Effect of Bulk Phase Composition on the Growth of PEO Coatings on the Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
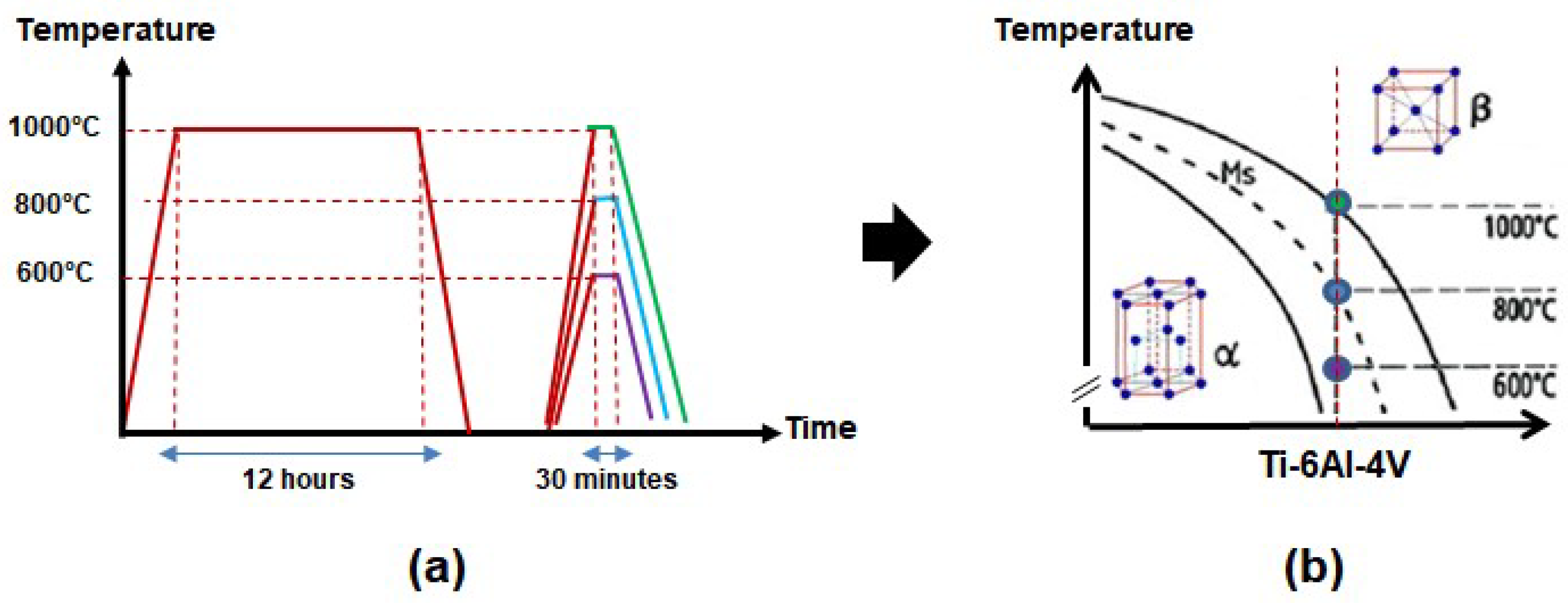
2.1. Sample Processing
2.2. Surface Modification
2.3. Sample Characterization
2.4. Sample Testing
3. Results
4. Conclusions
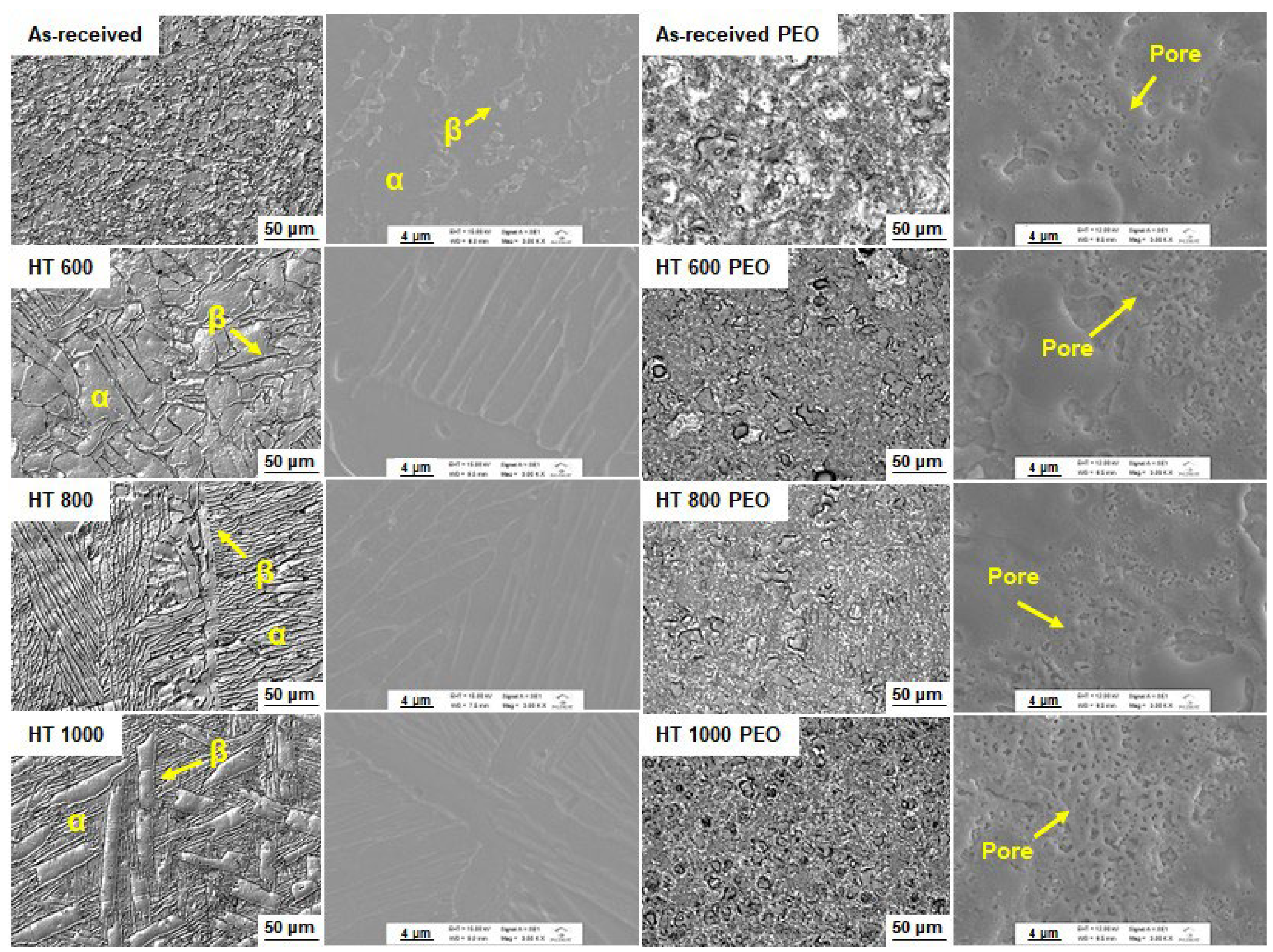
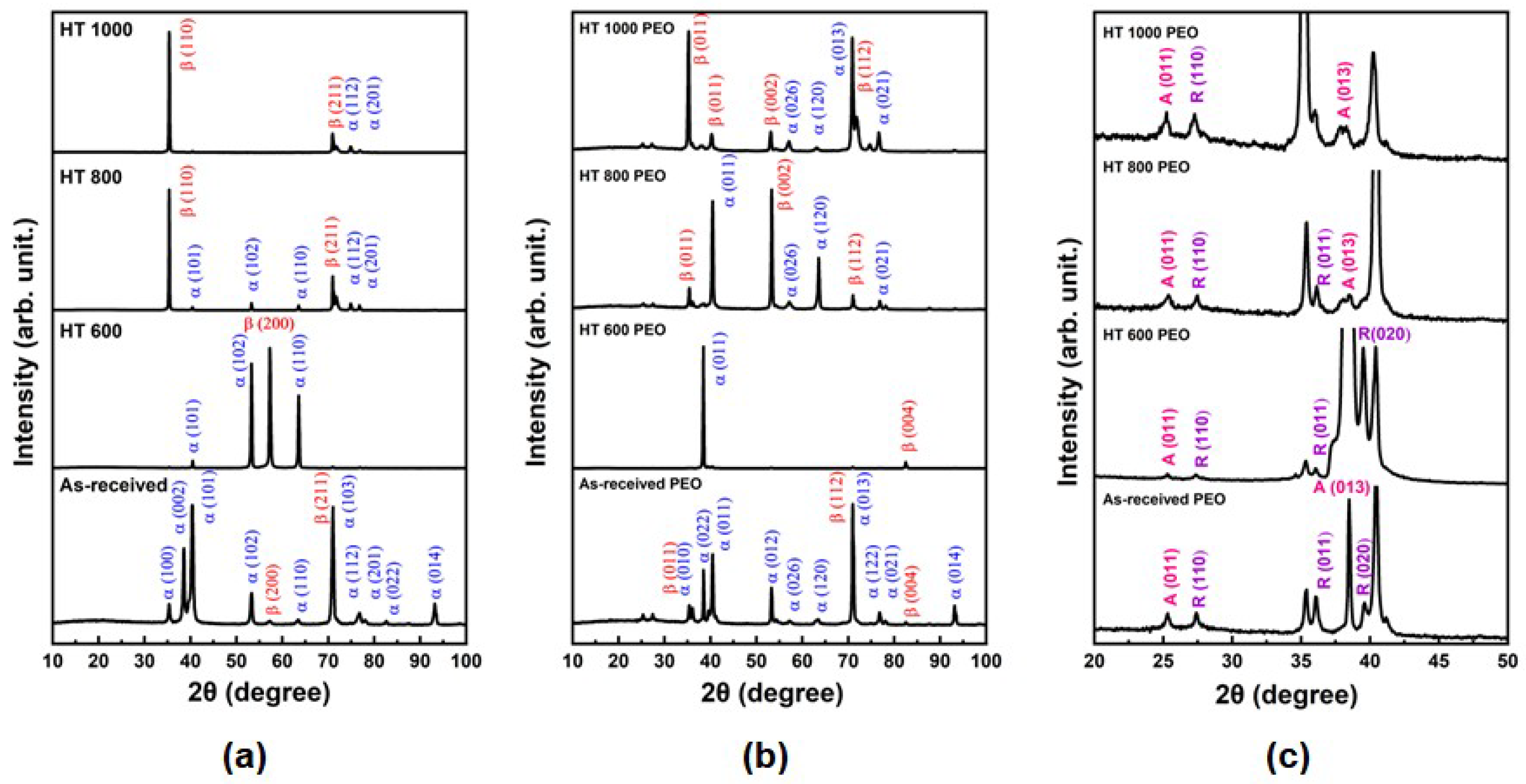
- The α/β phase proportion changed with the temperature of the heat treatments, leading to α phase plates and β phase precipitate formation in the boundaries;
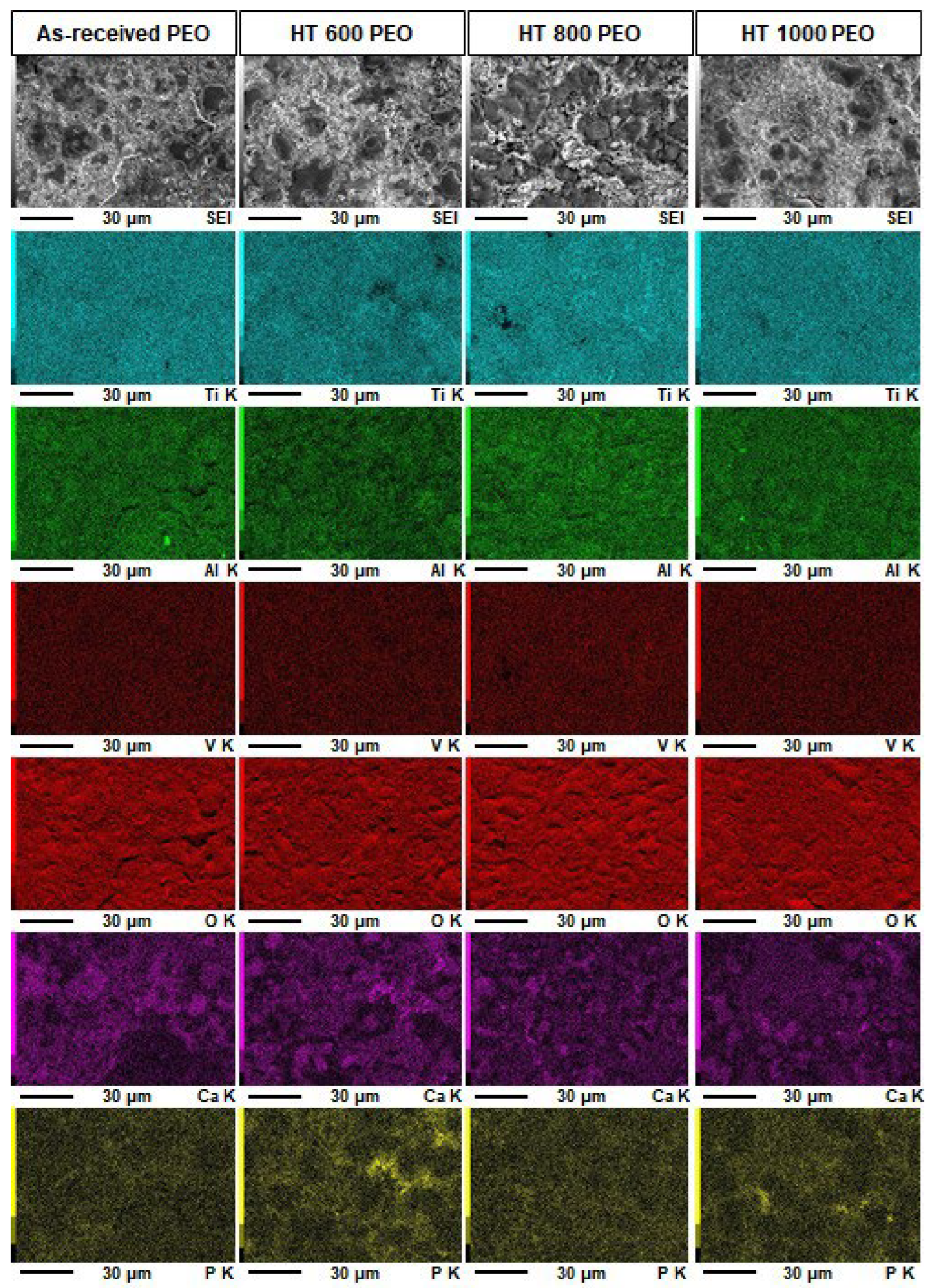
- All PEO-treated samples possessed a microsized porous surface of TiO2 with equal amounts of anatase and rutile;
- The amounts of Al and V were depleted in the oxide layer, while Ca and P were enriched. The chemical bonding detected in the outer layer gave evidence for the incorporation of calcium, phosphorus, absorbed water, and organic molecules;
- The PEO-treated samples possessed a microsized roughness and thickness, with hydrophilic contact angles and surface energy composed mostly of the dispersive component;
- The elastic modulus showed a gradual decay with the β phase precipitation, while the Vickers microhardness was exclusively affected by the alloying elements and the work-hardening effect;
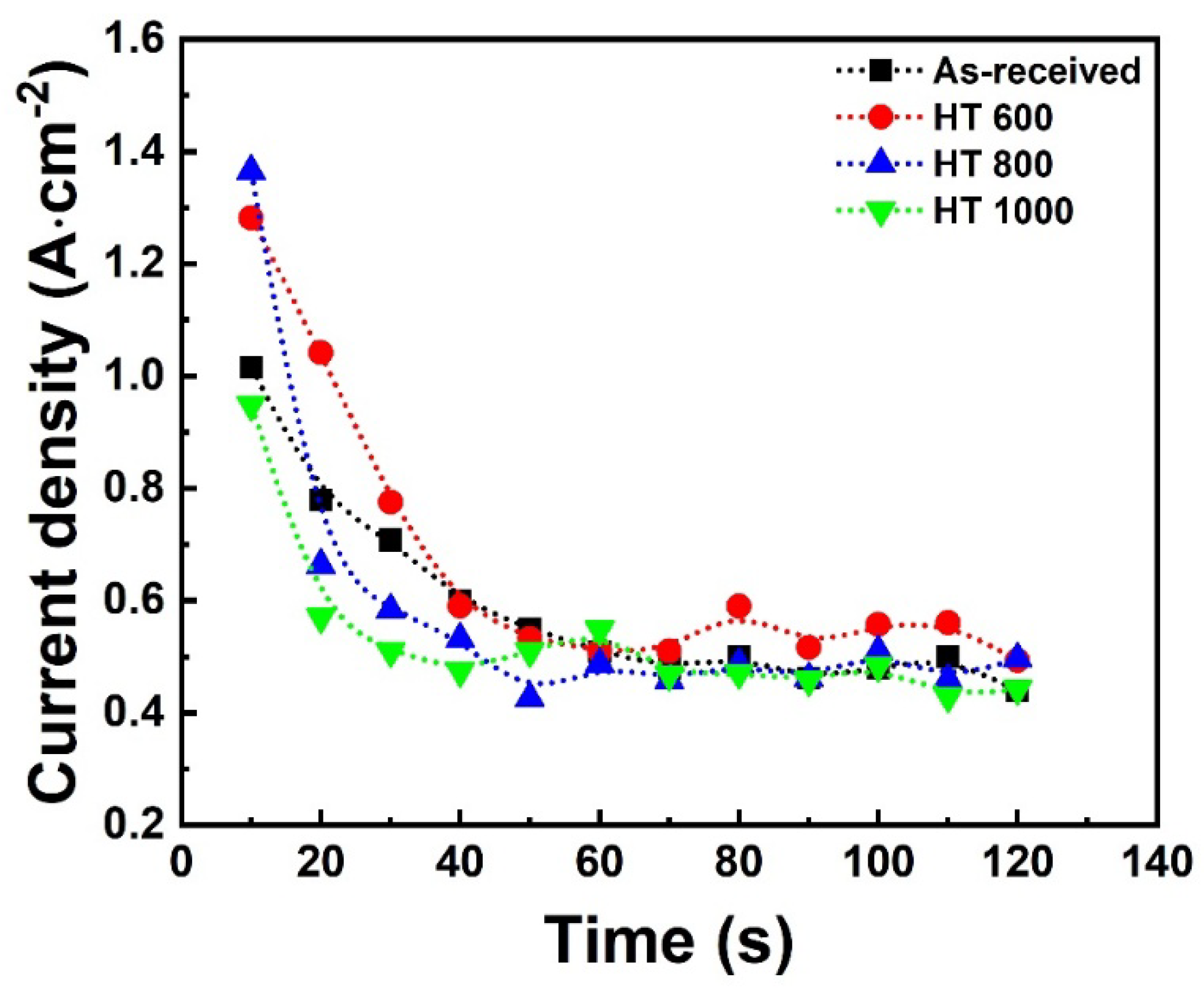
- The OCP curves indicated a more stable protective layer for the PEO-treated samples than the bulk, while the PDP curves highlighted their superior corrosion resistance. The EIS indicated the presence of multiple protective elements in the oxide layer of the PEO-treated samples, which beneficially contributed to corrosion resistance. Further biological testing can provide a better view of the protective ability of the PEO treatment;
- The findings show that the α/β phase proportion considerably affected the mechanical properties of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, while the PEO treatment had an effect on the anticorrosion properties and surface aspects. Thus, combining heat and PEO treatments makes it possible to handle the surface and bulk properties of this commercial biomaterial to provide superior performance for usage as biomedical implants.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEO | Plasma electrolytic oxidation |
