Thermal Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Multicomponent Mg-Li-Zn-Al-Y Alloys under Hot Compression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
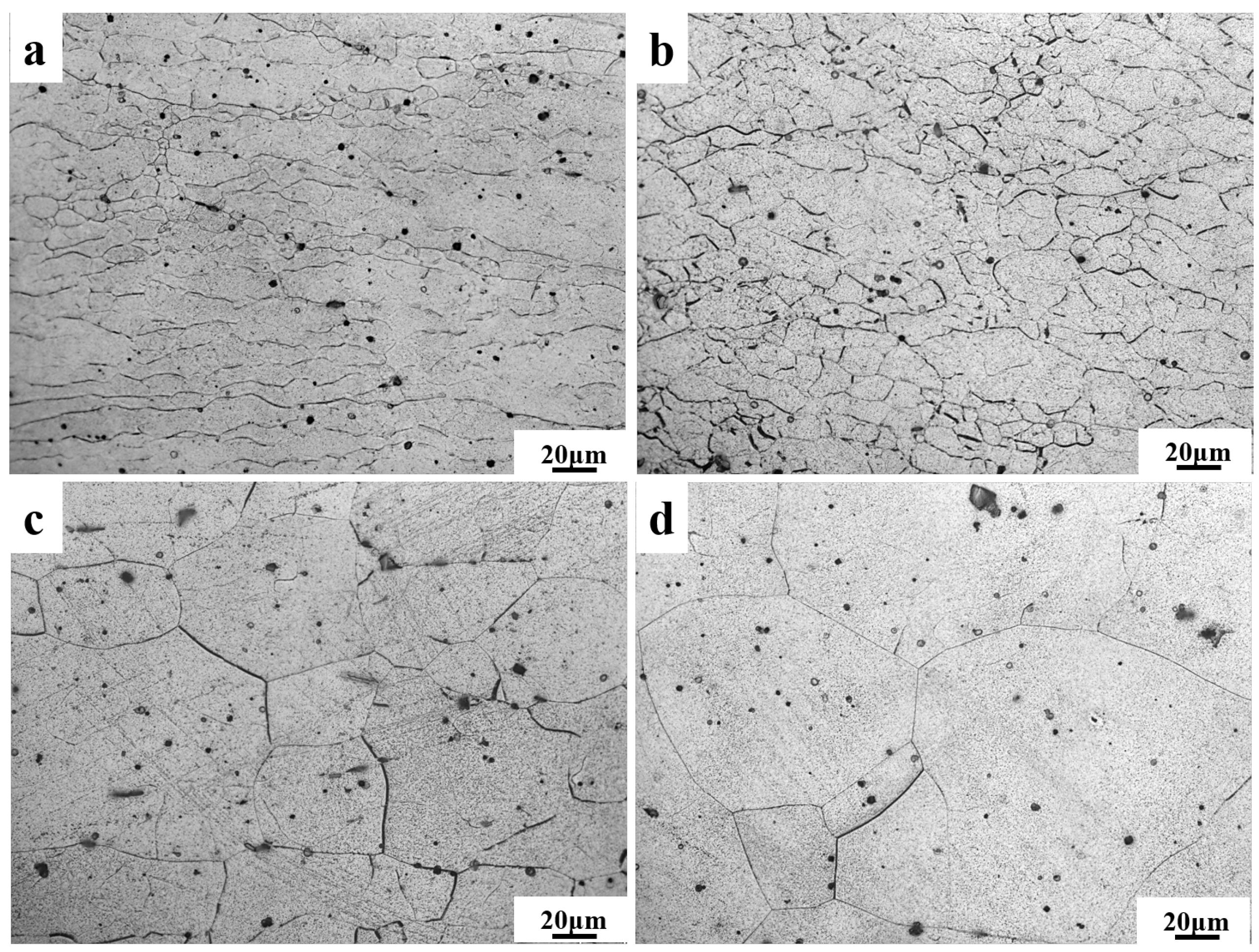
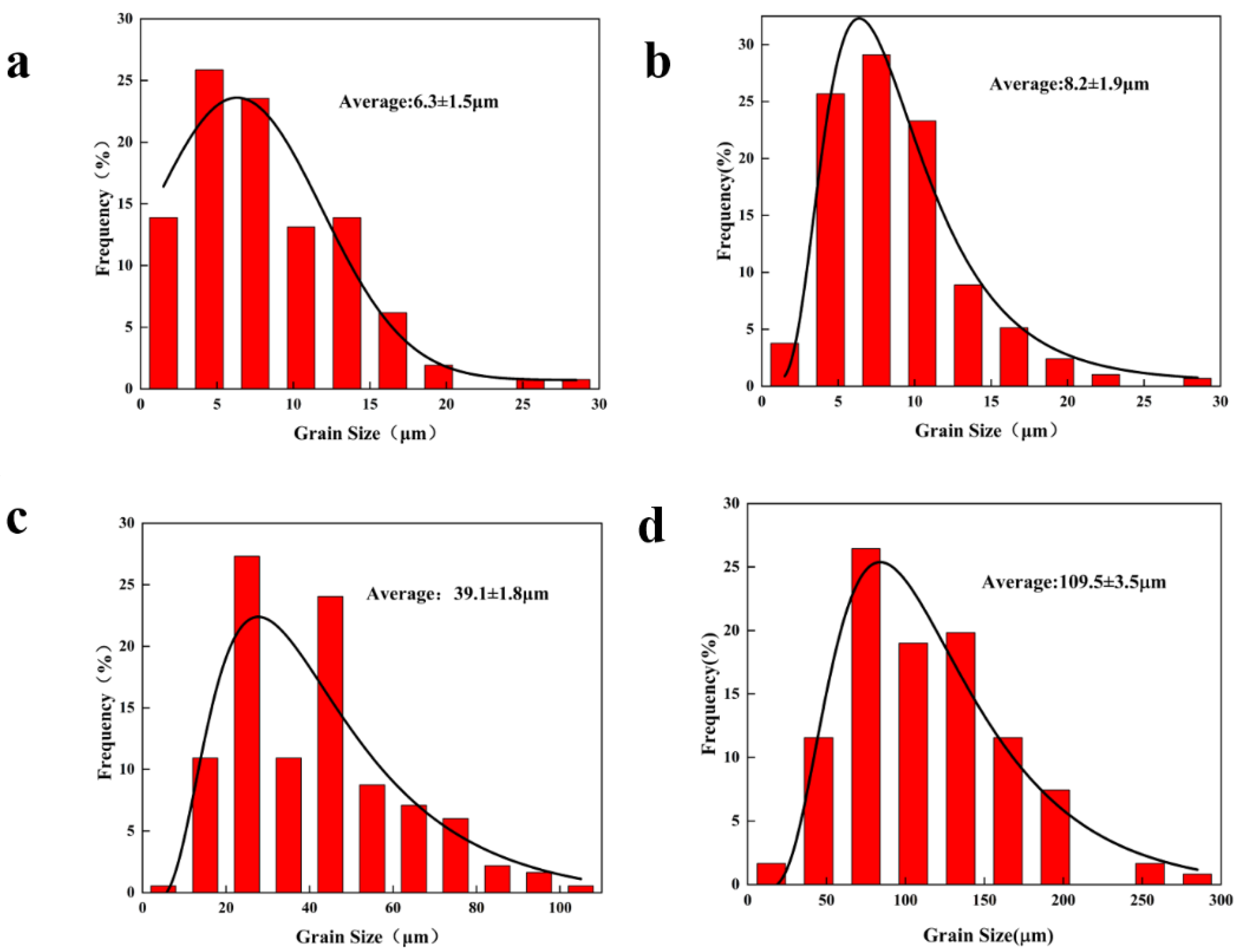
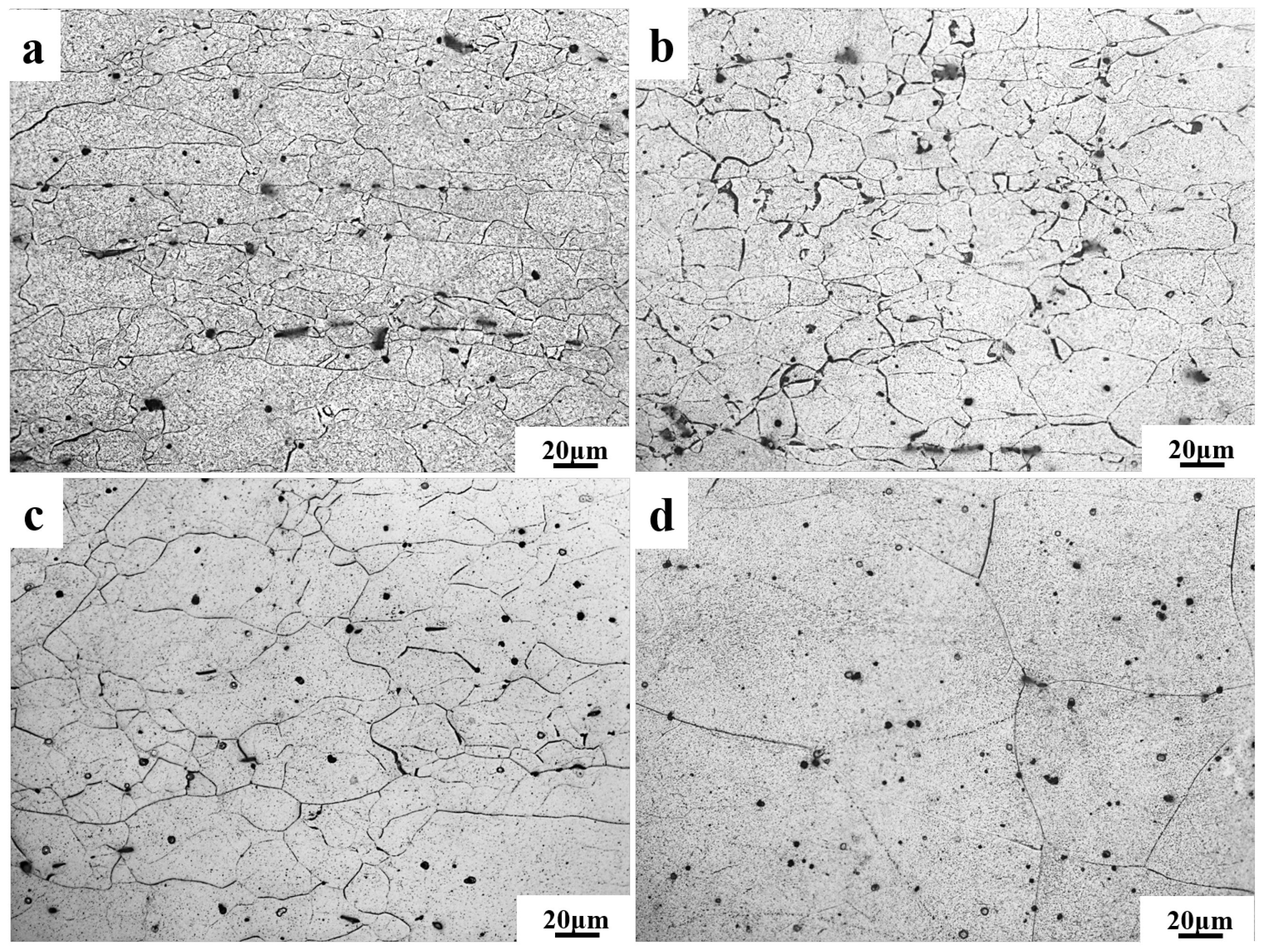
3.1. The Microstructure of the Alloys in a Hot Compression State
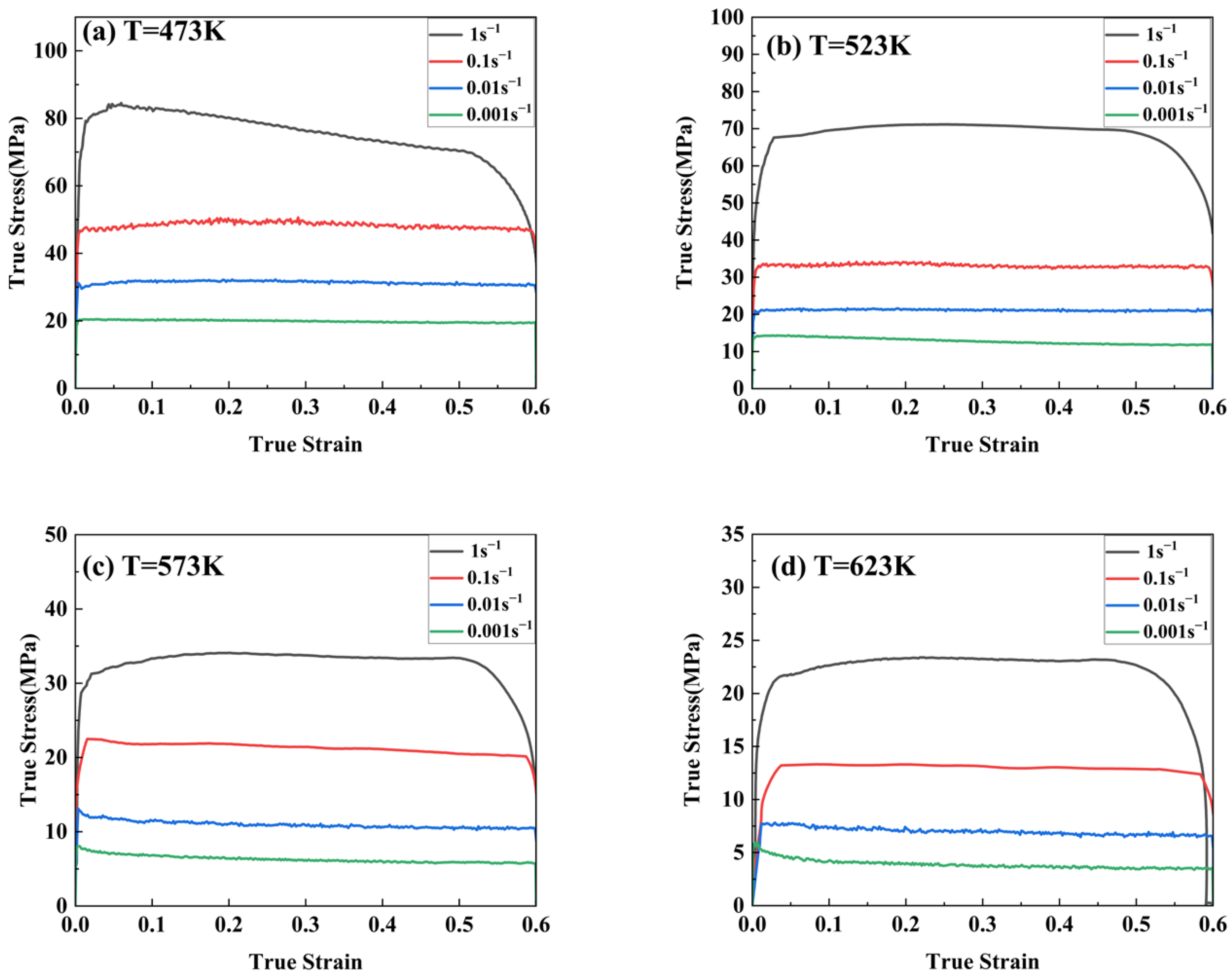
3.2. Flow Behavior
