Development of Vitamin C-Loaded Electrospun Nanofibers of Mixture of Polysaccharides of Pullulan/Xanthan Gum for Fast Dissolving Oral Film Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Solution for Electrospinning
2.3. Preparation of Nanofibrous Film via Electrospinning
2.4. Characterization of Solution
2.5. Morphological Characterization of Nanofibrous Films
2.6. Encapsulation Efficiency of VC
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.8. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of Nanofibrous Films
2.9. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.10. Mechanical Characterization of Nanofibrous Films
2.11. Water Dissolution Testing of Nanofibrous Films
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Solutions
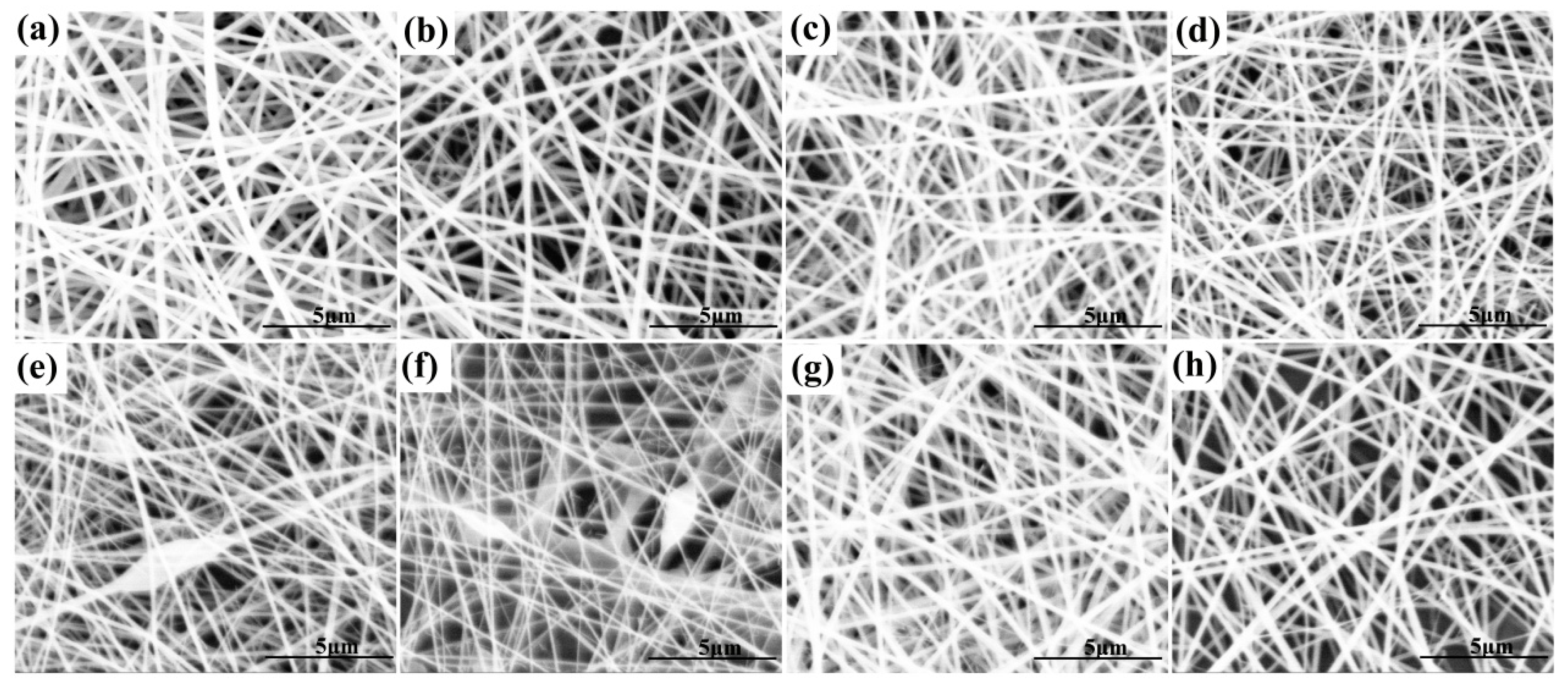
3.2. Morphological Characterization of Nanofibrous Films
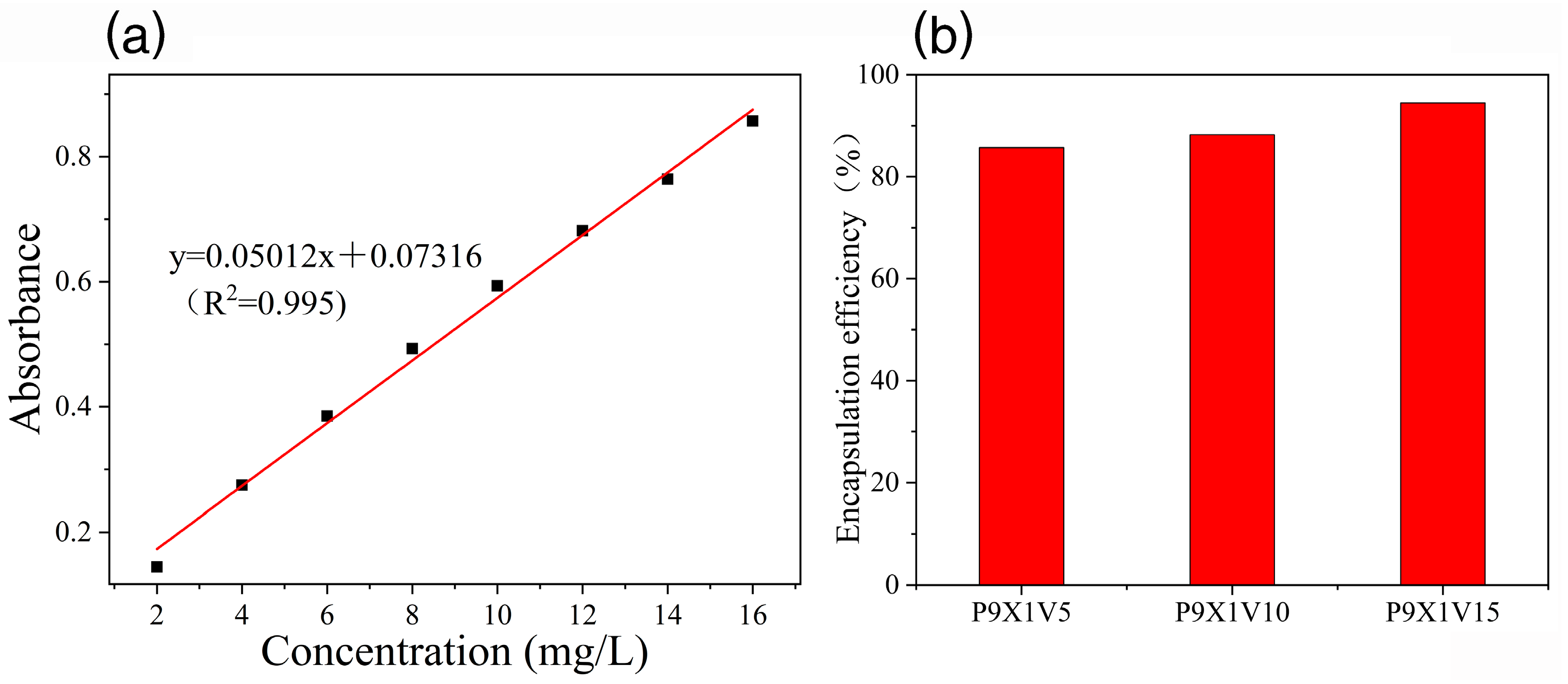
3.3. Encapsulation Efficiency of VC
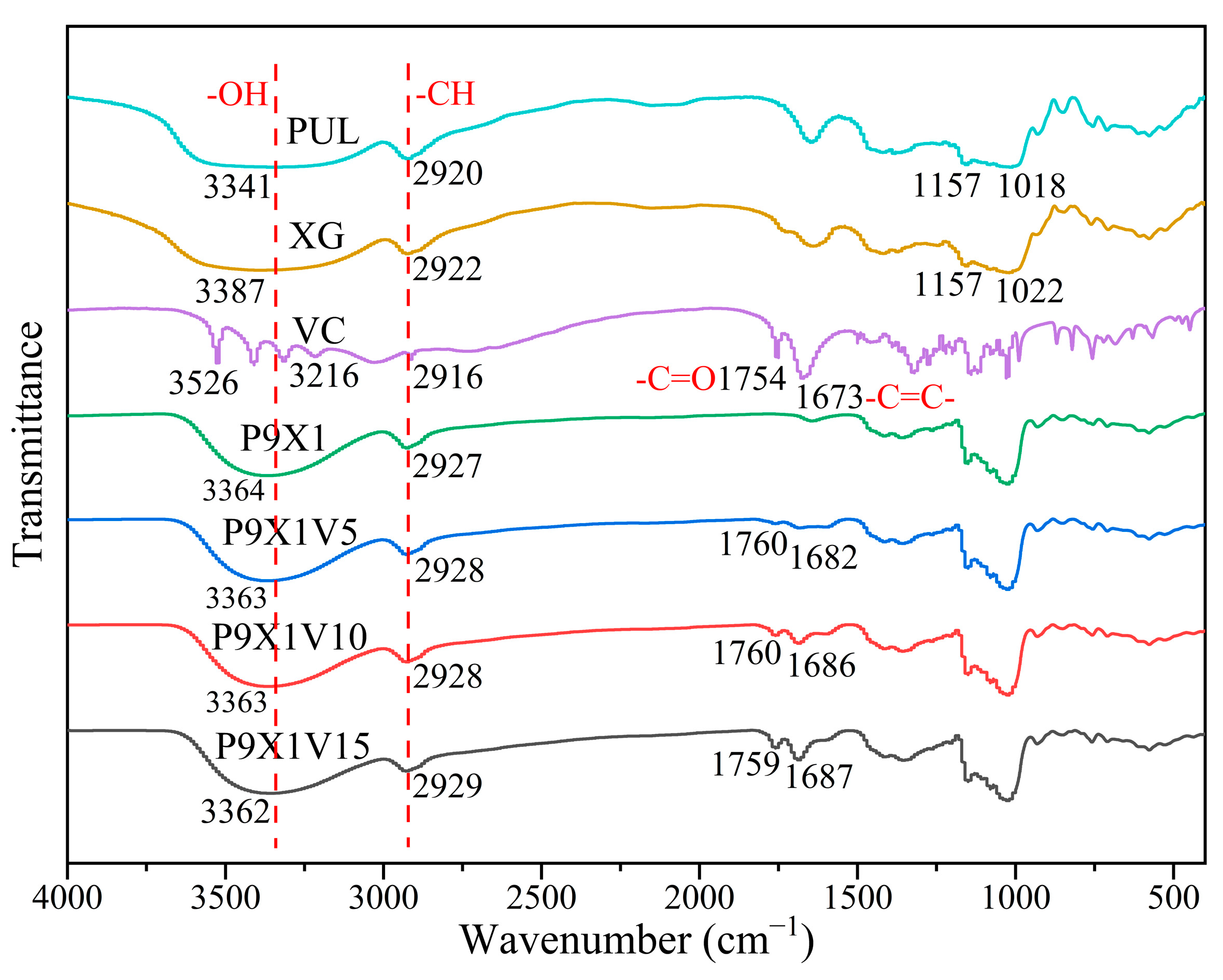
3.4. FTIR Analysis
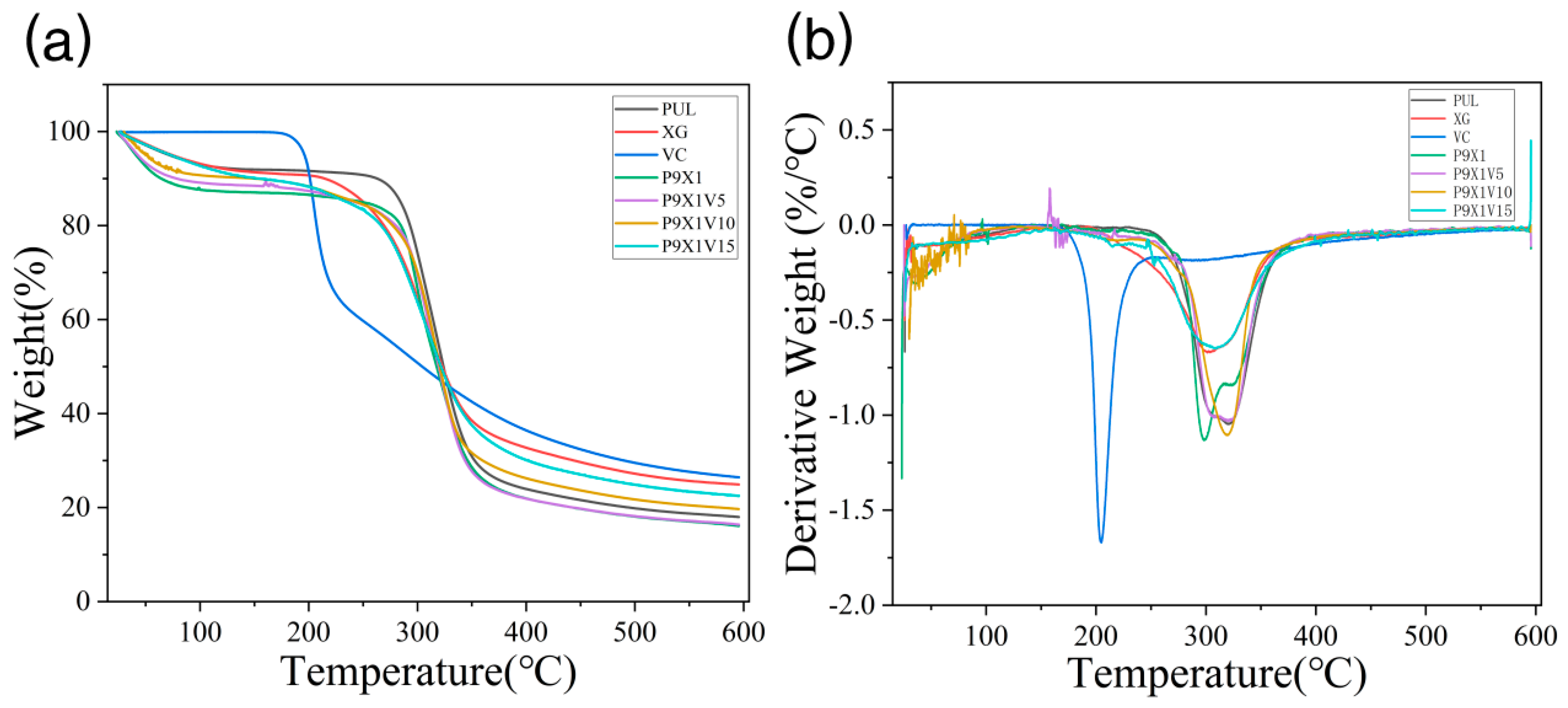
3.5. Thermal Stability
3.6. XRD Analysis
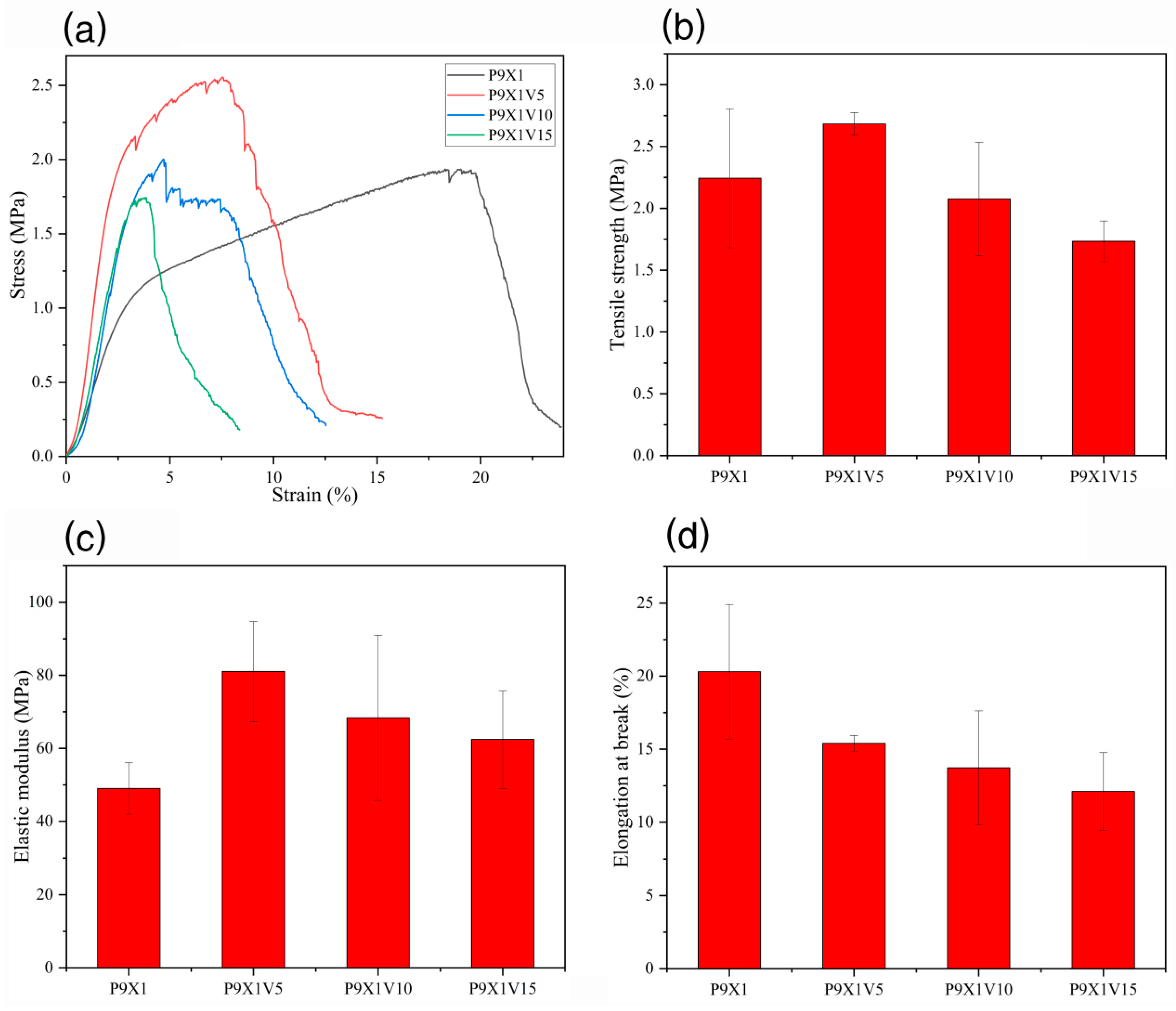
3.7. Mechanical Properties of Nanofibrous Films
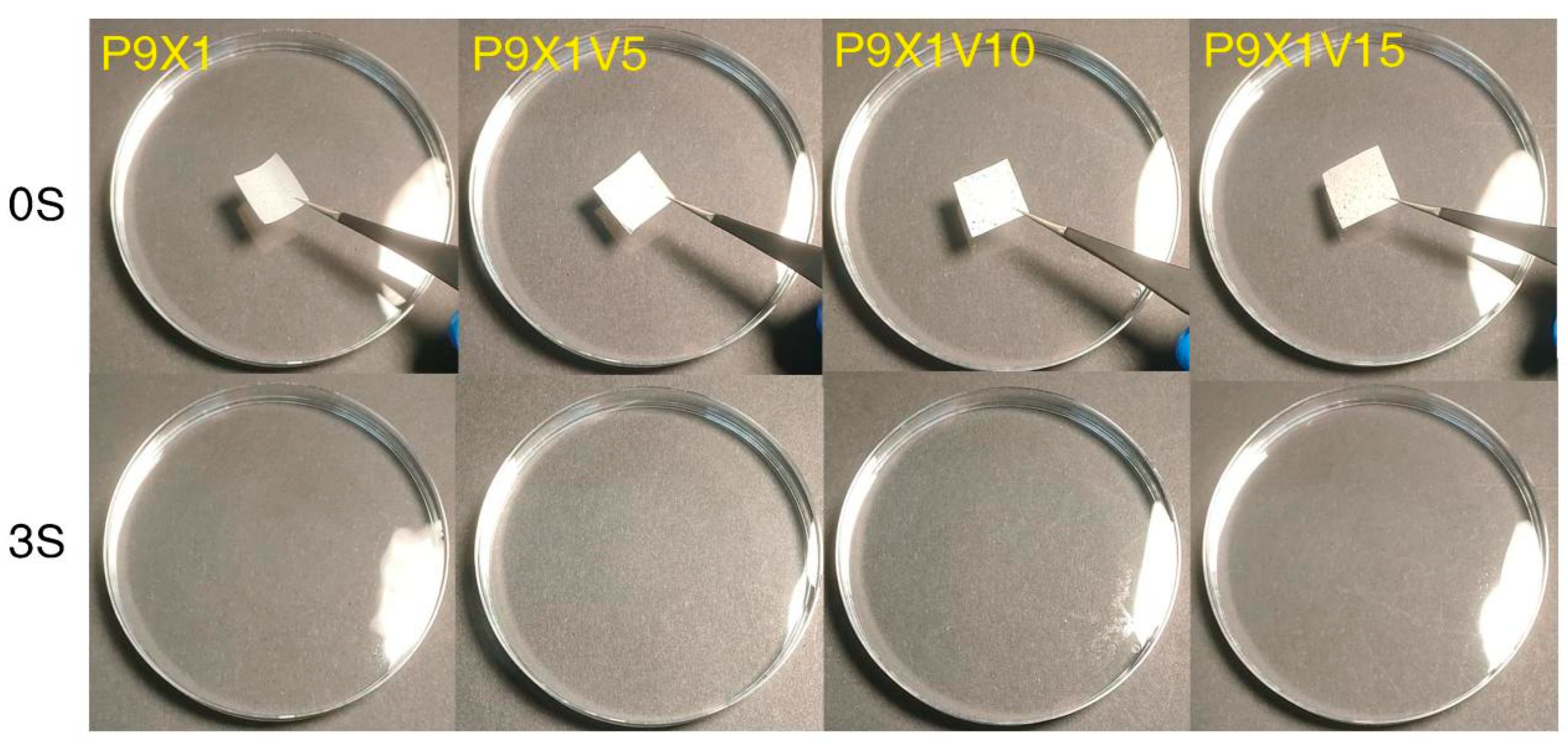
3.8. Water Dissolution Properties of Nanofibrous Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waghmare, P.; Vrunal, M.; Mithun, M. Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving oral film containing extracts of ocimum sanctum and glycyrrhiza glabra to treat mouth ulcer. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2023, 12, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.-Y.; Jia, X.-W.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.-H.; Wang, H. Fast dissolving oral films for drug delivery prepared from chitosan/pullulan electrospinning nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Chandra, A.; Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Fast dissolving oral films: An innovative drug delivery system and dosage form. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2010, 2, 576–583. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.; Sakho, E.H.M.; Kalarikkal, N.; Oluwafemi, S.O.; Wu, J. Nanomaterials for Solar Cell Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Uyar, T.; Kny, E. Electrospun Materials for Tissue Engineering and Biomedical Applications: Research, Design and Commercialization; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Wang, X.; Yu, J. Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications; William Andrew: Cary, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Yu, D.-G.; Aidana, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, S. Fast Dissolution Electrospun Medicated Nanofibers for Effective Delivery of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balusamy, B.; Celebioglu, A.; Senthamizhan, A.; Uyar, T. Progress in the design and development of “fast-dissolving” electrospun nanofibers based drug delivery systems—A systematic review. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 482–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Yu, Y.; Branford-White, C.; Williams, G.R.; Yu, D.-G.; Nie, W.; Zhu, L.-M. Preparation of ultrafine fast-dissolving feruloyl-oleyl-glycerol-loaded polyvinylpyrrolidone fiber mats via electrospinning. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzadeh, Z.; Honarvar, M.; Ghavami, M. Modeling the Release of Betaine Extracted from Sugar Beet Molasses in the Structure of Fast-Dissolving Electrospun Fibers of Plantago ovata Seed Gum. Food Biophys. 2022, 17, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Zheng, M.; Guo, X.; Song, B.; et al. Fast-Dissolving Protein Nanofibrous Membrane for Dual Drug Oral Delivery. Coatings 2023, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekarforoush, E.; Faralli, A.; Ndoni, S.; Mendes, A.C.; Chronakis, I.S. Electrospinning of Xanthan Polysaccharide. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.O.; Williams, P.A. Handbook of Hydrocolloids; xxii; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; p. 450. [Google Scholar]
- Petri, D.F.S. Xanthan gum: A versatile biopolymer for biomedical and technological applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padil, V.V.; Cheong, J.Y.; KP, A.; Makvandi, P.; Zare, E.N.; Torres-Mendieta, R.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Kim, I.-D.; Varma, R.S. Electrospun fibers based on carbohydrate gum polymers and their multifaceted applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tomasula, P.; De Sousa, A.M.M.; Liu, S.