T700 Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composite Material Hygrothermal Aging Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Establishing Model for the Mechanical Performance Hygrothermal Aging
2.1. Moisture Absorption and Diffusion Characteristics
2.2. Model for Mechanical Performance Under Hygrothermal Aging
3. Experimental Section
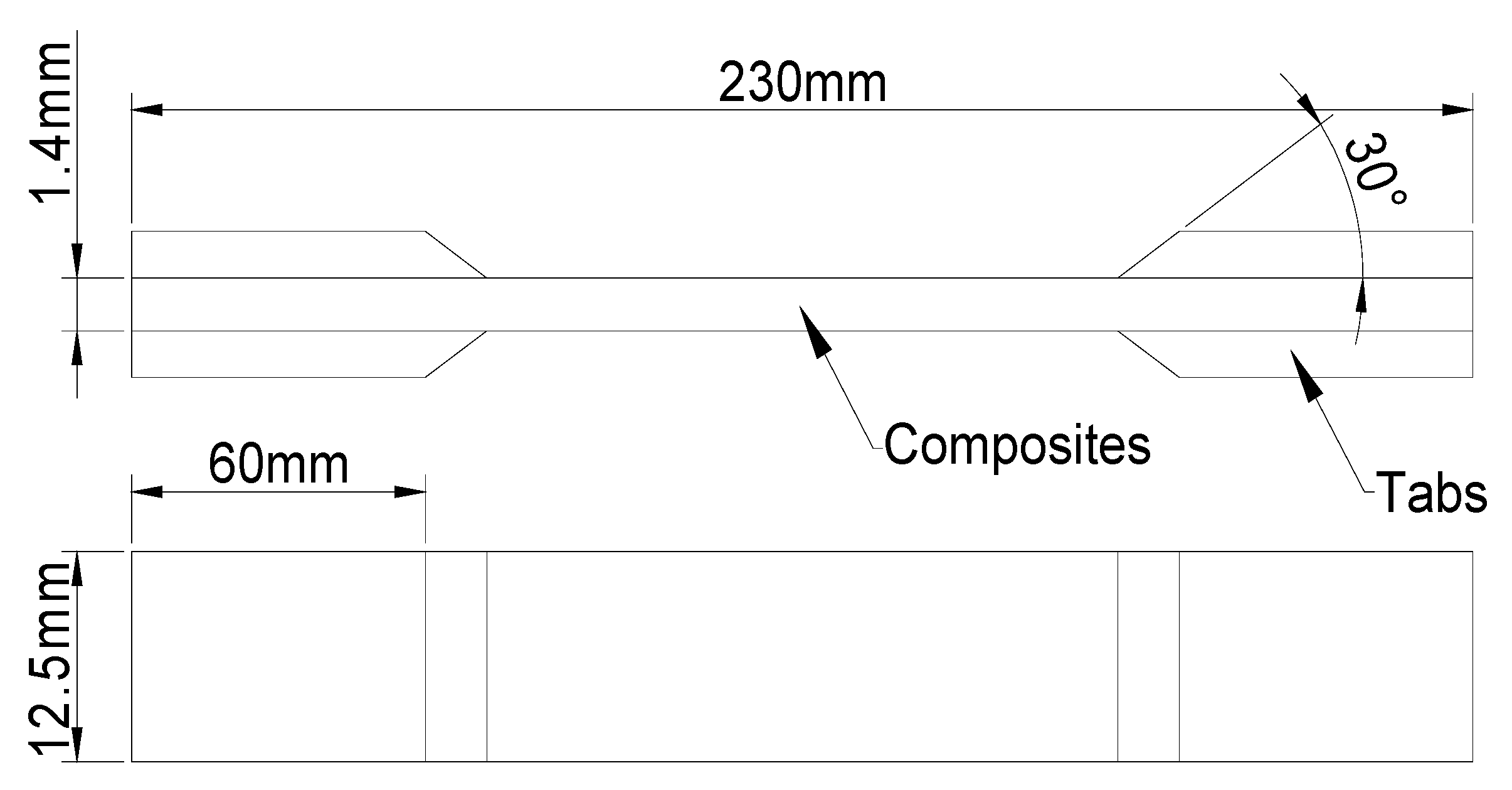
3.1. Experimental Materials
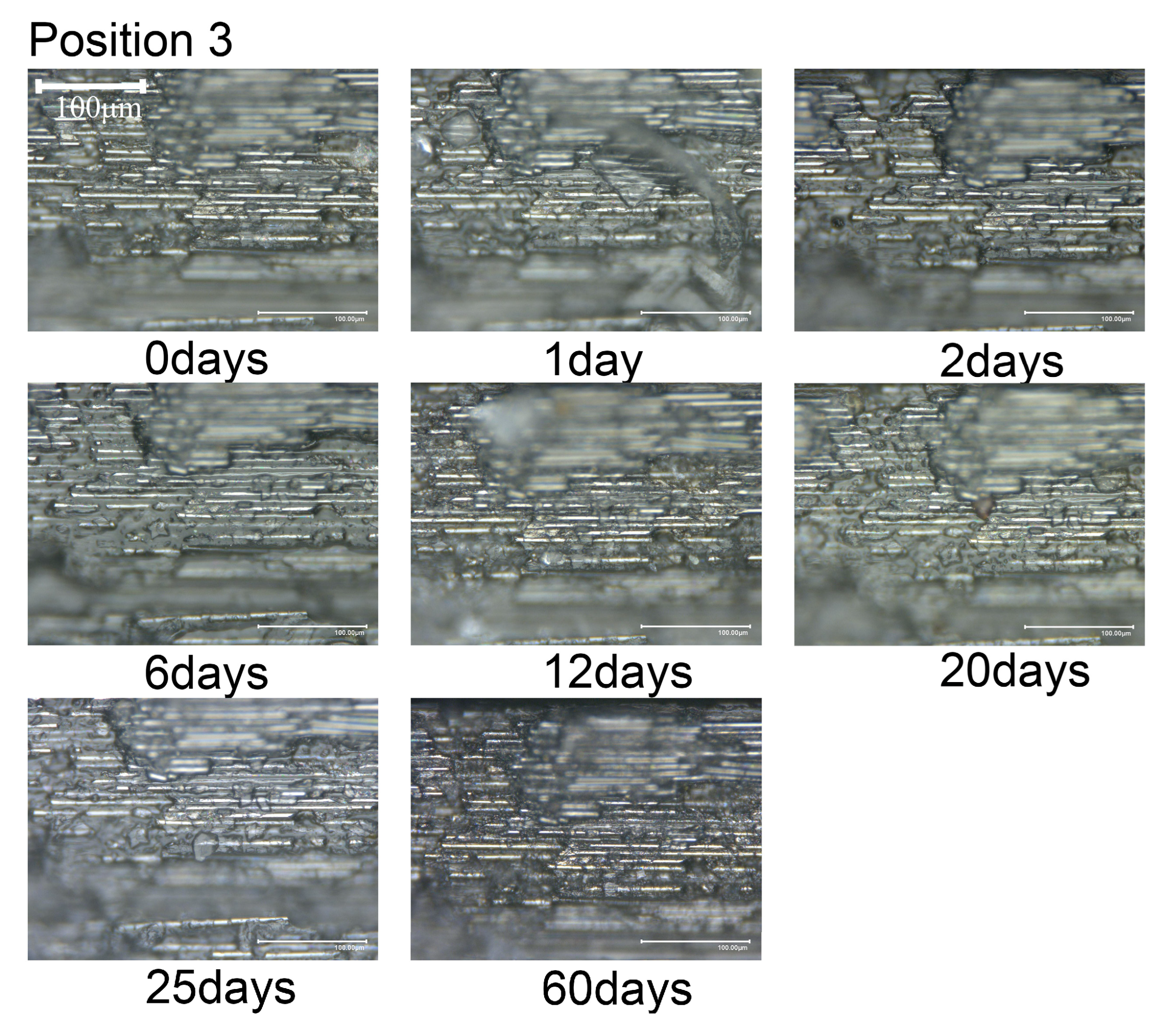
3.2. Composite Material Seawater Immersion Experiment
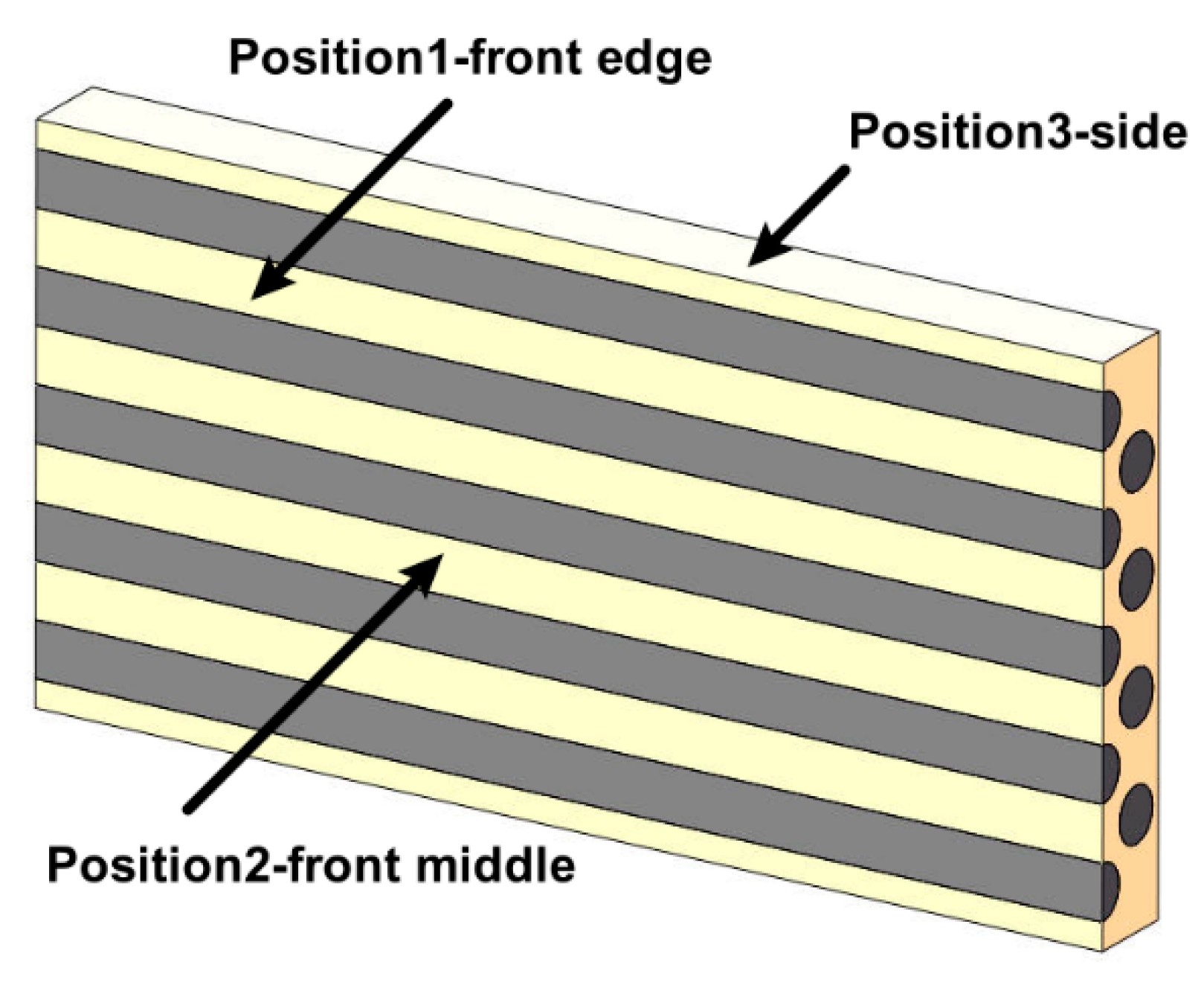
3.3. Mechanical Performance Testing
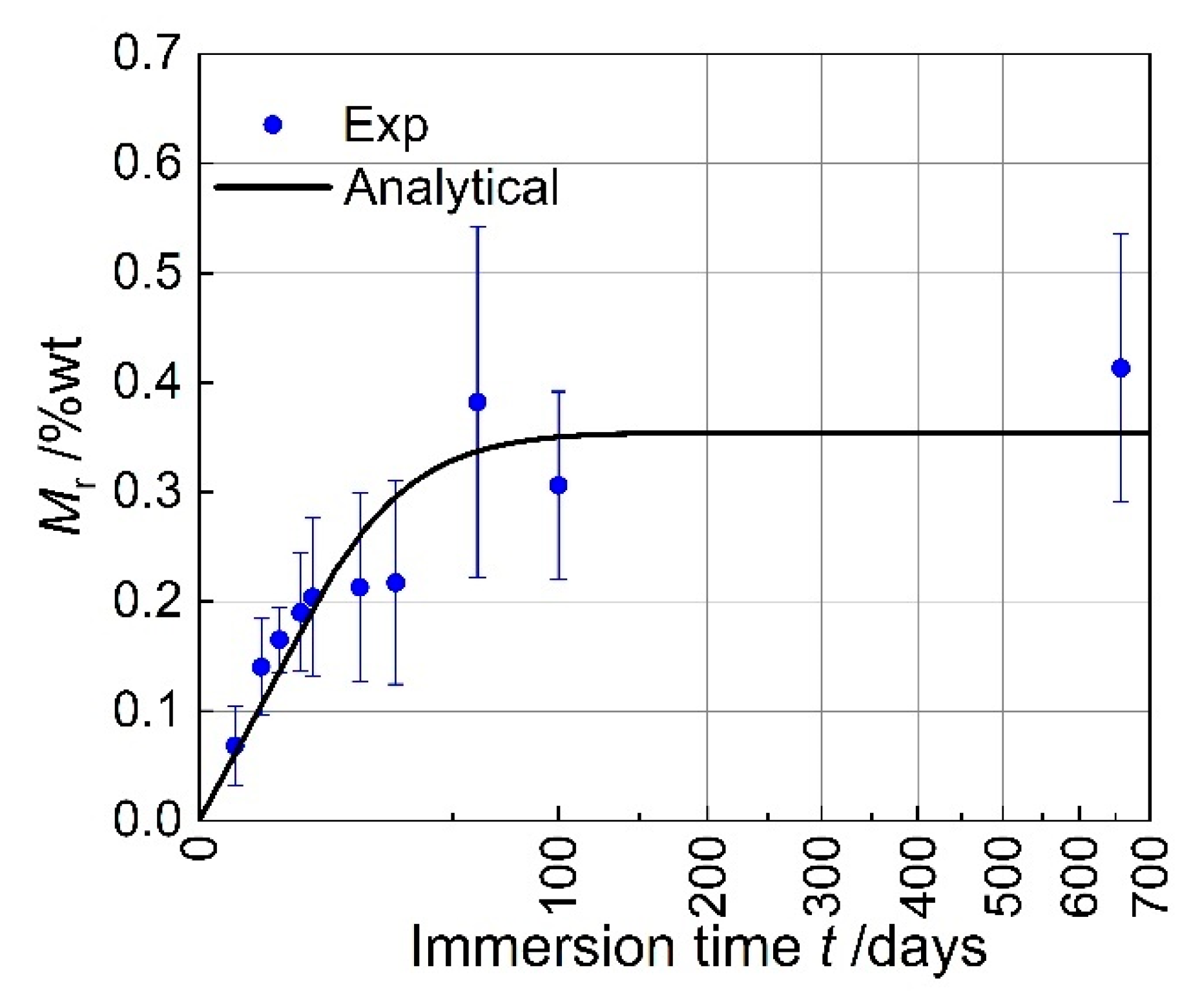
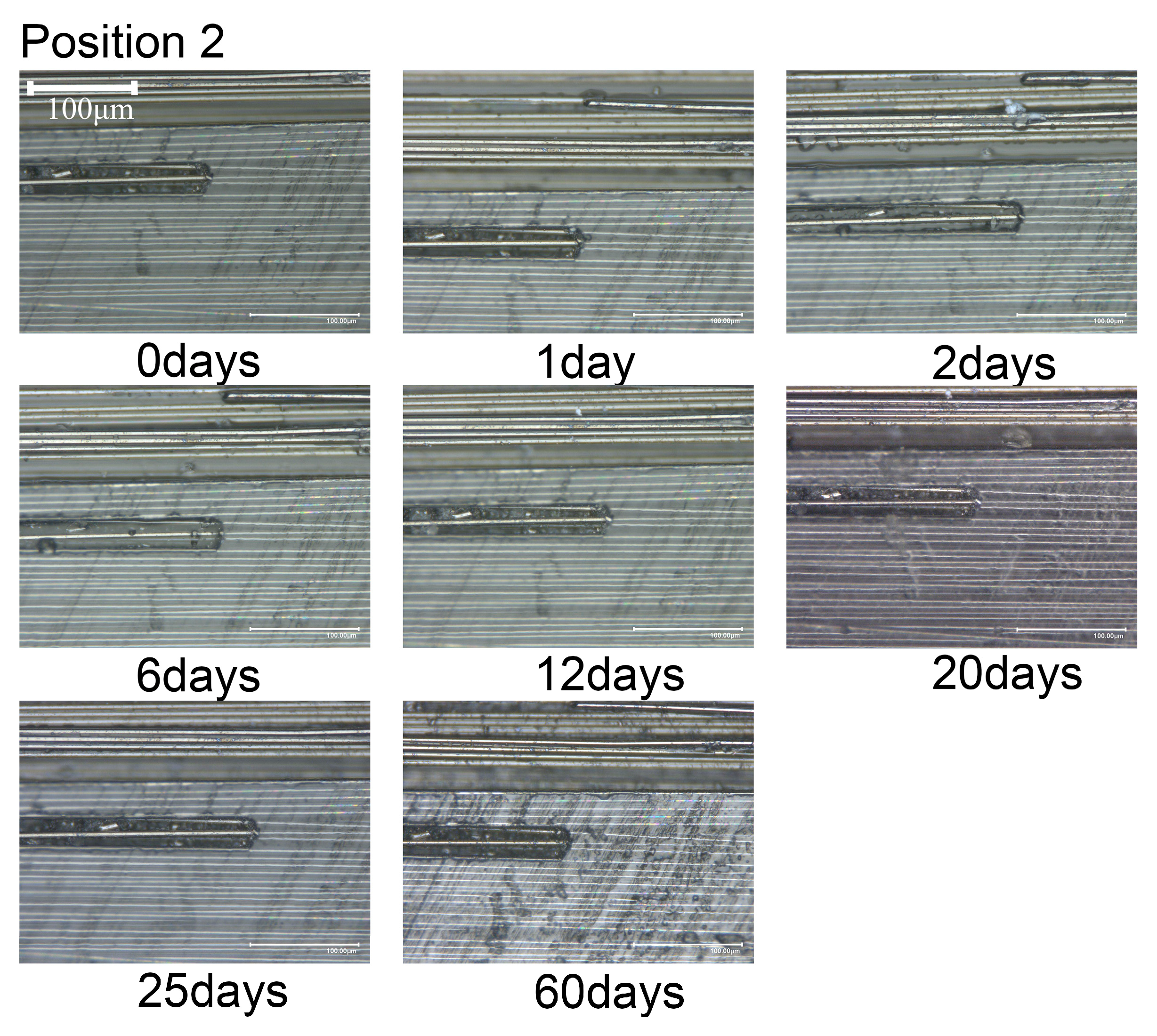
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibson, R.F. Principles of Composite Material Mechanics, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781498720694. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, B. Fatigue in Composites: Science and Technology of the Fatigue Response of Fibre-Reinforced Plastics; Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-85573-608-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, S.W. Strength & Life of Composites; Composites Design Group, Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780981914305. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, P.P.; Liu, C.; Iacono, S.; Corti, G.; Hu, Y. Microstructural Characterization and Property of Carbon Fiber Reinforced High-Density Polyethylene Composites Fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling. Materials 2023, 16, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceti, P.; Carminati, L.; Bettini, P.; Sala, G. Hygrothermal Ageing of Composite Structures. Part 1: Technical Review. Compos. Struct. 2023, 319, 117076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zeeuw, C.; Teixeira de Freitas, S.; Zarouchas, D.; Schilling, M.; Lopes Fernandes, R.; Dolabella Portella, P.; Niebergall, U. Creep Behaviour of Steel Bonded Joints under Hygrothermal Conditions. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 91, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, M.; Thariq, M.; Saba, N. (Eds.) Durability and Life Prediction in Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-08-102290-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Tian, J.; Xian, G. Hydrothermal Ageing of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites Applied for Construction: A Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 1017–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.; Cavallaro, P.; Torres, J.; Ponte, D.; Warner, E.; Chenwi, I.; Shukla, A. Effects of Water Saturation and Low Temperature Coupling on the Mechanical Behavior of Carbon and E-Glass Epoxy Laminates. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2021, 4, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, G.; Chen, W. Development of a Hygrothermal Constitutive Model for Epoxy Resin Considering the Glass Transition Temperature and Its Applications. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 261, 108697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Wang, H.; Bi, Y. Effect of Hygrothermal Aging on Compression Behavior of CFRP Material with Different Layups. Compos. Part B 2024, 270, 111134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, G.; Kisa, M.; Ozen, M.; Acikgoz, A.; Işıker, Y.; Aytar, E. Nano-Gelcoat Application of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites for Marine Application: Structural, Mechanical, and Thermal Analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Jiang, D.; Ju, S.; Zhang, J. The Distinctions of the Interfacial Nanostructures and Properties between Carbon Fiber Reinforced Fast and Conventional Curing Epoxy Composites Subjected to Hydrothermal Treatments. Polym. Test. 2024, 134, 108428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Deng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H. Multi-Scale Moisture Diffusion Modeling and Analysis of Carbon/Kevlar-Fiber Hybrid Composite Laminates under the Hygrothermal Aging Environment. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 229, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Su, H.; Zhou, K. A Phase-Field Model for Mixed-Mode Cohesive Fracture in Fiber-Reinforced Composites. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 421, 116753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zou, J.; Liu, M.; Han, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Liang, B.; Hu, N.; Zhang, W. Investigating the Role of Fibre-Matrix Interfacial Degradation on the Ageing Process of Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polymer under Hydrothermal Conditions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2025, 259, 110922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Luo, B.; Han, W.; Suo, H.; Niu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, H. Deterioration of Carbon Fiber/Matrix Interface in Humid Environments and Influence of Silicon Coupling Agent Modification: An Atomistic Investigation. Compos. Struct. 2024, 344, 118330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboura, S.; Abdessalem, A.; Fitoussi, J.; Ben Daly, H.; Tcharkhtchi, A. On the Mechanical Properties and Damage Mechanisms of Short Fibers Reinforced Composite Submitted to Hydrothermal Aging: Application to Sheet Molding Compound Composite. Eng. Fail Anal. 2022, 131, 105806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandagopal, R.A.; Boay, C.G.; Narasimalu, S. An Empirical Model to Predict the Strength Degradation of the Hygrothermal Aged CFRP Material. Compos. Struct. 2020, 236, 111876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.I.; Bosze, E.J.; Barjasteh, E.; Nutt, S.R. Influence of Hygrothermal Environment on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber/Fiberglass Hybrid Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F. Moisture Diffusion and Hygrothermal Aging in Bismaleimide Matrix Carbon Fiber