Highlights
- Rapid, eco-friendly modification process of nanocellulose aerogels to produce a CO2 adsorbent.
- The chemical modification of nanocellulose with amine moieties enhances the adsorption capacity by providing many active binding sites that promote interactions between the aerogel and CO2 molecules.
- Scalability and industrial reuse of nanomaterials for their application in CO2 capture and storage technologies.
Abstract
This study evaluated the stability and reusability of amino-functionalized nanocellulose aerogels as CO2-adsorbent materials. The modified aerogels, synthesized via a controlled silylation using N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ethylenediamine (DAMO), demonstrated excellent thermal stability up to 250 °C (TGA) and efficient CO2 adsorption through chemisorption, which was the main adsorption mechanism. The performance of the aerogels was assessed using both adsorption isotherms and the decay pressure technique, revealing that CO2 adsorption capacity increased with higher amino group loading (4.62, 9.24, and 13.87 mmol of DAMO). At 298 K and 4 bar, CO2 adsorption capacity increased proportionally with the amino group concentration, reaching values of 3.17, 5.98, and 7.86 mmol of CO2 g−1 polymer, respectively. Furthermore, over 20 adsorption/desorption cycles, the aerogels maintained 95% CO2 desorption at ambient temperature, indicating their potential for industrial use. These findings highlight the aerogels suitability as stable, reusable materials for large scale CO2 capture and storage technologies.
1. Introduction
CO2 is considered the most important greenhouse gas, due to the continuous increase in atmospheric CO2 concentration from 310 ppm in 1960 to 410 ppm in 2019 [1]. To reduce CO2 concentrations, it is necessary to implement measures such as: reducing deforestation, promoting the use of more efficient energy, using renewable energy sources, and applying carbon capture and storage (CCS) as well as capture and storage utilization (CCU) technologies [2]. The main carbon capture technologies are based on absorption and adsorption operations, membrane separation, and cryogenic distillation technologies, the first two being the most studied [3].
Adsorption technologies using solid porous materials seems to be an efficient alternative for CO2 capture due to its reusable nature, low cost, versatility, and easy operations. The literature reports on different adsorbent materials with high selectivity, including amine-modified silica, amines supported on porous carbon, and/or on other metal oxides such as alumina, zeolites, metal oxides, and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) [4,5]. The development of some of these materials is limited due to drawbacks such as their hydrophilic nature, which requires a drying step prior to use. Therefore, the introduction of hydrophobic sites has been considered to overcome this limitation. In fact, hydrophobic microporous solids are more resistant to the presence of water vapor but tend to absorb less CO2 [4,6]. Furthermore, the high temperatures required for the regeneration of these materials after being used for CO2 adsorption is also a major obstacle [4,6]. To address the limitations presented by inorganic absorbents, during the last decade, the use of bio-based absorbents for CO2 capture has been extensively investigated, emphasizing cellulose nanofibril (CNF) [7,8].
The chemical modification of CNF for CO2 capture using silane coupling agents is considerably investigated [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Gebald et al. (2014) was the first to suggest the use of nanocelluloses as a solid support for CO2 adsorption, achieving an adsorption of 1.39 mmol CO2 g−1 [14].
Similarly, nanocellulose adsorbents were modified using aminosilanes, namely N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropylmethyldimethoxysilane, phthalimide (1,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxoisoindole), N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropylmethyldimethoxysilane, (3-trimethoxysilylpropyl) diethylenediamine, and N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropylmethyldimethoxysilane (AEAPDMS), achieving a CO2 adsorption of between 0.5 and 5 mmol CO2 g−1 [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Valdebenito et al. (2018) reported the synthesis of nanocellulose thin films for CO2 adsorption from corn husks, oat hulls, and kraft pulp, and modified them using 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane, N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane, [3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ethylenediamine, and (3-trimethoxysilylpropyl) diethylenetriamine. The nanocellulose film derived from kraft pulp, modified using [3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ethylenediamine, had the highest CO2 adsorption capacity of 2.11 mmol g−1 at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. It is worth noting that this modified nanocellulose thin film has the highest amine content, but the lowest surface area, demonstrating that chemisorption was the dominant adsorption type [8].
Due to the significant effect of amino loading on CO2 adsorption capacity, it would be valuable to further explore how this variable affects the maximum CO2 reversible adsorption capacity of the aerogel (CO2 adsorption and desorption stages) and its lifespan.
The main objective of this study was to evaluate the maximum reversible CO2 adsorption capacity, stability, and lifespan of amino-functionalized nanocellulose aerogels as CO2 adsorbent materials. By using the decay pressure technique, which allows measurements at pressures higher than atmospheric, to assess the effect of pressure on CO2 adsorption, this approach provides valuable insights into the potential of these materials for long-term use in CCS and CCU technologies.
2. Materials and Methods
The nanocellulose hydrogels were obtained from commercial cellulose (kraft pulp), N-[3-(Trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ethylenediamine (DAMO), (2,2,6,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyl-1-oxyl) TEMPO, NaClO, NaClO2, NaOH, glacial acetic acid, and ethanol, which were purchased from Merck/Sigma Aldrich, Santiago de, Chile.
2.1. Synthesis of Nanocellulose Aerogels
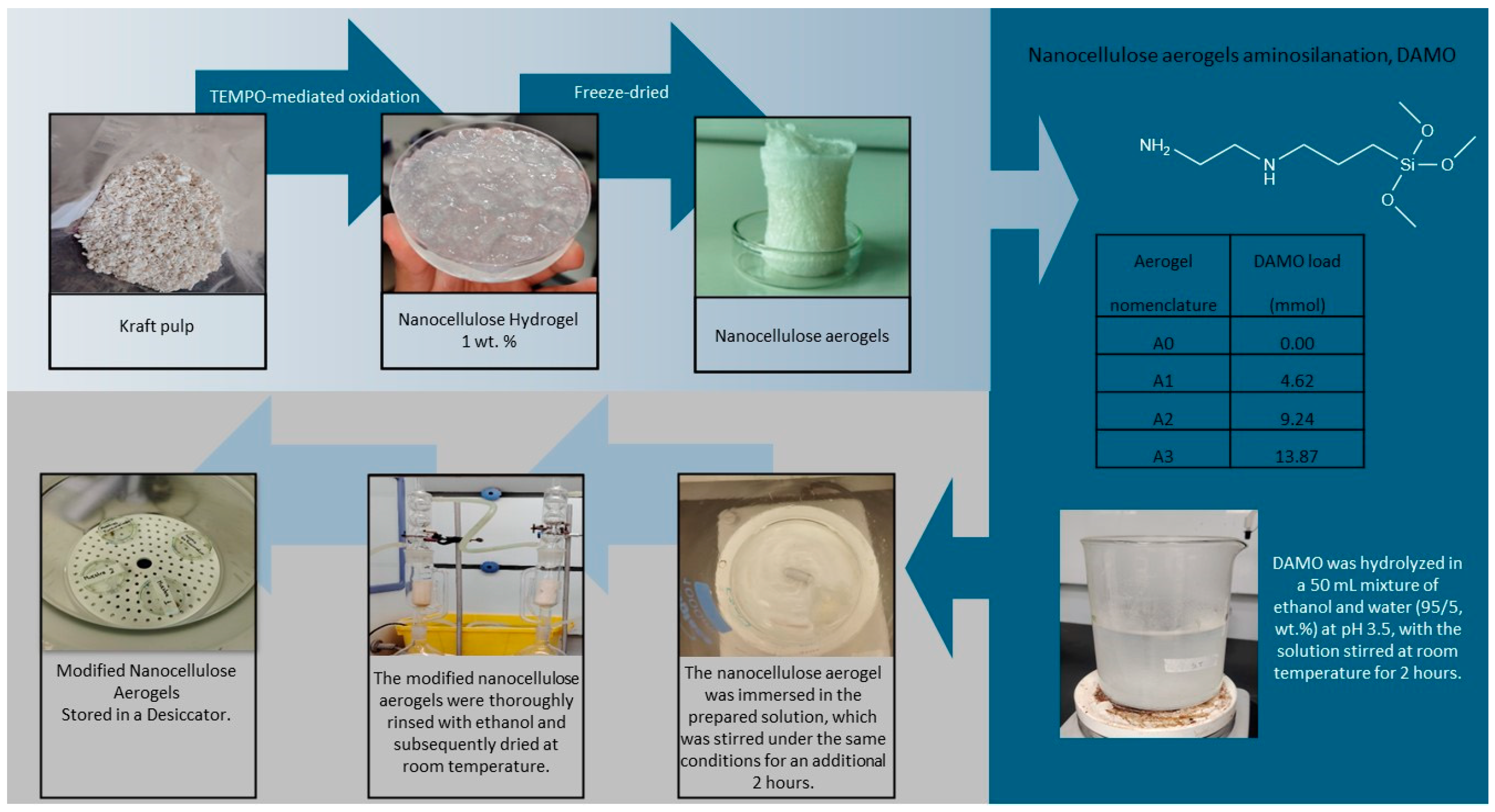
The TEMPO-mediated oxidation of cellulose suspension was carried out according to Saito et al. (2005) with some modifications [15]. The oxidized fibers were dispersed in deionized water with a pulp concentration of 1 wt.% and then homogenized with a high-pressure homogenizer (NS1001L PANDA 2K-GEA) 8 times at a pressure drop of 800 bar to produce nanocellulose hydrogels. To produce nanocellulose aerogels from hydrogels, the freeze-dried technique of an aqueous suspension of nanocellulose was used. This suspension was poured into a mold, then the samples were frozen at –21 °C for at least 24 h to be lyophilized (FreeZone 6, Labconco) at –41 °C and 0.01 mbar for 12–30 h depending on the amount of water to remove. At the end of this process, nanocellulose aerogels were obtained.
