Stress-Induced Magnetic Anisotropy in Fe-Based Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Alloys: Mechanisms, Advances and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
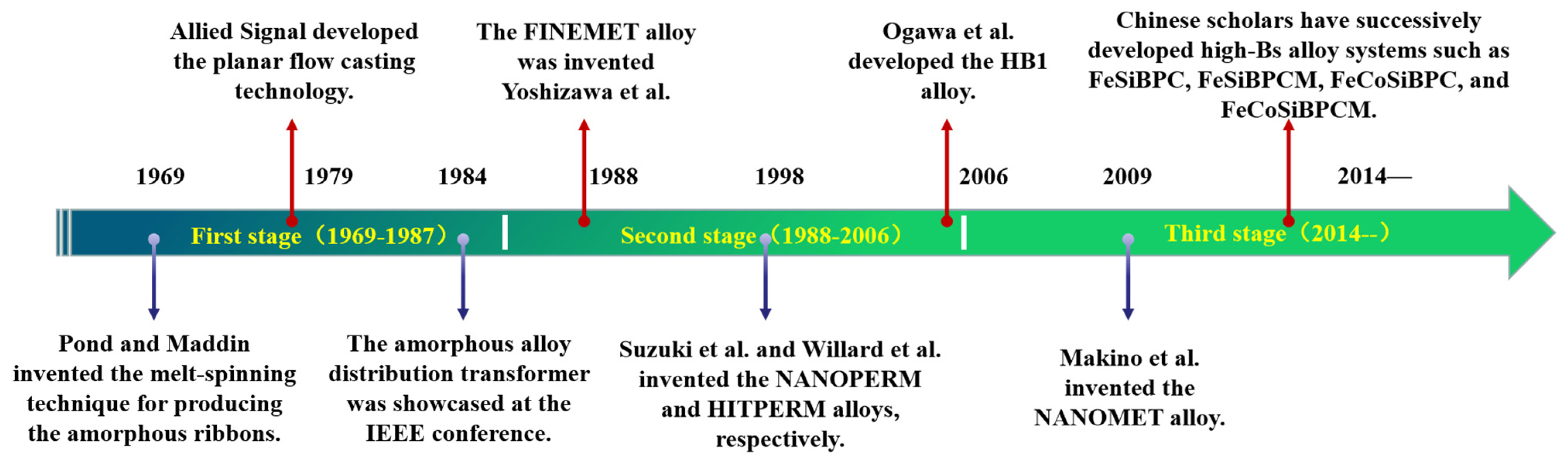
2. Development History of Fe-Based Soft Magnetic Alloys
2.1. Development and Application of Fe-Based Amorphous Soft Magnetic Alloys
