Bacteriorhodopsin-Based pH Sensor for Cell Culture Condition Regulation
Highlights
- The innovative exploitation of the photochemical attributes of bacteriorhodopsin (bR), a photosensitive protein, enables instantaneous and non-invasive pH monitoring in cell culture scenarios.
- The H+ sensing component in the bR-based pH sensor is derived from a bio-based protein that exhibits excellent stability and biocompatibility. It would not introduce contamination to the components of the medium for pH monitoring.
- The bR-based pH sensor is capable of real-time pH monitoring within 72 h, providing accurate biological indicators for the improvement of cell culture conditions.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of bR-Based pH Sensor
2.3. Characterization of bR-Based pH Sensor
2.4. Detection of the Photo Signals
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. The pH Results of Medium
3. Results
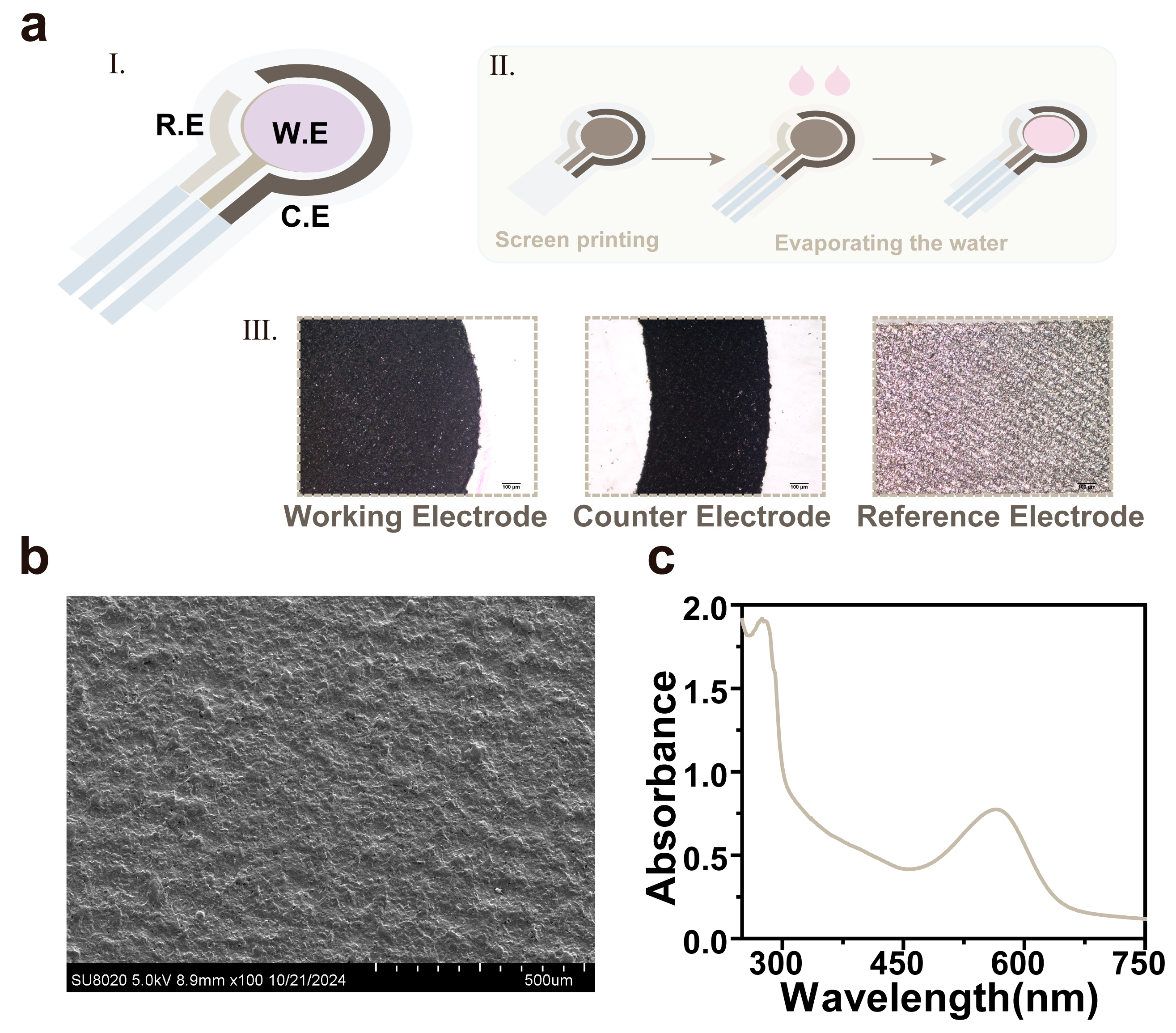
3.1. Characterization of the bR-Based pH Sensor
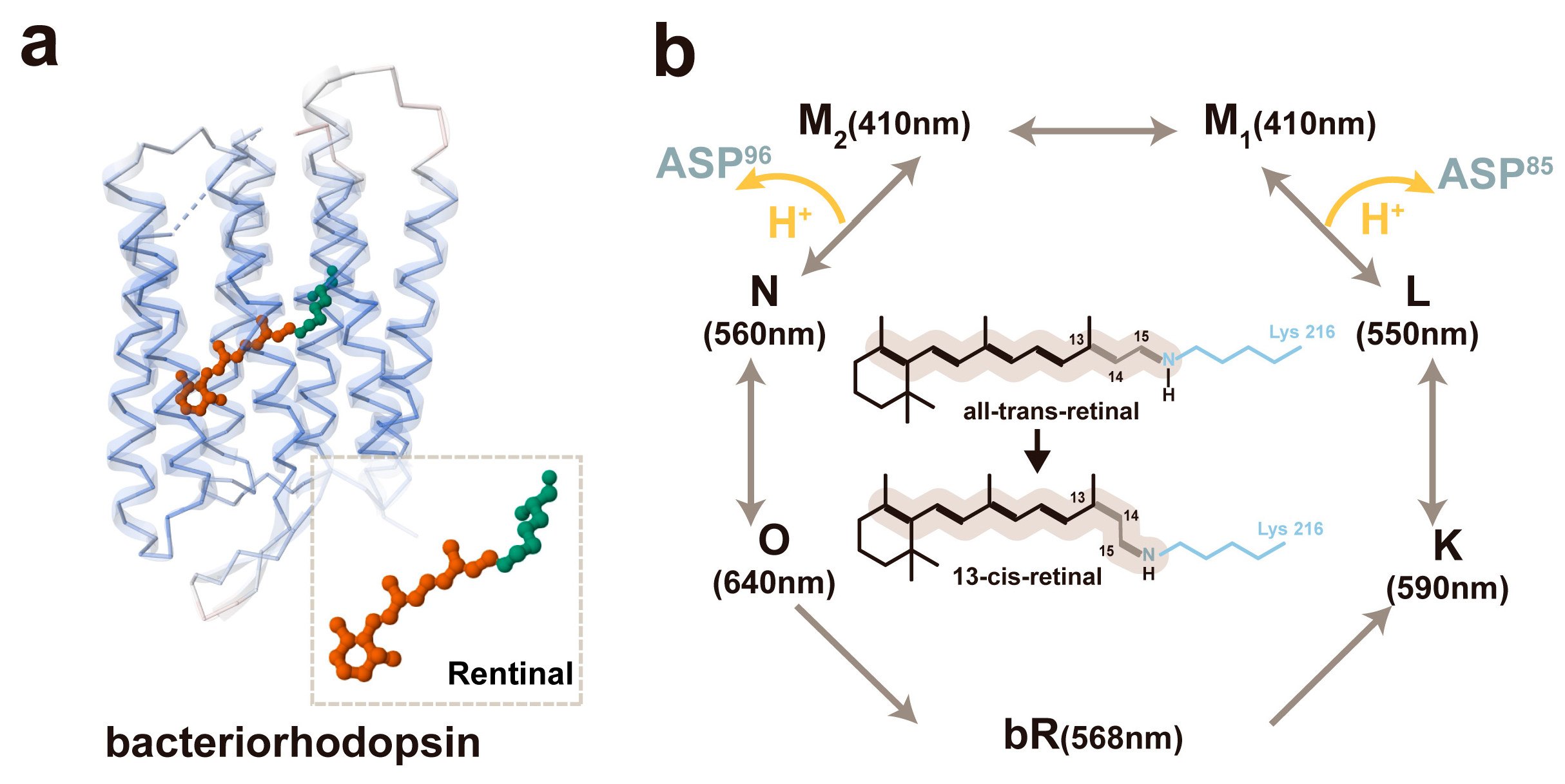
3.2. The Mechanism of the bR-Based pH Sensor
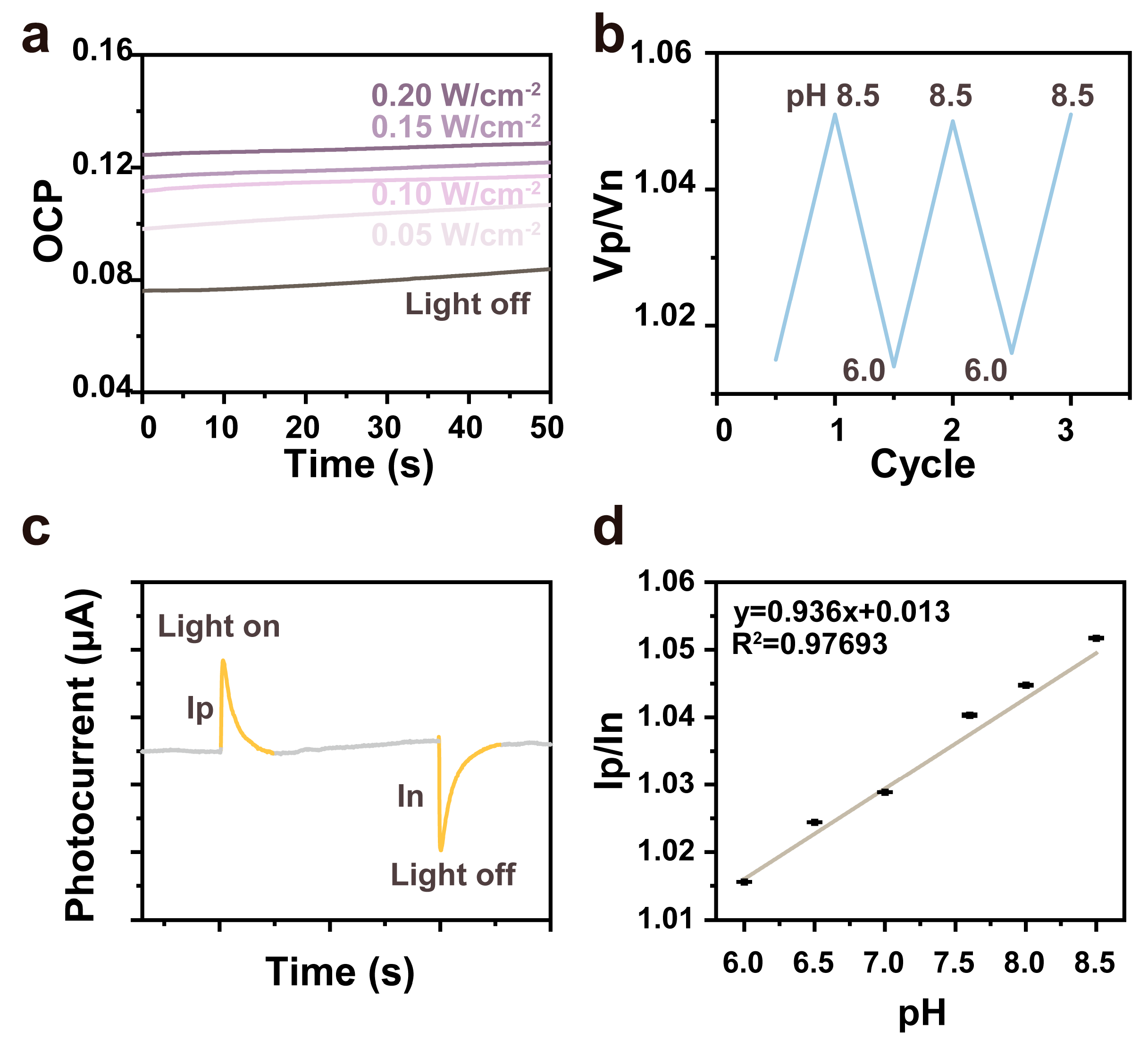
3.3. The Photo Signals of the pH Sensor
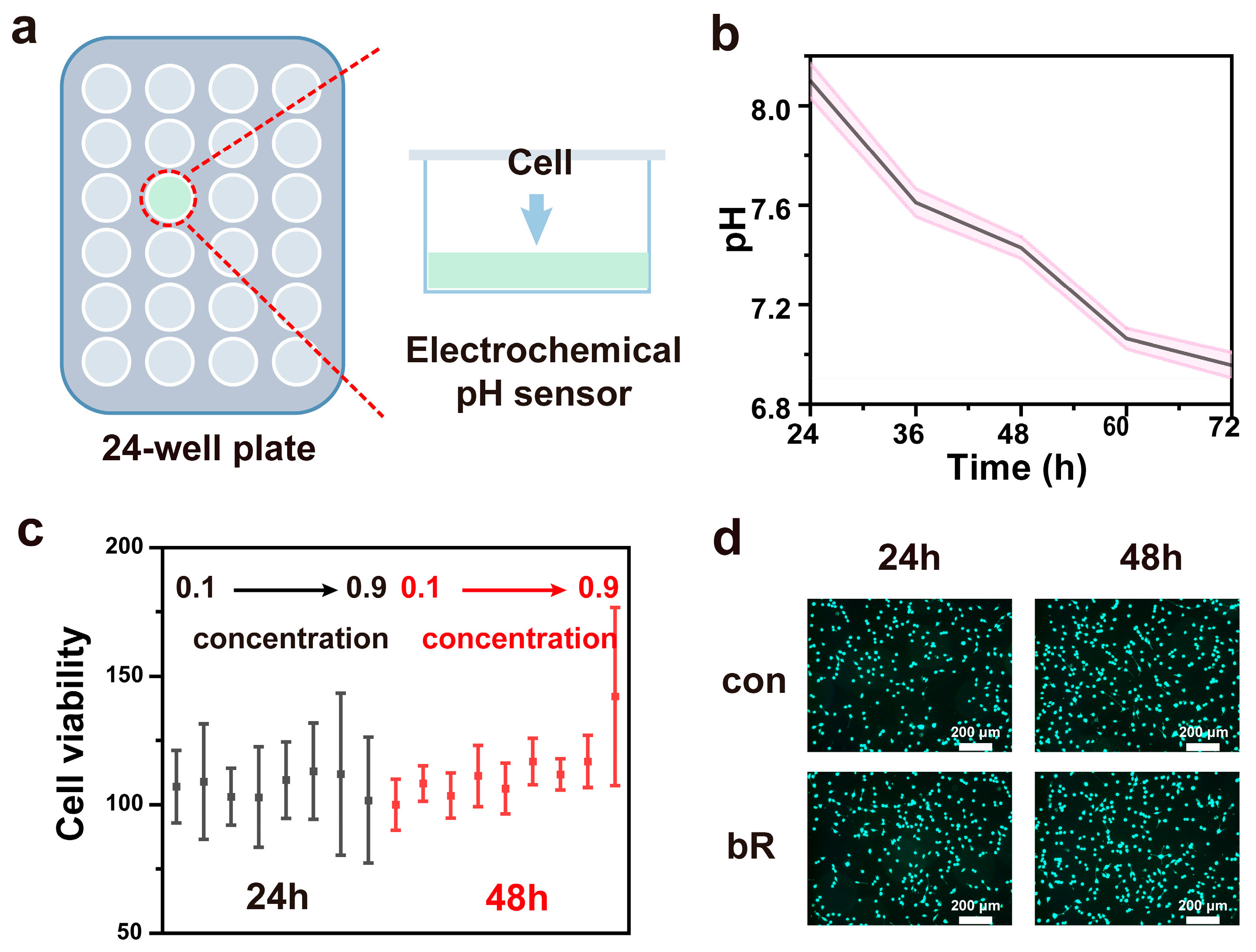
3.4. Medium pH Monitoring with pH Sensor
4. Discussion
4.1. Enhancement of Sensor Sensitivity and Stability for pH Monitoring
4.2. Integration of pH Sensor with Cell Culture Systems