2.2. Nanocellulose Aerogel Silylation with N-[3-(Trimethoxysilyl) Propyl] Ethylenediamine (DAMO)
The obtained aerogels were functionalized with 3 different amino group loads, i.e., 4.62, 9.24, and 13.87 mmol portions of DAMO (see Figure 1), which were hydrolyzed in a 50 mL mixture of ethanol/water (95/5, wt.%). The pH was adjusted to 3.5 by adding acetic acid, and the solution was stirred at room temperature for 2 h. Then, nanocellulose aerogel was immersed into this solution. The solution was stirred for 2 h at room temperature. This protocol was repeated for the 3 amino group loadings. The modified nanocellulose aerogels were thoroughly washed with ethanol (soxhlet extraction with ethanol) before being dried at room temperature in a closed system and stored in a desiccator to avoid humidity [8].
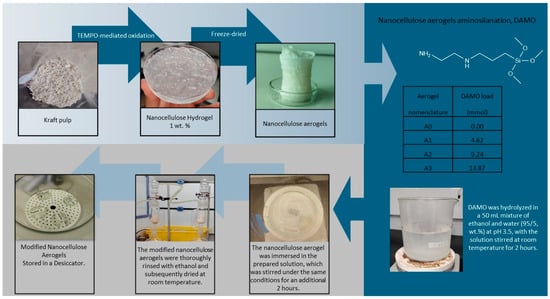
Figure 1.
Reaction scheme preparation of amino-modified nanocellulose aerogels.
2.3. Characterization
The analysis of functional groups in the nanocellulose aerogel was carried out through infrared spectroscopy. The IR measurements were performed with an Agilent Tensor 27 instrument (Malaysia) in Fourier transform mode (FTIR). The Agilent MicroLab PC software (version IQ/OQ, 21 CFR Part 11 compliant) was used for data acquisition. A total of 40 scans were collected across a spectral range of 400 to 4000 cm−1 [7,8].
The carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen contents in the nanocellulose aerogels were quantified using an EA 3000 Elemental Analyzer, from Perkin Elmer, Chile. The analysis was performed in triplicate for each sample. The samples were weighed on a microbalance (Sartorius CP2-P) between 1.5 and 2.5 mg for each sample. Each sample was subsequently placed in a previously tared tin capsule. The elemental analyzer was calibrated using 5-level L-cysteine (0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mg), and the encapsulated sample was loaded into the equipment. The 21 CFR software (version Part 11) was used for data acquisition.
Thermo-gravimetric analysis was performed using a STA 6000 apparatus from Perkin Elmer Chile, at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 up to 800 °C under the nitrogen atmosphere (flow rate = 90 mL min−1). About 30 mg of each sample were analyzed. The Pyris software (version 13.4.0.0036) was used for data acquisition [7,8,13].
Scanning electron microscopy (VP-SEM) analysis was performed. The samples were adhered to the sample holder with double-sided carbon tape. The sample was visualized using a backscatter detector (BSE) in variable pressure without any further sputtering under the following parameters: 10 KV energy, 20 Pa pressure, and WD 10 mm in a scanning electron microscope (Hitachi SU3500, Tokyo, Japan). The images were acquired and analyzed with Hitachi software controller and Image J 1.53k Java 1.8.0_172 Software (Wayne Rasband and contributors, National Institutes of Health, Betheda, MA, USA) [8,9,13].
For the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, an Axis Ultra DLD electron spectrometer was used. Survey scans were recorded using monochromated Al Kα irradiation with a 50 W, 0.1 eV step, and 160 eV analyzer pass energy. Analysis = 700 um × 300 um; charge neutralizer, ON; narrows scans (elemental quantification and peak fitting), pass energy = 20 eV; energy calibration, C 1s C-(C, H) component @285.0 eV [7,8].
2.4. CO2 Adsorption Measurements
The CO2 adsorption was measured through CO2 adsorption isotherms at 273 K (relative pressure: 0.00002–0.02) using Micromeritis Tristar II 3020 equipment, with samples degassed at room temperature for 48 h. The adsorption isotherms were adjusted using the BET, Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models (see Table 1) [7,8,13].

Table 1.
Isotherm models.
The pressure decay technique was used to determine CO2 adsorption capacity. The dual-chamber gas sorption cell followed the method of Koros et al. (1976). Before measurements, 0.7 g−1 g of the sample were weighed and dried for 1 h at 70 °C (343 K). CO2 sorption experiments were carried out at 25 °C (298 K) and at 4 bar. CO2 sorption capacity was calculated using Equations (1) and (2) [16].
Here, wCO2/g is the weight of gas adsorbed by the sample, Pi and Ti give the pressure and the temperature in the gas chamber, respectively, and those parameters at equilibrium are represented as Peq and Teq; Vgc is the gas chamber’s volume, Vp is the volume of the sample, and Vt is the total volume of the sorption cell. The coefficient of compressibility “Z” for CO2 was obtained via the Span–Wagner equations of state [16,17].
2.5. Nanocellulose Aerogel Adsorption/Desorption Cycle Study (TGA)
Adsorption/desorption cycle analysis was performed on a STA 6000 apparatus from Perkin Elmer; it used a flow of 50 mL min−1 of N2 (99.999% purity) for 24 h for sample degassing. Then, a 20 mL min−1 of CO2 flow (99.999% purity) was added and was maintained for 30 min. Subsequently, N2 conditions were resumed for 30 min. The analysis was carried out at room temperature 298 K 20 times.
3. Results
3.1. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis (FTIR)
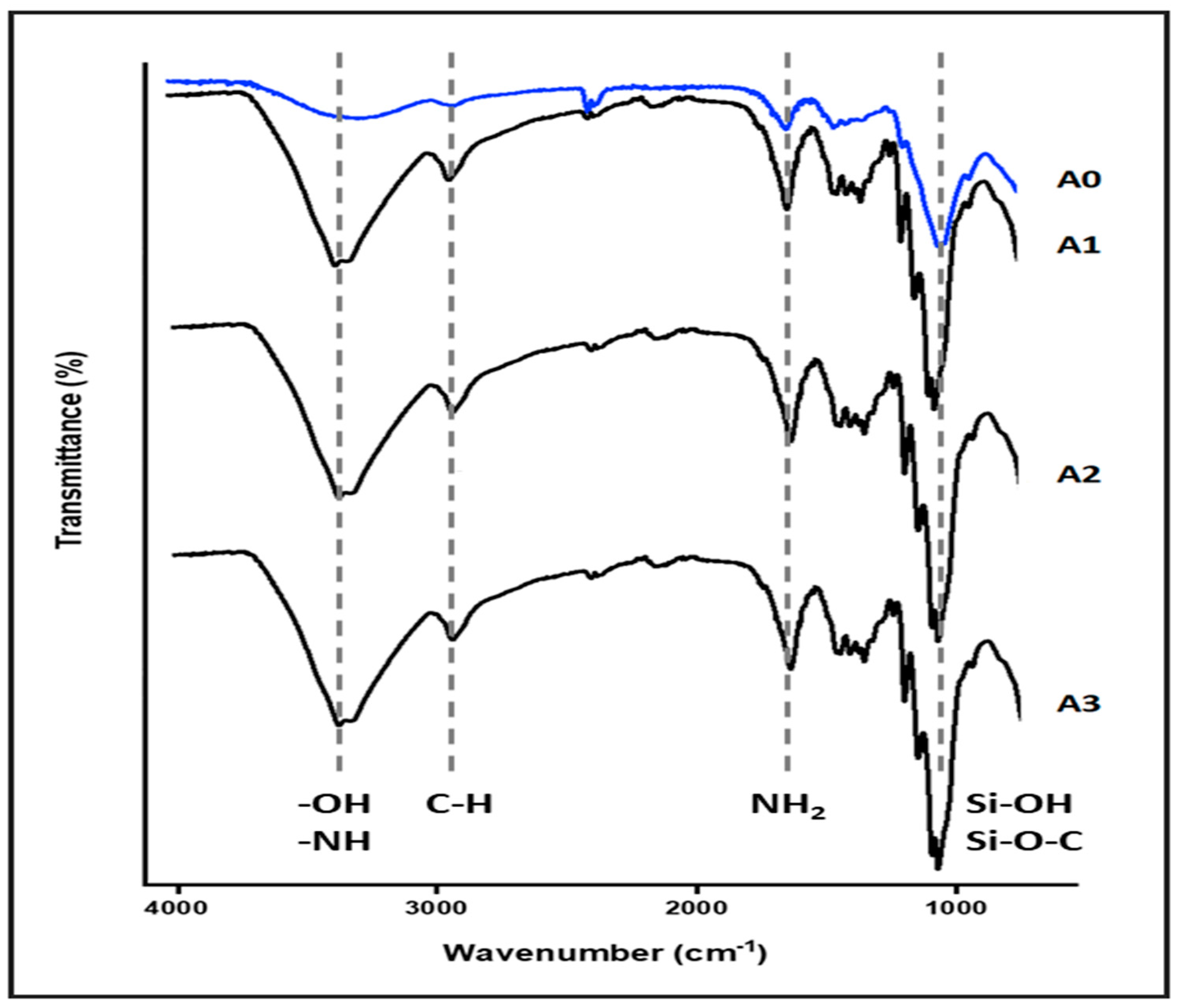
The FTIR spectra of both nanocellulose aerogel unmodified and modified with di-aminosilane are shown in Figure 2. The spectrum of unmodified aerogel (A0) exhibited typical bands for cellulose, such as O-H stretching at 3200 cm−1, C-H stretching at 2900 cm−1, CH2 symmetric bending at 1400 cm−1, and O-H and C-H bending as well as C-C and C-O stretching at 1380, 1310, and 1250 cm−1 respectively.
