Characterization of the Microstructure and Interfacial Morphology of Magnetic Pulse Welded Steel/Al Tubes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- An interface with effective metallurgical bonding was successfully obtained at the intermediate part of the joint. No obvious IMC layer could be traced owing to the low heat input of the magnetic pulse welding (MPW), while the transition zone was distributed in the trough of the wave. That is to say, only element diffusion occurred during the MPW process. The thickness of the transition layer was approximately 6 μm;
- (2)
- The interface of the as-welded joint could be divided into three zones—the bonded zone in the center, and unbonded zones on both sides. The formation of the wavy interface depended on the collision velocity and collision angle. The amplitude of the wavy interface increased gradually with the decrease in the collision velocity and the increase in the collision angle. Appropriately reducing the collision velocity and increasing the collision angle could improve the bonding quality of the interface;
- (3)
- The 6061 aluminum alloy and 20# steel tubes were successfully joined by the MPW process. The qualified mechanical properties of the joint could be attributed to the formation of a wavy interface. The microhardness at the interface was higher than that on both sides, owing to work hardening, and was approximately 226 HV. In addition, precisely controlling the coil size and achieving a better alignment between the outer and the inner tubes could improve the properties of the welded joint;
- (4)
- To further understand the relationship of the mechanical properties of the MPW joint with the specific interface microstructure, systematic analyses of the mechanical properties are preferred. Besides this, not only the joining between the tubes, but also the joining of specimens with other shapes, e.g., plates, can also be taken into account as attributable to the unique advantages of the MPW technique.