Modelling and Optimization of Machined Surface Topography in Ball-End Milling Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
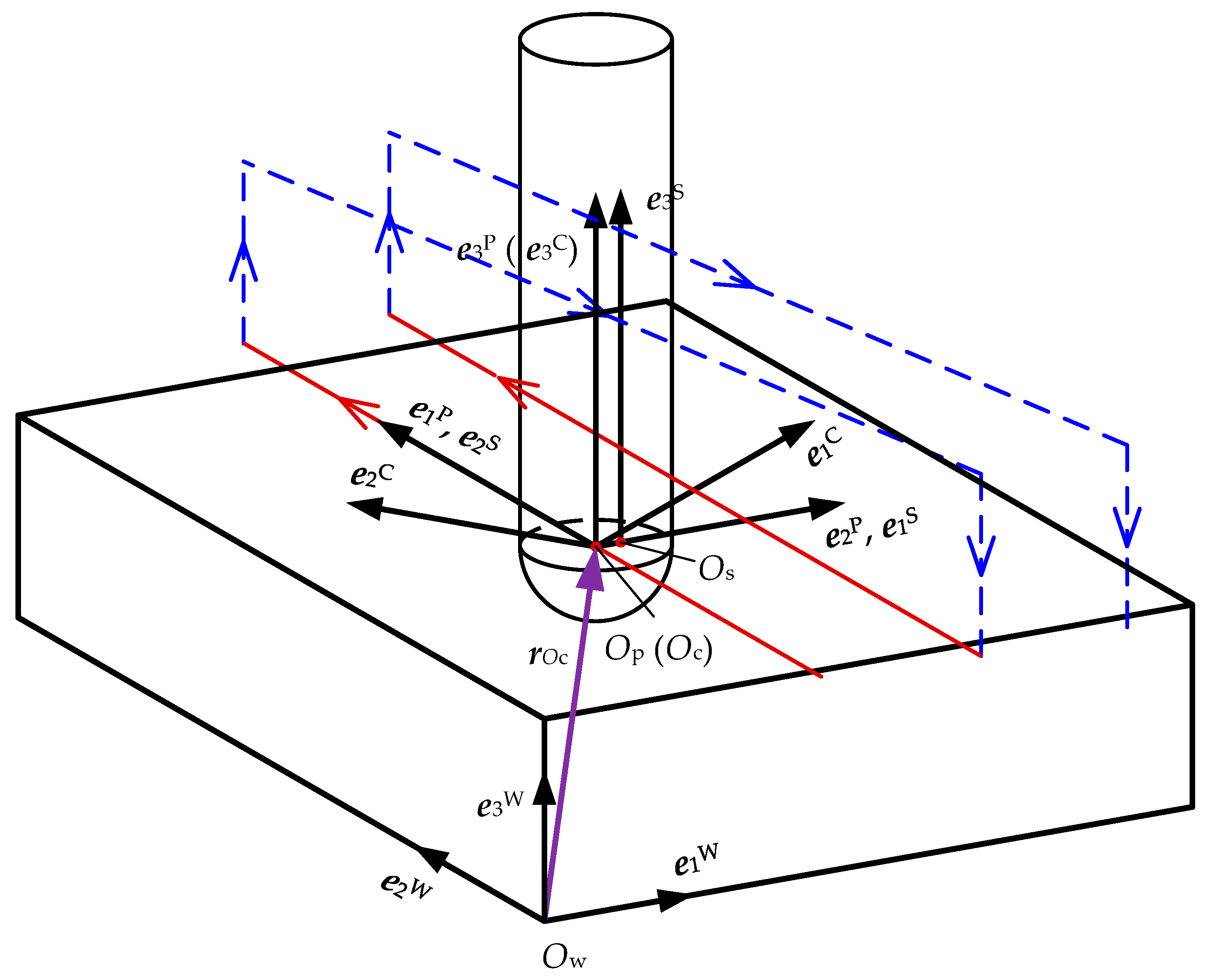
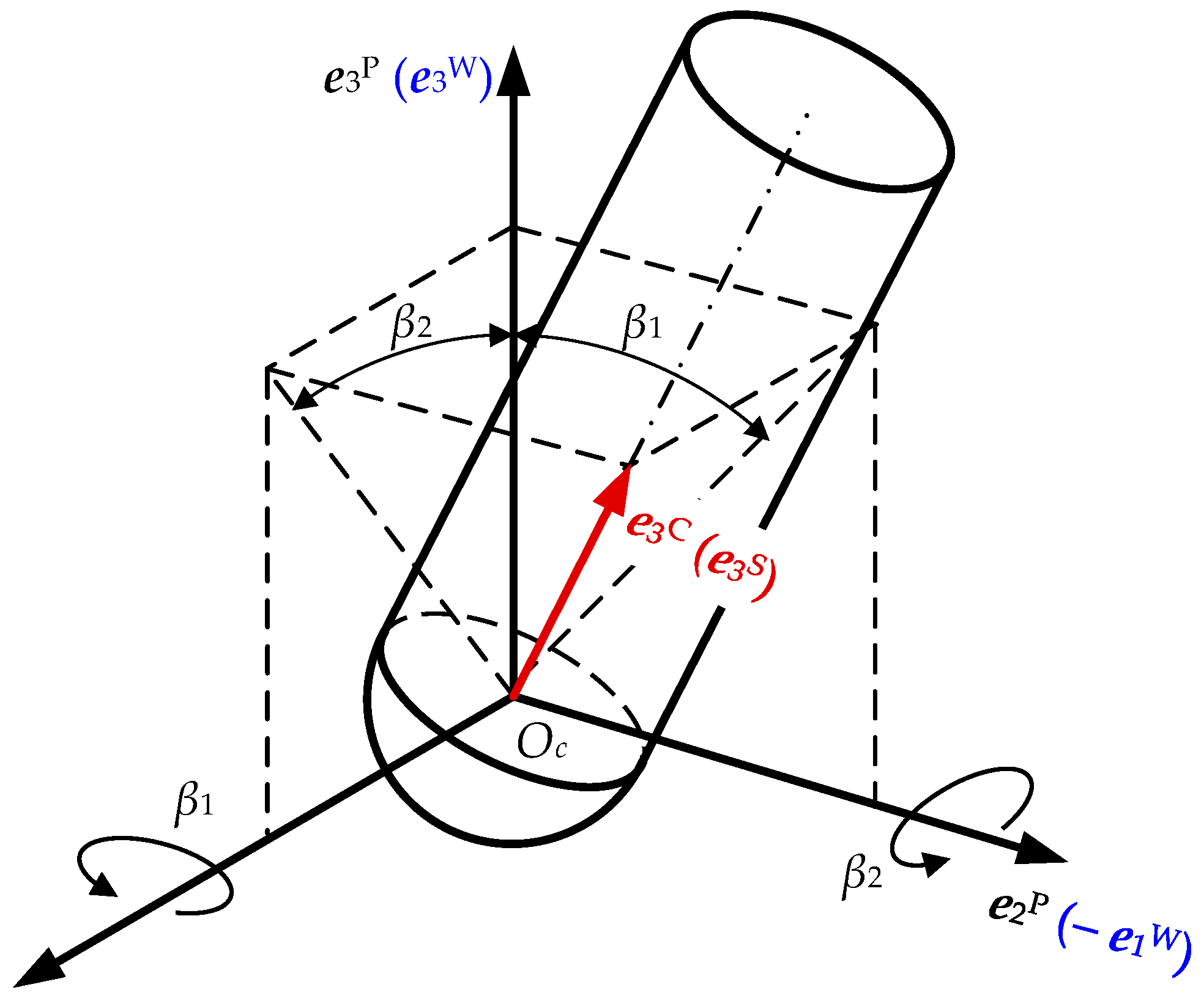
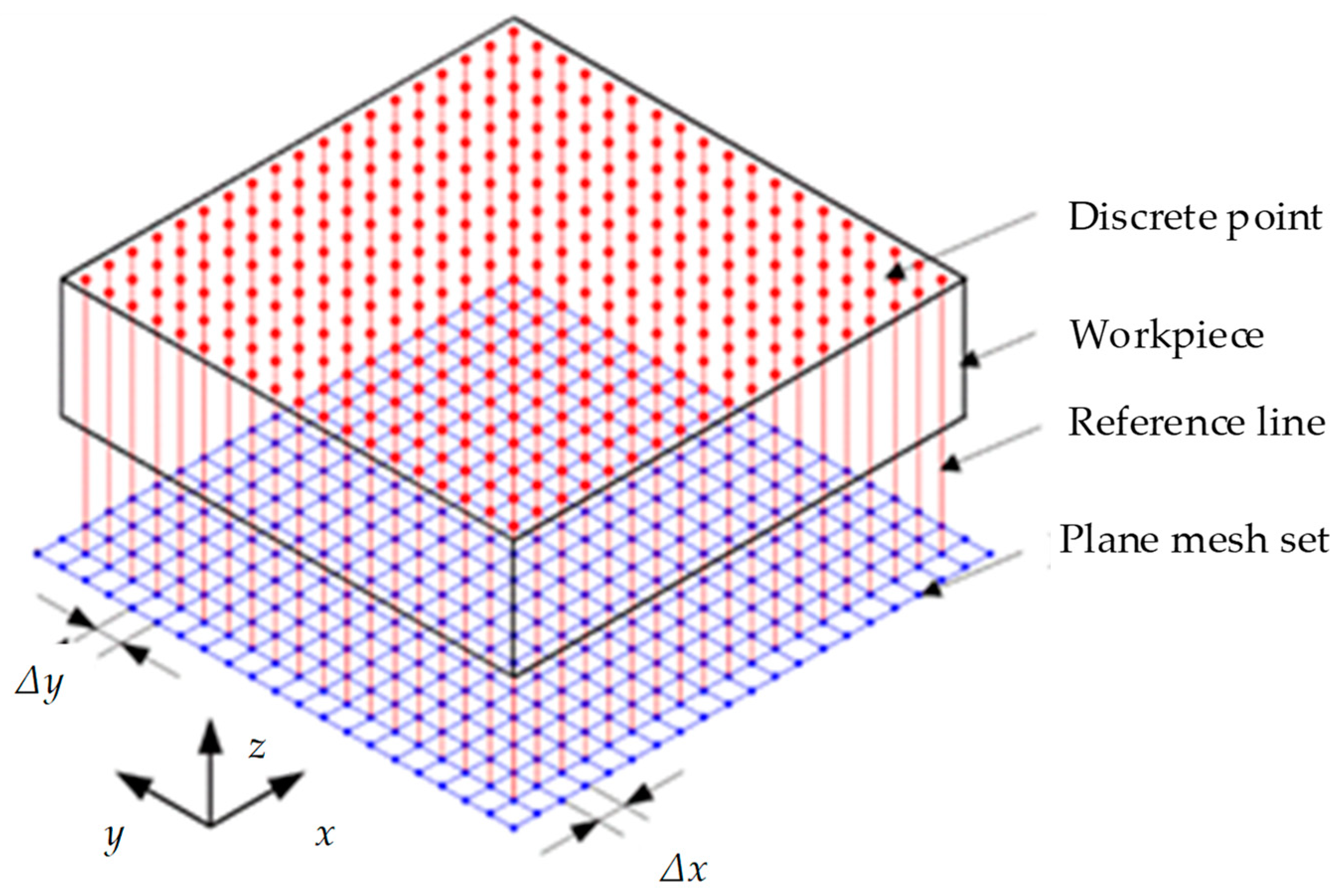
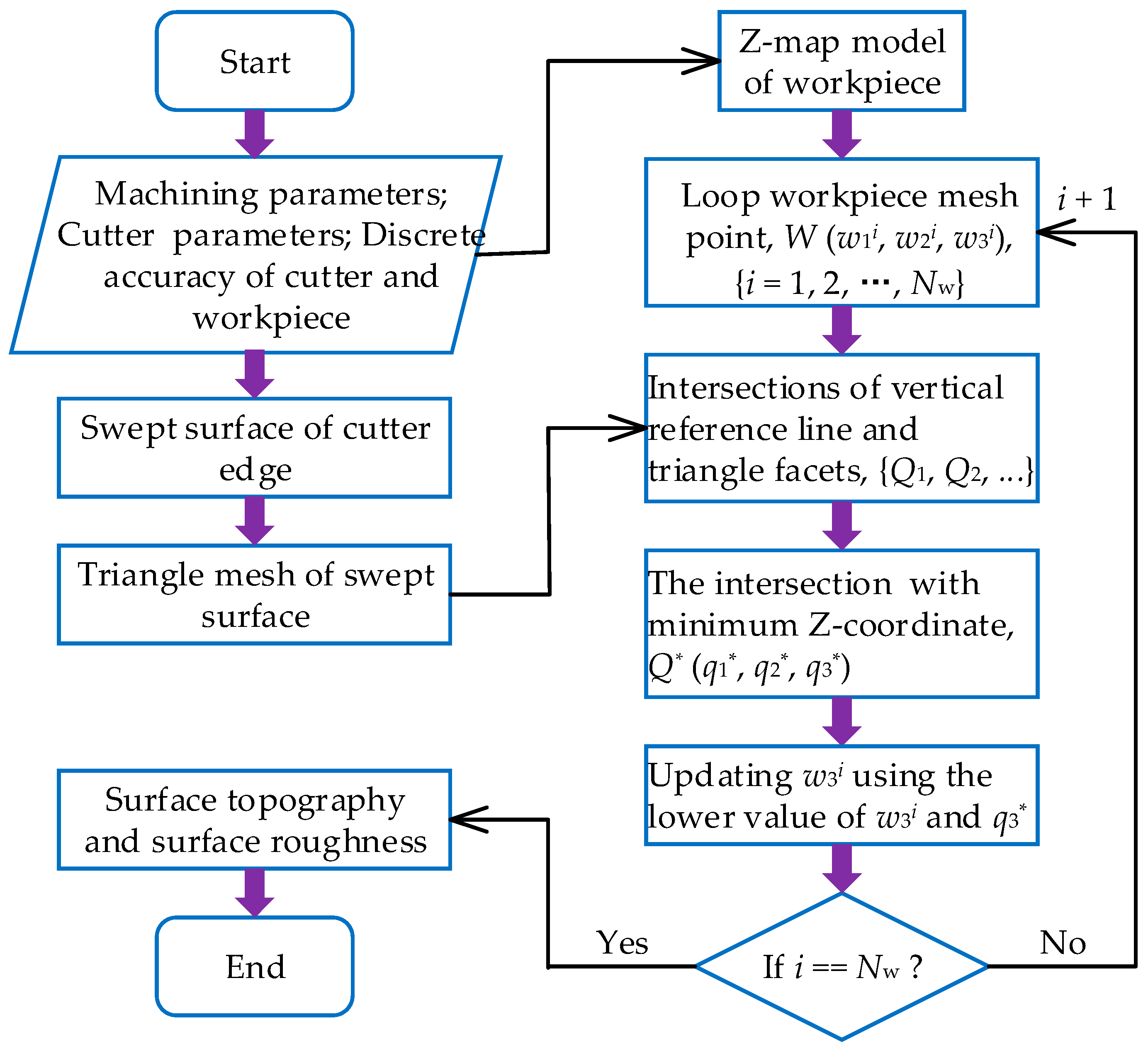
2. Modeling of Machined Surface Topography
3. Results and Discussion
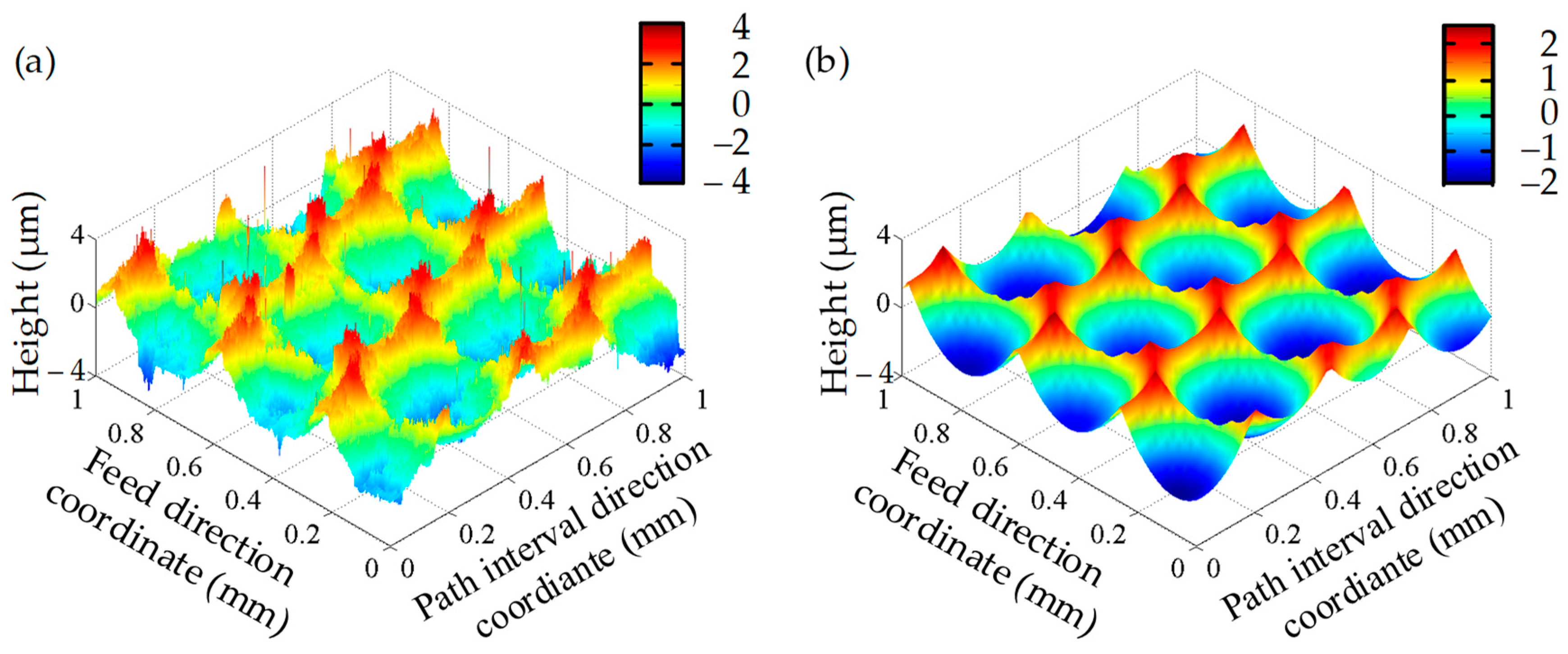
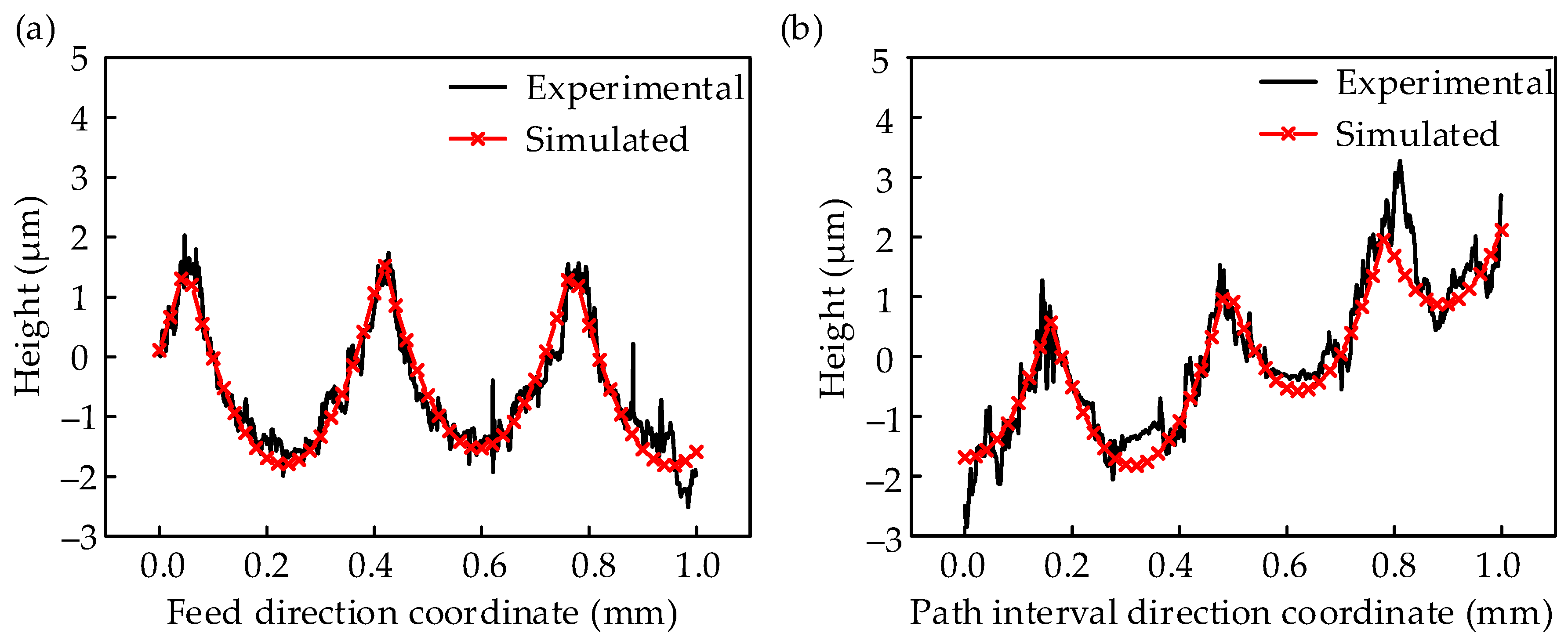
3.1. Experimental Verification
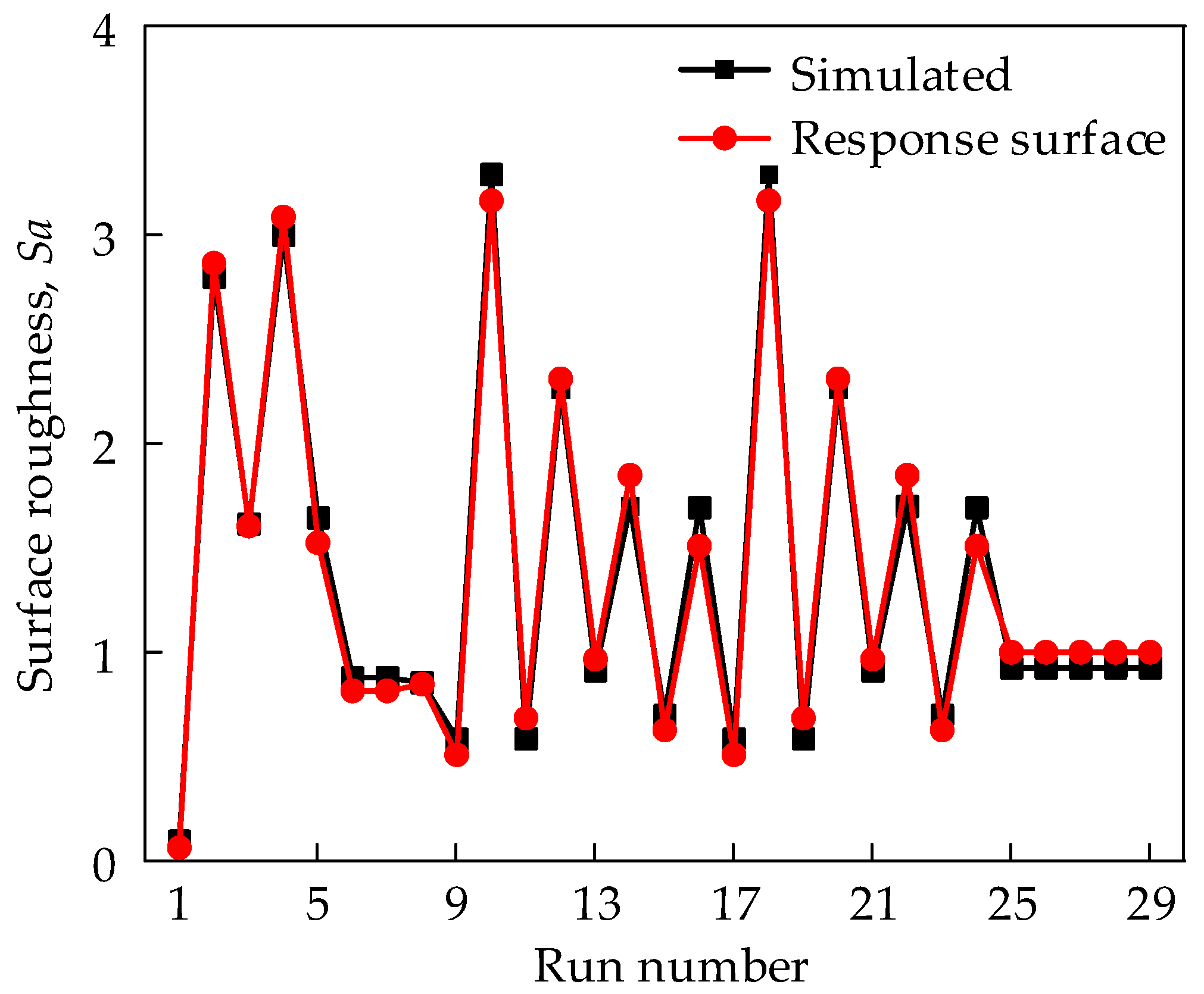
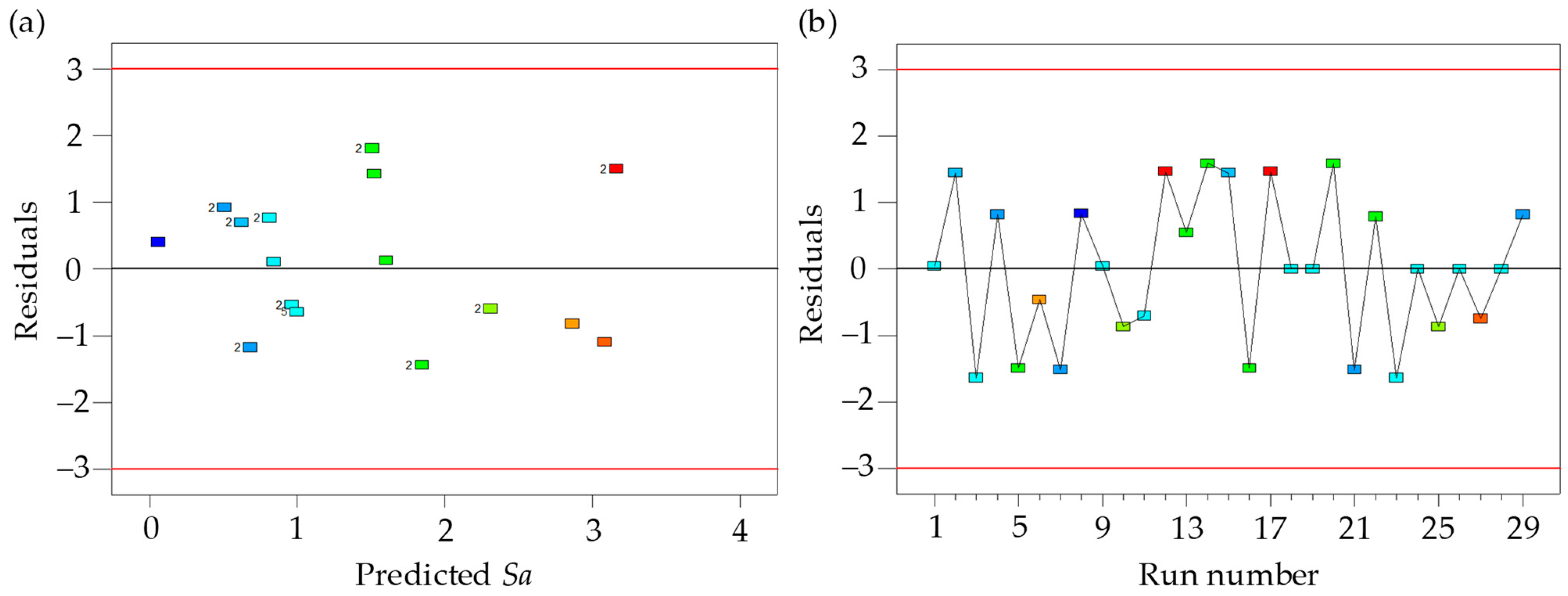
3.2. Cutting Parameters Optimization
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A novel surface topography model was developed using triangular approximation and Z-map methods. The consistency between the simulated and experimental results shows that the model can replace the milling experiment when studying the surface topography and roughness during ball-end milling processes;
- (2)
- A response surface-reduced quadratic model was developed based on the proposed surface topography simulation algorithm. The model can effectively characterize the correlation of Sa and cutting parameters (i.e., feed per tooth, radial depth of cut, tilt, and lead angles) based on ANOVA results;
- (3)
- An optimization model was developed for improving the machining efficiency by means of the response surface model. The material removal rate (i.e., product of feed per tooth and radial depth of cut) can be improved effectively under the surface roughness constraints;
- (4)