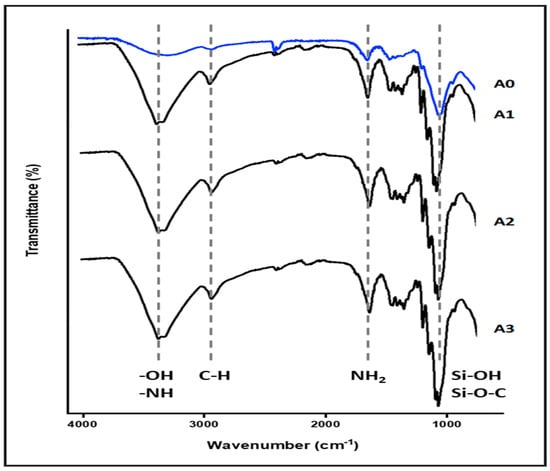
Figure 2.
Nanocellulose aerogel FTIR spectra.
The spectrum of aerogel modified (A1, A2, and A3) showed the successful grafting of di-amino silane on nanocellulose. The band at 2900 cm−1 was assigned to C-H stretching, the O-H stretching at 3200 cm−1 was replaced for the band at 3300 cm−1 assigned to N-H stretching. Also, the band at 1700 cm−1 assigned to N-H flexion and the appearance of signals associated with vibrations from silicon-based linkages were observed at 1240 cm−1, and between 1180 and 700 cm−1 (Si-OH, Si-O-C) [8,9,13,14].
3.2. Elemental Analysis (C, H, and N)
The elemental distribution over the surface was confirmed by elemental analysis (C, H, and N) and are shown in Table 2. The constituents C, O, and N show that the grafting of the amino group took place in the polymer. From Table 2, it can be observed that increasing the amino group content in the aerogel led to an increase in the nitrogen percentage. Interestingly, a linear relationship was observed between the amino group content and nitrogen content due to the grafting of amino groups onto the nanocellulose matrix.

Table 2.
Nanocellulose aerogel elemental analysis.
3.3. Nanocellulose Aerogel Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
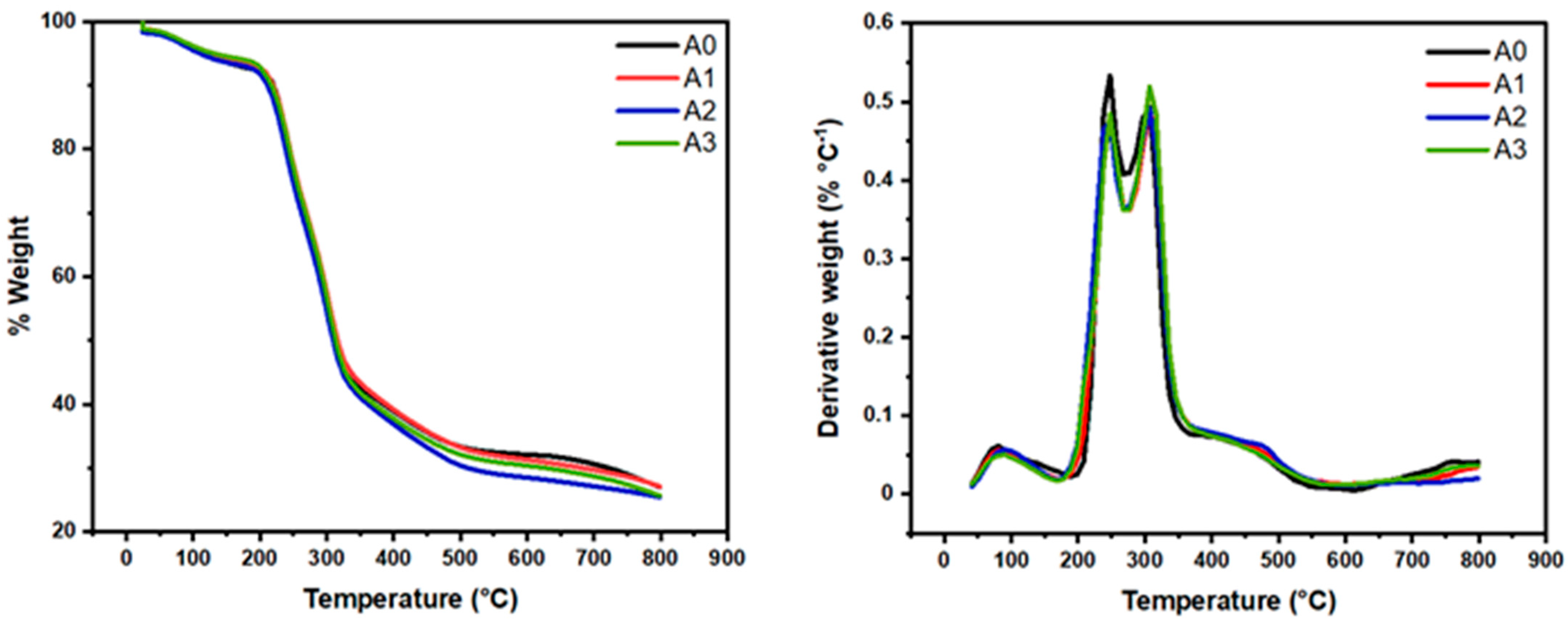
The functionalized aerogels (A1, A2, and A3) were compared to unmodified A0. The weight loss and derivative of weight loss versus temperature plots (Figure 3) for A0 show multiple degradation events. The onset of thermal degradation is practically the same for A0 and A1 aerogels.
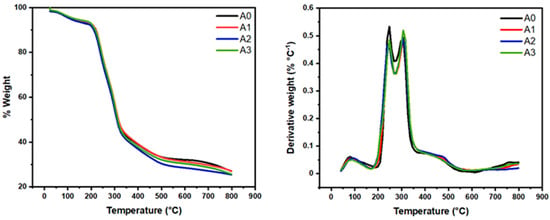
Figure 3.
TGA/DTG curves of nanocellulose aerogels.
All sample thermograms demonstrate two weight loss events preceding the main decomposition step, as can be seen from Figure 3. The first degradation (at between 90 and 100 °C) may be attributed to loss of some bound volatile material, probably residual water. Similarly, the peak around 240 °C in all aerogel’s samples, correspond to hemicelluloses that were not removed during the pulping process. Finally, the peak around 320° in all samples corresponds to the degradation temperatures of the cellulose [7,8,9,14]. The developed nanomaterials (biodegradable materials) exhibited adequate thermal stability up to 240 °C, which is one of the pre-requisites of the CO2 capture materials at the industrial scale.
