A Green Electromagnetic Energy Harvester with Up-Frequency and Unidirectional Rotation for Smart Pavement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
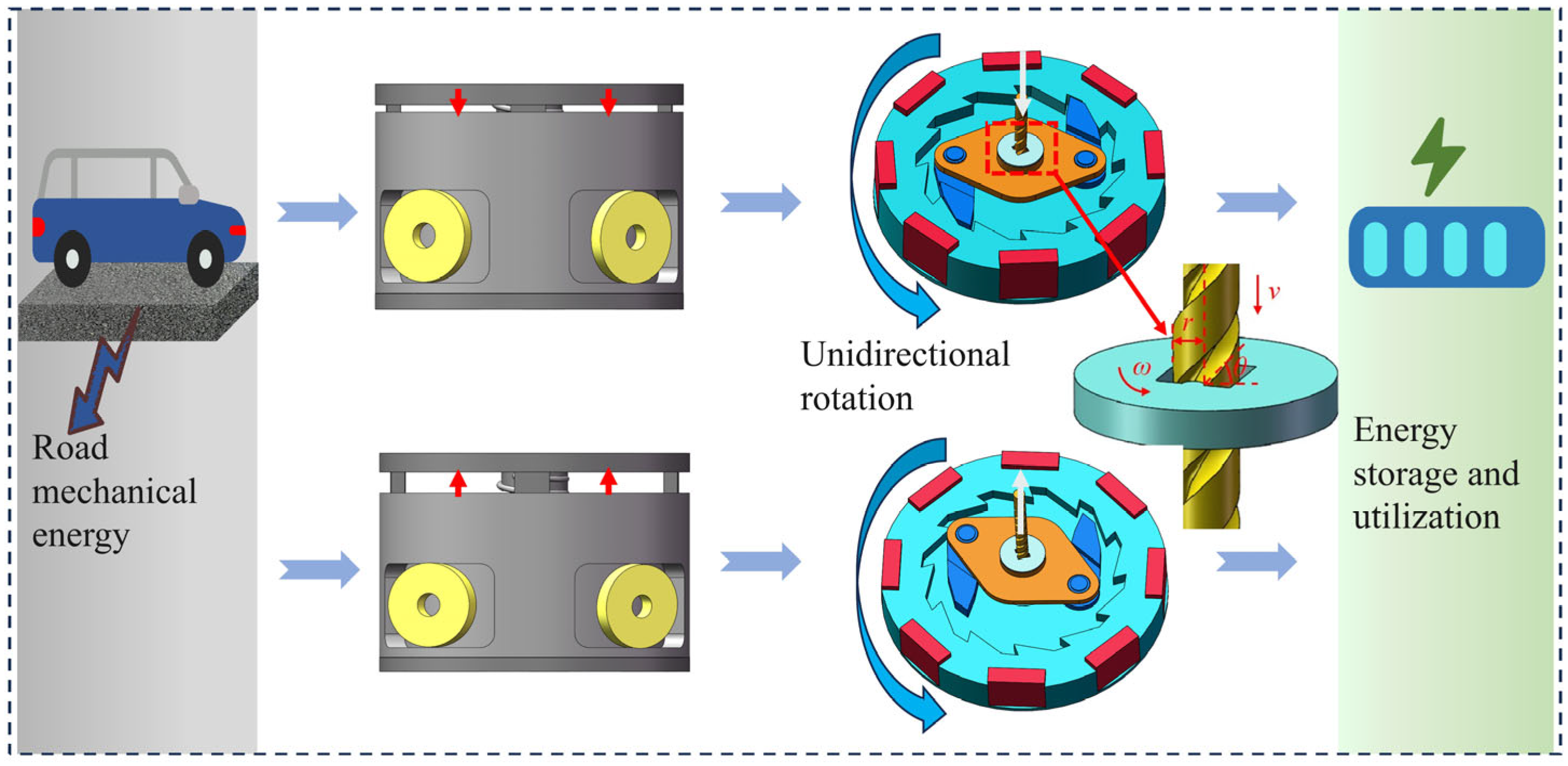
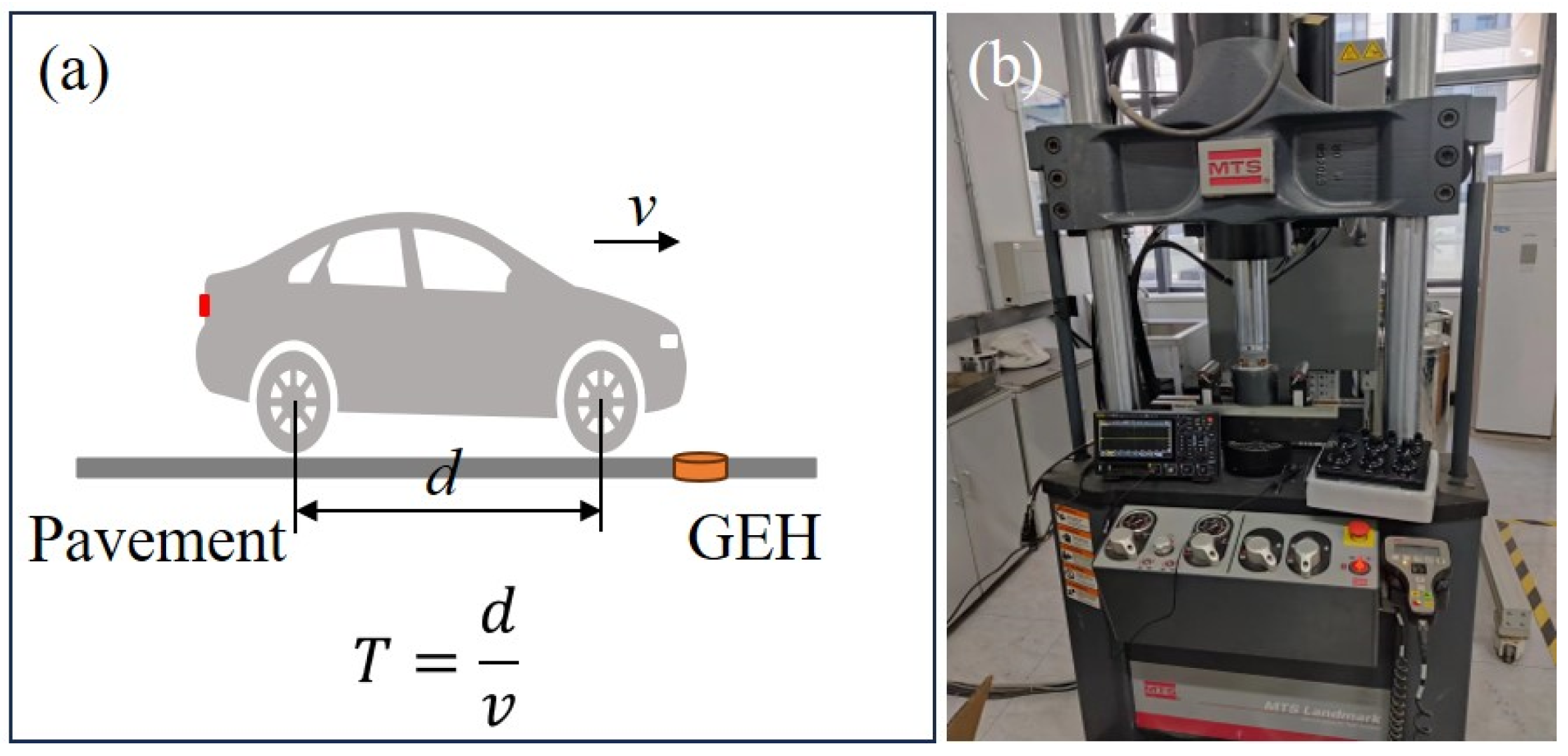
2. Design and Working Mechanism of the GEH
2.1. Structural Design Overview
2.2. Working Principle of the GEH
3. Output Optimization of the GEH
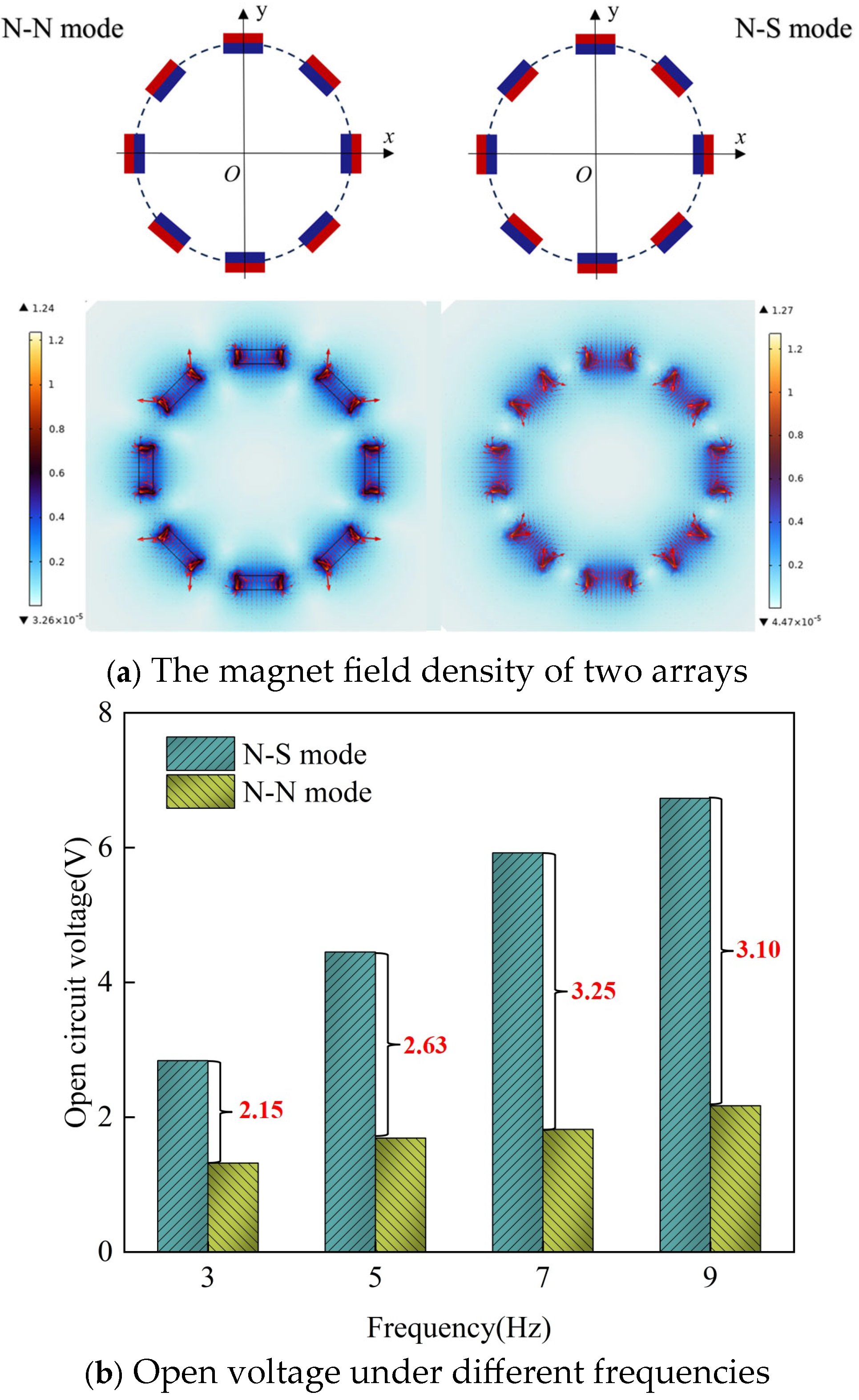