2.2. Development and Application of Fe-Based Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Alloys

2.3. Development and Application of Fe-Based Soft Magnetic Alloys with High Bs
3. Annealing Methods for Inducing Magnetic Anisotropy
3.1. Conventional Stress Annealing
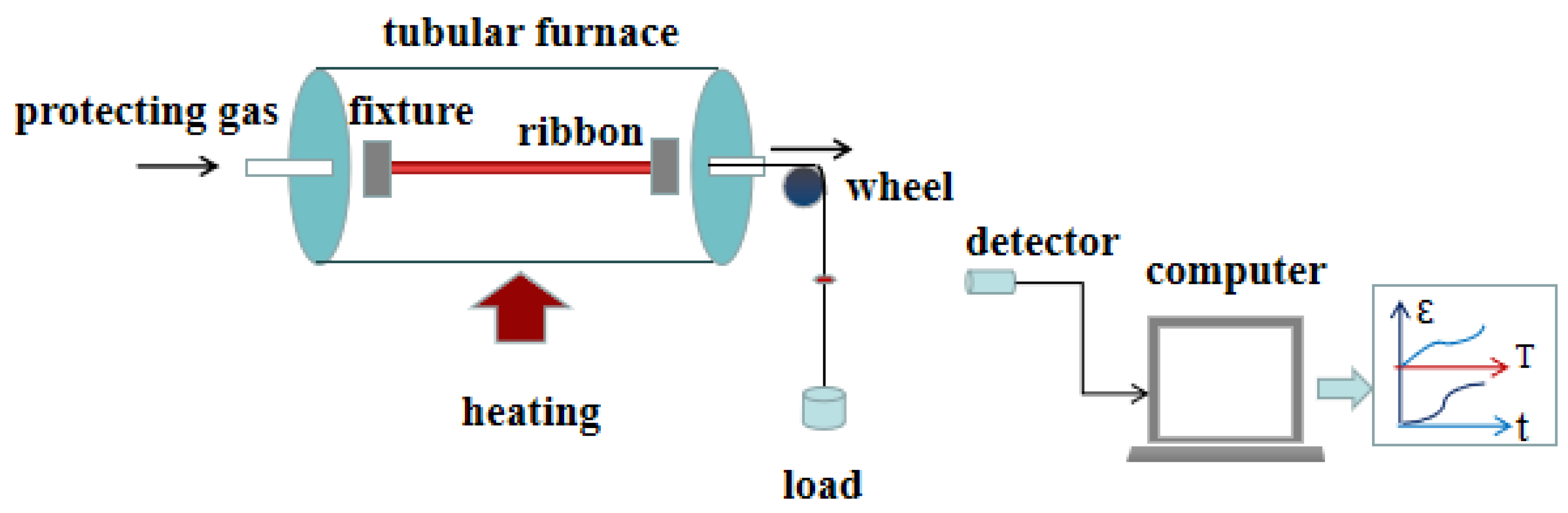
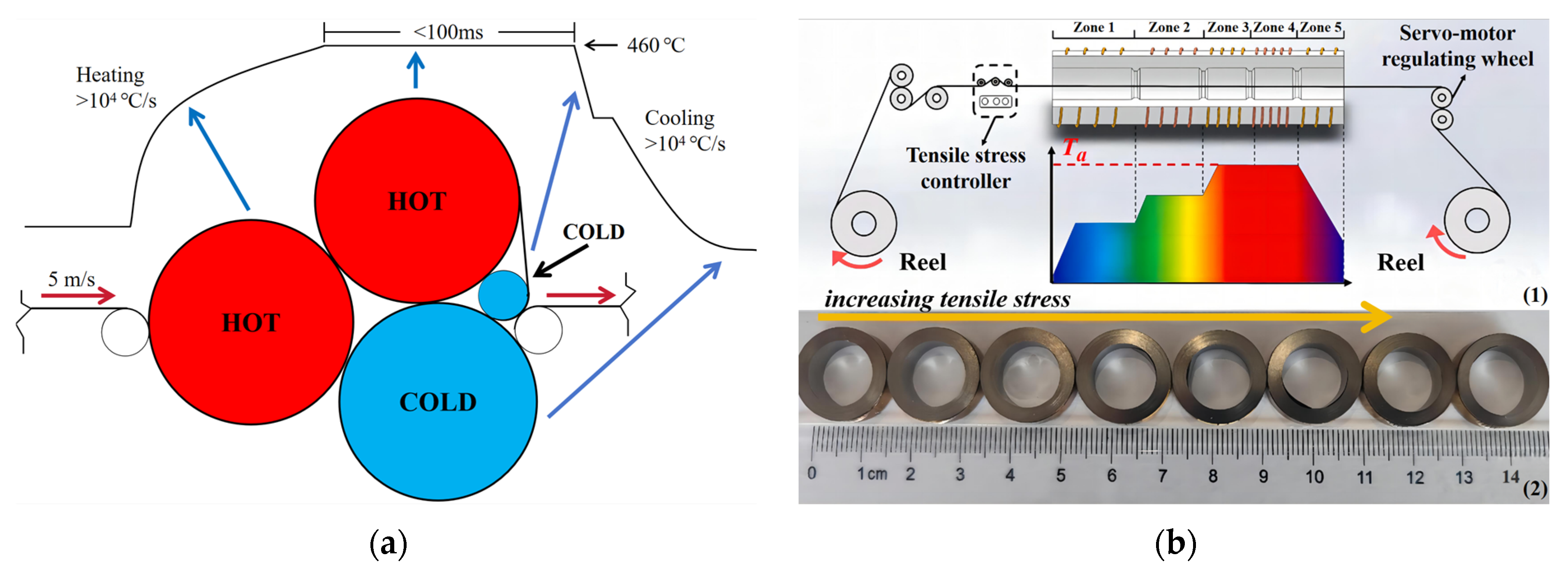
3.2. Rapid Stress Annealing