| MAO | Micro-arc oxidation |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| OM | Optical microscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| OCP | Open-circuit potential |
| PDP | Potentiodynamic polarization |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| EEC | Equivalent electrical circuit |
| |Z| | Impedance modulus |
| Z′ | Real component of the impedance |
| Z″ | Imaginary component of the impedance |
| CPE | Constant phase element |
| Rs | Solution resistance |
| Rp | Polarization resistance |
| Cdl | Imperfect capacitor |
| Rpore | Polarization resistance of the porous layer |
| Cpore | Pure capacitor of the porous layer |
| Rox | Polarization resistance of the inner oxide layer |
| Cox | Pure capacitor of the inner oxide layer |
| W | Warburg element |
| n/p | Exponent of the imperfect capacitor |
| χ2 | Goodness-of-fitness factor |
References
- Elhadad, A.A.; Romero-Resendiz, L.; Rossi, M.C.; Rodríguez-Albelo, L.M.; Lascano, S.; Afonso, C.R.M.; Alcudia, A.; Amigó, V.; Torres, Y. Findings and Perspectives of β-Ti Alloys with Biomedical Applications: Exploring beyond Biomechanical and Biofunctional Behaviour. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 3550–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Dong, K.; Han, E.-H. Research Progress on the Corrosion Behavior of Titanium Alloys. Corros. Rev. 2023, 41, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM F136-13; Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R56401). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Liu, S.; Shin, Y.C. Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V Alloy: A Review. Mater. Des. 2019, 164, 107552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, B.O.; Torrento, J.E.; Grandini, C.R.; Galindo, E.L.; Pintão, C.A.F.; Santos, A.A.; Lisboa-Filho, P.N.; Pontes, F.M.L.; Correa, D.R.N. Development of Ti–Al–V Alloys for Usage as Single-Axis Knee Prostheses: Evaluation of Mechanical, Corrosion, and Tribocorrosion Behaviors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Micro-Arc Oxidation in Titanium and Its Alloys: Development and Potential of Implants. Coatings 2023, 13, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliofkhazraei, M.; Macdonald, D.D.; Matykina, E.; Parfenov, E.V.; Egorkin, V.S.; Curran, J.A.; Troughton, S.C.; Sinebryukhov, S.L.; Gnedenkov, S.V.; Lampke, T.; et al. Review of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of Titanium Substrates: Mechanism, Properties, Applications and Limitations. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 5, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokosz, K.; Hryniewicz, T.; Dudek, Ł. Phosphate Porous Coatings Enriched with Selected Elements via PEO Treatment on Titanium and Its Alloys: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Blawert, C.; Serdechnova, M.; Karlova, P.; Dovzhenko, G.; Wieland, D.C.F.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Role of Polymorph Microstructure of Ti6Al4V Alloy on PEO Coating Formation in Phosphate Electrolyte. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 428, 127890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, G.C.; Grandini, C.R.; Rau, J.V. Comprehensive Review of PEO Coatings on Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Implants. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesode, P.; Barve, S. Surface Modification of Titanium and Titanium Alloy by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Process for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafizadeh, M.; Yazdi, S.; Bozorg, M.; Ghasempour-Mouziraji, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Zarrabian, M.; Cavaliere, P. Classification and Applications of Titanium and Its Alloys: A Review. J. Alloys Compd. Commun. 