3.1. Optimization of the Number and Arrangement of Magnets
3.2. Effects of Magnet Mass
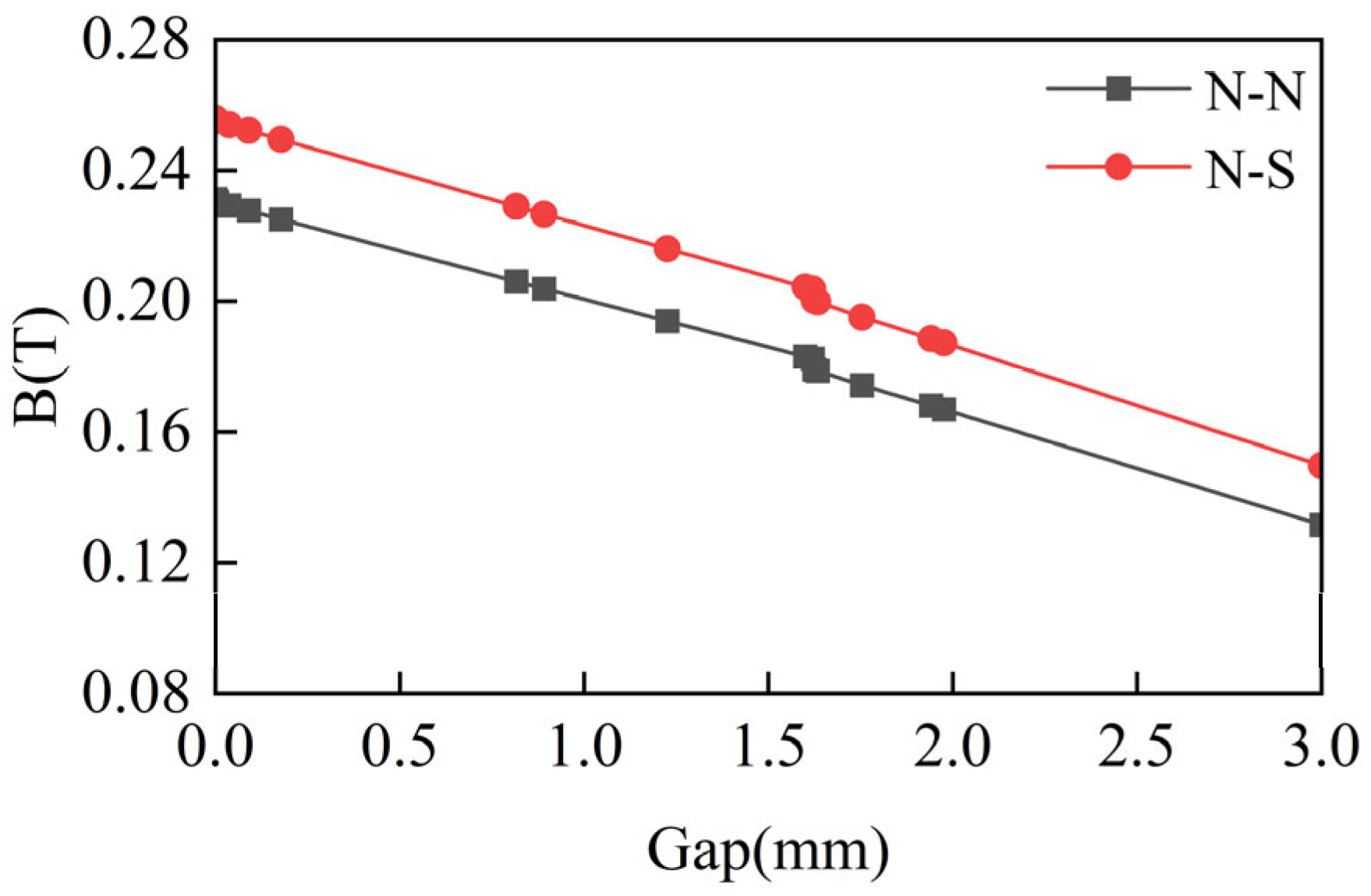
3.3. Determination of Coil and Magnet Distance
4. Electrical Performance Test
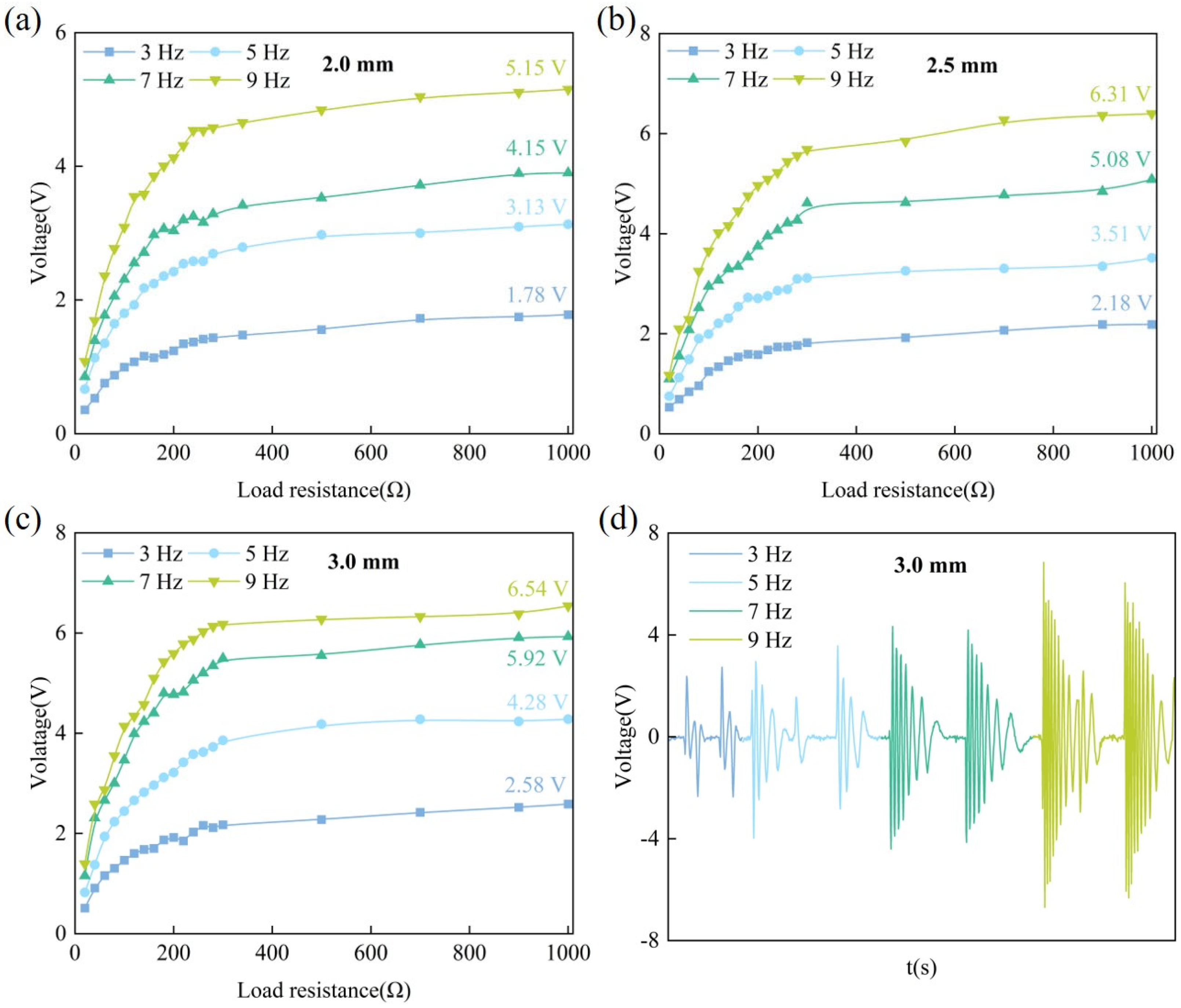
4.1. Voltage
4.1.1. Open-Circuit Voltage
4.1.2. Output Voltage
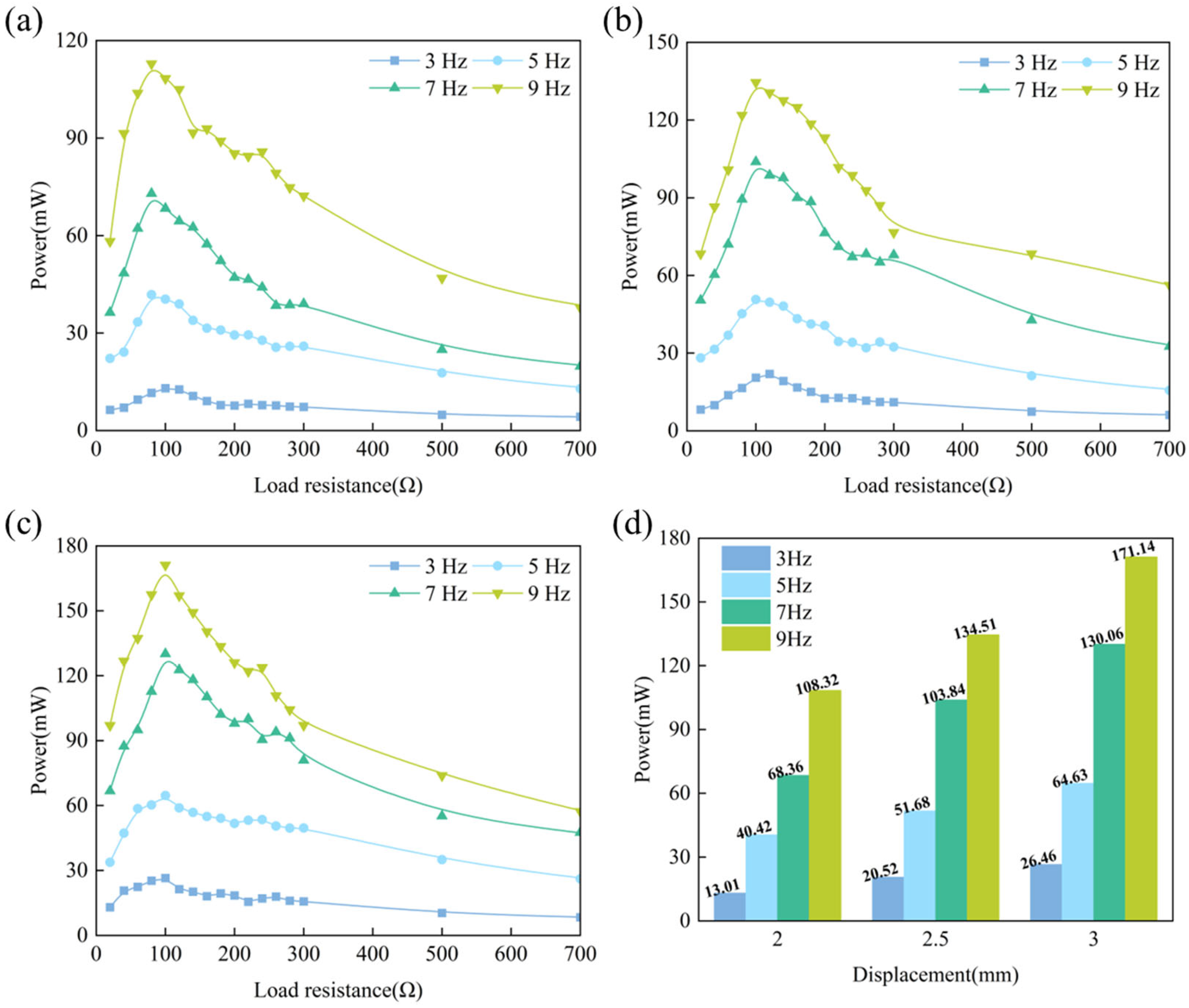
4.2. Output Power
4.3. Output Power Density
| Reference | Energy Harvesting Method | Area or Volume | Frequency | Voltage (V) | Power (W) | Power Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [38] | Electromagnetic | 0.12 m2 | 1~2 Hz | - | 3.21 × 10−3 | 0.027 W/m2 |
| [22] | Electromagnetic | 1.125 m2 | 0.5~2 Hz | 0.13 | 3.21 × 10−3 | 0.0028 W/m2 |
| [24] | Electromagnetic | - | 1~5 mm/s | 6.93 | - | - |
| [32] | Piezoelectric | 4.5 × 10−5 m3 | 80 km/h | 61.0 | 0.62 | 13.80 W/m3 |
| [30] | Electromagnetic | 5.5 × 10−3 m3 | 6 km/h | 51.2 | 0.54 | 98.18 W/m3 |
| [39] | Electromagnetic–triboelectric | 4 × 10−4 m3 | 0.1~0.5 Hz | 7.0 | - | 50.81 W/m3 |
| [36] | Piezoelectric | 2.83 × 10−4 m3 | 4 Hz | 7.48 | 5.19 × 10−5 | 0.18 W/m3 |
| [37] | Piezoelectric | 1.2 × 10−2 m3 | 13 Hz | 80.0 | 0.52 | 43.33 W/m3 |
| [40] | Piezoelectric–electromagnetic | 2.3 × 10−3 m3 | 10 Hz | 31.2 | 0.010 | 4.53 W/m3 |
| This work | Electromagnetic | 1.34 × 10−4 m3 | 9 Hz | 6.73 | 0.17 | 1277.16 W/m3 |
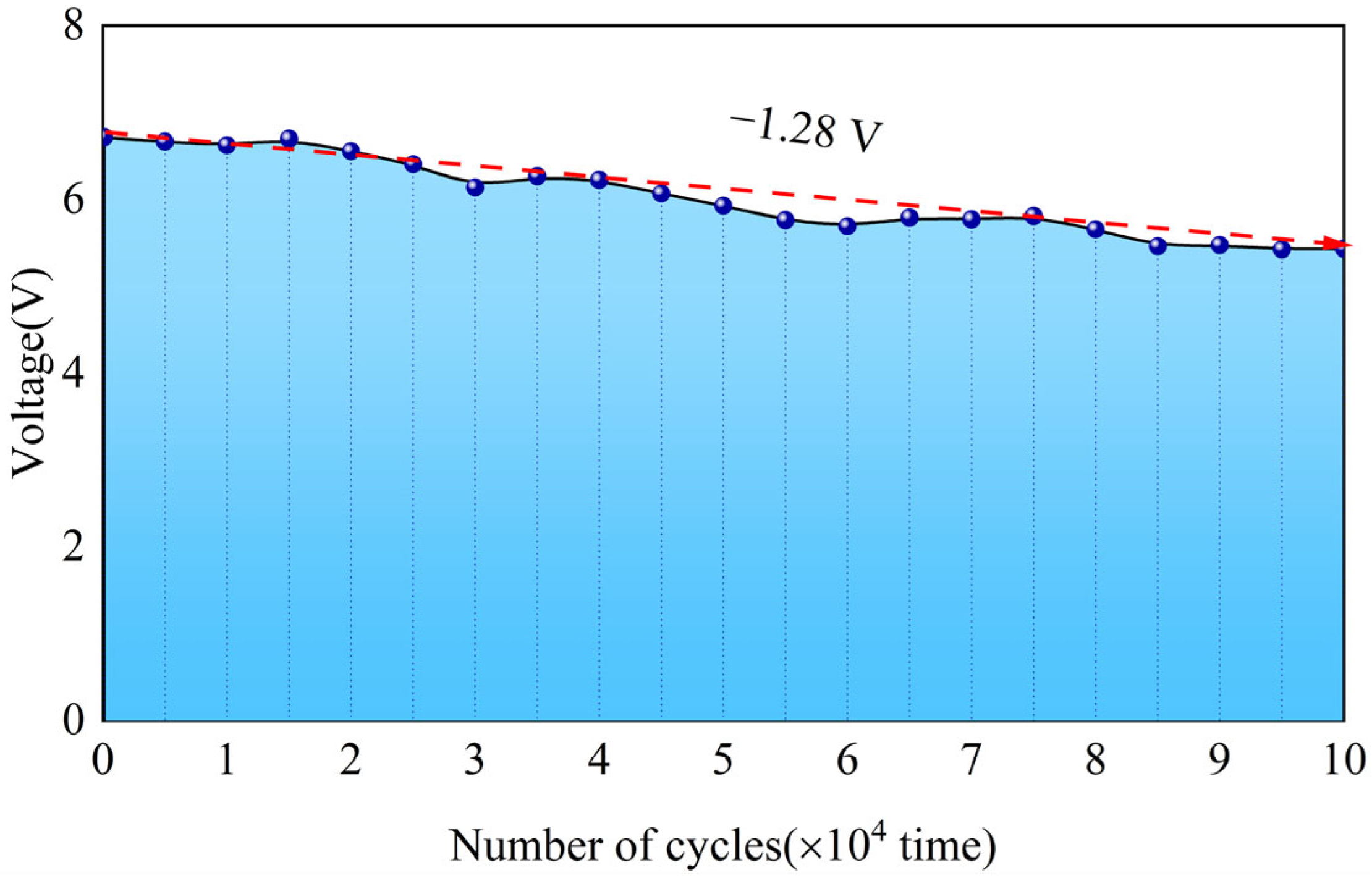
