Mechanical Properties and σ-Phase Precipitation in FeCoCrNiMox (x = 0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.8, 1.3) High-Entropy Alloys: Insights from First-Principles Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Computational Details
2.2. Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. First-Principles Calculation
3.1.1. Thermodynamic and Dynamic Stability Analysis
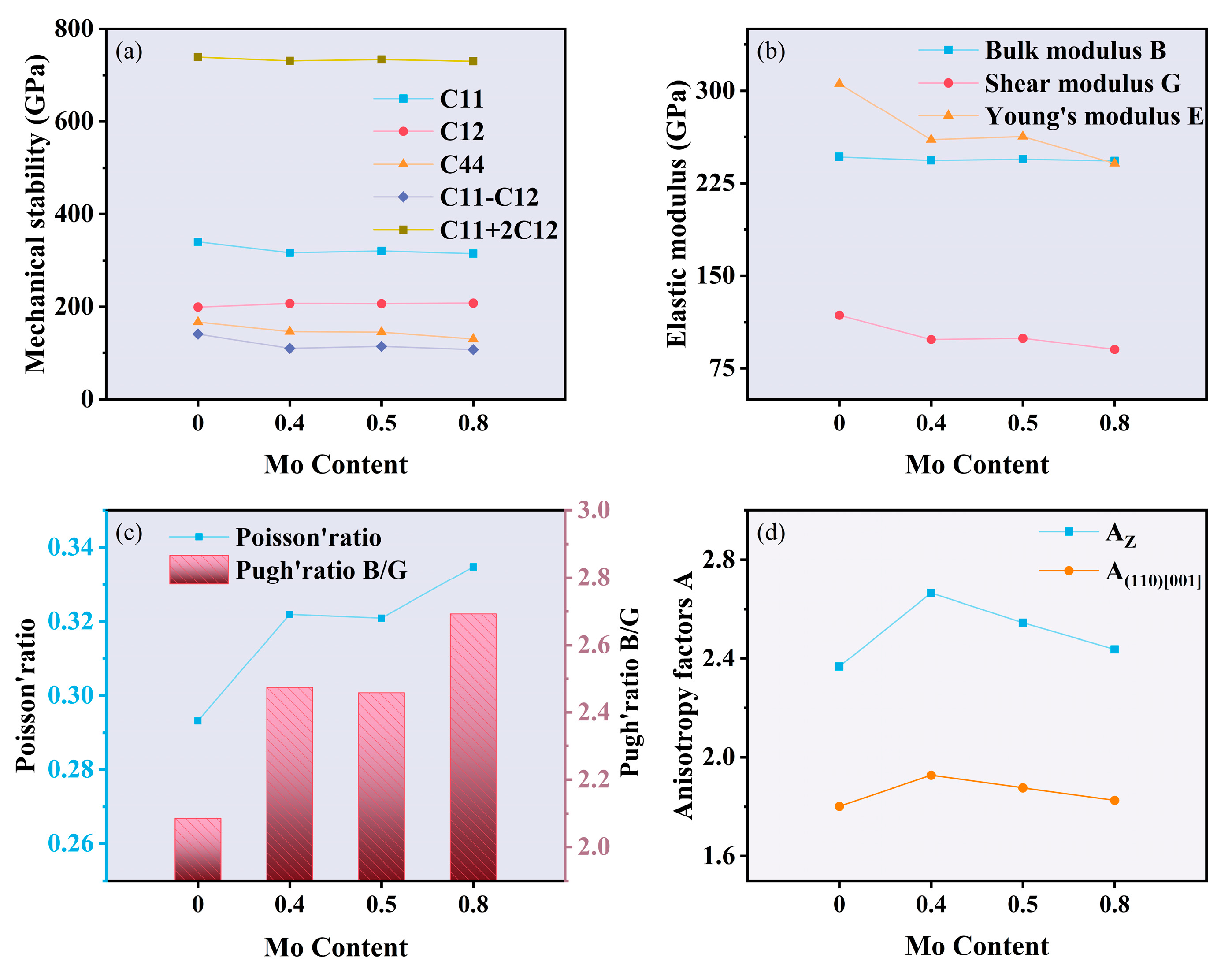
3.1.2. Effect of Mo Content on Mechanical Properties
3.1.3. Effect of Mo Content on Electronic Structure
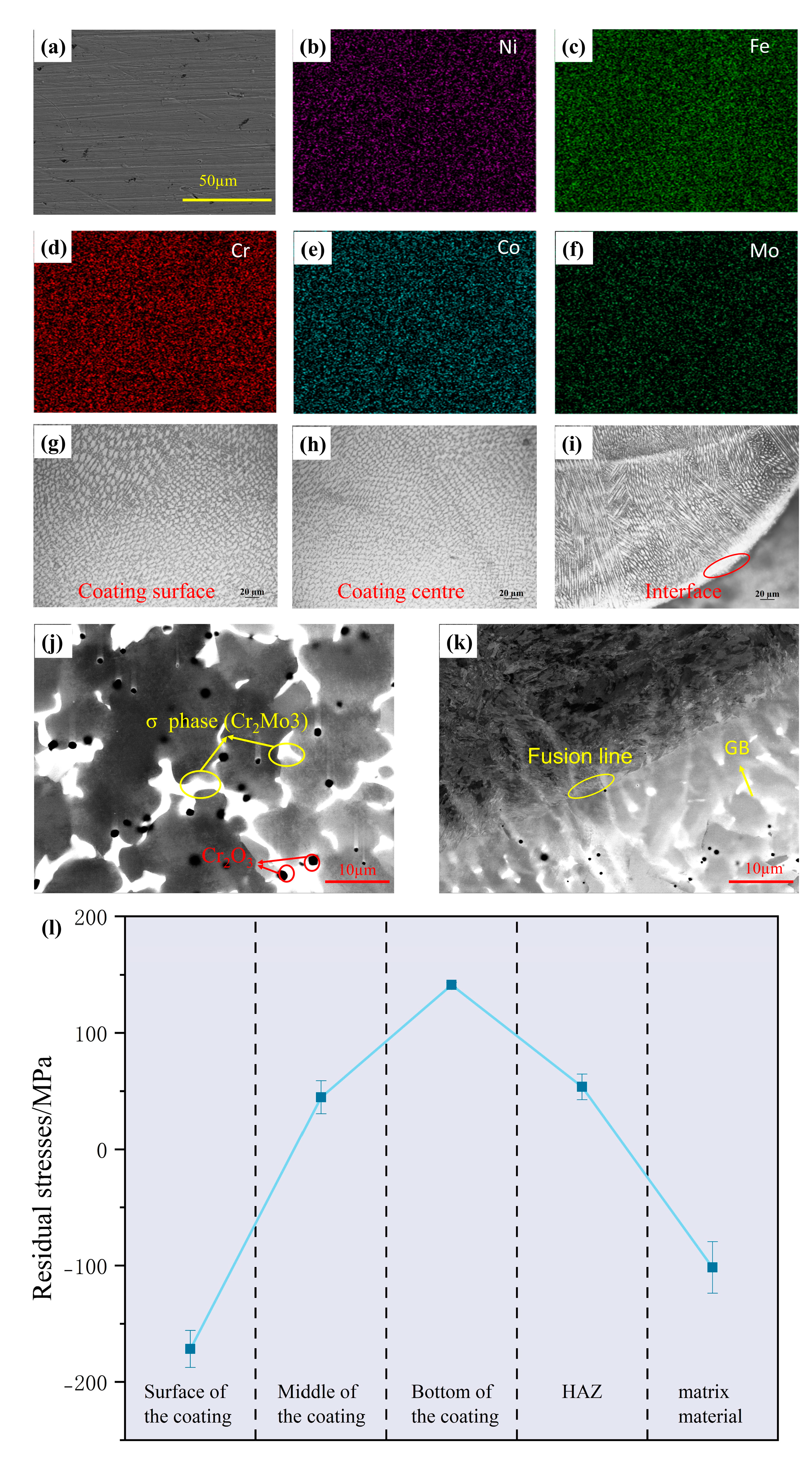
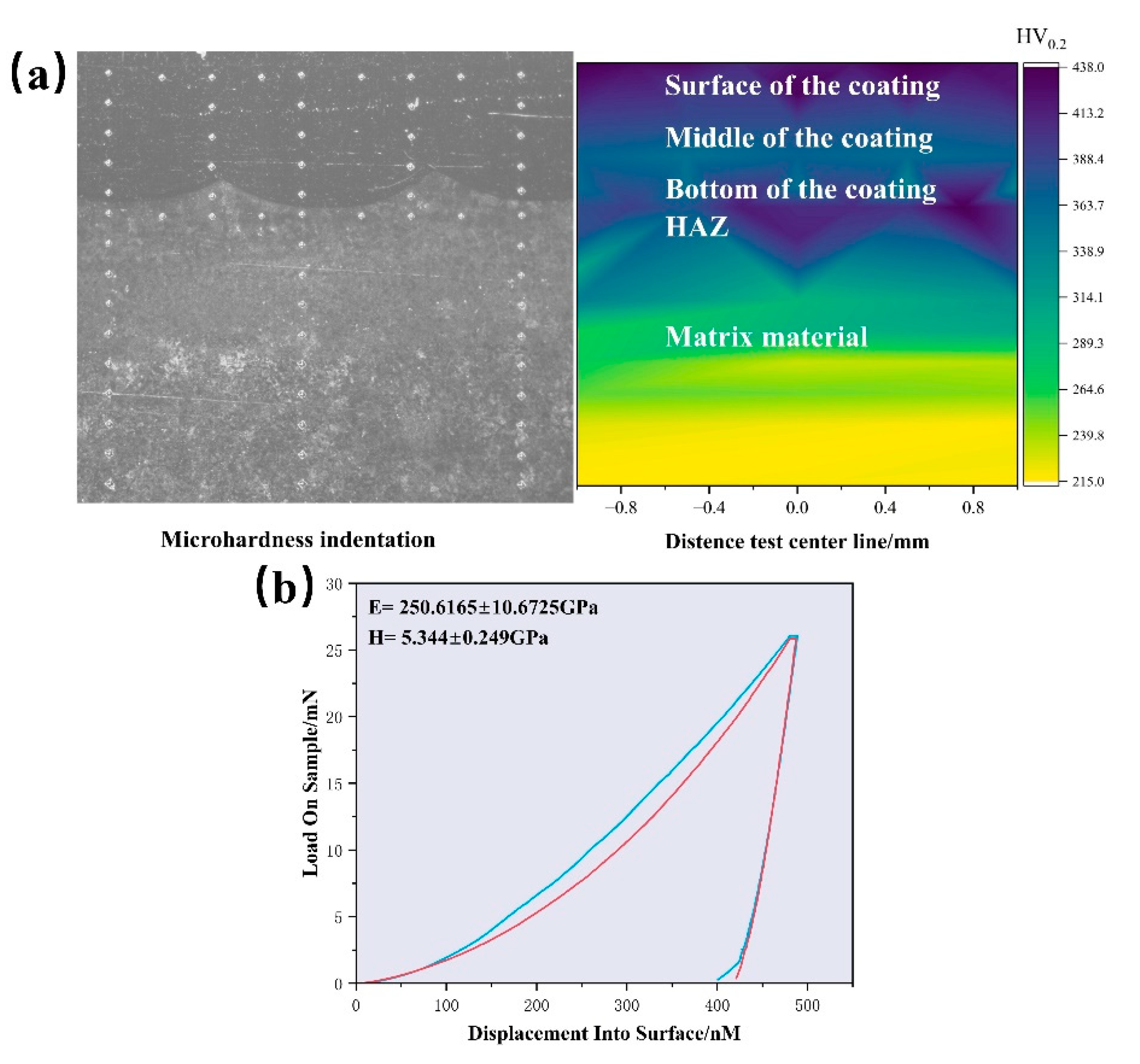
3.2. Microstructure and Microhardness
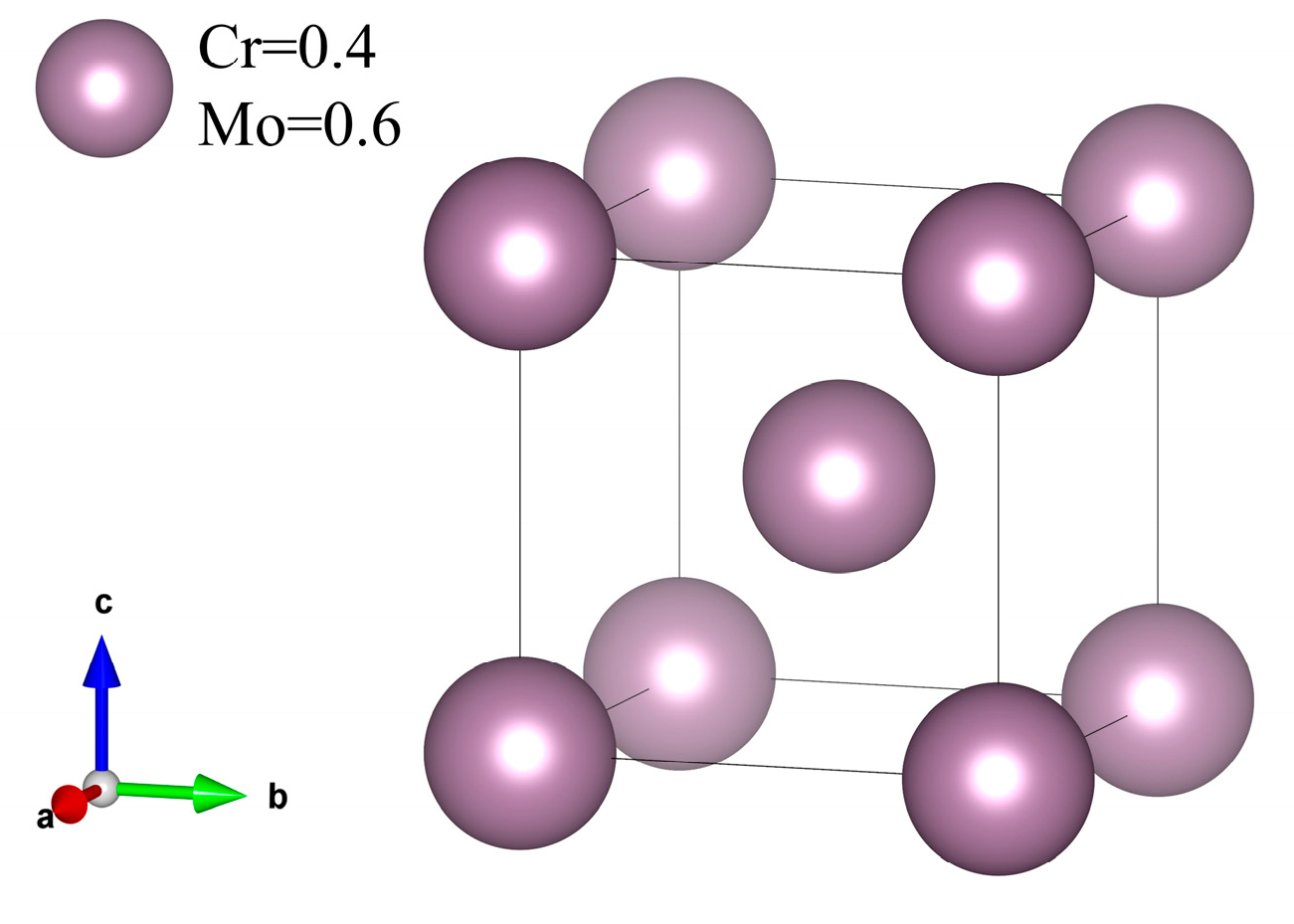
3.3. Elastic Properties of σ Phase
4. Conclusions
- (1)
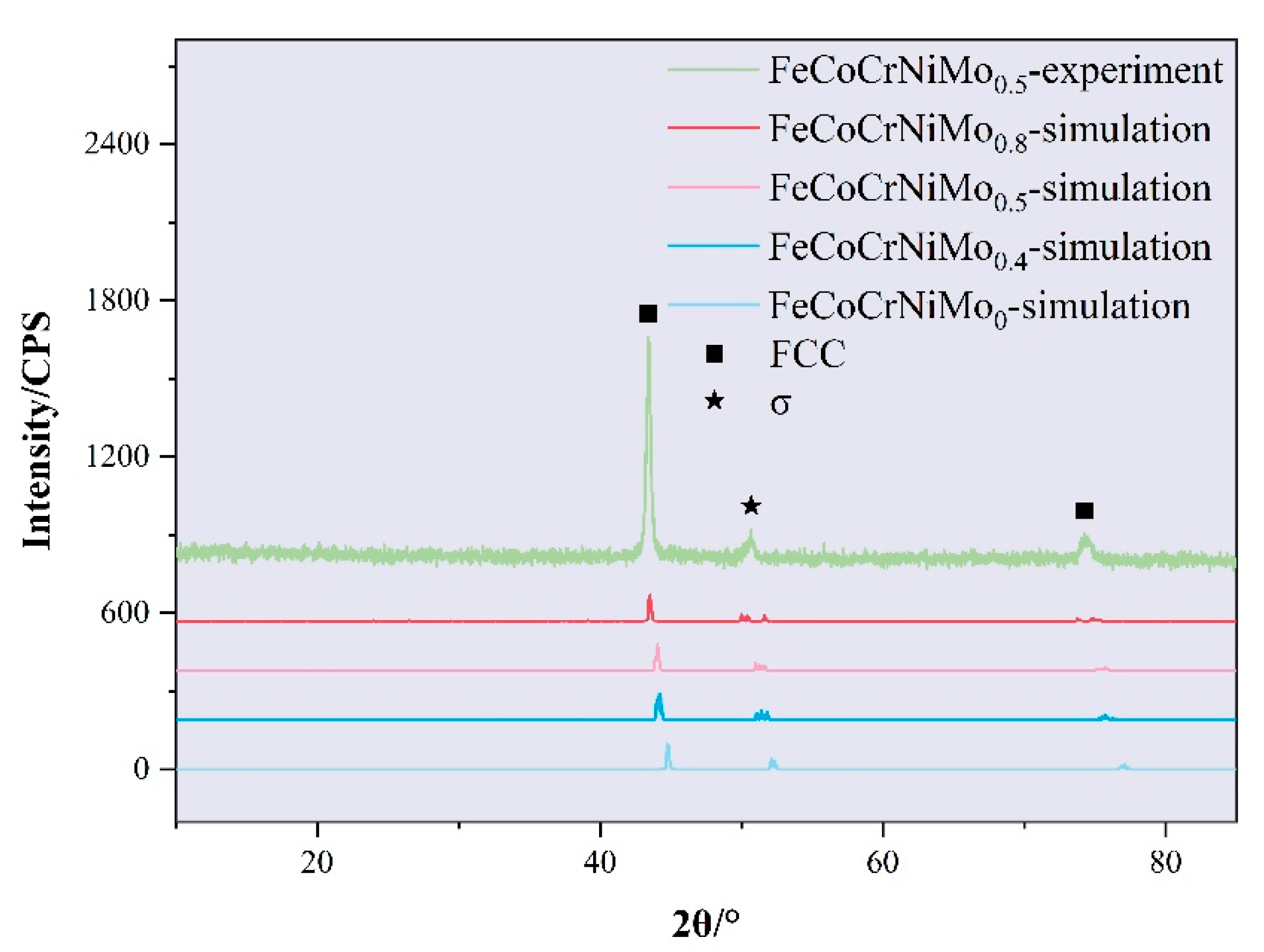
- The addition of molybdenum increases the ductility and anisotropy of the FeCoCrNiMox HEAs FCC phase, though it slightly reduces strength and stiffness, as confirmed by electronic structure calculations. As the Mo content increases, lattice distortion in the coating becomes more pronounced, with a corresponding leftward shift in the diffraction peak. The Young’s modulus measured by nanoindentation closely aligns with first-principles calculations, showing a deviation of approximately 4.9%;
- (2)
- The FeCoCrNiMo0.5 HEAs coatings exhibit a transition from columnar crystals at the bottom to equiaxed crystals at the surface. The surface hardness reaches 437.91 HV0.2, while the bottom shows slightly lower hardness. Residual stress tests show that the coating surface experiences residual compressive stress due to rapid cooling, while the bottom exhibits significant residual tensile stress. This is attributed to the thermal expansion coefficient mismatch and the directional growth of columnar crystals between the coating and substrate. Furthermore, a large number of σ phases were precipitated in the coating due to the deviation of Cr and Mo elements;
- (3)
