Friction and Wear of Tungsten Carbide Dies in the Dry Drawing of Steel Wire
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
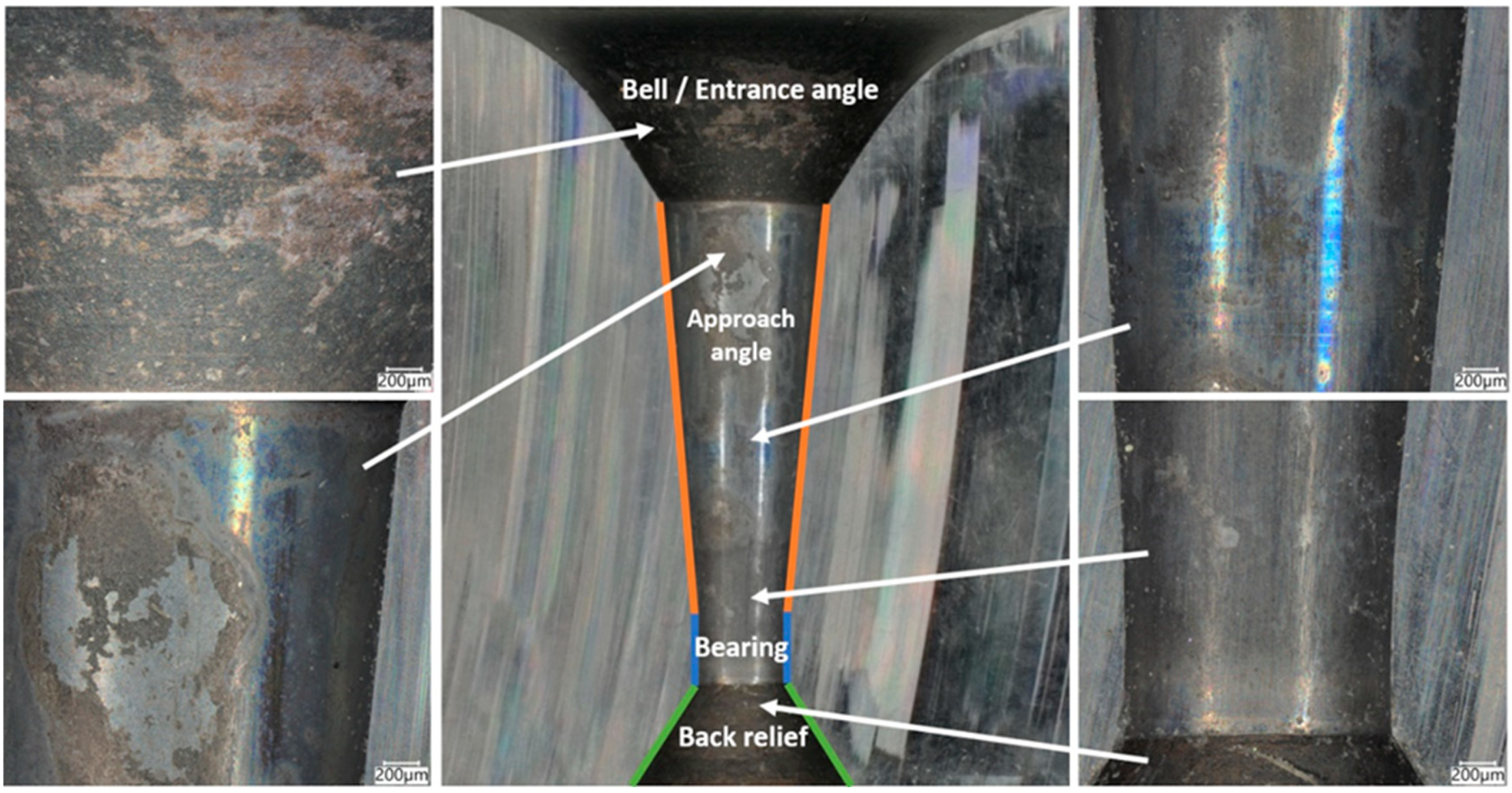
2.1. Conical Drawing Dies with a Cemented Carbide Insert
2.2. Numerical Modeling of Steel Wire Drawing
- -
- material: C45 steel.
- -
- wire drawing in a single sequence from a diameter of 5.5 mm to a diameter of 4.75 mm.
- -
- conical drawing dies with the angle of 2 = 10°.
- -
- drawing speed of 1 and 5 m/s.
- -
- friction coefficients: 0.01, 0.04, 0.07, and 0.1.
- -
- initial temperature: drawing die = 500 °C and wire = 50 °C.
- -
- thermal conductivity of C45 steel: temperature-dependent.
- -
- the dependence of the hardness of the cemented carbide on the temperature was taken from [36].
- -
- carbide density: 14,700 kg/m3·s
- -
- carbide thermal conductivity: 80 W/(m-K).
- -
- carbide heat capacity: 0.2 J/(g-K).
