Design of an Optical Device Based on Kirigami Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
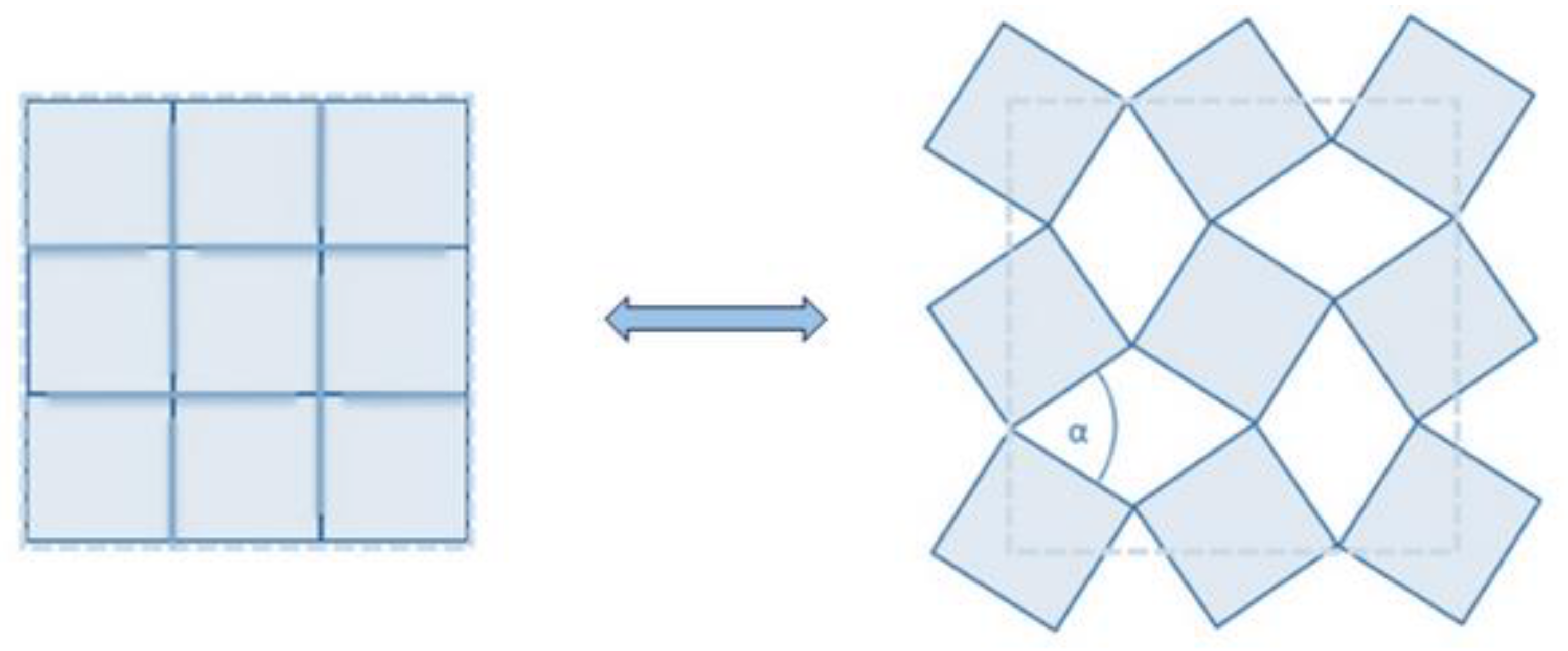
- Choice of the system geometry: rotating squares (first choice because a rotation is required for exploiting optical properties);
- -
- Rotating squares’ manufacturing using an acrylic sheet (first choice);
- -
- Rotating squares’ manufacturing using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS, flexible manufacturing, second choice) to reach higher transparency;
- -
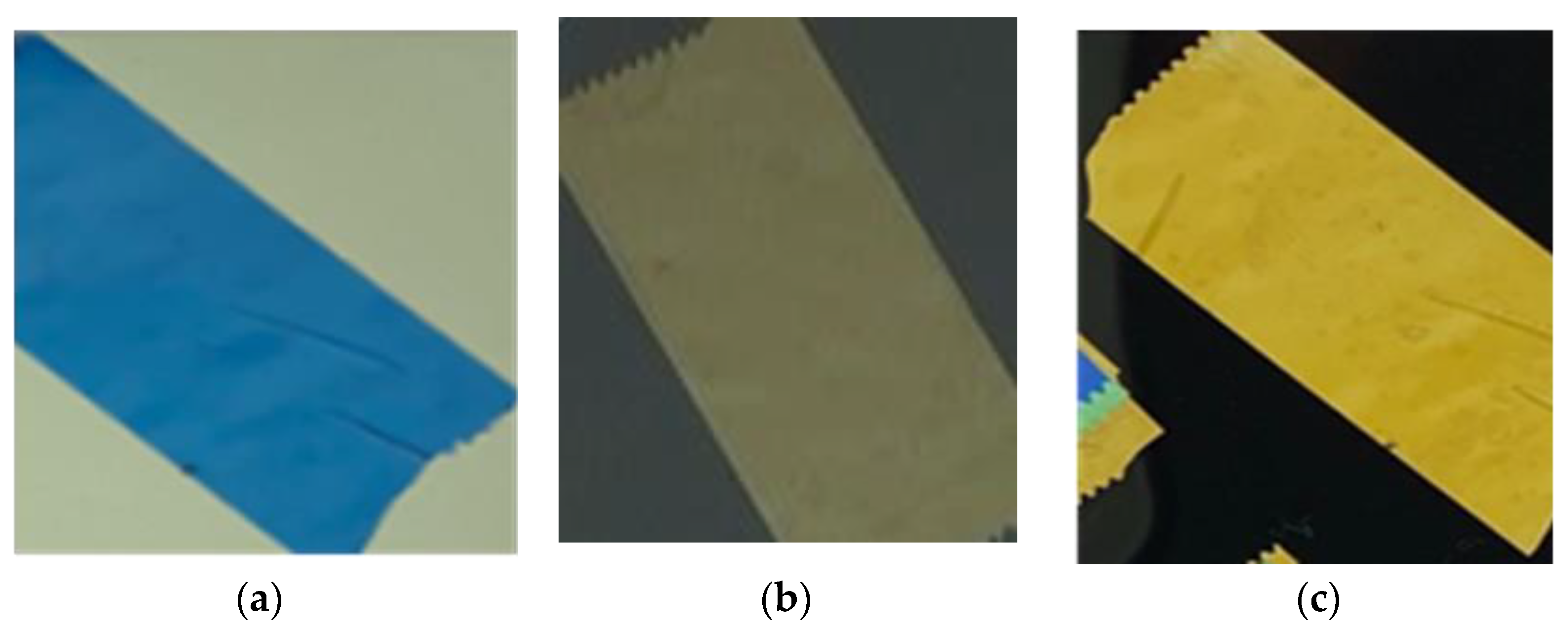
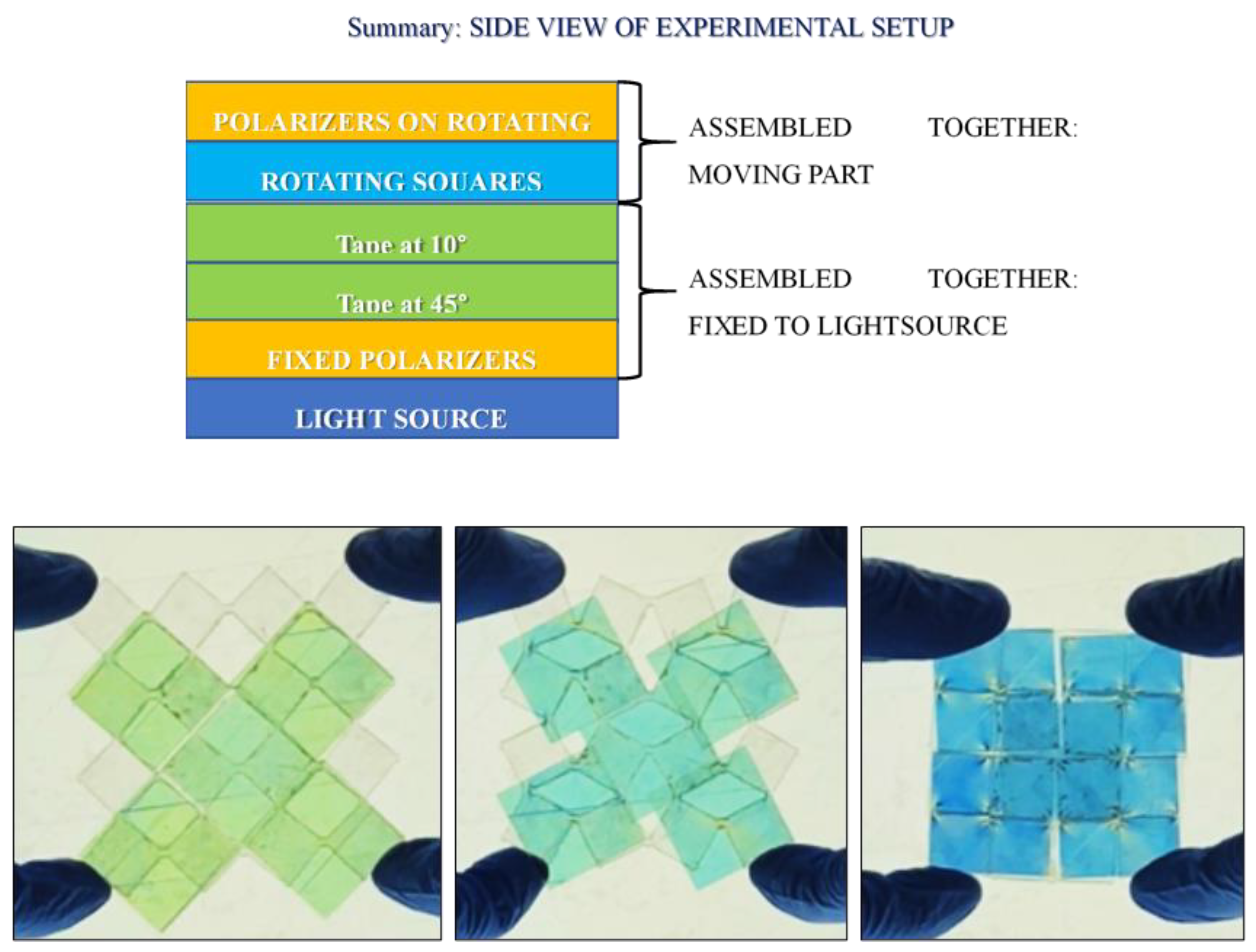
- Cellotape application on the fixed polarizer to obtain color changing.
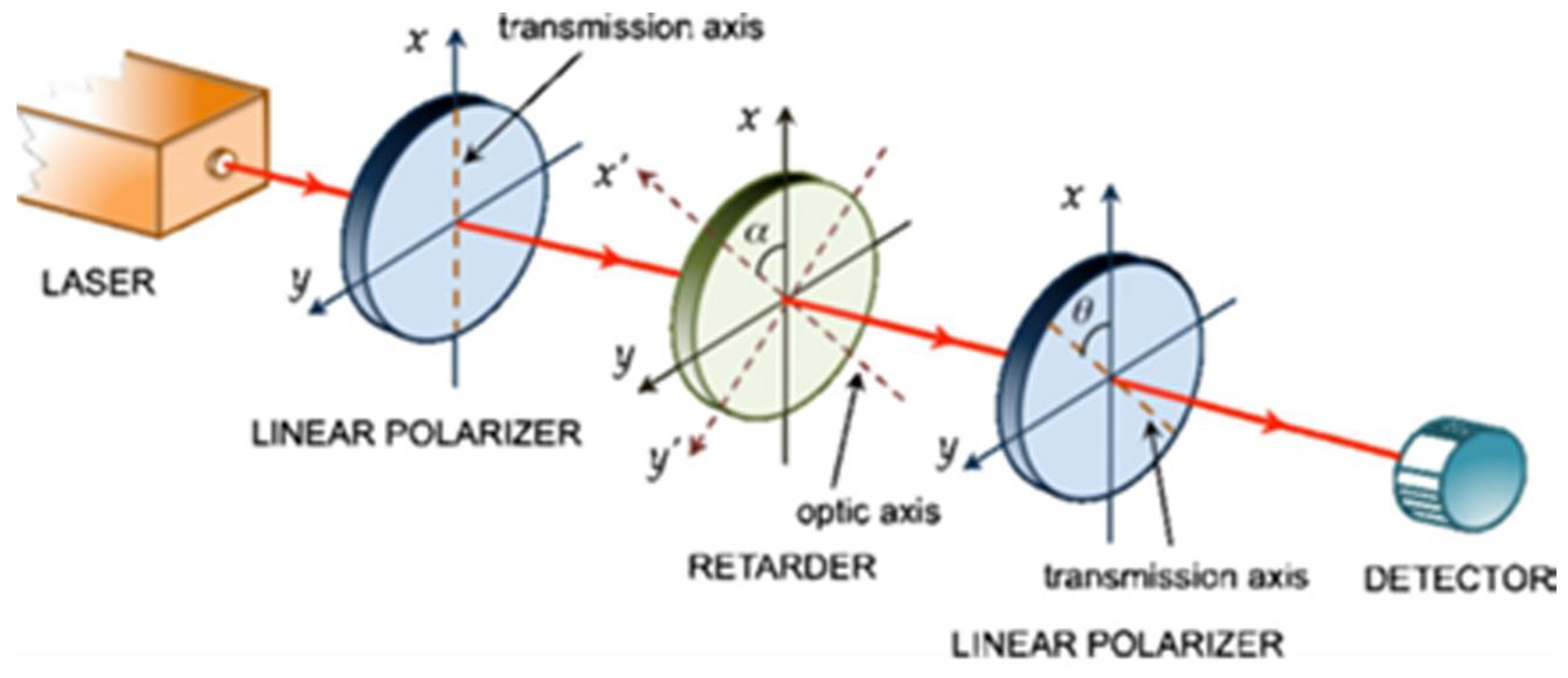
2.1. Light Modulation
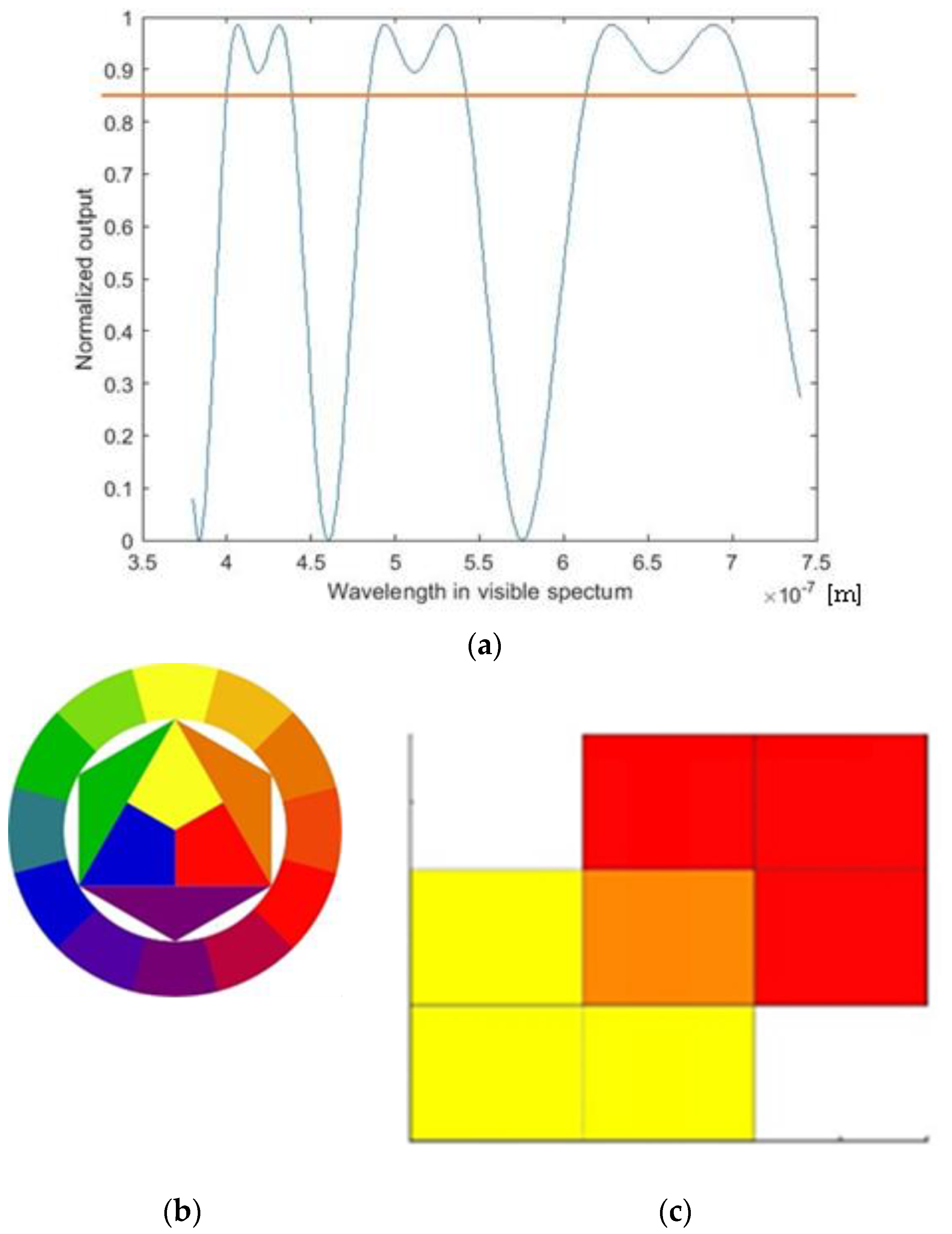
2.2. Birefringence: The Physical Property Used for Obtaining Colors
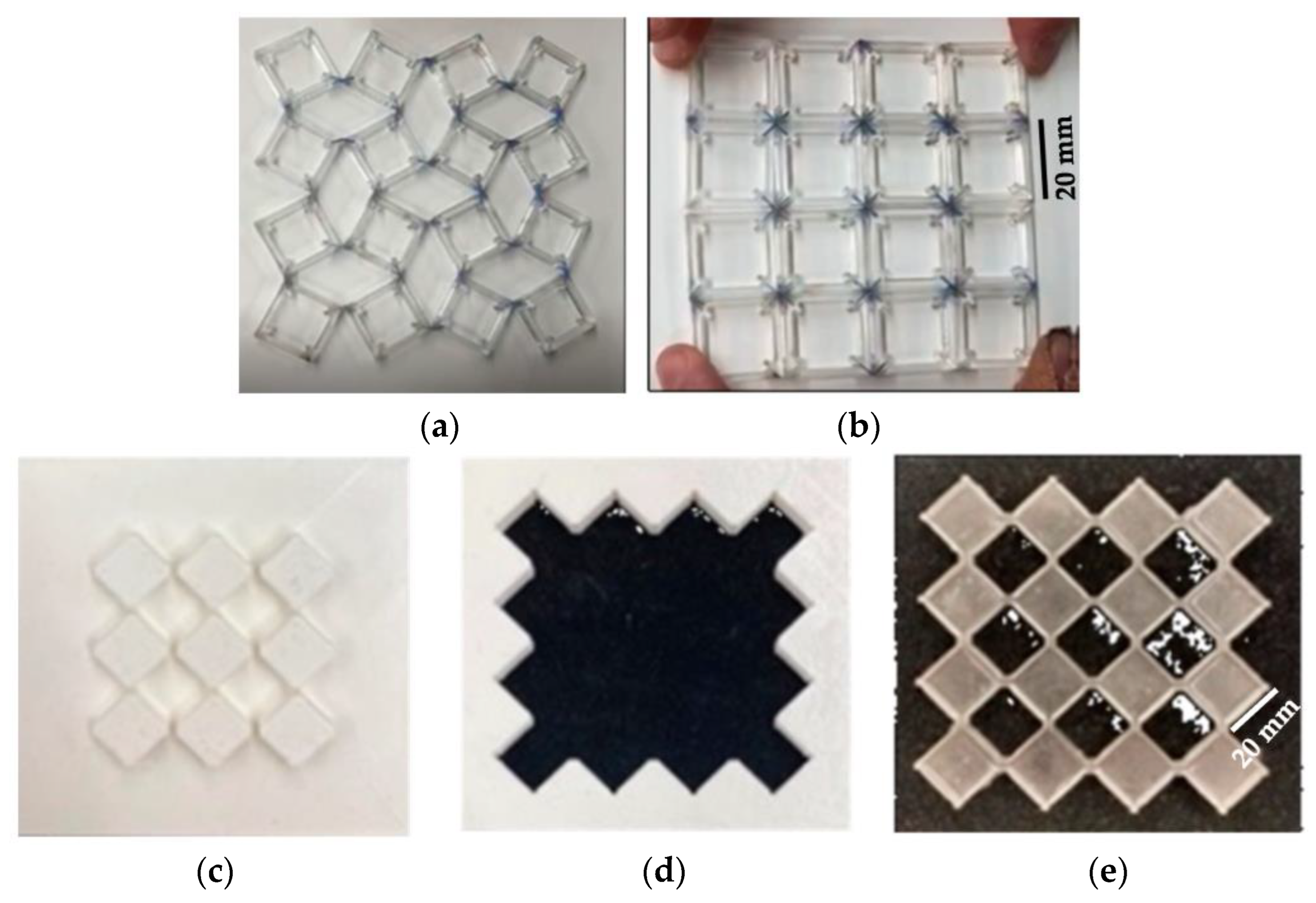
2.3. Manufacturing of Rotating Squares
- Set the position of the acrylic sheet on the honeycomb table;
- Set the height precisely in order to have the maximum laser power on the cutting surface, close the top, and set the cut parameters (power: 70%, speed: 5%);
