Effects of Samarium Doping on the Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
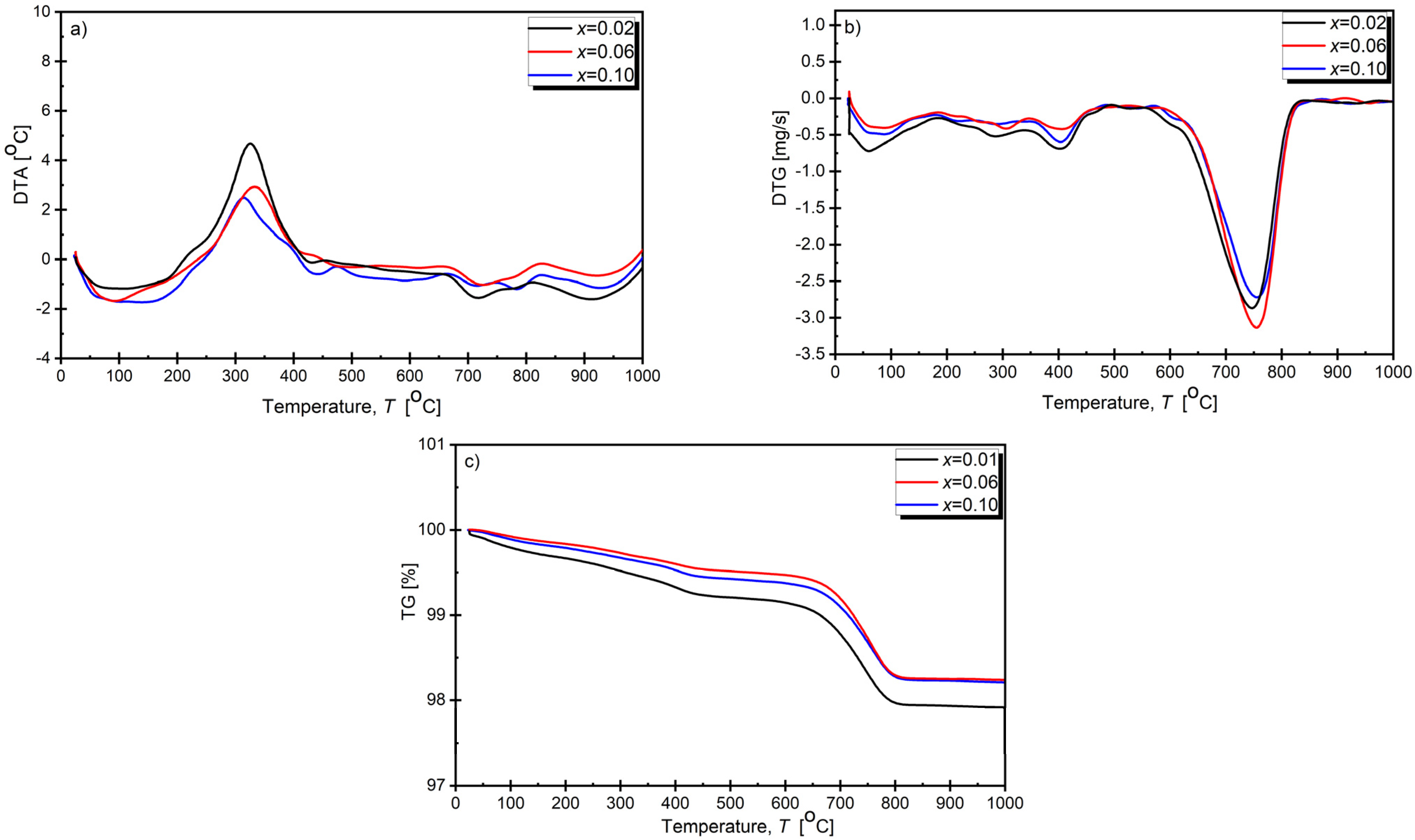
3.1. Thermal Analysis
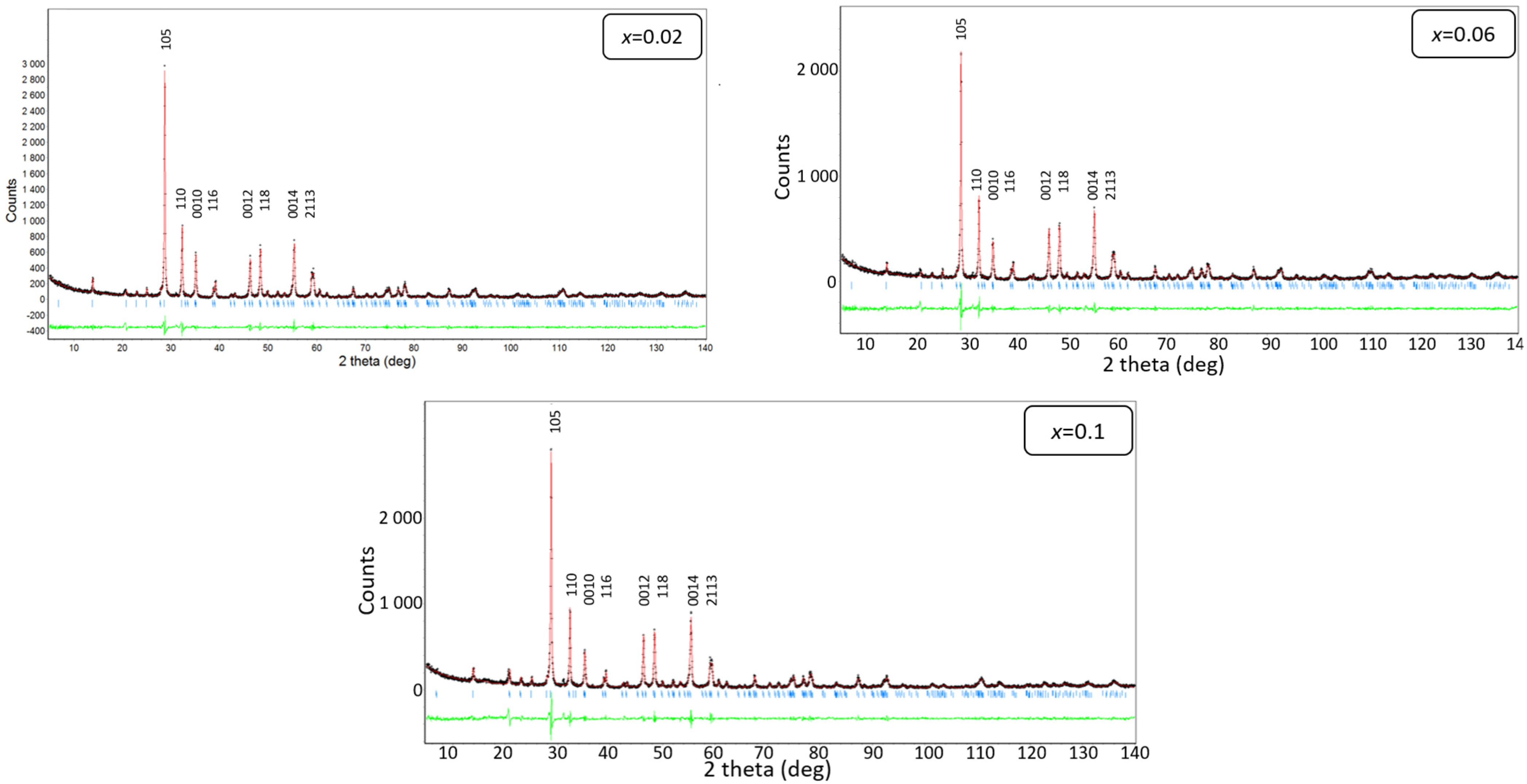
3.2. X-ray Diffraction
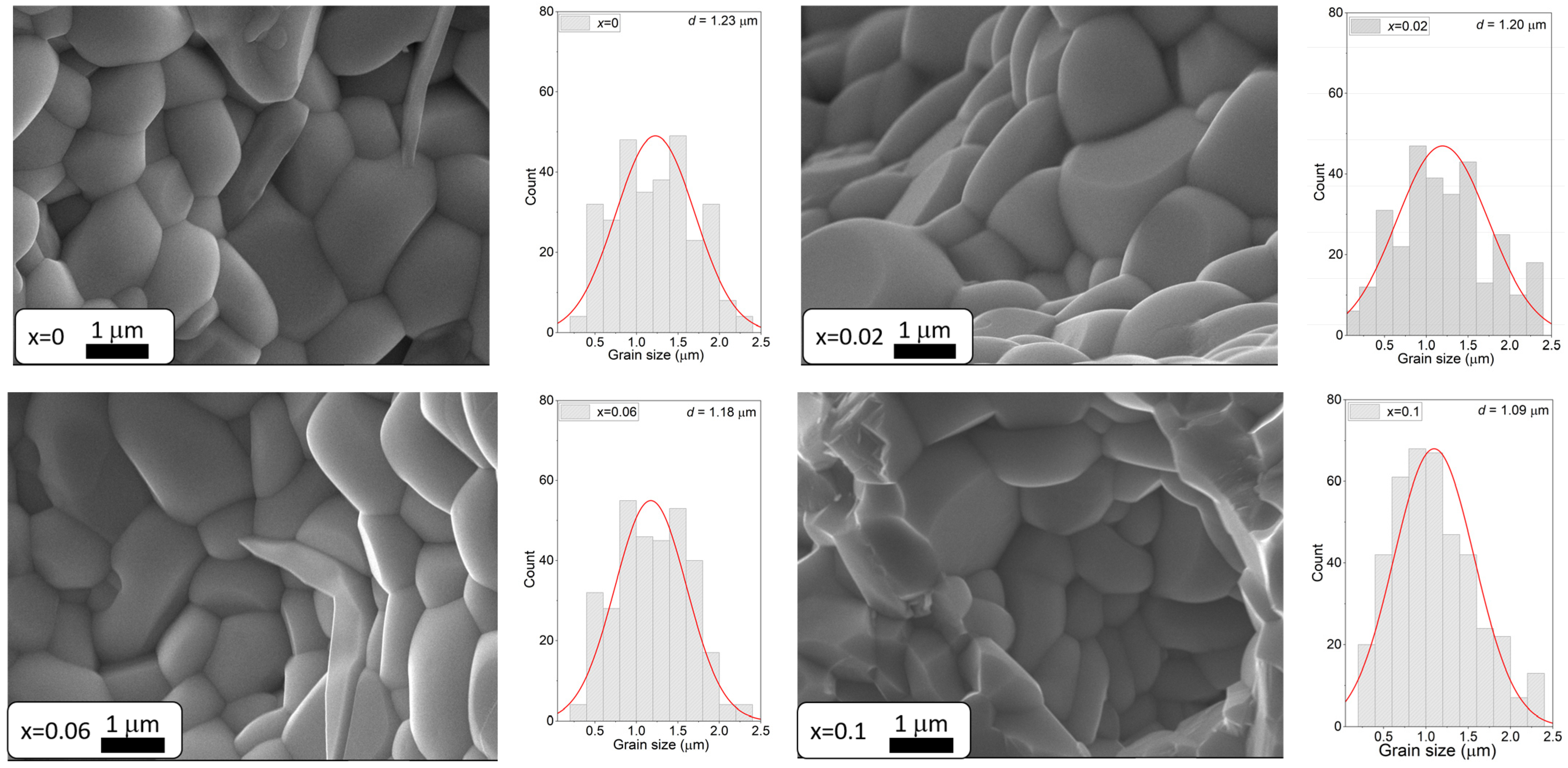
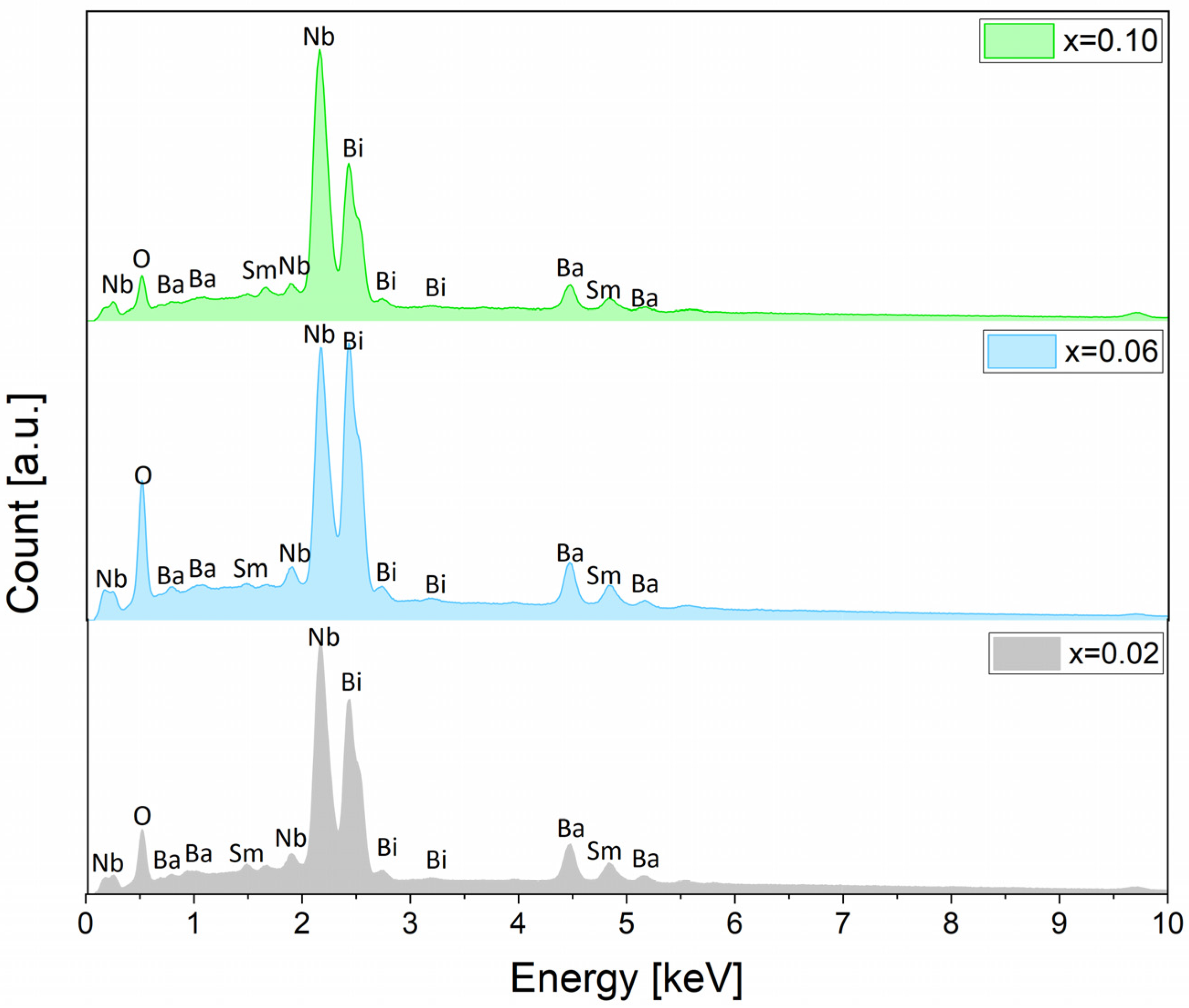
3.3. Analysis of Microstructure and Chemical Composition
3.4. Mechanical Properties
- VL1—the average velocity of the longitudinal ultrasonic wave measured perpendicular to the sample’s pressing direction;
- VL2—the average velocity of the longitudinal ultrasonic wave measured parallel to the sample’s pressing direction.
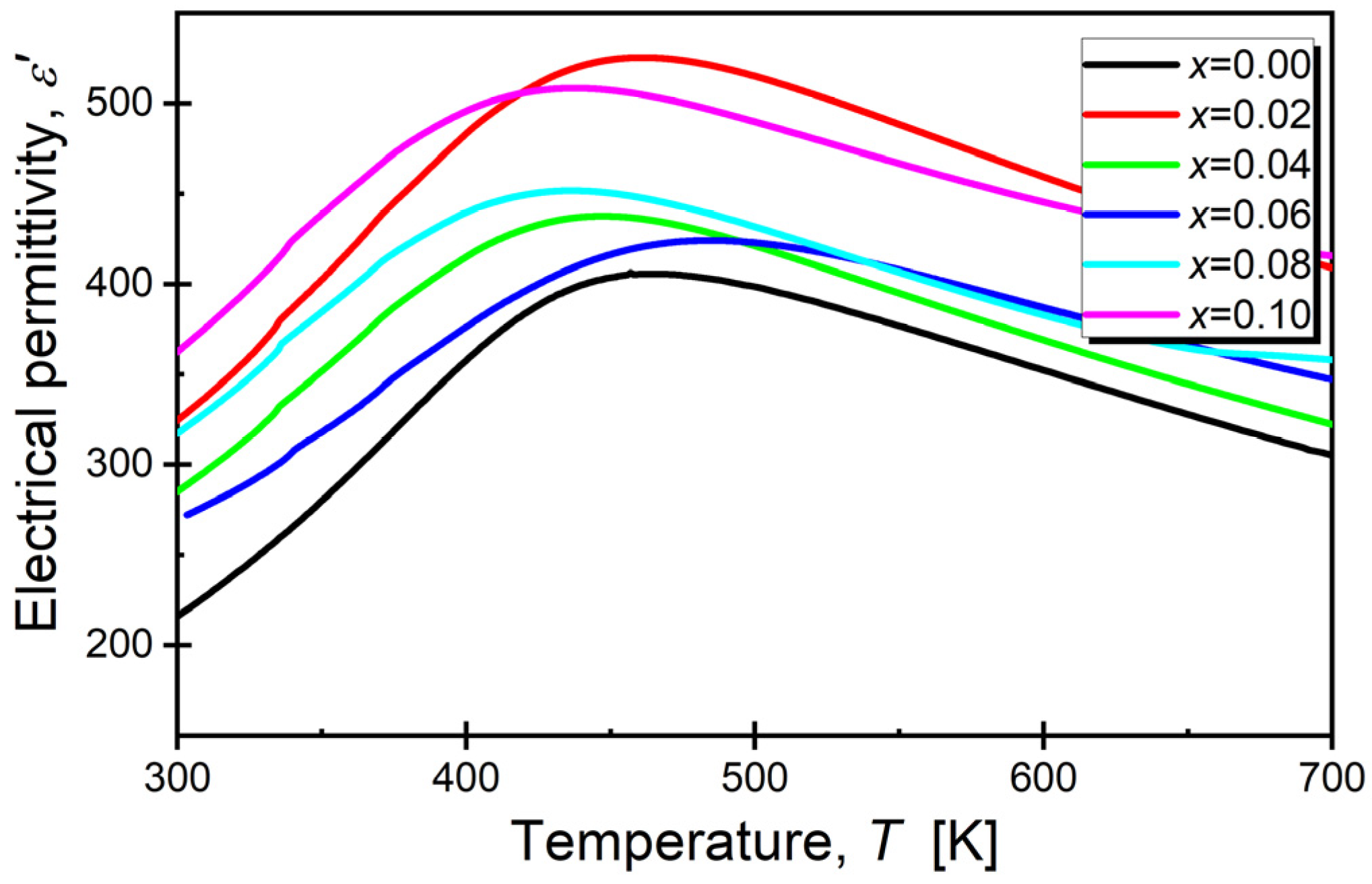
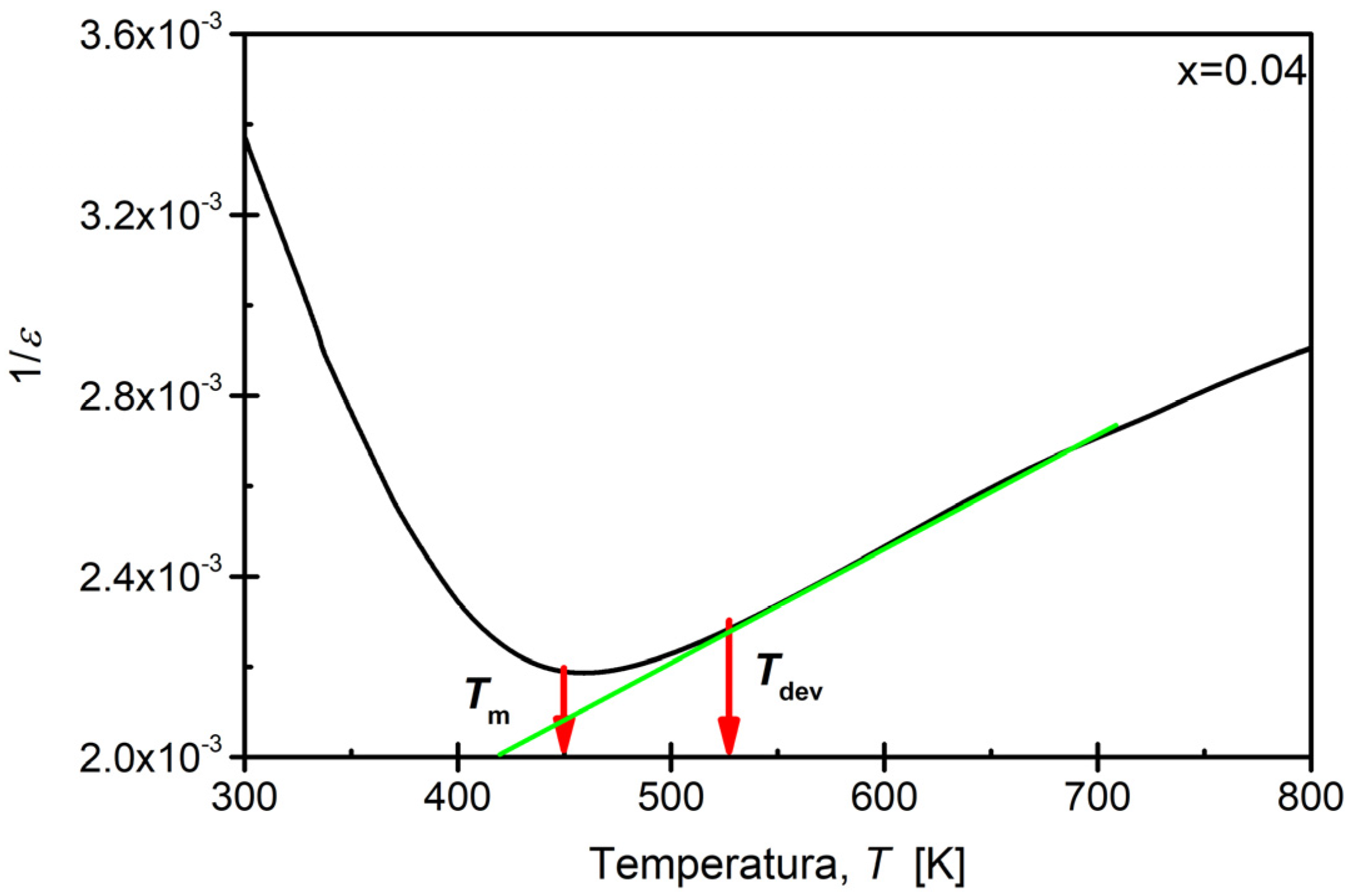
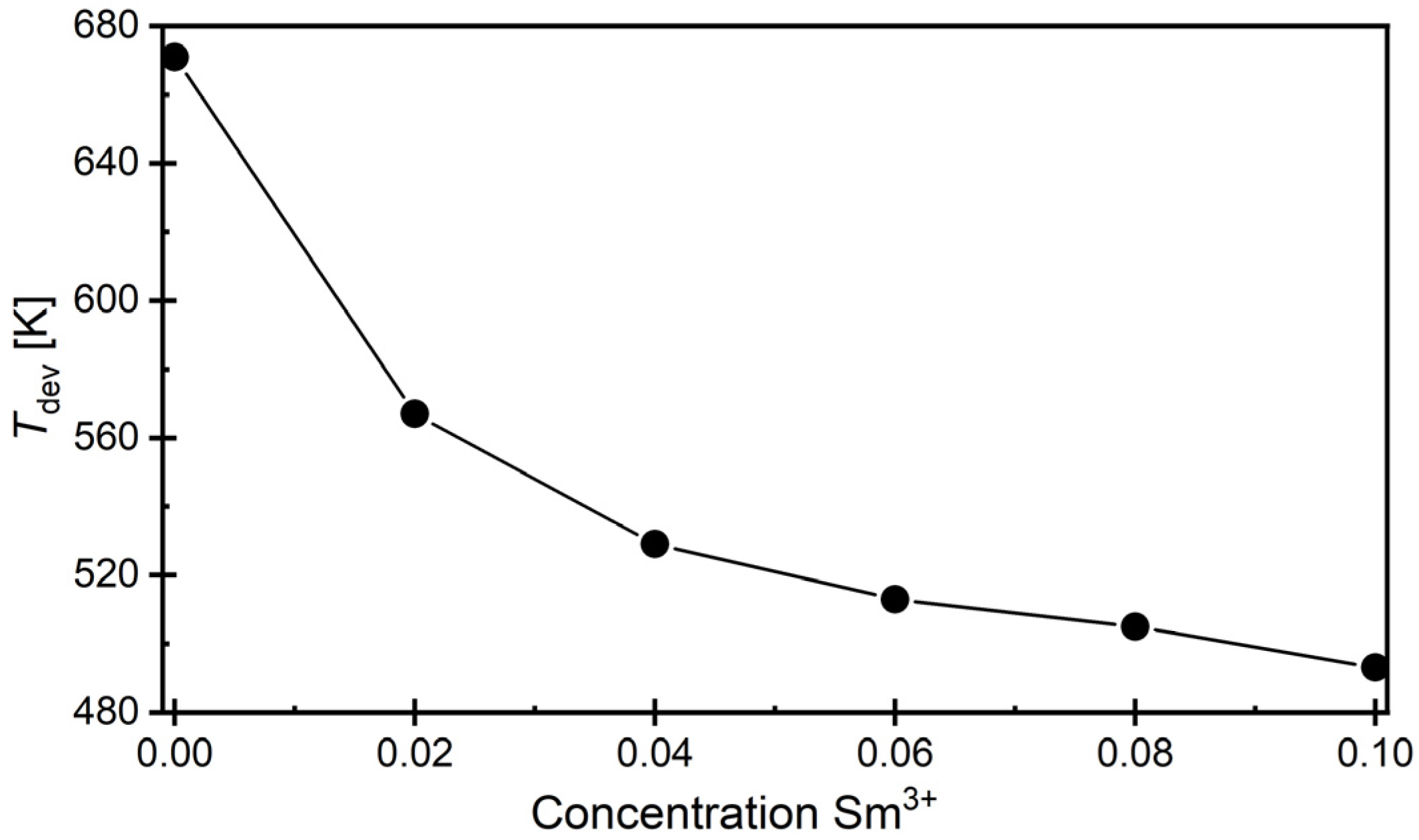
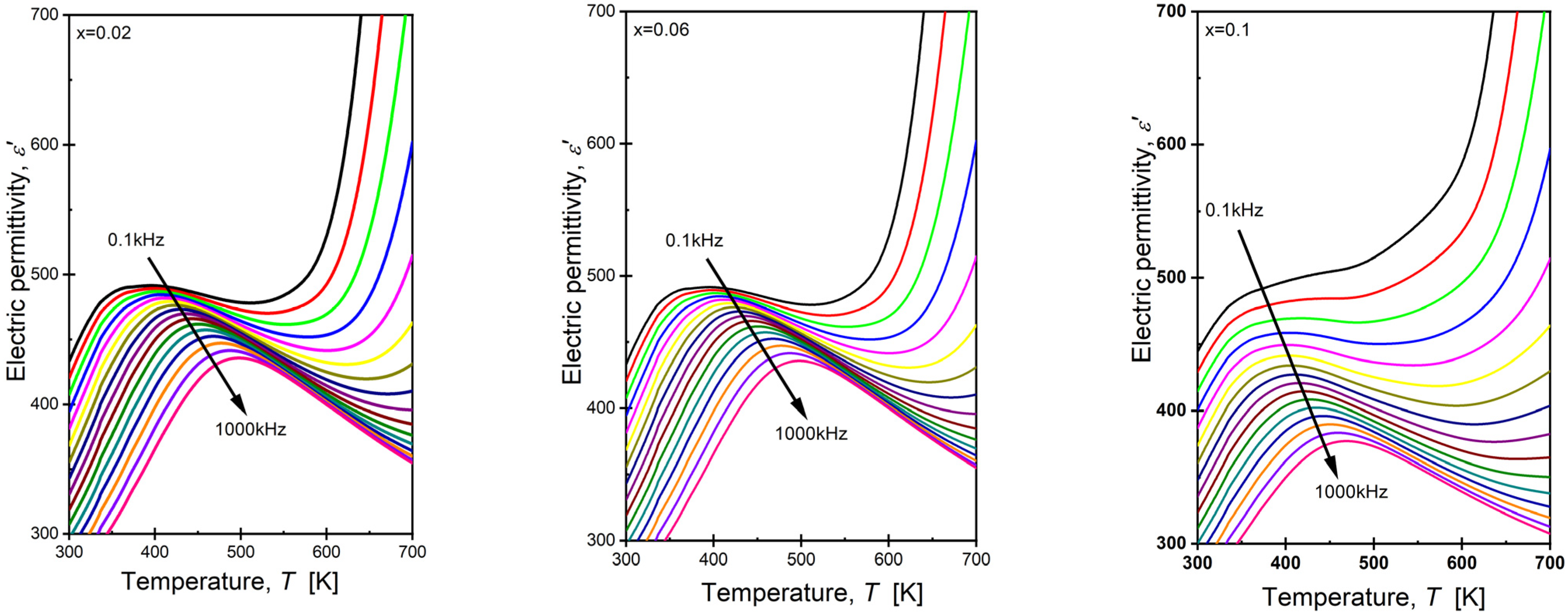
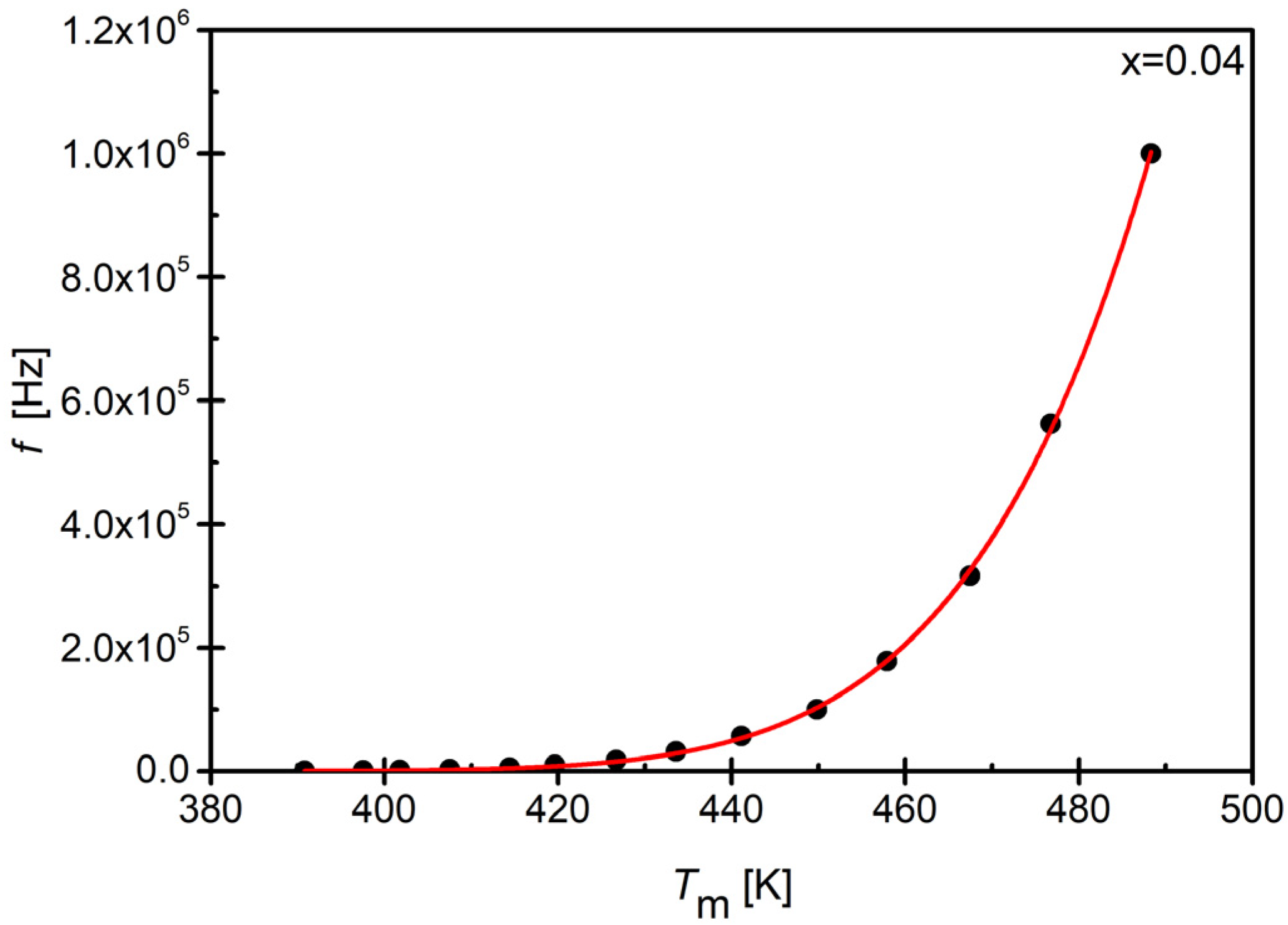
3.5. Dielectric Properties
- εmax—maximum value of electric permittivity;
- C—the Curie-like constant;
- γ—the diffuseness parameter.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raddaoui, Z.; El Kossi, S.; Dhahri, J.; Abdelmoula, N.; Taibi, K. Study of Diffuse Phase Transition and Relaxor Ferroelectric Behavior of Ba0.97Bi0.02Ti0.9Zr0.05Nb0.04O3 Ceramic. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2412–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouitaa, N.; Ahjyaje, F.Z.; Lamcharfi, T.; Abdi, F.; Haddad, M.; Sajieddine, M.; Ounacer, M. Investigation of Relaxor and Diffuse Dielectric Phase Transitions of Ba1−xBixTi0.8Fe0.2O3 Materials. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.W.; Hong, C.-H.; Choi, B.-Y.; Kim, H.-P.; Han, H.-S.; Hwang, Y.; Jo, W.; Wang, K.; Li, J.-F.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. A Brief Review on Relaxor Ferroelectrics and Selected Issues in Lead-Free Relaxors. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2016, 68, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; He, Z.; Xu, H.; Lin, C. Research on Low-Frequency Bender Disk Transducer Driven by Multiple Relaxor Ferroelectric Single Crystal Disks. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 216, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Shen, K.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, R.; Shi, X.; Zeng, T.; Li, G. The Thermal Depolarization Behavior of PMN-PT-BZT Relaxor Ferroelectric Ceramics from the Standpoint of Domain Structure Transitions. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 23970–23976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Jiang, X.; Kim, J.; Luo, J.; Geng, X. Giant Electrostrains Accompanying the Evolution of a Relaxor Behavior in Bi(Mg,Ti)O3–PbZrO3–PbTiO3 Ferroelectric Ceramics. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 3687–3694. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Das, K.; Roy, A. Improving the Energy Density and Flexibility of PMN-0.3PT Based Piezoelectric Generator by Composite Designing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 376, 115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakbamrung, P.; Lallart, M.; Guyomar, D.; Muensit, N.; Thanachayanont, C.; Lucat, C.; Guiffard, B.; Petit, L.; Sukwisut, P. Performance Comparison of PZT and PMN-PT Piezoceramics for Vibration Energy Harvesting Using Standard or Nonlinear Approach. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 163, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; De, P.S.; Roy, A. Revisiting Lead Magnesium Niobate-Lead Titanate Piezoceramics for Low-Frequency Mechanical Vibration-Based Energy Harvesting. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 945, 169221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, S.H.; Tiwari, S.; Gaur, A.; Maiti, P. PVDF–PZT Nanohybrid Based Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting Applications. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Song, D.P.; Yin, Y.; Chen, L.Z.; Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.Y. Ferroelectric Polarization and Fatigue Characterization in Bismuth-Based Aurivillius Thin Films at Lower Voltage. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 248, 114408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P. Stealing a Lead on Lead. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Molla, A.R. Zirconia Assisted Crystallization of Ferroelectric BaBi2Nb2O9 Based Glass-Ceramics: Kinetics, Optical and Dielectrical Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Rai, R.; Sharma, S.; Shandilya, M.; Tiwari, A. State-of-the-Art of Lead-Free Ferroelectrics: A Critical Review. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2015, 6, 453–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.F. Prospects for Ferroelectrics: 2012–2022. ISRN Mater. Sci. 2013, 2013, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.H.; Kang, B.S.; Bu, S.D.; Noh, T.W.; Lee, J.; Jo, W. Lanthanum-Substituted Bismuth Titanate for Use in Non-Volatile Memories. Nature 1999, 401, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardiel, T.; Caballero, A.C.; Villegas, M. Aurivillius Ceramics: Bi4Ti3O12-Based Piezoelectrics. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 116, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, M.T.; Millan, P.; Duran-Martin, P.; Jimenez, B.; Castro, A. Solid Solutions of Lead-Doped Bismuth Layer of Aurivillius n = 2 and n = 3 Oxides: Structural and Dielectric Characterization. Mater. Res. Bull. 1998, 33, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentschler, T. Substitution of Lead into the Bismuth Oxide Layers of the n = 2- and n = 3-Aurivillius Phases. Mater. Res. Bull. 1997, 32, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, K.; Thomas, J.K.; zur Loye, H.C. Synthesis and Ionic Conductivity of a New Series of Modified Aurivillius Phases. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Habrajska, G. Synteza i Badania Właściwości Ceramiki BaBi2Nb2O9; Wydawnictwo Gnome: Katowice, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J. Doping level effects in Gd/Cr co-doped Bi₃TiNbO₉ Aurivillius-type ceramics with improved electrical properties. J. Materiom. 2022, 8, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, P.; Ramirez, A.; Castro, A. Substitutions of Smaller Sb3+ and Sn2+ Cations for Bi3+ in Aurivillius-Like Phases. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1995, 14, 1657–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Millan, P.; Martinez-Lope, M.J.; Torrance, J.B. Substitutions for Bi3+ into (Bi2O2)2+ Layers of the Aurivillius (Bi2O2)(An−1BnO3n+1) Oxides. Solid State Ion. 1993, 63, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Ha, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.K.; Seong, S.; Hur, H.H. A New Manganese Oxide with the Aurivillius Structure: Bi2Sr2Nb2MnO12−δ. Solid State Commun. 1999, 111, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Milan, R.; Enjalbert, R. Structural Evolution of the Aurivillius Framework in the Solid Solutions Bi2WO6-Sb2WO6. Mater. Res. Bull. 1995, 30, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwal, A.; Kumar, B.; Verma, M.; Shandilya, A.; Singh, B.; Bokolia, R. Improved optical characteristics in BaBi₂Nb₂O₉ ferroelectric ceramic infused with transition metal ion (W⁶⁺) and rare earth ions (Er³⁺/Yb³⁺). J. Lumin. 2024, 275, 120809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, H.; Bu, X.; Chen, Z.; Du, J.; Li, L.; Wen, F.; Bai, W.; Zheng, P.; Wu, W.; et al. Enhanced Energy Storage Performance in Bismuth Layer-Structured BaBi2Me2O9 (Me = Nb and Ta) Relaxor Ferroelectric Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 15907–15914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiming, W.; Shijing, L.; Xiaowei, W.; Jinhong, B.; Ping, L.; Ling, W. Synthesis, Structures and Photocatalytic Activities of Microcrystalline ABi2Nb2O9 (A=Sr, Ba) Powders. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Debasis, D.; Tanmay, G.K.; Panchanan, P. Studies of Dielectric Characteristics of BaBi2Nb2O9 Ferroelectrics Prepared by Chemical Precursor Decomposition Method. Solid State Sci. 2007, 9, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Dong, X.; Chen, H. Structural and Electrical Properties of W⁶⁺-Doped Bi₃TiNbO₉ High-Temperature Piezoceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macquart, R.; Kennedy, B.J.; Vogt, T.; Howard, C.J. Phase Transition in BaBi2Nb2O9: Implications for Layered Ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sunarso, J.; Shao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Sun, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Research progress and materials selection guidelines on mixed conducting perovskite-type ceramic membranes for oxygen production. RSC Adv. 2011, 1, 1661–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanovic, D. Hysteresis in Piezoelectric and Ferroelectric Materials. In The Science of Hysteresis; Mayergoyz, I., Bertotti, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Banwal, A.; Bokolia, R. Efficient Tunable Temperature Sensitivity in Thermally Coupled Levels of Er3+/Yb3+ Co-Doped BaBi2Nb2O9 Ferroelectric Ceramic. J. Lumin. 2023, 263, 120071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szutkowska, M.; Smuk, B.; Kalinka, A.; Czechowski, K.; Bućko, M.; Boniecki, M. Selected Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Al2O3-ZrO2nano Ceramic Composites. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2011, 48, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pasiut, K.; Partyka, J.; Bućko, M.M.; Grandys, M.; Kurpaska, Ł.; Piekarczyk, W. An Impact of the Molar Ratio of Na2O/K2O on Nanomechanical Properties of Glaze Materials Containing Zirconium Oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkova, L.A.; Nikolaichik, V.; Barkovskii, N.V.; Fedotov, V. Thermal Stability of Bi2O3. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 52, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Madhan, K.; Elumalai, D.; Kalaiselvi, B.J. Structural and Thermal Characterization of Sr Doped BaTiO3. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2015, 10, 2524–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Rerak, M.; Makowska, J.; Osińska, K.; Goryczka, T.; Zawada, A.; Adamczyk-Habrajska, M. The Effect of Pr Doping Contents on the Structural, Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials 2022, 15, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, P.; Szostak, E.; Hetmańczyk, J.; Zachariasz, P.; Majda, D.; Suchanicz, J.; Karolus, M.; Bochenek, D.; Osińska, K.; Jędryka, J.; et al. Thermal Stability and Non-Linear Optical and Dielectric Properties of Lead-Free K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 Ceramics. Materials 2024, 17, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaraghavulu, R.; Buddhudu, S. Structural and Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Ferroelectric Ceramic Powders by a Solid State Reaction Method. Ferroelectrics 2014, 460, 1563–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhak, D.; Dhak, P.; Pramanik, P. Influence of Substitution on Dielectric Diffuseness in Ba(1−x)Bi(2+2x/3)Nb2O9 Ceramics Prepared by Chemical Precursor Decomposition Method. J. Electroceram. 2011, 27, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D. Relations Between Physical Properties of the Biferroic Pb(Fe1−xNbx)O3 Ceramics and Their Composition Change. Phys. Status Solidi A 2008, 154, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bochenek, D.; Płońska, M.; Dudek, J.; Surowiak, Z. Applications of the Thermal Analysis in Preparation and Investigation of the Ceramic Ferroics and Multiferroics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 101, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.; Costa, M.E.V.; Avdeev, M.; Kholkin, A.L.; Bapstista, J.L. Relaxor Properties of Ba-Based Layer Perovskites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A. The Rietveld Method; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczyk, M.; Ujma, Z.; Pawełczyk, M. Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Nguzen, C.; Seraji, S.; Forbess, M.; Limmer, S.J. Processing and Properties of Strontium Bismuth Vanadate Niobate Ferroelectric Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Kimura, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Sintering of Platelike Bismuth Titanate Powder Compacts with Preferred Orientation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, B.R.; Venkataraman, B.H. Effect of Rare Earth Ion Doping on the Structural, Microstructural and Diffused Phase Transition Characteristics of BaBi2Nb2O9 Relaxor Ferroelectrics. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 16365–16369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarczyk, W.; Kata, D.; Lis, J.; Galos, K. Metodyka Ultradźwiękowych Badań Płytek Typu Gres Porcellanato. Mater. Ceram. 2008, 60, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Pelaiz-Barranco, A.; Calderon-Pinar, F.; Garcia-Zaldivar, O.; Gonzalez-Abreu, Y. Relaxor Behaviour in Ferroelectric Ceramics. Adv. Ferroelectr. 2012, 2012, 85–107. [Google Scholar]