- The elastic properties of the σ phase were calculated using the stress–strain method, showing low bulk modulus, shear modulus, and Poisson’s ratio. Its hardness is 22.7 GPa, classifying it as a brittle, hard phase. The presence of the σ phase alters the coating’s properties, contributing to its increased hardness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaneme, K.K.; Bodunrin, M.O.; Oke, S.R. Processing, alloy composition and phase transition effect on the mechanical and corrosion properties of high entropy alloys: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.F.; Gong, M.; Peng, L.M. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of an Al0.5CoCrFeCuNi high-entropy alloy in as-cast and heat-treated/quenched conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 567, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.C.; Chen, C.S.; Chu, C.P. Age hardening reaction of the Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Curtin, W.A.; Tasan, C.C. High entropy alloys: A focused review of mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 435–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.M.; Aitken, Z.H.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Greer, J.R. Effect of temperature on small-scale deformation of individual face-centered-cubic and body-centered-cubic phases of an Al0.7CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-W.; Lu, Y.-S.; Lai, Z.-H.; Yen, H.-W.; Lee, Y.-L. Comparative corrosion behavior of Fe50Mn30Co10Cr10 dual-phase high-entropy alloy and CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 842, 155824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yan, S.; Chen, H.; Gou, G. Unprecedented combination of strength and ductility in laser welded NiCoCr medium entropy alloy joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 803, 140501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minouei, H.; Kheradmandfard, M.; Rizi, M.S.; Jalaly, M.; Kim, D.-E.; Hong, S.I. Formation mechanism of high-entropy spinel thin film and its mechanical and magnetic properties: Linking high-entropy alloy to high-entropy ceramic. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 576, 151719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-M.; Liu, X.-B.; Zhu, Z.