3. Results
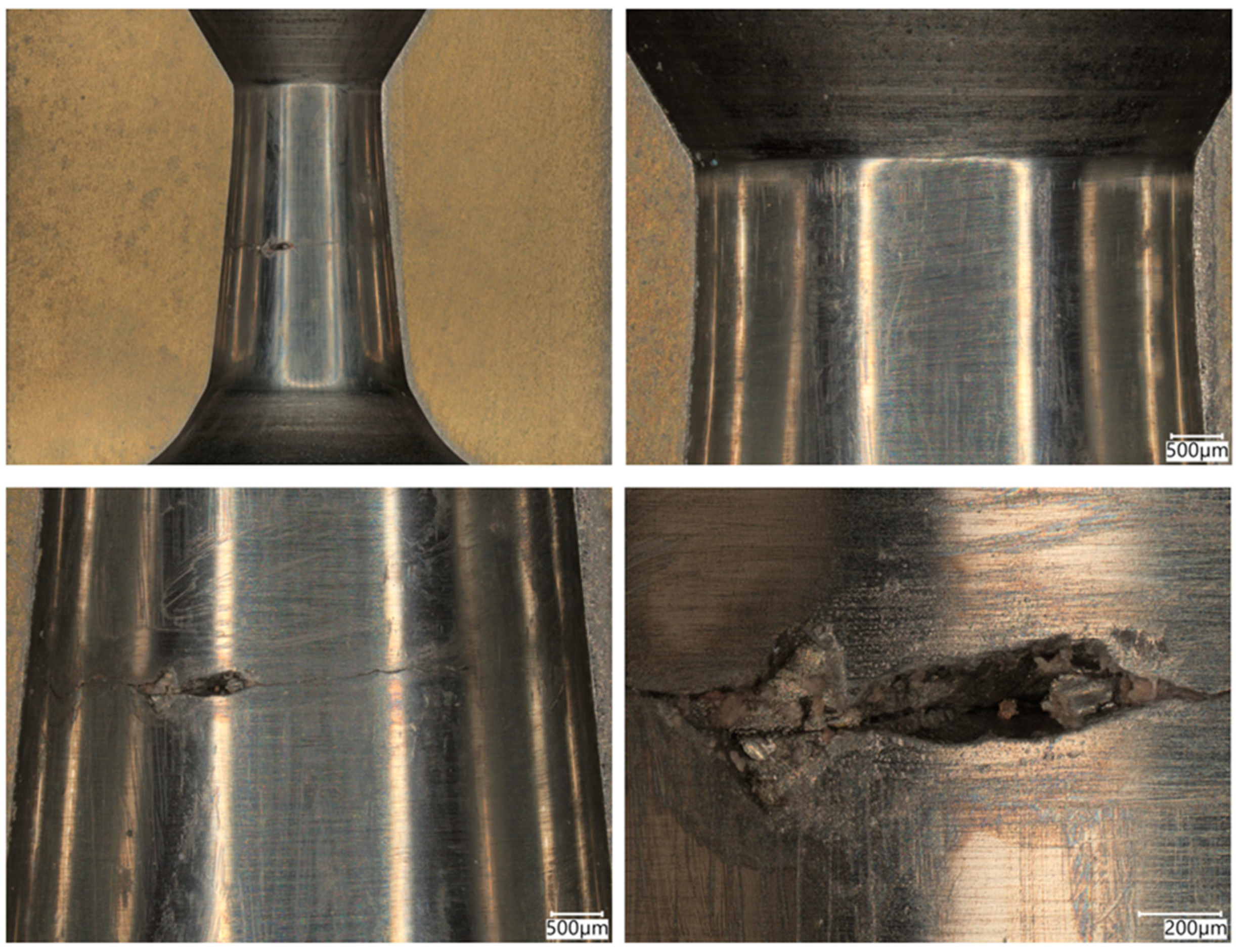
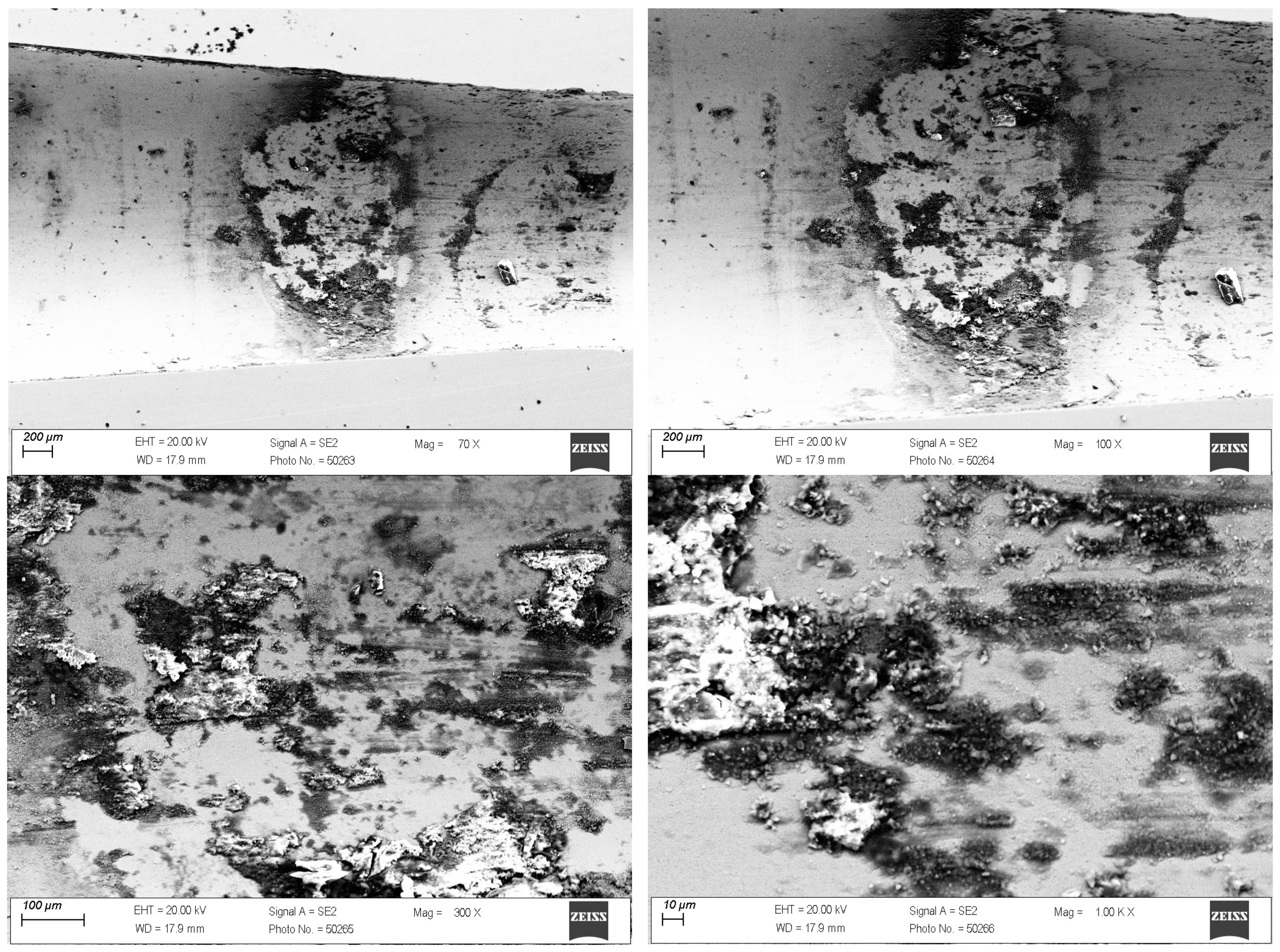
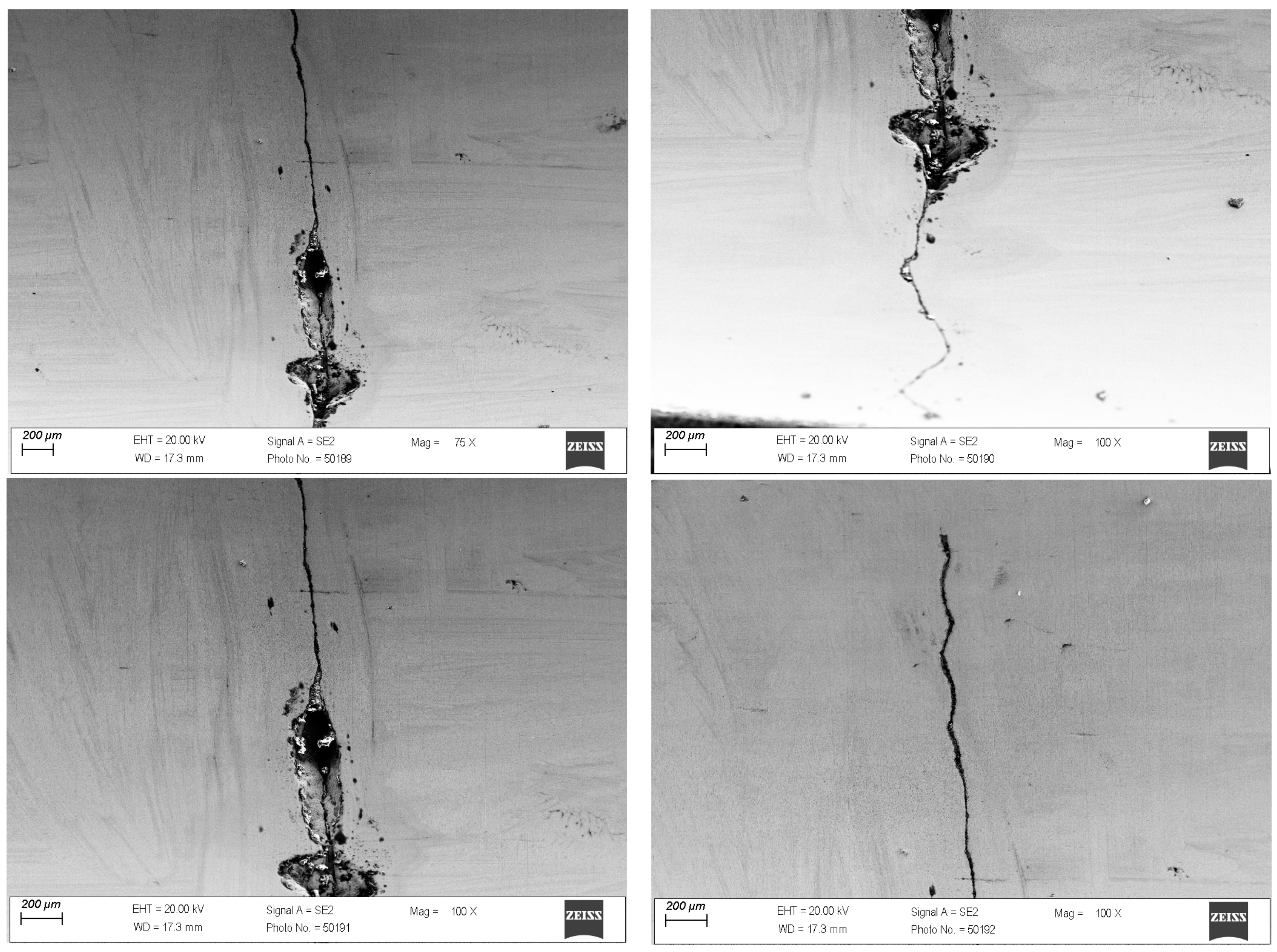
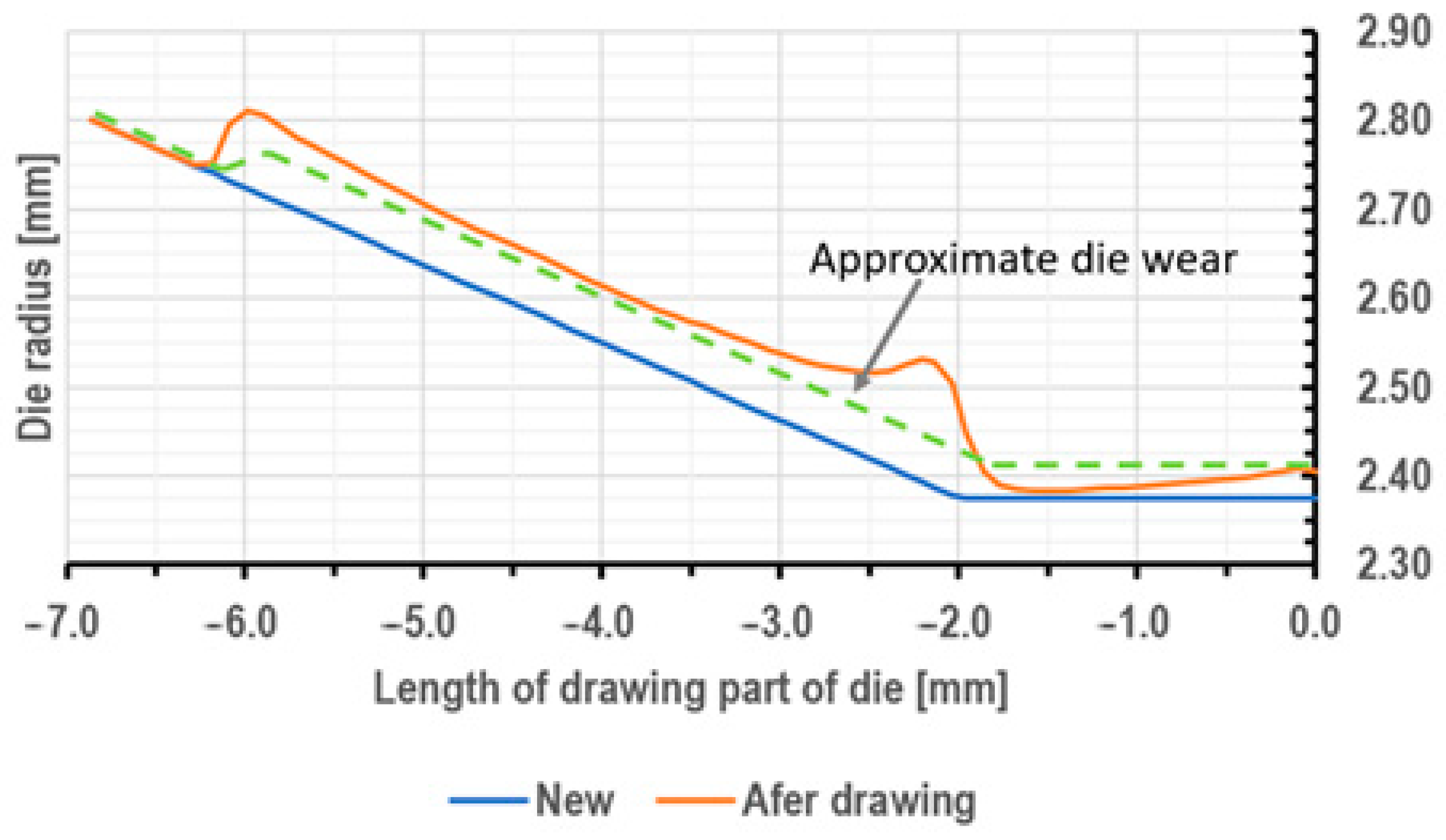
3.1. Tests of the Surface Layer of Drawing Dies
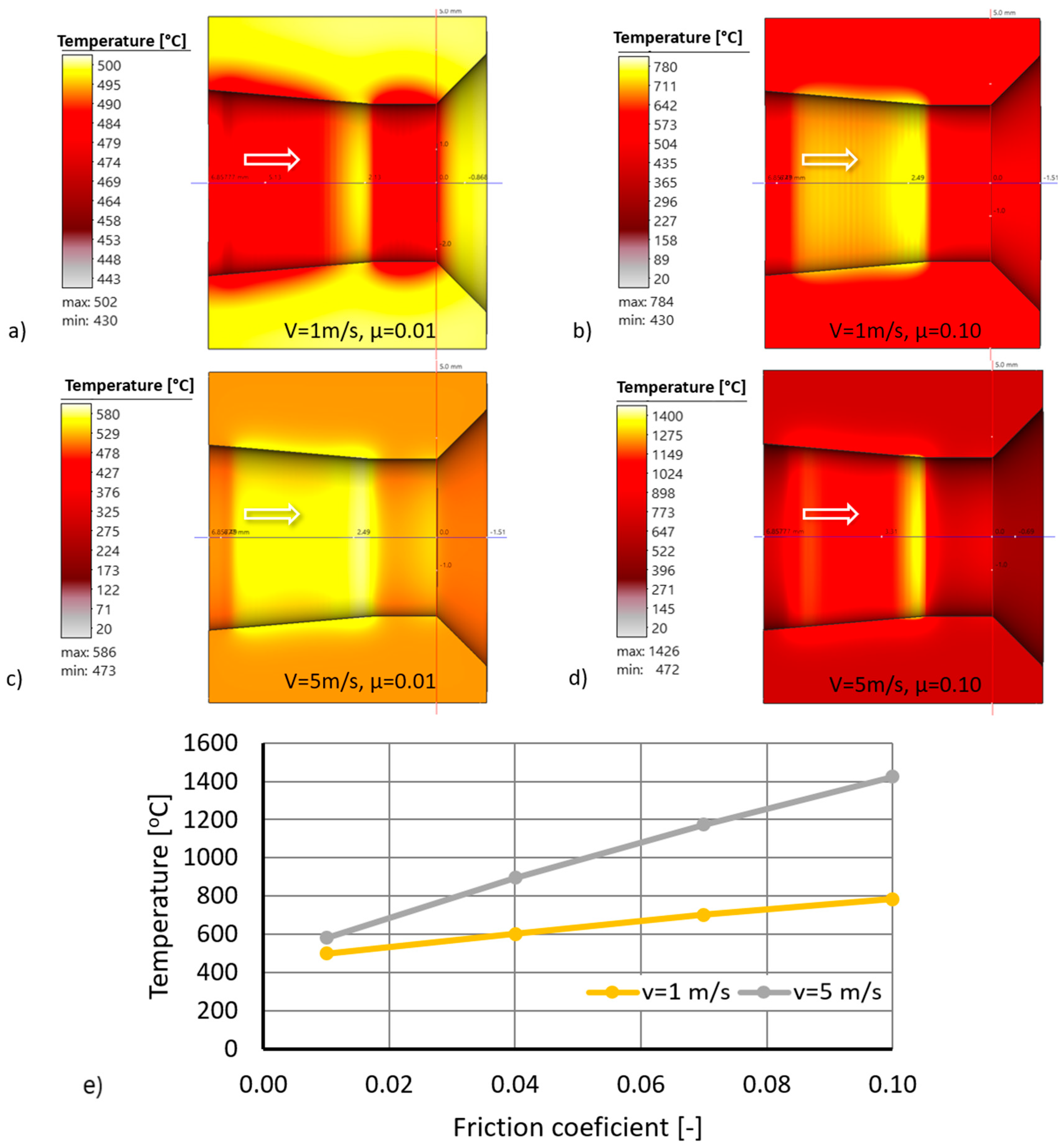
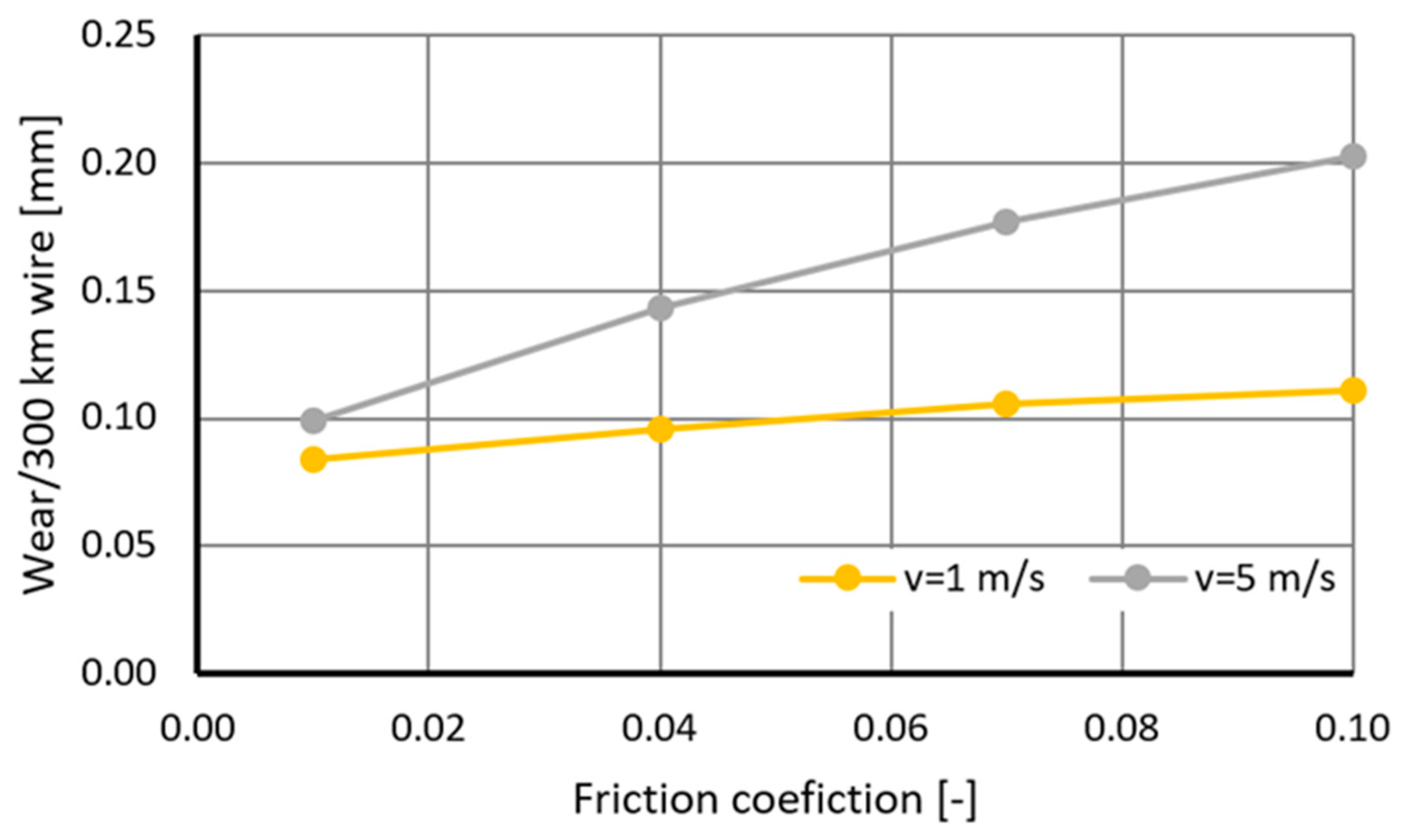
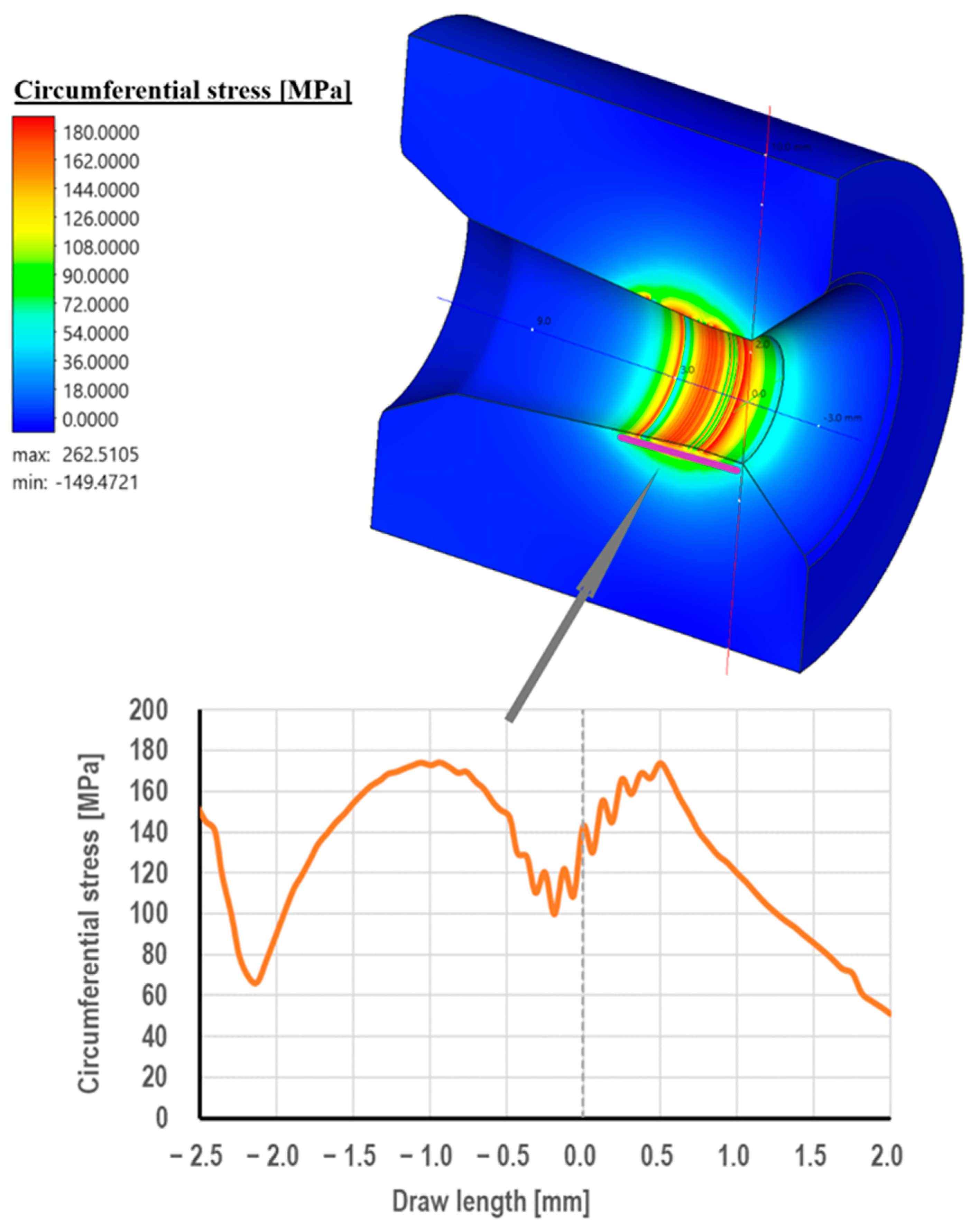
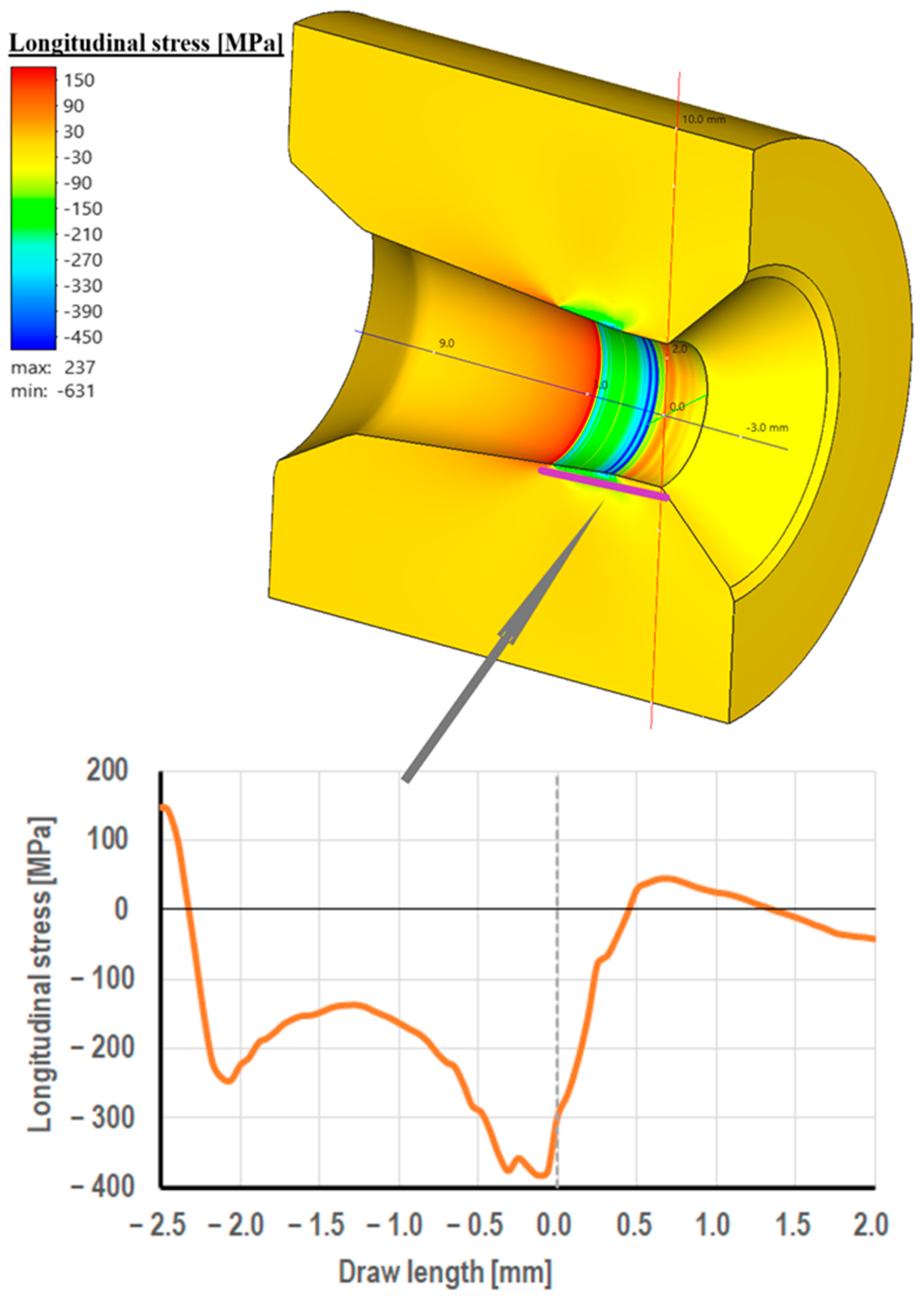
3.2. Computer Simulations of Wire Drawing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gierzyńska-Dolna, M.; Pilarczyk, J.W. Methods of testing and criteria for estimating lubricants used in drawing processes. Wire J. Int. 2001, 3, 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, R.N. Wire Technology: Process Engineering and Metallurgy; Butterworth–Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Golis, B.; Pilarczyk, J.W.; Hyja, H.; Blazejowski, Z. Steel Tire Cord Technology; Wire Association International: Madison, CT, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Enghag, P.; Larsson, R.; Pettersson, K. Investigation of force and friction in wire drawing. Wire Ind. 2001, 5, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, R.N. Physical conditions in the lubricant layer. Wire J. Int. 1997, 8, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Byon, S.M.