- Eren, E.; Kurama, S.; Solodov, I. Characterization of Porosity and Defect Imaging in Ceramic Tile Using Ultrasonic Inspections. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurama, S.; Gultekin, E.E. Characterization of Silicate Ceramics Using Ultrasonics Test Method. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 92, 194–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kozielski, L.; Adamczyk, M.; Lisińska-Czekaj, A.; Czekaj, D.; Zachariasz, R.; Pawełczyk, M.; Pilch, M. Mechanical Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Ceramics Obtained by Different Measurements Techniques. World J. Eng. 2013, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, A.; James Raju, K.C. Impact of Sm-Substitution and Microwave Sintering on Dielectric and Mechanical Properties of SrBi4Ti4O15 Ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 19698–19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongmee, N.; Watcharapasorn, A.; Jiansirisomboon, S. Effects of Dy Substitution for Bi on Phase, Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of Layer-Structured Bi4−xDyxTi3O12 Ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 458, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaiselvi, B.J.; Sridaran, R.; Murugan, R. Dielectric Properties of Sr1−xBi2+(2/3)x(VxNb1−x)2O9 [X = 0.1 and 0.2] Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2006, 32, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.Y.; Wei, Y.F.; Leu, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chung, H.H.; Diao, C.C. The Influence of V₂O₅ on the Characteristics of BaBi₂Nb₂O₉ Ceramics. In Proceedings of the Global Roadmap for Ceramics & ICC2 Proceedings: 2nd International Congress on Ceramics, Verona, Italy, 29 June–4 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Smolenskii, A.; Izupov, W.A. Dielectric Polarization and Losses of Some Complex Compounds. Zh. Tekhn. Fiz. 1958, 28, 1419. [Google Scholar]
- Smoleński, G.A.; Agranovskaya, A.J. Synthesis and Piezoelectric Properties of Pb0.98Sm0.02[(Zry,Ti1−y)0.98(Fe1/23+,Nb1/25+)0.02]O3 Ceramics. Sov. Phys. Solid State 1959, 1, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Shimakawa, Y.; Kubo, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Goto, S.; Kamiyama, T.; Asano, H.; Izumi, F. Crystal Structure and Ferroelectric Properties of ABi2Ta2O9 (A = Ca, Sr, and Ba). Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, C.; Ravishankar, N.; Varma, K.B.R.; Maglione, M.; von Der Mühll, R.; Etourneau, J. Relaxor Behavior of K0.5La0.5Bi2Nb2O9 Ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 042905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, C.; Narayanan, R.; Maglione, M.; Varma, K.B.R. Relaxor Behavior of Ka0.5La0.5Bi2Ta2O9 Ceramics. Solid State Commun. 2006, 139, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K.; Nomura, S. Critical Exponents of the Dielectric Constants in Diffused-Phase-Transition Crystals. Ferroelectrics 1982, 44, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvartsman, V.V.; Kleemann, W.; Dec, J.; Xu, Z.K.; Lu, S.G. Diffuse Phase Transition in BaTi1−xSnxO3 Ceramics: An Intermediate State Between Ferroelectric and Relaxor Behavior. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 124111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Nagata, K. Effects of Grain Size and Porosity on Electrical and Optical Properties of PLZT Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1973, 56, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Viehland, D. Grain Size Dependence of Relaxor Characteristics in La-Modified Lead Zirconate Titanate. Ferroelectrics 1997, 193, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.C.; Matin, M.A.; Hossain, A.K.M.A. Rietveld Refinement Structure, Electric, Dielectric, and Ferroelectric Properties of Lead-Free Ba0.985Sr0.015Zr0.10Ti0.90O3 Ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 4916–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keburis, P.; Banys, J.; Brillingas, A.; Prapuolenis, J.; Kholkin, A.; Costa, M.E. Dielectric Properties of Relaxor Ceramics BBN. Ferroelectrics 2007, 353, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholkin, A.L.; Avdeev, M.; Costa, M.E.V.; Baptista, J.L.; Dorogotsev, S.N. Dielectric Relaxation in Ba-Based Layered Perovskites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Katiyar, R.S. Dielectric Behavior of Lead Magnesium Niobate Relaxors. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, Z. Das Temperaturabhaengigkeitsgesetz der Viskositaet von Fluessigkeiten. Physik 1921, 22, 645. [Google Scholar]
- Taganstev, A.K. Vogel-Fulcher Relationship for the Dielectric Permittivity of Relaxor Ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirc, R.; Blinc, R. Vogel-Fulcher Freezing in Relaxor Ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 020101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mole Fraction x | Lattice Parameters | V [Å3] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a0 [Å] | b0 [Å] | c0 [Å] | ||
| 0.00 [48] | 3.9406 | 3.9406 | 25.6378 | 398.1 |
| 0.02 | 3.9303 | 3.9303 | 25.6248 | 395.8 |