2024, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, J.; Kumar, R.; Sahoo, A.K.; Panda, A. Enhancement of Material Properties of Titanium Alloys through Heat Treatment Process: A Brief Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 23, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, A.R.; Santos, L.S.; Lepienski, C.M.; Kuroda, P.B.; Kuromoto, N.K. Characterization of the Morphology, Structure and Wettability of Phase Dependent Lamellar and Nanotube Oxides on Anodized Ti-10Nb Alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, S.A.; Necula, B.S.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.E.; Duszczyk, J.; Apachitei, I. Biofunctional Surfaces by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation on Titanium Biomedical Alloys. Surf. Eng. 2016, 32, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibisi, P.N.; Popoola, A.P.I.; Arthur, N.K.K.; Pityana, S.L. Review on Direct Metal Laser Deposition Manufacturing Technology for the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuz, N.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Rangel, E.C.; Cruz, N.C.; Possato, L.G.; Coan, K.S.; Grandini, C.R.; Correa, D.R.N. Exploiting the Effect of PEO Parameters on the Surface of AISI 1020 Low-Carbon Steel Treated in a TaOH-Rich Electrolyte. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 477, 130374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothi Prakash, C.G.; Prasanth, R. Approaches to Design a Surface with Tunable Wettability: A Review on Surface Properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 108–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Engin, A.; Tezcaner, A.; Evis, Z. Historical Development of Simulated Body Fluids Used in Biomedical Applications: A Review. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukács, Z.; Kristóf, T. Determination of Kinetic Parameters from a New Quadratic Approximation of the Butler-Volmer Equation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 918, 116443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.C.N.