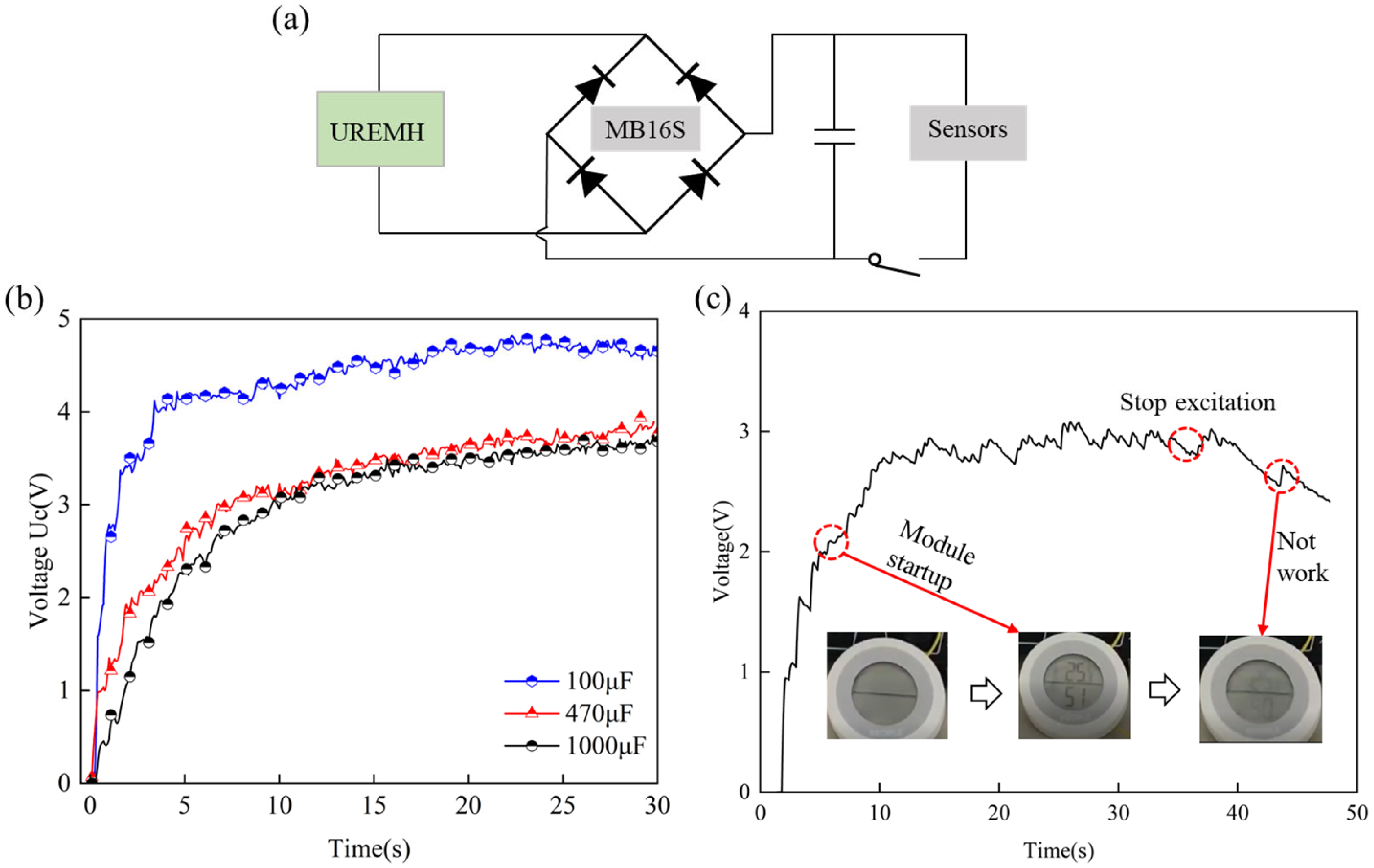
4.4. Long-Lasting Stability
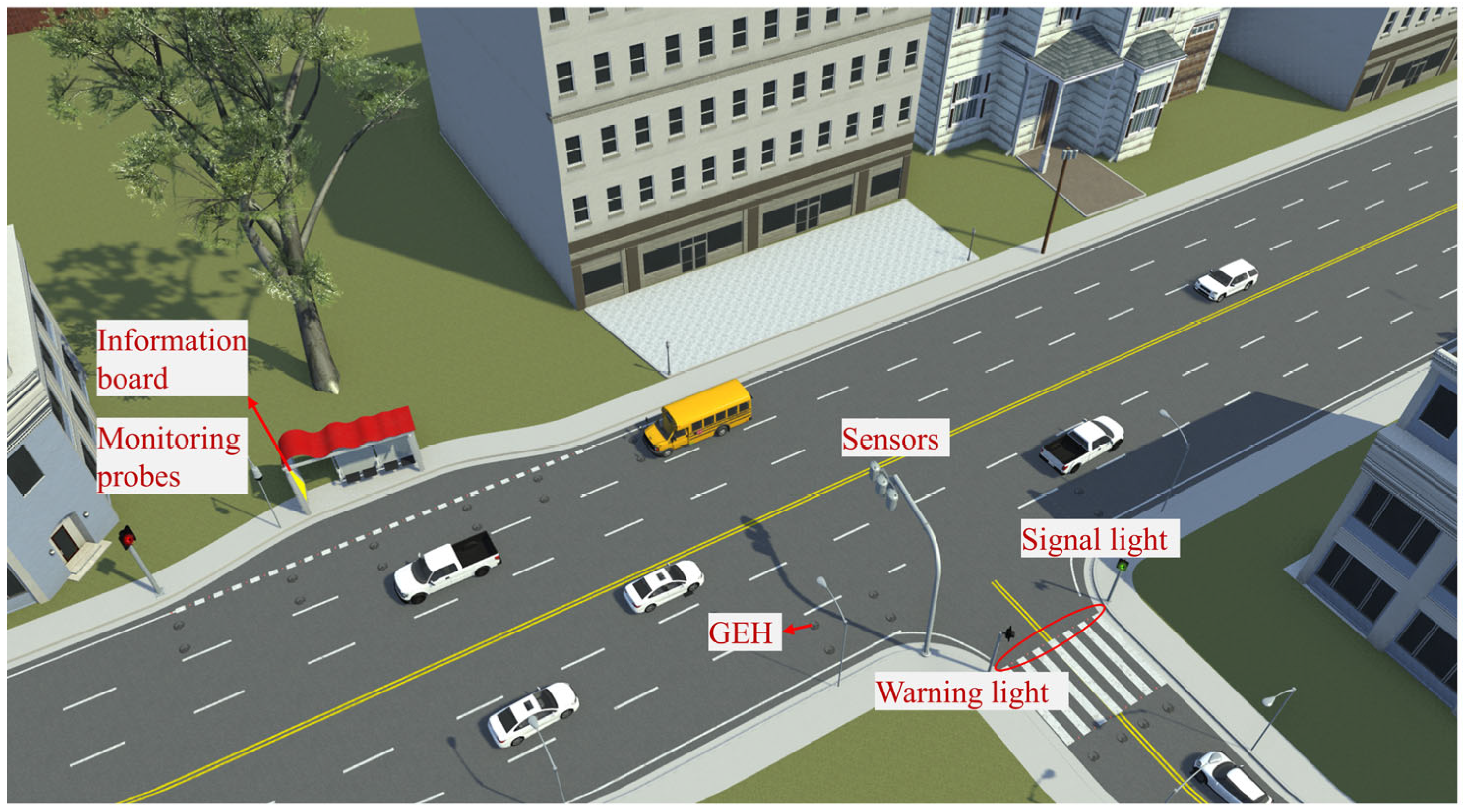
4.5. Actual Verification and Planning
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The energy harvester can collect the road mechanical energy efficiently through the up-frequency and unidirectional rotation mechanism under the limited vertical displacement of 3.0 mm.
- (2)
- The results show that the electrical performance of the GEH is improved when the frequency and displacement increase. Under 9 Hz excitation conditions, the output power of the GEH is 171.14 mW, the open circuit voltage is 6.73 V, and the output voltage drops by only 1.28 V after 100,000 consecutive loads.
- (3)
- At a frequency of 5 Hz, the electronic hygrothermograph can work and the capacitor charge voltage exceeds 3.3 V, which proves the GEH has the prospect of power supply for low-power sensors.
