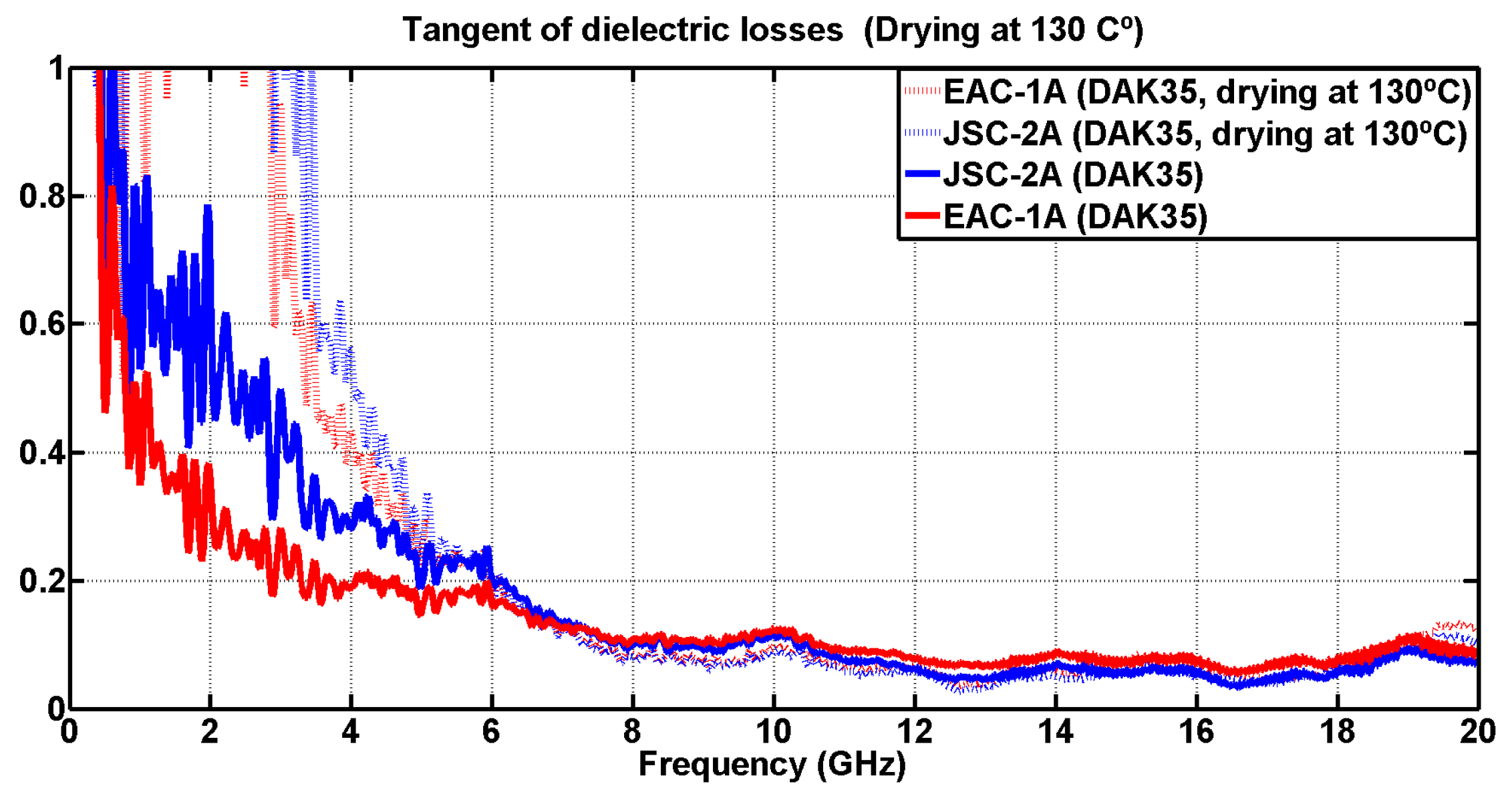
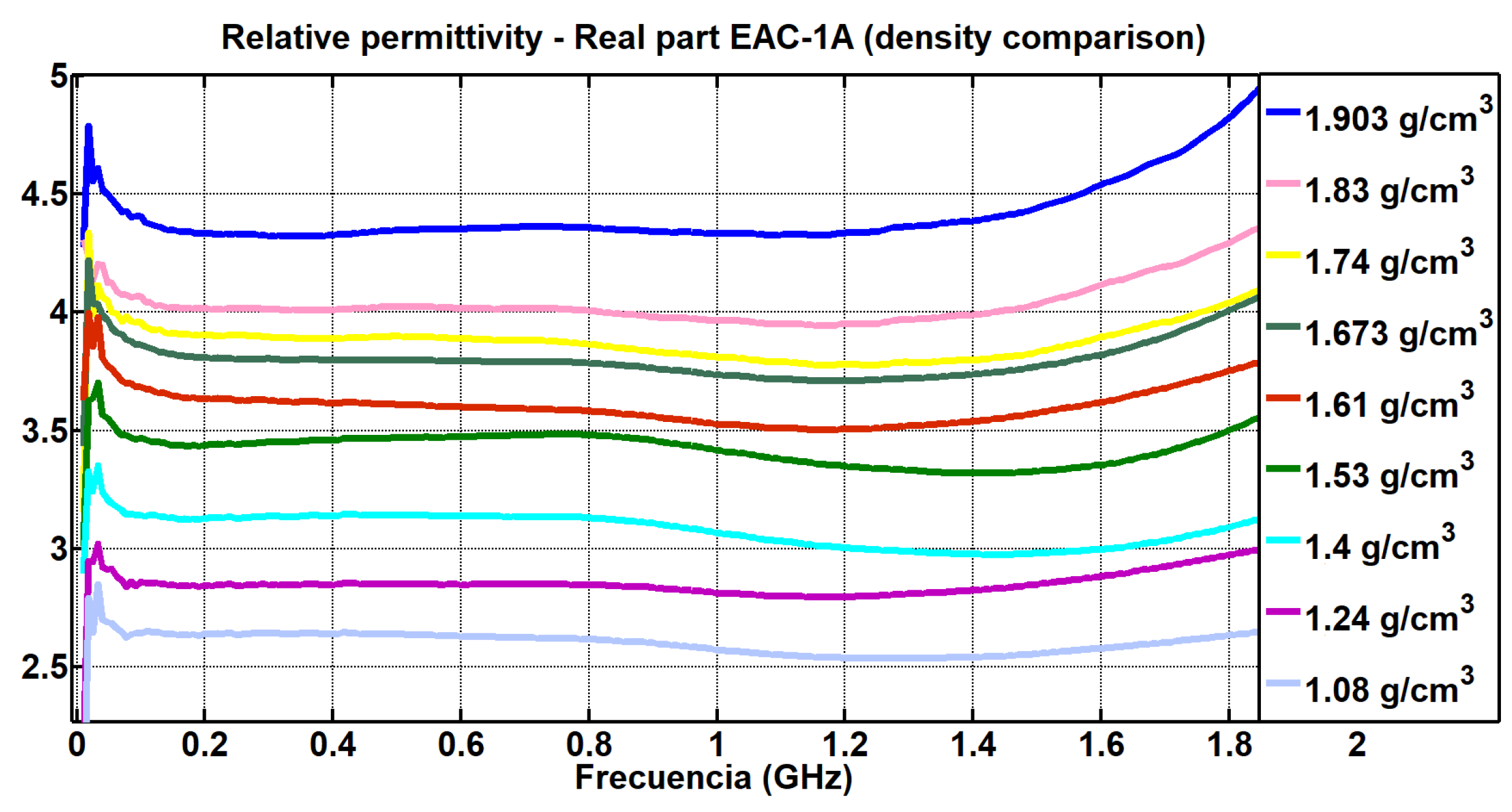
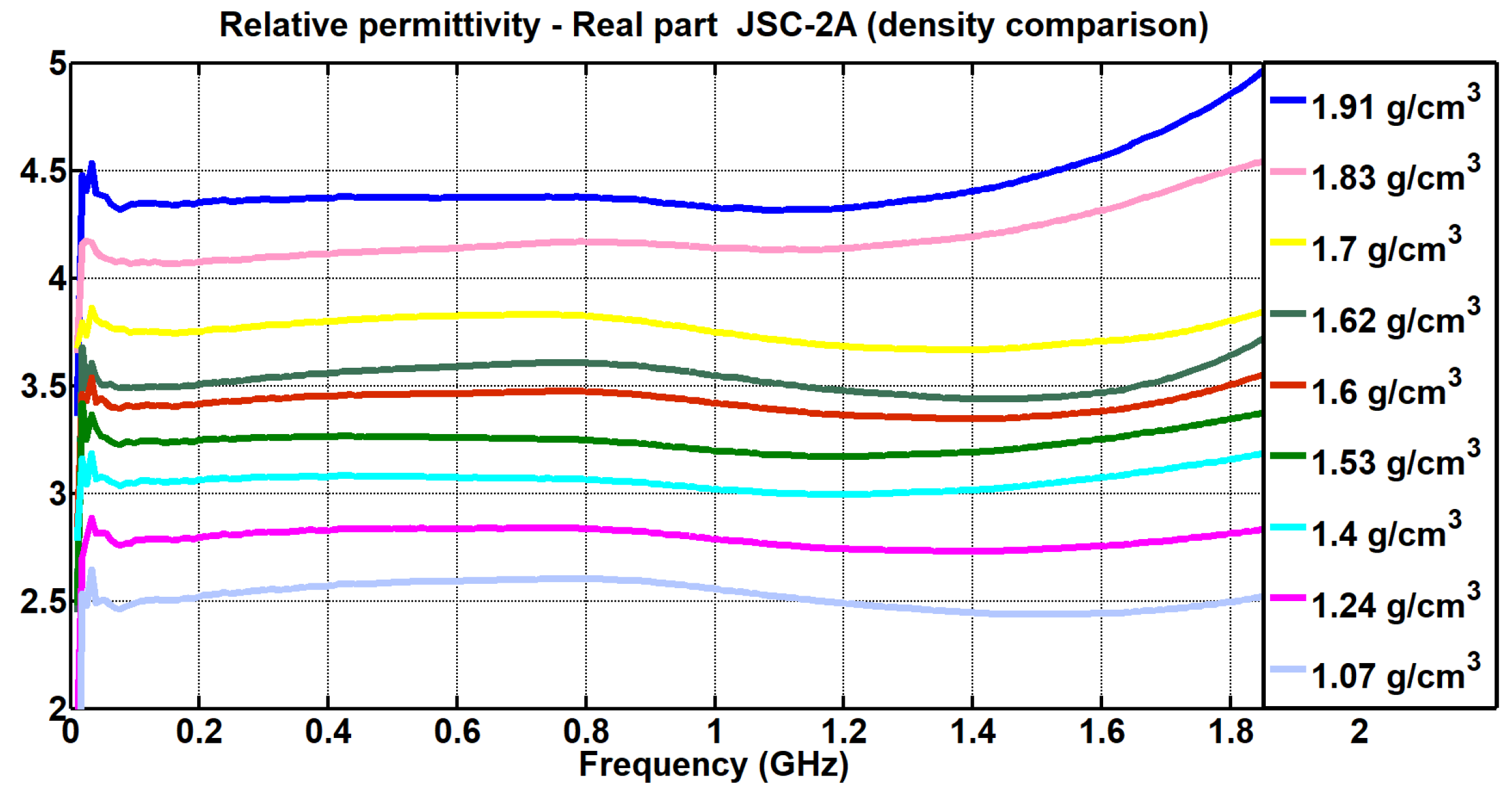
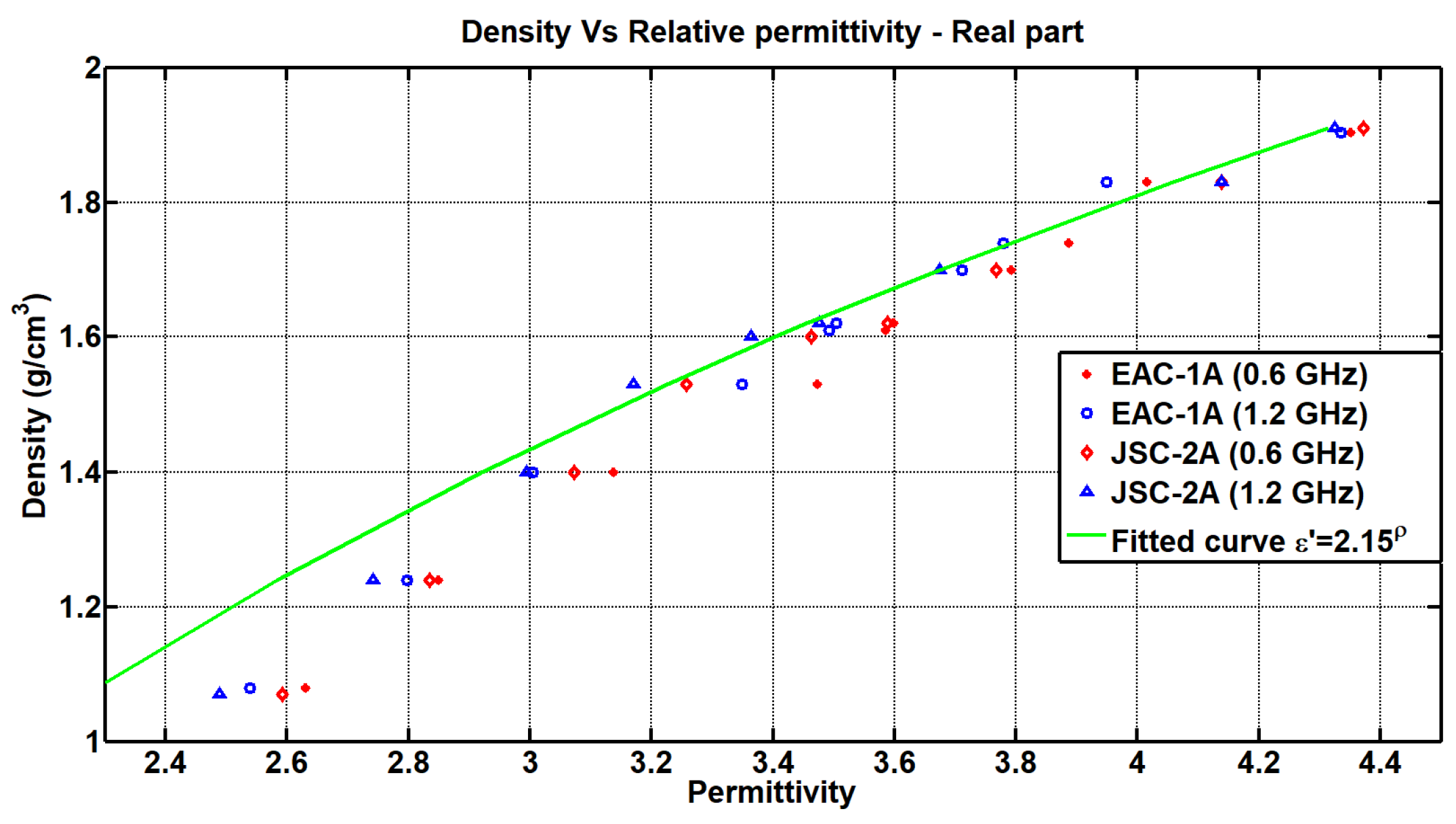
| Frequency (GHz) | EAC-1A |
|---|---|
| (0–6] EpsiMu | = −0.0432f + 4.0397 tan = −0.0015f + 0.0659 |
| [6–20] DAK-3.5 | = −0.0432f + 4.0397 tan = −0.0039f + 0.1429 |
| Frequency (GHz) | JSC-2A |
|---|---|
| (0–6] EpsiMu | = −0.0172f + 3.8299 tan = 0.0005f + 0.0364 |
| [6–20] DAK-3.5 | = 0.0136f + 3.4003 tan = −0.0058f + 0.1550 |
| Type of Sample | Acronym | Type | Place |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lunar simulants | JLU | 1 | Jilin University |