| 0.04 | 3.9291 | 3.9291 | 25.6127 | 395.4 |
| 0.06 | 3.9285 | 3.9285 | 25.6089 | 395.2 |
| 0.08 | 3.9259 | 3.9259 | 25.5957 | 394.5 |
| 0.10 | 3.9285 | 3.9285 | 25.6059 | 395.1 |
| Mole Fraction x | BaBi2−xSmxNb2O9 | |
|---|---|---|
| VL [m/s] | VT [m/s] | |
| 0.00 [54] | 3647.7 | 2187.5 |
| 0.02 | 4383.6 | 2585.2 |
| 0.04 | 4572.4 | 2569.0 |
| 0.06 | 4527.8 | 2579.3 |
| 0.08 | 4585.4 | 2582.6 |
| 0.10 | 4539.2 | 2569.2 |
| x (Sm) | Poisson’s Ratio, μ | Young’s Modulus, E [GPa] | Modulus of Stiffness, G [GPa] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 [57] | 0.219 | 76.07 | 31.20 |
| 0.02 | 0.233 | 119.51 | 48.45 |
| 0.04 | 0.269 | 119.06 | 46.90 |
| 0.06 | 0.229 | 127.71 | 51.94 |
| 0.08 | 0.268 | 123.35 | 48.65 |
| 0.10 | 0.264 | 114.23 | 45.18 |
| x (Sm) | Tm [K] (100 [kHz]) | εmax |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 [48] | 456.0 | 406.5 |
| 0.02 | 459.2 | 525.6 |
| 0.04 | 449.8 | 437.6 |
| 0.06 | 436.7 | 424.2 |
| 0.08 | 436.3 | 451.8 |
| 0.10 | 437.7 | 508.7 |
| x (Sm) | BaBi2−xSmxNb2O9 |
|---|---|
| γ | |
| 0.00 [48] | 1.45 |
| 0.02 | 178 |
| 0.04 | 177 |
| 0.06 | 188 |
| 0.08 | 189 |
| 0.10 | 190 |
| x (Sm) | BaSmxBi2−xNb2O9 | |
|---|---|---|
| ΔTm [K] | Δεmax | |
| 0.00 [48] | 92.59 | 68.0 |
| 0.02 | 99.70 | 50.3 |
| 0.04 | 98.31 | 47.9 |
| 0.06 | 117.31 | 66.5 |
| 0.08 | 106.01 | 61.5 |
| 0.10 | 64.21 | 92.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rerak, M.; Makowska, J.; Goryczka, T.; Wodecka-Duś, B.; Osińska, K.; Tytko, G.; Adamczyk-Habrajska, M. Effects of Samarium Doping on the Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials 2024, 17, 4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17204952
Rerak M, Makowska J, Goryczka T, Wodecka-Duś B, Osińska K, Tytko G, Adamczyk-Habrajska M. Effects of Samarium Doping on the Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials. 2024; 17(20):4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17204952
Chicago/Turabian StyleRerak, Michał, Jolanta Makowska, Tomasz Goryczka, Beata Wodecka-Duś, Katarzyna Osińska, Grzegorz Tytko, and Małgorzata Adamczyk-Habrajska. 2024. "Effects of Samarium Doping on the Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics" Materials 17, no. 20: 4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17204952
APA StyleRerak, M., Makowska, J., Goryczka, T., Wodecka-Duś, B., Osińska, K., Tytko, G., & Adamczyk-Habrajska, M. (2024). Effects of Samarium Doping on the Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials, 17(20), 4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17204952