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Rangel, E.C.; da Cruz, N.C.; Correa, D.R.N. Production of Porous ZrO2–TiO2 Ceramic Coatings on the Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V Alloy via AC PEO Treatment and Their Effects on the Corrosion Behavior in 0.9% NaCl. Coatings 2024, 14, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D.R.N.; Rocha, L.A.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Gemini-Piperni, S.; Archanjo, B.S.; Achete, C.A.; Werckmann, J.; Afonso, C.R.M.; Shimabukuro, M.; Doi, H.; et al. Growth Mechanisms of Ca- and P-Rich MAO Films in Ti-15Zr-XMo Alloys for Osseointegrative Implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 344, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.; Kossenko, A.; Borodianskiy, K. Study of the Effect of Current Pulse Frequency on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Coating Formation by Micro Arc Oxidation. Materials 2019, 12, 3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ni, S.; Ma, L.; Li, M. Porous Construction and Surface Modification of Titanium-Based Materials for Osteogenesis: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 973297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Valverde, N.; López-Valverde, A.; Aragoneses, J.M.; Macedo de Sousa, B.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Ramírez, J.M. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of Calcium-Phosphate Coating on the Osseointegration of Titanium Implants. Materials 2021, 14, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cabezón, C.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Amigo Borrás, V.; Raquel, B.; Rodriguez Cabello, J.C.; Ibañez Fonseca, A.; Martin-Pedrosa, F. Application of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Coating on Powder Metallurgy Ti-6Al-4V for Dental Implants. Metals 2020, 10, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, E.; Parfenova, L.; Mukaeva, V.; Farrakhov, R.; Stotskiy, A.; Raab, A.; Danilko, K.; Rameshbabu, N.; Valiev, R. Biofunctionalization of PEO Coatings on Titanium Implants with Inorganic and Organic Substances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 404, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhy, B.; Priyadarshini, P.; Sen, A.K. Effect of Surface Energy and Roughness on Cell Adhesion and Growth—Facile Surface Modification for Enhanced Cell Culture. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15467–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsonnet, L.; Reybier, K.; Jaffrezic, N.; Comte, V.; Lagneau, C.; Lissac, M.; Martelet, C. Relationship between Surface Properties (Roughness, Wettability) of Titanium and Titanium Alloys and Cell Behaviour. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2003, 23, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraf, M.; Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Alipour, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liana Sukiman, N. A State-of-the-Art Review of the Fabrication and Characteristics of Titanium and Its Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Bio Des. Manuf. 2022, 5, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.; Zinigrad, M.; Borodianskiy, K. Ceramic Coating on Ti-6Al-4V by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation in Molten Salt: Development and Characterization. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 408, 126847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.G.; Choe, H.C. Corrosion Behaviors of Bioactive Element Coatings on PEO-Treated Ti-6Al-4V Alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 376, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cabezón, C.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L.; Borrás, V.A.; Bayón, R.; Salvo-Comino, C.; Garcia-Hernandez, C.; Martin-Pedrosa, F. Improvements in Tribological and Anticorrosion Performance of Porous Ti-6Al-4V via PEO Coating. Friction 2021, 9, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.-J.; Choe, H.-C.; Brantley, W.A. Electrochemical Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V after Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation in Solutions Containing Ca, P, and Zn Ions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 320, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilimon, V.S.; Shibli, S.M.A. A Review on the Application-Focused Assessment of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Coatings Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazanas, A.C.; Prodromidis, M.I. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy—A Tutorial. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2023, 3, 162–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

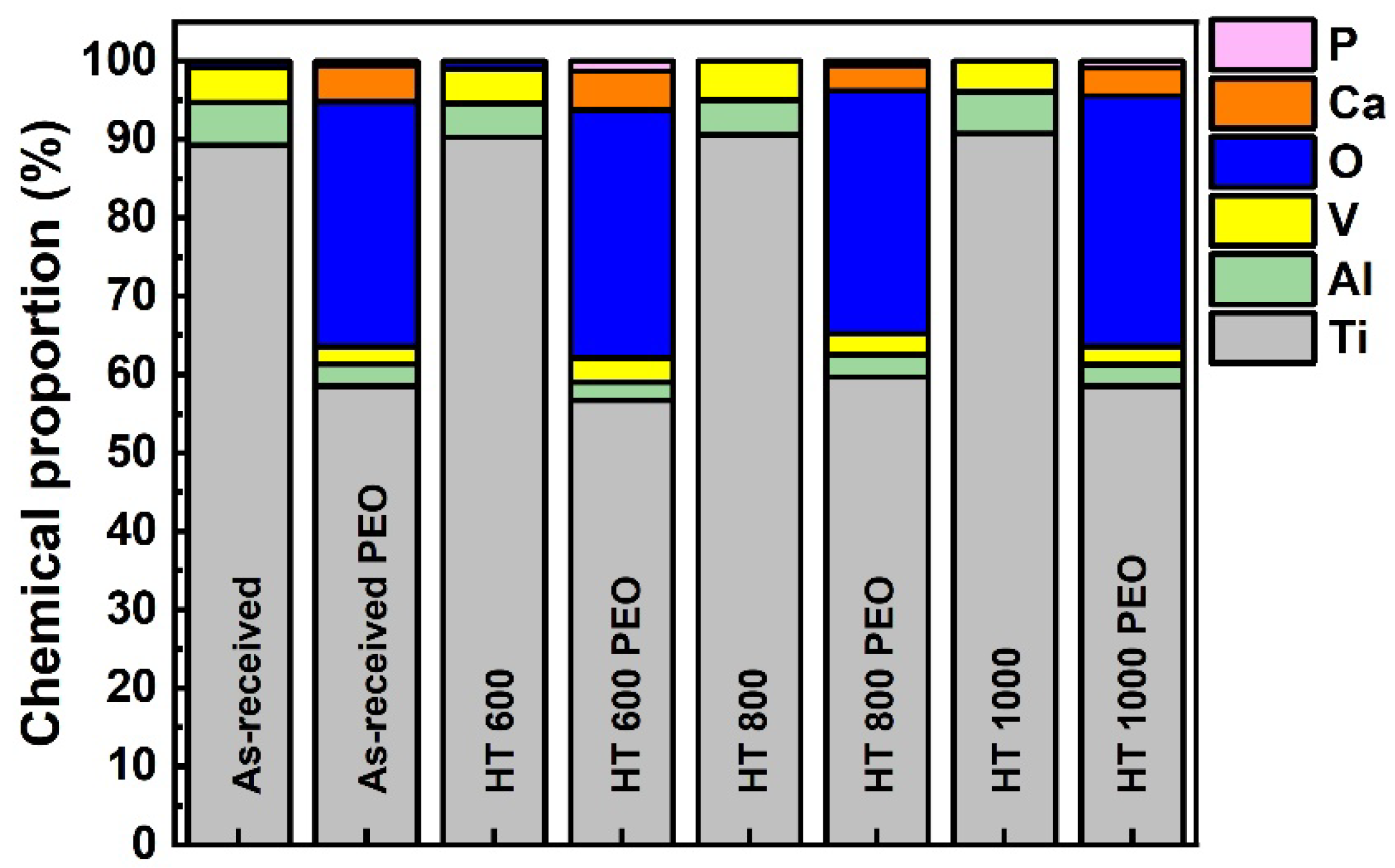

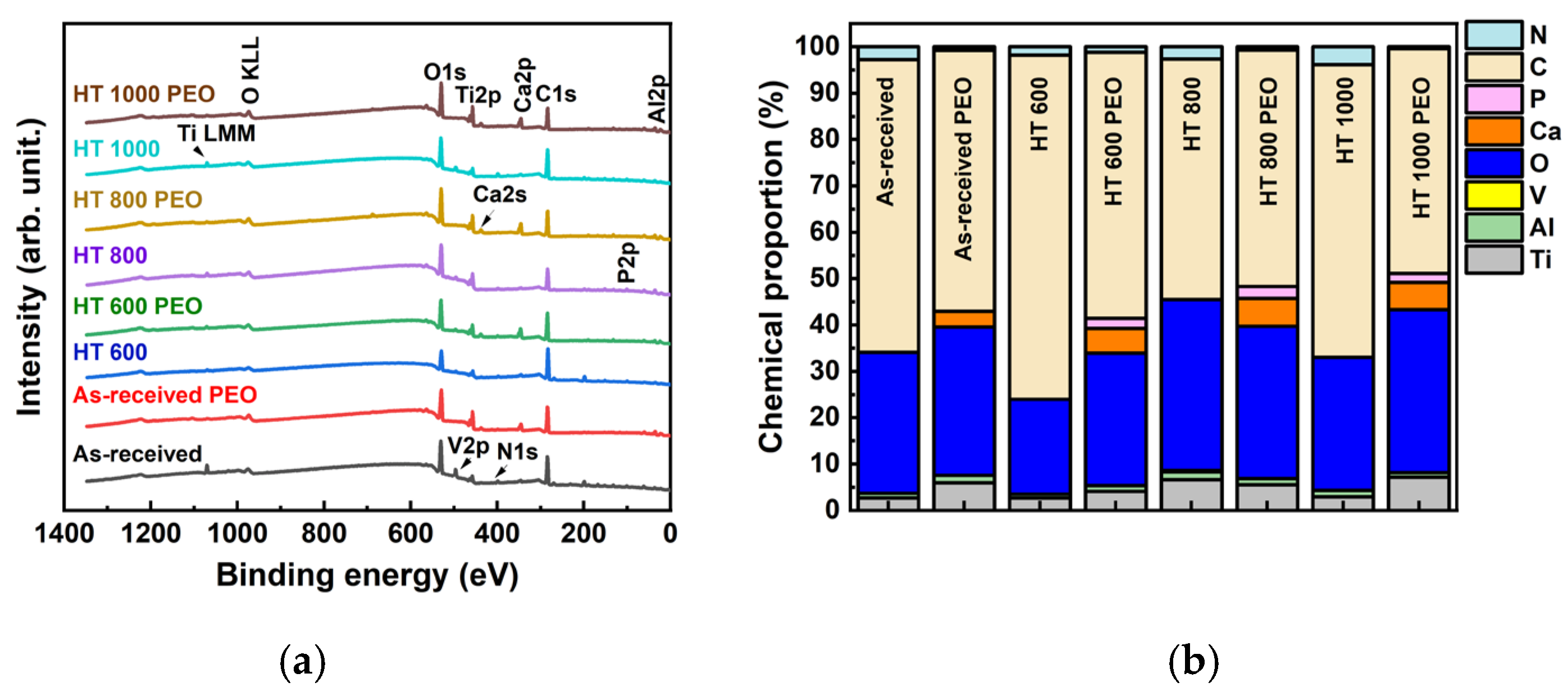

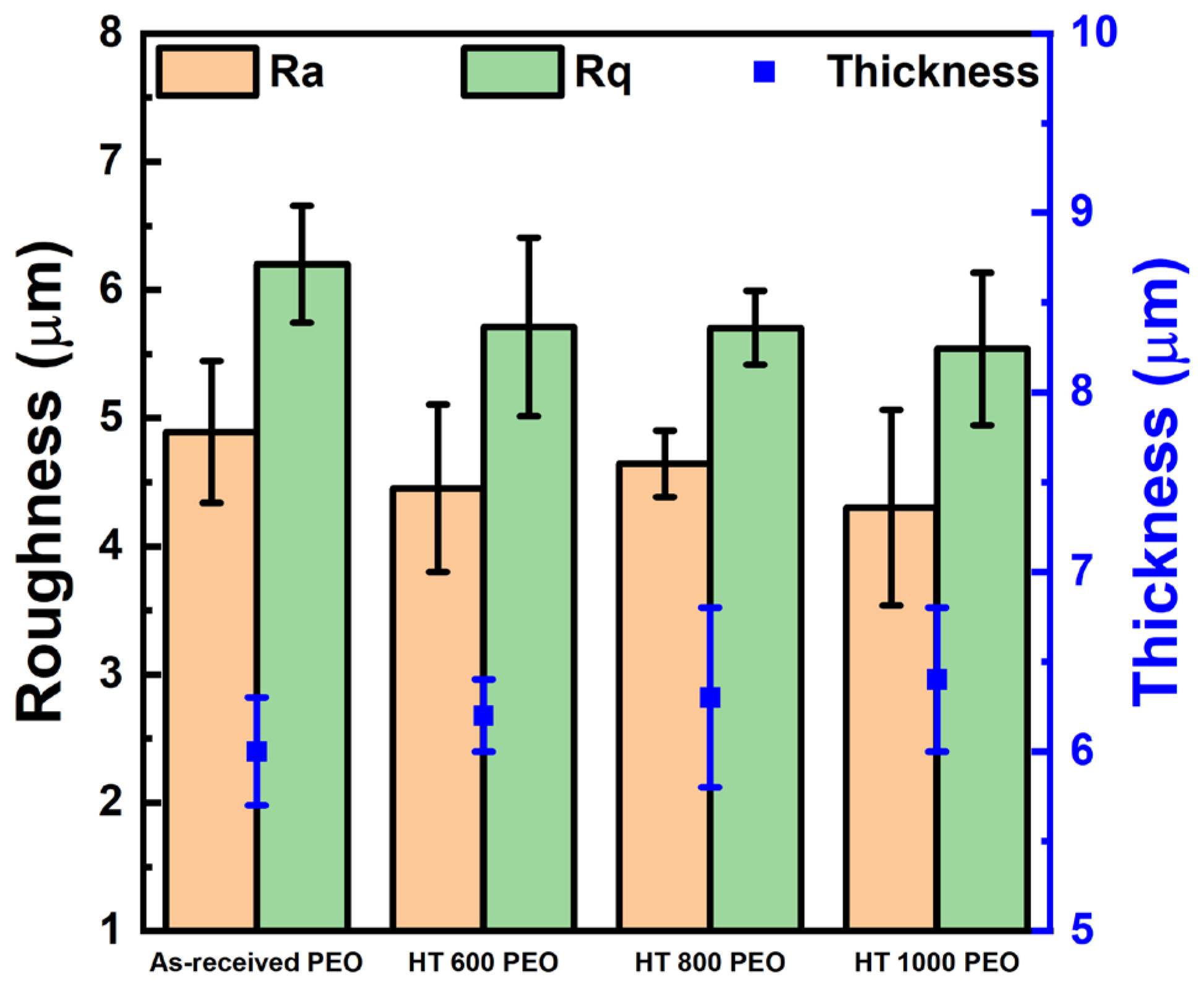

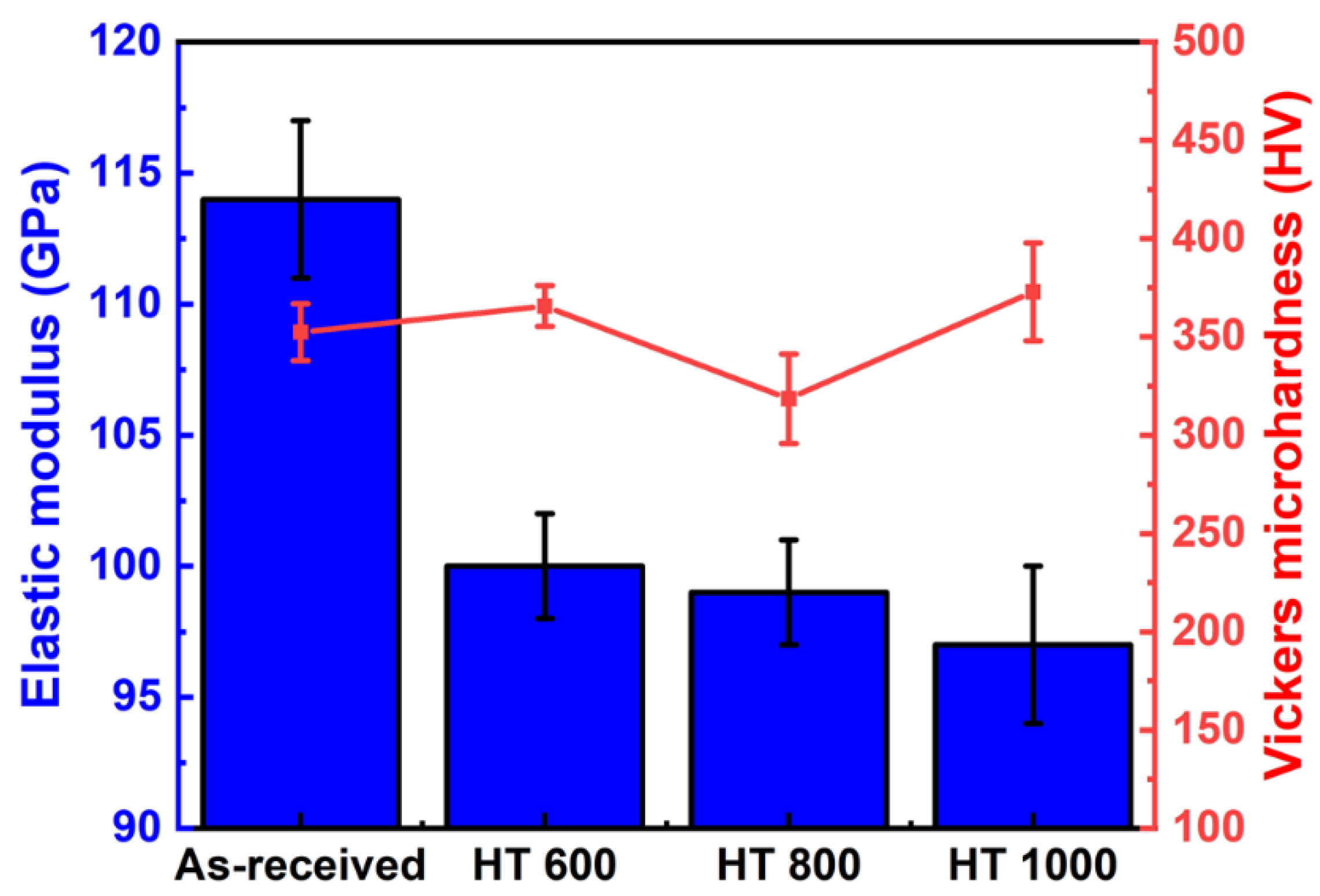

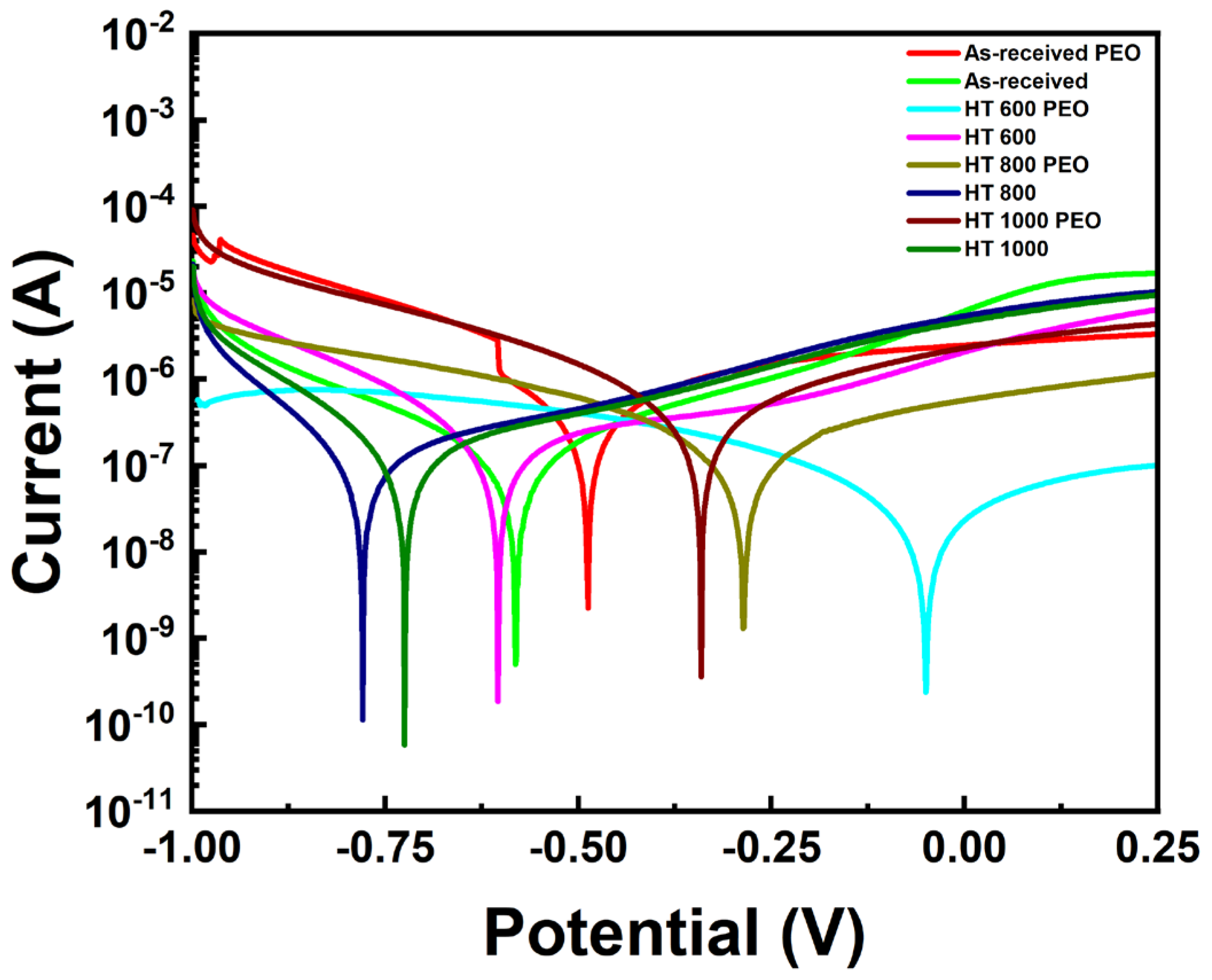
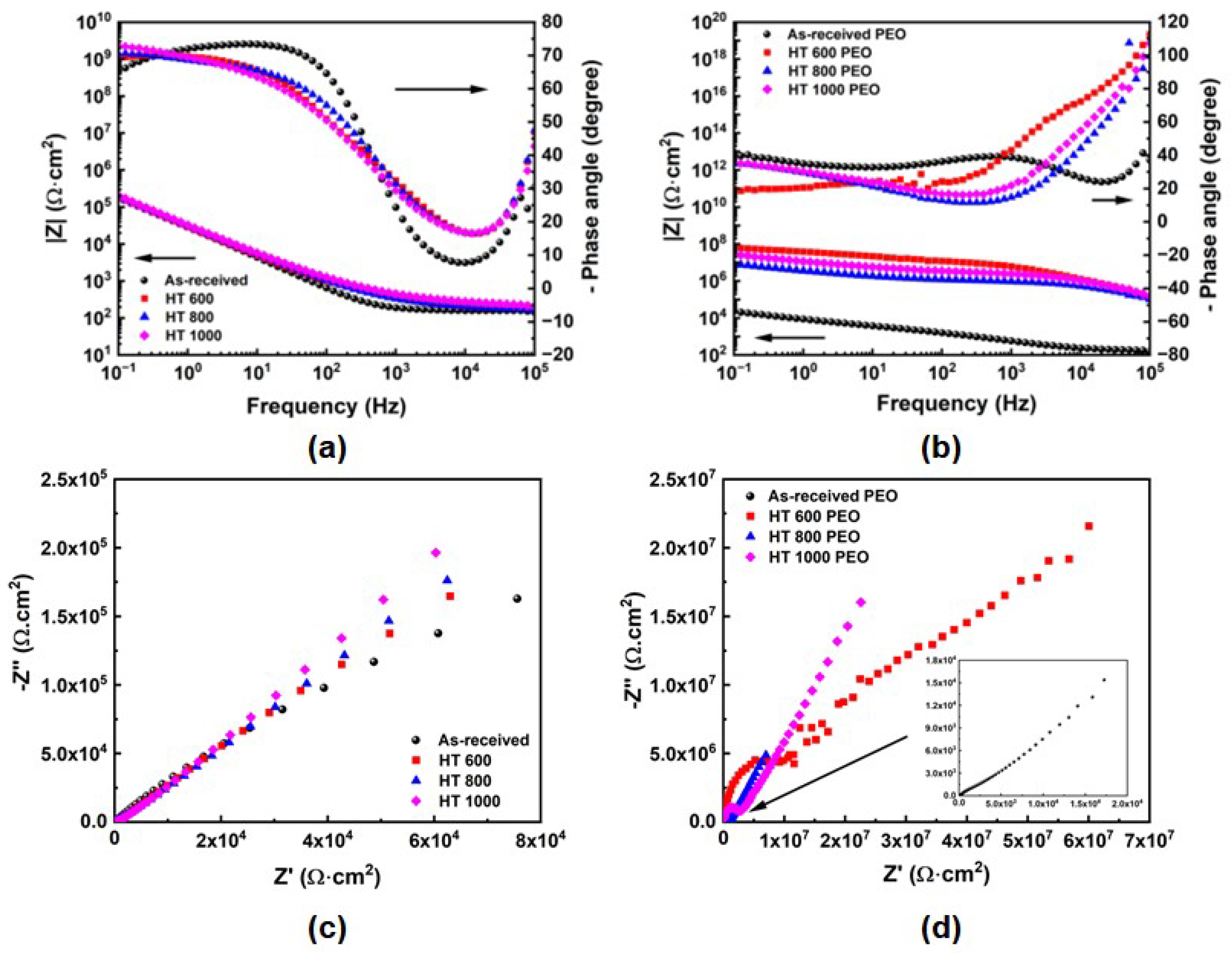
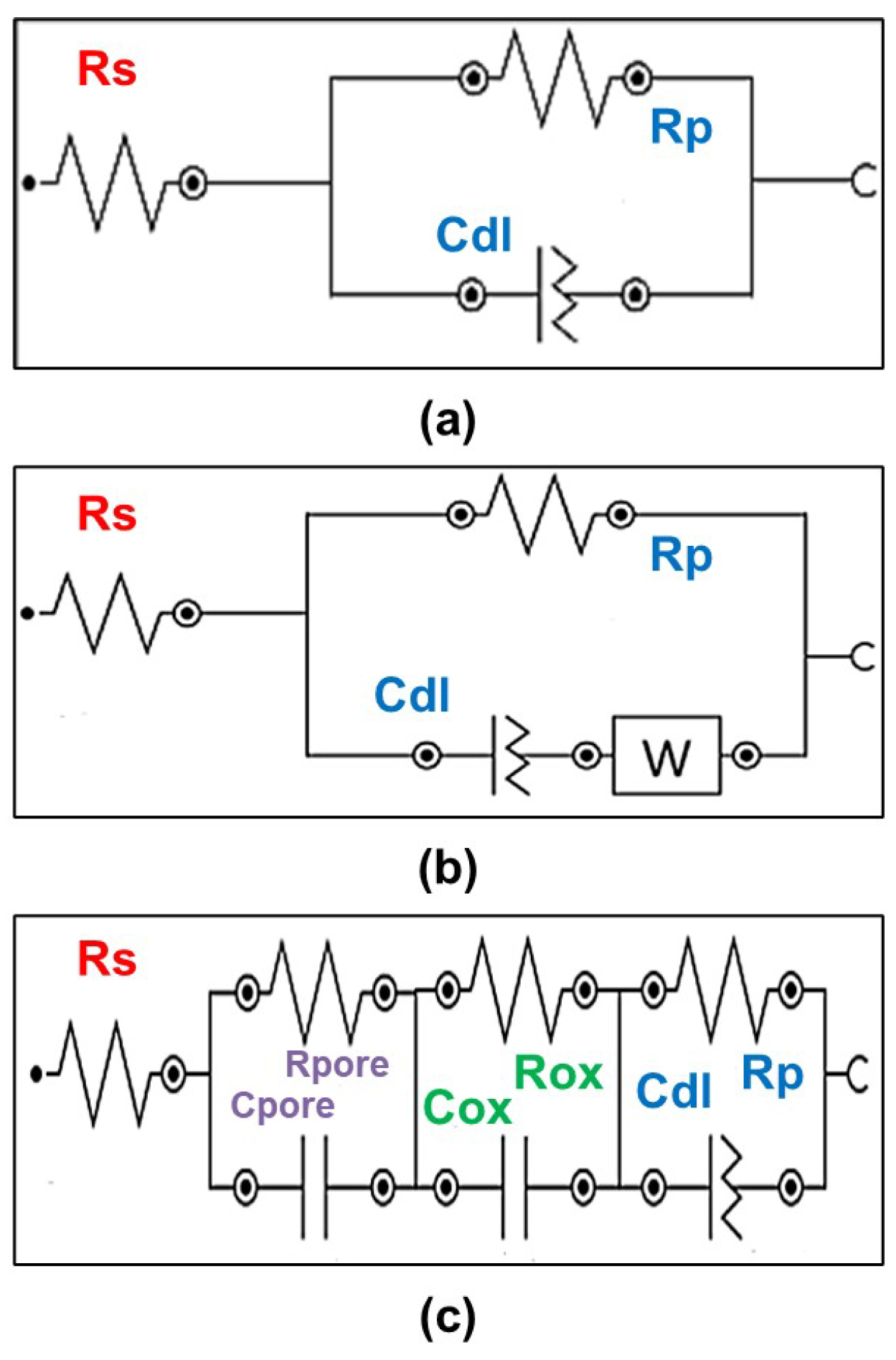
| Sample | Condition |
|---|---|
| As-received | Raw metal |
| HT 600 | Heat-treated at 600 °C |
| HT 800 | Heat-treated at 800 °C |
| HT 1000 | Heat-treated at 1000 °C |
| As-received PEO | PEO-treated raw metal |
| HT 600 PEO | Heat-treated at 600 °C and PEO-treated |
| HT 800 PEO | Heat-treated at 800 °C and PEO-treated |
| HT 1000 PEO | Heat-treated at 1000 °C and PEO-treated |
| Sample | Ecorr (mV) | jcorr (nA·cm−2) | Rp (kΩ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-received | −580 | 120 | 544 |
| As-received PEO | −490 | 120 | 98 |
| HT 600 | −600 | 180 | 252 |
| HT 600 PEO | −50 | 70 | 2380 |
| HT 800 | −780 | 120 | 381 |
| HT 800 PEO | −290 | 260 | 565 |
| HT 1000 | −720 | 140 | 402 |
| HT 1000 PEO | −340 | 640 | 164 |
| Parameters | As-Received | HT 600 | HT 800 | HT 1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs (MΩ·cm2) | 1.52 × 10−4 | 1.55 × 10−4 | 1.68 × 10−4 | 2.18 × 10−4 |
| Rp (MΩ·cm2) | 7.63 × 10−3 | 1.29 | 4.69 | 7.63 |
| Cdl (µMho·sn) | 7.31 | 8.65 | 8.26 | 7.88 |
| n/p | 0.842 | 0.87 | 0.821 | 0.856 |
| W (µMho·s1/2) | - | 69.7 | 99.0 | 57.8 |
| χ2 | 0.053511 | 0.025978 | 0.03358 | 0.021966 |