- The complex interaction between cutting edge and workpiece is neglected in the proposed model, so the cutting edge trajectory error, cutting edge micro-geometry and workpiece material deformation should be considered in the next study to secure a reliable prediction of surface topography.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Man, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. A modified normal contact stiffness model considering effect of surface topography. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J.-J. Eng. 2015, 229, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, N.; Sorgato, M.; Parenti, P.; Annoni, M.; Lucchetta, G. Effects of micromilled NiP mold surface topography on the optical characteristics of injection molded prismatic retroreflectors. Precis. Eng. 2020, 61, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Movahhedy, M.R. Extraction of surface curvatures from tool path data and prediction of cutting forces in the finish milling of sculptured surfaces. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 45, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Han, S.; Li, A.; Wang, D. Effects of inclination angles on geometrical features of machined surface in five-axis milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 65, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S. Effects of feed per tooth and radial depth of cut on amplitude parameters and power spectral density of a machined surface. Materials 2020, 13, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Wu, J.; Fang, Z.; Yuan, S.; Yan, R.; Bai, Q. Modeling and controlling of surface micro-topography feature in micro-ball-end milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 2657–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L. Modeling and on-line simulation of surface topography considering tool wear in multi-axis milling process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, T.B.; Zhao, J. Surface generation modeling of micro milling process with stochastic tool wear. Precis. Eng. 2020, 61, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, S.; Wassila, B.; Gilles, D. Cutter workpiece engagement region and surface topography prediction in five-axis ball-end milling. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2017, 22, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, Y. Analysis of milling surface roughness prediction for thin-walled parts with curved surface. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, O.; El-Wardany, T.; Ng, E.; Elbestawi, M.A. An improved cutting force and surface topography prediction model in end milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Yuan, J. Modeling of surface topography based on cutting vibration in ball-end milling of thin-walled parts in ball-end milling of thin-walled parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 101, 1837–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cao, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, J. Geometry simulation and evaluation of the surface topography in five-axis ball-end milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondani, F.G.; Bissacco, G. Effect of cutting edge micro geometry on surface generation in ball end milling. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2019, 68, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, B.M.; Elbestawi, M.A. Geometric simulation of ball-end milling operations. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2001, 123, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, G.; Wan, M.; Gao, T.; Bassir, D.H. A new algorithm for the numerical simulation of machined surface topography in multiaxis ball-end milling. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2008, 130, 0110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Li, P.Y.; Yang, Z.C.; Landers, R.G. Geometrical simulation and analysis of ball-end milling surface topography. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 1885–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.T.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.W. Swept surface-based approach to simulating surface topography in ball-end CNC milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhu, M.W.; Li, Z.H. The effect of characteristics of free-form surface on the machined surface topography in milling of panel mold. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Q.; Wang, Q.H. Modeling and simulation of the surface topography in ball-end milling based on biharmonic spline interpolation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 99, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, M.K.; Puri, A.B.; Maity, A. Optimization of surface roughness in ball-end milling using teaching-learning-based optimization and response surface methodology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B-J. Eng. 2017, 231, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, M.K.; Puri, A.B.; Maity, A. Modelling and application of response surface optimization to optimize cutting parameters for minimizing cutting forces and surface roughness in high-speed, ball-end milling of Al2014-T6. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2017, 39, 5117–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Ren, J.X.; Yao, C.F. Multi-objective optimization of multi-axis ball-end milling Inconel 718 via grey relational analysis coupled with RBF neural network and PSO algorithm. Measurement 2017, 102, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buj-Corral, I.; Ortiz-Marzo, J.A.; Costa-Herrero, L.; Vivancos-Calvet, J.; Luis-Pérez, C. Optimal