3.3. Stress Annealing Combined with Magnetic Field
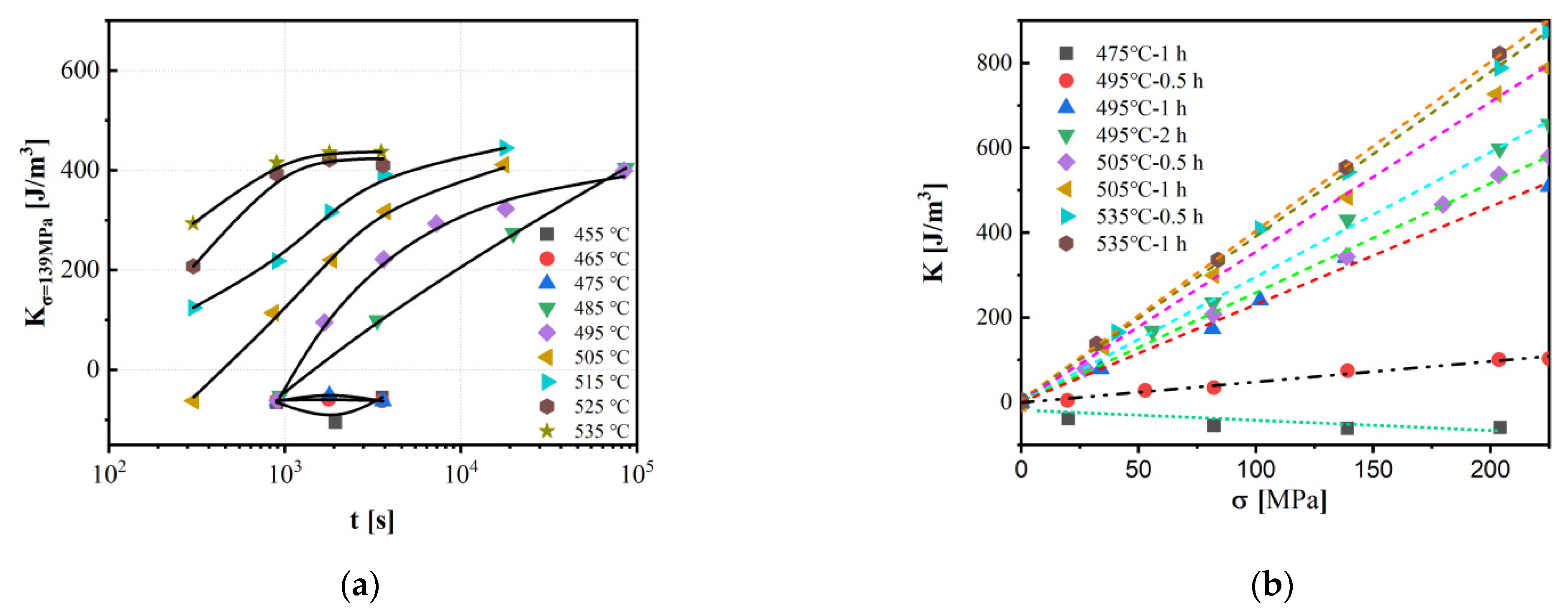
4. Influence of Annealing Parameters on Magnetic Anisotropy
5. Influence of Alloy Composition on Magnetic Anisotropy
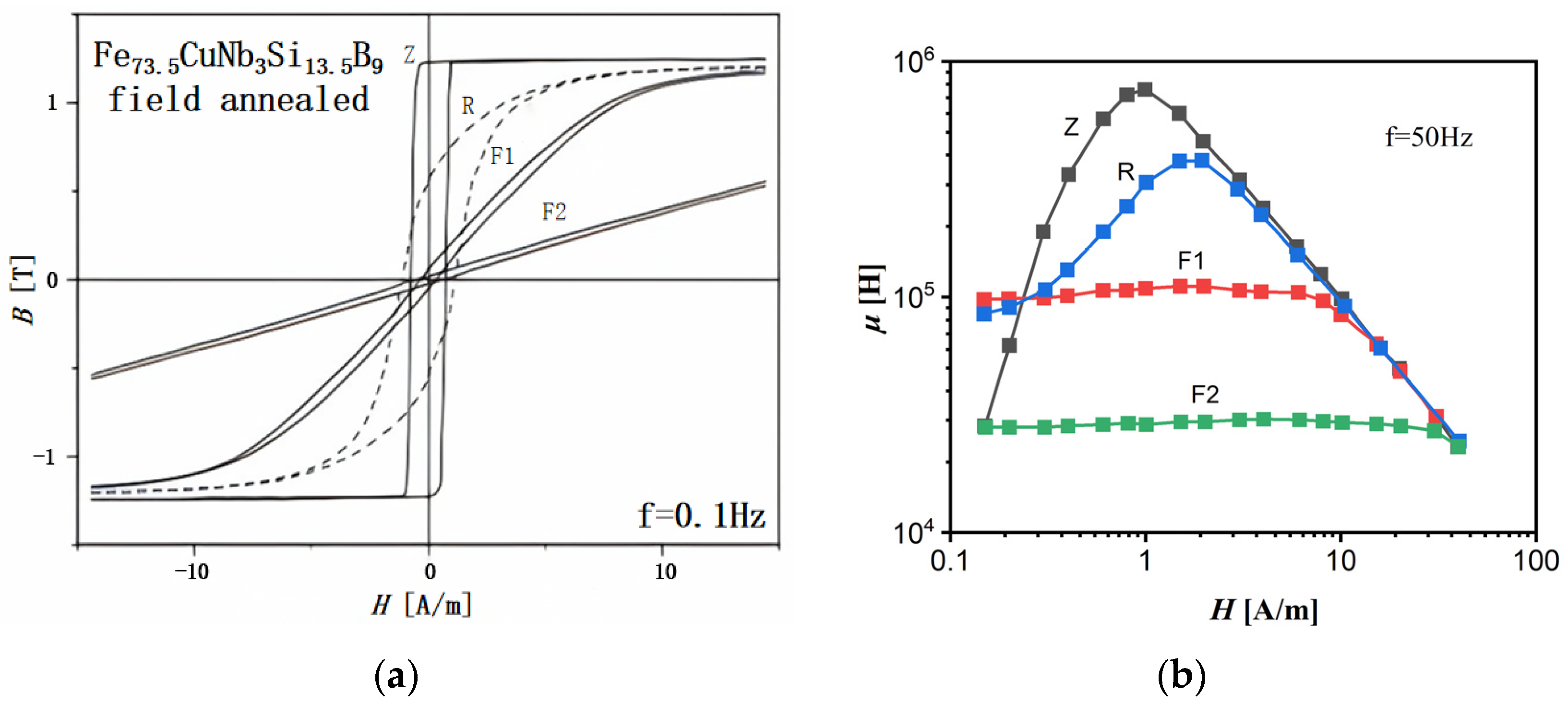
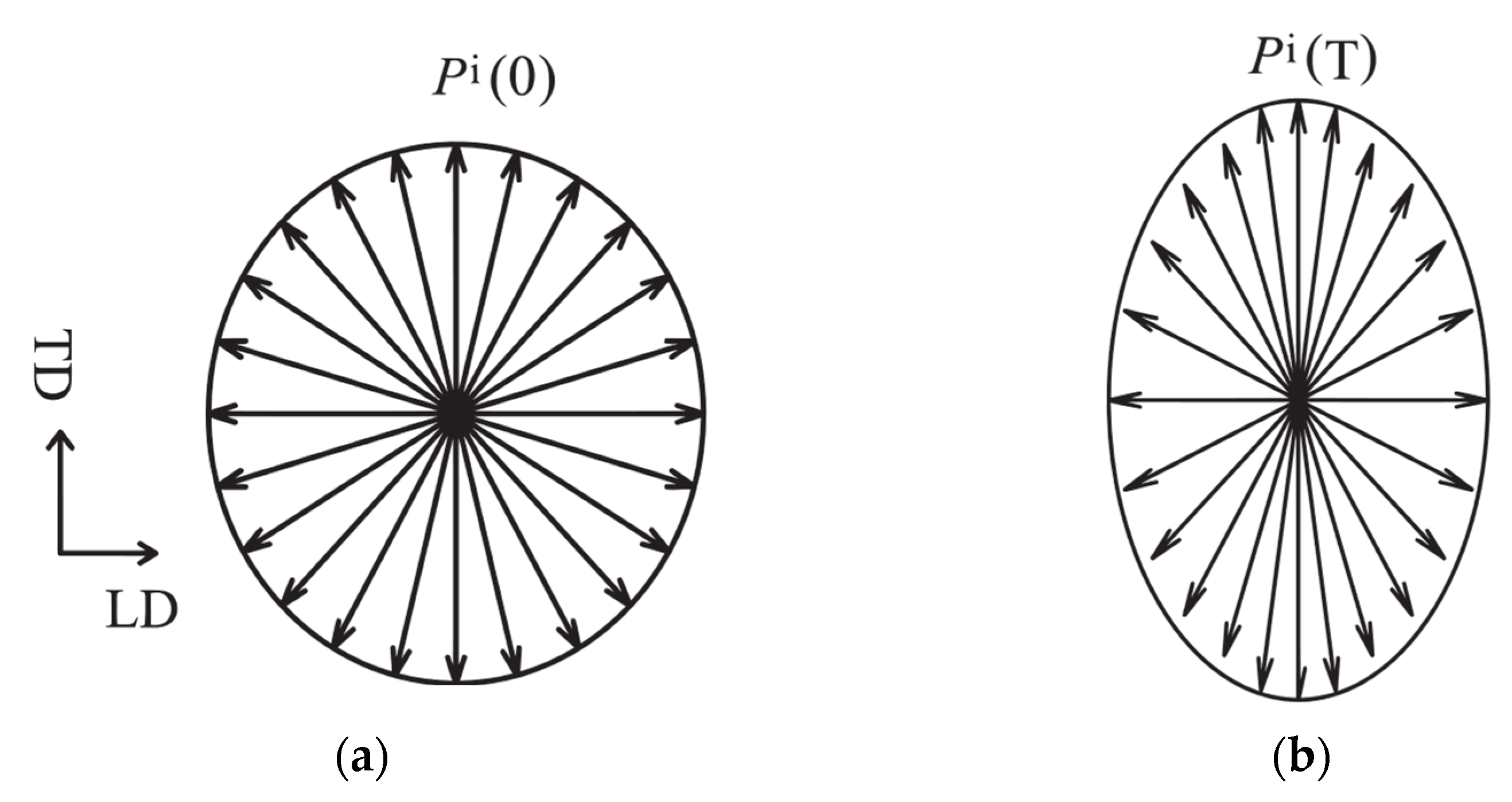
6. Physical Mechanisms of Stress-Induced Magnetic Anisotropy
6.1. Atomic Pair Ordering Model
6.2. Magneto-Elastic Coupling Model
6.3. Distribution Anisotropy Model
7. Summary and Perspectives
- (1)
- MA induction via SA (conventional, rapid, and hybrid magnetic-field-assisted methods) is highly sensitive to annealing parameters (temperature, time, stress magnitude, and heating/cooling rates). The precise control of these parameters enables tailored MA for optimized soft magnetic performance.
