Studies of Auxetic Structures Assembled from Rotating Rectangles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement
2.1. Modified Structure of ‘Rotating Rectangles’
2.2. Analytical Models Based on Geometric Transformations
2.2.1. Properties of a 4 × 4 Structure (for a Fixed Value of x)
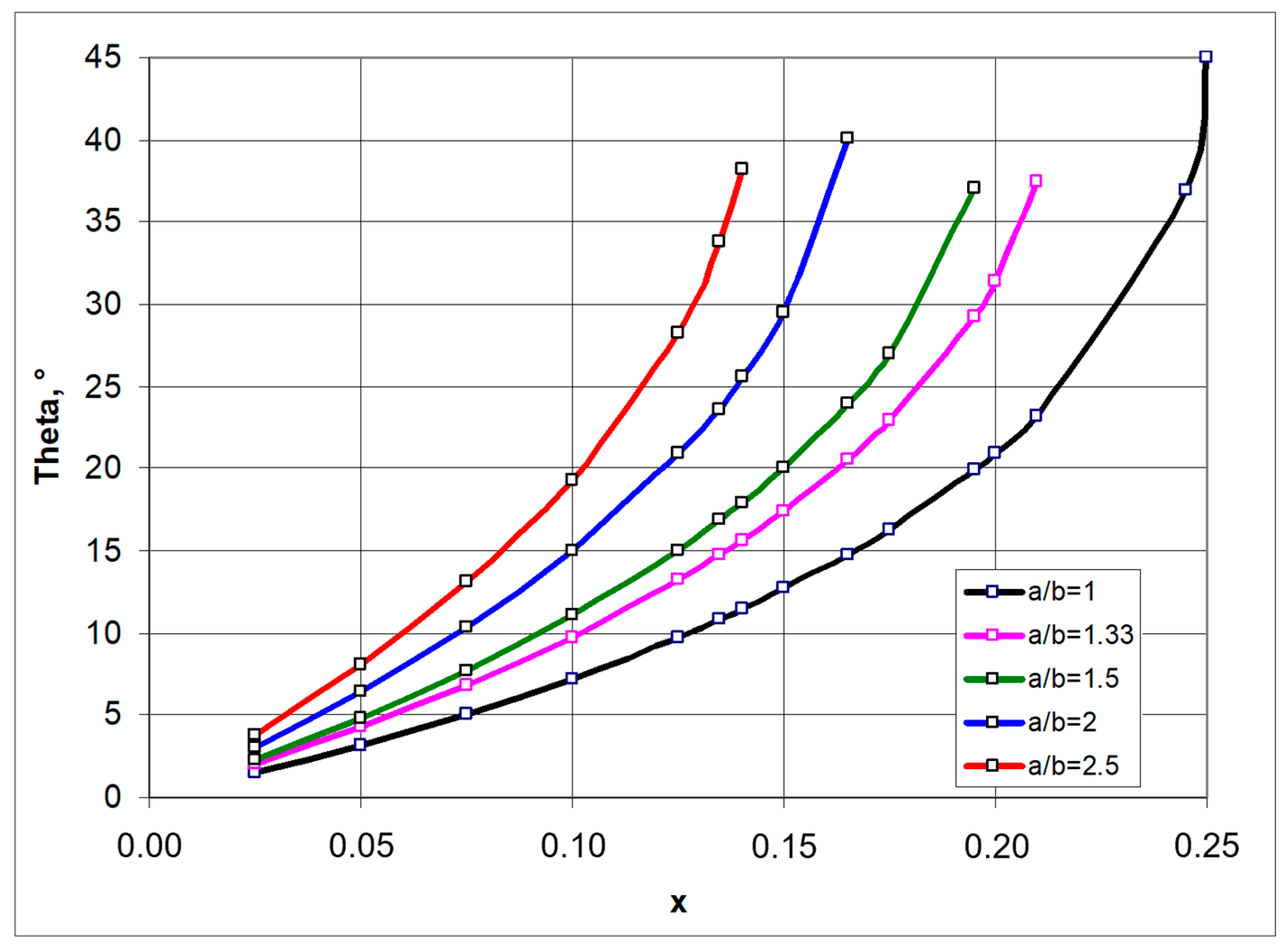
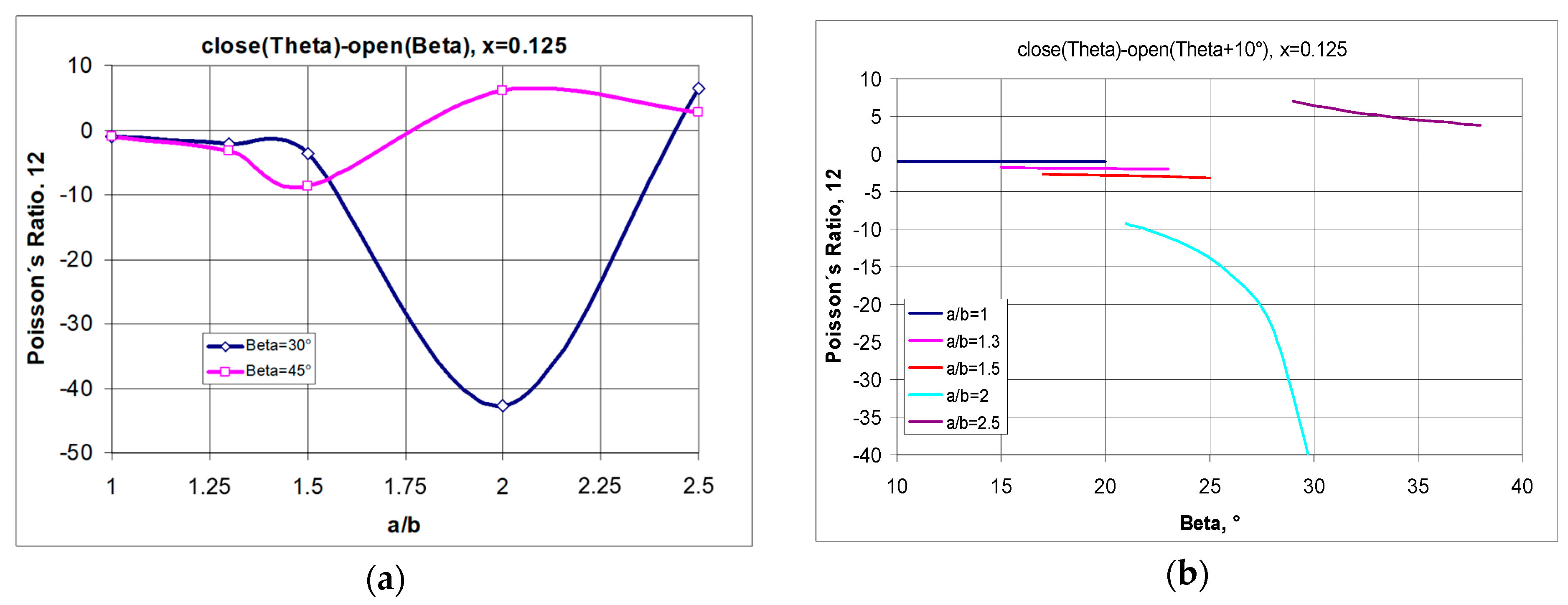
2.2.2. Properties of the 4 × 4 Structure (for Different Values of x)
3. Models of Auxetic Structures
3.1. Examples of Conditionally Auxetic Structures
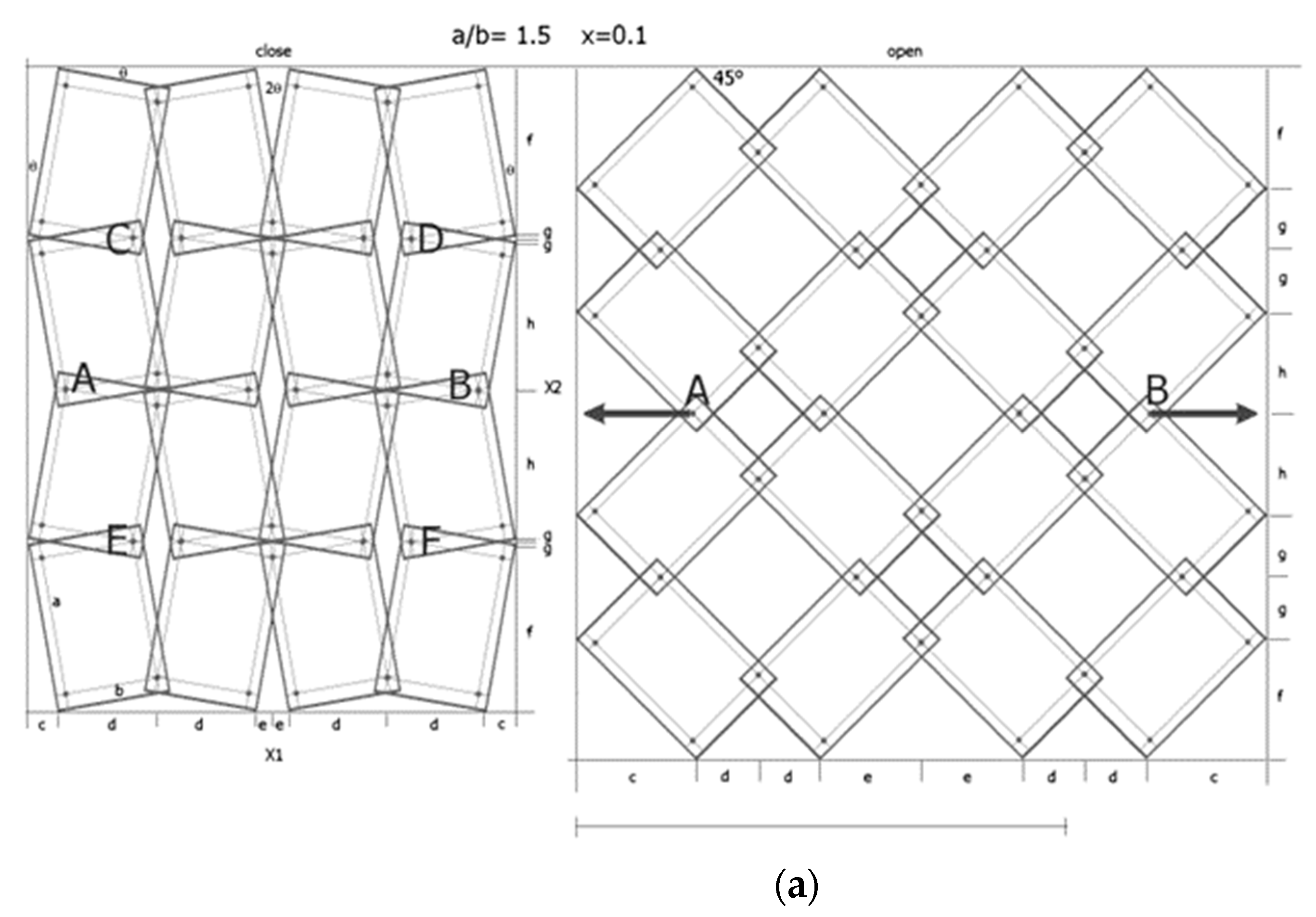
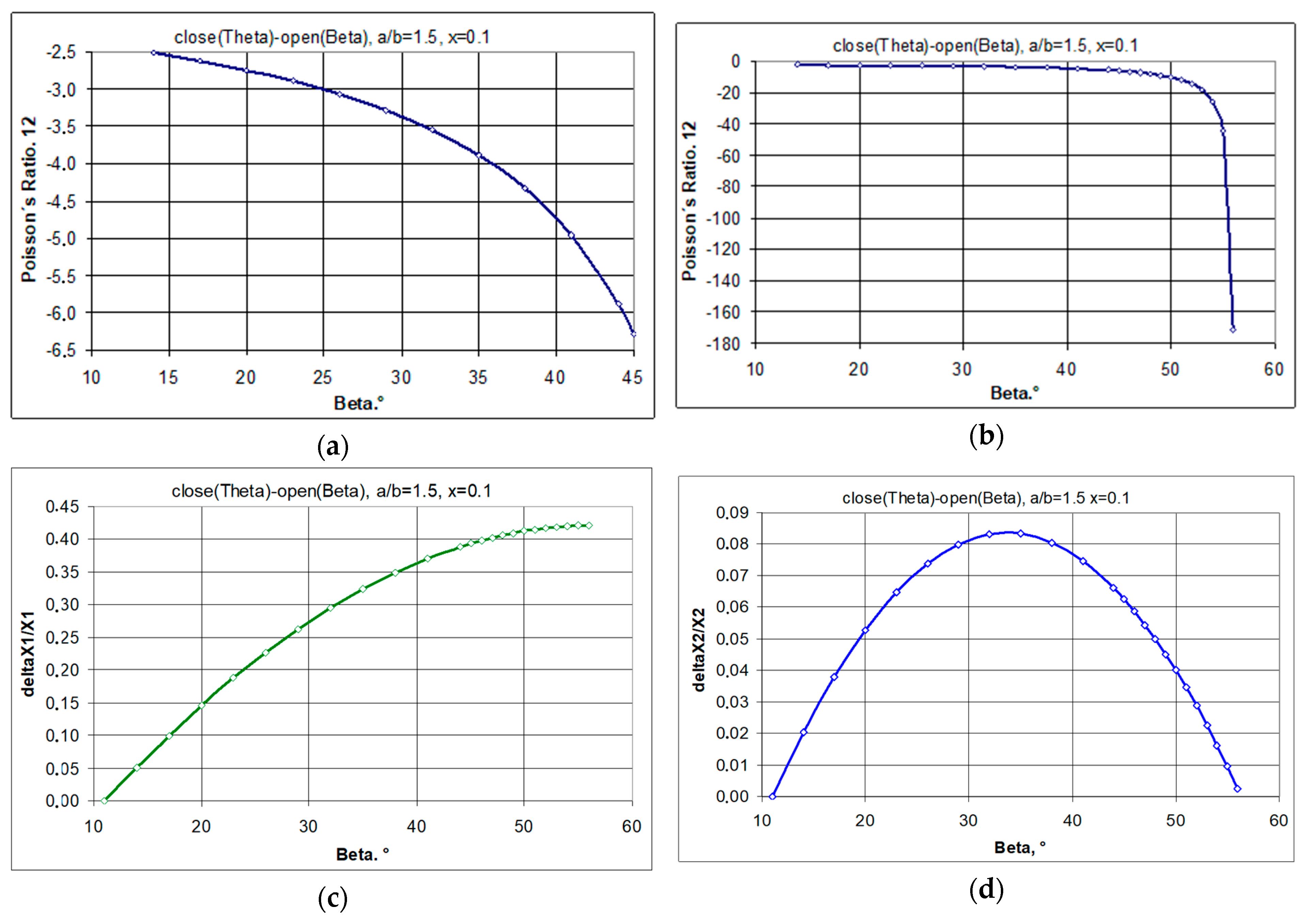
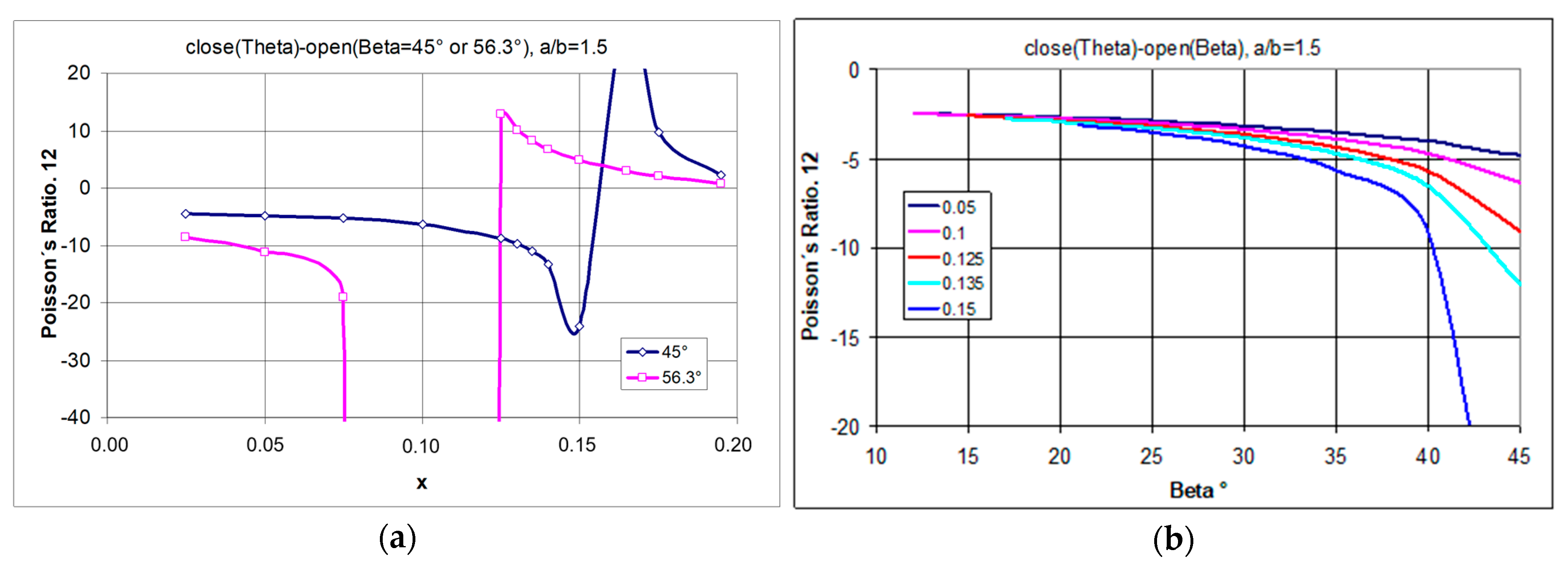
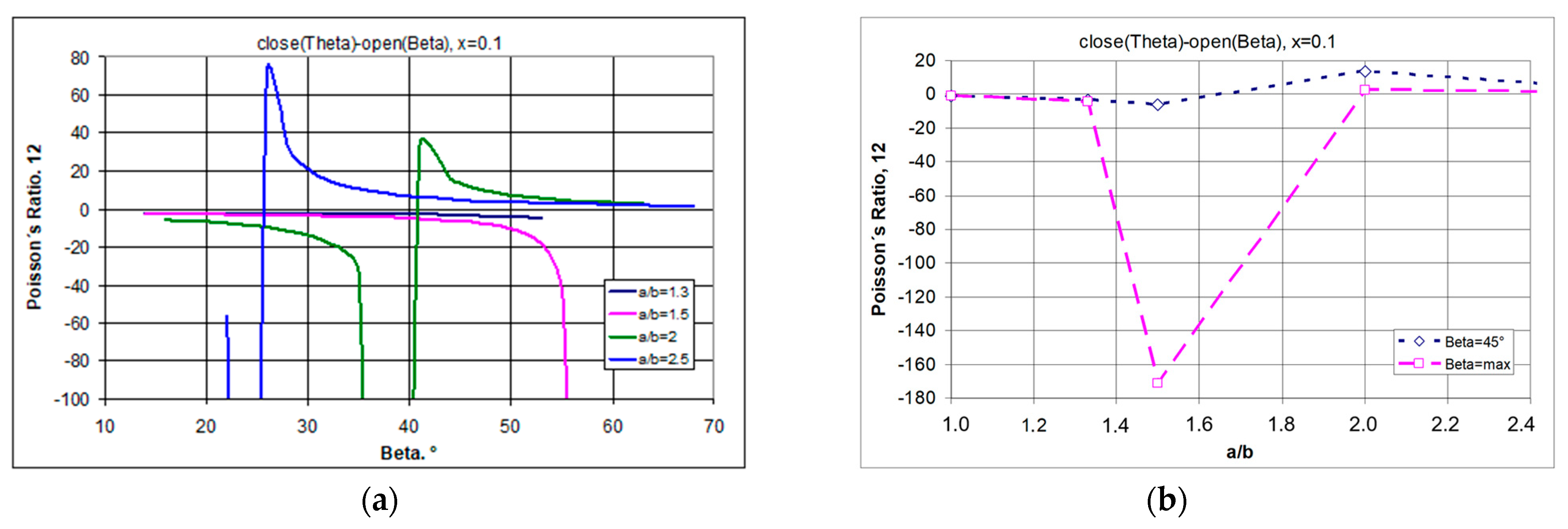
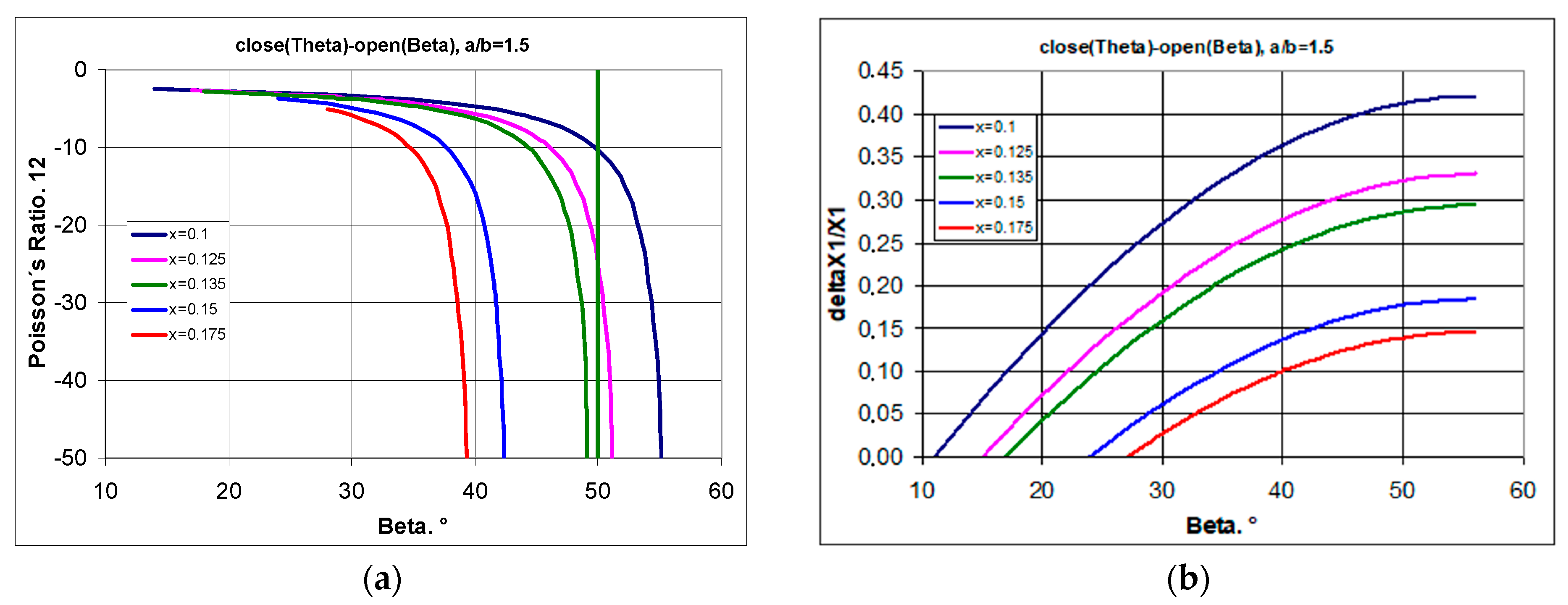
3.1.1. A 4 × 4 Structure Model, for a/b = 1.5 and x = 0.1
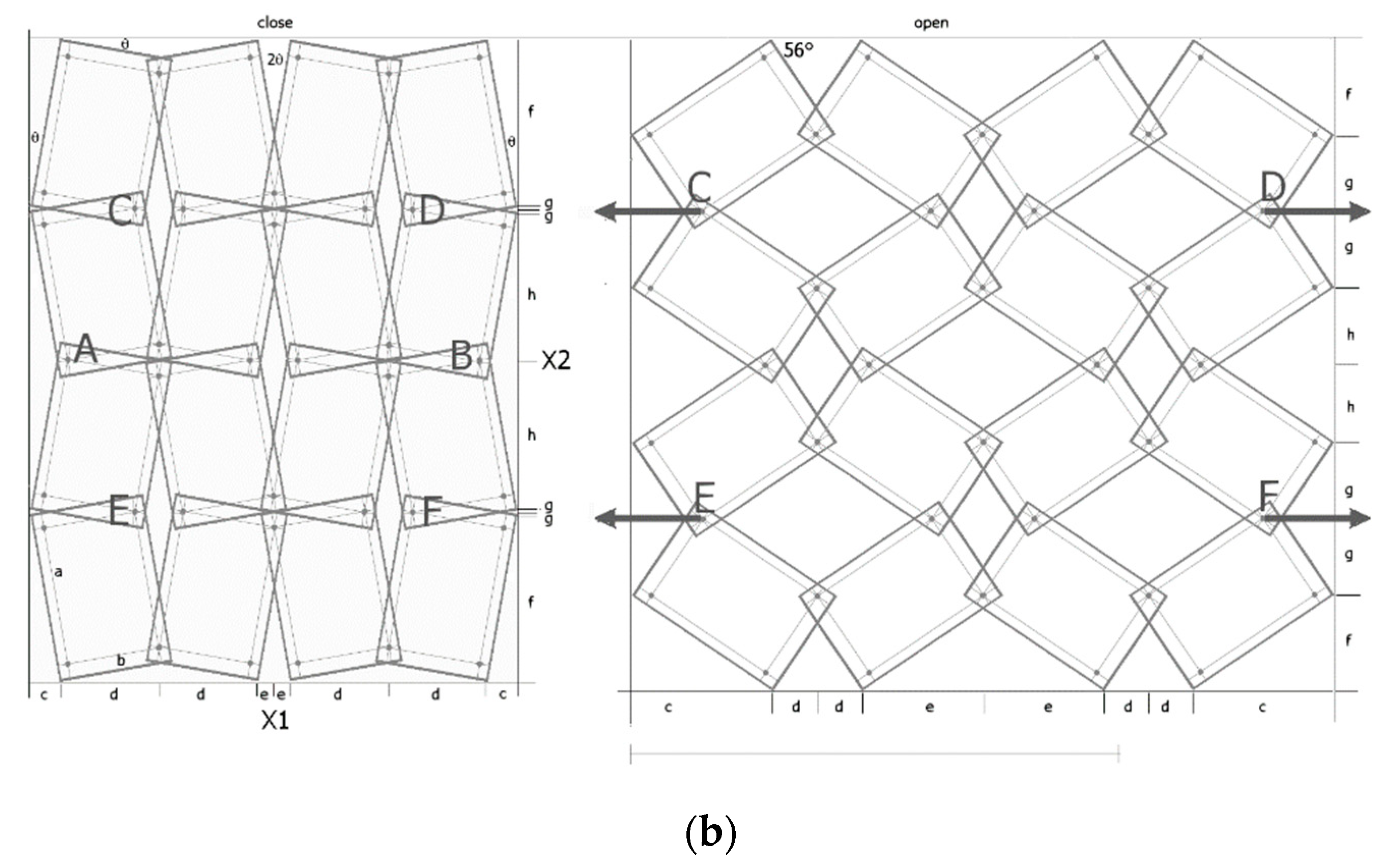
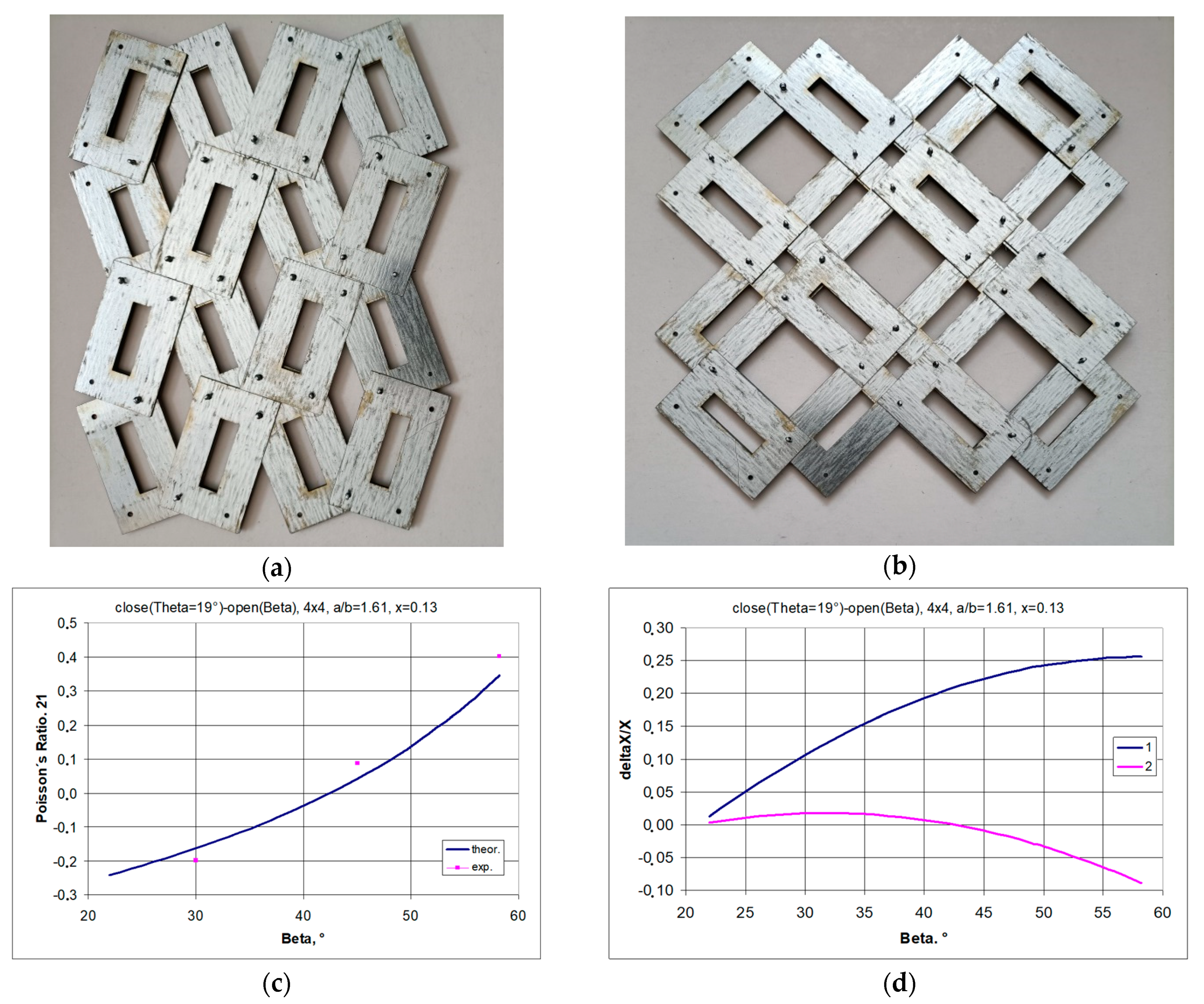
3.1.2. A 4 × 4 Structure Model, for a/b = 42/26 = 1.61, x = 5.5/42 = 0.1309, θ = 19°
3.1.3. A 10 × 4 structure Model, a/b = 25/12.5 = 2, x = 2.5/25 = 0.1, θ = 15°—Figure 15