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, W.; Lin, X.; Nagl, S. In Situ Live Monitoring of Extracellular Acidosis near Cancer Cells Using Digital Microfluidics with an Integrated Optical pH Sensor Film. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 14456–14463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Li, X.-R.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Li, G.-P.; Shen, H.-Y.; Li, Y.-T.; Ren, T.-L. Review on Bacteriorhodopsin-Based Self-Powered Bio-Photoelectric Sensors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 162, 107501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Widdicombe, B.; Zhang, X.; Zielinski, J.L.; Cheng, T.; Gunatilaka, A.; Leung, K.K.; Plaxco, K.W.; Rajasekharan Unnithan, R.; et al. Dual-Purpose Aptamer-Based Sensors for Real-Time, Multiplexable Monitoring of Metabolites in Cell Culture Media. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 26127–26139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Tu, J.; Li, T.; Li, Y.-T.; Zhang, G.-J. A pH-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Monitoring of Cancer Cell External Acid Environment. Talanta 2023, 252, 123764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, N.; Li, S.; Lu, S.; Xiang, Y. A Novel Light-Driven pH-Biosensor Based on Bacteriorhodopsin. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liang, D.; Lu, S.; Aurbach, D.; Xiang, Y. Unidirectional Electron Injection and Accelerated Proton Transport in Bacteriorhodopsin Based Bio-p-n Junctions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, H.I.A.; Elfiki, A.A. Bacteriorhodopsin of Purple Membrane Reverses Anisotropy Outside the pH Range of Proton Pumping Based on Logic Gate Realization. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E. pH in Nature, Humans and Skin. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, A.; Otani, Y.; Miyasa, R.; Makino, Y.; Kawamura, I.; Okitsu, T.; Wada, A.; Naito, A. Photoreaction Pathways of Bacteriorhodopsin and Its D96N Mutant as Revealed by in Situ Photoirradiation Solid-State NMR. Membranes 2022, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, H.I.A. Exploring Isotropic Tendency for the Blue Membrane Containing Wild-Type Bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys. Chem. 2023, 300, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Tsunoda, S.P.; Singh, M.; Tomida, S.; Hososhima, S.; Konno, M.; Nakamura, R.; Watanabe, H.; Bulzu, P.-A.; Banciu, H.L.; et al. Schizorhodopsins: A Family of Rhodopsins from Asgard Archaea That Function as Light-Driven Inward H+ Pumps. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, A.; Zhang, T.; Wen, L.; Shi, Z.; Shi, L. A pH Monitoring Algorithm for Orifice Plate Culture Medium. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xu, F.; Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Mao, H. A Cell State Monitoring System with Integrated In Situ Imaging and pH Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, M.; Qi, G.; Xia, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, P.; Sheves, M.; Jin, Y. Oriented Bacteriorhodopsin/Polyaniline Hybrid Bio-Nanofilms as Photo-Assisted Electrodes for High Performance Supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 8268–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximychev, A.V.; Kholmansky, A.S.; Levin, E.V.; Rambidi, N.G.; Chamorovsky, S.K.; Kononenko, A.A.; Erokhin, V.V.; Checulaeva, L.N. Oriented Purple Membrane Multilayers of Halobacteria Fabricated by Langmuir–Blodgett and Electrophoretic Sedimentation Techniques. Adv. Mater. Opt. Electron. 