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, F.; Chen, L.H.; Luo, Y.P. Research on energy consumption for improving light vehicle manufacturing technology of automotive industry in China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 538–541, 2864–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskos, P.; Capros, P.; De, V.A. CO2 and energy efficiency car standards in the EU in the context of a decarbonisation strategy: A model-based policy assessment. Energy Policy. 2015, 84, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrenho, A.C.; Norman, J.B.; Allwood, J.M. The impact of reducing car weight on global emissions: The future fleet in Great Britain. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 375, 20160364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, X.M.; Zhu, P.; Wang, W.R. Lightweight design of automobile component using high strength steel based on dent resistance. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krbata, M.; Krizan, D.; Eckert, M.; Kaar, S.; Dubec, A.; Ciger, R. Austenite decomposition of a lean medium Mn steel suitable for quenching and partitioning process: Comparison of CCT and DCCT diagram and their microstructural changes. Materials 2022, 15, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Rometsch, P.A.; Couper, M.J. Effect of pre-ageing and natural ageing on the paint bake response of alloy AA6181A. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 571, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.T.; Goto, Y.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Microstructure and lap shear strength of the weld interface in ultrasonic welding of Al alloy to stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 2016, 116, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kumai, S.; Arai, T.; Aizawa, T. Interfacial microstructure and strength of steel/aluminum alloy lap joint fabricated by magnetic pressure seam welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 471, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Fu, X.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.H.; Chen, S. A short review on laser welding/brazing of aluminum alloy to steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 112, 2399–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Sano, T.; Munekane, M.; Ohata, M.; Hirose, A. Microscale tensile test of galvannealed steel/aluminum dissimilar joint for estimation of intrinsic interfacial strength. Scr. Mater. 