Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Li Alloys with Different Li Contents Prepared by Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Powder Preparation
2.2. Forming Process
2.3. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Forming Process Optimization
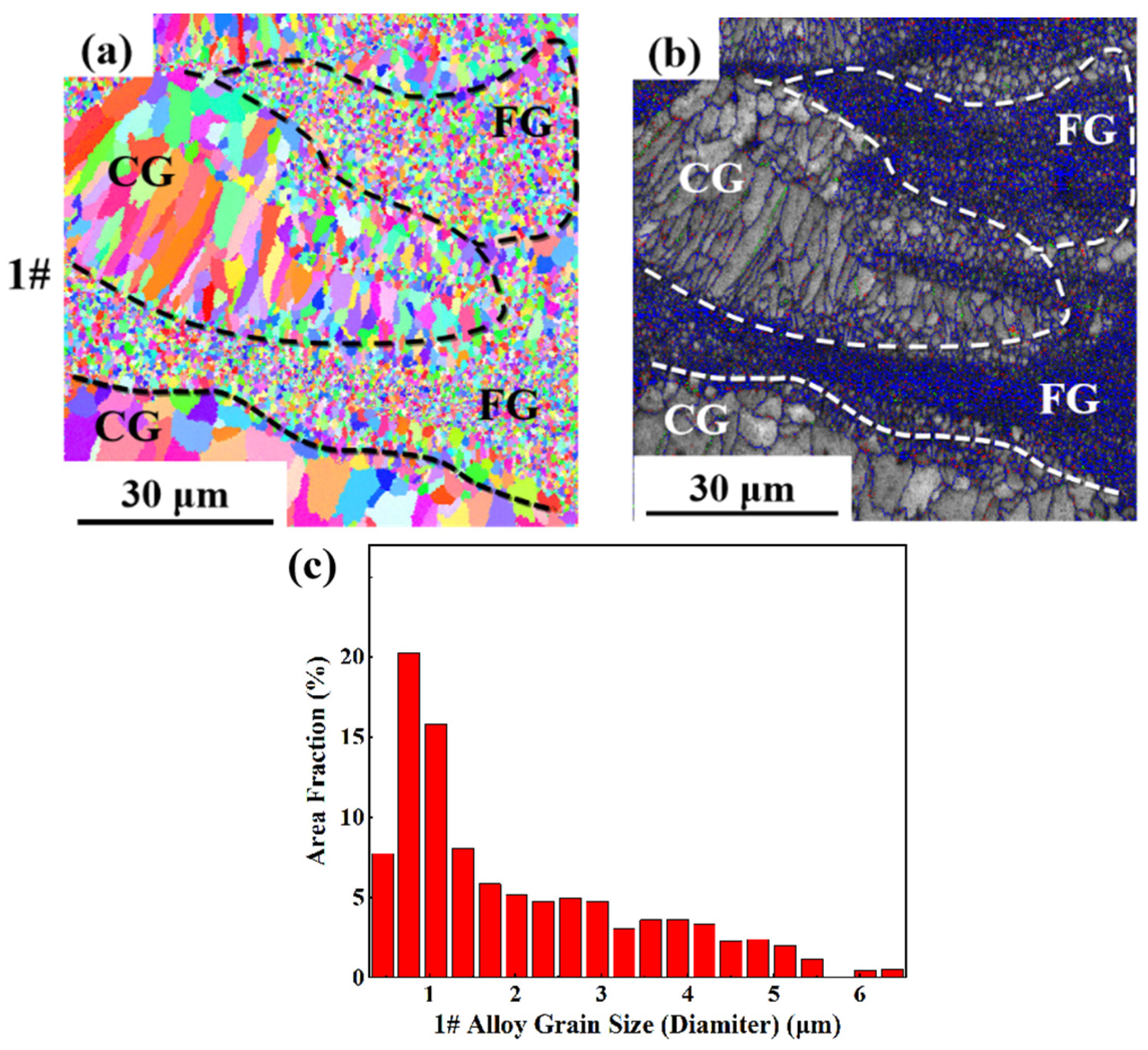
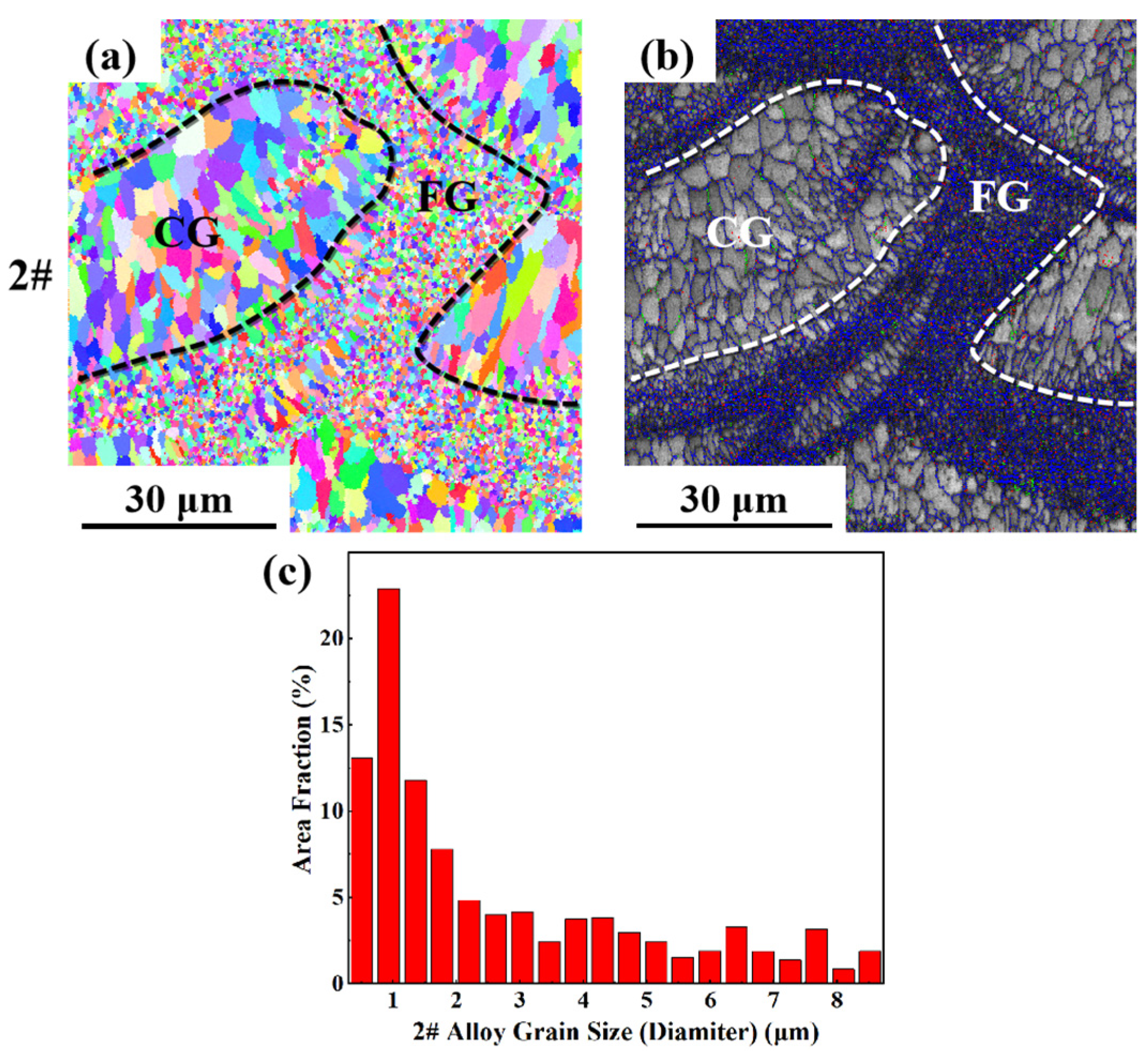
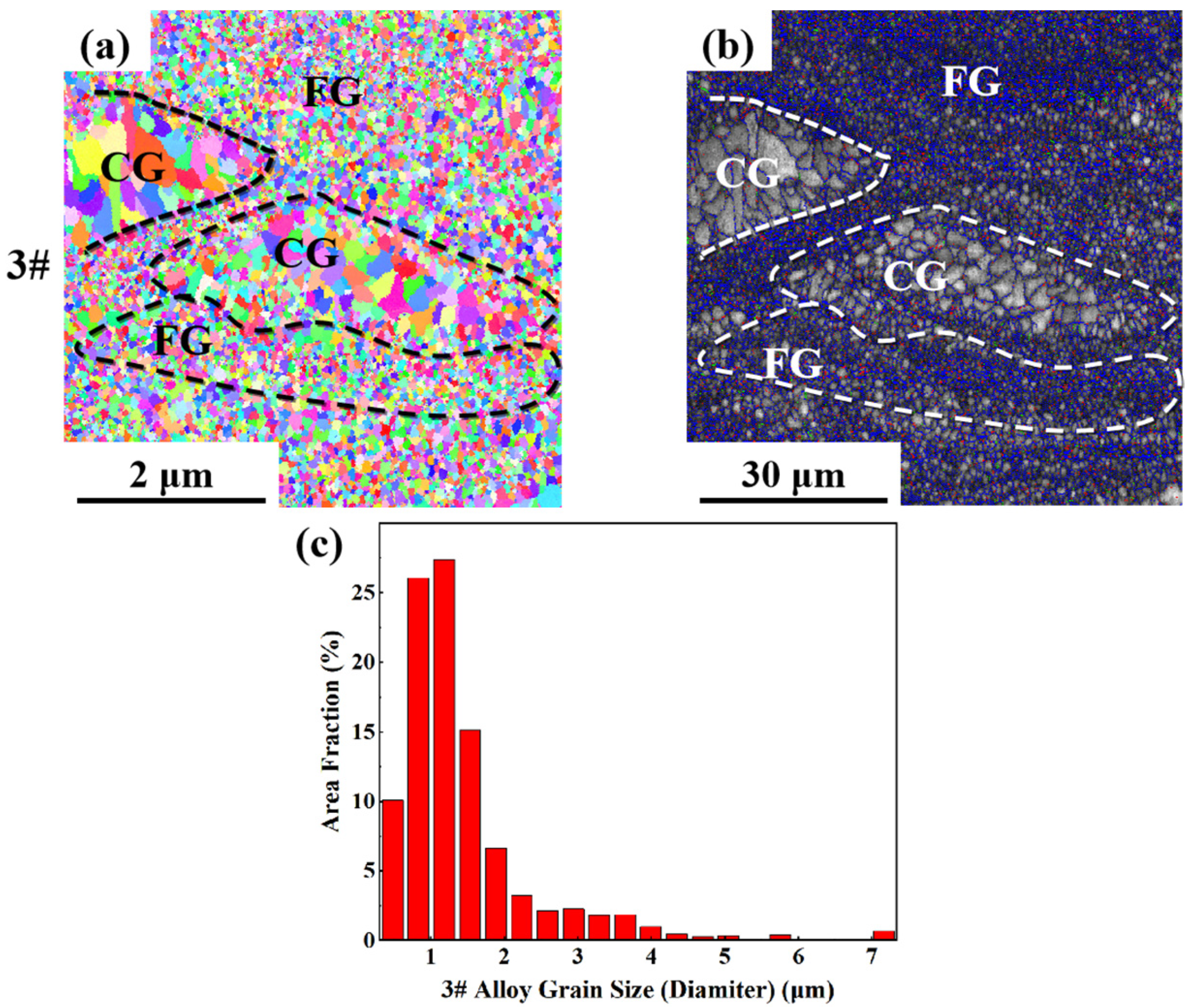
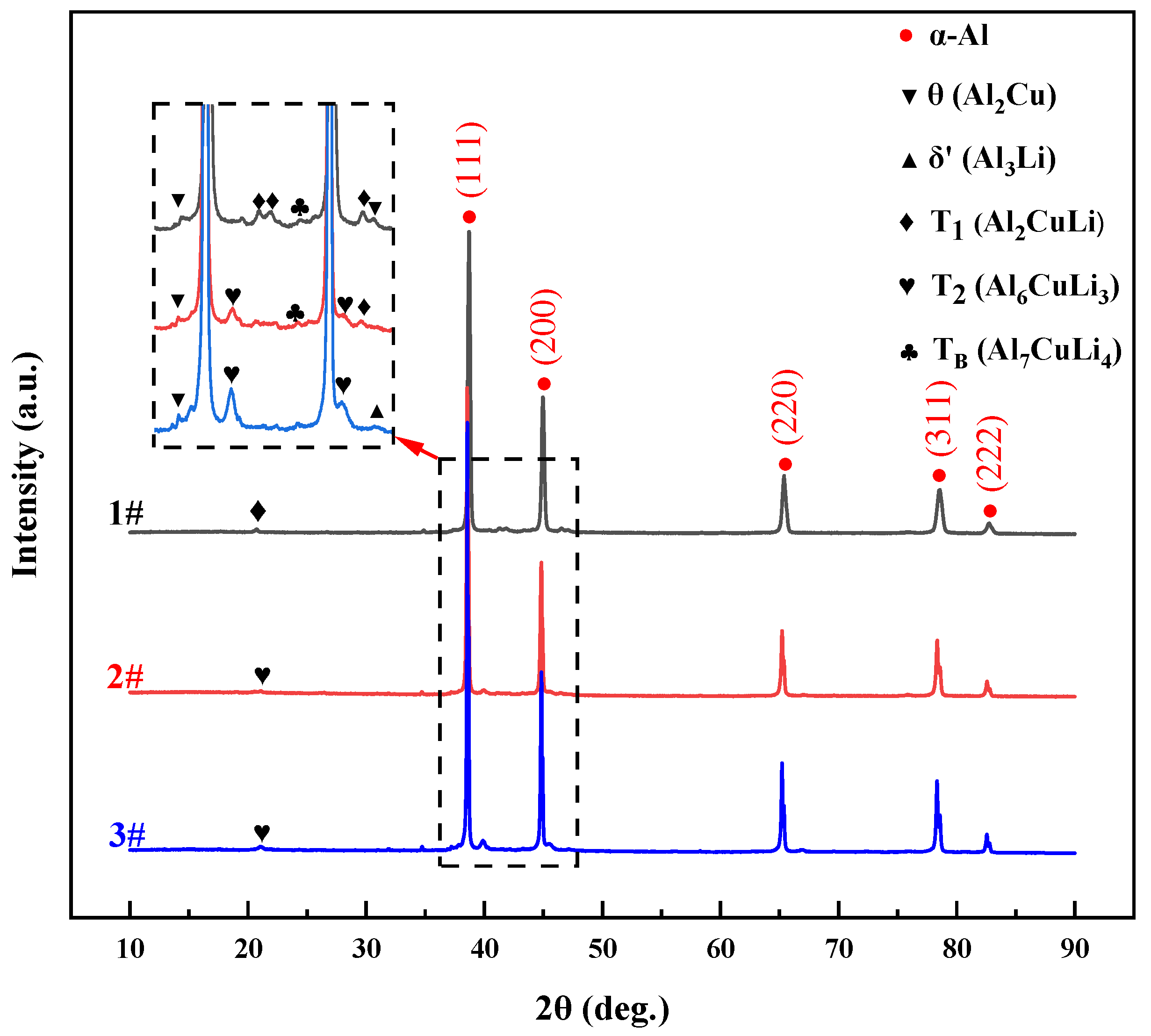
3.2. Microstructure and Phase Analysis