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, Y. Effect of coating material and lubricant on forming force and surface defects in wire drawing process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (Engl. Ed.) 2011, 21, s104–s110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enghag, P. Steel Wire Technology; Materialteknik HB: Orebro, Swedan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, E.; Levrau, C. Analysis of the lubrication by a pseudoplastic fluid: Application to wire drawing. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliga, M.; Wartacz, R.; Hawryluk, M. The multi-stage drawing process of zinc-coated medium-carbon steel wires in conventional and hydrodynamic dies. Materials 2020, 13, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, A.S. Drawing with pressure system dies. In Proceedings of the WAI International Technical Conference Mexico, Cozumel, Mexico, 14–16 December 2004; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Pilarczyk, J.W.; Nitkiewicz, Z.; Kucharska, B.; Małecki, T. Analysis of Textures of Wires Drawn in Pressure and Roller Dies with ODF. Mater. Sci. Forum 2005, 495–497, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváček, M. A central film thickness formula for elastohydrodynamic lubrication of cylinders with soft incompressible coatings and a non-Newtonian piecewise power-law lubricant in steady rolling motion. Wear 1997, 205, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitkov, V. Hydrodynamic friction in dies. Wire Ind. 2007, 74, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, E.; Levrau, C.; Mantel, M.; Dinh, N.T. Identification of the work of plastic deformation and the friction shear stress in wire drawing. Wear 2012, 286–287, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-L.; Chu, H.-M.; Chen, M.-D. The partially wetted bearing—Extended Reynolds equation. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitkov, V. Research of wire drawing under conditions of hydrodynamic friction. Wire Cable Technol. Int. 2006, 3, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Theis, H.E. Handbook of Metalforming Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Avitzur, B. Application of hydrodynamic lubrication in wire drawing and extrusion. Wire