Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Chemically Supported Anionic Functional Group Ionic Liquids and Its Enhanced Adsorption Performance Towards Vanadium (V)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Characterization Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Instruments
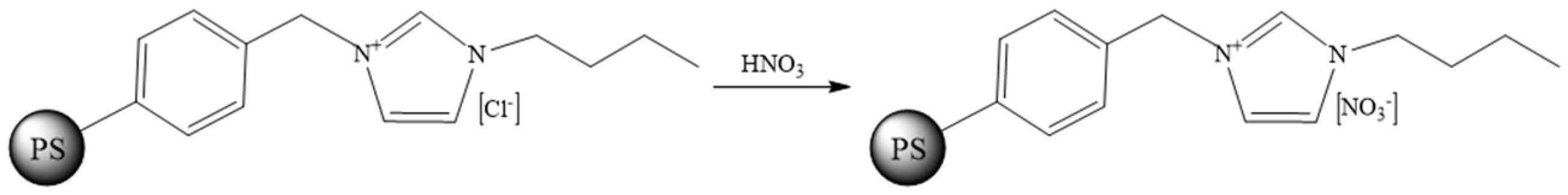
2.2. Synthesis of CSILs
2.3. Static Adsorption
2.4. Cyclic Use
2.5. Characterization and Analysis Method
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Effects of Preparation Parameters on the Properties of PS[C4mim][NO3]
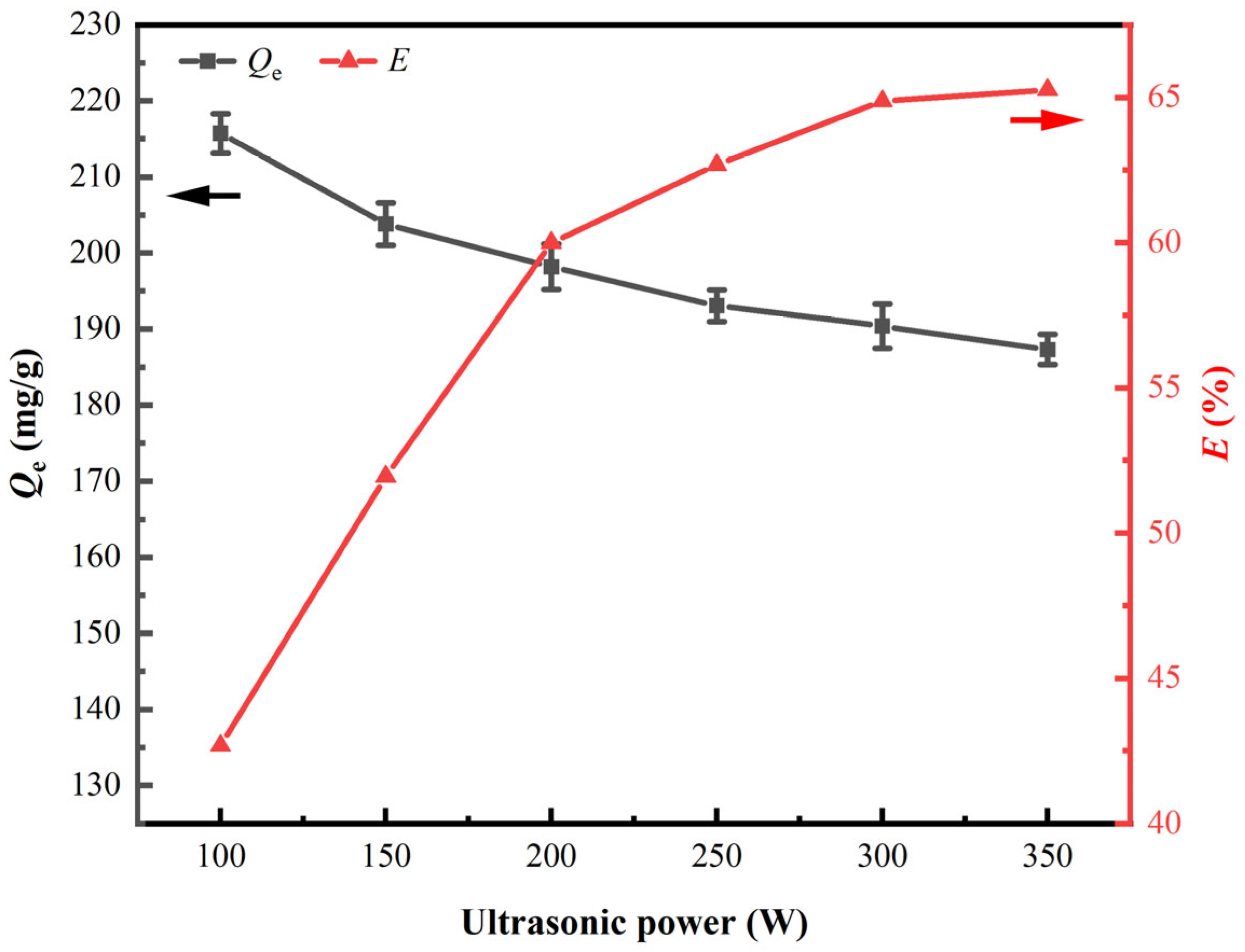
3.1.1. Ultrasonic Power
3.1.2. Reaction Time
3.1.3. HNO3 Dosage
3.2. Static Adsorption Performance of PS[C4mim][NO3]
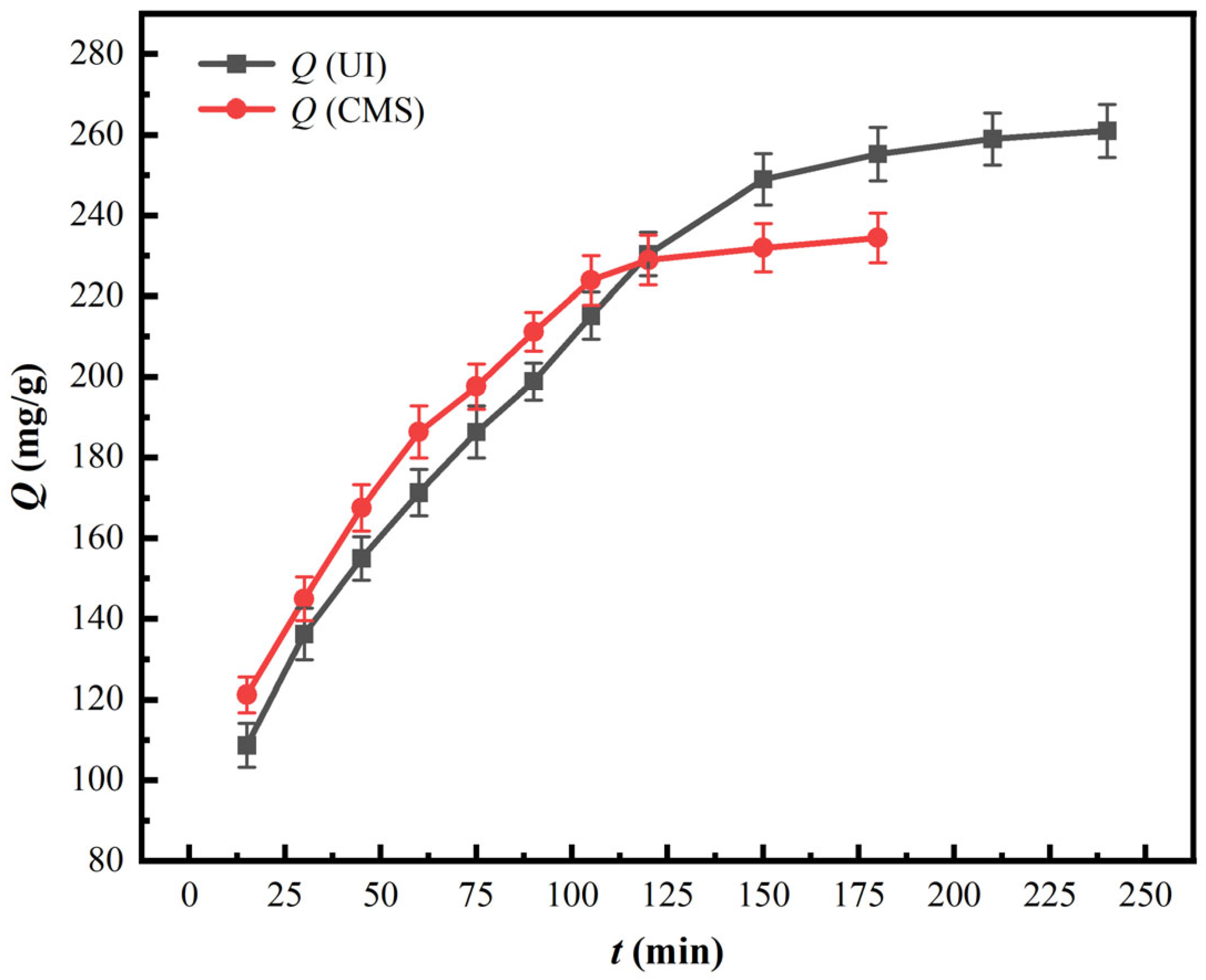
3.2.1. Impacts of Contact Time
3.2.2. Impacts of Initial Vanadium (V) Concentration
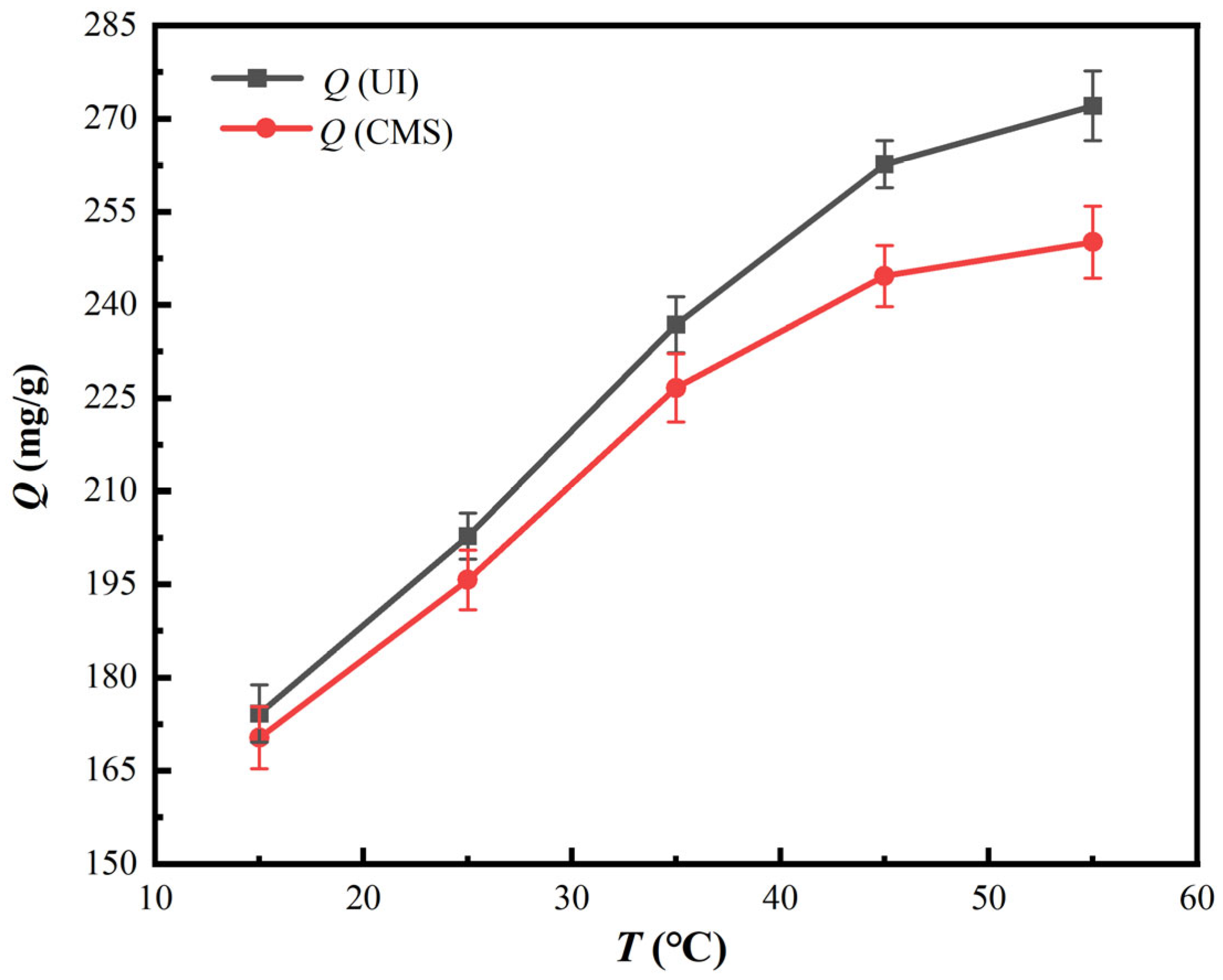
3.2.3. Impacts of Adsorption Temperature
3.3. Adsorption Mechanisms of PS[C4mim][NO3] Towards Vanadium (V)
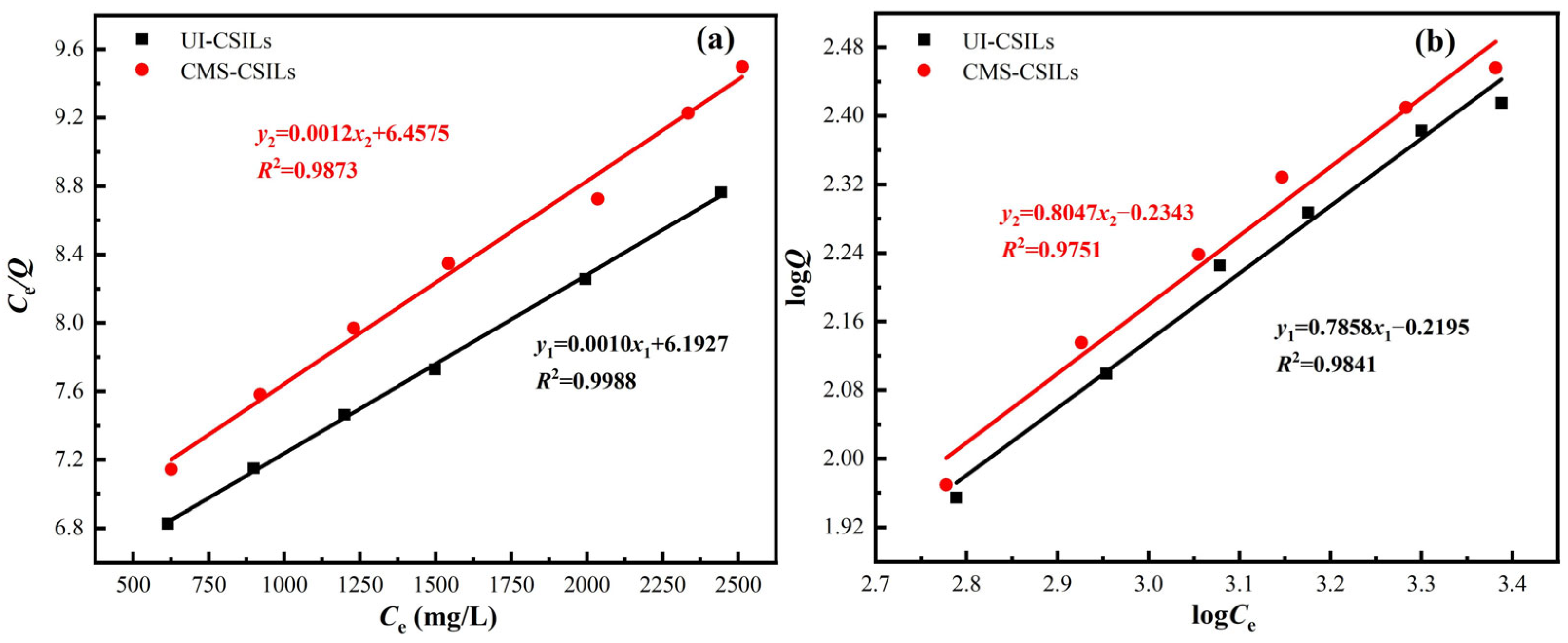
3.3.1. Adsorption Isotherm of Vanadium(V) onto PS[C4mim][NO3]
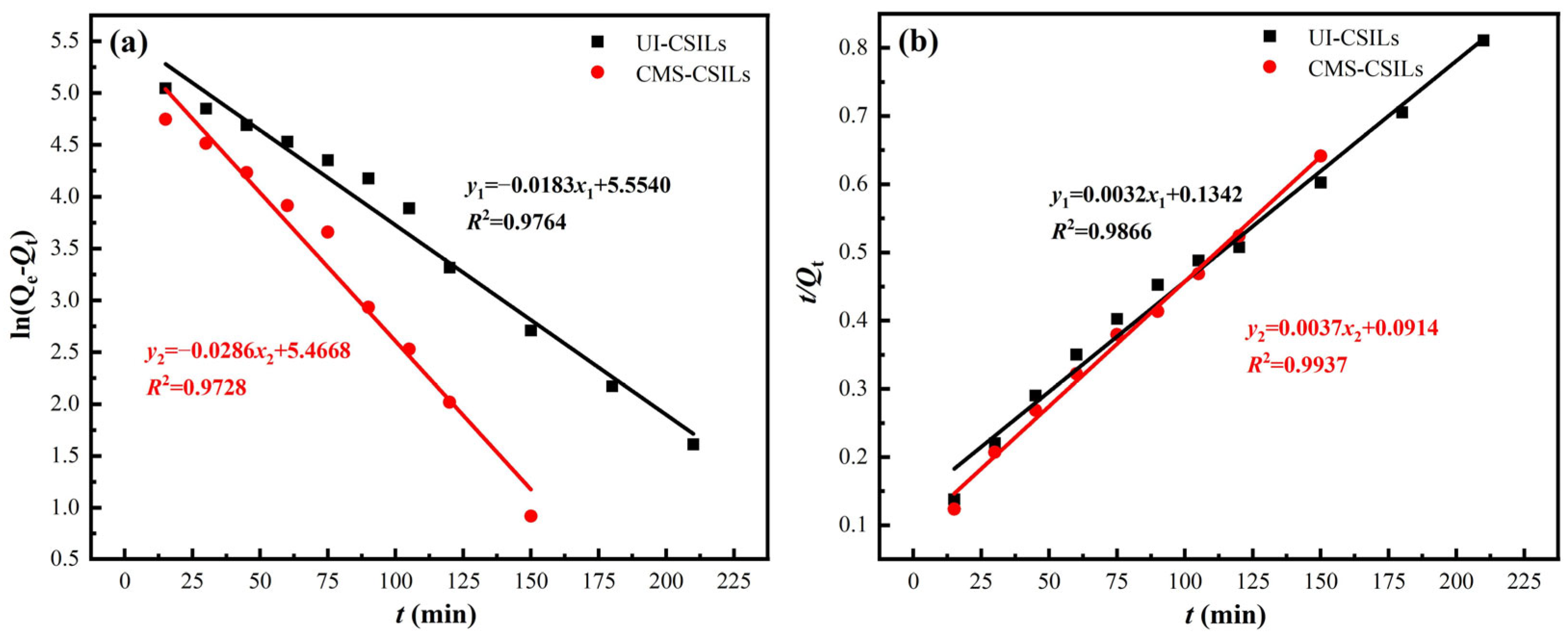
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics of Vanadium (V) onto PS[C4mim][NO3]
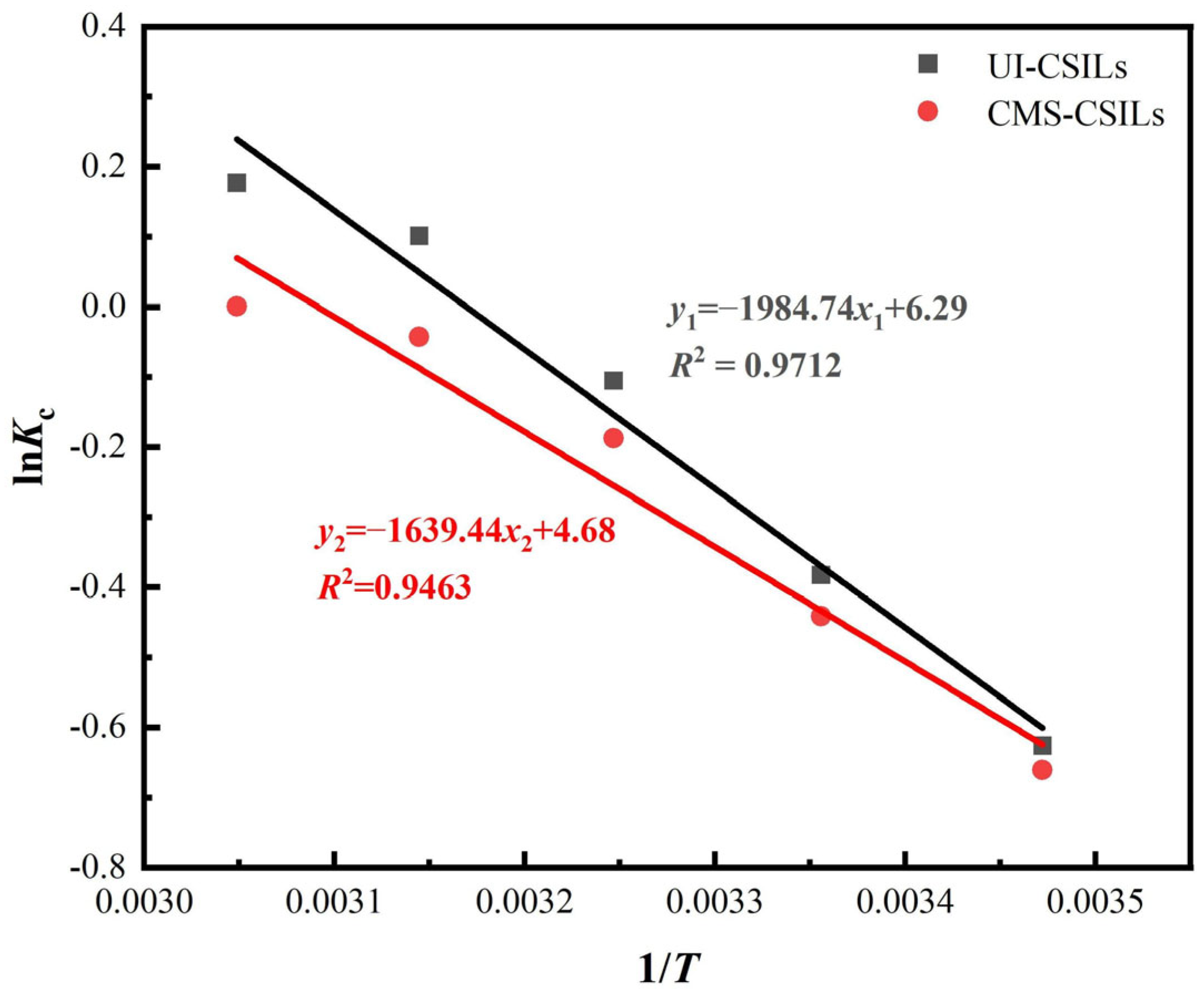
3.3.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics of Vanadium (V) onto PS[C4mim][NO3]
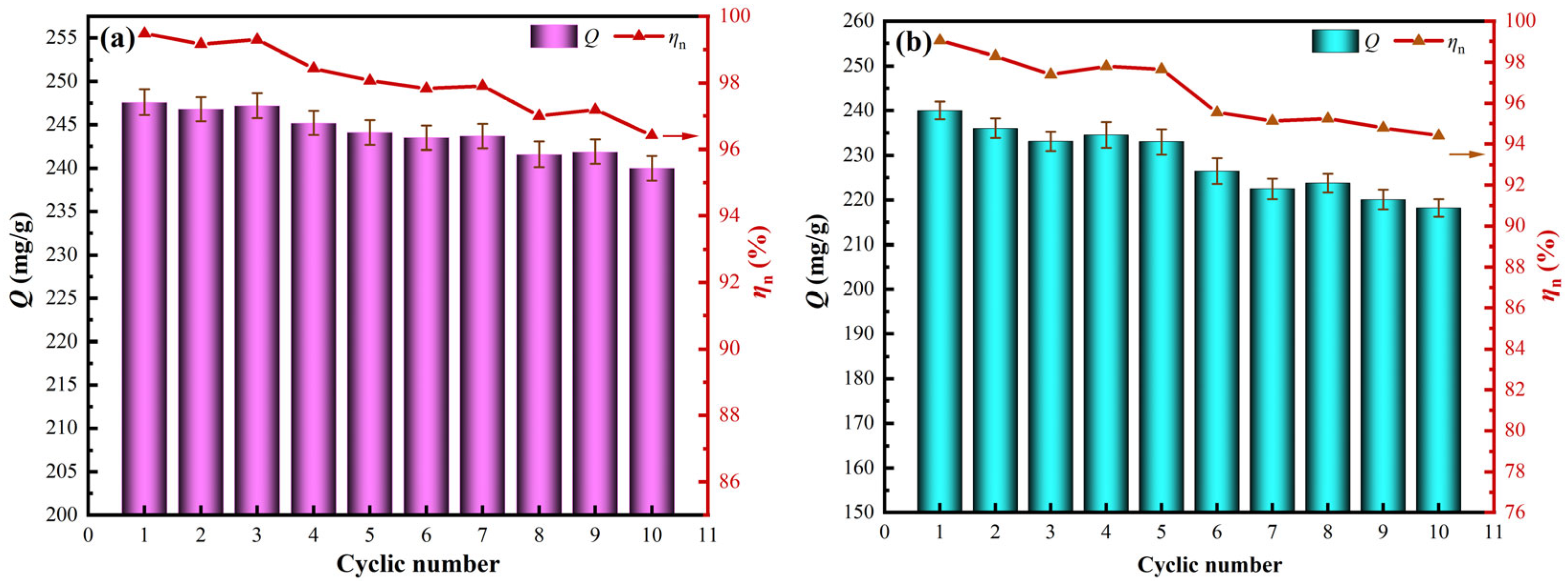
3.4. Cyclic Adsorption Stability
3.5. Characterization and Analysis of PS[C4mim][NO3]
3.5.1. Functional Groups Analysis
3.5.2. Microstructure and Element Distribution Analysis
3.6. Comparisons of Vanadium Adsorption Performance of PS[C4mim][NO3] and Other Materials
4. Conclusions and Prospect
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSILs | Chemically supported ionic liquids |
| UI | Ultrasound irradiation |
| CMS | Conventional mechanic stirring |
| PS[C4mim][NO3] | Polystyrene [1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium][nitrate] |
| UI-CSILs | Chemically supported ionic liquids synthesized by ultrasound irradiation |
| CMS-CSILs | Chemically supported ionic liquids synthesized by conventional mechanic stirring |
| ILs | Ionic liquids |
| SIRs | Solvent-impregnated resins |
| IL-IRs | Ionic liquids-impregnated resins |
| ACs | Activated carbons |
| PVMo | Vanadium polyoxometalate |