-X.; Zhou, A.; Zhou, H.-B.; Zhang, S.-H. Study of tribological property of laser-cladded FeCoCrNiMnx high-entropy alloy coatings via experiment and molecular dynamics simulation. Tribol. Int. 2024, 191, 109106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Shen, J.Q.; Geng, K.P.; Hu, S.S. Fabrication of FeCoCrNiMnAl0.5-FeCoCrNiMnAl gradient HEA coating by laser cladding technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 412, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Guan, Y.J.; Jin, G.; Cui, X.F.; Liu, E.B.; Feng, L.T.; Li, X.Y. In-situ synthesis of a FeCoCrNiCu/FeCoCrNiAl composite high entropy alloy coating by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 461, 129447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.F.; Zhu, J.Q.; Cao, J.J.; Qiu, Z.G.; Chang, C.; Yan, X.C.; Yin, S.; Liu, M. Pitting corrosion mechanism of BCC+FCC dual-phase structured laser cladding FeCoCrNiAl0.5Ti0.5 HEAs coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 980, 173643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zhao, T.; Du, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D. Effect of molybdenum content on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of FeCoCrNiMox high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 46, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Quan, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S. Effect of Mo addition on structures and properties of FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy film by direct current magnetron sputtering. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 895, 162709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Peng, W.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, J.; He, Q.; Zhao, K.; Xi, S. Design and characterization on microstructure evolution and properties of laser-cladding Ni1.5CrFeTi2B0.5Mox high-entropy alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 408, 126793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Tan, H.; Liang, M.; Xie, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S. Mechanical and tribological properties of (FeCoNi)88-x(AlTi)12Mox high-entropy alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 105, 105845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Fu, H.G.; Wang, K.M.; Yang, X.J.; Zong, B.; Lin, J. Effect of Mo addition on microstructure and wear resistance of laser clad AlCoCrFeNi-TiC composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 623, 157071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, J. New studies on wear and corrosion behavior of laser cladding FeNiCoCrMox high entropy alloy coating: The role of Mo. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 102, 105721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, K.; Bała, P.; Kozieł, T.; Cios, G.; Schell, N.; Muszka, K. Effect of Mo on Phase Stability and Properties in FeMnNiCo High-Entropy Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2022, 53, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Walle, A.; Tiwary, P.; de Jong, M.; Olmsted, D.L.; Asta, M.; Dick, A.; Shin, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.-Q.; Liu, Z.-K. Efficient stochastic generation of special quasirandom structures. Calphad 2013, 42, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Yao, Y.; Yao, Z.P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, P.; Qin, W.; Wu, X.H. Construction of FeCrVTiMoX high-entropy alloys with enhanced mechanical properties based on electronegativity difference regulation strategy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 957, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudiaf, K.; Bouhemadou, A.; Al-Douri, Y.; Khenata, R.; Bin-Omran, S.; Guechi, N. Electronic and thermoelectric properties of the layered BaFAgCh (Ch = S, Se and Te): First-principles study. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 759, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaddach, A.J.; Niu, C.; Koch, C.C.; Irving, D.L. Mechanical Properties and Stacking Fault Energies of NiFeCrCoMn High-Entropy Alloy. JOM 2013, 65, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Min, T.; Yang, Y.; Ma, S.; Yi, D. The electronic, mechanical properties and theoretical hardness of chromium carbides by first-principles calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5242–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Leng, E.G.; Huang, Y.H.; Jin, N. First-principles study of the stability and mechanical properties for binary Mo–Re alloys. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2024, 693, 416401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayun, S.; Lilova, K.; Salhov, S.; Navrotsky, A. Enthalpies of formation of high entropy and multicomponent alloys using oxide melt solution calorimetry. Intermetallics 2020, 125, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y. First-principles investigation of the new phases and electrochemical properties of MoSi2 as the electrode materials of lithium ion battery. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 779, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Mao, P.Y.; Jiang, H.; Wan, Y.Y.; Guan, W.M. Insight into the effect of Mo and Re on mechanical and thermodynamic properties of NbSi2 based silicide. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5274–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, T.; Ma, H.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Insight into the vacancy effects on mechanical and electronic properties of V5Si3 silicides from first-principles calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2020, 98, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Guo, F. Pressure dependence of mechanical and thermodynamic properties of Al2Si4Sr3: A first-principles study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2023, 1230, 114400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Güler, M.; Uğur, G.; Uğur, Ş. A first-principles study for the elastic and mechanical properties of Ti64, Ti6242 and Ti6246 alloys. Eur. Phys. J. B 2021, 94, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Fan, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Cao, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Bai, P. Effects of Al and La elements on mechanical properties of CoNiFe0.6Cr0.6 high-entropy alloys: A first-principles study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.H.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z.Z.; Peng, M.J.; Zhu, P.X.; He, J.H. Elastic constants of AlB2-type compounds from first-principles calculations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 51, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Hu, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, Q. Effect of Cu additions on mechanical properties of Ni3Sn4-based intermetallic compounds: First-principles calculations and nano-indentation measurements. Vacuum 2019, 164, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Qian, X.; Yang, Q.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, X.; Quan, G.; Jiang, B. First-principles calculations of structural, elastic and electronic properties of second phases and solid solutions in Ti–Al–V alloys. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 591, 412241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Phase stability, mechanical properties and melting points of high-entropy quaternary metal carbides from first-principles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 6267–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.L.; Pan, Y. Influence of high pressure on the structure, hardness and brittle-to-ductile transition of NbSi2 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xu, C.-R.; Ding, N.; Chen, X.-T.; Duan, J.-M.; Tang, B.-Y. The intrinsic mechanical properties of NbTaTiZr and the influence of alloying elements Mo and W: A first-principles study. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 911, 165109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, J.; Yan, M.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y. First-principles study of NiAl alloyed with rare earth element Ce. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.N.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L. First-principles study of electronic structures and phase stabilities of ternary intermetallic compounds in the Mg-Y-Zn alloys. Acta Phys. Sin. 2015, 64, 187102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.P.; Zhang, L.Q.; Guo, Z.Q. Ab initio investigation of phase stability, thermo-physical and mechanical properties of (Mo0.2Cr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2X0.2)Si2 (X = W, V) high-entropy refractory metal silicides. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 203, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Song, C.; Wang, M.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yu, K.; Xu, L. Al and Mo synergistic enhancement of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy laser cladding layer. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2572–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, K.N.; Song, Q.; Cui, H.Z.; Li, W.S.; Wang, C.M. The effect of multi-element alloying on the structure and properties of laser cladding nickel-based coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 454, 129174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.B.; Luo, Z.Y.; Gou, G.Q.; Chen, W.J. Effects of Mo content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladded FeCoCrNiMox (x = 0.2, 0.5) high-entropy alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 482, 130697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, J.Y.; Sun, S.Y.; Feng, K.Y.; Zhang, Y.B.; Cao, M.Q. Microstructural evolution and phase transformation of Inconel 718 alloys fabricated by selective laser melting under different heat treatment. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 39, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, G.H.; Wang, Y.F. Microstructure characteristics and mechanical behaviour of a selective laser melted Inconel 718 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Niu, H.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Modeling hardness of polycrystalline materials and bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cui, S.; Yi, Y.; Xing, X.; Wang, X.; Li, W. Effect of Mo Element on the Mechanical Properties and Tribological Responses of CoCrFeNiMox High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.W.; Park, J.M.; Moon, J.; Choi, W.M.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, H.S. Effect of μ-precipitates on the microstructure and mechanical properties of non-equiatomic CoCrFeNiMo medium-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
