Effects of Doping on Elastic Strain in Crystalline Ge-Sb-Te
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
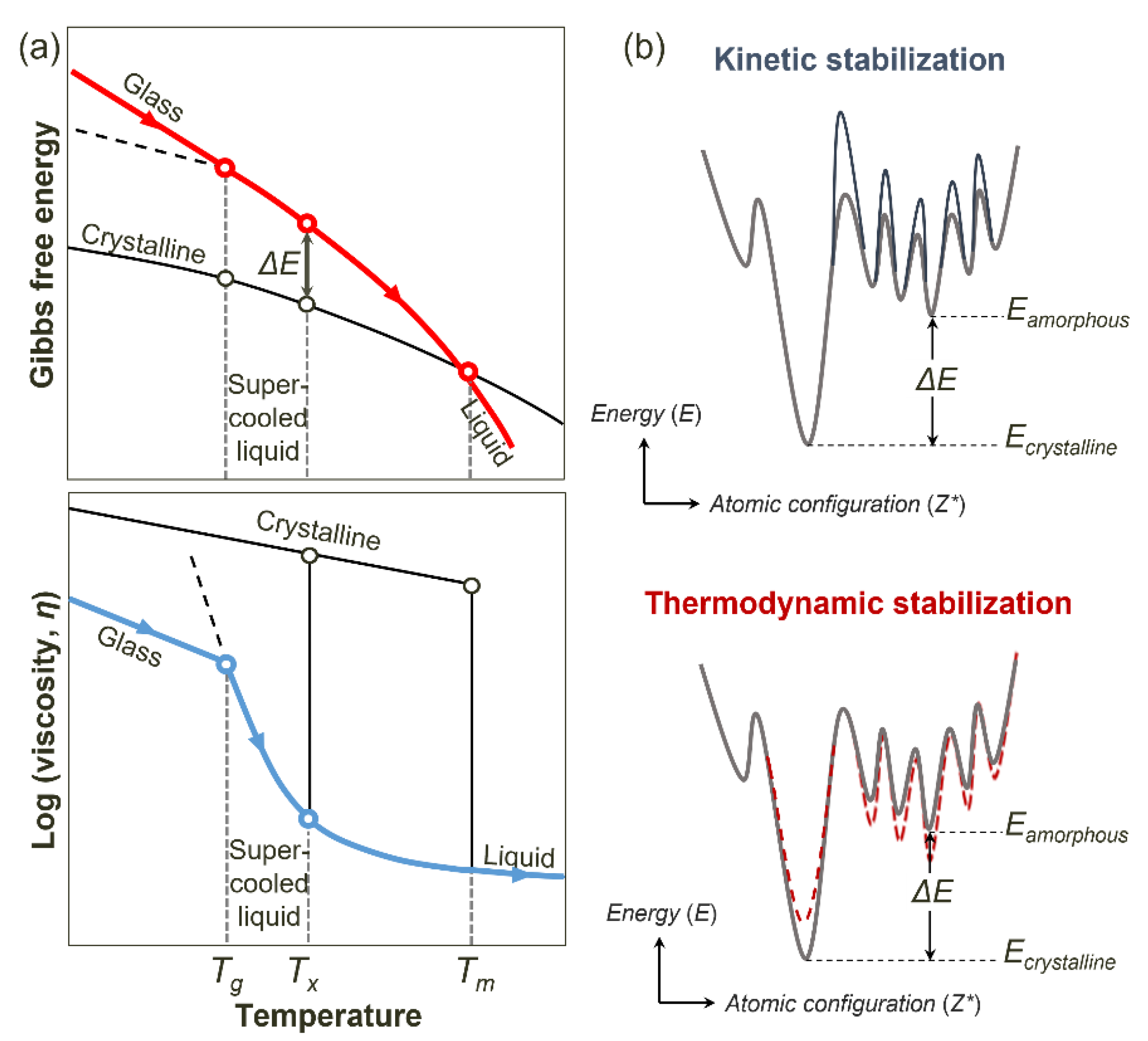
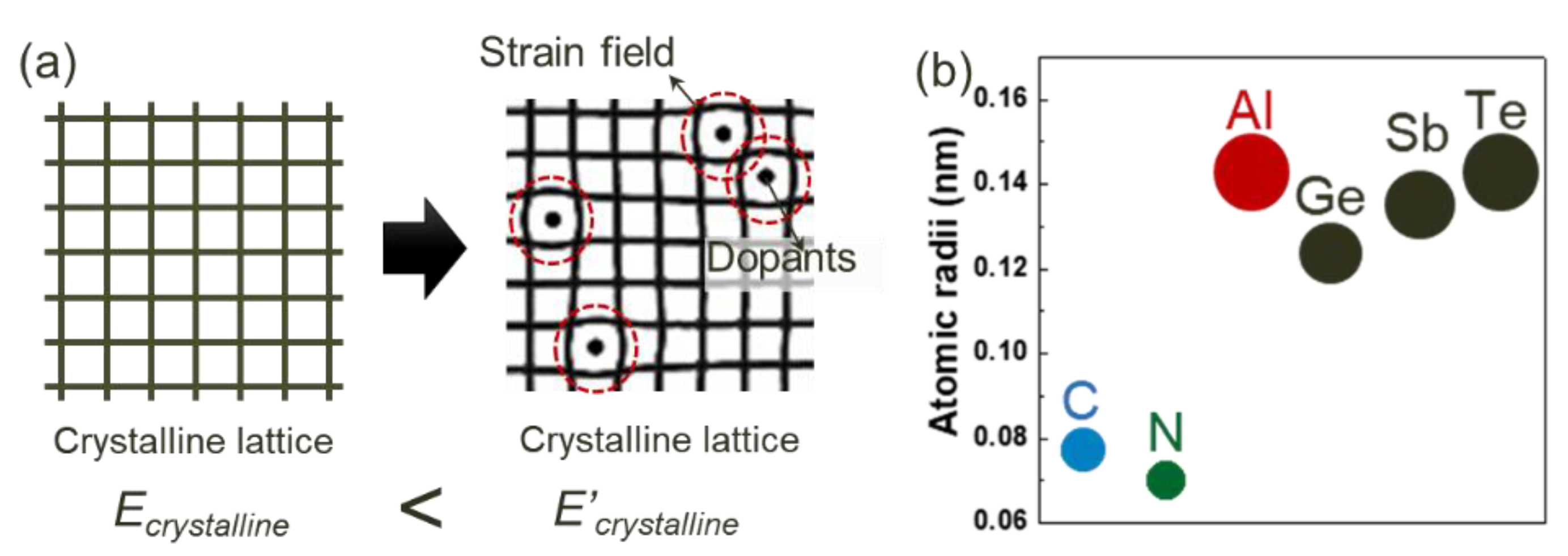
3.1. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Stabilization of Amorphous GST by Doping
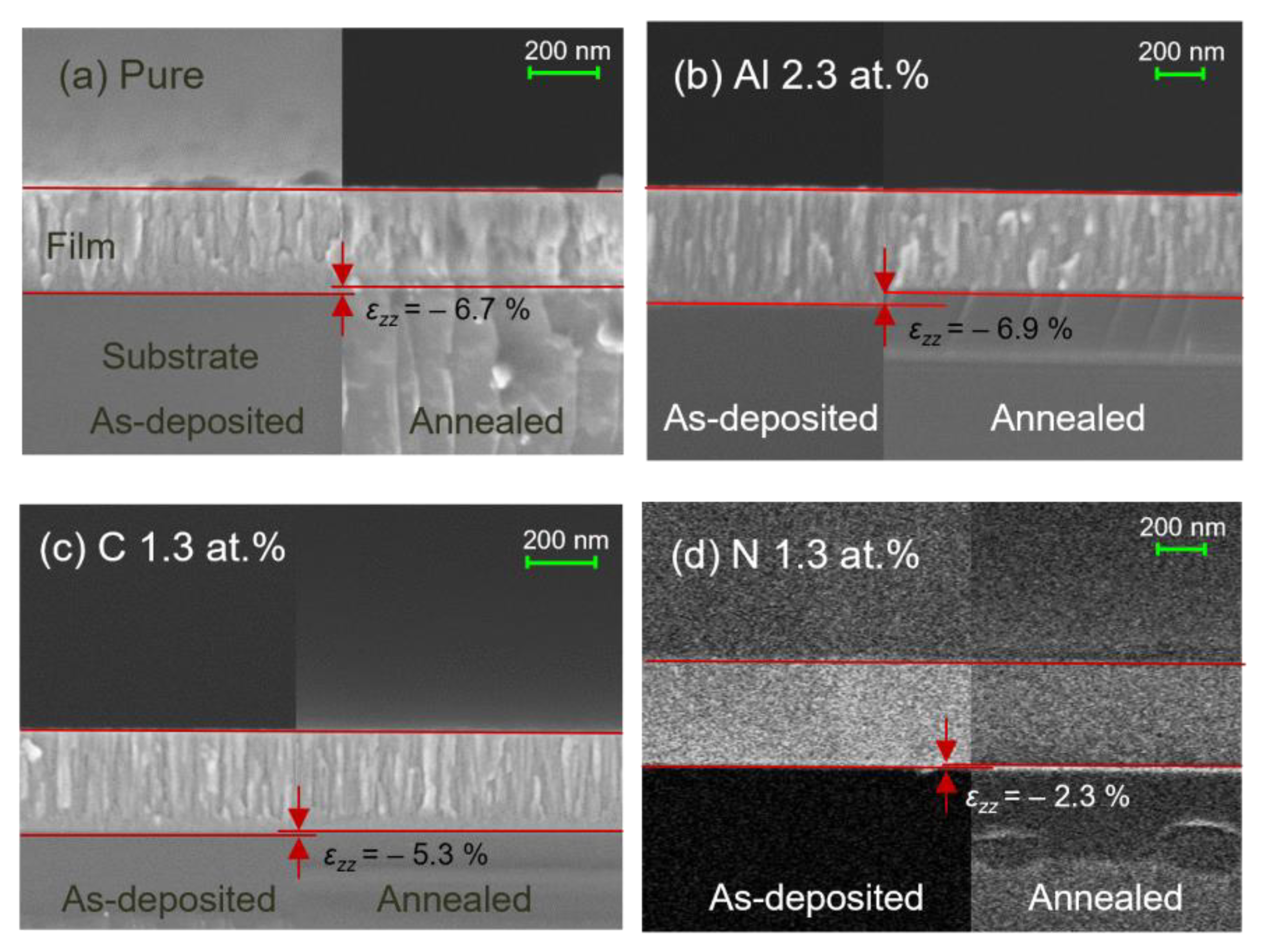
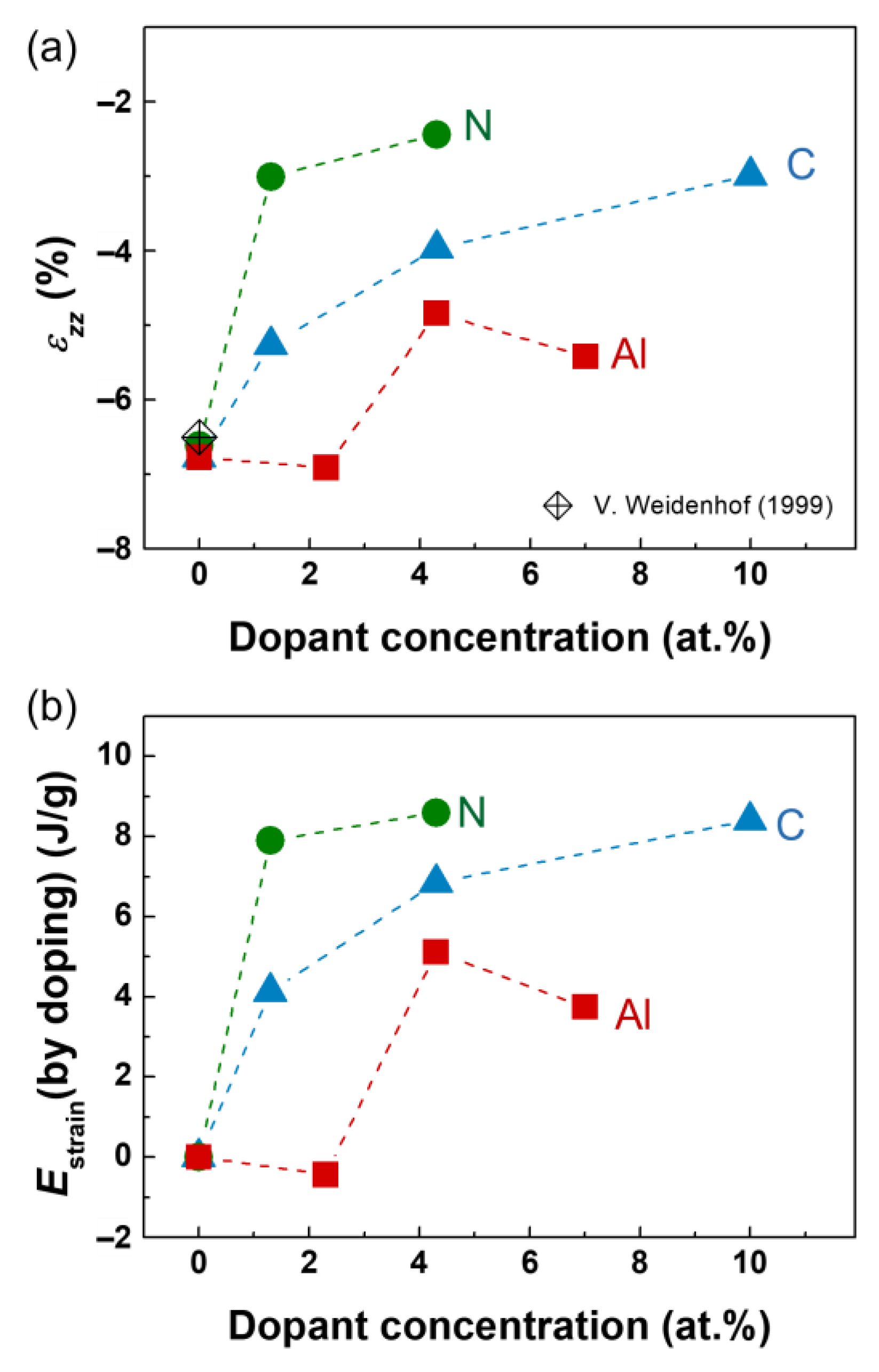
3.2. Elastic Stain and Stress Induced by Crystallization
3.3. Elastic Strain Energy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lencer, D.; Salinga, M.; Grabowski, B.; Hickel, T.; Neugebauer, J.; Wuttig, M. A Map for Phase-Change Materials. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S. Current Status of the Phase Change Memory and Its Future. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting 2003, Washington, DC, USA, 8–10 December 2003; pp. 10.1.1–10.1.4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-F.; Schrott, A.; Lee, M.H.; Raoux, S.; Shih, Y.H.; Breitwisch, M.; Baumann, F.H.; Lai, E.K.; Shaw, T.M.; Flaitz, P.; et al. Endurance Improvement of Ge2Sb2Te5-Based Phase Change Memory. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Memory Workshop, Monterey, CA, USA, 10–14 May 2009; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Liao, Y.B.; Chiang, M.H.; Lin, C.L.; Hsu, W.C.; Chiang, P.C.