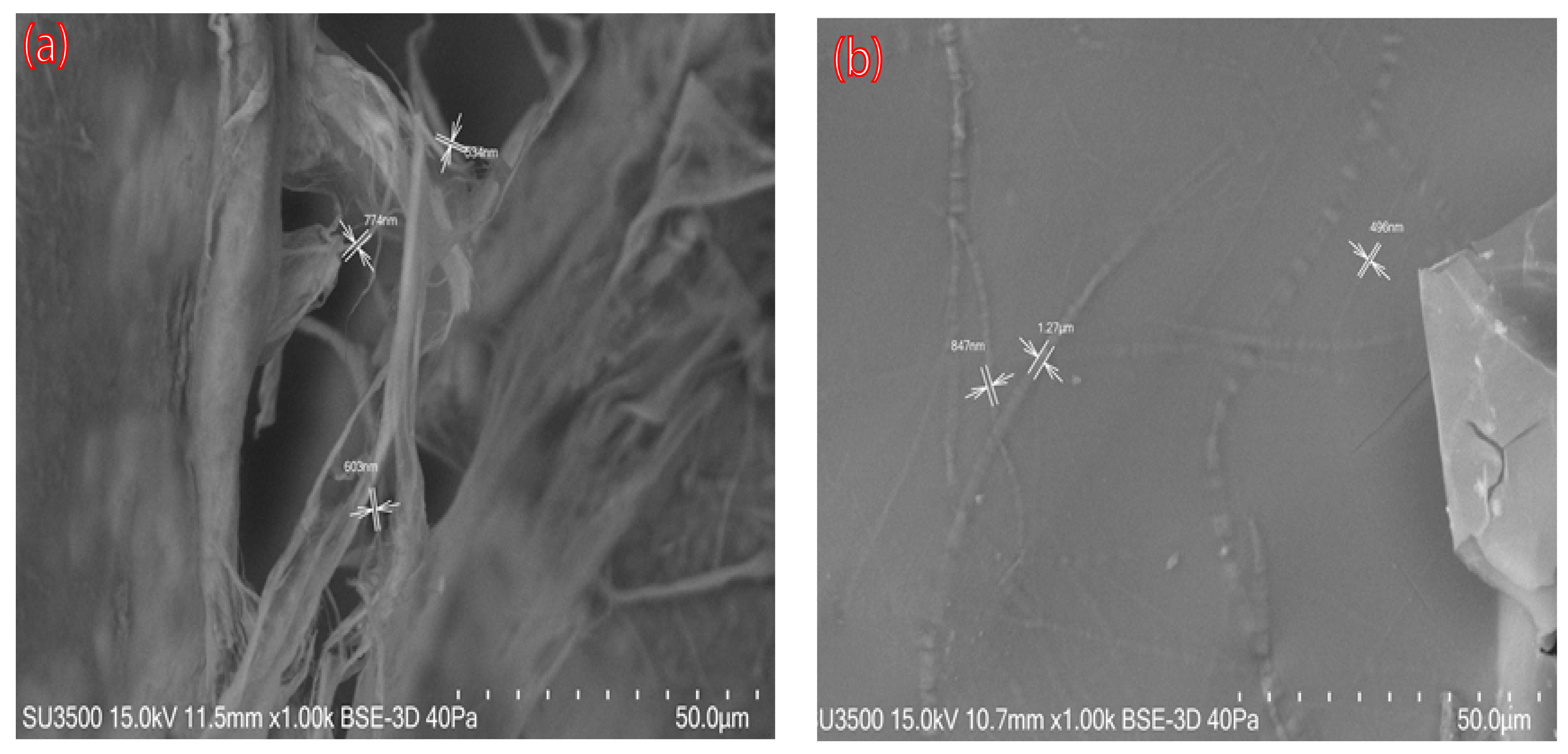
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (VP-SEM)
SEM images of nanocellulose aerogels modified with DAMO A0 and A1 (A1; like A2 and A3 images) are shown in Figure 4. The unmodified aerogel exhibited a random pore structure and disorderly cross-linked CNFs were observed. After amino group grafting, many planar structures with individual CNFs irregularly attached to the cellulose sheet were observed (Figure 4b). These results are in accordance with previously reported studies in the literature [9,13].
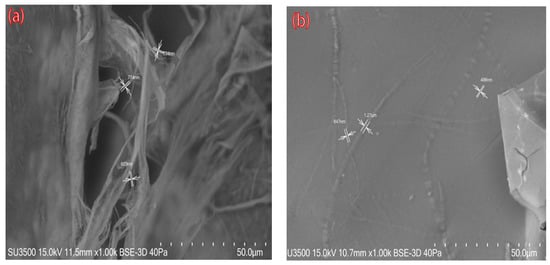
Figure 4.
SEM images of nanocellulose aerogels: (a) A0, unmodified nanocellulose aerogel; (b) A1, DAMO-grafted nanocellulose aerogel.
3.5. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
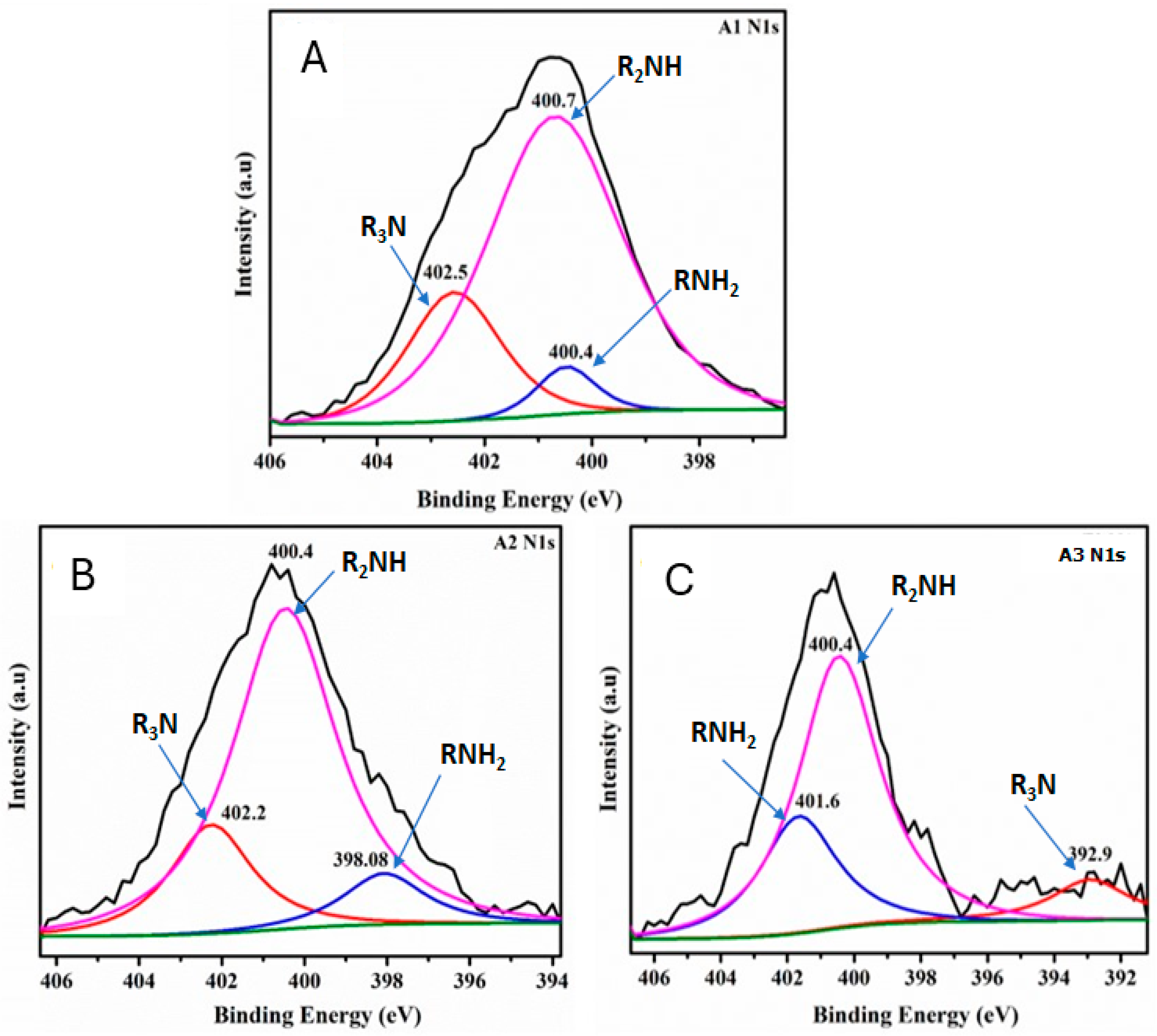
XPS measurements were next performed to further analyze the chemical composition and surface electronic state of the CNF aerogel samples (Figure 5). The binding energy (BE) peaks from the N1s at 398–402 eV appeared in the A1, A2, and A3 samples. The N1s spectrum of modified CNF aerogels (Figure 5A–C) can be fitted to three peaks with the BE at 400 (R2NH and RNH2) and 402.0 (R3N) eV, demonstrating that the DAMO was anchored to the surface of CNF aerogels [7,8,13].
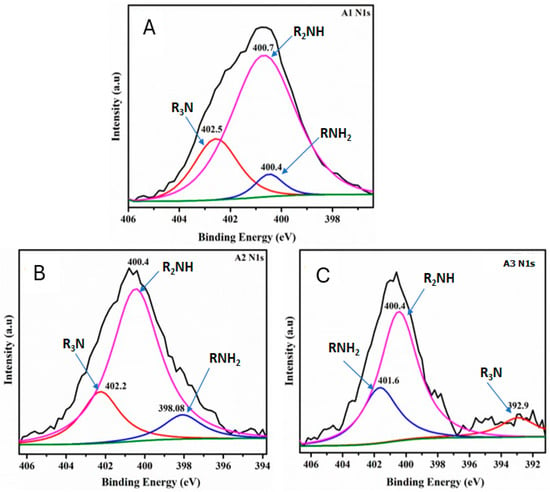
Figure 5.
