Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solutions in an Adsorption Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Used Materials
2.2. Used Methods
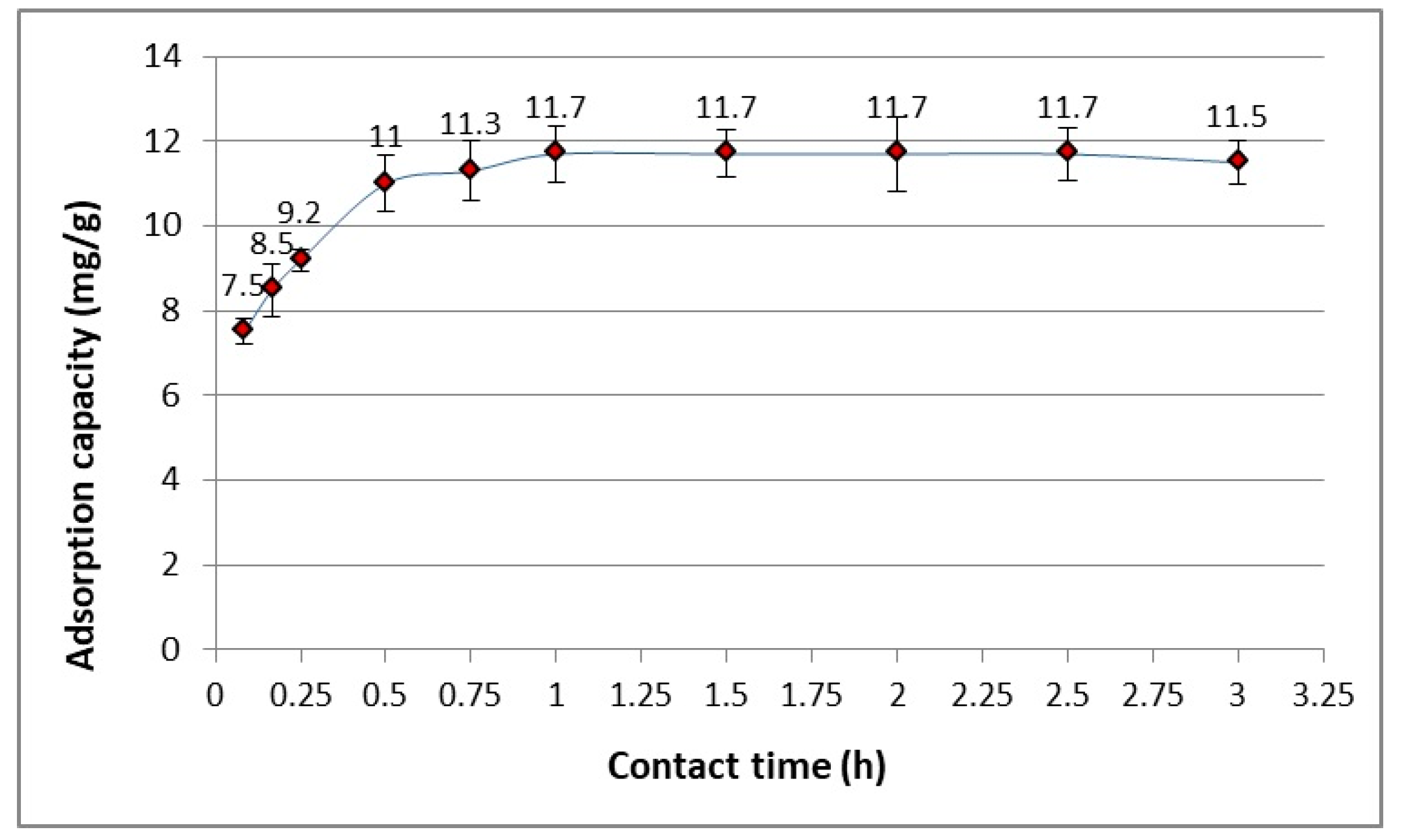
2.2.1. Adsorption Kinetics Studies
- qe—Equilibrium adsorption capacity of ACT in the adsorbent—solid phase [mg/g];
- V—Volume of adsorptive ACT solution [dm3];
- C0—Initial adsorbate ACT concentration in liquid phase [mg/dm3];
- Ce—Equilibrium adsorbate concentrations in the solution [mg/dm3];
- m—Mass of adsorbent used [g].
