Seed-Assisted Crystallization in the Hydrothermal Synthesis of FAU Zeolite from Acid-Treated Residue Glass Powder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acid Leaching in Residue Glass Powder
2.1.1. Study of the Optimal Temperature for Acid Leaching
2.1.2. Study of the Optimal Experimental Condition for Acid Leaching
2.2. Syntheses of FAU Zeolites
2.2.1. Synthesis of FAU-X Zeolite Seeds
2.2.2. Study of Optimal Seed Dosage in the Synthesis of FAU Zeolite with Untreated and Acid-Treated Residues
2.3. Characterization of the Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Acid Leaching in Residue Glass Powder
3.2. Synthesis of FAU-X Zeolite
3.2.1. Effect of Seed Crystals Amount
3.2.2. Influence of Cations in Framework Type
3.2.3. Interzeolite Transformations
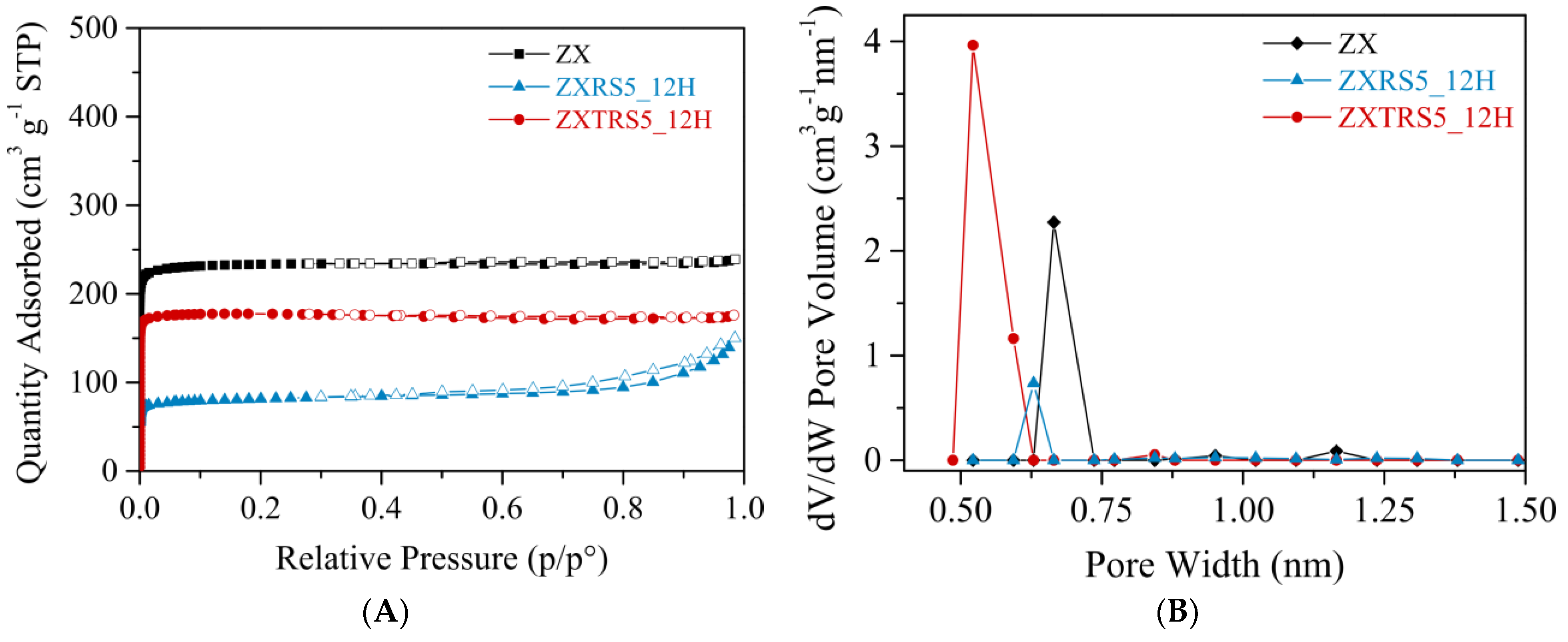
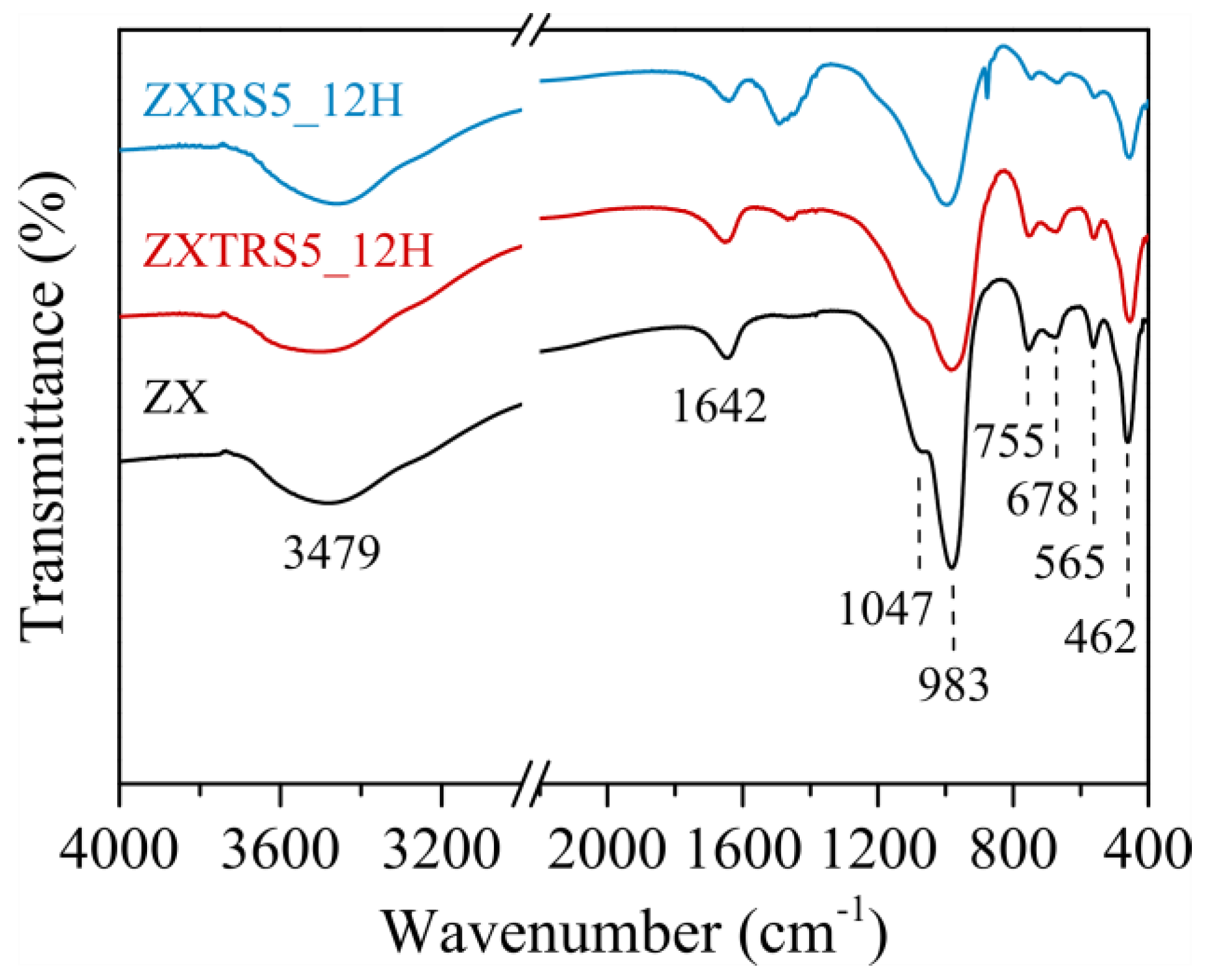
3.3. Characterization of Samples ZXRS5 and ZXTRS5
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCusker, L.B.; Olson, D.H.; Baerlocher, C. Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types, 6th ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, C.; McCusker, L. Database of Zeolite Structures. 2021. Available online: http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Reiprich, B.; Weissenberger, T.; Schwieger, W.; Inayat, A. Layer-like fau-type zeolites: A comparative view on different preparation routes. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckee, D. Separation of an Oxygen-Nitrogen Mixture. U.S. Patent 3,140,932, 14 July 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Krol, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite aggregate with potential use as a sorbent of heavy metal cations. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1183, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nahas, S.; Osman, A.I.; Arafat, A.S.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Salman, H.M. Facile and affordable synthetic route of nano powder zeolite and its application in fast softening of water hardness. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, S.; Sen, S. Rapid ultrasound assisted hydrothermal synthesis of highly pure nanozeolite x from fly ash for efficient treatment of industrial effluent. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleque, A.; Alam, M.M.; Hoque, M.; Mondal, S.; Haider, J.B.; Xu, B.; Johir, M.; Karmakar, A.K.; Zhou, J.; Ahmed, M.B.; et al. Zeolite synthesis from low-cost materials and environmental applications: A review. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zones, S. Translating new materials discoveries in zeolite research to commercial manufacture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, S.; Hashishin, T.; Morikawa, T.; Yamashita, K.; Matsuda, M. Selective synthesis of zeolites a and x from two industrial wastes: Crushed stone powder and aluminum ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Wang, C.; Zeng, L.; Ma, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C. Lithium Extraction and Hydroxysodalite Zeolite Synthesis by Hydrothermal Conversion of α-Spodumene. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9498–9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieseki, L.; Ribeiro, D.B.; Sobrinho, E.V.; Melo, D.M.A.; Pergher, S.B.C. Síntese de zeólitas utilizando resíduo sílico-aluminoso proveniente do processo de extração de lítio. Cerâmica 2013, 59, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.; Dantas, E.; Pergher, S.; Melo, D.; Melo, M. Synthesis of high value-added zeolitic materials using glass powder residue as a silica source. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinaches, P.; Rebitski, E.P.; Alves, J.A.; Melo, D.M.; Pergher, S.B. Unconventional silica source employment in zeolite synthesis: Raw powder glass in MFI synthesis case study. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinaches, P.; Alves, J.A.; Melo, D.M.; Pergher, S.B. Raw powder glass as a silica source in the synthesis of colloidal mel zeolite. Mater. Lett. 2016, 178, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayehi, M.; Garbarino, G.; Delahay, G.; Busca, G.; Tounsi, H. Synthesis of high value-added Na-P1 and Na-FAU zeolites using waste glass from fluorescent tubes and aluminum scraps. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Zhao, H.; Tang, J. Recycling of typical difficult-to-treat e-waste: Synthesize zeolites from waste cathode-raytube funnel glass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlier, M.; Atalay-Oral, Ç. Preparation of zeolite X coatings on soda-lime type glass plates. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wang, D.; Ye, S. Synthesis of micro-mesoporous glass-analcime composite structure with soda-lime-silica glass as raw material. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2019, 12, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.H.; Elmes, V.K.; Hurt, A.P.; Coleman, N.J. Synthesis of feldspathoids and zeolite K-F from waste amber container glass. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, T.; Ota, H.; Dong, Q.; Miura, A.; Yonesaki, Y.; Kumada, N.; Takahashi, H. Preparation of porous material from waste bottle glass by hydrothermal treatment. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, A.R.; Manna, P.K.; Wroczynskyj, Y.; van Lierop, J.; Cicek, N.; Tranmer, G.K.; Yuan, Q. Cost-effective zeolite synthesis from waste glass cullet using energy efficient microwave radiation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 221, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, A.R.; Yuan, Q. Microwave synthesis of zeolites from waste glass cullet using indirect fusion and direct hydrothermal methods: A comparative study. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 2400–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, A.R.; Yuan, Q. Microwave synthesis of zeolites from waste glass cullet using landfill leachate as a novel alternative solvent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 223, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzano, R.; D’Alessandro, C.; Spagnuolo, M.; Romagnoli, M.; Medici, L. Facile Zeolite Synthesis from Municipal Glass and Aluminum Solid Wastes. Clean 2015, 43, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Choi, M.; Song, H.J.; Park, J.E.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Lee, C.G.; Kim, D.W. Synthesis of uniform-sized zeolite from windshield waste. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 166, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Choi, M.; Kim, D.S.; Song, H.J.; Kim, D.W. Windshield-waste-driven synthesis of hydroxy sodalite. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 123, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Swain, B.; Im, B.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Lee, C.G.; Kim, D.G. Synthesis of zeolite using aluminum dross and waste lcd glass powder: A waste to waste integration valorization process. Metals 2019, 9, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujiguchi, M.; Kobashi, T.; Oki, M.; Utsumi, Y.; Kakimori, N.; Nakahira, A. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite A from crushed particles of aluminoborosilicate glass used in LCD panels. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 2, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujiguchi, M.; Kobashi, T.; Utsumi, Y.; Kakimori, N.; Nakahira, A. Synthesis of zeolite a from aluminoborosilicate glass used in glass substrates of liquid crystal display panels and evaluation of its cation exchange capacity. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujiguchi, M.; Kobashi, T.; Utsumi, Y.; Kakimori, N.; Nakahira, A. Synthesis of FAU zeolite from aluminoborosilicate glass and elution behavior of glass components. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 122, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayehi, M.; Tounsi, H.; Garbarino, G.; Riani, P.; Busca, G. Reutilization of silicon- and aluminum-containing wastes in the perspective of the preparation of SiO2-Al2O3 based porous materials for adsorbents and catalysts. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieseki, L.; Bertella, F.; Treichel, H.; Penha, F.G.; Pergher, S.B.C. Acid treatments of montmorillonite-rich clay for Fe removal using a factorial design method. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Kang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Gu, L.; Liu, H.; Bao, J.; Wang, T.; Yuan, P.; Zhu, H.; Bai, Z.; et al. Seed-assisted, template-free synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from natural aluminosilicate minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 158, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Guan, D.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, N. Rapid green synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from leached illite clay. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 280, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Lu, X.; Wang, T.; Yan, Y. Submicron ZSM-5 synthesized by green and fast route. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Zhou, T.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, J.; Xi, B. Pure zeolite x synthesized from coal fly ash by pretreatment with solid alkali and using seed crystal. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 479, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundy, C.S.; Cox, P.A. The hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites: Precursors, intermediates and reaction mechanism. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 82, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintova, S. Verified Syntheses of Zeolitic Materials; Synthesis Commission of the International Zeolite Association: Caen, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D3906-19; Standard Test Method for Determination of Relative X-Ray Diffraction Intensities of Faujasite-Type Zeolite-Containing Materials. ATMS International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- de Boer, J.; Linsen, B.; van der Plas, T.; Zondervan, G. Studies on pore systems in catalysts: Vii. description of the pore dimensions of carbon blacks by the t method. J. Catal. 1965, 4, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, P. Free-energy density functional for hard spheres. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 2672–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, P.; Marconi, U.M.B.; Evans, R. Phase equilibria of fluid interfaces and confined fluids. Mol. Phys. 1987, 60, 573–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navrotsky, A.; Trofymluk, O.; Levchenko, A.A. Thermochemistry of microporous and mesoporous materials. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3885–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treacy, M.M.J.; Higgins, J.B. Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, M.; Oleksiak, M.D.; Chinta, S.; Rimer, J.D. Controlling crystal polymorphism in organic-free synthesis of na-zeolites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, R.C.; Bieseki, L.; Melguizo, P.V.; Pergher, S.B.C. Environmentally Friendly Zeolites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, G.G.; Rendón, A.M.; Fuentes, G.R. Zeolitas: Características, Propriedades y Aplicaciones Industriales, 2nd ed.; Edit Editorial Innovación Tecnológica: Caracas, Venezuela, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-H.; Lin, Y.-W.; Lin, K.-L. Parameter optimization, characterization, and crystallization mechanisms underlying the synthesis of zeolite a using liquid crystal display waste glass and sandblasting waste as alternative raw materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayehi, M.; Delahay, G.; Tounsi, H. Synthesis and characterization of ecofriendly materials zeolite from waste glass and aluminum scraps using the hydrothermal technique. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigen, E.M.; Khatami, H.; Szymanski, H.A. Infrared Structural Studies of Zeolite Frameworks. In Molecular Sieve Zeolites-I; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; pp. 201–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Chemical Composition (%, wt.) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | K2O | Others | |
| RGP | 66.94 | 3.31 | 8.80 | 14.84 | 3.60 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 1.17 |
| TRGP01_25C | 78.76 | 3.22 | 2.50 | 10.11 | 3.10 | 0.49 | 0.37 | 1.45 |
| TRGP01_80C | 87.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 4.29 | 2.00 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.67 |
| Samples | [HCl] (mol L−1) | L/S ratios a (mL (2g)−1) | Time (min) | Ca2+ Removed (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRGP02_1 | 0.50 | 20 | 60 | 43.06 |
| TRGP02_2 | 0.50 | 20 | 240 | 54.38 |
| TRGP02_3 | 0.50 | 60 | 60 | 55.26 |
| TRGP02_4 | 0.50 | 60 | 240 | 69.27 |
| TRGP02_5 | 3.00 | 20 | 60 | 56.60 |
| TRGP02_6 | 3.00 | 20 | 240 | 72.44 |
| TRGP02_7 | 3.00 | 60 | 60 | 56.33 |
| TRGP02_8 | 3.00 | 60 | 240 | 71.97 |
| Time | Relative Crystallinity to FAU Phase (RCFAU, %) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% wt. | 1% wt. | 5% wt. | ||||
| RGP | TRGP | RGP | TRGP | RGP | TRGP | |
| 12 h | 0 | 39 | 8 | 52 | 20 | 81 |
| 24 h | 0 | 39 | 15 | 49 | 18 | 77 |
| 36 h | 0 | 40 | 12 | 51 | 15 | 78 |
| 48 h | 3 | 46 | 12 | 42 | 17 | 77 |
| Samples | SBET a (m2 g−1) | SExt. b (m2 g−1) | Vmicro b (cm3 g−1) | Vmeso b,c (cm3 g−1) | Vmeso d (cm3 g−1) | Pore Size e (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZX | 967 | 61 | 0.335 | 0.035 | - | 0.67 |
| ZXTRS5_12H | 742 | 45 | 0.258 | 0.014 | - | 0.52 |
| ZXRS5_12H. | 323 | 53 | 0.103 | 0.129 | 0.122 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sousa, P.B.F.; Bieseki, L.; Pergher, S.B.C. Seed-Assisted Crystallization in the Hydrothermal Synthesis of FAU Zeolite from Acid-Treated Residue Glass Powder. Materials 2025, 18, 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071393
Sousa PBF, Bieseki L, Pergher SBC. Seed-Assisted Crystallization in the Hydrothermal Synthesis of FAU Zeolite from Acid-Treated Residue Glass Powder. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071393
Chicago/Turabian StyleSousa, Paulla B. F., Lindiane Bieseki, and Sibele B. C. Pergher. 2025. "Seed-Assisted Crystallization in the Hydrothermal Synthesis of FAU Zeolite from Acid-Treated Residue Glass Powder" Materials 18, no. 7: 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071393
APA StyleSousa, P. B. F., Bieseki, L., & Pergher, S. B. C. (2025). Seed-Assisted Crystallization in the Hydrothermal Synthesis of FAU Zeolite from Acid-Treated Residue Glass Powder. Materials, 18(7), 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071393