- Cut the frame starting from a CAD drawing previously saved as a .dxf file;
- Wait 30 s and open the top of the machine;
- Obtain the final item, and in the case of an additional undesired part, remove it;
- Obtain a plastic sheet (a blue one has been chosen for our purposes with a 0.90 mm thickness) and put it on the honeycomb table;
- Set the height again;
- Cut the design for the hinges (power: 7%, speed: 20%);
- Obtain the final item and remove all the undesired parts.
3. Results
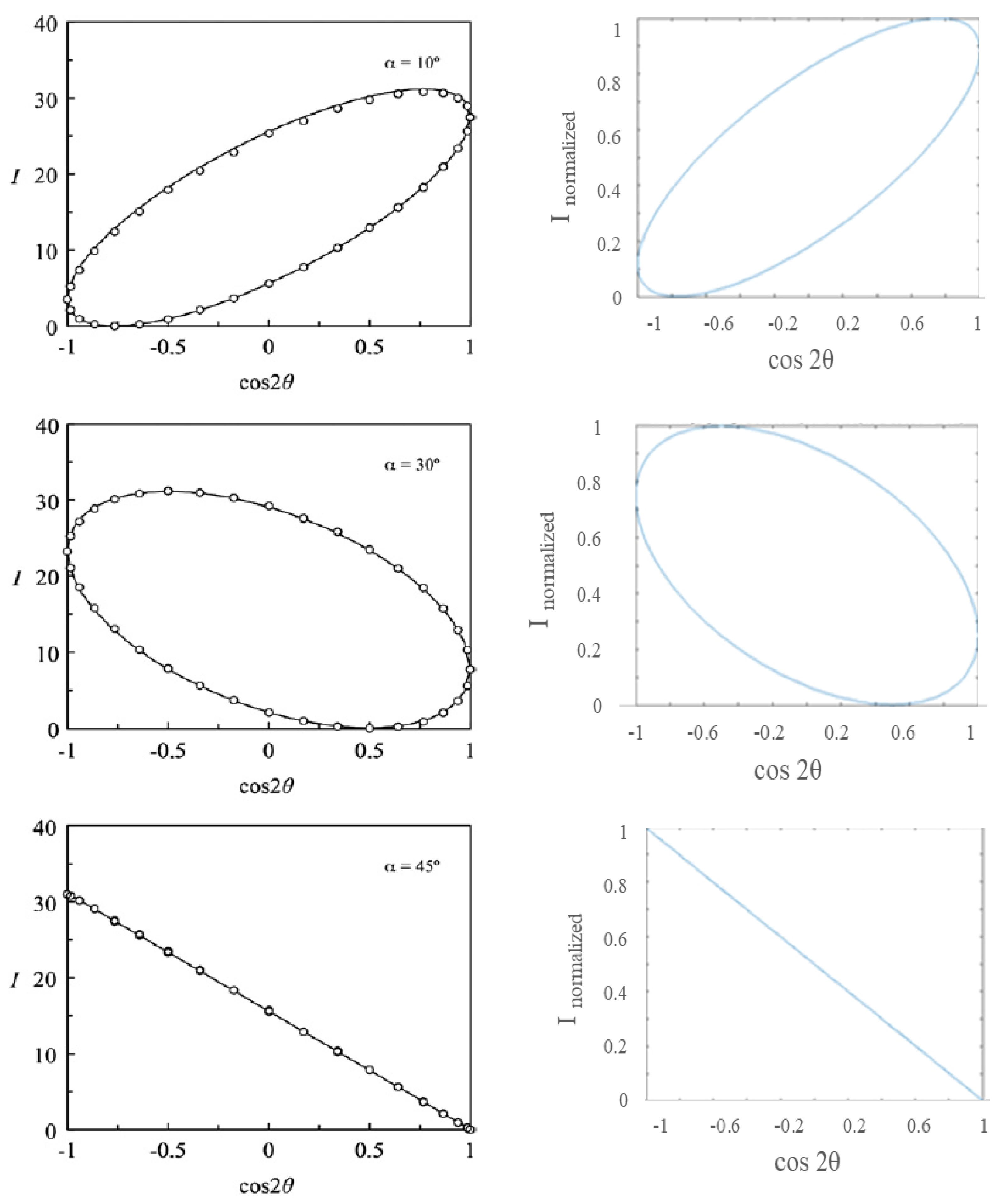
3.1. Light Modulation
3.2. Birefringence: The Physical Property Used for Obtaining Colors
3.3. Manufacturing of Rotating Squares
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, X.; Gusev, V.E.; Tournat, V.; Deng, B.; Bertoldi, K. Frequency-doubling effect in acoustic reflection by a nonlinear, architected rotating-square metasurface. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 052209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.; Rajeshkumar, V. An Overview of Metamaterials in Biomedical Applications. In Proceedings of the