J. 1976, 9, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Helmetag, K.; Carlone, R.; Kirsch, G. Thermal behavior in solid wiredrawing lubricants. Wire J. Int. 2006, 39, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Mezger, T. The Rheology Handbook; Vincentz Network: Hannover, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dolzhanskiy, A.M.; Druyan, V.M.; Golja, M. Technological lubricants research in wire drawing process. Metalurgija 2001, 40, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Damm, H. Dry drawing lubricants and borax. Wire J. Int. 2011, 10, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Suliga, M.; Muskalski, Z. The influence of single draft on trip effect and mechanical properties of 0.09C-1.57Mn-0.9Si steel wires. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2009, 54, 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- Pilarczyk, J.W.; Markowski, J.; Muskalski, Z.; Golis, B.; Pikos, B. Numerical analysis of drawing of steel wires in diffrent dies–concave, convex, sigmoidal and conical. In Proceedings of the Inc. Wire & Cable Technical Symposium 75th Annual Convention Atlanta. Conference Proceedings of The Wire Association International, Atlanta, GA, USA, May 2005; pp. 303–325. [Google Scholar]
- Eickemeyer, J.; Vogel, H.-R.; Reichert, J.; Rehm, M. Metal drawing by means of solid soap films. J. Mech. Work. Technol. 1996, 61, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliga, M.; Wartacz, R.; Michalczyk, J. High speed multi-stage drawing process of hot-dip galvanised steel wires. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 7639–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikos, B.; Pilarczyk, J.W.; Golis, B.; Włudzik, R.; Krac, J. Effect of drawing in sigmoidal, concave, convex and conical dies on mechanical properties of high carbon steel wires. In Proceedings of the International Wire &Cable Conference. e Proceedings of The Wire Association International, Bologna, Italy, 2007; pp. 216–227. [Google Scholar]
- Pikos, B.; Pilarczyk, J.W.; Knap, F.; Krnac, J. Design of convex, concave, and sigmoidal dies. In Global Technologies for Emerging Markets; Wire Association International Inc.: New Delhi, India, 2006; pp. 160–170. [Google Scholar]