machining strategy selection in ball-end milling of hardened steels for injection molds. Materials 2019, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkata-Rao, K. Power consumption optimization strategy in micro ball-end milling of D2 steel via TLBO coupled with 3D FEM simulation. Measurement 2019, 132, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, H.A.; Joshi, S.S. Modeling of machined surface quality in high-speed ball-end milling of Inconel-718 thin cantilevers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 78, 1751–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Amini, C.; Cuadrado, N.; Travieso-Rodriguez, J.A.; Llumà, J.; Vilaseca, M. Experimental validation of ball burnishing numerical simulation on ball-end milled martensitic stainless-steel considering friction and the initial surface topography. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, K.; Eifler, M.; Klauer, K.; Huttenlochner, K.; Kirsch, B.; Ziegler, C.; Aurich, J.C.; Seewig, J. Determination of the surface topography of ball end micro milled material measures. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2021, 24, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauer, K.; Eifler, M.; Kirsch, B.; Seewig, J.; Aurich, J.C. Ball end micro milling of areal material measures: Influence of the tilt angle on the resulting surface topography. Prod. Eng.-Res. Dev. 2020, 14, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, E.M.; Brandão, L.C.; Ribeiro Filho, S.L.M.; De Oliveira, J.A. Integrated optimization using mixture design to confirm the finishing of AISI P20 using different cutting strategies and ball nose end mills. Measurement 2014, 47, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.G. Study