N1s XPS deconvolution curves for samples A1 (A), A2 (B), and A3 (C). The pink, red, and blue curves represent the R2NH, R3N, and RNH2 groups, respectively, indicating the anchoring of nitrogen-containing functional groups onto the aerogel samples. The black line corresponds to baseline noise, while the green line represents the baseline.
The N1s deconvolution spectrum reveals that as the amino group loading in the aerogels increases (Figure 5A–C), the signal intensity for the R3N and R2NH groups decreases, while the intensity of the RNH2 group increases. Consequently, aerogel A3 exhibits the highest percentage of NH2 groups grafted onto the nanocellulosic matrix, making them available for CO2 capture.
Another finding observed in the N1s deconvolution spectra is that as the amino group content increases (Figure 5A–C), the peak corresponding to the RNH2 group shifts toward the higher binding energy region. This shift can be attributed to changes in local electronegativity caused by the formation of the carbamate ion. The formation of this ion alters the electronic density, resulting in the RNH2 peak moving to higher binding energies.
Additionally, this phenomenon may be influenced by polarization effects, which enhance the reactivity of the RNH2 group toward CO2. This increased reactivity contributes to a higher CO2 adsorption capacity in aerogels modified with a greater amino group content. Such behavior could be explained by the overlap of C-N atomic orbitals. In other words, changes in the amino group charge induce alterations in the electronic density of the covalent bond, facilitating CO2 chemisorption and improving the aerogel’s performance.
3.6. CO2 Absorption Isotherms at 273 K
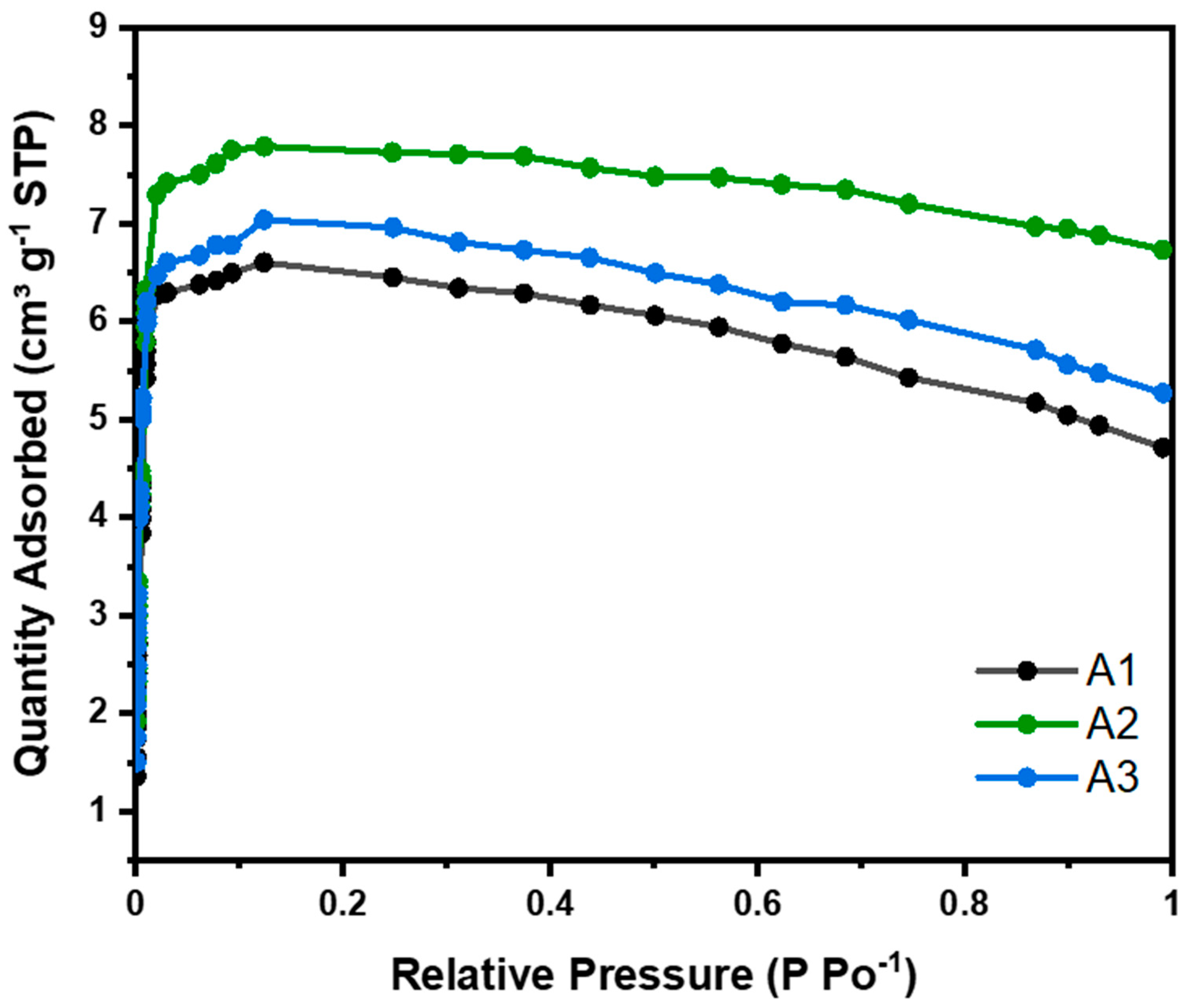
CO2 adsorption isotherms were carried out at 273 K for all samples studied and were classified as type 1 (see Figure 6) in the Brunauer–Deming–Deming–Teller (BDDT) isotherm classification, corresponding to microporous solids. This classification indicates monolayer adsorption, typical of microporous materials with strong adsorbate–adsorbent interactions. To calculate the CO2 adsorption capacity, the experimental data were fitted to Langmuir, BET, Freundlich, and Temkin models (see Supporting Information). The deviation from the typical type 1 isotherm behavior observed in Figure 6 at higher relative pressures, resulting from volume swelling, has been corrected in the linearized adsorption isotherms of CO2 (Langmuir and BET), as presented in the Supplementary Information (Supporting Information).
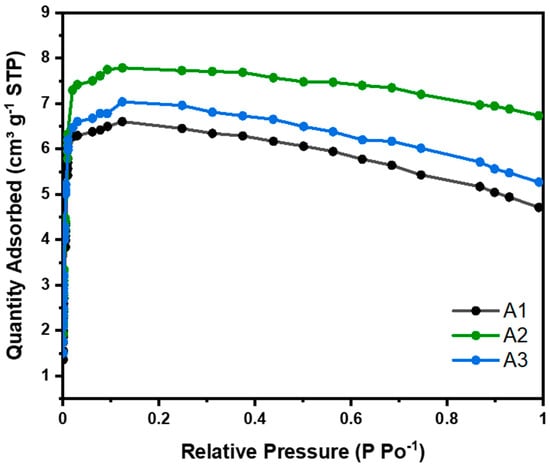
Figure 6.
Nanocellulose aerogel CO2 adsorption isotherms at 273 K.
As the relative pressure increased, the CO2 adsorption capacity reached a maximum at approximately 0.4 bar (micropore filling) and subsequently decreased gradually. This phenomenon has also been reported in other studies and can be attributed to the nonlinearity of the apparent CO2 density with temperature and pressure [18,19].
Table 3 shows some parameters derived from the adsorption isotherms for nanocellulose aerogels at 273 K. Qm corresponds to the amount adsorbed in cm3 g−1, calculated for each linearized isotherm model under standard temperature and pressure conditions. Based on this parameter, the adsorbed amount Xo (mmol g−1) from Table 4 is determined using the ideal gas law equation. R is the correlation coefficient, indicating how well our experimental data fit each model. Based on these criteria, the isotherm classification (BDDT), and the reaction mechanism, the most suitable model is selected. The adsorption isotherms at 273 K are kept at low temperatures to measure the amount of CO2 that can be adsorbed by a material at different relative pressures. At these temperatures, the adsorption is physical, allowing for the evaluation of the material’s maximum adsorption capacity without the effects of chemical reactions at higher temperatures. This technique is very useful for characterizing porous materials and comparing their adsorption capacity under controlled conditions. However, the results obtained at these temperatures may not represent the material behaviors at temperatures more relevant to practical applications, such as CO2 capture in environmental or industrial conditions.

Table 3.
Isotherms parameters.

Table 4.
Nanocellulose aerogels: BET Area, Qm a and X0 b.
For physical adsorption in multilayers, the BET model was used to calculate the amount of CO2 adsorbed. Nanocellulose aerogels modified with different amino-silane loads, i.e., 4.62, 9.24, and 13.87 mmol, showed CO2 adsorptions of 0.21, 0.25, and 0.22 mmol CO2 g−1. At 273 K (see Table 4), this adsorption was due to physisorption. No significant differences were observed in the adsorption of the three aerogels studied. Aerogel A2 showed slightly higher CO2 adsorption, due to having a slightly larger surface area than the others, as can be seen in Table 4.