2020, 186, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Su, J.H.; Gao, C.K.; Zhao, Y.X.; Liu, H.B.; Joao, P.O.; Tan, C.W.; Yu, Z.S. Effect of heat input on interfacial microstructure, tensile and bending properties of dissimilar Al/steel lap joints by laser welding-brazing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 142, 107218. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Qin, G.L.; Ao, Z.Y.; Wang, L.Y. Interfacial microstructure and shear properties of aluminum alloy to steel fusion-brazed welded joint. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Gu, D.Y.; Sun, D.Q. Research on interface characteristic of laser welding joints of steel/aluminum dissimilar materials. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.X.; Wang, H.P.; Chen, N.N.; Wang, M.; Carlson, B.E. Characterization of intermetallic compound at the interfaces of Al-steel resistance spot welds. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 242, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Xiao, J.; Gai, S.N.; Chen, S.J. Electrode-embedded linear actuating enhanced resistance spot welding of aluminium alloy and dual phase steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 132, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.Z.; Hua, X.M.; Chen, N.N.; Mou, G.; Ji, X.R.; Li, F. Effect of the microstructure of IMCs and zinc accumulation on the mechanical properties of aluminum/galvanized steel joints in the VP-CMT process. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Pierce, D.; Nayir, S.; Ahsan, R.U.; Kim, D.; Unocic, K.; Lee, Y.; Jadhav, S.; Karim, M.A.; Nandwana, P. Wire directed energy deposition of steel-aluminum structures using cold metal transfer process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 4537–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Z.T. Wettability, microstructure and properties of 6061 aluminum alloy/304 stainless steel butt joint achieved by laser-metal inert-gas hybrid welding-brazing. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 2018, 28, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Y.M.; Xu, J. Numerical simulation of arc-droplet-weld pool behaviors during the external magnetic field-assisted MIG welding-brazing of aluminum to steel. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 194, 108530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, F.Y.; Niu, S.C.; Zhu, B.H.; Wu, L.J.; Xia, H.B.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.M.; Tan, C.W. Effect of pulse frequency on the nanosecond pulsed laser welded Al/steel lapped joint. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 143, 107335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Kang, L.; Wang, T.; Yi, L.L.; Sang, K.X.; Lu, Y.T. The influences of nanoparticles on the microstructure evolution mechanism and mechanical properties of laser welded stainless steel/aluminum. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Harangozó, D.; Németh, D.; Kocsis, B.; Sysyn, M.; Kurhan, D.; Brautigam, A. Investigation of heat-affected zones of thermite rail weldings. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2024, 22, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.H.; Jing, L.J.; Wang, S.L.; Li, G.Y.; Cui, J.J.; Tang, X.H.; Jiang, H. Mechanical properties and joining mechanisms of Al-Fe magnetic pulse welding by spot form for automotive application. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 76, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.J.; Sun, G.Y.; Xu, J.R.; Xu, Z.D.; Huang, X.D.; Li, G.Y. A study on the critical wall thickness of the inner tube for magnetic pulse welding of tubular Al-Fe parts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 227, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yu, H.P.; Li, H.H. Optimization of novel coil structure parameters for controlling Al/Fe magnetic pulse welding process. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 134, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotri, R.; Faes, K.; De, A. Magnetic pulse welding of copper to steel tubes-Experimental investigation and process modelling. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembalge, O.B.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, S.K. Magnetic pulse welding of AA6061 and AISI 1020 steel tubes: Numerical and experimental investigation. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 101, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Singh, G.; Mandal, M.; Chakraborty, R.; Arora, K.S. Non-destructive evaluation and corrosion study of magnetic pulse welded Al and low C steel joints. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 309, 128315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kore, S.D.; Date, P.P.; Kulkarni, S.V. Electromagnetic impact welding of aluminum to stainless steel sheets. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 208, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.P.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, M.F. An innovative coil for magnetic pulse welding of dissimilar sheet metals: Numerical simulation and experiments. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 324, 118230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.H.; Chen, D.D.; Tang, B.W.; Wang, F.F.; Jiang, H.; Li, G.G.; Cui, J.J. Miniaturized S-shaped flexible magnetic pulse welding coil design for engineering applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 104, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psyk, V.; Scheffler, C.; Linnemann, M.; Landgrebe, D. Process analysis for magnetic pulse welding of similar and dissimilar material sheet metal joints. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.Q.; Xiao, A.; Cui, X.H.; Guo, Y.Z.; Lin, Y.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, P. Magnetic pulse welding of aluminum to steel tubes using a field-shaper with multiple seams. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 65, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.H.; Mao, J.Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.Y.; Cui, J.J. Formation mechanism of transition zone and amorphous structure in magnetic pulse welded Al-Fe joint. Mater. Lett. 2019, 245, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Wen, J.P.; Xie, J.L.