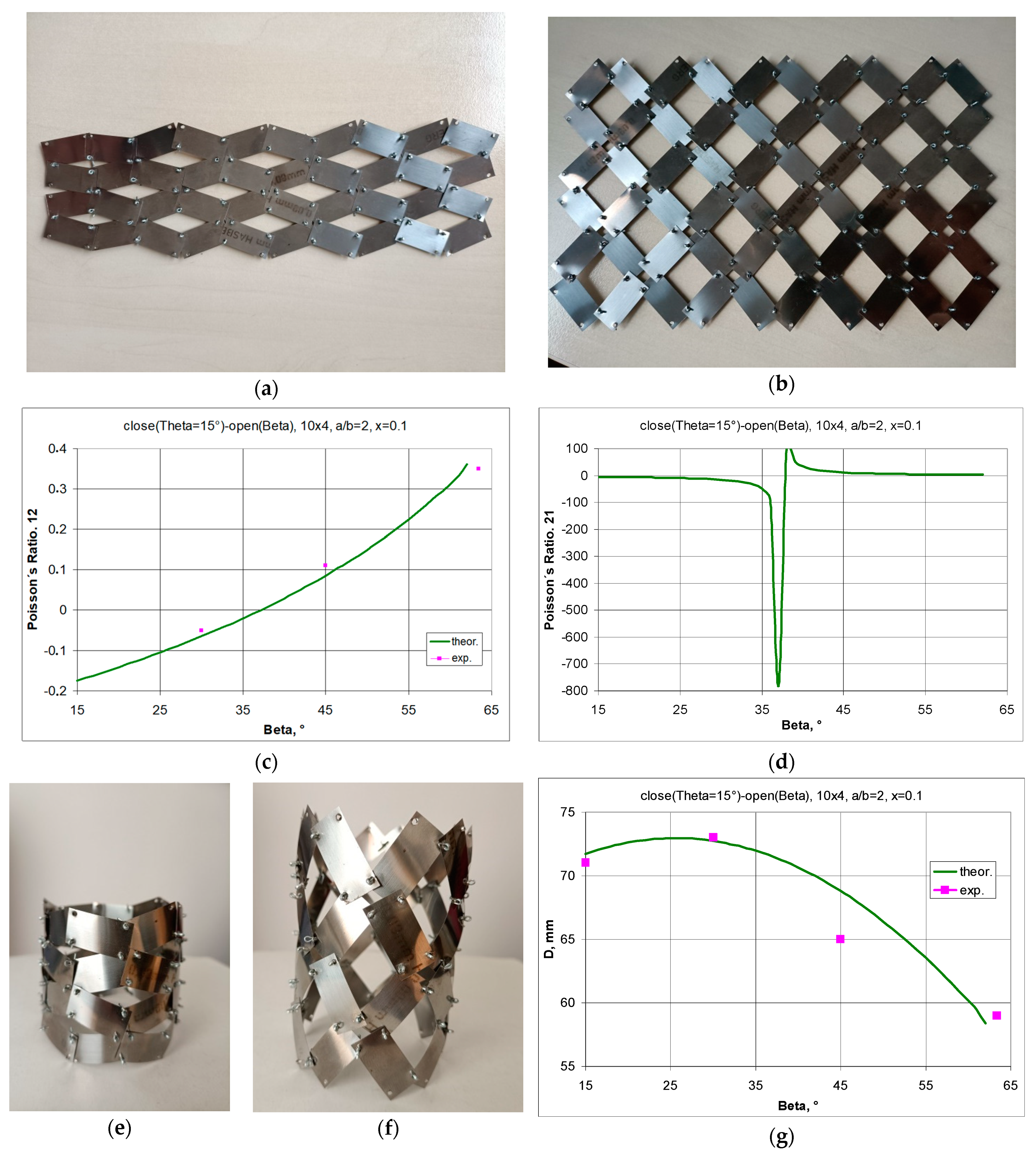
4. Summary
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Resch, R.D. Geometrical Device Having Articulated Relatively Movable Sections. U.S. Patent 3,201,894, 24 August 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Resch, R.D. Self-Supporting Structural Unit Having a Series of Repetitious Geometrical modules. U.S. Patent 3,407,558, 29 October 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Grima, J.N.; Evans, K.E. Auxetic behavior from rotating squares. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2000, 19, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, J.N.; Alderson, A.; Evans, K.E. Negative Poisson’s Ratios from Rotating Rectangles. Comp. Meth. Sci. Technol. 2004, 10, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima-Cornish, J.N.; Grima, J.N.; Attard, D. Mathematical modeling of auxetic systems: Bridging the gap between analytical models and observation. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2021, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, R.F. An isotropic three-dimensional structure with Poisson’s ratio = −1. J. Elast. 1985, 15, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, K.W. Two-dimensional isotropic system with a negative Poisson ratio. Phys. Lett. A 1989, 137, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozek, A.; Strek, T. Numerical Analysis of Dynamic Properties of an Auxetic Structure with Rotating Squares with Holes. Materials 2022, 15, 8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeren, F.G.J.; van der Wijk, V.; Herder, J.L. Spatial pseudo-rigid body model for the analysis of a tubular mechanical metamaterial. Math. Mech. Solids 2020, 25, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.K.; Gatt, R.; Mizzi, L.; Dudek, M.R.; Attard, D.; Evans, K.E.; Grima, J.N. On the dynamics and control of mechanical properties of hierarchical rotating rigid unit auxetics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, A.; Castagnetti, D.; Mizzi, L.; Spaggiari, A. Rotating squares auxetic metamaterials with improved strain tolerance. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.N.; Busfield, J.J.C.; Rehman, I.U. Auxetic oesophageal stents: Structure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 527–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, J.; Qu, J.; Huang, J.; Hui, D. Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slann, A.; White, W.; Scarpa, F.; Boba, K.; Farrow, I. Cellular plates with auxetic rectangular perforations. Phys. Status Solidi 2015, 252, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.J.; Smith, C.W.; Evans, K.E.; Lethbridge, Z.D.A.; Walton, R.I. An analytical model for producing negative Poisson’s ratios and its application in explaining off-axis elastic properties of the NAT-type zeolites. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5697–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warisaya, K.; Sato, J.; Tachi, T. Freeform Auxetic Mechanisms Based on Corner Connected Tiles. J. Int. Assoc. Shell Spat. Struct. J. IASS 2022, 63, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, J.N.; Manicaro, E.; Attard, D. Auxetic behaviour from connected different-sized squares and rectangles. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 467, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, A.; Rezvanpour, H. Computational Study of Non-Porous Auxetic Plates with Diamond Shape Inclusions. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gao, Z.; Yue, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, B. Hard-particle rotation enabled soft–hard integrated auxetic mechanical metamaterials. Proc. R. Soc. 2019, 475, 20190234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Wen, J.; Cheng, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, H.; Gumbsch, P. Programmable gear-based mechanical metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakovsky, M.; Ermanni, P. A thin-shell shape adaptable composite metamaterial. Compos. Struct. 2020, 246, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tao, Z.; Xie, M.Y. Design and analysis of an auxetic metamaterial with tuneable stiffness. Compos. Struct. 2022, 281, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, E.; Soltanizadeh, H.; Chen, Y.; Min, Y.; Pooya Sareh, X. Selective hinge removal strategy for architecting hierarchical auxetic metamaterials. Comm. Mater. 2022, 3, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, H.; Javan, A.R.; Ghaedizadeh, A.; Shen, J.; Xu, S.; Xie, M.Y. Design of Hierarchical Structures for Synchronized Deformations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizzi, L.; Spaggiari, A. Lightweight mechanical metamaterials designed using hierarchical truss elements. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Seifi, S.; Zhou, Z.-L.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, M. Designing novel structures with hierarchically synchronized deformations. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2018, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Shin, J.-H.; Costa, A.; Kim, T.A.; Kunin, V.; Li, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, S.; Han, H.N.; Choi, I.S.D.; et al. Engineering the shape and structure of materials by fractal cut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17390–17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhullar, S.K.; Ko, J.; Ahmed, J.F.; Jun, M.B.G. Design and Fabrication of Stent with Negative Poisson’s Ratio. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2014, 2, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, J.N.; Mizzi, L.; Azzopardi, K.M.; Gatt, R. Auxetic perforated mechanical metamaterials with randomly oriented cuts. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovski, P.D.; Novak, N.; Borovinšek, M.; Vesenjak, M.; Ren, Z. In-Plane Deformation Behavior and the Open Area of Rotating Squares in an Auxetic Compound Fabric. Polymers 2022, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plewa, J.; Plonska, M.; Lis, P. Investigation of Modified Auxetic Structures from Rigid Rotating Squares. Materials 2022, 15, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plewa, J.; Płońska, M.; Junak, G. Studies of Auxetic Structures Assembled from Rotating Rectangles. Materials 2024, 17, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030731
Plewa J, Płońska M, Junak G. Studies of Auxetic Structures Assembled from Rotating Rectangles. Materials. 2024; 17(3):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030731
Chicago/Turabian StylePlewa, Julian, Małgorzata Płońska, and Grzegorz Junak. 2024. "Studies of Auxetic Structures Assembled from Rotating Rectangles" Materials 17, no. 3: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030731
APA StylePlewa, J., Płońska, M., & Junak, G. (2024). Studies of Auxetic Structures Assembled from Rotating Rectangles. Materials, 17(3), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030731