-C.; Tunick, M.; Liu, K.; Liu, L. Electrospinning Pullulan Fibers from Salt Solutions. Polymers 2017, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahriari-Khalaji, M.; Hu, G.; Chen, L.; Cao, Z.; Andreeva, T.; Xiong, X.; Krastev, R.; Hong, F. Functionalization of Aminoalkylsilane-Grafted Bacterial Nanocellulose with ZnO-NPs-Doped Pullulan Electrospun Nanofibers for Multifunctional Wound Dressing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 3933–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.W.; Qin, Z.Y.; Xu, J.X.; Kong, B.H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Preparation and characterization of pea protein isolate-pullulan blend electrospun nanofiber films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceituno-Medina, M.; Mendoza, S.; Lagaron, J.M.; López-Rubio, A. Photoprotection of folic acid upon encapsulation in food-grade amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.) protein isolate–Pullulan electrospun fibers. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosou, C.; Krokida, M.; Biliaderis, C.G. Composite pullulan-whey protein nanofibers made by electrospinning: Impact of process parameters on fiber morphology and physical properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponrasu, T.; Chen, B.H.; Chou, T.H.; Wu, J.J.; Cheng, Y.S. Fast Dissolving Electrospun Nanofibers Fabricated from Jelly Fig Polysaccharide/Pullulan for Drug Delivery Ap-plications. Polymers 2021, 13, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiung, E.; Celebioglu, A.; Chowdhury, R.; Kilic, M.E.; Durgun, E.; Altier, C.