- Pikos, B.; Pilarczyk, J.W.; Milenin, A.; Krnac, J. Longitudinal residua stress of high-carbon steel wires drawn in sigmoidal, convex, concave and conical dies. In Proceedings of the Wire&Cable Symposium. 77th Annual Convention, Cleveland, May. e Proceedings of the Wire Association International, Cleveland, OH, USA, 5–10 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wistreich, J.G. the fundamentals of wire drawing. Met. Rev. 1958, 3, 97–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas-Boca, I.M.; Tintelecan, M.; Pop, M.; Iluţiu-Varvara, D.-A.; Mihu, A.M. The Wire Drawing Process Simulation and the Optimization of Geometry Dies. Procedia Eng. 2017, 181, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillström, P.; Jarl, M. Wear of die after drawing of pickled or reverse bent wire rod. Wear 2007, 262, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, S.; Depraetere, E.; Giroux, O. Wear mechanism of tungsten carbide dies during wet drawing of steel tyre cords. Wear 2003, 255, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotyńska, I.; Kut, S. The influence of die shape and back tension force on its wear in the process of wire drawing. Arch. Met. Mater. 2019, 64, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliga, M.; Szota, P.; Gwoździk, M.; Kulasa, J.; Brudny, A. The Influence of Temperature in the Wire Drawing Process on the Wear of Drawing Dies. Materials 2024, 17, 4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A. Podstawy Nauki o Materiałach; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suliga, M.; Szota, P.; Kulasa, J.; Brudny, A.; Burdek, M. Friction and Wear of Tungsten Carbide Dies in the Dry Drawing of Steel Wire. Materials 2025, 18, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071409
Suliga M, Szota P, Kulasa J, Brudny A, Burdek M. Friction and Wear of Tungsten Carbide Dies in the Dry Drawing of Steel Wire. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071409
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuliga, Maciej, Piotr Szota, Joanna Kulasa, Anna Brudny, and Marek Burdek. 2025. "Friction and Wear of Tungsten Carbide Dies in the Dry Drawing of Steel Wire" Materials 18, no. 7: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071409
APA StyleSuliga, M., Szota, P., Kulasa, J., Brudny, A., & Burdek, M. (2025). Friction and Wear of Tungsten Carbide Dies in the Dry Drawing of Steel Wire. Materials, 18(7), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071409