on surface defects in five-axis ball-end milling of tool steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 89, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.28~0.40 | 0.20~0.80 | 0.60~1.00 | 1.40~2.00 | 0.30~0.55 | 0.05~0.10 | Bal |
| Density (kg/m3) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Hardness (HRC) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7800 | 207 | 30~36 | 1140 | 29.0 |
| No. | Spindle Speed, n (r/min) | Feed per Tooth, fz (mm/tooth) | Radial Depth of Cut, ae (mm) | Axial Depth of Cut, ap (mm) | Tilt Angle, β1 (°) | Lead Angle, β2 (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 5000 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.3 | −8 | 4 |
| 2# | 6500 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.15 | −12 | 0 |
| 3# | 6500 | 0.56 | 0.2 | 0.1 | −16 | 4 |
| No. | Experimental Sa (μm) | Predicted Sa (μm) | Relative Deviation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value | Standard Deviation | |||
| 1# | 0.8158 | 0.0656 | 0.8227 | 0.85 |
| 2# | 0.9289 | 0.0871 | 0.9087 | −2.17 |
| 3# | 1.8723 | 0.0985 | 2.1246 | 13.48 |
| Std | Feed per Tooth, fz (mm) | Radial Depth of Cut, ae (mm) | Tilt Angle, β1 (°) | Lead Angle, β2 (°) | Simulated Roughness, Sa (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 4 | 4 | 0.0937 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 4 | 4 | 2.7981 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 4 | 4 | 1.6139 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4 | 4 | 2.9981 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 1.644 |
| 6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 8 | 0 | 0.8779 |
| 7 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0 | 8 | 0.8779 |