Baraka et al. (2024), indicate that most cellulose nanofiber aerogels reported in the literature have a BET surface area ranging from 7.1 to 335 m2 g−1. Therefore, our results are in close agreement (see Table 4, 154 m2 g−1) when obtained through the same drying method (freeze-drying) and functionalization method (liquid phase) [20].
3.7. CO2 Absorption Capacity Through Pressure Decay Technique at 298 K and 4 Bar
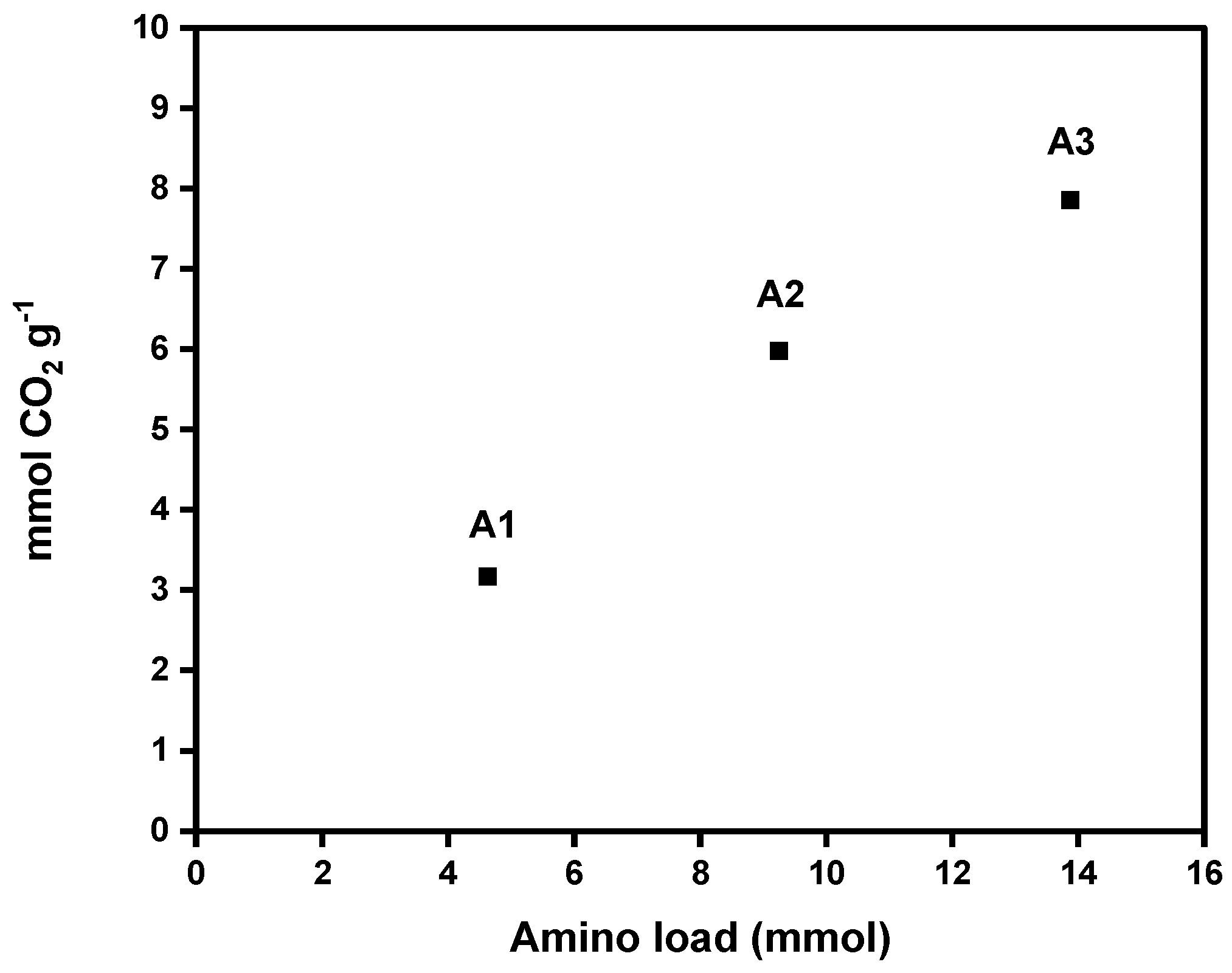
Figure 7 shows CO2 adsorption capacities of each aerogel (A1, A2, and A3). The values obtained for the DAMO-modified nanocellulose aerogels ranged from 3.17 to 7.86 mmol CO2 g−1 at 25 °C, proving a significant increase in CO2 adsorption with an increase in amino group content in the nanocellulose aerogel. These results are promising. The literature reports CO2 adsorption capacities of amine-modified cellulose nanofiber (CNF) aerogels ranging from 1.39 to 2.4 mmol g−1 (Table 5). These values are lower than those achieved in the present work at the same adsorption temperature (see Table 5). Sepahvand et al. (2020) obtained 5.2 mmol g−1 of CO2 adsorption from CNF aerogels modified with phthalimide (1.5% phthalimide content) under the same freeze-drying and liquid phase functionalization methods, using a nonlinear amine (phthalimide). However, this value is lower than the adsorption capacities achieved by the samples A2 and A3, which attained CO2 capture values of 5.98 and 7.86 mmol g−1, respectively.
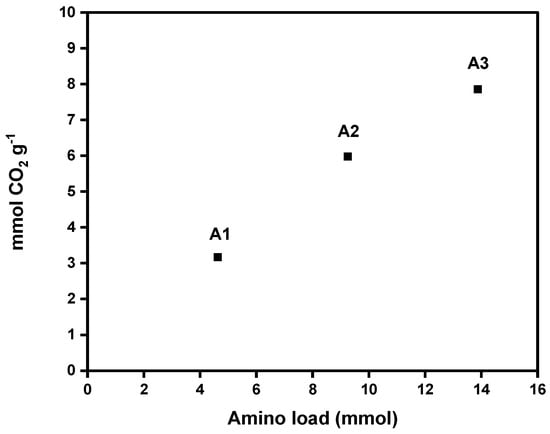
Figure 7.
Amino group load effect on the CO2 adsorption capacity of nanocellulose aerogels calculated by the pressure decay technique.

Table 5.
CO2 adsorption capacity of various cellulosic materials.
Moreover, it can be observed that the obtained results are higher than the adsorption capacities of other typical adsorbents used in CO2 capture. For example, the APTS-modified MCM-41 reached a value of 1.33 mmol CO2 g−1 [21]. Furthermore, MCM-41 exhibited a higher BET surface area (1602 m2 g−1) than the nanocellulose aerogels studied in the present work.
The high adsorption values obtained are mainly explained by the chemisorption mechanisms between the amino groups and CO2 molecules. The reaction of CO2 with DAMO involves a direct reaction between the carbon atom of CO2 and the nitrogen atom of the amine, forming a covalent bond [22,23]. Therefore, the chemical modification of nanocellulose with amine moieties enhances the adsorption capacity by providing many active binding sites that promote interactions between the aerogel and CO2 molecules [22,23]. The molar ratio of amine introduced could also significantly influence the CO2 adsorption efficiency of modified nanocellulose aerogels. A high concentration of amine promotes a high adsorption capacity [24].
This trend is consistent with the results obtained from the XPS analysis proving the higher % NH2 where a linear tendency was observed. With a higher amino group loading, there was an increased nitrogen content (amino group according to the supported amine reaction mechanism via carbamate ions) that was grafted onto the nanocellulosic matrix. Additionally, there was also greater CO2 adsorption capacity measured at room temperature. Regarding our results, a significant increase in CO2 adsorption is observed with a slight increase in DAMO loading (4.62, 9.24, and 13.87 mmol of DAMO, respectively). The pressure decay technique can be used at different temperatures and pressures, allowing for a simulation closer to real operating conditions. It is useful for studying the kinetics of adsorption and desorption and the adsorption capacity [20].
Unlike most studies reported in the literature, this research uses the pressure decay technique to determine the maximum reversible adsorption CO2 capacity of amino-functionalized CNF aerogel. This method allows for pressures above atmospheric levels, making it possible to evaluate how increased pressure affects the adsorbent capacity at room temperature. This approach more accurately simulates the higher-pressure conditions typical of industrial carbon capture and utilization processes. The high CO2 adsorption capacity of sample A3 (with the biggest amino group load), compared to literature review studies (see Table 5), is largely attributed to raising the pressure from around 1 bar to 4 bar [25]. The higher CO2 pressure enhanced CO2 density and its interaction with amino groups on the aerogel surface, promoting efficient carbamate ion formation and enabling greater CO2 capture.
