Morphology and Structure of TiO2 Nanotube/Carbon Nanostructure Coatings on Titanium Surfaces for Potential Biomedical Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Sample Characterization
3. Results
3.1. SEM Investigation
3.2. EDX Analysis
3.3. XRD Analysis
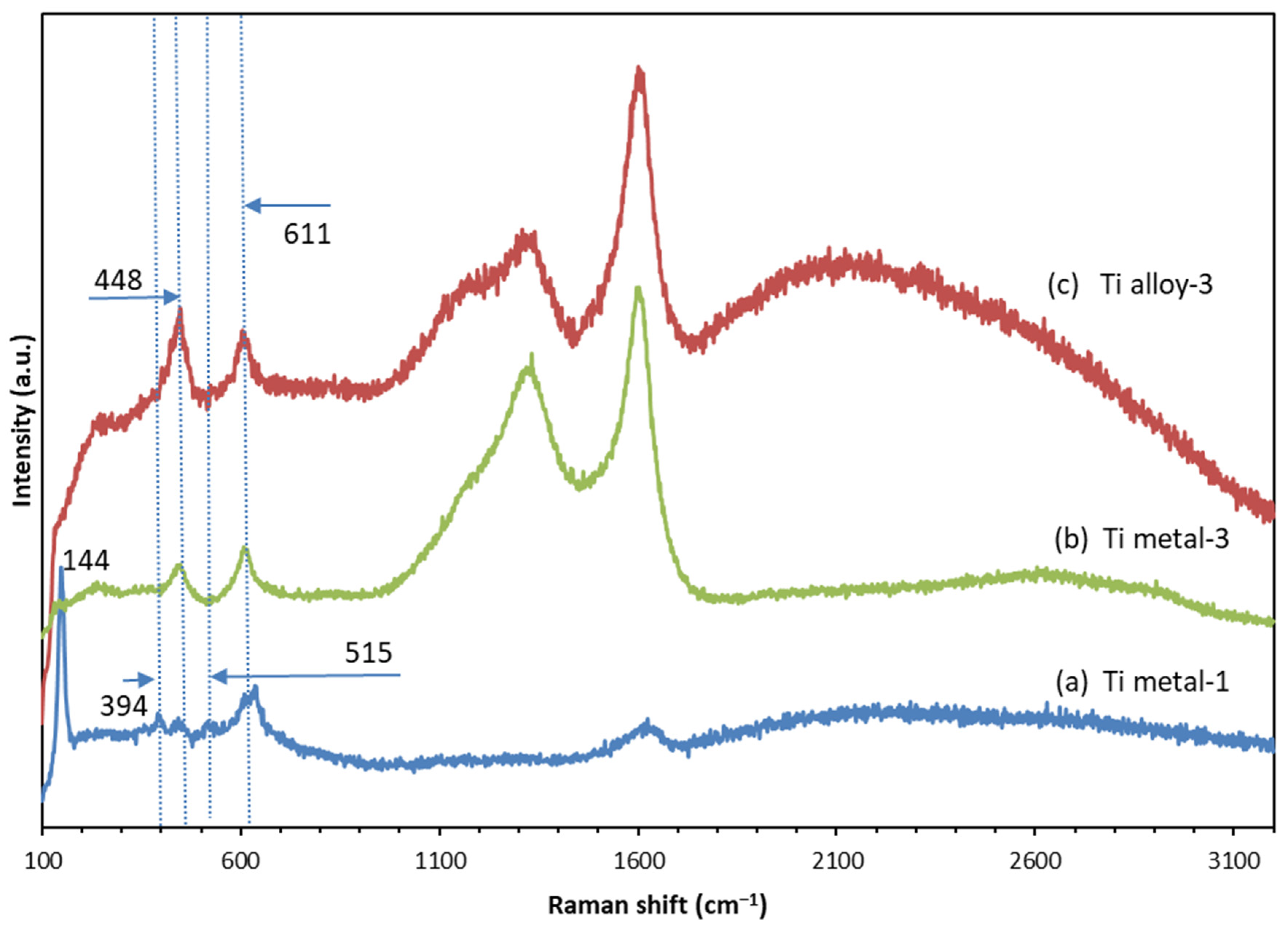
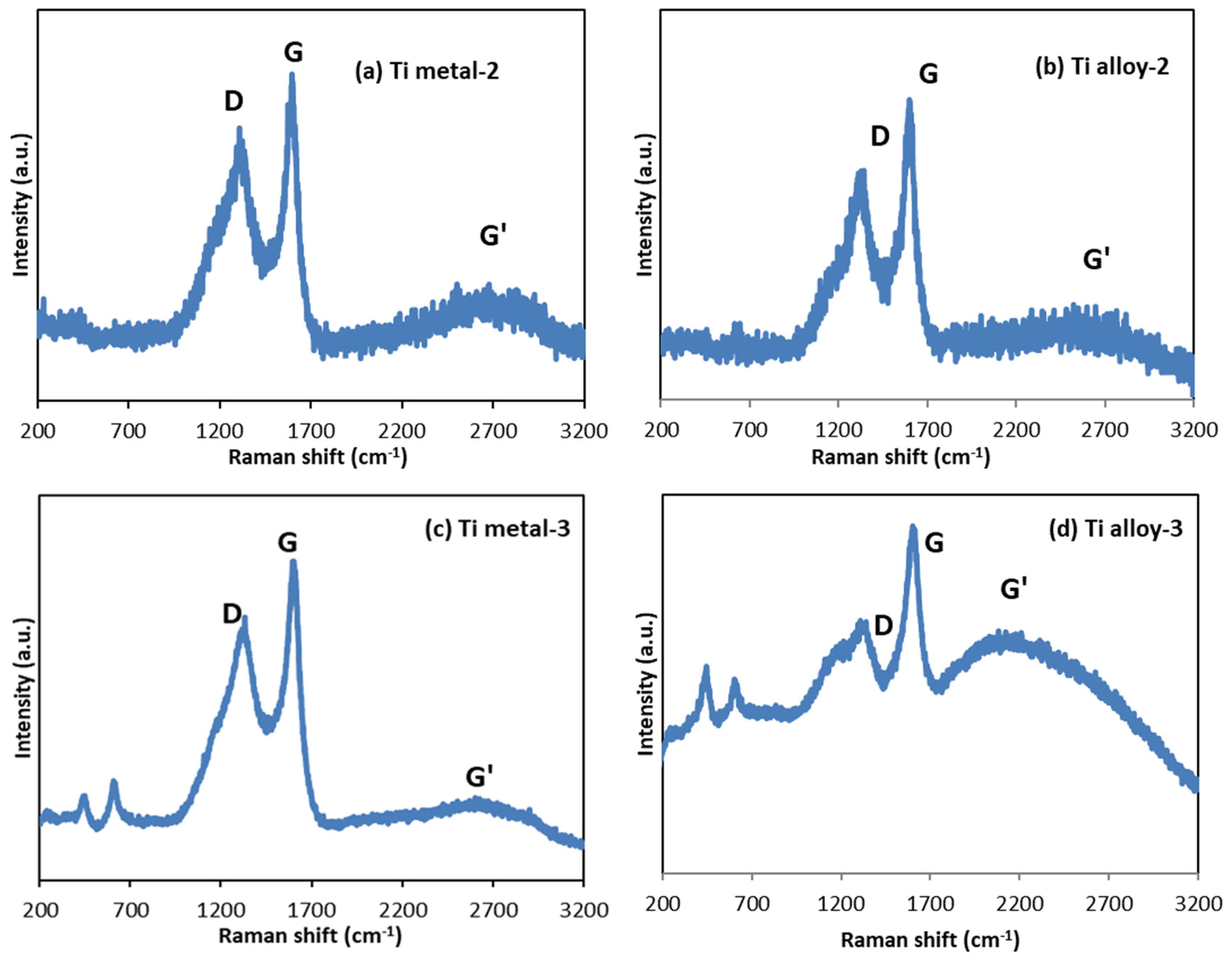
3.4. Raman Spectroscopy
4. Discussion
4.1. TiO2 Nanotubes Coating
4.2. CNTs Coating
4.3. Bilayer of TiO2 Nanotubes/Carbon Nanostructure Coating
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balazic, M.; Kopac, J.; Jackson, M.J.; Ahmed, W. Titanium and titanium alloy applications in medicine. Int. J. Nano Biomater. 2007, 1, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chu, P.K.; Ding, C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 47, 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stich, T.; Alagboso, F.; Křenek, T.; Kovářík, T.; Alt, V.; Docheva, D. Implant-bone-interface: Reviewing the impact of titanium surface modifications on osteogenic processes in vitro and in vivo. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; KS, S.K.; Grandhi, V.V.; Gupta, V. The effects of titanium implant surface topography on osseointegration: Literature review. JMIR Biomed. Eng. 2019, 4, e13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiati, L.; Eales, M.G.; Nobbs, A.H.; Su, B.; Tsimbouri, P.M.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M.; Dalby, M.J. Impact of surface topography and coating on osteogenesis and bacterial attachment on titanium implants. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, 2041731418790694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dhara, S.; Saha, P. Enhancing the biocompatibility of Ti6Al4V implants by laser surface microtexturing: An in vitro study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, M.P.; Nikolova, V.; Ivanova, V.L.; Valkov, S.; Petrov, P.; Apostolova, M.D. Mechanical properties and in vitro biocompatibility evaluation of TiN/TiO2 coated Ti6Al4V alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyan, B.D.; Lotz, E.M.; Schwartz, Z. Roughness and hydrophilicity as osteogenic biomimetic surface properties. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mei, S.; Chu, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. The influence of hierarchical hybrid micro/nano-textured titanium surface with titania nanotubes on osteoblast functions. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5072–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Tsukimura, N.; Yamada, M.; Ogawa, T. Enhanced bone-integration capability of alkali-and heat-treated nanopolymorphic titanium in micro-to-nanoscale hierarchy. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7297–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Daraio, C.; Chen, L.H.; Pisanic, T.R.; Fiñones, R.R.; Jin, S. Significantly accelerated osteoblast cell growth on aligned TiO2 nanotubes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 78, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Brammer, K.S.; Li, Y.J.; Teng, D.; Engler, A.J.; Chien, S.; Jin, S. Stem cell fate dictated solely by altered nanotube dimension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, H.; Lü, W.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Effects of TiO2 nanotubes with different diameters on gene expression and osseointegration of implants in minipigs. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6900–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikova, T.D.; Hahm, M.G.; Hashim, D.P.; Narayanan, N.T.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M. Mechanism of TiO2 nanotubes formation on the surface of pure Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 939, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudhair, D.; Bhatti, A.; Li, Y.; Hamedani, H.A.; Garmestani, H.; Hodgson, P.; Nahavandi, S. Anodization parameters influencing the morphology and electrical properties of TiO2 nanotubes for living cell interfacing and investigations. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikova, T.D. Influence of technological parameters on titanium nanotubes formation. Resour.-Sav. Technol. Prod. Press. Process. Mater. Mech. Eng. 2013, 1, 150–160. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, M.; Mazare, A.; Schmuki, P.; Iglic, A. Influence of anodization parameters on morphology of TiO2 nanostructured surfaces. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2016, 7, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, S.; Kostarelos, K.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. The winding road for carbon nanotubes in nanomedicine. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przekora, A.; Benko, A.; Nocun, M.; Wyrwa, J.; Blazewicz, M.; Ginalska, G. Titanium coated with functionalized carbon nanotubes—A promising novel material for biomedical application as an implantable orthopaedic electronic device. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 45, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warowicka, A.; Maciejewska, B.M.; Litowczenko, J.; Kościński, M.; Baranowka-Korczyc, A.; Jasiurkowska-Delaporte, M.; Koziol, K.K.; Jurga, S. MWCNT based matrices as a platform for adhesion and growth of cells. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 136, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkov, O.V.; Pukha, V.E.; Starikova, S.L.; Khadem, M.; Starikov, V.V.; Maleev, M.V.; Kim, D.-E. Highly wear-resistant and biocompatible carbon nanocomposite coatings for dental implants. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, G. Biomedical applications of the graphene-based materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Fan, Y.; Cui, F.-Z. Biomedical investigation of CNT based coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.; Yeow, J.-W. Carbon nanotubes for biomedical applications. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2005, 4, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haniu, H.; Saito, N.; Matsuda, Y.; Tsukahara, T.; Usui, Y.; Narita, N.; Hara, K.; Aoki, K.; Shimizu, M.; Ogihara, N. Basic potential of carbon nanotubes in tissue engineering applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 343747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliev, T. The advances in biomedical applications of carbon nanotubes. C 2019, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Flahaut, E.; Golzio, M. Overview of carbon nanotubes for biomedical applications. Materials 2019, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.S.; Atala, A. Carbon nanotube applications