- (2)
- Alloy composition critically governs MA. Strategic doping (e.g., Co, Mn, Cr) modulates the magnetostriction coefficient and enhances MA. Optimal soft magnetism arises from balancing the α-Fe(Si) nanocrystalline phase and residual amorphous matrix, ensuring near-zero magnetostriction and minimized energy losses.
- (3)
- Three main models have been proposed to explain stress-induced MA: the atomic pair ordering model (limited in explaining the relationship between MA and Si concentration), the MEC model (which may not fully account for the irreversibility of MA), and the distribution anisotropy model (which requires further experimental validation). The distribution anisotropy model provides a new perspective by considering the preferential clustering of nanocrystals and the inelastic deformation of the amorphous matrix.
- (1)
- Clarifying unresolved debates, including the reversibility of stress-induced MA, the equivalence between internal stress and macroscopic annealing stress, and the correlation between MA and saturation magnetostriction coefficient, is essential to unravel the stress-sensitive mechanisms in Fe-based alloys.
- (2)
- Integrating theoretical modeling, computational simulations (e.g., molecular dynamics or phase-field methods), and experimental validation will bridge atomic-scale mechanisms to macroscopic magnetic properties.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPA | Lattice plane anisotropy |
| MA | Magnetic anisotropy |
| SA | Stress annealing |
| FA | Free annealing |
| MEC | Magneto-elastic coupling |
| MCA | Magneto-crystalline anisotropy |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| NA | Nanocrystalline |
| AM | Amorphous |
| MAE | Magnetic anisotropy energy |
| DOS | Density of states |
| SOC | Spin orbit coupling |
| Bs | Saturation induction |
| μe | Effective magnetic permeability |
| Hc | Coercivity |
| Tc | Crystalline temperature |
| D | Grain size |
| H | Magnetic field |
| K | Density of magnetic anisotropy energy |
| Tensile stress | |
| Ta | Annealing temperature |
| t | Annealing time |
| λs | Saturation magnetostriction coefficient |
| ϵ | Young’s modulus |
| Kn | Normalized magnetic anisotropy |
| Kd | Nanocrystal distribution induced magnetic anisotropy |
| Ke | Lattice plane induced magnetic anisotropy |
| dn | Normalized lattice plane anisotropy |
| Tn | Tempering frequency |
References
- Duwez, P.; Lin, S.C.H. Amorphous ferromagnetic phase in iron-carbon-phosphorus alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1967, 38, 4096–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, W.; Willens, R.H.; Duwez, P. Non-crystalline structure in solidified gold-silicon alloys. Nature 1960, 187, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, Y.; Oguma, S.; Yamauchi, K. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 6044–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Grain size dependence of coercivity and permeability in nanocrystalline ferromagnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1990, 26, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Alben, R.; Becker, J.J.; Chi, M.C. Random anisotropy in amorphous ferromagnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1978, 49, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Makino, A.; Kataoka, N.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. High saturation magnetization and soft magnetic properties of bcc Fe-Zr-B and Fe-Zr-B-M (M = Transition Metal) alloys with nanoscale grain size. Mater. Trans. JIM 1991, 32, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, M.A.; Laughlin, D.E.; McHenry, M.E.; Thoma, D.; Sickafus, K.; Cross, J.O.; Harris, V. Structure and magnetic properties of (Fe0.5Co0.5)88Zr7B4Cu1 nanocrystalline alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 6773–6777. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, A.; He, M.; Kubota, T.; Inoue, A. FeSiBPCu nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys with high Bs of 1.9 Tesla produced by crystallizing hetero-amorphous phase. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; He, M.; Kubota, T.; Inoue, A. New excellent soft magnetic FeSiBPCu nanocrystallized alloys with high of 1.9 T from nanohetero-amorphous phase. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4302–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.B.; Huan, H.H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.C.; Wang, J.H. Magnetic properties, anisotropy, and domain structure of Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy induced by continuous stress-annealing treatment. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 569, 170430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kang, S.J.; Zhu, Q.K.; Zhang, K.W.; Hu, J.F.; Jiang, Y. Tailoring the thermal stability and soft magnetic properties of Fe80−xNixSi7B8P4Cu1 amorphous nanocrystalline alloys based on the magnetic domain structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, N.M.; Adoo, N.A.; Meakins, E.; Keylin, V.; Feichter, G.E.; Noebe, R.D. The effect of stress-annealing on the mechanical and magnetic properties of several Fe-based metal-amorphous nano-composite soft magnetic alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 600, 122037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Wang, M.G.; Zhao, Z.K. Recent advances and future developments in Fe-based amorphous soft magnetic composites. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 616, 122440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, M.; Hono, K.; Yanai, T.; Fukunaga, H.; Yoshizawa, Y. Direct evidence for structural origin of stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in Fe-Si-B-Nb-Cu nanocrystalline alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2859–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutor, R.K.; Xu, X.J.; Fan, X.Z.; He, X.W.; Fang, Y.Z. Transverse anisotropy field and lattice plane anisotropy of stress annealed Fe-Cu-Nb-Si-B ribboon. Chin. J. Phys. 2018, 56, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutor, R.K.; Xu, X.J.; Fan, X.Z.; He, X.W.; Lu, X.A.; Fang, Y.Z. Effects of applying tensile stress during annealing on the GMI and induced anisotropy of Fe-Cu-Nb-Si-B alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 471, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutor, R.K.; Fan, X.Z.; He, X.W.; Xu, X.J.; Lu, X.A.; Jiang, J.Z.; Fang, Y.Z. Formation mechanism of stress-induced anisotropy in stress-annealed Fe-based nanocrystalline ribbon alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 774, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.F.; Shi, L.X.; Chen, S.Q.; Shao, Y.; Chen, N.; Jia, J.L. Research progress and application prospect of Fe-based soft magnetic amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pond, R.; Maddin, R. A method of producing rapidly solidified filamentary castings. Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 1969, 245, 2457–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, M.C. Continuous Casting Method for Metallic Strips. U.S. Patent AU2904877A, 29 March 1979. [Google Scholar]
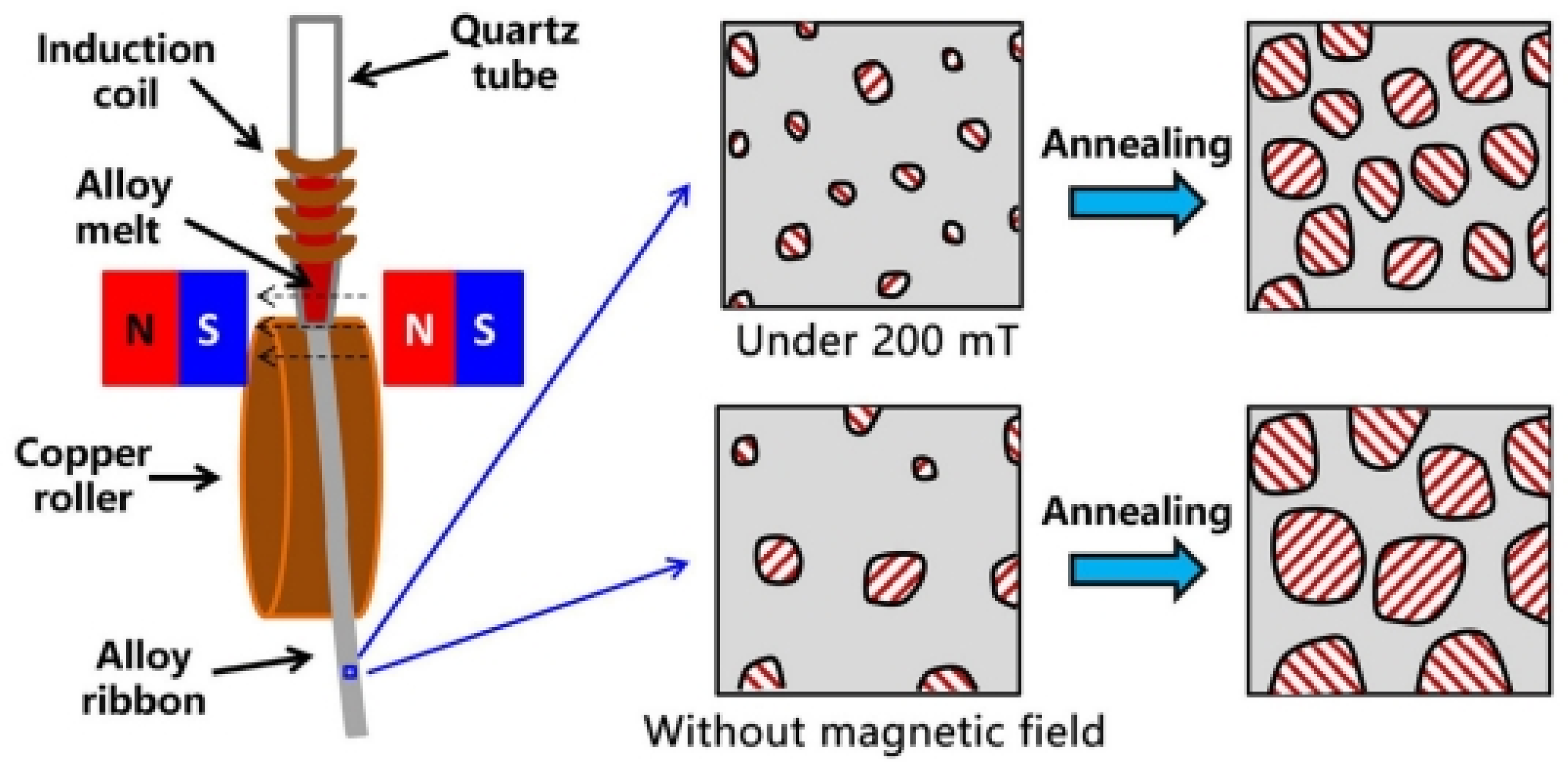
- Jia, X.J.; Dong, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.Q.; He, A.N.; Li, J.W. Influence of static magnetic field on rapid solidifiedstructure and nanocrystallization behavior of Fe-Si-B-Cu soft magnetic alloys with pre-existinga-Fe nanocrystals. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 9594–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Makino, A.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Soft magnetic properties of nanocrystalline bcc Fe-Zr-B and Fe-M-B-Cu (M= transition metal) alloys with high saturation magnetization. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 70, 6232–6237. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, Y.; Naoe, M.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Hasegawa, R. Magnetic properties of high Bs Fe-based amorphous material. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, 675–677. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, A.; Kubota, T.; Chang, C.; Makabe, M.; Inoue, A. FeSiBP bulk metallicglasses with unusual combination of high magnetization and high glassforming ability. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 3024–3027. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shuang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A.D.; Wang, J.G.; Yang, Y. Amorphouse-nanocrystalline alloys: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Mater. Today Adv. 2019, 4, 100027. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.D.; Men, H.; Ma, A.B.; Shen, B.L. Soft magnetic properties in Fe84−xB10C6Cux nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 326, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.D.; Zhao, C.L.; He, A.N.; Chang, C.T.; Wang, X.M. Composition design of high Bs Fe-based amorphous alloys with good amorphous-forming ability. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 656, 729–734. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, A.D.; Liu, T.; Chen, P.B.; He, A.N.; Li, Q.; Luan, J.; Liu, C.T. Design of Fe-based nanocrystalline alloys with superior magnetization and manufacturability. Mater. Today 2021, 42, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.Y.; Zang, B.W.; Song, L.J.; Huo, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.Q. Ultra-fine microstructure and exceptional low coercivity developed in a high-Bs Fe-Si-B-P alloy by co-alloying Ni, Mo, and Cu. Scr. Mater. 2023, 236, 115666. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Jia, X.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, G.Q.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Luan, J.H.; Jiao, Z.B. Formation and crystallization behavior of Fe-based amorphous precursors with pre-existing ɑ-Fe nanoparticles structure and magnetic properties of high-Cu-content Fe-Si-B-Cu-Nb nanocrystalline alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 65, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Hono, K. Atom probe microanalysis and nanoscale microstruc- tures in metallic materials. Acta. Mater. 1999, 47, 3127–3145. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, L.; Závěta, K.; Heczko, O.; Duhaj, P.; Vlasák, G.; Schneider, J. Magnetic anisotropy in as-quenched and stress- annealed amorphous and nanocrystalline Fe73.5CulNb3Si13.5B9 alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1992, 112, 275–277. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, M.H.; Peng, H.X. Giant magnetoimpedance materials: Fundamentals and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 323–420. [Google Scholar]
- Chernenkov, Y.P.; Ershov, N.V.; Fedorov, V.I.; Lukshina, V.A.; Potapov, A.P. X-ray diffraction studies of the structure of nanocrystalsin Fe73.5CulNb3Si13.5B9 soft magnetic alloys before and after thermomechanical treatment. Phys. Solid State 2010, 52, 554–560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhukova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Talaat, A.; Blanco, J.M.; Churyukanova, M.; Zhukov, A. Effect of stress annealing on magnetic properties and GMI effect of Co- and Fe-rich microwires. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 707, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Corte-Leon, P.; Zhukova, V.; Blanco, J.M.; González-Legarreta, L.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukov, A. Stress-induced magnetic anisotropy enabling engineering of magnetic softness of Fe-rich amorphous microwires. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 510, 166939. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Qin, Y.J.; Fang, Z.; Fan, X.Z.; Yang, H.Y.; Kuang, F.L.; Zhai, Y.; Miao, Y.L.; Zhao, Z.X.; He, J.J.; et al. Mechanism of stress induced irreversible magnetic anisotropy in Fe-based alloy ribbons. Acta Phys. Sin. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, F.; Desmoulins, J.B.; Hérisson, D.; Rialland, J.F.; Costa, F. Stress-induced anisotropy in Finemet-and Nanoperm-type nanocrystalline alloys using flash annealing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 215–216, 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, F.; Abi, R.L.; Moutoussamy, J.; Coillot, C. Trilayer GMI sensors based on fast stress-annealing of FeSiBCuNb ribbons. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2008, 142, 459–463. [Google Scholar]