- t—contact time [h];
- q—the amount of adsorbate (depend on time);
- qekin—the value of q in dynamic equilibrium, i.e., q (t → ∞) = qe;
- k1—kinetic constant [1/h].
- k2—kinetic constant [mg/g·h].
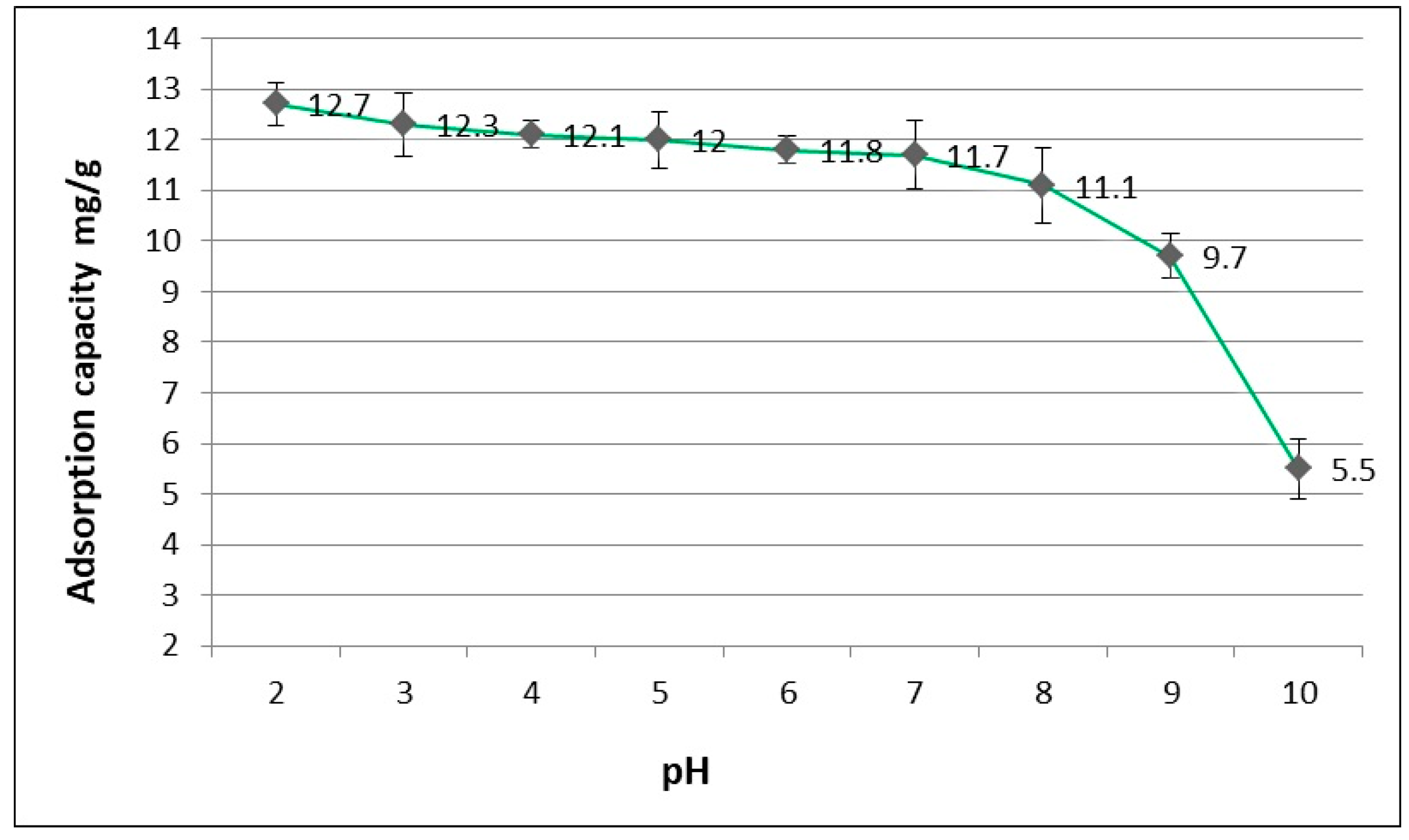
2.2.2. The Influence of pH on the Adsorption Process
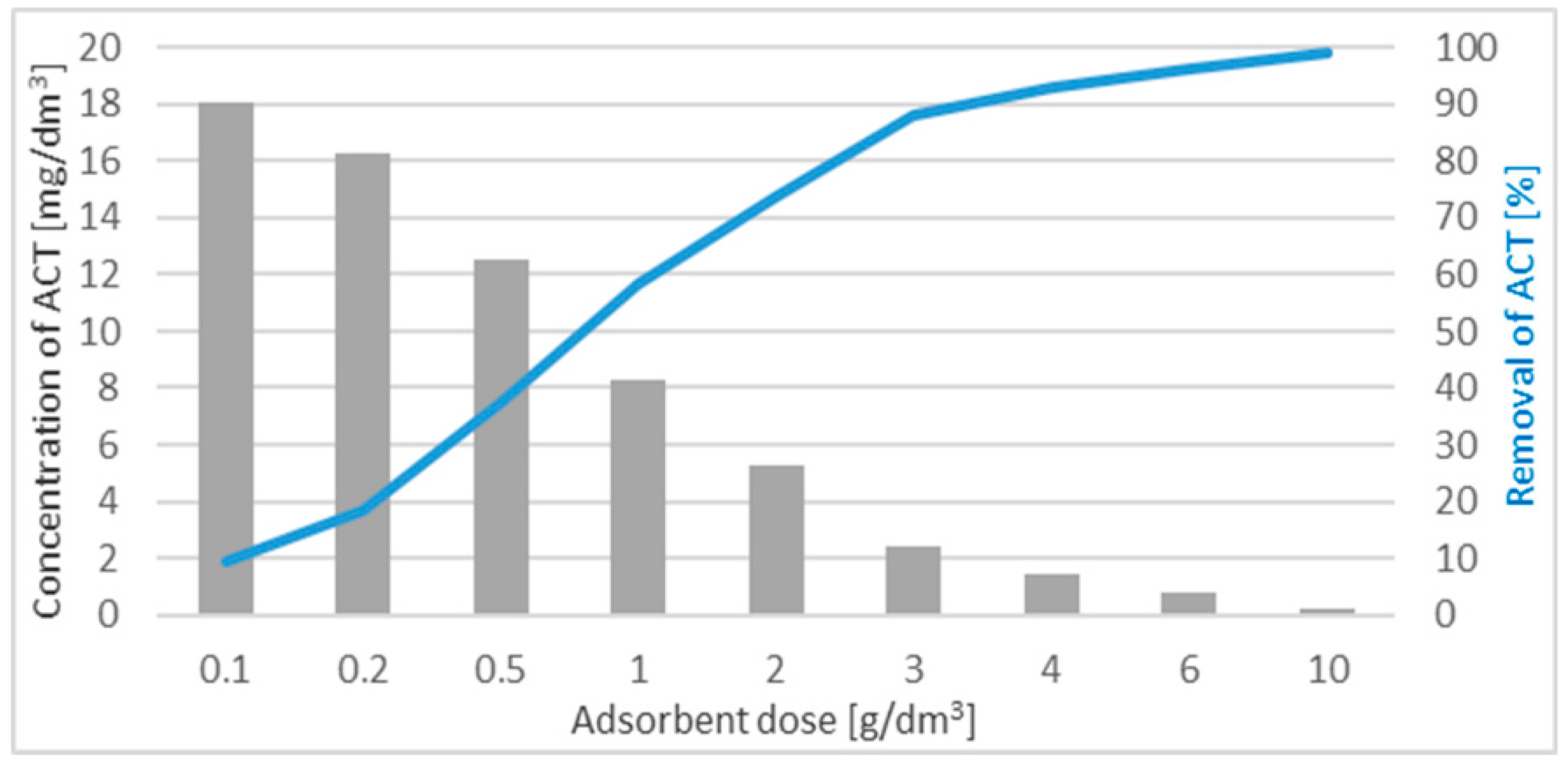
2.2.3. The Influence of the WD-Extra Doses on the Adsorption Effectiveness
2.2.4. Adsorption Equilibrium Studies
- K—adsorption equilibrium constant, related to the sorption capacity of the material, and the subscripts KF, KL correspond to the isotherm name, respectively [dm3/mg];
- n—isotherm constant determining heterogeneity of sorbent surface (dimensionless);
- qe—equilibrium adsorption capacity [mg/g];
- qm—maximum adsorption capacity [mg/g];
- Ce—equilibrium concentration [mg/dm3].