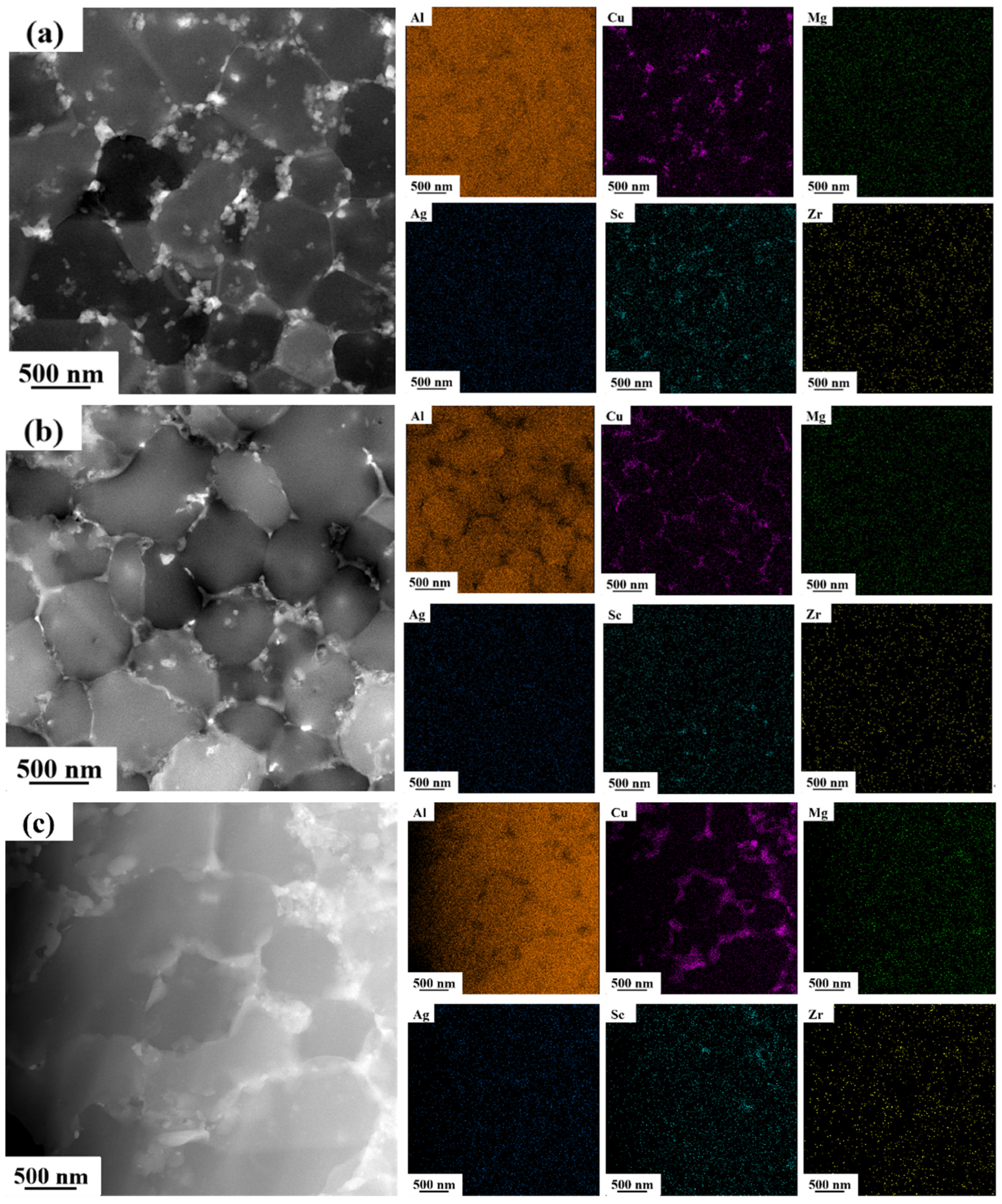
3.2.1. Microstructure
3.2.2. XRD Phase Analysis
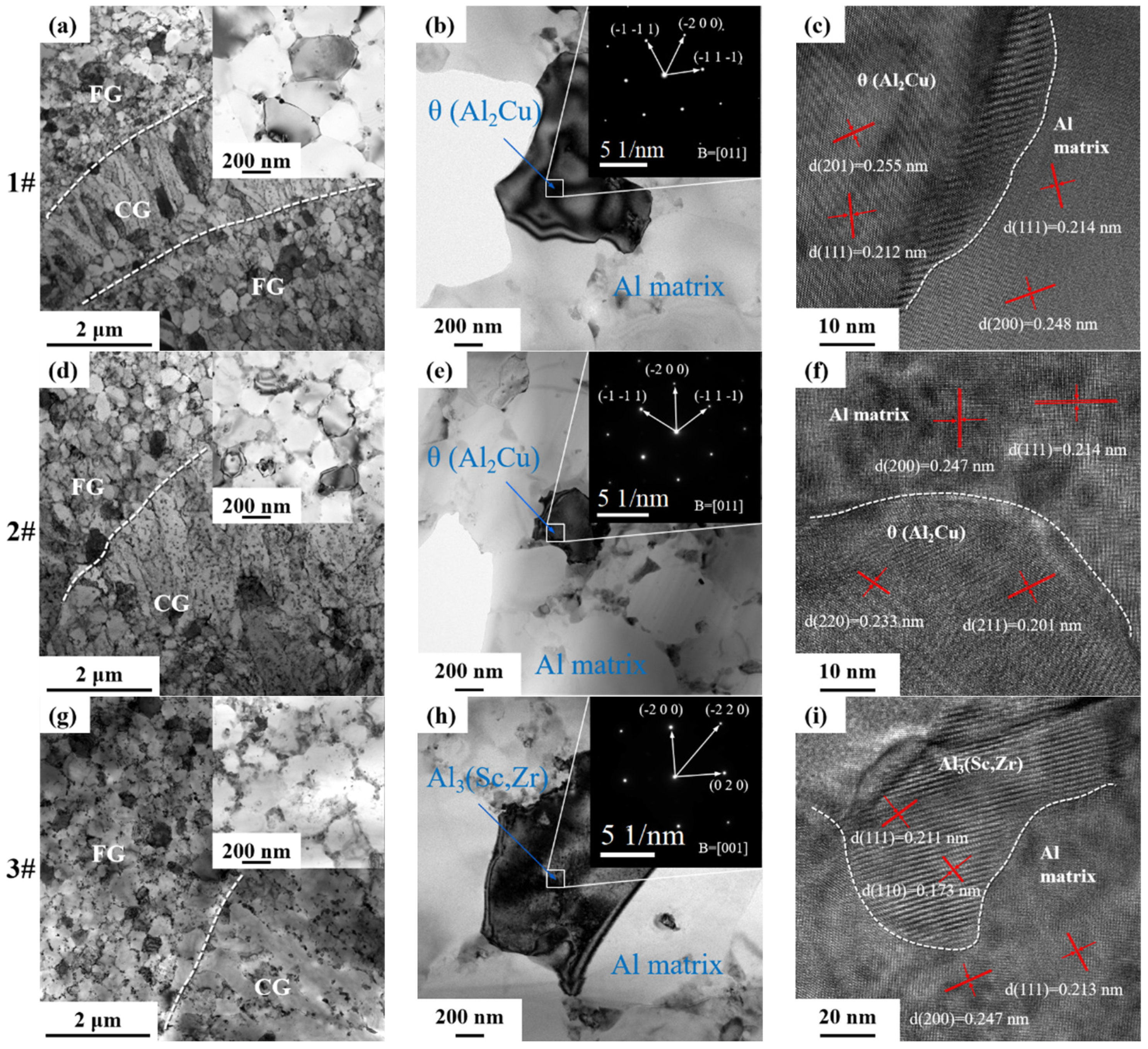
3.3. TEM Morphology and Analysis
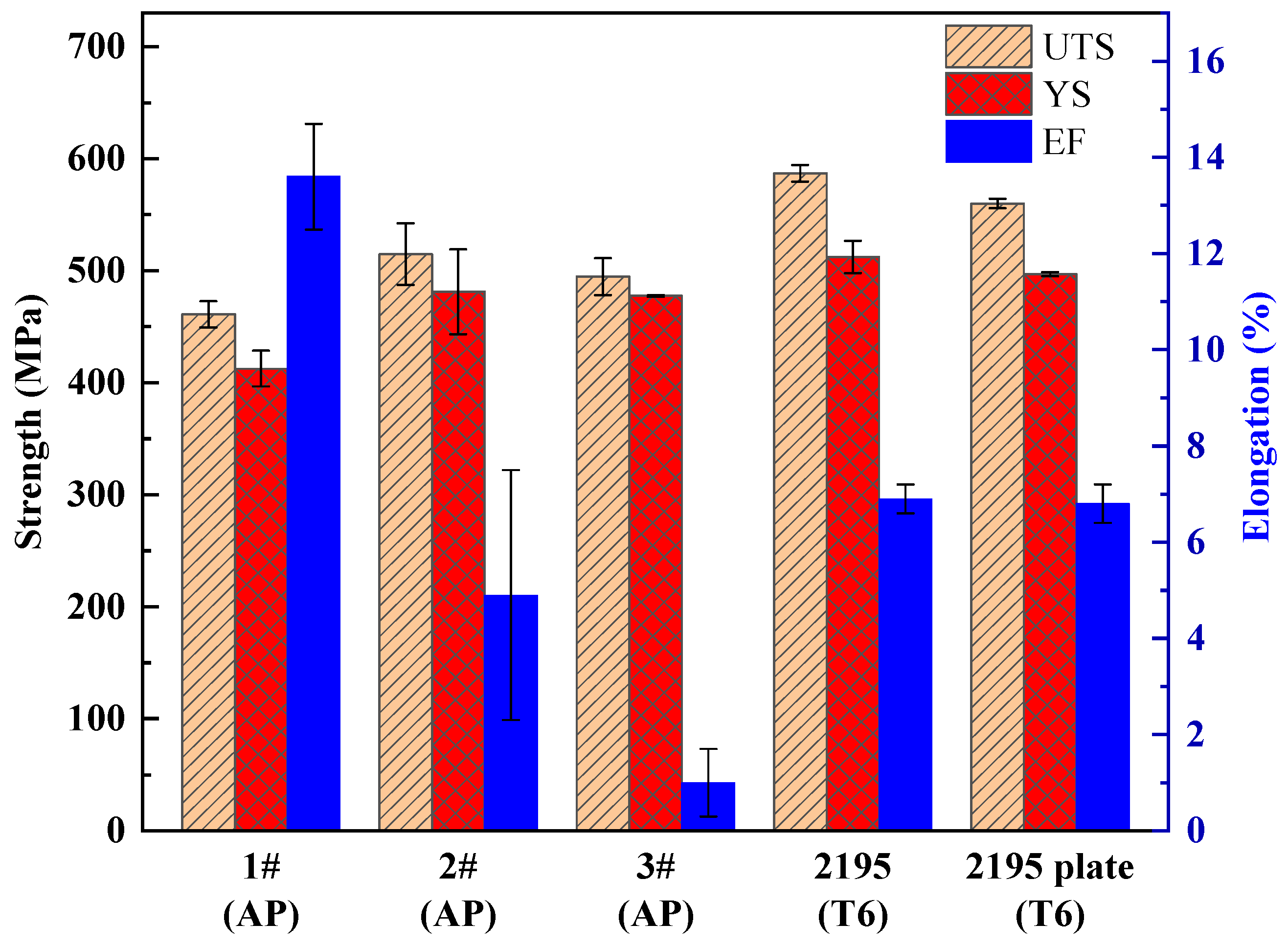
3.4. Mechanical Propertie