for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, A.O.; Antunes, E.F.; Palma, M.B.; Pacheco-Soares, C.; Trava-Airoldi, V.J.; Corat, E.J. Monolayer formation of human osteoblastic cells on vertically aligned multiwalled carbon nanotube scaffolds. Cell Biol. Int. 2010, 34, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Mahalingam, P.; Karthik, M. Large scale synthesis of carbon nanotubes. E-J. Chem. 2009, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikova, T. Synthesis of Carbon Nano-Tubes on Anodized Titanium Surface with no Metal Catalyst. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, M.; Paramguru, K.; Mohapatra, S. Growth of carbon nanotubes on nanoporous titania templates. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 2640–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, E.; He, C.; Du, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, N. Low-temperature synthesis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes over Cu catalyst. Mater. Lett. 2012, 72, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Homma, Y. Carbon nanotube growth from diamond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6922–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.J.; Choi, W.B.; Jeong, K.S.; Chu, J.U.; Park, G.S.; Song, S.; Yoo, I.K. Selective Growth of Carbon Nanotubes on Pre-patterned Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.J.; Maksimova, N.I.; Engstler, J.; Joshi, R.; Schierholz, R.; Feile, R. Catalyst free growth of a carbon nanotube–alumina composite structure. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2008, 361, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ren, W.; Gao, L.; Li, S.; Pei, S.; Liu, C.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, H.-M. Metal-catalyst-free growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2082–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Takagi, D.; Chiashi, S.; Homma, Y. The growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes on a silica substrate without using a metal catalyst. Carbon 2010, 48, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ando, Y. Chemical vapor deposition of carbon nanotubes: A review on growth mechanism and mass production. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 3739–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Cai, Q.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, L. Metal-catalyst-free growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes on substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2094–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S. Growth of carbon nanotubes from titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8019–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikici, T.; Toparli, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of nanostructured and microstructured TiO2 films. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 661, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieerad, A.; Zalnezhad, E.; Bushroa, A.; Hamouda, A.; Sarraf, M.; Nasiri-Tabrizi, B. Self-organized TiO2 nanotube layer on Ti–6Al–7Nb for biomedical application. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 265, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, L.; Anandan, C.; Rajendran, N. Electrochemical behavior and effect of heat treatment on morphology, crystalline structure of self-organized TiO2 nanotube arrays on Ti–6Al–7Nb for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 50, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathyunes, L.; Khalil-Allafi, J.; Sheykholeslami, S.O.R.; Moosavifar, M. Biocompatibility assessment of graphene oxide-hydroxyapatite coating applied on TiO2 nanotubes by ultrasound-assisted pulse electrodeposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 87, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardcastle, F.D. Raman Spectroscopy of Titania (TiO2) Nanotubular Water-Splitting Catalysts. J. Ark. Acad. Sci. 2011, 65, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gomez, L.; Ishikawa, F.N.; Madaria, A.; Ryu, K.; Wang, C.; Badmaev, A.; Zhou, C. Comparison of graphene growth on single-crystalline and polycrystalline Ni by chemical vapor deposition. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 3101–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olteanu, D.; Filip, A.; Socaci, C.; Biris, A.R.; Filip, X.; Coros, M.; Rosu, M.C.; Pogacean, F.; Alb, C.; Baldea, I. Cytotoxicity assessment of graphene-based nanomaterials on human dental follicle stem cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.M.Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.J.; Peng, Y.Z.; Xing, Y.; Feng, Z.X.; Tan, J.; Tao, J.M.; Li, Z.L.; Wang, Y.R.; et al. Interface and strengthening mechanisms of Al matrix composites reinforced with in-situ CNTs grown on Ti particles. Mater. Des. 2023, 229, 111923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorio, A.; Saito, R. Raman spectroscopy for carbon nanotube applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Lu, R.; Liang, S.; Cui, X.; Chi, H.; Zou, L. Facile synthesis of homogeneously dispersed carbon nanotubes on TC4 alloy powder by in-situ CVD and its growth behavior. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 9928–9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decha-umphai, D.; Chunate, H.-T.; Phetrattanarangsi, T.; Boonchuduang, T.; Choosri, M.; Puncreobutr, C.; Lohwongwatana, B.; Khamwannah, J. Effects of post-processing on microstructure and adhesion strength of TiO2 nanotubes on 3D-printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagar, S.; Wang, J.; Berndt, C.C.; Ivanova, E.P.; Wen, C. Cell response of anodized nanotubes on titanium and titanium alloys. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 2726–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Park, I.S.; Park, H.H.; Lee, M.H.; Bae, T.S.; Duncan, W.; Swain, M. The effect of annealing temperatures on surface properties, hydroxyapatite growth and cell behaviors of TiO2 nanotubes. Surf. Interface Anal. 2011, 43, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shao, R.; Huang, X.; Zheng, K.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, Q. Structure and photoluminescence properties of graphene nanoflakes grown on zinc oxide films by hot filament chemical vapor deposition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2016, 64, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Z.; Mao, S.; Han, Z.J.; Cen, K.; Chen, J.; Ostrikov, K.K. Emerging energy and environmental applications of vertically-oriented graphenes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Large area CVD growth of graphene. Synth. Met. 2015, 210, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummeli, M.H.