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, H.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Yin, L.M.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, G. Intermetallic compounds growth and morphology evolution of Al6061/SS304 electromagnetic pulse welding joint interface during post-weld heat treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 4001–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Shribman, V.; Ben-Artzy, A.; Aizenshtein, M. Interface phenomena and bonding mechanism in magnetic pulse welding. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 3449–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Zhou, B.B.; Zhang, X.; Sun, T.; Li, G.Y.; Cui, J.J. Mechanical properties and interfacial microstructures of magnetic pulse welding joints with aluminum to zinc-coated steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 788, 139425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Artzy, A.; Stern, A.; Frage, N.; Shribman, V.; Sadot, O. Wave formation mechanism in magnetic pulse welding. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2010, 37, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.H.; Xia, Z.H.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.Y.; Cui, J.J. Microstructures and mechanical properties of the welded AA5182/HC340LA joint by magnetic pulse welding. Mater. Charact. 2018, 138, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.; Weddeling, C.; Lueg-Althoff, J.; Tekkaya, A.E. Analytical approach for magnetic pulse welding of sheet connections. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 230, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.F.; Zhang, G.C. Effect of preheat & post-weld heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy welded sheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2022, 841, 143081. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.J.; Wang, S.L.; Yuan, W.; Li, G.Y. Effects of standoff distance on magnetic pulse welded joints between aluminum and steel elements in automobile body. Automot. Innovation 2020, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zou, Y.; Liu, X.M.; Kenji, M. Special grain boundaries