4. Conclusions
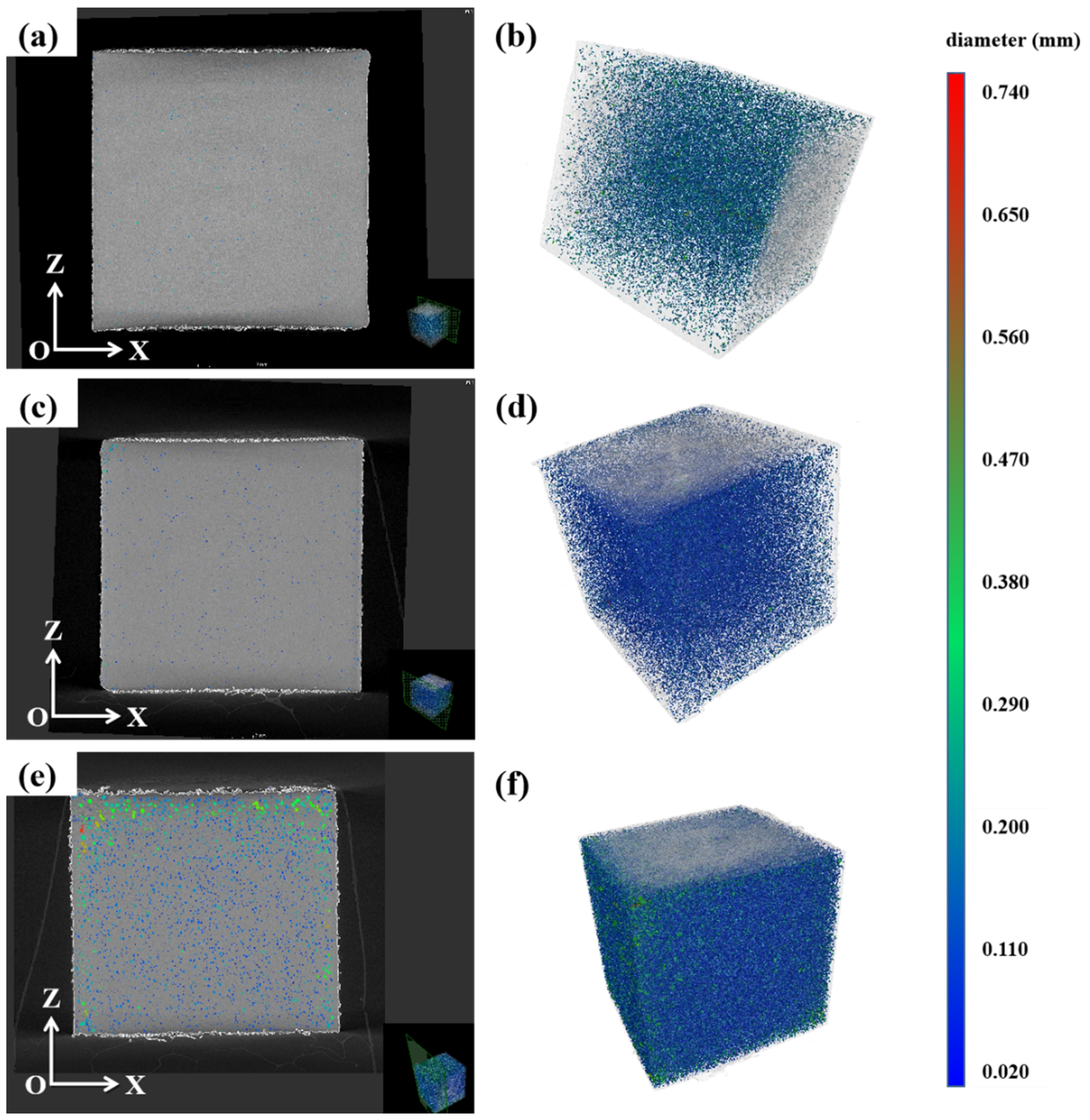
- The alloys with different Li contents successfully prepared by SLM technology are crack-free, with good surface quality and high densifications of 99.51%, 98.96% and 92.01%, respectively.