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Scott, A.; Borrnert, F.; Warner, J.H.; Hoffman, V.; Lin, J.-H.; Cuniberti, G.; Buchner, B. Direct low-temperature nanographene CVD synthesis over a dielectric insulator. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4206–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lindvall, N.; Cole, M.T.; Wang, T.; Booth, T.J.; Bøggild, P.; Teo, K.B.; Liu, J.; Yurgens, A. Controllable chemical vapor deposition of large area uniform nanocrystalline graphene directly on silicon dioxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 044103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fu, L.; Liu, N.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, L.; Liu, Z. Segregation growth of graphene on Cu–Ni alloy for precise layer control. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 11976–11982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chou, H.; Ji, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, S.; Jiang, W.; Hao, Y.; Kang, J.; Ren, Y.; Piner, R.D. Growth mechanism and controlled synthesis of AB-stacked bilayer graphene on Cu–Ni alloy foils. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7731–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Kraemer, S.; Sarkar, D.; Li, H.; Ajayan, P.M.; Banerjee, K. Controllable and rapid synthesis of high-quality and large-area Bernal stacked bilayer graphene using chemical vapor deposition. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
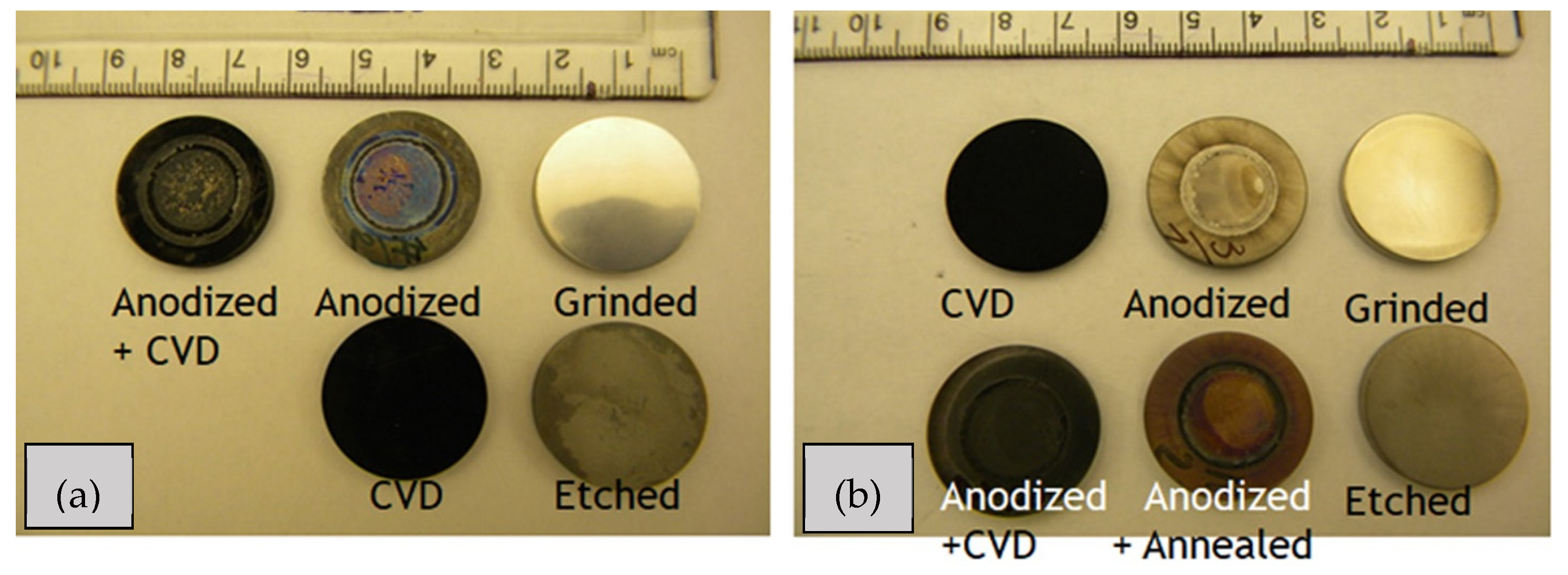
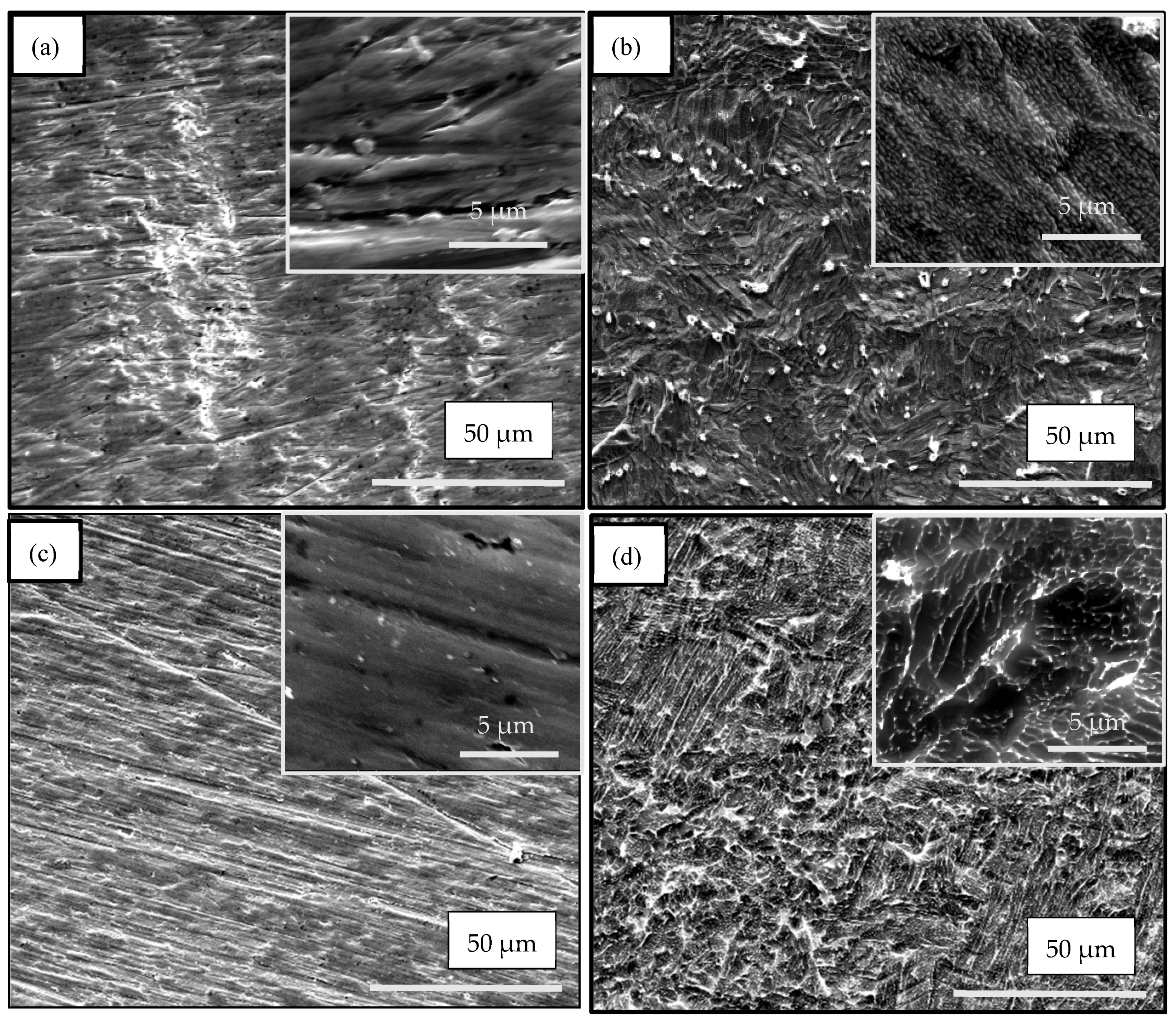
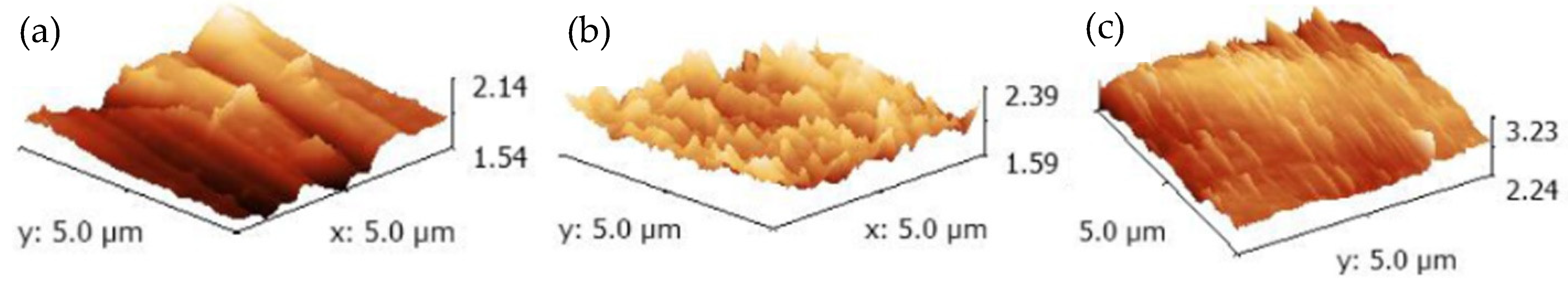
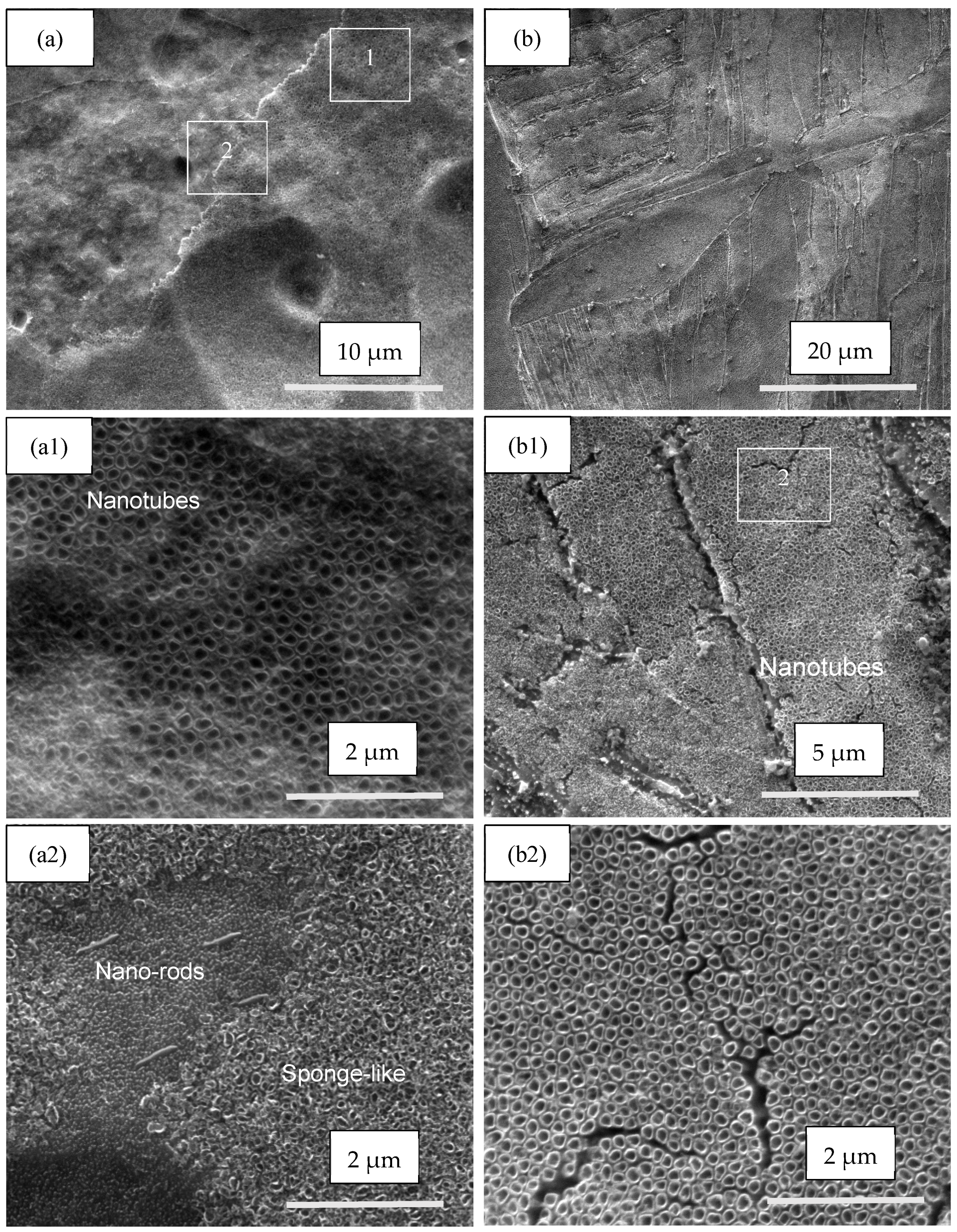

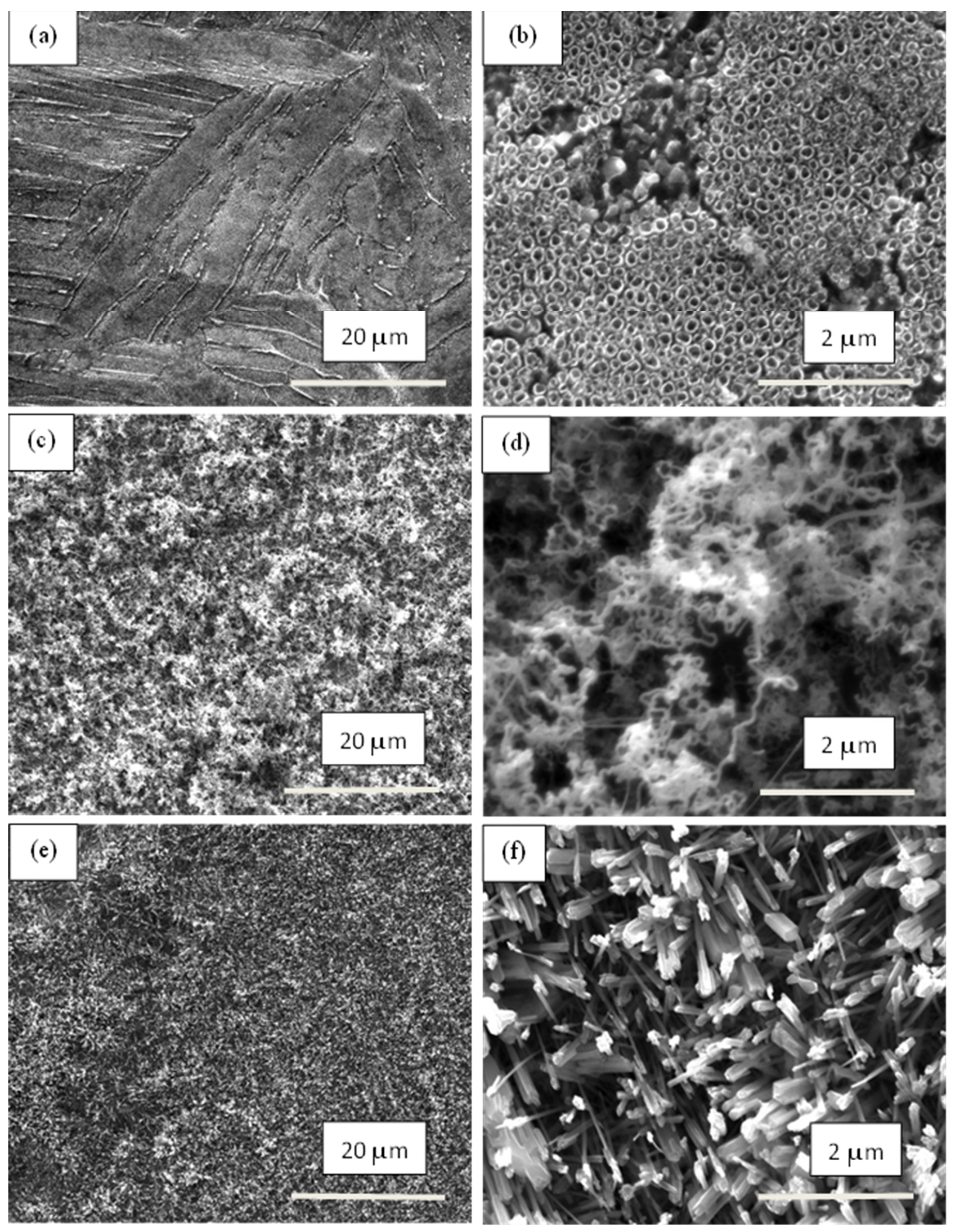
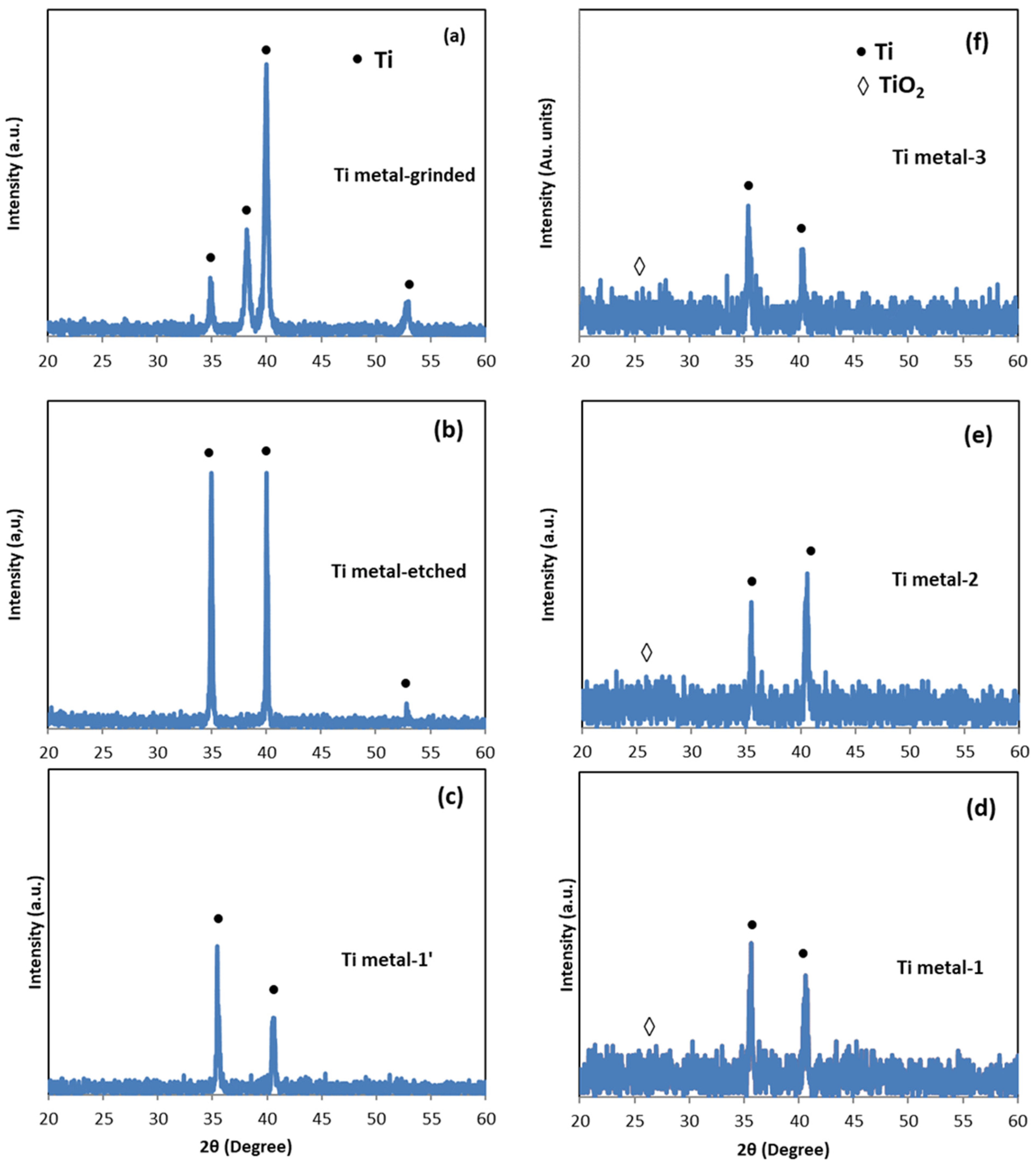

| Samples | Anodization | CVD Process | Annealing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Treatment | Notation | |||
| Group 1 | Ti metal-1′ | 25 V, 7 h 1 | |||
| Pure Ti | Group 1 | Ti metal-1 | 25 V, 7 h | 550 °C, 2 h, argon | |
| Grade 2 | Group 2 | Ti metal-2 | 650 °C, 1 h | 550 °C, 2 h, argon | |