| FTIR | Fourier infrared spectrometer |
| SEM-EDS | Scanning electron microscope furnished with energy-dispersive spectrometer |
| PS[C4mim][Cl] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride supported on Merrifield resins |
References
- Imtiaz, M.; Rizwan, M.S.; Xiong, S.L.; Li, H.L.; Ashraf, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Shahzad, M.; Rizwan, M.; Tu, S.X. Vanadium, recent advancements and research prospects: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.F.; Bao, S.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, B.; Ding, W.; Gan, W.G. Selective leaching mechanisms of zinc from industrial waste using hybrid acids: Sustainable synthesis of Nano-ZnO. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, B.G.; Zou, S.Q.; Liu, Q.S.; Yang, M. Highly selective adsorption of vanadium (V) by nano-hydrous zirconium oxide-modified anion exchange resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petranikova, M.; Tkaczyk, A.H.; Bartl, A.; Amato, A.; Tunsu, C. Vanadium sustainability in the context of innovative recycling and sourcing development. Waste Manag. 2020, 113, 521–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.; Jones, A.; Rogerson, M.; Greenway, G.M.; Lisbona, D.F.; Burke, I.T.; Mayes, W.M. Removal and recovery of vanadium from alkaline steel slag leachates with anion exchange resins. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bao, S.X.; Zhang, Y.M. Effects of key impurities (Al, Fe, P, Si and Na) on the precipitation process of vanadium in the novel ultrasound-assisted precipitation system. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 224, 106233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.B.; Yang, X.H.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Efficient removal and recovery of vanadium (IV and V) from high acidic waste water with resins D851 and D201: A comparative study. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.Y.; Zhao, J.M.; Wang, F.C.; Huo, F.; Liu, H.Z. Selective extraction of vanadium from chromium by pure [C8mim][PF6]: An anion exchange process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 131, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.J.; Liu, M.; Yuan, B.; He, J.; Wu, P.; Liu, C.J.; Jiang, W. Separation of vanadium and chromium by