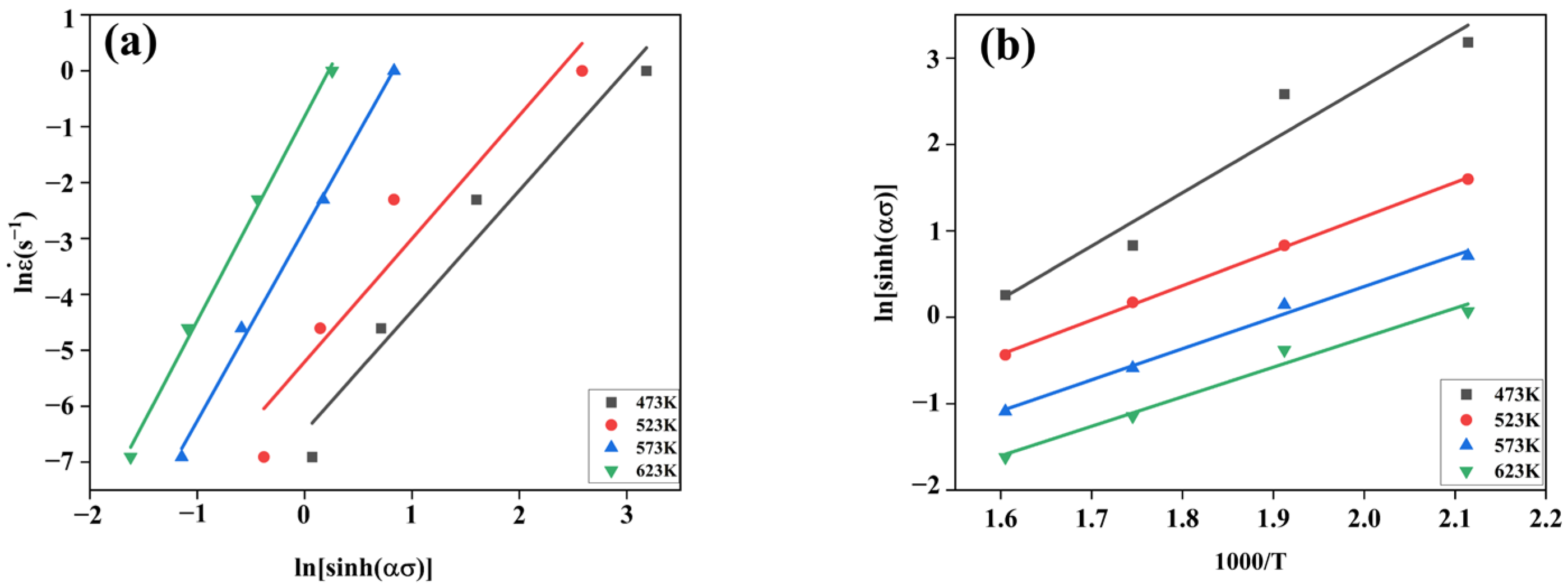
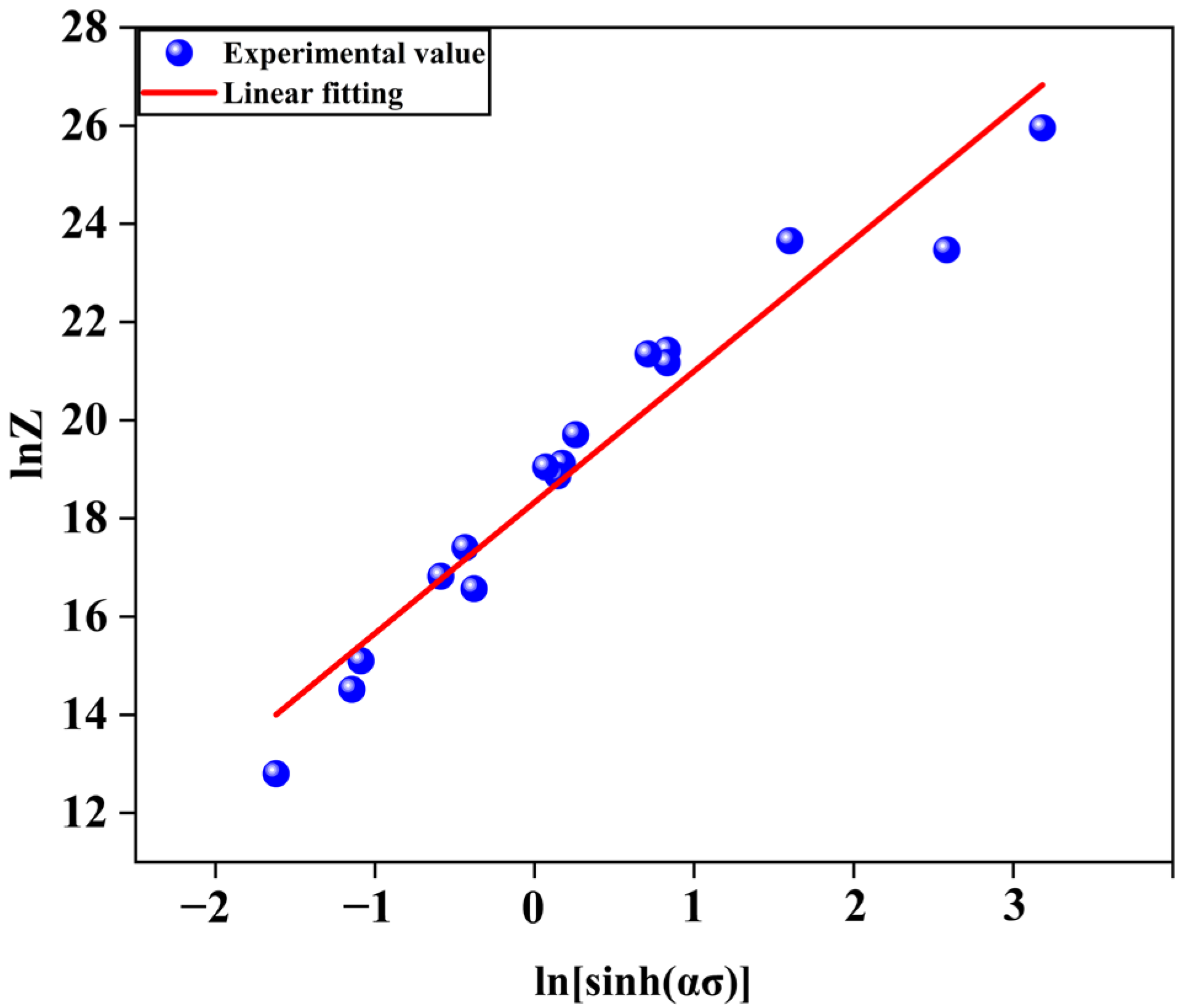
3.3. Constitutive Equation
- (1)
- In all stress states, the flow stress model is in the form of a hyperbolic sine function:
- (2)
- At low stress levels, that is, when σ < 0.8, the flow stress model is in the form of a power exponential function:
- (3)
- In the high stress state, that is, when σ > 1.2, the flow stress model is in the form of an exponential function:
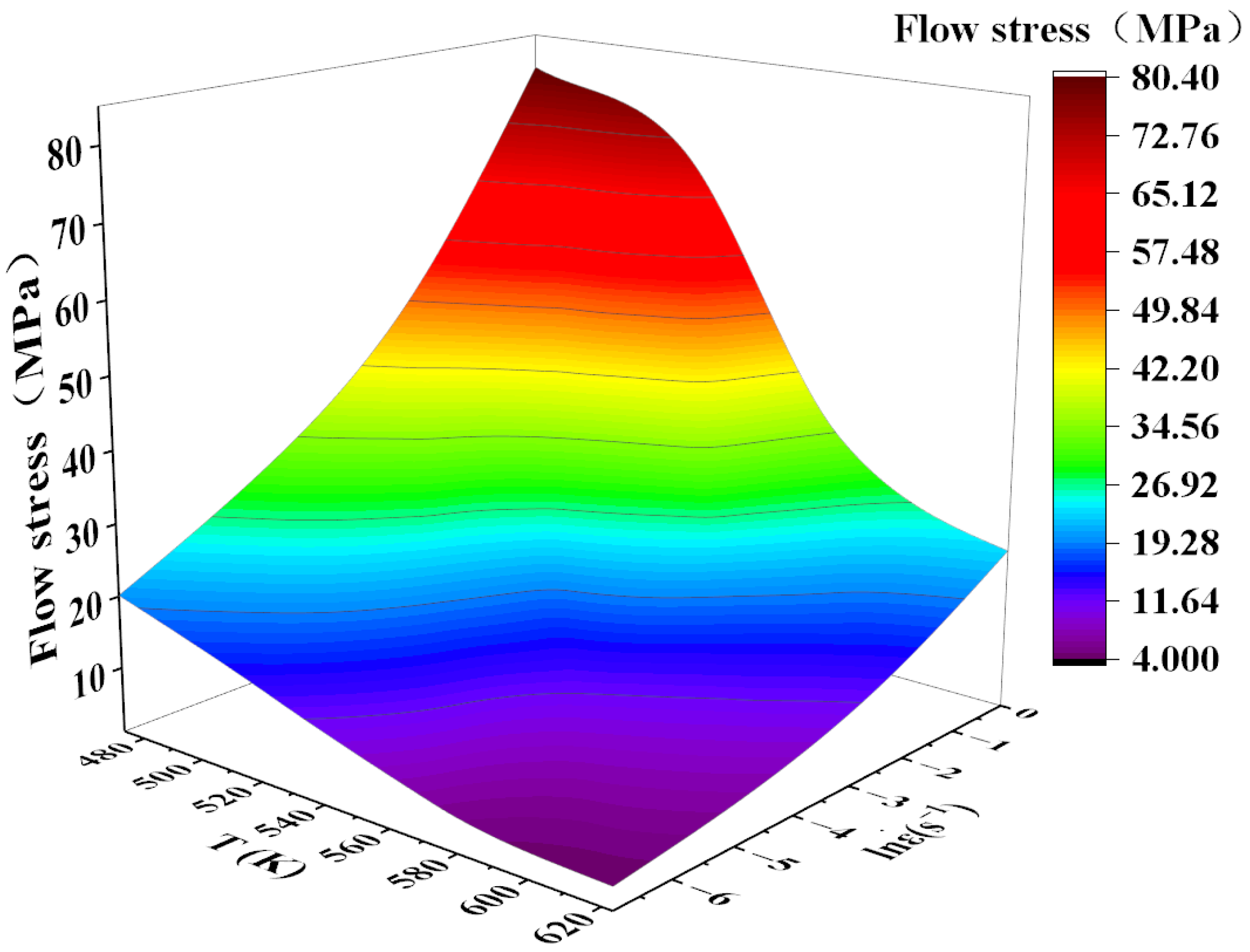
3.4. Characterization of Processing Maps
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Regarding the Mg-11.5Li-2.5Zn-0.35Al-0.3Y alloy, at a temperature of 623 K, its rheological stresses appear to increase rapidly in the grains at a strain rate of 0.01 s−1~0.1 s−1. At a strain rate of 0.001 s−1 and temperatures ranging from 573 K to 623 K, the grains appear to increase rapidly. This alloy should be processed under these conditions when thermoplastic processing is avoided as much as possible.
- (2)
- By calculating the deformation activation energy of the Mg-11.5Li-2.5Zn-0.35Al-0.3Y alloy, Q = 102.0701 (KJ/mol), the peak stress of this alloy can be described using the following constitutive equation:
- (3)
- The accuracy of the model was verified by comparing the model’s prediction values with the experimental values. The correlation coefficient R = 0.9690 was calculated, indicating that the established stress-compensated Arrhenius-type constitutive model is able to well describe the relationship between the flow stress and the deformation temperature and strain rate of the Mg-11.5Li-2.5Zn-0.35Al-0.3Y alloy during hot compression.