| JSC | 1 | John Space Center | |
| 1A | |||
| 1A (1% CIP) | |||
| 1A (AGGL) | |||
| Lunar regolith | 70,051 | 20 | Apollo mission 17 |
| Type of Sample | Acronym | Type | Place |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lunar simulants | LHS | 1 | Lunar highlands simulant |
| LMS | 1 | Lunar mare simulant | |
| CAS | 1 | Chinese Academy Science | |
| Lunar regolith | 14,163 | 164 | Apollo mission 14 |
| CE | 5 | Cheng’E mission |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos Somolinos, D.; Plaza Gallardo, B.; Cidrás Estévez, J.; Stepanyan, N.; Cowley, A.; Auñón Marugán, A.; Poyatos Martínez, D. Electromagnetic Characterization of EAC-1A and JSC-2A Lunar Regolith Simulants. Materials 2024, 17, 3633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153633
Ramos Somolinos D, Plaza Gallardo B, Cidrás Estévez J, Stepanyan N, Cowley A, Auñón Marugán A, Poyatos Martínez D. Electromagnetic Characterization of EAC-1A and JSC-2A Lunar Regolith Simulants. Materials. 2024; 17(15):3633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153633
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos Somolinos, David, Borja Plaza Gallardo, José Cidrás Estévez, Narek Stepanyan, Aidan Cowley, Alicia Auñón Marugán, and David Poyatos Martínez. 2024. "Electromagnetic Characterization of EAC-1A and JSC-2A Lunar Regolith Simulants" Materials 17, no. 15: 3633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153633
APA StyleRamos Somolinos, D., Plaza Gallardo, B., Cidrás Estévez, J., Stepanyan, N., Cowley, A., Auñón Marugán, A., & Poyatos Martínez, D. (2024). Electromagnetic Characterization of EAC-1A and JSC-2A Lunar Regolith Simulants. Materials, 17(15), 3633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153633