Conference: Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Taipei, Taiwan, 25–28 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Lyu, Y.; Bosiakov, S.; Zhu, H.; Ren, Y. A review on the mechanical metamaterials and their applications in the field of biomedical engineering. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1273961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafsanjani, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Bertoldi, K. Kirigami skins make a simple soft actuator crawl. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaar7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic Networks for Soft Robotics that Actuate Rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Fang, Y.; Liu, R.; Hu, R.; Zhou, J.; Hu, B. Reconfigurable mechano-responsive soft film for adaptive visible and infrared dual-band camouflage. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 2756–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokanović, B.; Geschke, R.H.; Beukman, T.S.; Milošević, V. Metamaterials: Characteristics, Design and Microwave Applications. SAIEE Afr. Res. J. 2010, 101, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Gupta, S.; Yadav, A.; Runthala, R. Analysis of MEMS and Metamaterial Based Sensors and Its Involvement in Nanotechnology. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Internet of Things and Connected Technologies (ICIoTCT), 2019: Internet of Things and Connected Technologies, Jaipur, India, 9–10 May 2019; Nain, N., Vipparthi, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1122. [Google Scholar]
- Babaee, S.; Pajovic, S.; Rafsanjani, A.; Bertoldi, K.; Traverso, G. Bioinspired kirigami metasurfaces as assistive shoe grips. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boatti, E.; Vasios, N.; Bertoldi, K. Origami Metamaterials for Tunable Thermal Expansion. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javid, F.; Wang, P.; Shanian, A.; Bertoldi, K. Architected Materials with Ultra-Low Porosity for Vibration Control. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5943–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grima, J.N.; Evans, K.E. Auxetic behavior from rotating squares. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2000, 19, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Domel, A.G.; Zhou, J.; Rafsanjani, A.; Bertoldi, K. Programmable Hierarchical Kirigami. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, G.; Yang, S.; Yi, Y.K.; Kamien, R.D.; Yin, J. Programmable kiri-kirigami metamaterials. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, A.E.; Melancon, D.; Zanati, M.; De Giorgi, M.; Bertoldi, K. Chiral mechanical metamaterials for tunable optical transmittance. Adv. Funct. Mater 2023, 33, 2214897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, Y.; Pu, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Liao, M.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Luo, X. Meta-optics empowered vector visual cryptography for high security and rapid decryption. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Yue, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J. Dynamic phase assembled terahertz metalens for reversible conversion between linear polarization and arbitrary circular polarization. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2022, 5, 210062-1–210062-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Lu, H.; Mao, D.; Du, Y.; Hua, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, J. Graphene-empowered dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2022, 5, 200098-1–200098-47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, R. Modern Optics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Chapter 13. [Google Scholar]
- Beléndez, A.; Fernández, E.; Francés, J.; Neipp, C. Birefringence of cellotape: Jones representation and experimental analysis. Eur. J. Phys. 2010, 31, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, E. Optics, 4th ed.; Pergamon Press Ltd.: London, UK, 2001; pp. 352–355. ISBN 0805385665. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.J.; Langley, A.J. On Producing Colours Using Birefringence Property of Transparent, Colourless Stretched Cellophane. Leonardo 1981, 14, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, A. Images and Models of Thought. Proceedings 2017, 1, 942. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.J.; Langley, A.J. Colours in cellophane. Color Res. Appl. 1979, 4, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ulsinc.com/product-matrix (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Malacara-Hernandez, D. Color Vision and Colorimetry: Theory and Applications; SPIE PRESS BOOK: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oleari, C.; Pavesi, M. Grassmann’s laws and individual color-matching functions for non-spectral primaries evaluated by maximum saturation technique in foveal vision. Color Res. Appl. 2008, 33, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilmann, F.; Grusche, S. An RGB approach to prismatic colours. Phys. Educ. 2013, 48, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Dow Corning PDMS Safety Datasheet. Available online: https://www.dow.com/content/dam/dcc/documents/en-us/productdatasheet/11/11-31/11-3184-sylgard-184-elastomer.pdf?iframe=true (accessed on 3 February 2023).



| Polarizer Angle | R | G | B | Color Output | R | G | B | Color Output | R | G | B | Color Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setup 1 (0°, 20°, 45°) | Setup 2 (0°, 35°, 80°) | Setup 3 (100°, 130°, 190°) | ||||||||||
| 0° | 40 | 71 | 100 | 18 | 48 | 100 | 85 | 90 | 84 | |||
| 32° | 52 | 25 | 78 | 38 | 101 | 106 | 115 | 114 | 94 | |||
| 65° | 87 | 51 | 25 | 94 | 125 | 81 | 99 | 98 | 68 | |||
| 90° | 110 | 100 | 41 | 115 | 111 | 48 | 67 | 67 | 39 | |||
| 138° | 86 | 125 | 99 | 80 | 40 | 38 | 33 | 39 | 53 | |||
| 165° | 48 | 97 | 102 | 42 | 28 | 87 | 66 | 71 | 74 | |||
| 180° | 43 | 70 | 97 | 23 | 47 | 97 | 82 | 87 | 81 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Giorgi, M. Design of an Optical Device Based on Kirigami Approach. Materials 2024, 17, 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17051211
De Giorgi M. Design of an Optical Device Based on Kirigami Approach. Materials. 2024; 17(5):1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17051211
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Giorgi, Marta. 2024. "Design of an Optical Device Based on Kirigami Approach" Materials 17, no. 5: 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17051211
APA StyleDe Giorgi, M. (2024). Design of an Optical Device Based on Kirigami Approach. Materials, 17(5), 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17051211