selective adsorption by titanium-based microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibania, S.; Mahmoudi, A.; Mokmeli, M. Separation of vanadium and iron from the steelmaking slag convertor using Aliquat 336 and D2EHPA: Effect of the aqueous species and the extractant type. Miner. Eng. 2022, 181, 107521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Gao, X.Z.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, H.M.; Liu, C.P.; Jin, R.C. Adsorption properties and mechanism for Fe(III) with solvent impregnated resins containing HEHEHP. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 137, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Liu, J.S.; Gao, X.Z.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, C.P. Adsorption behavior of indium(III) on modified solvent impregnated resins (MSIRs) containing sec-octylphenoxy acetic acid. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 121, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erto, A.; Silvestre-Albero, A.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Balsamo, M.; Lancia, A.; Montagnaro, F. Carbon-supported ionic liquids as innovative adsorbents for CO2 separation from synthetic flue-gas. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Akhmedov, N.G.; Duan, Y.H.; Luebke, D.; Hopkinson, D.; Li, B.Y. Amino acid-functionalized ionic liquid solid sorbents for post-combustion carbon capture. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8670–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Leo, C.P.; Mohammad, A.W.; Shaari, N.; Ang, W.L. Recent applications of ionic liquids in separation technology. Molecules 2010, 15, 2405–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhao, L. Covalently bonded ionic liquid onto cellulose for fast adsorption and efficient separation of Cr(VI): Batch, column and mechanism investigation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Bao, S.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, B.; Liang, Y.; Hou, X.C.; Yang, S.Y.; Ping, Y.; Zhou, Z.C. Adsorption property and mechanism of vanadium(V) by supported bifunctionalized ionic liquid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 681, 132753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Bao, S.