3.8. Nanocellulose Aerogel Lifespan
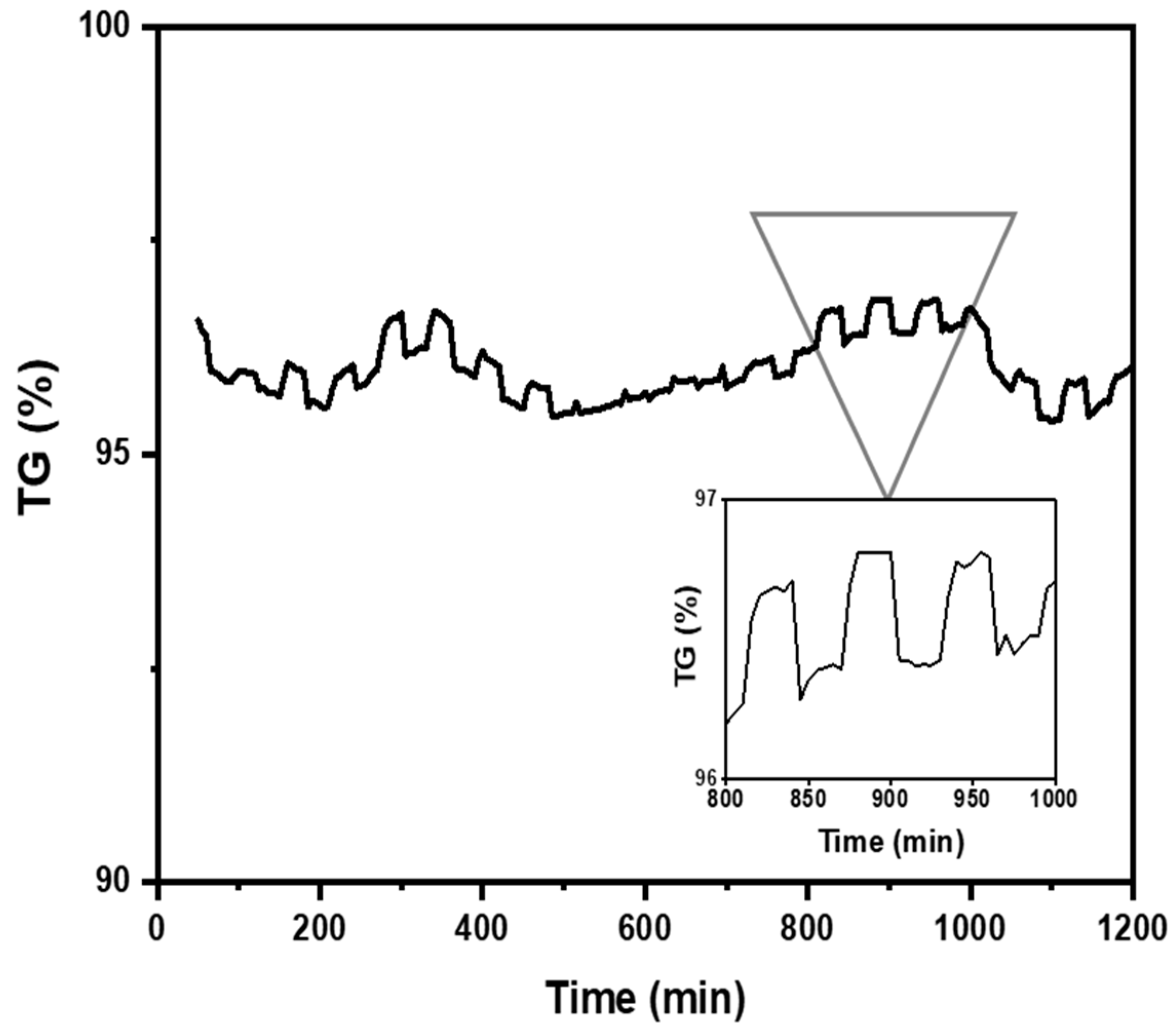
The study of CO2 adsorption/desorption cycles was conducted using the aerogel that exhibited the highest CO2 adsorption, specifically sample A3. Figure 8 shows that the CO2 desorption was fast and was complete after 30 min. A total of 95 wt.%. of the absorbed CO2 was desorbed during 20 adsorption/desorption cycles (reversible adsorption) measured at room temperature (298 K) in the thermobalance (TGA). It can be concluded that this number of cycles is likely higher since after 20 cycles, the aerogel continued to exhibit the same behavior as in the first cycle. Gebald et al. (2011) and Zhu et al. (2011) reported that CO2 desorption was fast and was complete after 30 min for a similar substrate. More than 85% of the CO2 was desorbed within 19 min at a packed bed temperature of below 80 °C [7,13,14].
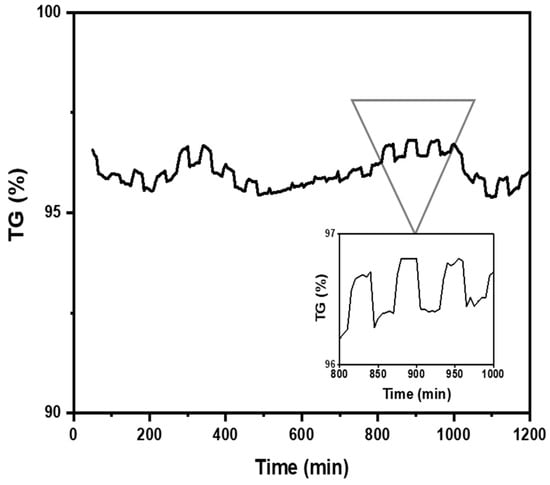
Figure 8.
Nanocellulose aerogel (A3) adsorption/desorption cycles at 298 K and 1 bar determined by thermogravimetric analysis.
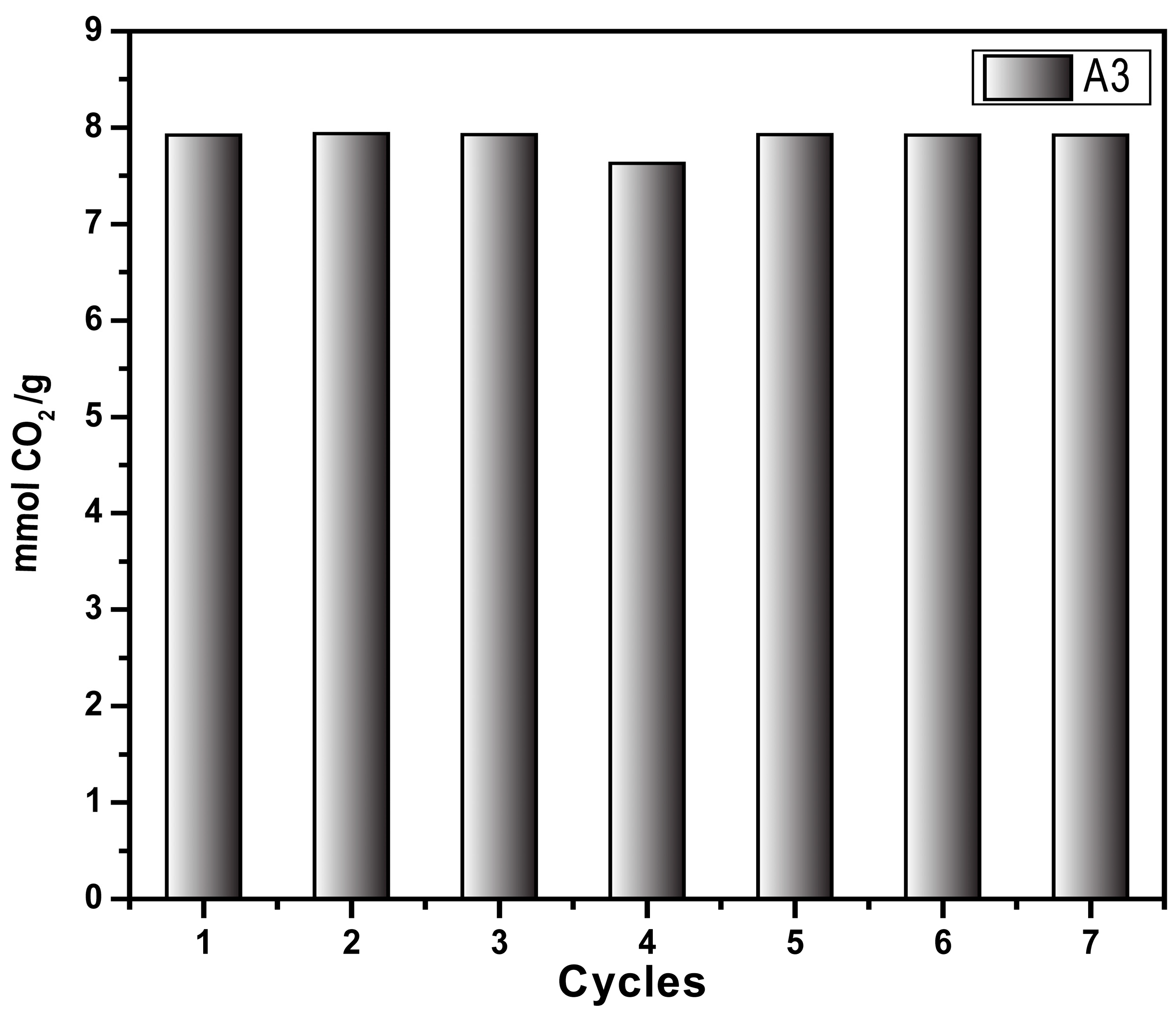
Figure 9 shows the sorption/desorption test (pressure decay technique) using the same sample (A3) across seven cycles. The sample was regenerated by heating to 70 °C for 20 min at the end of each sorption test. The results prove that the sample retains the CO2 sorption capacity for up to seven cycles; this could likely be higher as the retained sample exhibited the same sorption capacity as in the first cycle, demonstrating the recyclability of the synthesized material. These results agree with results obtained from the adsorption/desorption cycles at 298 K determined by thermogravimetric analysis. Both techniques demonstrated the stability and reusability of the synthesized materials, which is one of the pre-requisites of the CO2-capture materials at the industrial scale.