3. Results of Studies and Discussion
3.1. The Kinetics of the Adsorption Process
3.2. The Influence of pH Initial ACT Solution
3.3. The Influence of the WD-Extra Dose on ACT Adsorption
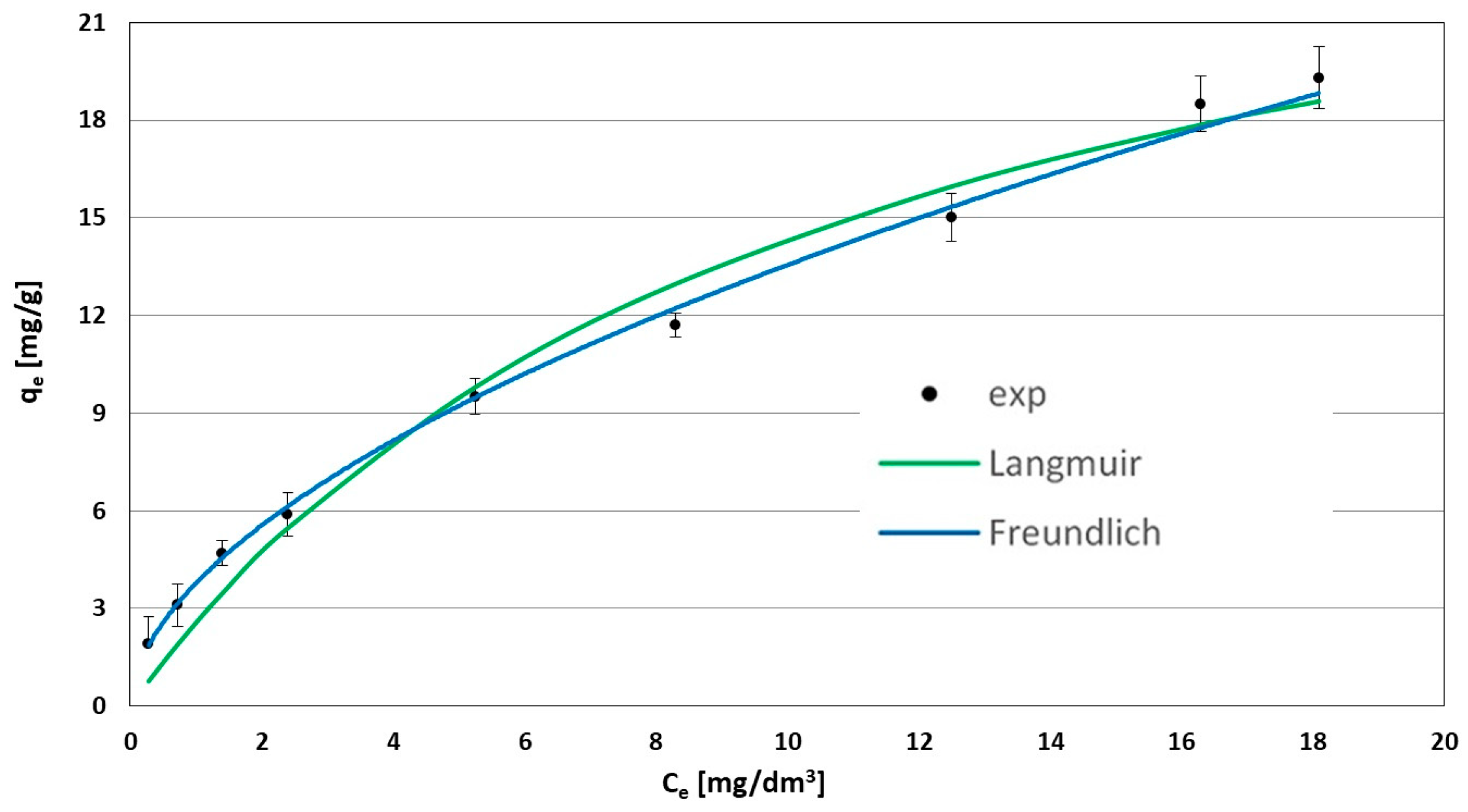
3.4. Determination of Isotherm Parameters
- N—number of experimental points;
- qe—equilibrium concentration of ACT in the sorbent (solid phase), (mg/g);
- qe mod—equilibrium concentration of ACT in the sorbent calculated from the model, (mg/g).