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, B.; Liang, Y.; Ding, W.; Hou, X.; Yang, S.; Ping, Y. Adsorption behavior of vanadium(V) by supported imidazolium-based difunctionalized ionic liquid. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 123245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, D.; Yu, D. Coated impregnated resin containing Alamine 336 for the selective adsorption of ReO4− from sulfuric acid solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, M.S.; Sherif, E.E.; Mekhamer, H.S.; Rahman, R.O.A. Assessment of Cyanex 301 impregnated resin for its potential use to remove cobalt from aqueous solutions. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, N.; Kumar, A.S.K.; Kalidhasan, S.; Rajesh, V. Trialkylamine impregnated macroporous polymeric sorbent for the effective removal of chromium from industrial wastewater. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.V.; Lee, J.C.; Jeong, J.; Pandey, B.D. Enhancing the adsorption of chromium (VI) from the acidic chloride media using solvent impregnated resin (SIR). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.M.; Ren, L.Y.; Xin, C.F.; Ding, W.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, W.C. A comprehensive review on the ultrasound-enhanced leaching recovery of valuable metals: Applications, mechanisms and prospects. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, I.V.; Santos, J.R.N.D.; Januario, M.A.P.; Correa, A.G. Greener organic synthetic methods: Sonochemistry and heterogeneous catalysis promoted multicomponent reactions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 78, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Bao, S.X.; Xu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Huang, J.G.; Ding, W.; Xin, C.F.; Chen, B. Biochar-based polarity reversal bipolar electrochemistry coupled with phytoextraction for rapid remediation of lead and zinc-contaminated soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Bian, G.A.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z. Adsorption of dibenzothiophene on Ag/Cu/Fe-Supported activated carbons prepared by ultrasonic-assisted impregnation. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 5818–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangestaninejad, S.; Mirkhani, V.; Moghadam, M.