Composites: Part II—Woven and Hybrid Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Springer, G.S. Moisture Absorption and Desorption of Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierron, F.; Poirette, Y.; Vautrin, A. A Novel Procedure for Identification of 3D Moisture Diffusion Parameters on Thick Composites: Theory, Validation and Experimental Results. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 2219–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, G.S.; Tsai, S.W. Thermal Conductivities of Unidirectional Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1967, 1, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, Z. Fatigue Behavior of Basalt Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Tendons for Prestressing Applications. J. Compos. Constr. 2016, 20, 04015079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, J.S.; Ugarte, C.M. Influence of Cross-Linking Density on the Glass Transition and Structure of Chemically Cross-Linked PVA: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2009, 18, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamis, C.C. Simplified Composite Micromechanics Equations of Hygral, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Eighth Annual Conference of the Sodety of the Plastics Industry(SPI) Reinforced Plas-tics/Composites Institute, Houston, TX, USA, 7–11 February 1983; Volume 15, pp. 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International ASTM D3171-22; Standard Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- National Standardization Administration GB/T 3354-2014; Test Method for Tensile Properties of Orientation Fiber Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2014.
- ASTM International ASTM D5229/D5229M-20; Standard Test Method for Moisture Absorption Properties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Ye, J.Q.; Sheng, H.Y. Free-Edge Effect in Cross-Ply Laminated Hollow Cylinders Subjected to Axisymmetric Transverse Loads. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2003, 45, 1309–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, E.; Osswald, T.A.; Rudolph, N. Plastics Handbook; Baur, E., Osswald, T.A., Rudolph, N., Eds.; Hanser Publications: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-56990-559-3. [Google Scholar]







| Parameter | Sample | Unit | T700 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | ρf | g∙cm−3 | 1.8 |
| Fiber diameter | df | μm | 7.62 |
| 1-direction tensile modulus | Ef1 | GPa | 230 |
| 2-direction tensile modulus | Ef2 | GPa | 18 |
| 12-direction shear modulus | Gf12 | GPa | 8.7 |
| 23-direction shear modulus | Gf23 | GPa | 5.8 |
| 12-direction Poisson’s ratio | υf12 | 0.2 | |
| 23-direction Poisson’s ratio | υf23 | 0.49 |
| Parameter | Sample | Unit | AF-4206A/B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | ρf | g∙cm−3 | 1.2 |
| Tensile modulus | Em | GPa | ≥3.0 |
| Shear modulus | Gm | GPa | ≥1.25 |
| Poisson’s ratio | υm | 0.33 | |
| Heat conductivity | Km | W∙mm−1∙°C−1 | 1.8034 × 10−4 |
| Specific heat capacity at constant volume | Cm,v | J∙kg−1∙°C−1 | 1046.7 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | αm | mm∙mm−1∙°C−1 | 6.48 × 10−5 |
| Coefficient of hydroscopic expansion | βm | mm∙mm−1∙%−1 | 0.33 |
| Diffusion coefficient | Dm | mm2∙s−1 | 0.25 × 10−6 |
| Glass transition temperature | Tg | °C | ≥120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Zheng, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z. T700 Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composite Material Hygrothermal Aging Model. Materials 2025, 18, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020369
Lu J, Zheng C, Wang L, Dai Y, Wang Z, Song Z. T700 Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composite Material Hygrothermal Aging Model. Materials. 2025; 18(2):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020369
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jinjie, Chuanxiang Zheng, Liang Wang, Yuchen Dai, Zhenyu Wang, and Zhaobo Song. 2025. "T700 Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composite Material Hygrothermal Aging Model" Materials 18, no. 2: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020369
APA StyleLu, J., Zheng, C., Wang, L., Dai, Y., Wang, Z., & Song, Z. (2025). T700 Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composite Material Hygrothermal Aging Model. Materials, 18(2), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020369