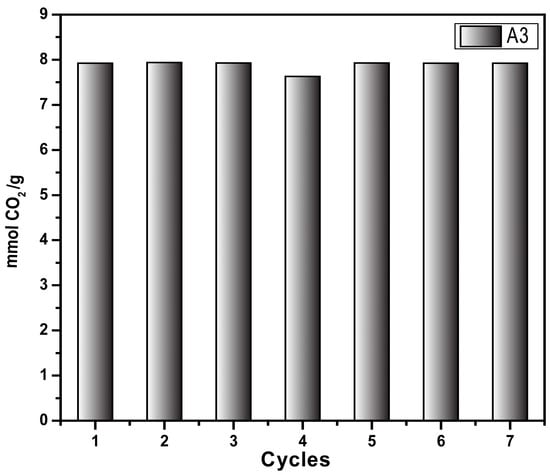
Figure 9.
CO2 capture cycle of aerogel A3 at 318.15 K and 4 bar through the pressure decay technique.
4. Conclusions
This study highlights the potential of DAMO-modified nanocellulose aerogels for scalable CO2 capture and storage applications. The predominant chemisorption mechanism, characterized by the interaction between CO2 molecules and amino groups to form covalent bonds, was found to be highly effective for CO2 adsorption. A significant increase in CO2 adsorption was observed with a slight increase in DAMO loading (4.62, 9.24, and 13.87 mmol of DAMO, respectively), ranging from 3.17 to 7.86 mmol CO2 g−1 at 298 K (25 °C) and 4 bar. The use of the decay pressure technique allowed the study to examine the effect of pressure on CO2 adsorption at pressures higher than atmospheric conditions, thus simulating real industrial conditions more closely.
The nanocellulose aerogels demonstrated excellent thermal stability at up to 240 °C and consistent performance across adsorption/desorption cycles, desorbing 95% of the adsorbed CO2 over 20 cycles at room temperature. This stability and reusability underscore their practicality for repeated use in industrial CO2 capture processes. These results support the feasibility of utilizing these biodegradable materials in scalable CO2 capture technologies, making them promising candidates for sustainable and efficient carbon capture alternatives.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ma18020243/s1, Figure S1: Adsorption isotherm A1, Figure S2: Adsorption isotherm A1 in BET coordinates, Figure S3: Adsorption isotherm A1 in Langmuir coordinates, Figure S4: Adsorption isotherm A1 in Freundlich coordinates, Figure S5: Adsorption isotherm A1 in Temkin coordinates, Figure S6: Adsorption isotherm A2, Figure S7: Adsorption isotherm A2 in BET coordinates, Figure S8: Adsorption isotherm A2 in Langmuir coordinates, Figure S9: Adsorption isotherm A2 in Freundlich coordinates, Figure S10: Adsorption isotherm A2 in Temkin coordinates, Figure S11: Adsorption isotherm A3, Figure S12: Adsorption isotherm A3 in BET coordinates, Figure S13: Adsorption isotherm A3 in Langmuir coordinates, Figure S14: Adsorption isotherm A3 in Freundlich coordinates, Figure S15: Adsorption isotherm A3 in Temkin coordinates, Figure S16: Adsorption isotherm A1, A2 and A3; Table S1: Adsorption isotherm data A1, Table S2: BET report A1, Table S3: Langmuir Report A1, Table S4: Freundlich Report A1, Table S5: Temkin Report A1, Table S6: Adsorption isotherm data A2, Table S7: BET report A2, Table S8: Langmuir Report A2, Table S9: Freundlich Report A2, Table S10: Temkin Report A2, Table S11: Adsorption isotherm data A3, Table S12: BET report A3, Table S13: Langmuir Report A3, Table S14: Freundlich Report A3, Table S15: Temkin Report A3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.V. and L.A.; methodology, E.E. and M.N.; software, F.S.; validation, O.V., C.A. and V.R.; formal analysis, F.V.; investigation, F.V.; resources, F.V.; data curation, C.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, F.V. and S.L.; writing—review and editing, L.A. and M.N.; visualization, A.N.; supervision, R.M.; project administration, F.V.; funding acquisition, F.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the ANID Subvención a la Instalación en la Academia año 2021 SA77210113.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks to the Proyect Subvención a la Instalación en la Academia año 2021 SA77210108, CIPA, ANID Regional, R23F0005, and Project FAA2024 of the Universidad Católica de la santísima Concepción.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Climate Change. Synthesis Report, IPCC. 2023. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/syr/ (accessed on 26 October 2024).
- IEA. IEA Energy Technology Perspectives 2020. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/energy-technology-perspectives-2020 (accessed on 26 October 2024).
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, S.; Kothandaraman, J.; Snowden-Swan, L.; Hefty, M.; Whitfield, M. Emerging Technologies Review: Carbon Capture and Conversion to Methane and Methanol; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.A.; Byun, J.; Yavuz, C.T. Carbon Dioxide Capture Adsorbents: Chemistry and Methods. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2017, 10, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardakhti, M.; Jafari, T.; Tobin, Z.; Dutta, B.; Moharreri, E.; Shemshaki, N.S.; Suib, S.; Srivastava, R. Trends in Solid Adsorbent Materials Development for CO2 Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34533–34559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.A.; Leo, C.P. A review on the emerging applications of cellulose, cellulose derivatives, and nanocellulose in carbon capture. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, M.; Jang, J.; Han, M.; Moon, Y.; Kim, J.; You, J.; Li, S.; Park, T.; Kim, J. Amino-functionalized nanocellulose aerogels for the superior adsorption of CO2 and separation of CO2/CH4 mixture gas. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdebenito, F.; García, R.; Cruces, K.; Ciudad, G.; Chinga-Carrasco, G.; Habibi, Y. CO2 adsorption of surface-modified cellulose nanofibril films derived from agricultural wastes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12603–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Dai, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S. Effects of amine loading on the properties of cellulose nanofibrils aerogel and its CO2 capturing performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jia, P.; Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z. The aminosilane functionalization of cellulose nanofibrils and the mechanical and CO2 adsorption characteristics of their aerogel. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 2874–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Aminosilane-grafted spherical cellulose nanocrystal aerogel with high CO2 adsorption capacity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16716–16726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, M.; Zhang, J. Gas phase synthesis of aminated nanocellulose aerogel for carbon dioxide adsorption. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepahvand, S.; Jonoobi, M.; Ashori, A.; Gauvin, F.; Brouwers, H.J.; Oksman, K.; Yu, Q. A promising process to modify cellulose nanofibers for carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebald, C.; Wurzbacher, J.A.; Tingaut, P.; Zimmermann, T.; Steinfeld, A. Amine-Based Nanofibrillated Cellulose as Adsorbent for CO2 Capture from Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9101–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Ion-exchange behavior of carboxylate groups in fibrous cellulose oxidized by the TEMPO-mediated system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 61, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, W.J.; Paul, D.R. Design considerations for measurement of gas sorption in polymers by pressure decay. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. Ed. 1976, 14, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, M.J. Fast and accurate core analysis by the full-immersion pressure-pulse decay: Part 1—Theory. SPE Res. Eval. Eng. 2020, 23, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Sang, S.; Liu, T.; Zheng, S. Effects of pore structure changes on the CH4 adsorption capacity of coal during CO2-ECBM. Fuel 2022, 330, 125529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K. High-Pressure adsorption of supercritical methane and carbon dioxide on Coal: Analysis of adsorbed phase density. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraka, F.; Labidi, J. The emergence of nanocellulose aerogels in CO2 adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, G.D.; Moreno, M.S.; Piqueras, C.M.; Benedictto, G.P.; Pereyra, A.M. Alternative Synthesis of MCM-41 Using Inexpensive Precursors for CO2 Capture. Inorganics 2023, 11, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J. Carbon Capture; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-1-4614-2215-0 (accessed on 26 October 2024).
- Jia, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, H. Comparison of characteristics of the cellulose nanocrystal aerogels aminosilane-functionalized through gas-phase reaction. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titinchi, S.J.; Piet, M.; Abbo, H.S.; Bolland, O.; Schwieger, W. Chemically Modified Solid Adsorbents for CO2 Capture. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 8153–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, M.; Gönel, A.G.; Bozbag, S.E.; Erkey, C. Thermodynamics of Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide on Various Aerogels. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 21, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).