- With the increase in laser power and energy density, the density decreases gradually. At high energy density, the cooling rate of the molten pool is slow and the internal high temperature residence time is long, which aggravates the volatilization of the low-melting-point elements Li and Mg, thus forming circular pores, resulting in reduced density.
- When the Li content is 1.0 wt.%, θ phase, T1 phase and TB phase occur; after 2.0 wt.%, the T1 and T2 phases are precipitated together; and at 3.0 wt.%, the δ’ phase precipitates together with the T2 phase.
- With the increase in Li content, the hardness, tensile strength and yield strength of 1#, 2# and 3# alloys increase first and then decrease, and the elongation and reduction in area decrease. The reason is that the change in Li content affects the T1 phase and the pore defects in the as-printed alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.S.; Yue, X.; Li, Q.Y.; Peng, H.L.; Dong, B.X.; Liu, T.S.; Yang, H.Y.; Fan, J.; Shu, S.L.; Qiu, F.; et al. Development and applications of aluminum alloys for aerospace industry. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 944–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kablov, E.N.; Antipov, V.V.; Oglodkova, J.S.; Oglodkov, M.S. Development and Application Prospects of Aluminum–Lithium Alloys in Aircraft and Space Technology. Metallurgist 2021, 65, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioja, R.J.; Liu, J. The Evolution of Al-Li Base Products for Aerospace and Space Applications. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3325–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Wu, S.J. Aluminum Lithium Alloys (Al-Li-Cu-X)-New Generation Material for Aerospace Applications. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 440, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanhill, R.J.H. Aerospace Applications of Aluminum–Lithium Alloys, Aluminum-Lithium Alloys; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 503–535. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Aty, A.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.H.; Ma, Y.; Chen, D. Strengthening mechanisms, deformation behavior, and anisotropic mechanical properties of Al-Li alloys: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 10, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Dong, Z.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Q.; Loh, L.E.; Sing, S.L. Review of selective laser melting: Materials and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, M.; Azevedo, J.; Araújo, A.; Reis, L.; Pinto, E.; Alves, N.; Santos, R.; Pedro Mortágua, J. Selective laser melting (SLM) and topology optimization for lighter aerospace componentes. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2016, 1, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, W.E. Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sames, W.J.; List, F.A.; Pannala, S.; Dehoff, R.R.; Babu, S.S. The metallurgy and processing science of metal additive manufacturing. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 315–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, J.J.; Seifi, M. Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review of Mechanical Properties. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 151–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, R.; Yuan, T.; Niu, P.; Wang, M.; Lin, Z. Microstructure, metallurgical defects and hardness of Al–Cu–Mg–Li–Zr alloy additively manufactured by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffeis, I.; Adjei-Kyeremeh, F.; Vroomen, U.; Richter, S.; Buhrig-Polaczek, A. Characterising the Microstructure of an Additively Built Al-Cu-Li Alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Tian, X.; He, B. Developing a novel lightweight Al–Mg–Li alloy for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing: Parameter optimization, microstructure evolution, and mechanical performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, F.; Calignano, F.; Lorusso, M.; Pakkanen, J.; Aversa, A.; Ambrosio, E.P.; Lombardi, M.; Fino, P.; Manfredi, D. On the Selective Laser Melting (SLM) of the AlSi10Mg Alloy: Process, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2017, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempen, K.; Thijs, L.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Kruth, J.P. Mechanical Properties of AlSi10Mg Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Phys. Procedia 2012, 39, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, E.; Heckenberger, U.; Holzinger, V.; Buchbinder, D. Additive manufactured AlSi10Mg samples using Selective Laser Melting (SLM): Microstructure, high cycle fatigue, and fracture behavior. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Qi, T.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, X. Selective laser melting of high strength Al–Cu–Mg alloys: Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 656, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H.; Yahata, B.D.; Hundley, J.M.; Mayer, J.A.; Schaedler, T.A.; Pollock, T.M. 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys. Nature 2017, 549, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Ke, L.; Zeng, X. Selective laser melting of Al7050 powder: Melting mode transition and comparison of the characteristics between the keyhole and conduction mode. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Chen, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, H. Effect of defocusing distance on laser powder bed fusion of high strength Al–Cu–Mg–Mn alloy. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2020, 15, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtke, K.; Palm, F.; Hawkins, A.; Emmelmann, C. Process and Mechanical Properties: Applicability of a Scandium modified Al-alloy for Laser Additive Manufacturing. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, A.B.; Dawson, K.; Heeling, T.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Schäublin, R.; Palm, F.; Wegener, K. Microstructural features of Sc- and Zr-modified Al-Mg alloys processed by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2017, 115, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, A.B.; Dawson, K.; Kern, K.; Palm, F.; Wegener, K. SLM-processed Sc- and Zr- modified Al-Mg alloy: Mechanical properties and microstructural effects of heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 701, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Correa, L.; González-Rovira, L.; de Dios López-Castro, J.; Botana, F.J. Pitting and intergranular corrosion of Scalmalloy® aluminium alloy additively manufactured by Selective Laser Melting (SLM). Corros. Sci. 2022, 201, 110273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Correa, L.; González-Rovira, L.; de Dios López-Castro, J.; Castillo-Rodríguez, M.; Botana, F.J.J.M.C. Effect of the heat treatment on the mechanical properties and microstructure of Scalmalloy® manufactured by Selective Laser Melting (SLM) under certified conditions. Mater. Charact. 2023, 196, 112549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awd, M.; Tenkamp, J.; Hirtler, M.; Siddique, S.; Bambach, M.; Walther, F. Comparison of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Scalmalloy® Produced by Selective Laser Melting and Laser Metal Deposition. Materials 2017, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, R.; Sun, J.; Hou, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. Effects of Sc and Zr on microstructure and properties of 1420 aluminum alloy. Mater. Charact. 2019, 154, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.M.; Alkahtani, S.A.; Doty, H.W.; Samuel, F.H. Role of Zr and Sc addition in controlling the microstructure and tensile properties of aluminum–copper based alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Xu, C.; Xuejiao, W.; Hanada, S.; Yamagata, H.; Hao, L.; Chaoli, M. High strength aluminum cast alloy: A Sc modification of a standard Al–Si–Mg cast alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 604, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taendl, J.; Orthacker, A.; Amenitsch, H.; Kothleitner, G.; Poletti, C. Influence of the degree of scandium supersaturation on the precipitation kinetics of rapidly solidified Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 117, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Z.; Ke, L.; Zeng, X. Effect of Zr content on formability, microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Zr modified Al-4.24Cu-1.97Mg-0.56Mn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; Yin, J.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, X. Effect of Zirconium addition on crack, microstructure and mechanical behavior of selective laser melted Al-Cu-Mg alloy. Scr. Mater. 2017, 134, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, P.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Jia, L.; Ni, D.; Xiao, B.; Ma, Z. Microstructural Evaluation and Tensile Properties of Al-Mg-Sc-Zr Alloys Prepared by LPBF. Crystals 2023, 13, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Zhai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, B.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Research on Microstructure and Cracking Behavior of Al-6.2Zn-2Mg-xSc-xZr Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Crystals 2022, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirmo, J.L. High Strength Aluminium Alloys in Laser-Based Powder Bed Fusion—A Review. Procedia CIRP 2021, 104, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotadia, H.R.; Gibbons, G.; Das, A.; Howes, P.D. A review of Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing of aluminium alloys: Microstructure and properties. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yürekli, B.; Ullsperger, T.; Matthäus, G.; Schade, L.; Nolte, S.; Rettenmayr, M. Microstructural aspects of additive manufacturing of Al Li alloys with high Li content. Mater. Des. 2021, 198, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Meng, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Li, P.; Zhou, J. Investigating the effect of the scanning speed on the characteristics of Al-Li alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 75, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zhang, X. Problems and issues in laser beam welding of aluminum–lithium alloys. J. Manuf. Process. 2014, 16, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Nie, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zeng, X. A high strength Al–Li alloy produced by laser powder bed fusion: Densification, microstructure, and mechanical properties. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Nie, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H. High strength Al–Li alloy development for laser powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; He, B.; Li, K.; Tu, Y.; Wang, H. Study on microstructure evolution and aging precipitation behavior of a novel Al-Li alloy fabricated by laser rapid melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 908, 164630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yürekli, B.; Schade, L.; Ullsperger, T.; Seyfarth, B.; Kohl, H.; Matthäus, G.; Liu, D.; Rettenmayr, M.; Nolte, S. Additive manufacturing of binary Al-Li alloys. Procedia CIRP 2020, 94, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qi, H.; Yin, Y.; Wu, X.; Jia, Q. Characterisation of the multiple effects of Sc/Zr elements in selective laser melted Al alloy. Mater. Charact. 2022, 183, 111653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochugovskiy, A.G.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V. Comparison of precipitation kinetics and mechanical properties in Zr and Sc-bearing aluminum-based alloys. Mater. Lett. 2020, 275, 128096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.D.; Prangnell, P.B. Dispersoid precipitation and process modelling in zirconium containing commercial aluminium alloys. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochugovskiy, A.G.; Tabachkova, N.Y.; Ghayoumabadi, M.E.; Cheverikin, V.V.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V. Joint effect of quasicrystalline icosahedral and L12-strucutred phases precipitation on the grain structure and mechanical properties of aluminum-based alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 87, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.L.; Jiang, D.M. Influence of Zr addition on the microstructure evolution and thermal stability of Al–Mg–Mn alloy processed by ECAP at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 452–453, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.J.; Humphreys, F.J. Interaction of recrystallization and precipitation: The effect of Al3Sc on the recrystallization behaviour of deformed aluminium. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monastyrska, T.O.; Berezina, A.L.; Molebny, O.A.; Kotko, A.V. Effect of alloying with transition metals on the aging of anomalously supersaturated solid solution of Al–Mg alloys. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 12, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Pan, W.; Liang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Cracking Behavior, Microstructure and Properties of Selective Laser Melted Al-Mn-Mg-Sc-Zr Alloy. Crystals 2022, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Pan, W.; Shao, S.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Fracture Behavior of Micron-Sized TiB(2)/AlZnMgCu(Sc,Zr) Composites Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2023, 16, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 20975.25-2020; Methods for Chemical Analysis of Aluminium and Aluminium Alloys-Part 25: Determination of Elements Content—Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometric Method. China Nonferrous Metal Industry Association: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Qu, M.; Guo, Q.; Escano, L.I.; Nabaa, A.; Hojjatzadeh, S.M.H.; Young, Z.A.; Chen, L. Controlling process instability for defect lean metal additive manufacturing. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T228.1-2010; Metallic Materials-Tensile Testing—Part 1 : Method of Test at Room Temperature. China Iron and Steel Industry Association: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Wang, P.; Deng, L.; Prashanth, K.G.; Pauly, S.; Eckert, J.; Scudino, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Cu alloys fabricated by selective laser melting of powder mixtures. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2263–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Kang, N.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, W. Strength-ductility synergy of selective laser melted Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy with a heterogeneous grain structure. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Kang, N.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Tan, H.; Yang, H.; Huang, W. Making selective-laser-melted high-strength Al–Mg–Sc–Zr alloy tough via ultrafine and heterogeneous microstructure. Scr. Mater. 2021, 203, 114052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, A.B.; Dawson, K.; Voegtlin, M.; Palm, F.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of as-processed scandium-modified aluminium using selective laser melting. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Bezençon, C.; Gäumann, M. Columnar to equiaxed transition in solidification processing. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2001, 2, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäumann, M.; Henry, S.; Cléton, F.; Wagnière, J.D.; Kurz, W. Epitaxial laser metal forming: Analysis of microstructure formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 271, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.-h.; RØYset, J.; Solberg, J.K.; Liu, Q. Formation of precipitates and recrystallization resistance in Al–Sc–Zr alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Jeun, J.-H.; Chun, H.-J.; Lee, Y.R.; Yoo, J.-T.; Yoon, J.-H.; Lee, H.-S. Effect of precipitates on mechanical properties of AA2195. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 669, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
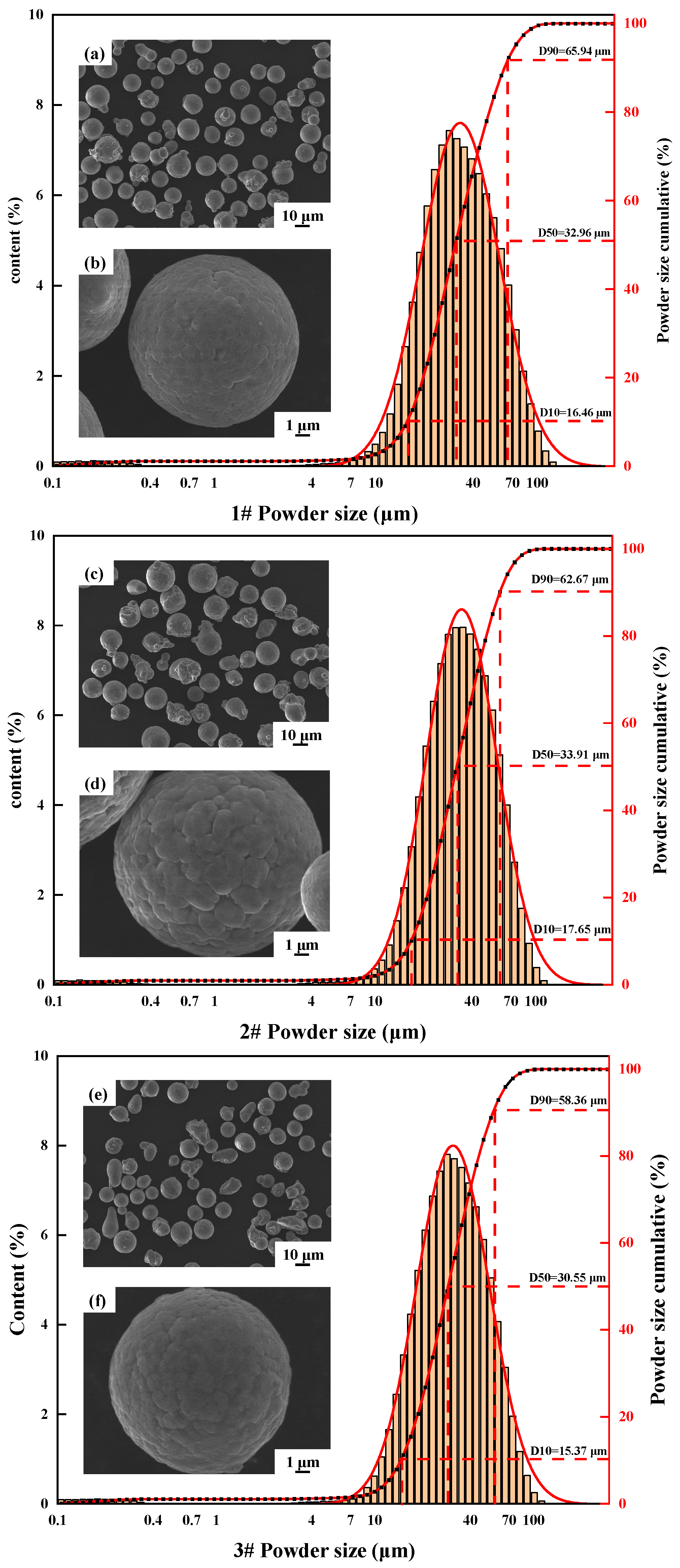
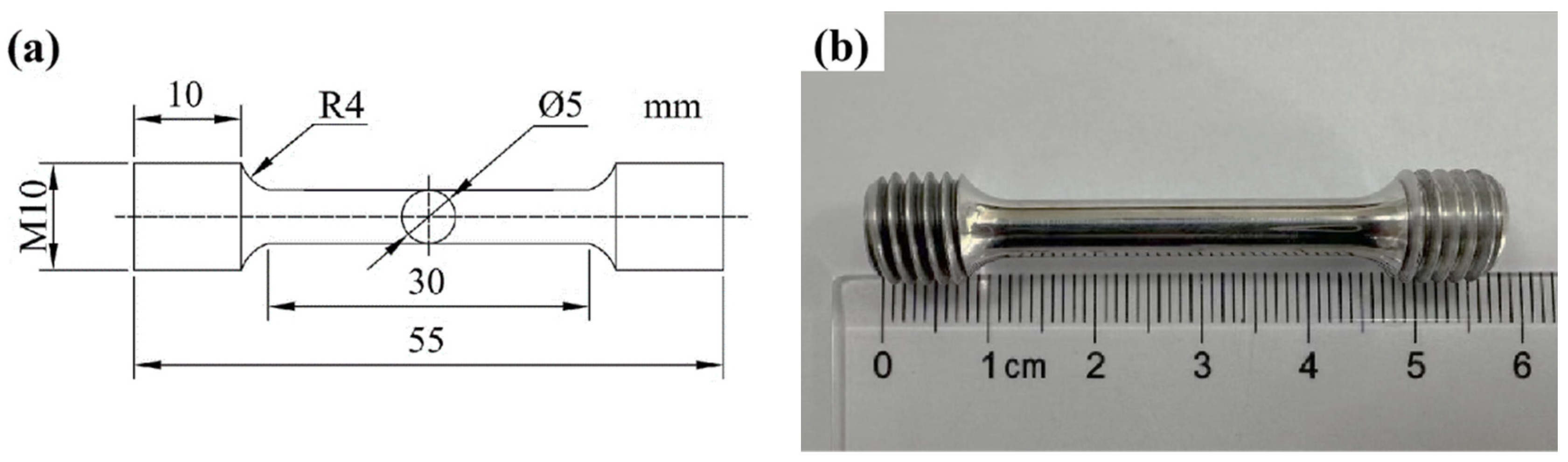
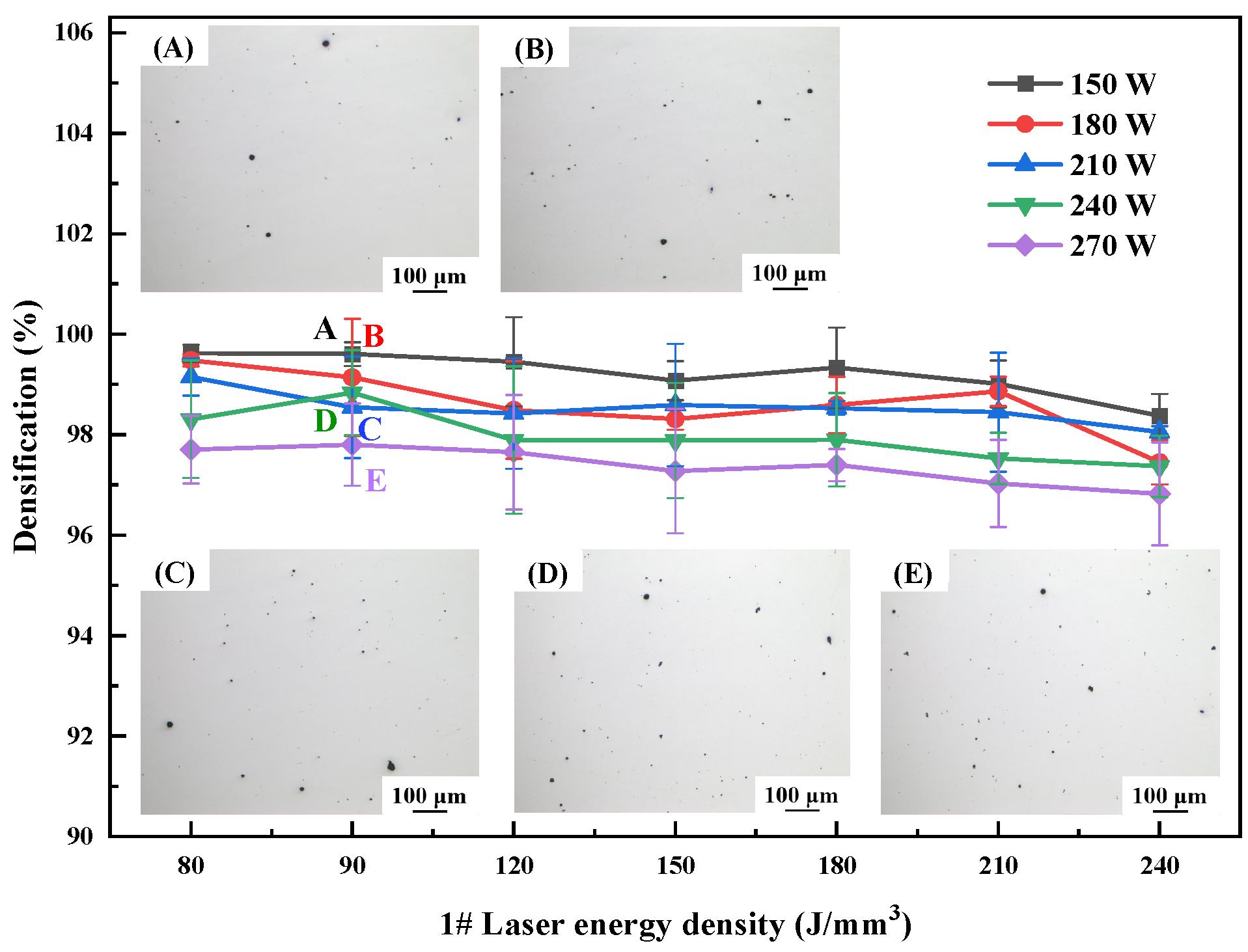
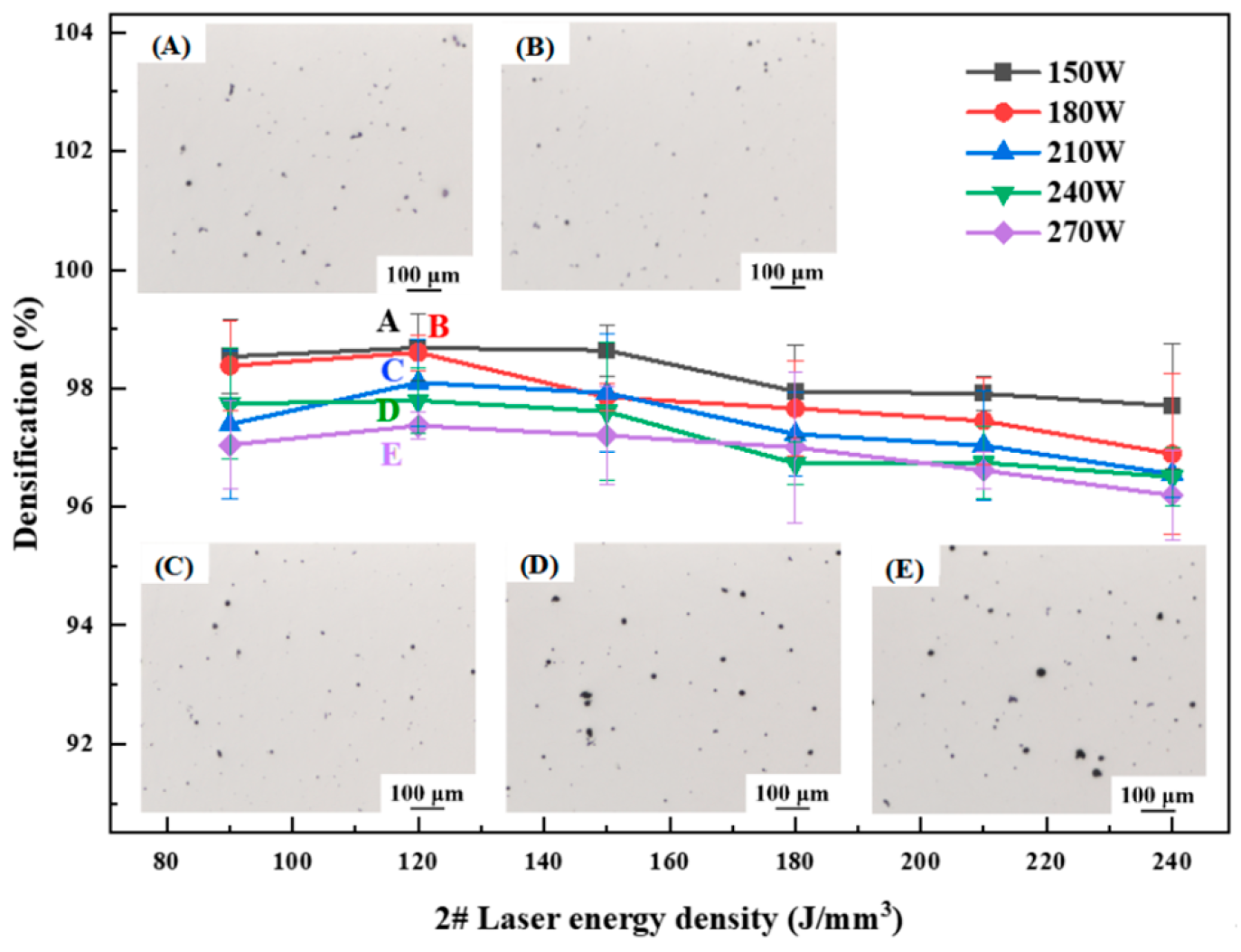


| Elements/wt.% | Cu | Li | Mg | Ag | Sc | Zr | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2195 | 3.7~4.3 | 0.8~1.2 | 0.25~0.8 | 0.25~0.6 | / | 0.08~0.16 | Bal. |
| 1# | 4 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | Bal. |
| 2# | 4 ± 0.2 | 2 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | Bal. |
| 3# | 4 ± 0.2 | 3 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | Bal. |
| Elements/wt.% | Cu | Li | Mg | Ag | Sc | Zr | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw powder | 1# | 3.78 ± 0.2 | 1.24 ± 0.3 | 0.59 ± 0.2 | 0.40 ± 0.1 | 0.80 ± 0.1 | 0.42 ± 0.1 | Bal. |
| 2# | 3.92 ± 0.2 | 2.67 ± 0.3 | 0.67 ± 0.2 | 0.53 ± 0.1 | 0.76 ± 0.1 | 0.42 ± 0.1 | Bal. | |
| 3# | 3.90 ± 0.2 | 3.71 ± 0.3 | 0.66 ± 0.2 | 0.58 ± 0.1 | 0.76 ± 0.1 | 0.52 ± 0.1 | Bal. | |
| As-printed sample | 1# | 4.08 ± 0.2 | 1.16 ± 0.3 | 0.50 ± 0.2 | 0.38 ± 0.1 | 0.76 ± 0.1 | 0.41 ± 0.1 | Bal. |
| 2# | 4.18 ± 0.2 | 2.26 ± 0.3 | 0.47 ± 0.2 | 0.42 ± 0.1 | 0.74 ± 0.1 | 0.42 ± 0.1 | Bal. | |
| 3# | 4.07 ± 0.2 | 3.24 ± 0.3 | 0.50 ± 0.2 | 0.48 ± 0.1 | 0.72 ± 0.1 | 0.52 ± 0.1 | Bal. | |
| Samples | UTS (MPa) | YS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# AP | 461 ± 12 | 413 ± 16 | 14 ± 1 | 73 ± 2 |
| 2# AP | 515 ± 28 | 481 ± 38 | 5 ± 3 | 76 ± 3 |
| 3# AP | 495 ± 17 | 478 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 74 ± 1 |
| 2195 T6 [41] | 587 ± 8 | 512 ± 14 | 7 ± 1 | / |
| 2195 plate-T6 [64] | 560 ± 4 | 497 ± 2 | 7 ± 1 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, S.; Liang, Z.; Yin, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Li Alloys with Different Li Contents Prepared by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2024, 17, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030657
Shao S, Liang Z, Yin P, Li X, Zhang Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Li Alloys with Different Li Contents Prepared by Selective Laser Melting. Materials. 2024; 17(3):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030657
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Shuobing, Zhuoheng Liang, Peng Yin, Xinyuan Li, and Yongzhong Zhang. 2024. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Li Alloys with Different Li Contents Prepared by Selective Laser Melting" Materials 17, no. 3: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030657
APA StyleShao, S., Liang, Z., Yin, P., Li, X., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Li Alloys with Different Li Contents Prepared by Selective Laser Melting. Materials, 17(3), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030657