- (4)
- Based on the DMM theory and instability criterion, the hot processing maps under different strains were established, and the Mg-11.5Li-2.5Zn-0.35Al-0.3Y alloy can safely undergo hot compression and plastic deformation between the strain rates of 0.001 s−1 and 1 s−1 and temperatures of 473 K~623 K. To improve the properties of this alloy, plastic deformation processing can be performed at low temperatures and high strain rates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, J.; Bao, R.; Wu, R.; Zhang, H. Achieving High Strength in a Mg–Li–Zn–Y Alloy by A-Mg Precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 846, 143272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Xu, D.K.; Cai, X.; Qiao, Y.X.; Sheng, L.Y. Effect of Rolling Ratios On the Microstructural Evolution and Corrosion Performance of an as-Rolled Mg-8 Wt.%Li Alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, J.; Rogal, Ł.; Kalita, D.; Fima, P. Development of New Age Hardenable Mg-Li-Sc Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Q.; He, G.; Cui, J.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F.; Eckert, J. Designing Lightweight Multicomponent Magnesium Alloys with Exceptional Strength and High Stiffness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 855, 143901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, F. A Review On Electromagnetic Shielding Magnesium Alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1906–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, L.; Tang, J.; Zhao, G.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C. A Comprehensive Analysis On Microstructure Evolution of Mg-5.65Zn-0.66Zr Alloy During Hot Deformation. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-L.; Xing, X.-G.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.-D.; Liang, W. Influence of Al-Si additions on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Mg-8Li dual-phase alloys. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2017, 24, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Mishra, R.S. Grain Size and Texture Effects On Deformation Behavior of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Mukai, T.; Ishikawa, K. Differential Speed Rolling of an Az31 Magnesium Alloy and the Resulting Mechanical Properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, Y.; Huang, H. Effect of Lithium Content On the Mechanical and Corrosion Behaviors of Hcp Binary Mg–Li Alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Liaw, P.K.; Bei, H.; Zhang, Z. Improvement of Mechanical Behaviors of a Superlight Mg-Li Base Alloy by Duplex Phases and Fine Precipitates. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2625–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Pan, F.; Jiang, B.; Zeng, Y. Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Duplex Mg–Li Alloy Under Extrusion with an Increasing Ratio. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Tan, J.; Pan, F. Microstructure, Texture and Mechanical Properties of the Rolled High Modulus Mg-Y-Zn-Al-Li Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 831, 142242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, M. Effects of the Addition of Y in Mg–8Li–(1,3)Al Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 516, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Khan, F.; Sahoo, B.N.; Panigrahi, S.K. A High Temperature Manufacturability Study of Ultrafine Grained Magnesium Rare-Earth Alloy Using Processing Map and Constitutive Analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 954, 