in the nugget zone of friction stir welded AA6061-T6 under various welding parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2016, 671, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, H.Q.; Yu, H.P. Improving the quality of Al-Fe tube joints manufactured via magnetic pulse welding using an inclined-wall field shaper. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 73, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.A.A.; Farhadi, P. Experimental investigation of explosive welding of cp-titanium/AISI 304 stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
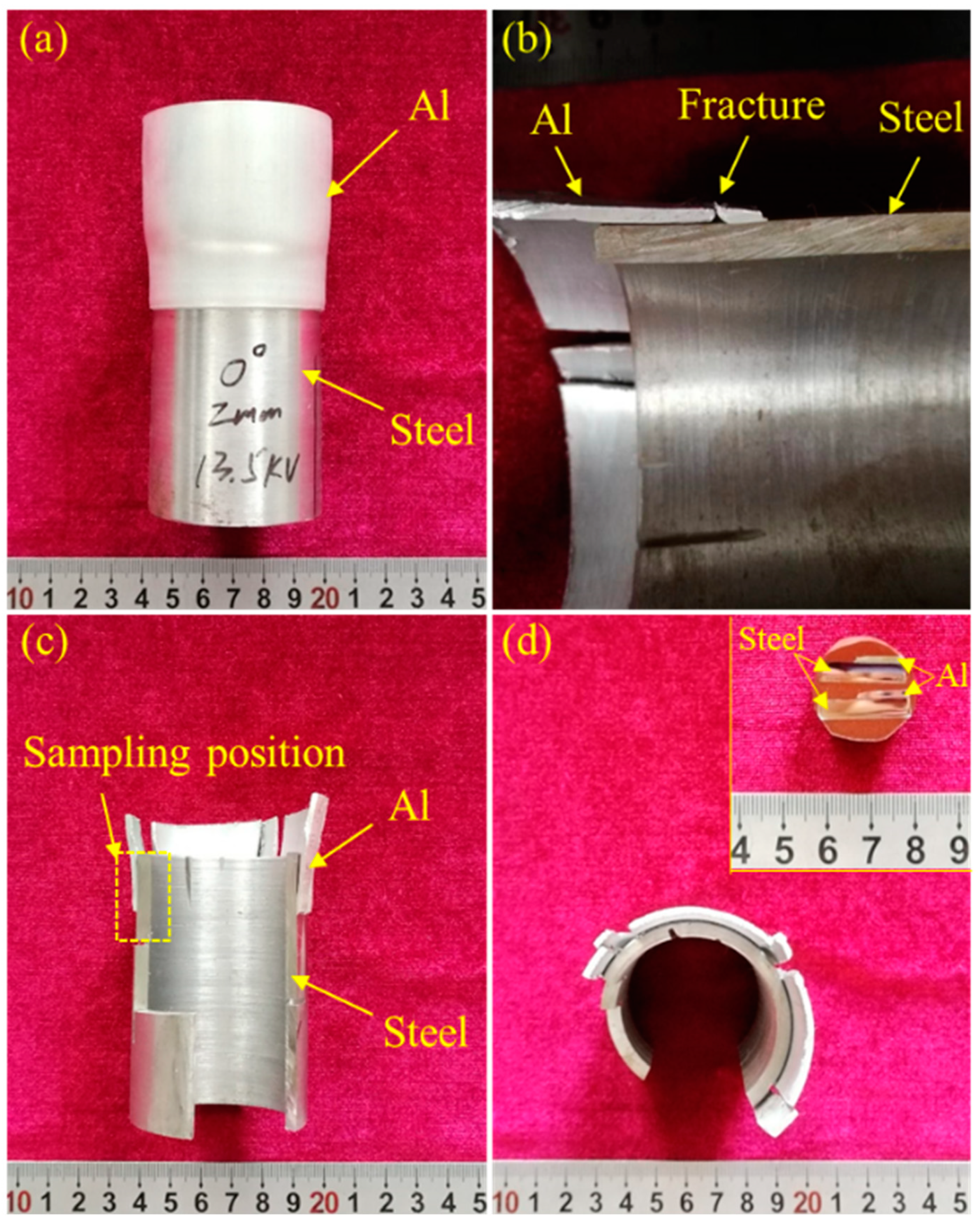


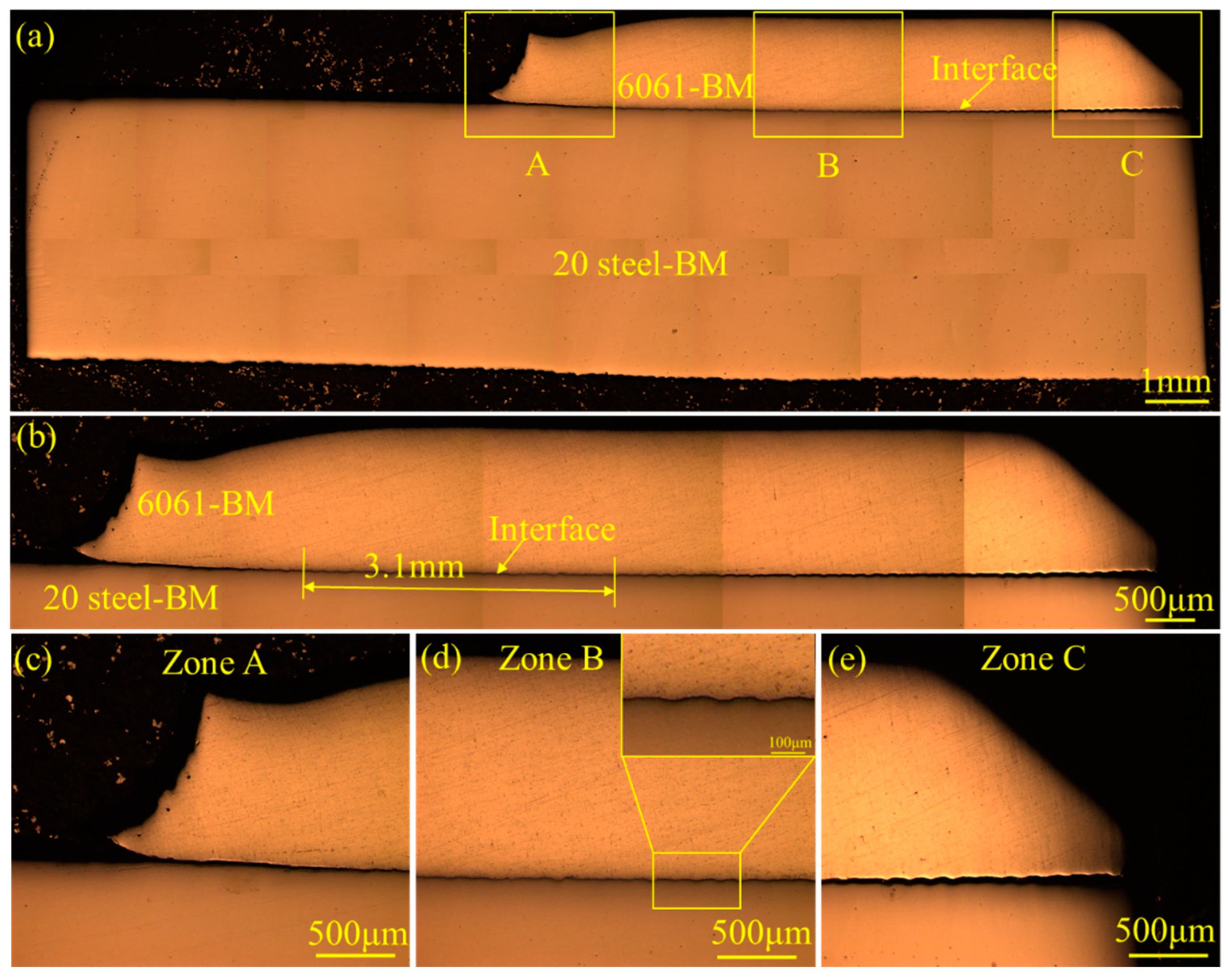

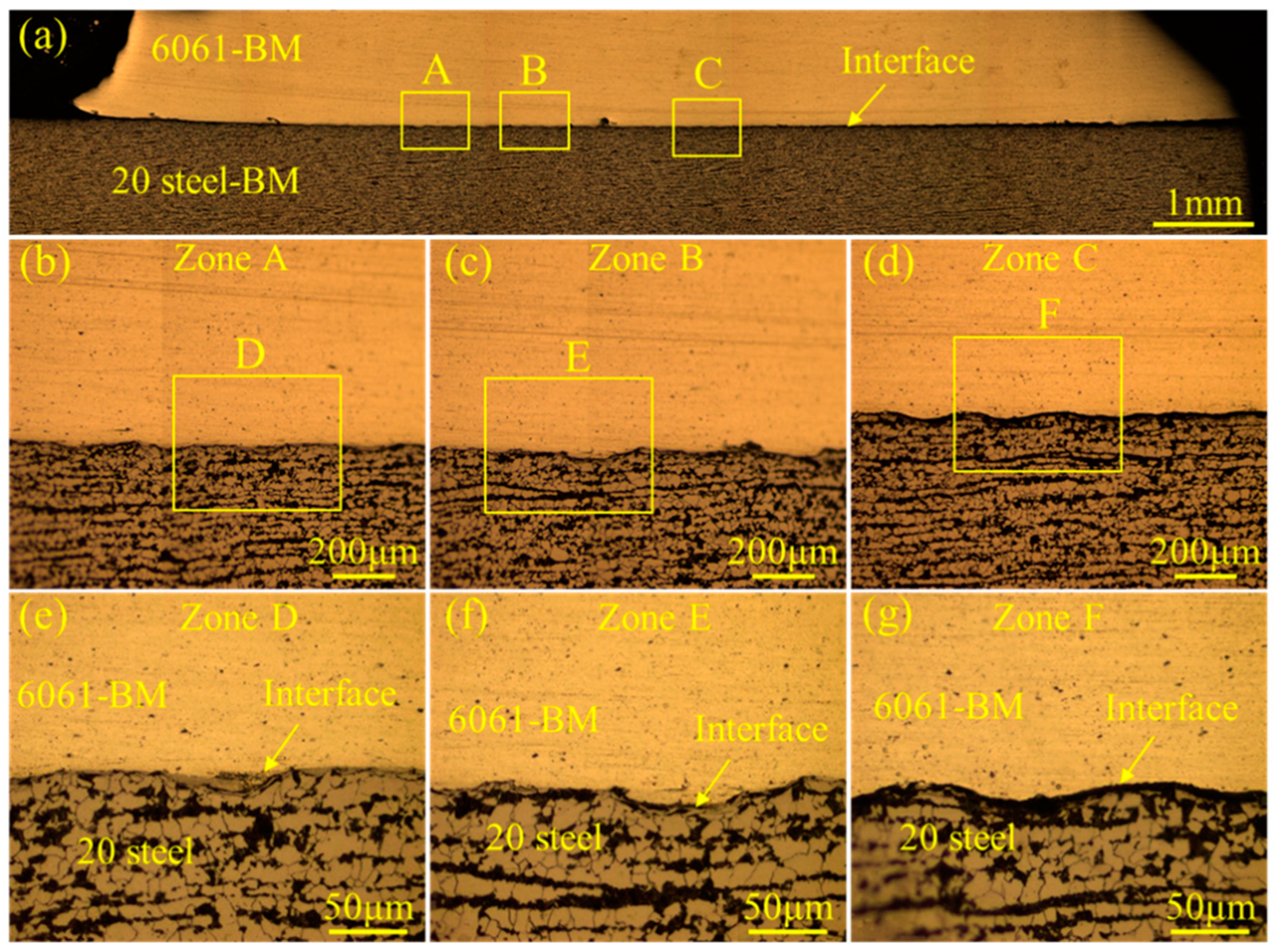
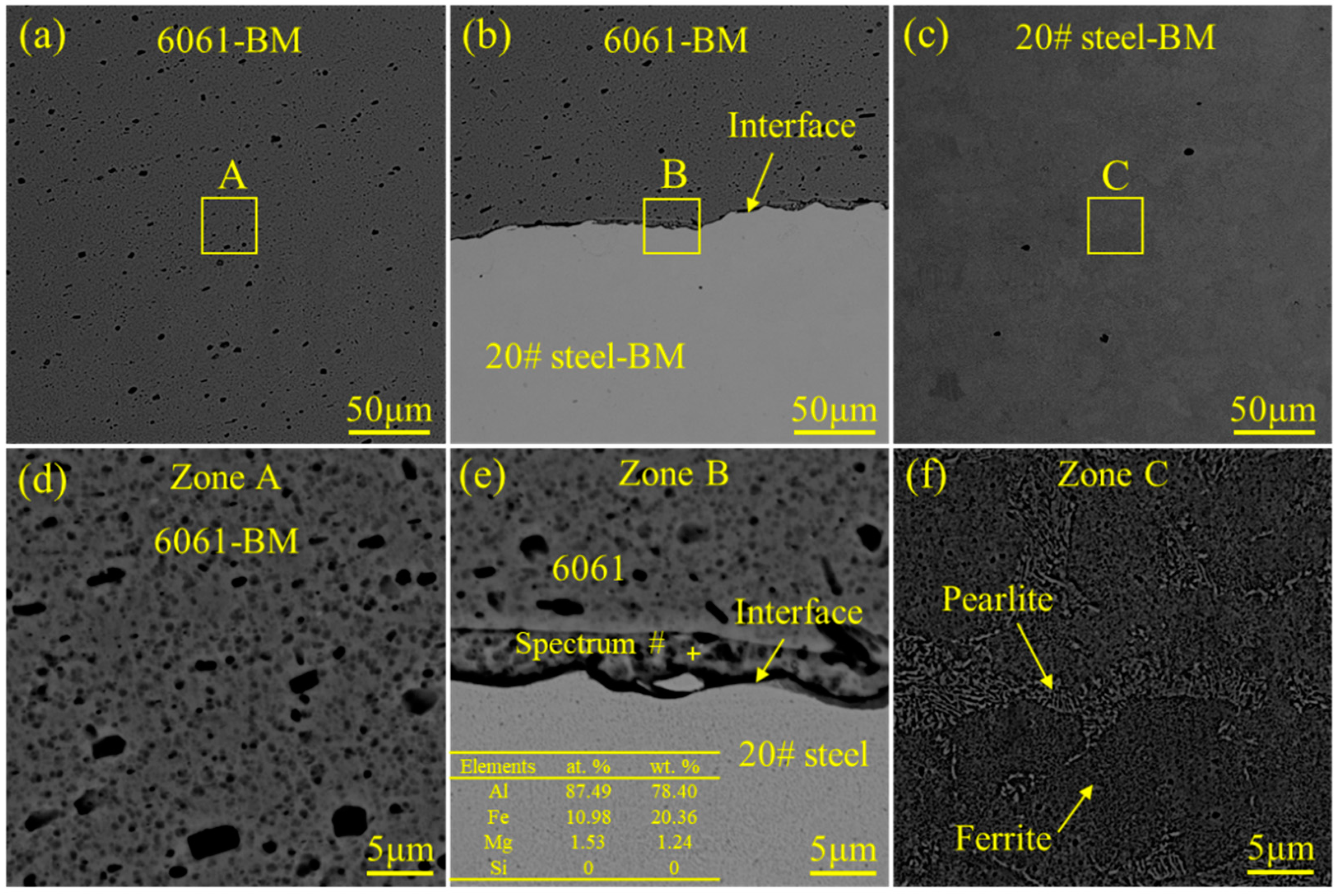
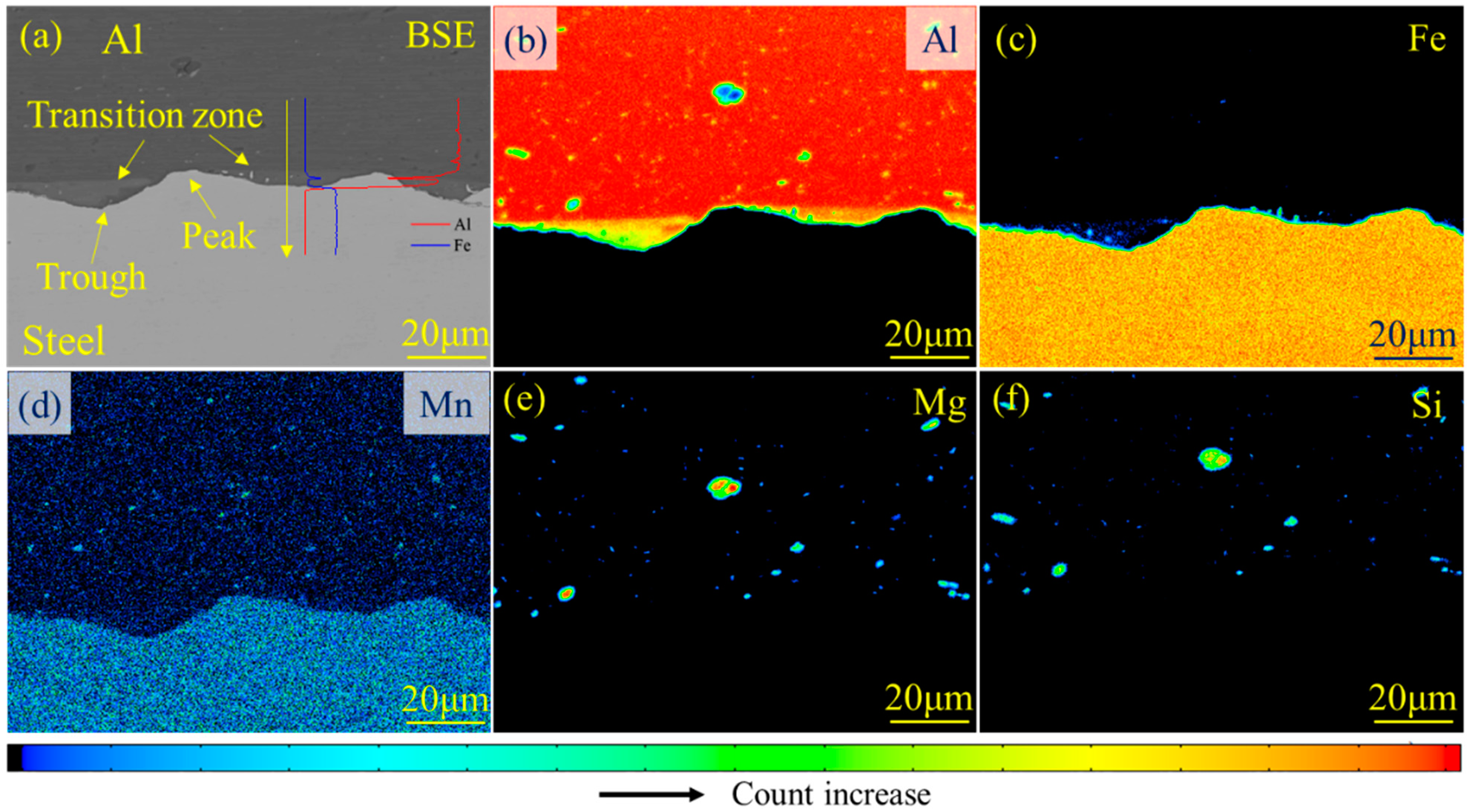

| Elements | Mg | Si | Cu | Cr | C | Ni | Mn | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20# steel | - | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | Bal. | - |
| 6061 | 0.8–1.2 | 0.4–0.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | - | 0.7 | 0.15 | - | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Li, B.; Wu, T.; Pan, H.; Ding, K.; Gao, Y. Characterization of the Microstructure and Interfacial Morphology of Magnetic Pulse Welded Steel/Al Tubes. Materials 2025, 18, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040757
Hu T, Li B, Wu T, Pan H, Ding K, Gao Y. Characterization of the Microstructure and Interfacial Morphology of Magnetic Pulse Welded Steel/Al Tubes. Materials. 2025; 18(4):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040757
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Tianhan, Bolong Li, Tianhai Wu, Hua Pan, Kai Ding, and Yulai Gao. 2025. "Characterization of the Microstructure and Interfacial Morphology of Magnetic Pulse Welded Steel/Al Tubes" Materials 18, no. 4: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040757
APA StyleHu, T., Li, B., Wu, T., Pan, H., Ding, K., & Gao, Y. (2025). Characterization of the Microstructure and Interfacial Morphology of Magnetic Pulse Welded Steel/Al Tubes. Materials, 18(4), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040757