| Parameters | As-Received PEO | HT 600 PEO | HT 800 PEO | HT 1000 PEO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs (MΩ·cm2) | 1.2 × 10−4 | 3.58 × 10−2 | 3.75 × 10−2 | 9.36 × 10−3 |
| Rpore (MΩ·cm2) | - | 6.59 | 8.44 × 10−1 | 2.06 |
| Cpore (pF) | - | 18.5 | 22.6 | 13.9 |
| Rox (MΩ·cm2) | - | 31.9 | 8.86 | 27.3 |
| Cox (nF) | - | 32.4 | 233 | 58.7 |
| Rp (MΩ·cm2) | 5.03 ×10−3 | 36.6 | 4.07 | 11.2 |
| Cdl (µMho·sn) | 14.7 | 3.49 × 10−3 | 75.2 × 10−3 | 17.7 × 10−3 |
| n/p | 0.557 | 0.600 | 0.559 | 0.559 |
| W (µMho·s1/2) | 46.6 | - | - | - |
| χ2 | 0.027026 | 0.41719 | 0.29647 | 0.46814 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neto, J.R.F.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Cruz, N.C.d.; Rangel, E.C.; Pinto, B.d.O.; Torrento, J.E.M.; Grandini, C.R.; Kaneko, U.F.; Correa, D.R.N. Effect of Bulk Phase Composition on the Growth of PEO Coatings on the Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050955
Neto JRF, Ribeiro RP, Cruz NCd, Rangel EC, Pinto BdO, Torrento JEM, Grandini CR, Kaneko UF, Correa DRN. Effect of Bulk Phase Composition on the Growth of PEO Coatings on the Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(5):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050955
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeto, José Roberto Ferreira, Rafael Parra Ribeiro, Nilson Cristino da Cruz, Elidiane Cipriano Rangel, Bruna de Oliveira Pinto, Jhuliene Elen Muro Torrento, Carlos Roberto Grandini, Ulisses Ferreira Kaneko, and Diego Rafael Nespeque Correa. 2025. "Effect of Bulk Phase Composition on the Growth of PEO Coatings on the Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V Alloy" Materials 18, no. 5: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050955
APA StyleNeto, J. R. F., Ribeiro, R. P., Cruz, N. C. d., Rangel, E. C., Pinto, B. d. O., Torrento, J. E. M., Grandini, C. R., Kaneko, U. F., & Correa, D. R. N. (2025). Effect of Bulk Phase Composition on the Growth of PEO Coatings on the Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials, 18(5), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050955