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Sheu, S.S.; Su, K.L.; et al. Impact of Resistance Drift on Multilevel PCM Design. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuit Design and Technology, ICICDT 2010, Grenoble, France, 2–4 June 2010; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simandan, I.-D.; Sava, F.; Buruiana, A.-T.; Galca, A.-C.; Becherescu, N.; Burducea, I.; Mihai, C.; Velea, A. Influence of Deposition Method on the Structural and Optical Properties of Ge2Sb2Te5. Materials 2021, 14, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-Y.; Cho, J.-Y.; Park, Y.-J.; Joo, Y.-C. Influence of Dopants on Atomic Migration and Void Formation in Molten Ge2Sb2Te5 under High-Amplitude Electrical Pulse. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Térébénec, D.; Bernier, N.; Castellani, N.; Bernard, M.; Jager, J.-B.; Tomelleri, M.; Paterson, J.; Cyrille, M.-C.; Tran, N.-P.; Giordano, V.M.; et al. Innovative Nanocomposites for Low Power Phase-Change Memory: GeTe/C Multilayers. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL) Rapid Res. Lett. 2022, 16, 2200054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.-M.; Yang, T.-Y.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, Y.K.; Horii, H.; Joo, Y.-C. Investigation of Crystallization Behaviors of Nitrogen-Doped Ge2Sb2Te5 Films by Thermomechanical Characteristics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 061904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhout, J.D.; Alverson, D.N.; Ginter, C.; Ravel, B.; Adams, D.P.; Butala, M.M.; Langhout, J.D.; Alverson, D.N.; Ginter, C.; Ravel, B.; et al. Local Structure Effects of Carbon-Doping on the Phase Change Material Ge2Sb2Te5. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 7867–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinga, M.; Carria, E.; Kaldenbach, A.; Bornhöfft, M.; Benke, J.; Mayer, J.; Wuttig, M. Measurement of Crystal Growth Velocity in a Melt-Quenched Phase-Change Material. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.S.P.; Raoux, S.; Kim, S.; Liang, J.; Reifenberg, J.P.; Rajendran, B.; Asheghi, M.; Goodson, K.E. Phase Change Memory. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 2201–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.S.; Noor, N.; Jin, C.; Scoggin, J.; Woods, Z.; Muneer, S.; Ciardullo, A.; Ha Nguyen, P.; Gokirmak, A.; Van Dijk, M.; et al. Phase Change Memory and Its Applications in Hardware Security. In Security Opportunities in Nano Devices and Emerging Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 93–114. ISBN 978-1-138-03577-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wuttig, M.; Salinga, M. Phase-Change Materials: Fast Transformers. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wei, T.; Hu, J.; Li, W.; Ling, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, M.; Song, Z. Universal memory based on phase-change materials: From phase-change random access memory to optoelectronic hybrid storage. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 058504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoux, S. Phase Change Materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2009, 39, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoux, S.; Xiong, F.; Wuttig, M.; Pop, E. Phase Change Materials and Phase Change Memory. MRS Bull. 2014, 39, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Wang, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhao, X. Optimization of a Ge2Sb2Te5-Based Electrically Tunable Phase-Change Thermal Emitter for Dynamic Thermal Camouflage. Materials 2024, 17, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.-Y.; Kim, D.; Park, Y.-J.; Yang, T.-Y.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Joo, Y.-C. The Phase-Change Kinetics of Amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5 and Device Characteristics Investigated by Thin-Film Mechanics. Acta Mater. 2015, 94, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Han, W.; Zhang, X. Ultrafast Dynamics of Different Phase States Ge2Sb2Te5 Film Induced by a Femtosecond Laser Pulse Irradiation. Materials 2022, 15, 6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Lotnyk, A.; Bryja, H.; Gerlach, J.W.; Rauschenbach, B. Structural Transitions in Ge2Sb2Te5 Phase Change Memory Thin Films Induced by Nanosecond UV Optical Pulses. Materials 2020, 13, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Cojocaru-Mirédin, O.; Mio, A.M.; Keutgen, J.; Küpers, M.; Yu, Y.; Cho, J.-Y.; Dronskowski, R.; Wuttig, M. Unique Bond Breaking in Crystalline Phase Change Materials and the Quest for Metavalent Bonding. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiouseloglou, A.; Navarro, G.; Sousa, V.; Persico, A.; Roule, A.; Cabrini, A.; Torelli, G.; Maitrejean, S.; Reimbold, G.; De Salvo, B.; et al. A Novel Programming Technique to Boost Low-Resistance State Performance in Ge-Rich GST Phase Change Memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruitenberg, G.; Ruitenberg, G. Crystallisation Kinetics and Optical Properties of Ge2Sb2Te5; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2001.