169991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, X.; Ren, F.; Wen, H.; Su, J.; Xie, W. Constitutive Modeling and Hot Deformation Behavior of Duplex Structured Mg–Li–Al–Sr Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yuan, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, G.; Shan, D.; Guo, B.; Jin, B.C. Modeling of Flow Behavior and Microstructure Evolution for Mg-6Gd-5Y-0.3Zr Alloy During Hot Deformation Using a Unified Internal State Variable Method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 7669–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Teng, B.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. A Cellular Automaton Coupled Fea Model for Hot Deformation Behavior of Az61 Magnesium Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wu, L.; Wu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M. Influence of Yttrium On Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of as-Cast Mg–5Li–3Al–2Zn Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 9045–9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liu, W.; Wu, G.; Ji, H.; Ding, W. Plastic Deformation and Heat Treatment of Mg-Li Alloys: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 99, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Pan, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H. Hot Compression Bonding Behavior and Constitutive Model of Spray Deposited 2195 Al-Cu-Li Alloy. Vacuum 2023, 211, 111896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.; Ye, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Liu, X. Hot Deformation Behavior and 3D Processing Maps of Aa7020 Aluminum Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 845, 156113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Zheng, Z.; Nie, Y.; Jian, H. Hot Deformation Behavior of 2060 Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z. Flow Curve Correction and Processing Map of 2050 Al–Li Alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, H.R.R.; Shahsavari, P. Strain-Dependent Constitutive Equations to Predict High Temperature Flow Behavior of Aa2030 Aluminum Alloy. Mech. Mater. 2016, 100, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, F.; Liu, Q. Simulation of Dynamic Recrystallization in Az80 Magnesium Alloy Using Cellular Automaton. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 140, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Han, E. Serrated Flow and Abnormal Strain Rate Sensitivity of a Magnesium–Lithium Alloy. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2941–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarebanzadeh, M.; Mahmudi, R.; Roumina, R. Constitutive Analysis and Processing Map of an Extruded Mg–3Gd–1Zn Alloy Under Hot Shear Deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 637, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, Q.D.; Ye, B.; Guo, W. Hot Deformation and Processing Maps of as-Extruded Mg–9.8Gd–2.7Y–0.4Zr Mg Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 576, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhai, J.; Lin, J. Hot Deformation Behavior of La43M Mg-Li Alloy Via Hot Compression Tests. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 7768–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zha, M.; Yu, Z.; Ma, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Jia, H.; Wang, H. Exploring the Hall-Petch Relation and Strengthening Mechanism of Bimodal-Grained Mg–Al–Zn Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 833, 155004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.V.R.K.; Gegel, H.L.; Malas, J.C.; Morgan, J.T.; Lark, K.A.; Doraivelu, S.M.; Barker, D.R. Modeling of Dynamic Material Behavior in Hot Deformation: Forging of Ti-6242. Metallurgical transactions. Metall. Trans A 1984, 15, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Luo, T.