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I.; Salavati, H. Hydrocarbon oxidation catalyzed by vanadium polyoxometalate supported on mesoporous MCM-41 under ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bao, S.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zheng, R.W. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of N235-impregnated resins for vanadium (V) adsorption. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.X.; Yu, J.L.; Tahmasebi, A.; Yin, F.K.; Gupta, S.; Li, X.C.; Lucas, J.; Na, C.; Wall, T. Ultrasonic-assisted preparation of highly reactive Fe-Zn sorbents supported on activated-char for desulfurization of COG. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 135, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, A.; Montoya, J.A.; Viniegra, M.; Navarrete, J.; Espinosa, G.; Vargas, A.; Del Angel, P.; Pérez, G. Isomerization of n-hexane over mono- and bimetallic Pd-Pt catalysts supported on ZrO2-Al2O3-WOx prepared by sol-gel. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 290, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Molina, A.; Ibarra-Armenta, J.G.; Quesada-Perez, M. Effect of ion dispersion forces on the electric double layer of colloids: A Monte Carlo simulation study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, A.E.; Swatloski, R.P.; Reichert, W.M.; Griffin, S.T.; Rogers, R.D. Traditional extractants in nontraditional solvents: Groups 1 and 2 extraction by crown ethers in room-temperature ionic liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Hamaguchi, H. Effect of water on the molecular structure and arrangement of nitrile-functionalized ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2777–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, K.R.; Stark, A. Selective catalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohol and alkylbenzenes in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.; Kanmani, M.; Debnath, A.; Bhowmik, K.L.; Saha, B. Ultrasonic assisted enhanced adsorption of methyl orange dye onto polyaniline impregnated zinc oxide nanoparticles: Kinetic, isotherm and optimization of process parameters. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 54, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Pastor, M.; Ayora-Canada, M.J.; Valcarcel, M.; Lendl, B. Association of methanol and water in ionic liquids elucidated by infrared spectroscopy using two-dimensional correlation and multivariate curve resolution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 10896–10902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.H.; Doraiswamy, L.K. Sonochemistry: Science and engineering. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 1215–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizhoosh, N.Y.; Khataee, A.; Hassandoost, R.; Soltani, R.D.C.; Doustkhah, E. Ultrasound-engineered synthesis of WS2@CeO2 heterostructure for sonocatalytic degradation of tylosin. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 67, 105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidhasan, S.; Kumar, A.S.K.; Rajesh, V.; Rajesh, N. An efficient ultrasound assisted approach for the impregnation of room temperature ionic liquid onto Dowex 1×8 resin matrix and its application toward the enhanced adsorption of chromium (VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołowicz, A.; Hubicki, Z. Removal of vanadium by ion exchange resins from model and real solutions from spent V2O5 catalyst. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 211, 105871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtian, K.; Porhemat, S.; Rezvani, A.R.; Ghaedi, M.S. Adsorption of semisoft pollutants onto Bi2S3/Ag2S-AC under the influence of ultrasonic waves as external filed. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 60, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, M.; Nibou, D.; Chegrouche, S.; Mellah, A. Kinetics and thermodynamics studies of chromium(VI) ions adsorption onto activated carbon from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2009, 48, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Q.; Traina, S.J.; Weavers, L.K. Sonolytic desorption of mercury from aluminum oxide: Effects of pH, chloride, and organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, S.Q.; Zhao, J.F. Simultaneous recovery of microalgae, ammonium and phosphate from simulated wastewater by MgO modified diatomite. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, S.; Nur, H.M.; Traore, A.M.; Yıldırım, E.; Emik, S. Fixed bed column adsorption of vanadium from water using amino-functional polymeric adsorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 209, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Z.; Chen, D.S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, H.X.; Wang, L.N.; Li, D.; Qi, T. A novel synergistic extraction method for recovering vanadium (V) from high-acidity chloride leaching liquor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 165, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Xie, B. Removal of V(V) from aqueous Cr(VI)-bearing solution using anion exchange resin: Equilibrium and kinetics in batch studies. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, F.; Teranishi, Y.; Nagai, N.; Uematsu, Y.; Toda, M.; Otani, M.; Saenjum, C.; Kawasaki, N. Feasibility of vanadium ion adsorption/desorption using nickel-aluminum complex hydroxides with different molar ratios. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2024, 20, 100656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.S.; Imam, D.M.; EI-Nadi, Y.A. Vanadium(V) removal and recovery by adsorption onto modified activated carbon derived from natural hydroxyapatite. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2021, 18, 2771–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.F. Insight into the adsorption mechanisms of vanadium(V) on a high-efficiency biosorbent (Ti-doped chitosan bead). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




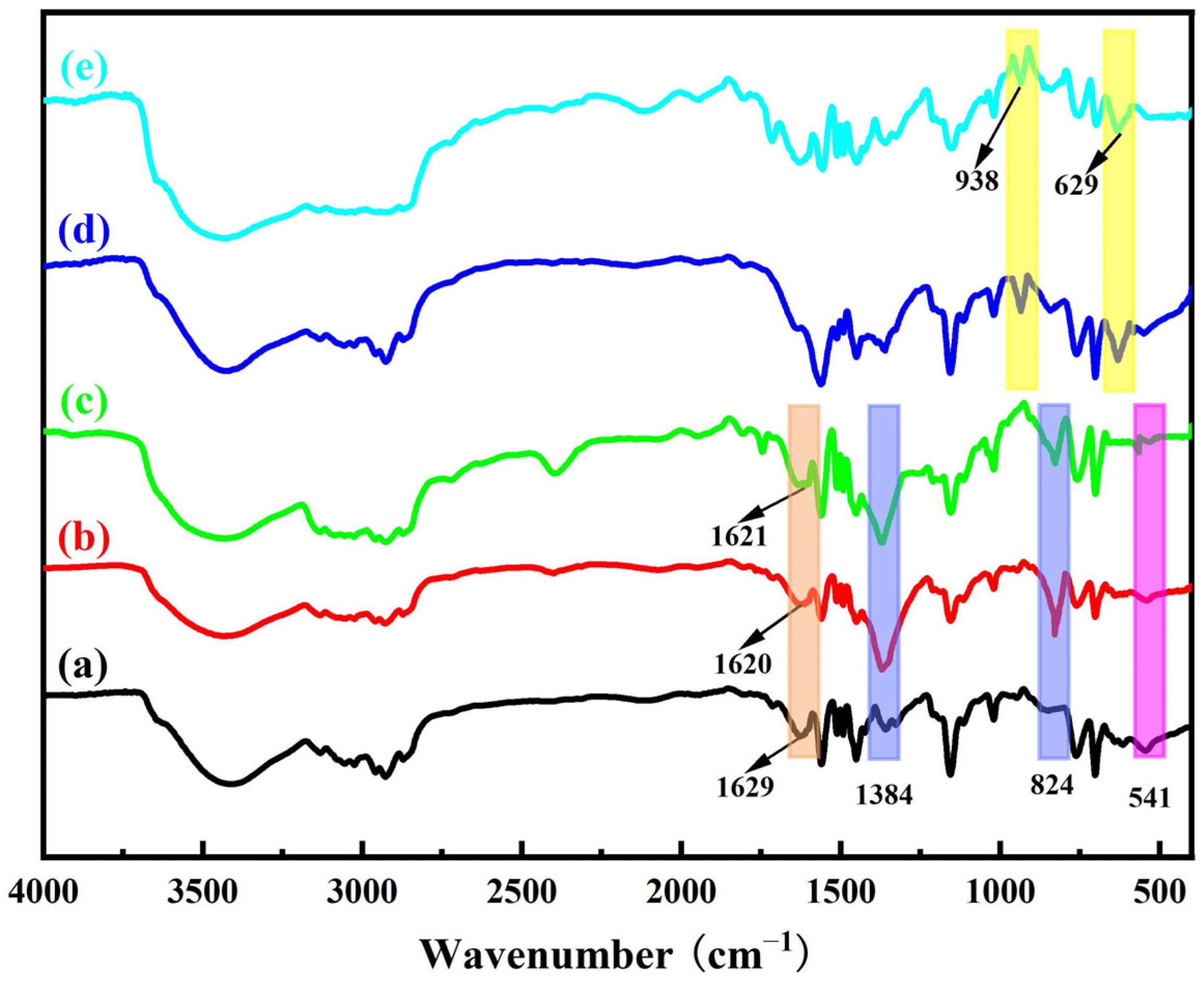
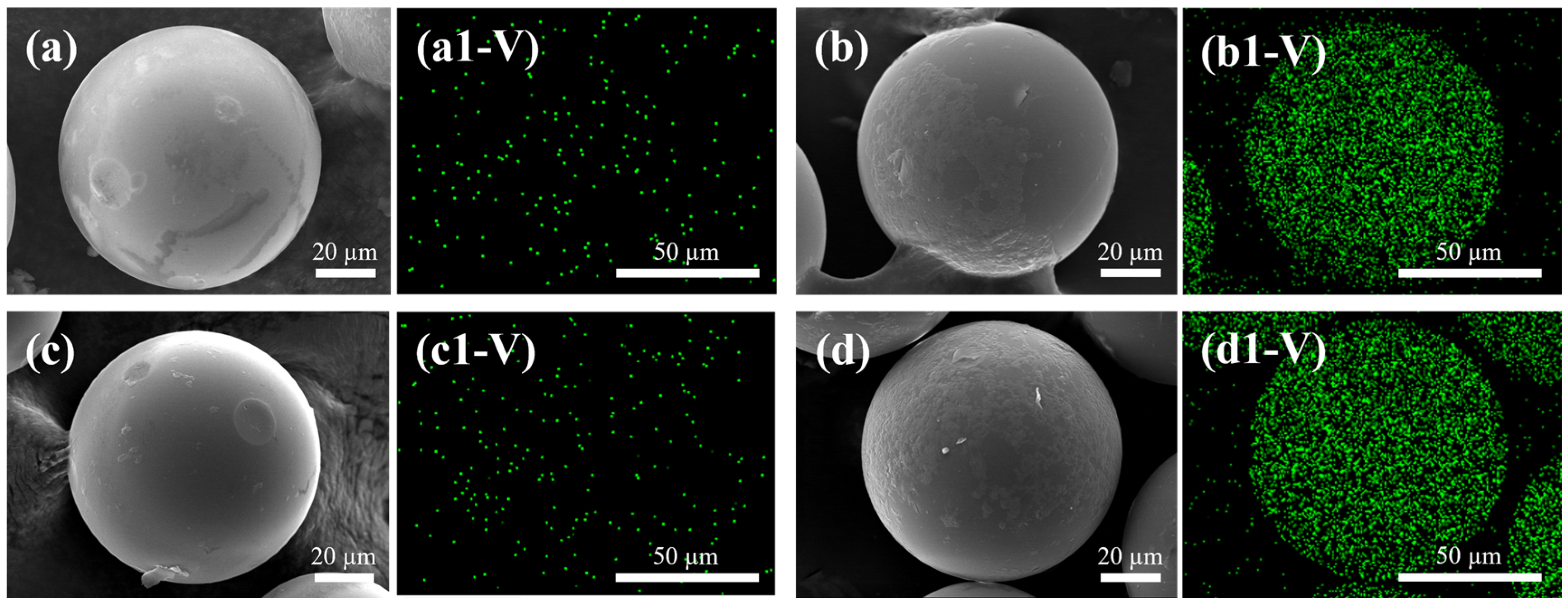
| Samples | N | C | H | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI-CSILs | 7.04 | 69.73 | 8.32 | 7.92 |
| CMS-CSILs | 7.71 | 69.08 | 7.84 | 8.38 |
| Supported ILs | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q0 (mg/g) | KL (L/g) | R2 | n | KF (L/g) | R2 | |
| UI-CSILs | 1000 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 0.9988 | 1.27 | 0.6033 | 0.9841 |
| CMS-CSILs | 833.33 | 1.9 × 10−4 | 0.9873 | 1.24 | 0.5830 | 0.9751 |
| Supported ILs | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe | k1 | R2 | Qe | k2 | R2 | |
| UI-CSILs | 254.68 | 0.0183 | 0.9764 | 312.50 | 7.6 × 10−5 | 0.9866 |
| CMS-CSILs | 236.70 | 0.0286 | 0.9728 | 270.27 | 1.5 × 10−4 | 0.9937 |
| Supported ILs | T (K) | ΔG (kJ/mol) | ΔS (kJ/mol·K) | ΔH (kJ/mol) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI-CSILs | 288 | 1.44 | 0.0523 | 16.50 | 0.9712 |
| 298 | 0.91 | ||||
| 308 | 0.39 | ||||
| 318 | −0.13 | ||||
| 328 | −0.65 | ||||
| CMS-CSILs | 288 | 1.48 | 0.0422 | 13.63 | 0.9463 |