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial nanofibers of pullulan/tetracycline-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes for Fast-Disintegrating oral drug delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospinning of uniform polystyrene fibers: The effect of solvent conductivity. Polymer 2008, 49, 5336–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska, I.; Czapka, T. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers with Antimicrobial Activity. Polymers 2022, 14, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Guo, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F. Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, F.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Fu, J.; Chen, M.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Encapsulation of tea polyphenols into high amylose corn starch composite nanofibrous film for active antimicrobial packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilchez, A.; Acevedo, F.; Cea, M.; Seeger, M.; Navia, R. Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers with Antioxidant Properties: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.S.; Veloso, C.M. Microencapsulation of natural dyes with biopolymers for application in food: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, D.; Margaritis, A. Biopolymer nanoparticle production for controlled release of biopharmaceuticals. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Ren, Z.; Chen, L.; Fu, C.; Ma, Z.F.; Li, Z. Advancement of Protein- and Polysaccharide-Based Biopolymers for Anthocyanin Encapsulation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 938829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Gao, Q. Effect of amylose content on the preparation for carboxymethyl starch/pullulan electrospun nanofibers and their properties as encapsulants of thymol. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrohydrodynamic encapsulation of eugenol-cyclodextrin complexes in pullulan nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Yeum, J.H.; Das, A.K. Effect of pullulan/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend system on the montmorillonite structure with property characterization of electrospun pullulan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/montmorillonite nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, B.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.; Wang, H. Fabrication and characterization of a novel polysaccharide based composite nanofiber films with tunable physical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosayebi, V.; Fathi, V.; Shahedi, M.; Soltanizadeh, N.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Fast-dissolving antioxidant nanofibers based on protein concentrate and gelatin developed using needleless elec-trospinning. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Solution | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Conductivity (μs/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| P10X0 | 1707 ± 0.82 | 5220 ± 8.16 |
| P9X1 | 1501 ± 0.82 | 5143 ± 4.71 |
| P8X2 | 1149 ± 0.82 | 4750 ± 8.16 |
| P7X3 | 1090 ± 0.82 | 4390 ± 8.16 |
| P6X4 | 1069 ± 0.82 | 4010 ± 8.16 |
| P5X5 | 1061 ± 1.25 | 3737 ± 9.43 |
| P9X1V5 | 1280 ± 0.47 | 5233 ± 4.71 |
| P9X1V10 | 1395 ± 0.47 | 5270 ± 8.16 |
| P9X1V15 | 1435 ± 0.47 | 5337 ± 4.71 |
| Nanofibrous Film | Voltage (kV) | Injection Speed (mL/h) | Roller Speed (rpm/min) | Microscopic Topography | Average Diameter of Nanofibers (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P10X0 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 198.26 ± 18.07 |
| P9X1 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 181.17 ± 21.03 |
| P9X1 | 18 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 206.63 ± 38.95 |
| P9X1 | 16 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 225.85 ± 51.45 |
| P8X2 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 161.52 ± 22.88 |
| P7X3 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 138.71 ± 23.55 |
| P6X4 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers with few beads | 124.56 ± 17.78 |
| P5X5 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers with few beads | 105.17 ± 21.09 |
| P9X1V5 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 197.89 ± 29.92 |