| 8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 8 | 8 | 0.8536 |
| 9 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 4 | 0 | 0.5844 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 4 | 0 | 3.2895 |
| 11 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 4 | 8 | 0.5847 |
| 12 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 4 | 8 | 2.2598 |
| 13 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0 | 4 | 0.9095 |
| 14 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0 | 4 | 1.6984 |
| 15 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 8 | 4 | 0.6976 |
| 16 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 8 | 4 | 1.6937 |
| 17 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0 | 4 | 0.5844 |
| 18 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0 | 4 | 3.2895 |
| 19 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 8 | 4 | 0.5847 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 8 | 4 | 2.2598 |
| 21 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 4 | 0 | 0.9095 |
| 22 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 4 | 0 | 1.6984 |
| 23 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 4 | 8 | 0.6976 |
| 24 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 4 | 8 | 1.6937 |
| 25 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 4 | 4 | 0.925 |
| 26 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 4 | 4 | 0.925 |
| 27 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 4 | 4 | 0.925 |
| 28 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 4 | 4 | 0.925 |
| 29 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 4 | 4 | 0.925 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value (Prob>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 21.11 | 10 | 2.11 | 145.73 | <0.0001 |
| fz | 13.76 | 1 | 13.76 | 949.88 | <0.0001 |
| ae | 2.33 | 1 | 2.33 | 161.02 | <0.0001 |
| β1 | 0.35 | 1 | 0.35 | 23.86 | 0.0001 |
| β2 | 0.35 | 1 | 0.35 | 23.86 | 0.0001 |
| fz × ae | 0.44 | 1 | 0.44 | 30.08 | <0.0001 |
| fz × β1 | 0.27 | 1 | 0.27 | 18.31 | 0.0005 |
| fz × β2 | 0.27 | 1 | 0.27 | 18.31 | 0.0005 |
| ae × β1 | 0.011 | 1 | 0.011 | 0.79 | 0.3883 |
| ae × β2 | 0.011 | 1 | 0.011 | 0.79 | 0.3883 |
| β1 × β2 | 0.14 | 1 | 0.14 | 9.50 | 0.0064 |
| fz2 | 3.07 | 1 | 3.07 | 212.15 | <0.0001 |
| ae2 | 0.39 | 1 | 0.39 | 26.87 | <0.0001 |
| β12 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 2.18 | 0.1615 |
| β22 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 2.18 | 0.1615 |
| Residual | 0.26 | 14 | 0.014 | ||
| Lack of fit | 0.26 | 14 | 0.019 | ||
| Pure error | 0.000 | 4 | 0.000 | ||
| Cor Total | 21.37 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Zhao, B.; Tan, D.; Wan, W. Modelling and Optimization of Machined Surface Topography in Ball-End Milling Process. Materials 2024, 17, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071533
Wang R, Zhao B, Tan D, Wan W. Modelling and Optimization of Machined Surface Topography in Ball-End Milling Process. Materials. 2024; 17(7):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071533
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Renwei, Bin Zhao, Dingzhong Tan, and Wenjie Wan. 2024. "Modelling and Optimization of Machined Surface Topography in Ball-End Milling Process" Materials 17, no. 7: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071533
APA StyleWang, R., Zhao, B., Tan, D., & Wan, W. (2024). Modelling and Optimization of Machined Surface Topography in Ball-End Milling Process. Materials, 17(7), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071533