| 298 | 1.05 | ||||
| 308 | 0.63 | ||||
| 318 | 0.21 | ||||
| 328 | −0.21 |
| Number | Materials | Vanadium Adsorption Capacity, mg/g | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nickel–aluminum complex hydroxides | 177.5 | [48] |
| 2 | Modified activated carbon derived from natural hydroxyapatite | 19.45 | [49] |
| 3 | Nano-hydrous zirconium oxide-modified anion exchange resin | 118.1 | [3] |
| 4 | Titanium-based microspheres | 153.2 | [9] |
| 5 | Amino-functional polymeric | 75.5 | [45] |
| 6 | Ti-doped chitosan bead | 210 | [50] |
| 7 | Ion exchange resins TP220 and M4195 | 247.81 and 208.79 | [40] |
| 8 | Anion exchange resin Dex-V | 25.42 | [47] |
| 9 | Anion exchange resins Amberlite IRA-400 | 27.4 | [5] |
| 10 | Ion exchange resins D851 and D201 | 162 and 104 | [7] |
| 11 | PS[C4mim][NO3] prepared by UI | 248.95 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Bao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ding, W.; Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Chemically Supported Anionic Functional Group Ionic Liquids and Its Enhanced Adsorption Performance Towards Vanadium (V). Materials 2025, 18, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061330
Chen B, Bao S, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Ding W, Ren L, Yang S, Zhang Y. Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Chemically Supported Anionic Functional Group Ionic Liquids and Its Enhanced Adsorption Performance Towards Vanadium (V). Materials. 2025; 18(6):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061330
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bo, Shenxu Bao, Yimin Zhang, Jiahao Zhou, Wei Ding, Liuyi Ren, Siyuan Yang, and Ye Zhang. 2025. "Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Chemically Supported Anionic Functional Group Ionic Liquids and Its Enhanced Adsorption Performance Towards Vanadium (V)" Materials 18, no. 6: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061330
APA StyleChen, B., Bao, S., Zhang, Y., Zhou, J., Ding, W., Ren, L., Yang, S., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Chemically Supported Anionic Functional Group Ionic Liquids and Its Enhanced Adsorption Performance Towards Vanadium (V). Materials, 18(6), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061330