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nosek, K.; Styszko-Grochowiak, K.; Gołaś, J. Determination of acidic pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater by using solid-phase extraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Geomatics Environ. Eng. 2012, 6, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warszewska, M.; Zima, A. Efficacy of Sorbent Use in Water Treatment during Accidental Contamination with Paracetamol, Analit 4. 2017, pp. 72–78. Available online: http://analit.agh.edu.pl/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/8_Warszewska_Martyna_Analit_4.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Szymonik, A.; Lach, J. Threat to the aquatic environment by the presence of pharmaceuticals. Environ. Eng. Pro. 2012, 15, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, H.N.P.; Le, G.K.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Bui, X.-T.; Nguyen, K.H.; Rene, E.R.; Vo, T.D.H.; Cao, N.-D.T.; Mohan, R. Acetaminophen micropollutant: Historical and current occurrences, toxicity, removal strategies and transformation pathways in different environments. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124391. [Google Scholar]
- Nourmoradi, H.; Moghadam, K.F.; Jafari, A.; Kamarehie, B. Removal of acetaminophen and ibuprofen from aqueous solutions by activated carbon derived from Quercus Brantii (Oak) acorn as a low-cost biosorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6807–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, A.M.; Shaik, B.; Nolan, K.; Urell, K.; Oelgemöller, M.; Tobin, J.; Morrissey, A. Treatment options for wastewater effluents from pharmaceutical companies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 649–666. [Google Scholar]
- Boron, M.; Pawlas, K. Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment—Literature Review. Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2015, 96, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K.; Zoh, K.D. Occurrence and removals of micropollutants in water environment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 21, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Lu, X.; Xu, W.; Gong, Q.; Ding, J.; Dan, B.; Xie, P. Removal of acetaminophen in the Fe2+/persulfate system: Kinetic model and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.J.; Park, Y.H.; Kang, I.S.; Myong, H.B.; Song, Y.S.; Kang, Y.J. Evaluation on the removal efficiency of pharmaceutical compounds in conventional drinking water treatment processes. Analytic. Scie. Tech. 2016, 29, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miera, R.; Shaikh, N.; Artyushkova, K.; Ali, A.M.S.; Santoro, C.; Thomson, B.M.; Howe, K.J.; Cerrato, J.M. Acetaminophen and caffeine removal by MnOx(s) and GAC media in column experiments. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, H.E.; El-Shahat, M.; Abdelhameed, R.M. Observable removal of pharmaceutical residues by highly porous photoactive cellulose acetate@MIL-MOF film. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus Menk, J.; do Nascimento AI, S.; Leite, F.G.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Jozala, A.F.; de Oliveira Junior, J.M.; Chaud, M.V.; Grotto, D. Biosorption of pharmaceutical products by mushroom stem waste. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloria, D.C.S.; Brito, C.H.V.; Mendonça, T.A.P.; Santos, E.B.; Gonçalves, M. Preparation of TiO2/activated carbon nanomaterials with enhanced photocatalytic activity in paracetamol degradation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 305, 127947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Shahid, M.; Ali, Z.; Nazir, A.; Alqahtani, F.O.; Zaheer, M.; Alshawwa, S.Z.; Iqbal, D.N.; Younas, U.; Bukhari, A.; et al. Paracetamol and amox-icillin adsorptive removal from aqueous solution using phosphoric acid activated-carbon. Z. Phys. Chem. 2023, 237, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largegren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handingarl 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski, W.; Rudzinski, W. Adsorption kinetics at solid/solution interfaces. The meaning of the pseudo-first- and pseudo-second-order equations. Chem. News 2011, 65, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bezak-Mazur, E.; Adamczyk, D. Changes in the surface chemistry of activated carbon WD-extra after regeneration with Fenton’s reagent used to adsorb naphthol green B, Annual Set the Environment Protection. Rocznik Ochrona Środowiska 2013, 15, 966–980. [Google Scholar]
- Skwarczynska-Wojsa, A.L.; Chacuk, A.; Modrzejewska, M.; Puszkarewicz, A. Sorption of calcium by chitosan hydrogel: Kinetics and equilibrium. Desalination 2022, 540, 116024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, I.V.; Tosheva, L.; Miller, G.; Doyle, A.M. FAU-Type Zeolite Synthesis from Clays and Its Use for the Simultaneous Adsorption of Five Divalent Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2021, 14, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszkarewicz, A.; Kaleta, J. The Efficiency of the Removal of Naphthalene from Aqueous Solutions by Different Adsorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Newcombe, G. Granular activated carbon Adsorption of 2-Methylisoborneol (MIB): Pilot- and laboratory-scale evaluations. J. Environ. Eng. ASCE 2010, 136, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
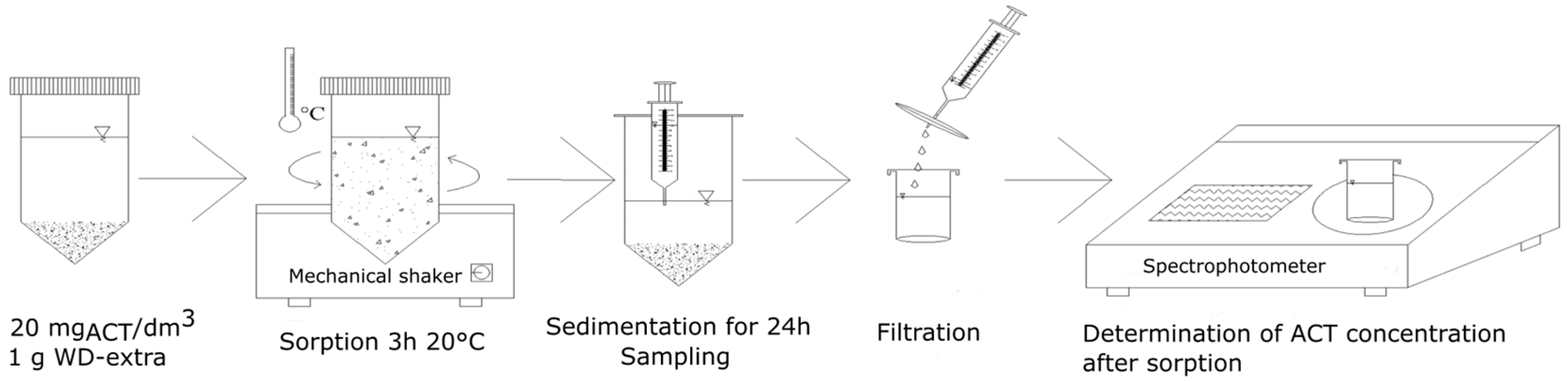


| Parameter | Volume | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density | 390–415 | [g/dm3] |
| Granulation | 1–1.5 | [mm] |
| Volume of pores (total) | 0.85–0.95 | [cm3/g] |
| Adsorption of iodine | 900–1000 | [mg/g] |
| Dechloration capacity | 4–5 | [cm] |
| Mechanical durability | 90 | [%] |
| WD-Extra | (PFO) Pseudo-First-Order | (PSO) Pseudo-Second-Order | ||
| k1 [1/h] | R2 | k2 [mg/g·h] | R2 | |
| 3.0584 | 0.8901 | 2.27 | 0.9993 | |
| Adsorbent | Constants of Isotherms | ME | σ | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WD-Extra | K | n | qm | |||
| Freundlich | KF = 3.7763 | 1.2828 | - | 3.72 | 0.36 | 0.999 |
| Langmuir | KL = 0.096 | - | 29.3 | 17.80 | 1.07 | 0.977 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skwarczynska-Wojsa, A.; Puszkarewicz, A. Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solutions in an Adsorption Process. Materials 2024, 17, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020431
Skwarczynska-Wojsa A, Puszkarewicz A. Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solutions in an Adsorption Process. Materials. 2024; 17(2):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020431
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkwarczynska-Wojsa, Agata, and Alicja Puszkarewicz. 2024. "Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solutions in an Adsorption Process" Materials 17, no. 2: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020431
APA StyleSkwarczynska-Wojsa, A., & Puszkarewicz, A. (2024). Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solutions in an Adsorption Process. Materials, 17(2), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020431







