A Hydrothermal and Combustion-Reduction Process with Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone as a Restricted Growth Agent and Galactose as a Reducing Agent for the Fabrication of Rod-like α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication and Characterization of β-FeOOH Nanorods
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 MNCs
2.4. MTT Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of β-FeOOH NRs
3.2. Optimization of Fabrication Conditions for β-FeOOH NRs
3.2.1. Optimization of FeCl3 Concentration
3.2.2. Optimization of PVP Concentration
3.2.3. Optimization of Hydrothermal Temperature
3.2.4. Optimization of Hydrothermal Time
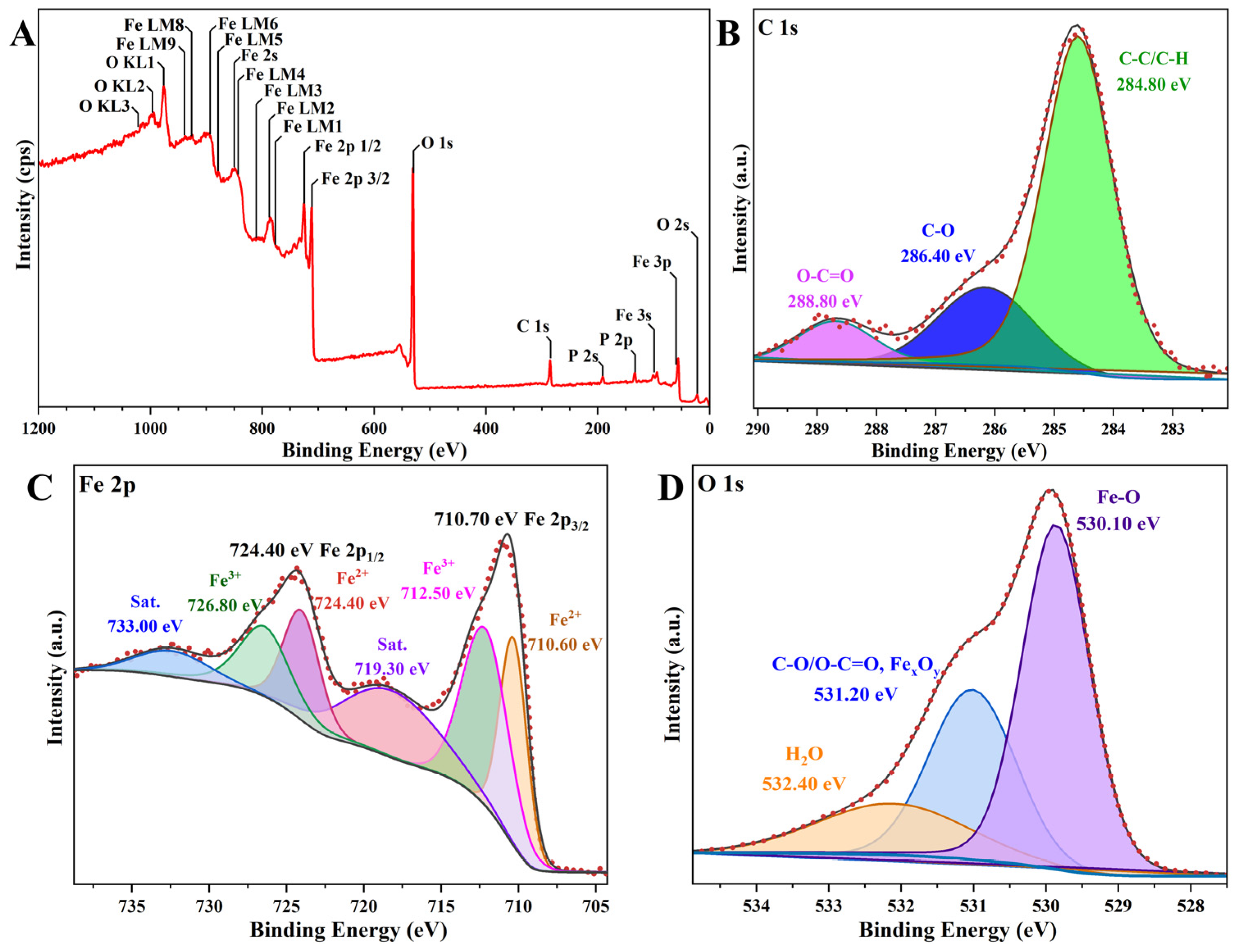
3.3. Characteristics and MTT Evaluation of α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 MNCs
3.4. Optimization of Preparation Conditions for α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 MNCs
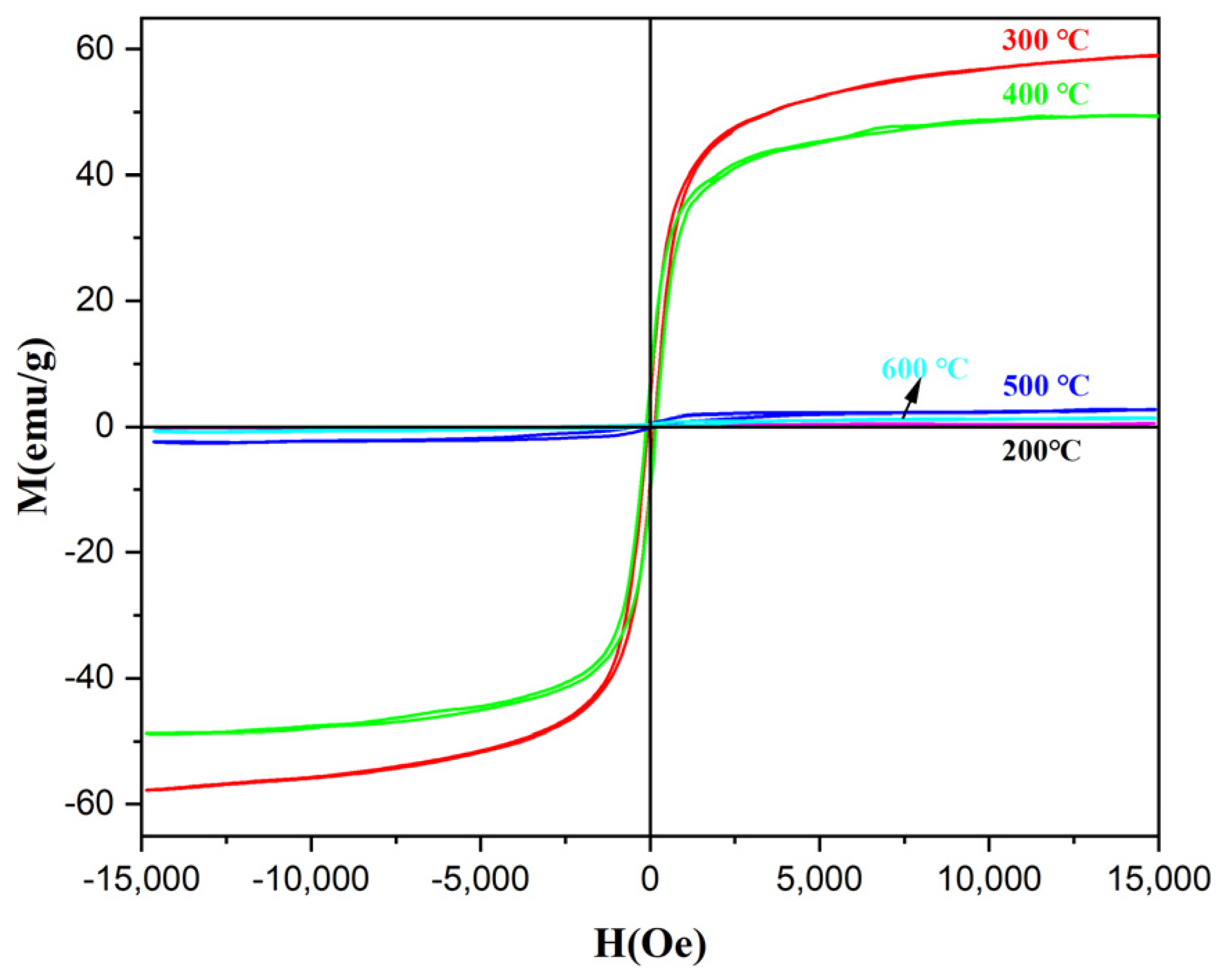
3.4.1. Optimization of Calcination Temperature
3.4.2. Optimization of Calcination Time
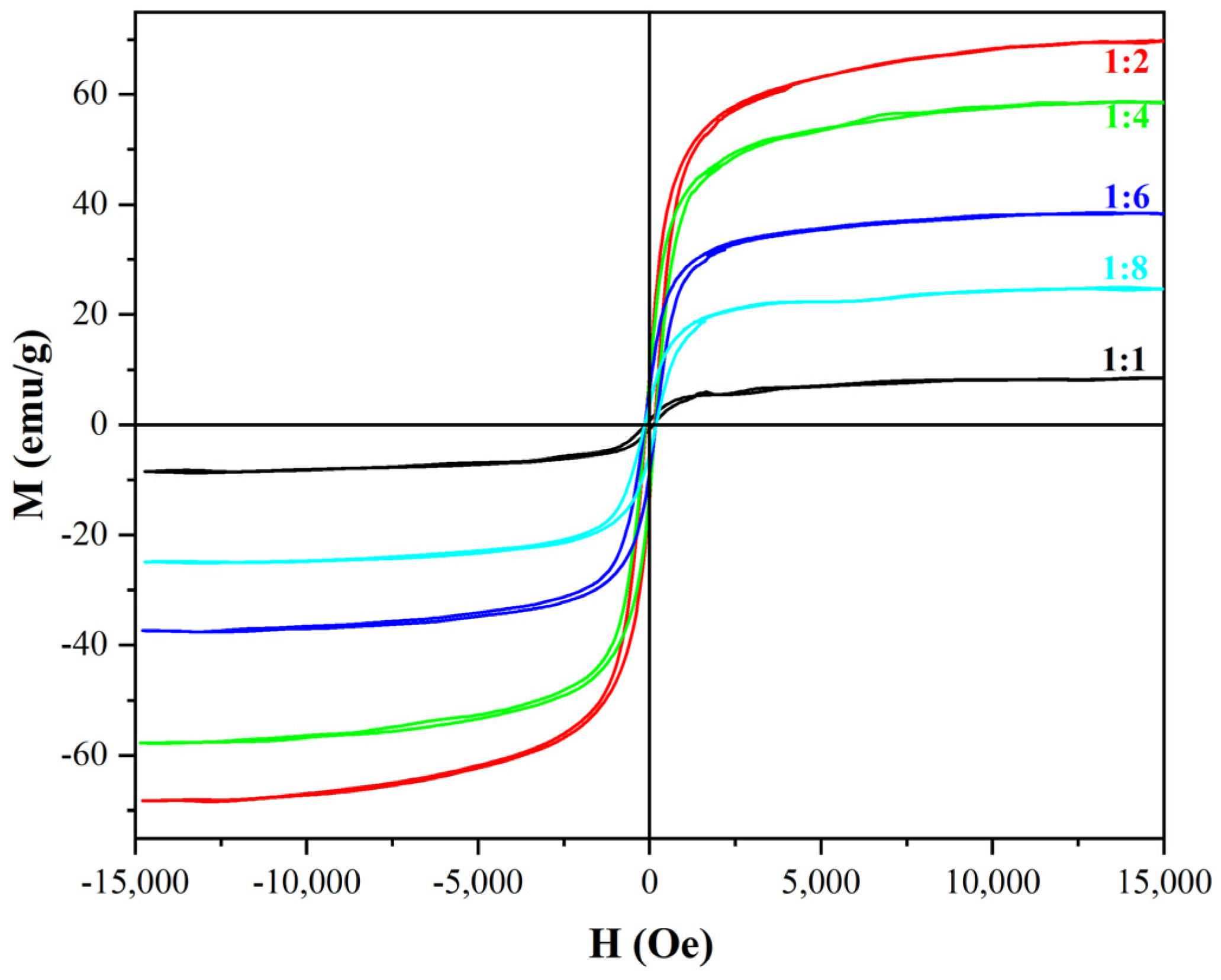
3.4.3. Optimization of Mass Ratio for β-FeOOH NRs and Galactose
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhao, S.H.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wu, L.P.; Liu, R.J. Fabrication and Characterization of Magnetic Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3 Heterogeneous Nanorods. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2024, 34, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Ouyang, H.Z.; Ling, C.; Ma, M.Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.J. Fabrication of Magnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterostructure Nanorods via the Urea Hydrolysis-Calcination Process and Their Biocompatibility with LO2 and HepG2 Cells. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 505711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Q.; Huang, R.; Hu, R.M.; Fan, J.J.; Zhang, D.L.; Ding, J.; Li, R. Phytic Acid-Modified Manganese Dioxide Nanoparticles Oligomer for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Targeting Therapy of Osteosarcoma. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2181743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yang, S.P.; Zheng, Z.L.; Li, Q.S.; Liu, C.C.; Hu, D.H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, R.P.; Gao, D.Y. Biomimetic Theranostic Agents with Superior NIR-II Photoacoustic and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performance for Targeted Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Deng, P.; Yin, R.T.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Ling, C.; Ma, M.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, S.S.; Liu, R.J. Effect and Mechanism of Paclitaxel Loaded on Magnetic Fe3O4@mSiO2-NH2-FA Nanocomposites to MCF-7 Cells. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucillo, P. Biomaterials for Drug Delivery and Human Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshev, N.; Kapralov, P.; Evstigneeva, S.; Lutsenko, O.; Shilina, P.; Zharkov, M.; Pyataev, N.; Darwish, A.; Timin, A.; Ostras, M.; et al. Yttrium-Iron Garnet Film Magnetometer for Registration of Magnetic Nano- and Submicron Particles: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. IEEE T. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 71, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ghoorchian, A.; Dashtian, K.; Kamalabadi, M.; Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A. Application of Magnetic Nanomaterials in Electroanalytical Methods: A Review. Talanta 2021, 225, 121974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhao, S.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.J. Construction of a Label-Free Electrochemical Biosensing System Utilizing Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3@Au with Magnetic-Induced Self-Assembly for the Detection of EGFR Glycoprotein. Vacuum 2024, 222, 112975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Ni, Y.; Yue, Y.; He, D.W.; Liu, R.J. Magnetically Induced Self-Assembly Electrochemical Biosensor with Ultra-Low Detection Limit and Extended Measuring Range for Sensitive Detection of HER2 Protein. Bioelectrochemistry 2024, 155, 108592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytov, R.A.; Usov, N.A. Specific Absorption Rate of Randomly Oriented Magnetic Nanoparticles in a Static Magnetic Field. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Tang, J.W.; Yang, Y.P.; He, N.; Li, S.S.; Liu, R.J. Construction of Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Magnetic Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3 Heterogeneous Nanorods for the Sensitive Detection of MUC1 Mucoprotein. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 10706–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ouyang, H.Z.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, H.D.; Sun, L.; Liu, R.J.; Li, S.S. Magnetic Self-Assembled Label-Free Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3 Heterogeneous Nanosheets for the Detection of Tau Proteins. Bioelectrochemistry 2024, 157, 108678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Xu, Z.H.; Sun, L.; Li, S.S.; Liu, R.J. Ultrasensitive Detection of PSA in Human Serum Using Label-Free Electrochemical Biosensor with Magnetically Induced Self-Assembly Based on α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4@Au Nanocomposites. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagare, A.; Dhadage, A.; Baithy, M.; Bhuyan, P.M.; Gogoi, P.; Athare, A.; Navgire, M. Sol-Gel Assisted β-Cyclodextrin Coated MoO3-Fe2O3 Nanocomposite for Photodegradation of Methylene Blue Dye. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024, 110, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Banerjee, A.M.; Pai, M.R.; Meena, S.S.; Patra, A.K.; Sastry, P.U.; Jagannath; Tripathi, A.K. Sol-Gel Mediated Synthesis and Characterization of Hierarchically Porous Fe2O3/SiO2 Monolithic Catalyst for High Temperature Sulfuric Acid Decomposition. Catal. Commun. 