| Group 3 | Ti metal-3 | 25 V, 7 h | 650 °C, 1 h | 550 °C, 2 h, argon | |
| Group 1 | Ti alloy-1′ | 30 V, 7 h 1 | |||
| Ti6Al4V | Group 1 | Ti alloy-1 | 30 V, 7 h | 550 °C, 2 h, argon | |
| alloy | Group 2 | Ti alloy-2 | 650 °C, 1 h | 550 °C, 2 h, argon | |
| Group 3 | Ti alloy-3 | 30 V, 7 h | 650 °C, 1 h | 550 °C, 2 h, argon | |
| Ti Metal-1′ | Ti Alloy-1′ | Ti Metal-3 | Ti Alloy-3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Ti 74.67 1 | Ti 53.85 | Ti 39.27 | 39.42 | 45.53 | Ti 38.65 |
| O 25.35 | O 39.80 | O 46.41 | 42.71 | 38.65 | O 36.97 |
| Al 5.78 | C 14.32 | 17.86 | 15.81 | Al 4.61 | |
| V 0.57 | V 0.00 | ||||
| C 19.76 | |||||
| Sample | Raman Shifts, cm−1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | Carbon Nanostructures | |||||||||
| A | A | R | A | R | A | D | G | G′ | ID/IG | |
| Ti metal-1 | 144 | 394 | 442 | 515 | 611 | 635 | ||||
| Ti metal-2 | 1308 | 1596 | 2692 | 0.84 | ||||||
| Ti metal-3 | 448 | 611 | 1332 | 1602 | 2604 | 0.82 | ||||
| Ti alloy-2 | 1344 | 1601 | 2650 | 0.76 | ||||||
| Ti alloy-3 | 448 | 611 | 1340 | 1605 | 2207 | 0.78 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dikova, T.; Hashim, D.P.; Mintcheva, N. Morphology and Structure of TiO2 Nanotube/Carbon Nanostructure Coatings on Titanium Surfaces for Potential Biomedical Application. Materials 2024, 17, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061290
Dikova T, Hashim DP, Mintcheva N. Morphology and Structure of TiO2 Nanotube/Carbon Nanostructure Coatings on Titanium Surfaces for Potential Biomedical Application. Materials. 2024; 17(6):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061290
Chicago/Turabian StyleDikova, Tsanka, Daniel P. Hashim, and Neli Mintcheva. 2024. "Morphology and Structure of TiO2 Nanotube/Carbon Nanostructure Coatings on Titanium Surfaces for Potential Biomedical Application" Materials 17, no. 6: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061290
APA StyleDikova, T., Hashim, D. P., & Mintcheva, N. (2024). Morphology and Structure of TiO2 Nanotube/Carbon Nanostructure Coatings on Titanium Surfaces for Potential Biomedical Application. Materials, 17(6), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061290