| P9X1V10 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 224.18 ± 30.99 |
| P9X1V15 | 20 | 1 | 400 | smooth nanofibers | 260.84 ± 39.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, E.; Geng, Z.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, A.; Tian, H. Development of Vitamin C-Loaded Electrospun Nanofibers of Mixture of Polysaccharides of Pullulan/Xanthan Gum for Fast Dissolving Oral Film Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040861
Cheng E, Geng Z, Xiang L, Zhao X, Xiang A, Tian H. Development of Vitamin C-Loaded Electrospun Nanofibers of Mixture of Polysaccharides of Pullulan/Xanthan Gum for Fast Dissolving Oral Film Applications. Materials. 2024; 17(4):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040861
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, En, Zhanhui Geng, Lubing Xiang, Xiaoying Zhao, Aimin Xiang, and Huafeng Tian. 2024. "Development of Vitamin C-Loaded Electrospun Nanofibers of Mixture of Polysaccharides of Pullulan/Xanthan Gum for Fast Dissolving Oral Film Applications" Materials 17, no. 4: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040861
APA StyleCheng, E., Geng, Z., Xiang, L., Zhao, X., Xiang, A., & Tian, H. (2024). Development of Vitamin C-Loaded Electrospun Nanofibers of Mixture of Polysaccharides of Pullulan/Xanthan Gum for Fast Dissolving Oral Film Applications. Materials, 17(4), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040861