- (4)
- In the follow-up study, field tests in the actual road environment will be carried out to verify the working performance of the GEH, and research on the assembled structure will be carried out according to the sensor power supply requirements of the smart road to expand the application of the energy harvester.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, H.; Kong, L.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Lu, L.; Li, D. An electromagnetic energy harvester for applications in a high-speed rail pavement system. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 243, 108018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Jiang, W.; Sha, A.; Xiao, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, T. Technology method and functional characteristics of road thermoelectric generator system based on Seebeck effect. Appl. Energy 2023, 331, 120459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, X.; Si, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yi, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, S. Development and Performance of Road Piezoelectric Transducer Based on 3d Printing Package. Energy Build. 2023, 291, 113097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zuo, L.; Luhrs, G.; Lin, L.; Qin, Y.-x. Electromagnetic Energy-Harvesting Shock Absorbers: Design, Modeling, and Road Tests. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y. Waterbomb-origami inspired triboelectric nanogenerator for smart pavement-integrated traffic monitoring. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5450–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, F.; Zhao, H. Thermoelectric, piezoelectric and photovoltaic harvesting technologies for pavement engineering. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, R.; Wang, S.; Yuan, H.; Cao, H. Structure optimization and performance of piezoelectric energy harvester for improving road power generation effect. Energy 2023, 270, 126896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Sha, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. A power-intensive piezoelectric energy harvester with efficient load utilization for road energy collection: Design, testing, and application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sha, A.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, W. Energy output of piezoelectric transducers and pavements under simulated traffic load. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, A.; Wang, H.; Yesner, G.; Safari, A.; Maher, A. Optimized design of layered bridge transducer for piezoelectric energy harvesting from roadway. Energy 2017, 141, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, Z.; Gao, Z.; Yu, G.; Wang, S. Preparation and performance research of stacked piezoelectric energy-harvesting units for pavements. Energy Build. 2019, 183, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Ding, G.; Fu, H.; Cai, G. Watt-level road-compatible piezoelectric energy harvester for LED-induced lamp system. Energy 2021, 229, 126085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moure, A.; Izquierdo Rodriguez, M.A.; Hernandez Rueda, S.; Gonzalo, A.; Rubio-Marcos, F.; Urquiza Cuadros, D.; Perez-Lepe, A.; Fernandez, J.F. Feasible integration in asphalt of piezoelectric cymbals for vibration energy harvesting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 112, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.; Shin, Y.-H.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.-y.; Kang, C.-Y. Flexible piezoelectric polymer-based energy harvesting system for roadway applications. Appl. Energy 2017, 197, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, L. Piezoelectric energy harvester for public roadway: On-site installation and evaluation. Appl. Energy 2016, 174, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.D.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, K.-B.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Woo, M.S.; Song, Y.; Hwang, W.; Jeon, D.H.; Kim, J.; et al. Uniform stress distribution road piezoelectric generator with free-fixed-end type central strike mechanism. Energy 2022, 239, 121812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Lin Wang, Z. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.; Chung, J.; Kim, B.; Yong, H.; Shin, G.; Cho, J.-W.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Triboelectric speed bump as a self-powered automobile warning and velocity sensor. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargari, S.; Daie Koozehkanani, Z.; Veladi, H.; Sobhi, J.; Rezania, A. A new Mylar-based triboelectric energy harvester with an innovative design for mechanical energy harvesting applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 244, 114489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Peter, W.T. Fabrication and testing of an energy-harvesting hydraulic damper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 065024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholikhani, M.; Beheshti Shirazi, S.Y.; Mabrouk, G.M.; Dessouky, S. Dual electromagnetic energy harvesting technology for sustainable transportation systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 230, 113804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholikhani, M.; Nasouri, R.; Tahami, S.A.; Legette, S.; Dessouky, S.; Montoya, A. Harvesting kinetic energy from roadway pavement through an electromagnetic speed bump. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, N.; Gu, Z.; Saafi, M. Crank shaft road electromagnetic road energy harvester for smart city applications. Appl. Energy 2023, 352, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Abid, M.M. A High-Voltage Mechanical Energy Harvester Using Crank-Shaft Mechanism for Applications in Toll Stations on Expressways. Energy Technol. 2024, 12, 2301079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, N.; Yuan, X.; Wei, T. Hydraulic-Based Rotary Electromagnetic Energy Harvester for Road Speed Bumps. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Control, Electronics and Computer Technology (ICCECT), Jilin, China, 26–28 April 2024; pp. 