1992, 1, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Hong, Y.J.; Sunwoo, S.-H.; Park, O.K.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, S. Low-Impedance Tissue-Device Interface Using Homogeneously Conductive Hydrogels Chemically Bonded to Stretchable Bioelectronics. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadi7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qiao, X.; Tao, R.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Cai, Y.; Luo, X. A Wearable Sensor Based on Multifunctional Conductive Hydrogel for Simultaneous Accurate pH and Tyrosine Monitoring in Sweat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 234, 115360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Xu, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, E.; Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Ouyang, H.; Yin, T.; Feng, H.; Luo, D.; et al. A Responsive Cascade Drug Delivery Scaffold Adapted to the Therapeutic Time Window for Peripheral Nerve Injury Repair. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Sheves, M.; Jin, Y. Bacteriorhodopsin/Ag Nanoparticle-Based Hybrid Nano-Bio Electrocatalyst for Efficient and Robust H 2 Evolution from Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2840–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Honig, T.; Ron, I.; Friedman, N.; Sheves, M.; Cahen, D. Bacteriorhodopsin as an Electronic Conduction Medium for Biomolecular Electronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheves, M.; Albeck, A.; Friedman, N.; Ottolenghi, M. Controlling the pKa of the Bacteriorhodopsin Schiff Base by Use of Artificial Retinal Analogues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 3262–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, S.; Kuramochi, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Tahara, T. Protein Dynamics Preceding Photoisomerization of the Retinal Chromophore in Bacteriorhodopsin Revealed by Deep-UV Femtosecond Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5422–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmatnejad, V.; Tolosa, M.; Ge, X.; Rao, G. Completely Noninvasive Multi-Analyte Monitoring System for Cell Culture Processes. Biotechnol. Lett. 2024, 46, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhao, D.; Wei, Z.; Zhong, W.; Wang, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, Z. Electroporation on Microchips: The Harmful Effects of pH Changes and Scaling Down. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E. Novel Bio-Optoelectronics Enabled by Flexible Micro Light-Emitting Diodes. Electronics 2021, 10, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Tong, J.; Liu, Y. Unveiling the Effect of Ti Micro-Alloying on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of the GH3536 Alloy Processed by Laser Metal Deposition in a Simulated Environment for PEMFCs. Materials 2024, 17, 5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z.; Ji, L. Development and Application of Nanogenerators in Humanoid Robotics. Nano Trends 2023, 3, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drymiskianaki, A.; Viskadourakis, Z.; Kenanakis, G. Hybrid Microwave/Solar Energy Harvesting System Using 3D-Printed Metasurfaces. Materials 2024, 17, 5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Chao, S.; Wang, Y.; Hou, L.; Bai, T.; Bai, J.; Man, X.; Cui, Z.; Wang, N.; et al. Zebra-Patterned Stretchable Helical Yarn for Triboelectric Self-Powered Multifunctional Sensing. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 16958–16966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Xie, S.; Fan, H.; Song, C.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, D.; Zeng, Z.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y. Bacteriorhodopsin-Based pH Sensor for Cell Culture Condition Regulation. Materials 2025, 18, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030478
Huang J, Xie S, Fan H, Song C, Zheng Q, Luo D, Zeng Z, Li Z, Lv Y. Bacteriorhodopsin-Based pH Sensor for Cell Culture Condition Regulation. Materials. 2025; 18(3):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030478
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiayin, Shiwang Xie, Haoqi Fan, Chen Song, Qiang Zheng, Dan Luo, Zhu Zeng, Zhou Li, and Yujia Lv. 2025. "Bacteriorhodopsin-Based pH Sensor for Cell Culture Condition Regulation" Materials 18, no. 3: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030478
APA StyleHuang, J., Xie, S., Fan, H., Song, C., Zheng, Q., Luo, D., Zeng, Z., Li, Z., & Lv, Y. (2025). Bacteriorhodopsin-Based pH Sensor for Cell Culture Condition Regulation. Materials, 18(3), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030478