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y. Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of as-Cast Mg–8Zn–1Al–0.5Cu–0.5Mn Alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3232–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Characterization of Flow Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Al–Zn–Mg–Sc–Zr Alloy Using Processing Maps. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, C.; Yang, J.; Lin, M. Hot Workability Analysis of Az61 Mg Alloys with Processing Maps. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 607, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



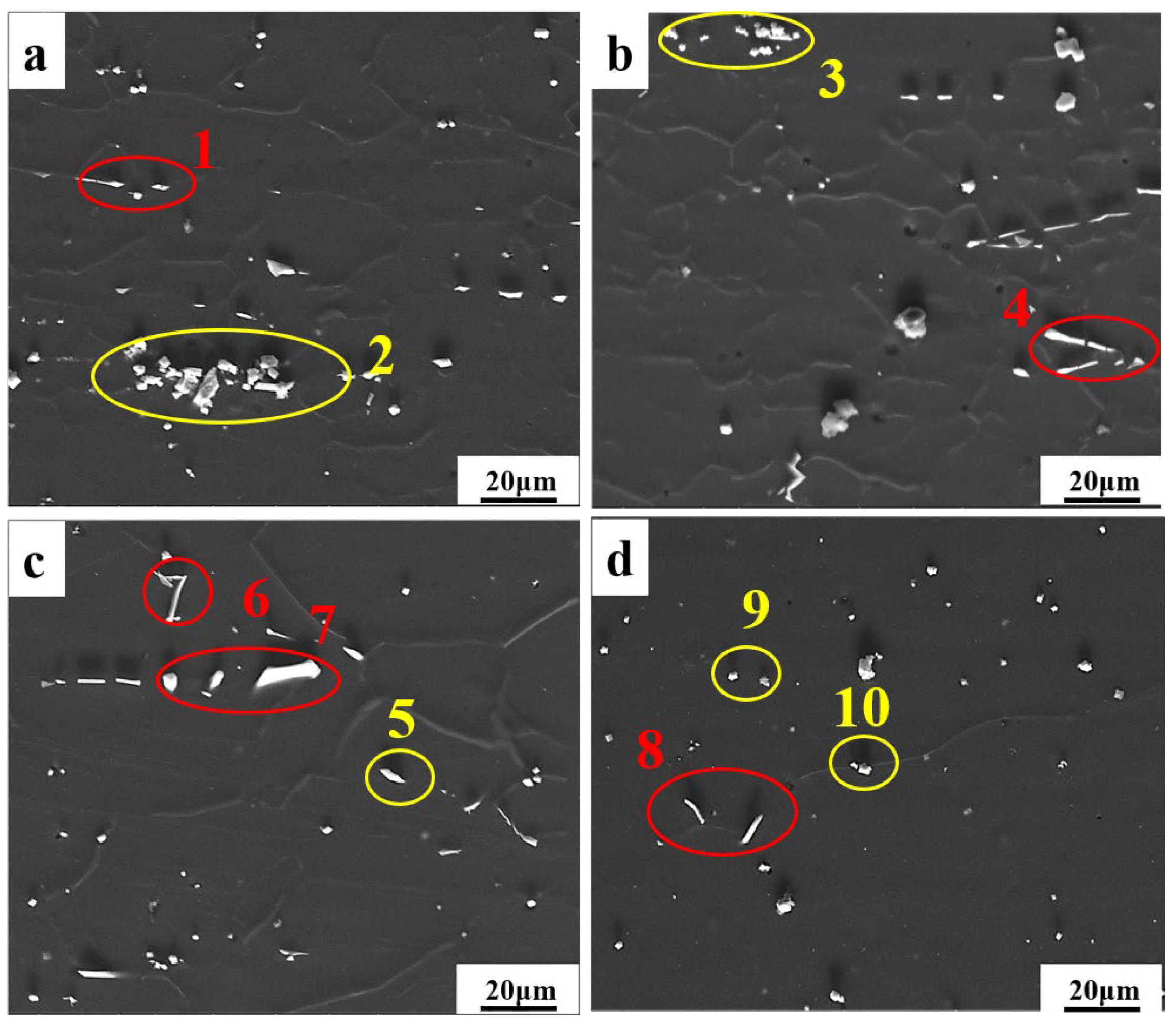
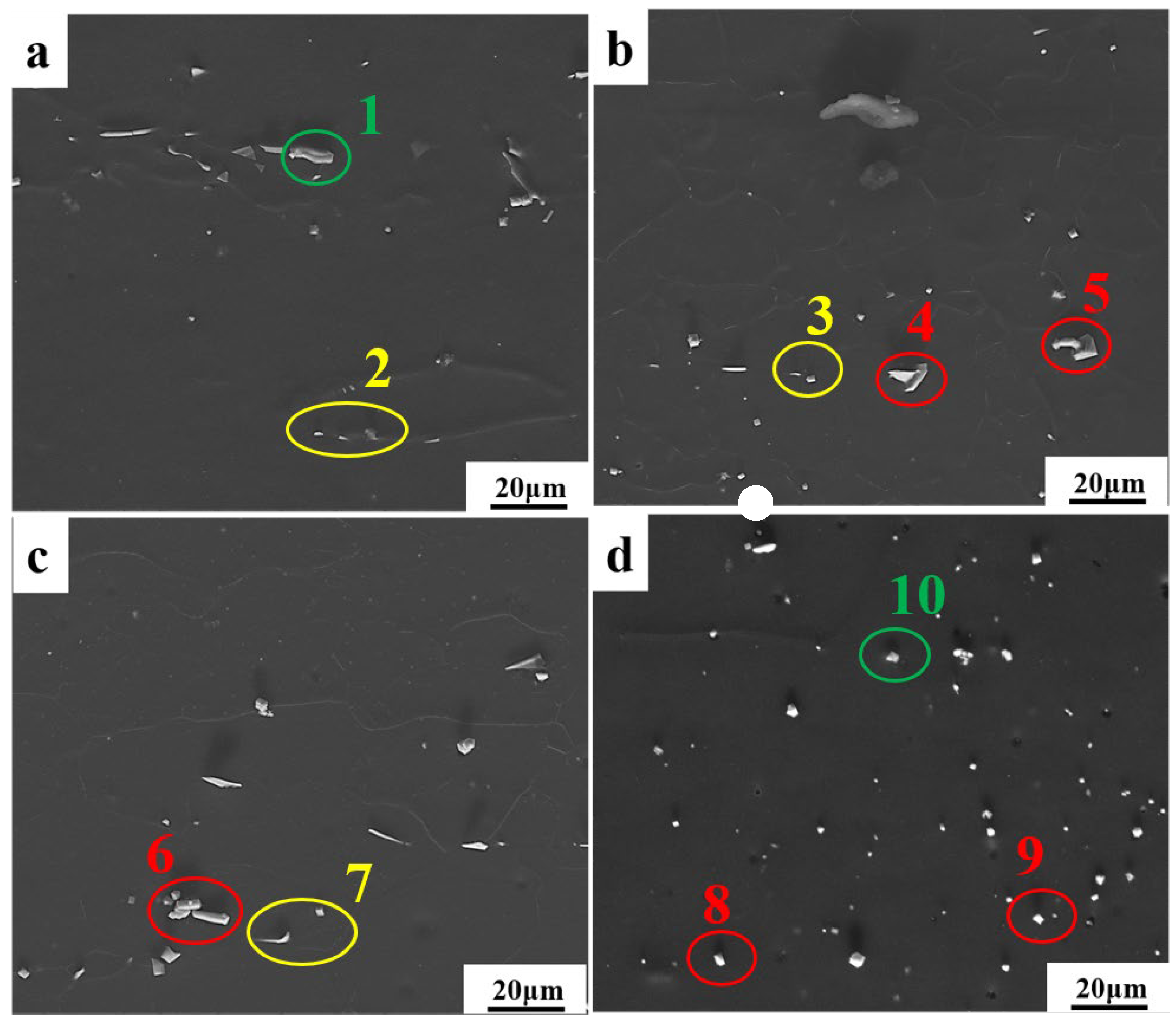


| Different Specimen | Position | Mg | Zn | Al | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | 53.7 | 6.1 | 25.7 | 14.4 |
| 2 | 48.2 | 0.0 | 7.9 | 43.9 | |
| b | 3 | 48.2 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 47.9 |
| 4 | 49.3 | 5.2 | 30.0 | 15.5 | |
| c | 5 | 21.7 | 7.7 | 43.6 | 26.9 |
| 6 | 68.7 | 3.3 | 18.8 | 9.2 | |
| 7 | 53.0 | 5.2 | 27.3 | 14.5 | |
| d | 8 | 42.7 | 6.7 | 33.1 | 17.5 |
| 9 | 46.8 | 0.0 | 4.2 | 49.0 | |
| 10 | 50.9 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 45.1 |
| Different Specimen | Position | Mg | Zn | Al | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | 58.2 | 4.1 | 24.9 | 12.7 |
| 2 | 35.4 | 0.0 | 17.3 | 39.4 | |
| b | 3 | 39.6 | 0.0 | 15.0 | 45.4 |
| 4 | 22.3 | 9.1 | 46.6 | 22.0 | |
| 5 | 18.5 | 0.0 | 54.3 | 27.2 | |
| c | 6 | 9.7 | 0.0 | 58.6 | 31.7 |
| 7 | 42.9 | 0.0 | 13.6 | 43.5 | |
| d | 8 | 42.6 | 0.0 | 37.7 | 19.7 |
| 9 | 40.8 | 2.1 | 40.8 | 20.6 | |
| 10 | 81.8 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 15.7 |
| 473 K | 523 K | 573 K | 623 K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 s−1 | 1.0685 | 1.0870 | 1.0632 | 1.0451 |
| 0.1 s−1 | 1.1067 | 1.0567 | 1.0567 | 1.0169 |
| 0.01 s−1 | 1.0578 | 1.0505 | 1.0505 | 1.0357 |
| 0.001 s−1 | 1.0467 | 1.0293 | 1.5627 | 1.0504 |
| α | n | A | Q (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0461 ± 0.0102 | 2.8600 ± 0.2704 | 9.1374 × 107 ± 1.2569 | 102.0701 ± 0.9597 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Bai, W.; Li, B.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Wei, G.; Liu, J. Thermal Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Multicomponent Mg-Li-Zn-Al-Y Alloys under Hot Compression. Materials 2024, 17, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020489
Yang K, Bai W, Li B, Chen H, Li G, Wei G, Liu J. Thermal Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Multicomponent Mg-Li-Zn-Al-Y Alloys under Hot Compression. Materials. 2024; 17(2):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020489
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kun, Weiwu Bai, Bin Li, Hao Chen, Guo Li, Guobing Wei, and Junwei Liu. 2024. "Thermal Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Multicomponent Mg-Li-Zn-Al-Y Alloys under Hot Compression" Materials 17, no. 2: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020489
APA StyleYang, K., Bai, W., Li, B., Chen, H., Li, G., Wei, G., & Liu, J. (2024). Thermal Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Multicomponent Mg-Li-Zn-Al-Y Alloys under Hot Compression. Materials, 17(2), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020489