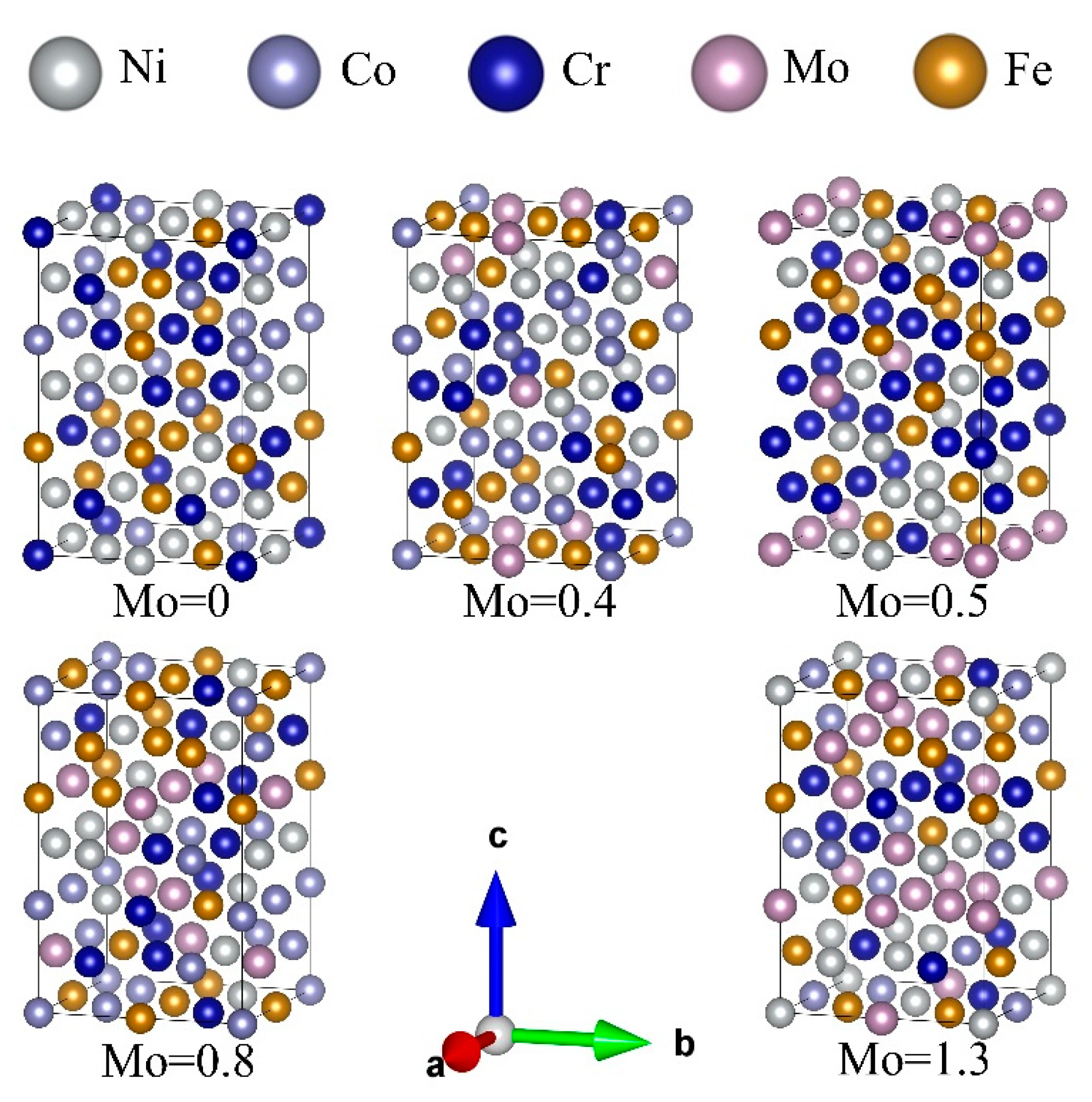
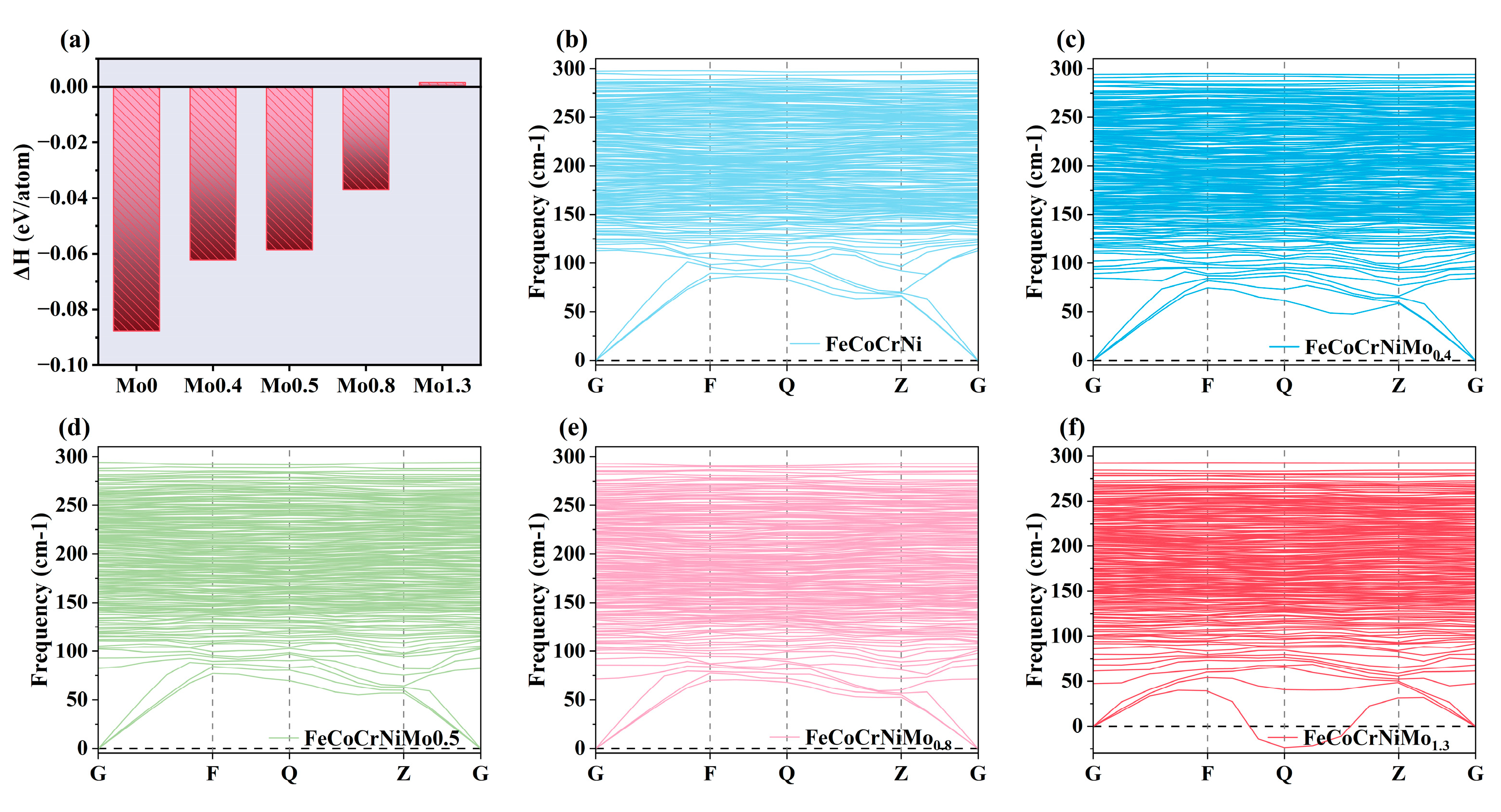


| δ% | VEC | |
|---|---|---|
| FeCoCrNiMo0 | 5.54 | 8.2500 |
| FeCoCrNiMo0.4 | 5.41 | 8.0625 |
| FeCoCrNiMo0.5 | 5.39 | 8.0624 |
| FeCoCrNiMo0.8 | 5.27 | 7.8749 |
| FeCoCrNiMo1.3 | 5.13 | 7.6875 |
| Elastic Properties | Elastic Constants | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | E | G | H | V | B/G | C11 | C12 | C44 | |
| Σ phase | 113.1 | 239.9 | 104.7 | 22.7 | 0.15 | 1.1 | 240.9 | 49.1 | 110.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Sun, H.; Sun, S.; Tang, W.; Gou, G. Mechanical Properties and σ-Phase Precipitation in FeCoCrNiMox (x = 0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.8, 1.3) High-Entropy Alloys: Insights from First-Principles Study. Materials 2025, 18, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061267
Li H, Jin J, Zhang Z, Yu J, Sun H, Sun S, Tang W, Gou G. Mechanical Properties and σ-Phase Precipitation in FeCoCrNiMox (x = 0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.8, 1.3) High-Entropy Alloys: Insights from First-Principles Study. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061267
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huimin, Junjun Jin, Zhiyi Zhang, Jinpeng Yu, Hairong Sun, Songling Sun, Weijie Tang, and Guoqing Gou. 2025. "Mechanical Properties and σ-Phase Precipitation in FeCoCrNiMox (x = 0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.8, 1.3) High-Entropy Alloys: Insights from First-Principles Study" Materials 18, no. 6: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061267
APA StyleLi, H., Jin, J., Zhang, Z., Yu, J., Sun, H., Sun, S., Tang, W., & Gou, G. (2025). Mechanical Properties and σ-Phase Precipitation in FeCoCrNiMox (x = 0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.8, 1.3) High-Entropy Alloys: Insights from First-Principles Study. Materials, 18(6), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061267