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Lin, R.; Zhou, S.; Yu, Y.; Ishida, A.; McGrath, M.; Kennedy, B.; Hajj, M.; Zuo, L. Design, simulation and experiment of a novel high efficiency energy harvesting paver. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, W.; Zheng, P.; Luo, D.; Zhang, Z. A novel road energy harvesting system based on a spatial double V-shaped mechanism for near-zero-energy toll stations on expressways. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 323, 112648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Jia, C.; Zheng, P.; Gong, Y.; Li, N.; Ahmed, A.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, D. A transverse deceleration energy harvester based on a sliding plate for self-powered applications in near-zero energy road tunnels. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 84, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Ahmadi, R.; Abazari, A.M. Footstep-powered floor tile: Design and evaluation of an electromagnetic frequency up-converted energy harvesting system enhanced by a cylindrical Halbach array. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 60, 103571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.-X.; Zhu, Q.-W.; He, J.-Y.; Zhao, L.-C.; Wei, K.-X.; Zhang, W.-M.; Du, R.-H.; Liu, S. Energy harvesting floor using sustained-release regulation mechanism for self-powered traffic management. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S.; Luo, J. Influences of Wire Diameters on Output Power in Electromagnetic Energy Harvester. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2022, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-H.; Jung, I.; Noh, M.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Kang, C.-Y. Piezoelectric polymer-based roadway energy harvesting via displacement amplification module. Appl. Energy 2018, 216, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ji, Y.; Lai, S.-K.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Wen, G.-L. A speed-amplified tri-stable piezoelectric-electromagnetic-triboelectric hybrid energy harvester for low-frequency applications. Nano Energy 2023, 114, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Cao, H. Optimization of piezoelectric device with both mechanical and electrical properties for power supply of road sensors. Appl. Energy 2024, 364, 123113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Fan, K.; Wang, F. An inertial rotary energy harvester for vibrations at ultra-low frequency with high energy conversion efficiency. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Cai, G.; Wang, L. Research on integrated electrical and mechanical response of piezoelectric asphalt pavement material under bidirectional cyclic loads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 375, 130957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingyong, P.; Thainiramit, P.; Jayasvasti, S.; Thanach-Issarasak, N.; Isarakorn, D. Evaluation of harvesting energy from pedestrians using piezoelectric floor tile energy harvester. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 113035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, H.; Gholikhani, M.; Amid Tahami, S.; Dessouky, S. Harvesting Energy from Pavement—Electromagnetic Approach. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Sibiu, Romania, 5–7 June 2019; Volume 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, H.; Asadi, E.; Saadatnia, Z.; Khajepour, A.; Khamesee, M.B.; Zu, J. A hybridized electromagnetic-triboelectric self-powered sensor for traffic monitoring: Concept, modelling, and optimization. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ru, X.; Hu, X. A hybrid piezoelectric-electromagnetic energy harvester used for harvesting and detecting on the road. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, R.; Du, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.; Lin, Z.; Tan, T. Broadband omnidirectional piezoelectric–electromagnetic hybrid energy harvester for self-charged environmental and biometric sensing from human motion. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, F.; Gulino, M.-S.; Laschi, M.; Lozito, G.M.; Pugi, L.; Reatti, A.; Vangi, D. Time-domain circuit modelling for hybrid supercapacitors. Energies 2021, 14, 6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

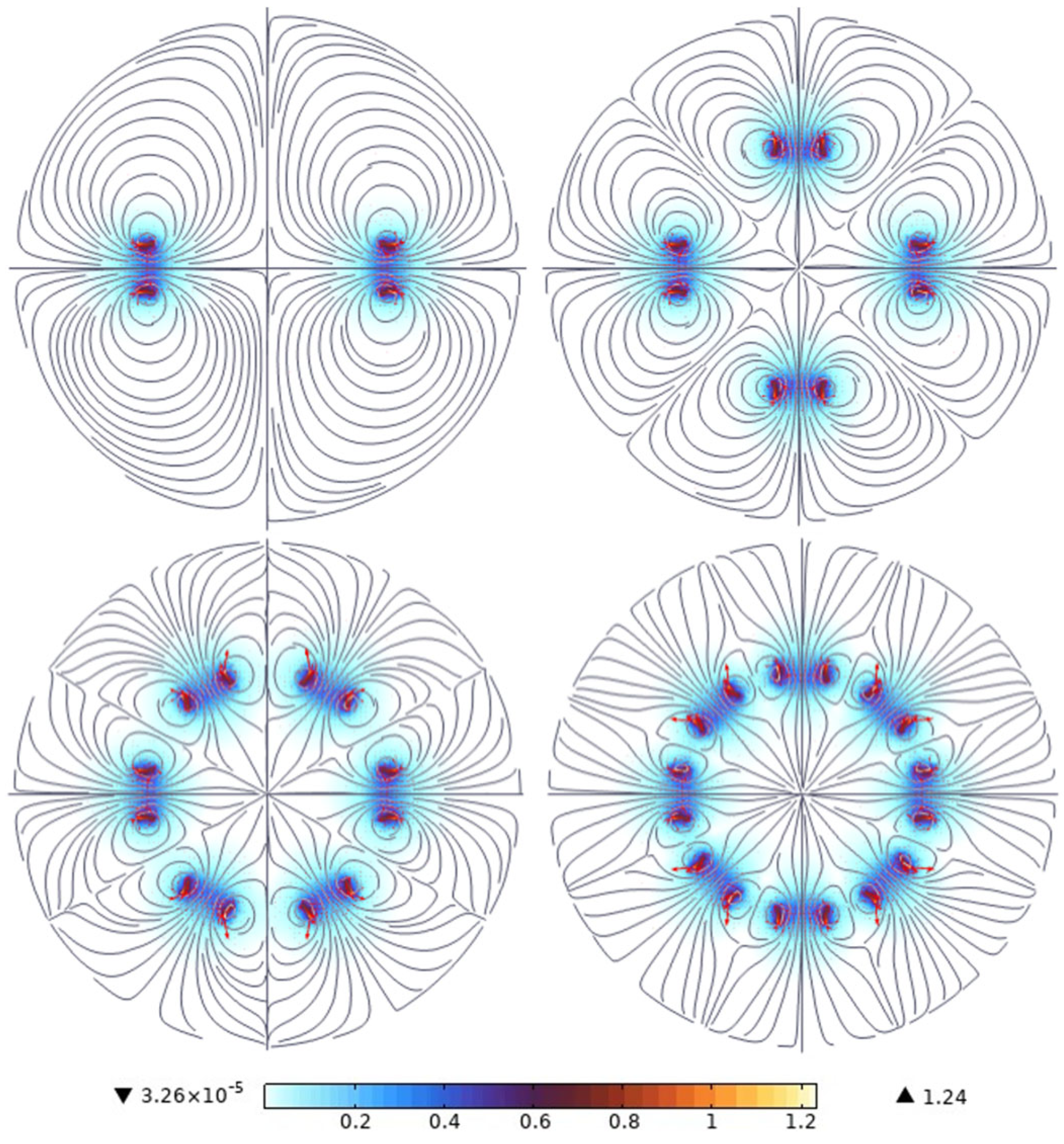


| Magnet Size (mm) | Magnet Material | Number of Magnets | Residual Flux Density Model (mT) | Reverse Permeability | Air Relative Magnetic Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 × 10 × 3 | N52 | 2~8 | 1.44 | 1.05 | 1 |
| Number of Magnets | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average magnetic field intensity (mT) | 18.3 | 35.6 | 48.2 | 57.5 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Material of magnets | NdFeB-N52 |
| Number of magnets | 8 |
| Volume of magnets | 10 × 10 × 3 mm3 |
| Copper wire diameter | 0.12 mm |
| Turns of each copper coil | 500 |
| Coil internal resistance | 24 Ω |
| Gap between the coil and magnet | 2 mm |
| Diameter of prototype | 61 mm |
| Height of prototype | 46 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mou, K.; Ji, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Y. A Green Electromagnetic Energy Harvester with Up-Frequency and Unidirectional Rotation for Smart Pavement. Materials 2025, 18, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040786
Mou K, Ji X, Li X, Zhou H, Wu Y, Fang Y. A Green Electromagnetic Energy Harvester with Up-Frequency and Unidirectional Rotation for Smart Pavement. Materials. 2025; 18(4):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040786
Chicago/Turabian StyleMou, Keliang, Xiaoping Ji, Xiaojuan Li, Haoyu Zhou, Yunrui Wu, and Yeyang Fang. 2025. "A Green Electromagnetic Energy Harvester with Up-Frequency and Unidirectional Rotation for Smart Pavement" Materials 18, no. 4: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040786
APA StyleMou, K., Ji, X., Li, X., Zhou, H., Wu, Y., & Fang, Y. (2025). A Green Electromagnetic Energy Harvester with Up-Frequency and Unidirectional Rotation for Smart Pavement. Materials, 18(4), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040786