- Njoroge, W.K.; Wöltgens, H.-W.; Wuttig, M. Density Changes upon Crystallization of Ge2Sb2.04Te4.74 Films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2002, 20, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencer, D.; Salinga, M.; Wuttig, M. Design Rules for Phase-Change Materials in Data Storage Applications. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2030–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mazzarello, R.; Wuttig, M.; Ma, E. Designing Crystallization in Phase-Change Materials for Universal Memory and Neuro-Inspired Computing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, T.; Jost, P.; Volker, H.; Woda, M.; Merkelbach, P.; Schlockermann, C.; Wuttig, M. Disorder-Induced Localization in Crystalline Phase-Change Materials. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, E.G.; Shi, L.P.; Zhao, R.; Chong, T.C. Investigation on Ultra-High Density and High Speed Non-Volatile Phase Change Random Access Memory (PCRAM) by Material Engineering. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2006, 918, 0918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttig, M.; Bhaskaran, H.; Taubner, T. Phase-Change Materials for Non-Volatile Photonic Applications. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttig, M.; Yamada, N. Phase-Change Materials for Rewriteable Data Storage. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.; Schropp, A.; Solís Céspedes, J.; Afonso, C.N.; Wuttig, M. Rewritable Phase-Change Optical Recording in Ge₂Sb₂Te₅ FIlms Induced by Picosecond Laser Pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 2250–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, I.; Weidenhof, V.; Njoroge, W.; Franz, P.; Wuttig, M. Structural Transformations of Ge2Sb2Te5 Films Studied by Electrical Resistance Measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4130–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttig, M.; Lüsebrink, D.; Wamwangi, D.; Wełnic, W.; Gilleßen, M.; Dronskowski, R. The Role of Vacancies and Local Distortions in the Design of New Phase-Change Materials. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttig, M. Towards a Universal Memory? Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, Q.; Jahan, C.; Toffoli, A.; Navarro, G.; Chandrashekar, S.; Noe, P.; Blachier, D.; Sousa, V.; Perniola, L.; Nodin, J.-F.; et al. Lowering the Reset Current and Power Consumption of Phase-Change Memories with Carbon-Doped Ge2Sb2Te5. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th IEEE International Memory Workshop, Milan, Italy, 20–23 May 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.-H.; Kim, S.-W.; Seo, J.-H.; Lee, H.-Y. Characteristics of Amorphous Ag0.1(Ge2Sb2Te5)0.9 Thin Film and Its Ultrafast Crystallization. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.H.; Kim, M.R.; Seo, H.; Park, J.W.; Yeon, C. Crystal Structure and Microstructure of Nitrogen-Doped Ge2Sb2Te5 Thin Film—IOPscience. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, S.-C.; Choi, J.-H. Density Functional Calculations on the Mechanical Properties of Nitrogen or Oxygen Doped Crystalline Ge2Sb2Te5. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 6113–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoux, S.; Salinga, M.; Jordan-Sweet, J.L.; Kellock, A. Effect of Al and Cu Doping on the Crystallization Properties of the Phase Change Materials SbTe and GeSb. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 044909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Xu, L.; Ahuja, R. Effect of Dopants on the Structure and Properties of Ge2Sb2Te5 Studied by Ab Initio Calculations. Solid State Commun. 2008, 148, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Chen, J.K.; Chen, T.P. Effects of Bi on Crystallisation in Ge–Sb–Te–Bi. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, C.-T.; Kuo, P.-C.; Hsu, W.-C.; Wu, T.-H.; Chen, P.-W.; Chen, S.-C. Ge2Sb2Te5 Thin Film Doped with Silver—IOPscience. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shen, X.; Nie, Q.; Wang, R.; Wu, L.; Lv, Y.; Chen, F.; Fu, J.; Dai, S.; Li, J. Improved Thermal and Electrical Properties of Al-Doped Ge2Sb2Te5 Films for Phase-Change Random Access Memory. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 375302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.; Shieh, H.-P.D. The Influence of Oxygen and Nitrogen Doping on GeSbTe Phase-Change Optical Recording Media Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2004, 107, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.-M.; Cho, J.-Y.; Yang, T.-Y.; Park, E.S.; Joo, Y.-C. Thermomechanical Analysis on the Phase Stability of Nitrogen-Doped Amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5 Films—IOPscience. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 061201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, H.; Dai, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Cui, C.; Miao, L. High Thermoelectric Performance Achieved in Sb-Doped GeTe by Manipulating Carrier Concentration and Nanoscale Twin Grains. Materials 2022, 15, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Han, S.; Kim, D.; Horii, H.; Nam, H.-S. Ab Initio Study on Influence of Dopants on Crystalline and Amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 043705–043710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Youn, Y.; Han, S. Enhanced Amorphous Stability of Carbon-Doped Ge2Sb2Te5: Ab Initio Investigation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 183501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisenko, K.B.; Chen, Y.; Cockayne, D.J.H.; Song, S.A.; Jeong, H.S. Understanding Atomic Structures of Amorphous C-Doped Ge2Sb2Te5 Phase-Change Memory Materials. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4335–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C.A. Relaxation in Liquids, Polymers and Plastic Crystals—Strong/Fragile Patterns and Problems. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1991, 131–133, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, Q.; Jahan, C.; Toffoli, A.; Navarro, G.; Chandrashekar, S.; Noé, P.; Sousa, V.; Perniola, L.; Nodin, J.-F.; Persico, A.; et al. Carbon-Doped Ge2Sb2Te5 Phase-Change Memory Devices Featuring Reduced RESET Current and Power Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2012 European Solid-State Device Research Conference (ESSDERC), Bordeaux, France, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 286–289. [Google Scholar]
- Weidenhof, V.; Friedrich, I.; Ziegler, S.; Wuttig, M. Atomic Force Microscopy Study of Laser Induced Phase Transitions in Ge2Sb2Te5. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 5879–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Ohbayashi, G.; Toriumi, Y.; Mori, Y.; Hashimoto, H. Crystal Structure of GeTe and Ge2Sb2Te5 Meta-Stable Phase. Thin Solid Film. 2000, 370, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target | Power | Gas Flow | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ge2Sb2Te5 | Ge2Sb2Te5 | DC 80 W | Ar: 40 sccm |
| N doped GST | Ge2Sb2Te5 | DC 80 W | Ar: 40 sccm N2: 2–12 sccm |
| Ge2Sb2Te5 | Ge2Sb2Te5 | RF 30 W | Ar: 20 sccm |
| C doped GST | Ge2Sb2Te5 | RF 30 W | Ar: 20 sccm |
| C | RF 11–89 W | ||
| Al doped GST | Ge2Sb2Te5 | RF 30 W | Ar: 20 sccm |
| C Doping | N Doping | Al Doping | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic radii [nm] | 0.077 | 0.070 | 0.143 |
| Structural effect | Interstitial (Free volume occupation) | Substitutional (Atomic position) | |
| Preferred bonds | C-Ge, C-Sb, C-C | Ge-N | Al-Sb, Al-Te |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y. Effects of Doping on Elastic Strain in Crystalline Ge-Sb-Te. Materials 2025, 18, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010132
Cho J-Y, Lee S-Y. Effects of Doping on Elastic Strain in Crystalline Ge-Sb-Te. Materials. 2025; 18(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010132
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Ju-Young, and So-Yeon Lee. 2025. "Effects of Doping on Elastic Strain in Crystalline Ge-Sb-Te" Materials 18, no. 1: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010132
APA StyleCho, J.-Y., & Lee, S.-Y. (2025). Effects of Doping on Elastic Strain in Crystalline Ge-Sb-Te. Materials, 18(1), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010132