2023, 179, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanimozhi, G.; Nibagani, N.; Nair, D.S.; Kumar, H.; Satyanarayana, N. A Synergic Effect of N-Graphene Wrapped α-Fe2O3 Nanofacets Prepared by Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Method for Lithium-Ion Battery. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 169, 110885. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.H.; Zhuang, X.Y.; Xu, J.H.; Ruan, L.X.; Jiang, Y.F.; Lin, J.X.; Zhang, X.M. Enhanced Photo-Fenton Activity of SnO2/α-Fe2O3 Composites Prepared by a Two-Step Solvothermal Method. Materials 2022, 15, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Srivastava, M.; Alhazmi, A.; Mohammad, A.; Khan, S.; Pal, D.B.; Haque, S.; Singh, R.; Mishra, P.K.; Gupta, V.K. Sustainable green approach to synthesize Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite using waste pulp of Syzygium cumini and its application in functional stability of microbial cellulases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, J.; Goenuellue, Y.; Ghamgosar, P.; You, S.; Mouzon, J.; Choi, H.; Vomiero, A.; Grosch, M.; Mathur, S. Electronically-Coupled Phase Boundaries in α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Nanocomposite Photoanodes for Enhanced Water Oxidation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkanad, K.; Hezam, A.; Shekar, G.C.S.; Drmosh, Q.A.; Kala, A.L.A.; AL-Gunaid, M.Q.A.; Lokanath, N.K. Magnetic recyclable α-Fe2O3–Fe3O4/Co3O4–CoO nanocomposite with a dual Z-scheme charge transfer pathway for quick photo-Fenton degradation of organic pollutants. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.J.; Huang, W.; Pan, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.L.; He, D.W. Covalent Immobilization and Characterization of Penicillin G Acylase on Magnetic Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterostructure Nanoparticles Prepared via a Novel Solution Combustion and Gel Calcination Process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.Z.; Yang, F.; Sun, Z.P. Hexagonal Bi-Pyramid α-Fe2O3 Microcrystals: Unusual Formation, Characterization and Application for Gas Sensing. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 889, 161515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Lv, Z.X.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, J.S.; Sun, Z.J.; He, D.W.; Liu, R.J. Label-Free Electrochemical Biosensor with Magnetic Self-Assembly Constructed via PNA-DNA Hybridization Process on α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Nanosheets for APOE Ε4 Genes Ultrasensitive Detection. Bioelectrochemistry 2025, 161, 108847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Fan, X.L.; Xue, J. A Novel Magnetic Manganese Oxide Halloysite Composite by One-Pot Synthesis for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. J. Alloy. Compd. 2023, 930, 167050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS Spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ Ions in Oxide Materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Huang, Q.S. In-Plane Structured Fe3O4/FeS Composite Loaded on Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Stabilized Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, P.; Hussain, S.; Jia, L.J.; Lin, D.; Yin, X.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, Z.H.; Wang, L.Y. FeS2/Carbon Hybrids on Carbon Cloth: A Highly Efficient and Stable Counter Electrode for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
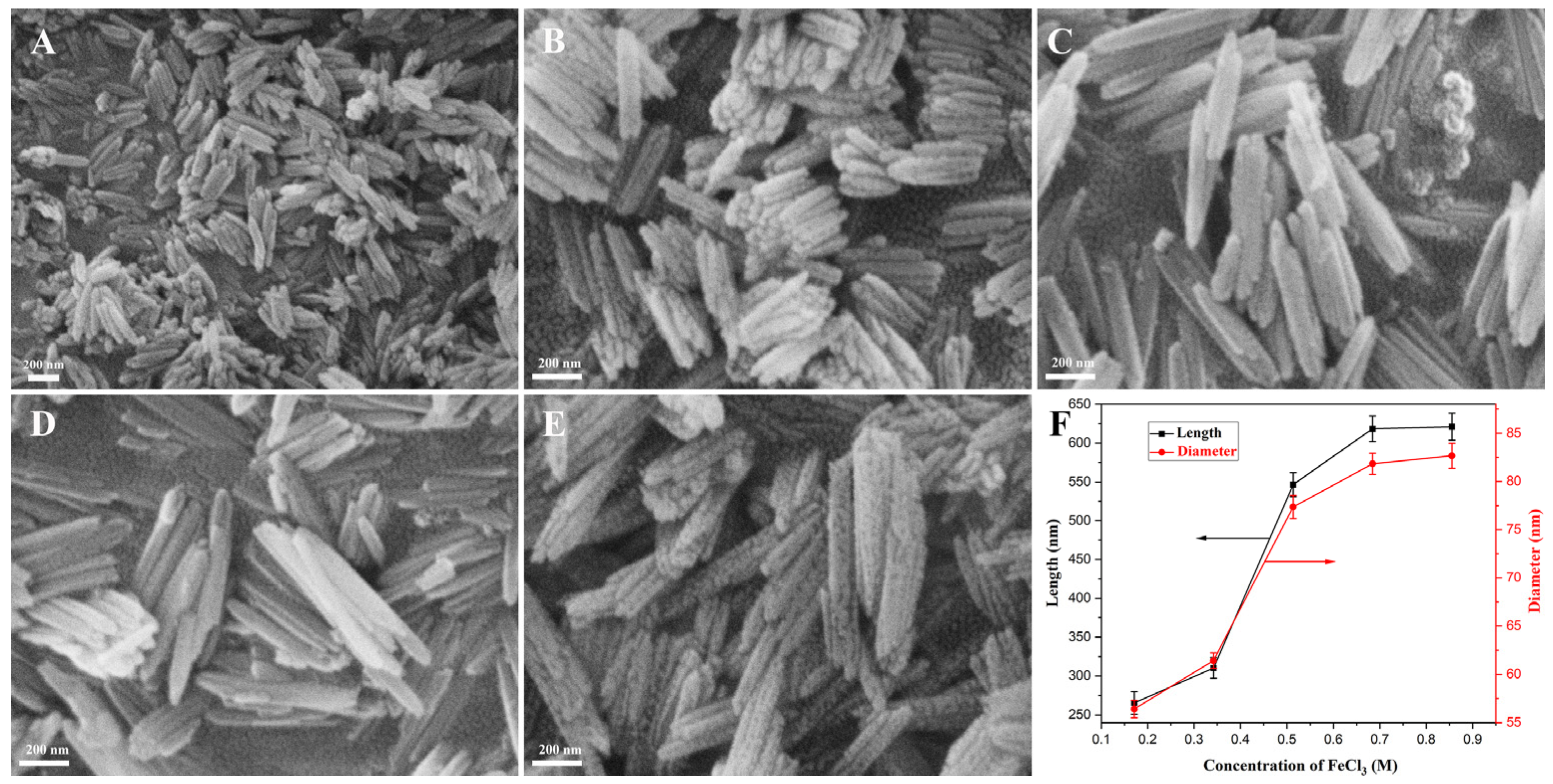
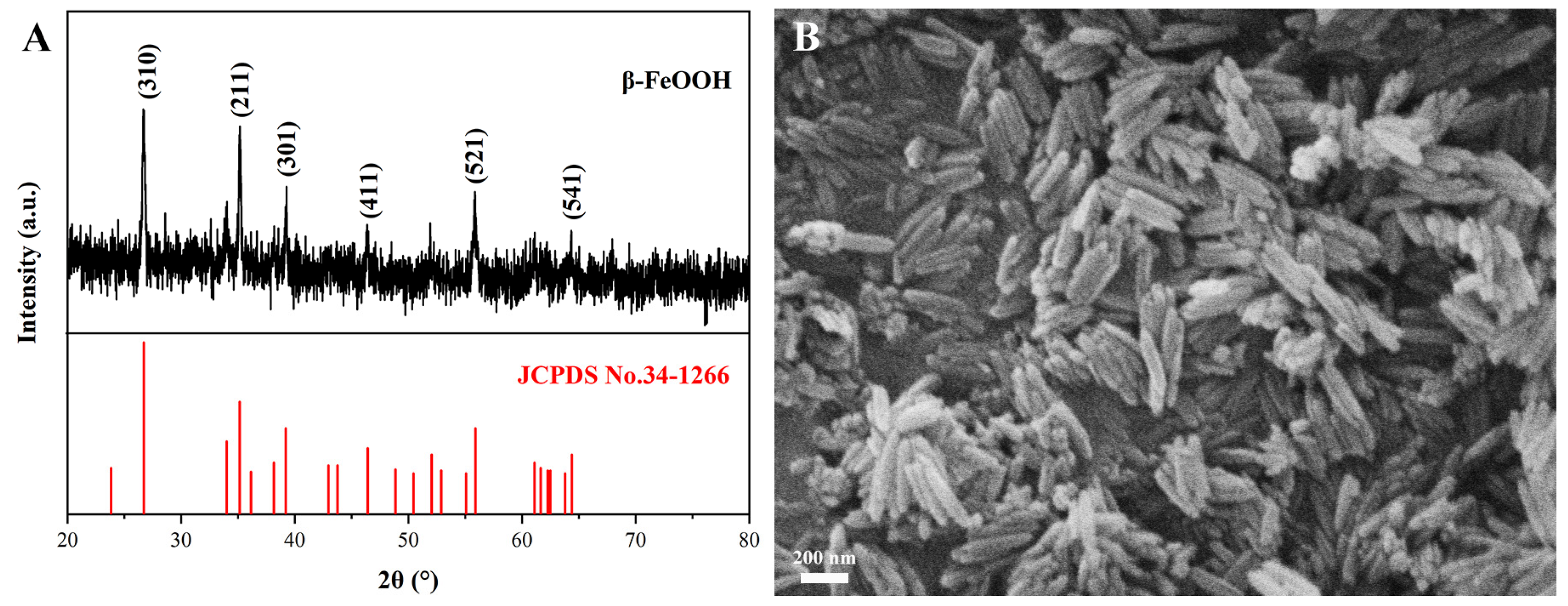

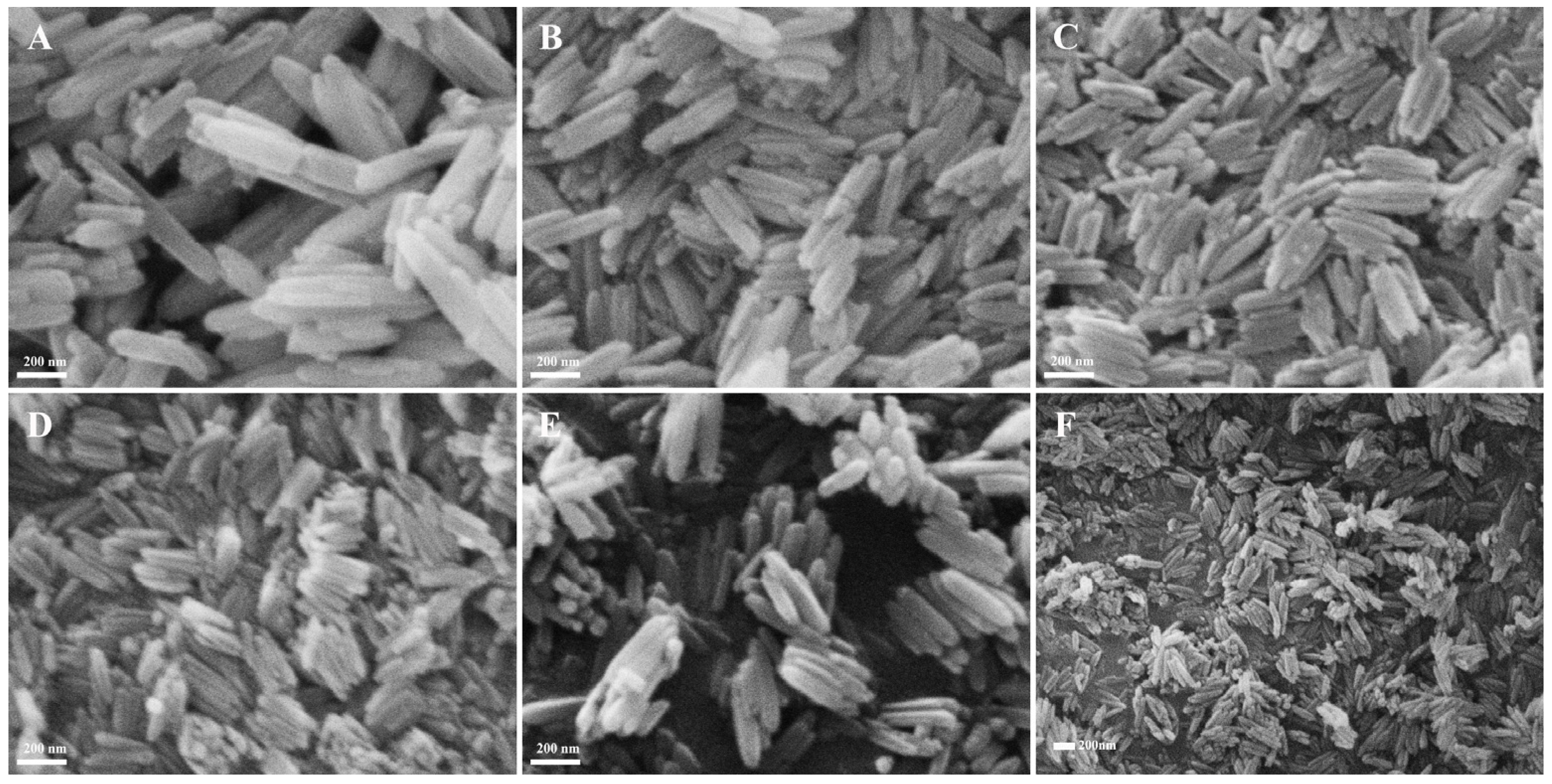
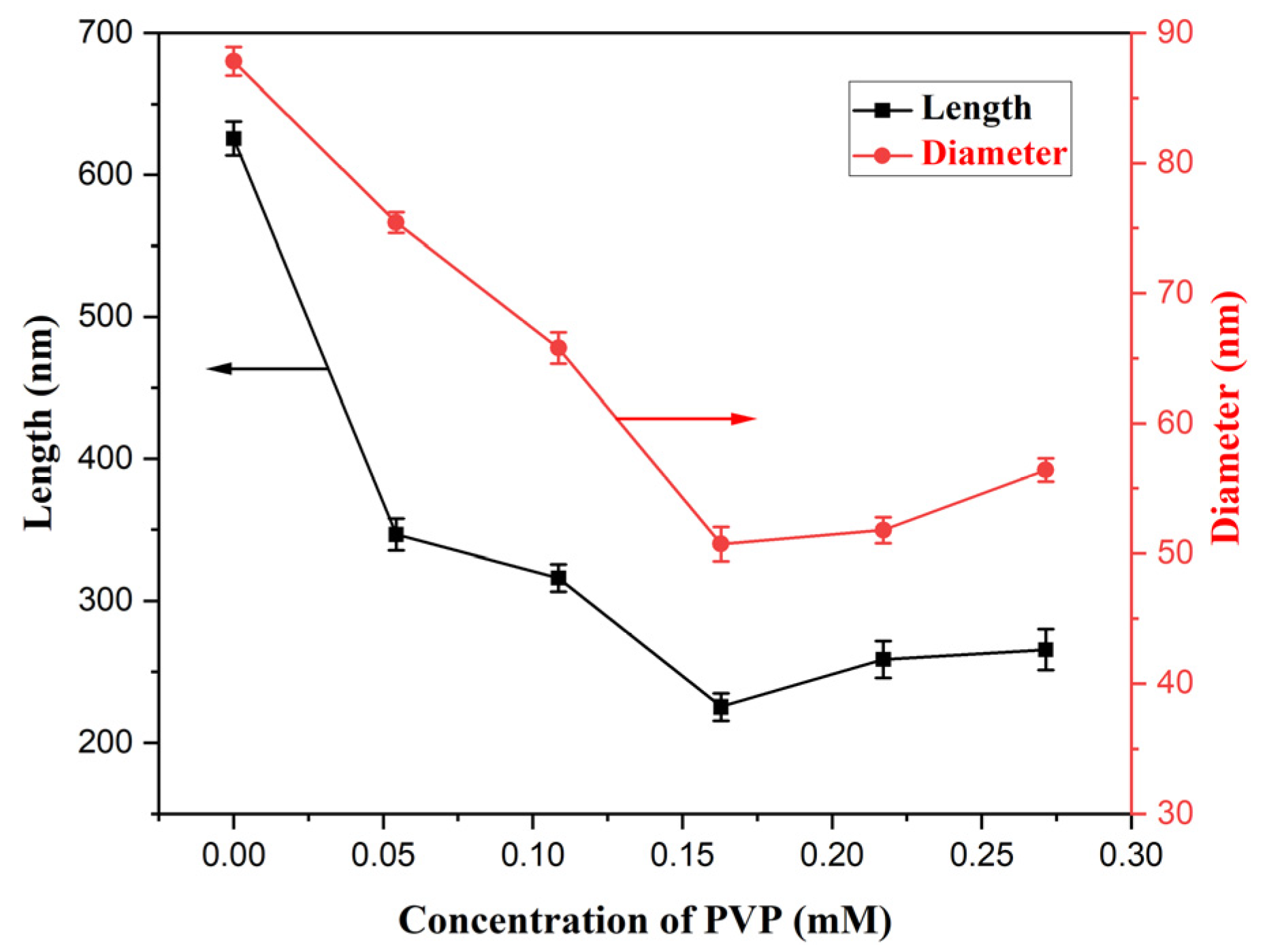
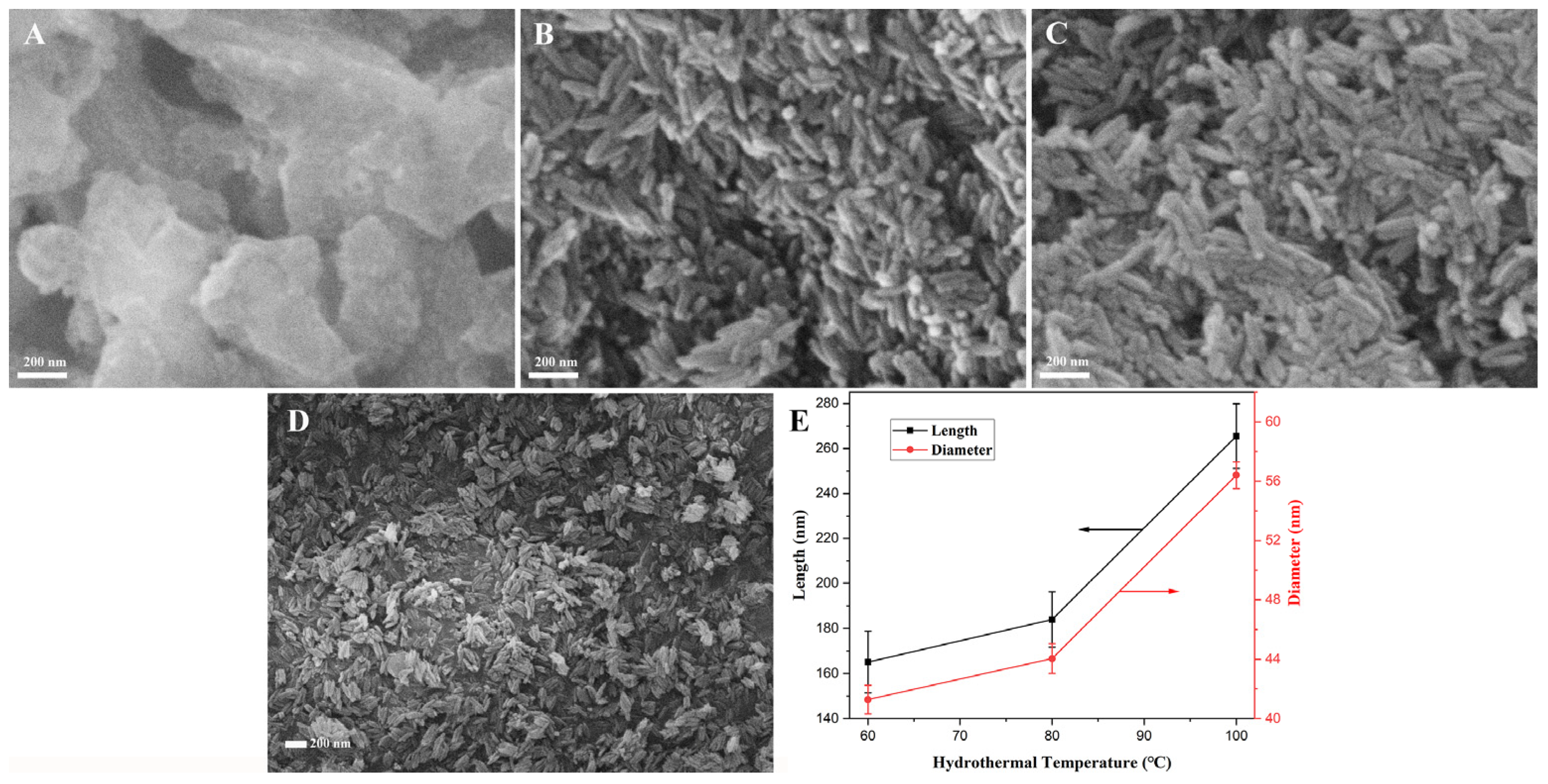





| FeCl3 (M) | PVP (mM) | Hydrothermal Time (h) | Hydrothermal Temperature (°C) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.171 | 0.271 | 10 | 100 | 28.19 |
| 0.342 | 0.271 | 10 | 100 | 14.63 |
| 0.513 | 0.271 | 10 | 100 | 8.90 |
| 0.684 | 0.271 | 10 | 100 | 7.27 |
| 0.855 | 0.271 | 10 | 100 | 5.25 |
| 0.171 | 0.271 | 10 | 80 | 24.30 |
| 0.171 | 0.271 | 10 | 60 | 6.91 |
| 0.171 | 0.271 | 10 | 40 | 0.91 |
| 0.171 | 0.000 | 10 | 100 | 25.19 |
| 0.171 | 0.054 | 10 | 100 | 28.10 |
| 0.171 | 0.109 | 10 | 100 | 28.56 |
| 0.171 | 0.163 | 10 | 100 | 30.13 |
| 0.171 | 0.217 | 10 | 100 | 29.31 |
| 0.171 | 0.163 | 2 | 100 | 1.47 |
| 0.171 | 0.163 | 4 | 100 | 23.87 |
| 0.171 | 0.163 | 6 | 100 | 26.66 |
| 0.171 | 0.163 | 8 | 100 | 33.31 |
| 0.171 | 0.163 | 12 | 100 | 33.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. A Hydrothermal and Combustion-Reduction Process with Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone as a Restricted Growth Agent and Galactose as a Reducing Agent for the Fabrication of Rod-like α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites. Materials 2025, 18, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051014
Bai Y, Wang Z, Li Y. A Hydrothermal and Combustion-Reduction Process with Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone as a Restricted Growth Agent and Galactose as a Reducing Agent for the Fabrication of Rod-like α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites. Materials. 2025; 18(5):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051014
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yuxuan, Zhou Wang, and Yongjin Li. 2025. "A Hydrothermal and Combustion-Reduction Process with Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone as a Restricted Growth Agent and Galactose as a Reducing Agent for the Fabrication of Rod-like α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites" Materials 18, no. 5: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051014
APA StyleBai, Y., Wang, Z., & Li, Y. (2025). A Hydrothermal and Combustion-Reduction Process with Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone as a Restricted Growth Agent and Galactose as a Reducing Agent for the Fabrication of Rod-like α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites. Materials, 18(5), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051014