- Herzer, G.; Budinsky, V.; Polak, C. Magnetic properties of FeCuNbSiB nanocrystallized by flash annealing under high tensile stress. Phys. Status Solidi B 2011, 248, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar]
- Kernion, S.J.; Paul, R.; Ohodnicki, J.; Grossmann, J.; Leary, A.; Shen, S.; Keylin, V.; Huth, J.F.; Horwath, J.; Lucas, M.S.; et al. Giant induced magnetic anisotropy in strain annealed Co-based nanocomposite alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 102408. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, R.; Takahashi, K.; Francoeur, B.; Couture, P. Magnetization kinetics in tension and field annealed Fe-based amorphous alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17A312. [Google Scholar]
- Günes, T. Novel method for construction of high performance nano-crystalline FeCuNbSiB toroidal core. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 804, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, A.; Pradeep, K.G.; Herzer, G.; Raabe, D.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.E. Magnetic microstructure in a stress-annealed Fe73.5Si15.5B7Nb3Cu1 soft magnetic alloy observed using off-axis electron holography and Lorentz microscopy. API Adv. 2016, 6, 056501. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Zhang, J.C.; Demidenko, O.; Sun, H.B.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.H. Influence of stress-induced anisotropy on domain structure and magneticproperties of Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy under continuous tension annealing. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 600, 122035. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Parsons, R.; Zang, B.; Onodera, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Shoji, T.; Kato, A. Nano-crystallization of amorphous alloys by ultra-rapid annealing: An effective approach to magnetic softening. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 613–618. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.J.; Gao, M.; Xu, W.; Huo, J.T.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, R.W.; Wang, W.H.; Perepezko, J.H. Inheritance from glass to liquid: β relaxation depresses the nucleation of crystals. Acta Mater. 2020, 185, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Makino, A. Competition driven nanocrystallization in high Bs and low coreloss Fe–Si–B–P–Cu soft magnetic alloys. Scr. Mater. 2015, 95, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, B.; Parsons, R.; Onodera, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Kato, A.; Liu, A.C.Y.; Suzuki, K. Effect of heating rate during primary crystallization on soft magnetic properties of melt-spun Fe-B alloys. Scr. Mater. 2017, 132, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, R.; Zang, B.; Onodera, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Shoji, T.; Kato, A.; Liu, A.C.Y.; Suzuki, K. Nano-crystallisation and magneticsoftening in F-B binary alloys induced by ultra-rapid heating. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 415001. [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur, B.; Couture, P. Continuous-annealing method for producing a flexible, curved, soft magnetic amorphous alloy ribbon. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Zhukov, A.P.; González, J. Stress and/or Field Induced Magnetic Anisotropy in the Amorphous Fe73.5Si15.5B7Nb3Cu1 Alloy: Influence on the Coercivity, Saturation Magnetostriction and Magneto-Impedance Response. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2015, 194, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Zhukov, A.P.; Val, J.J.D.; Arellano, A.R.D.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of stress and/or field annealing on the magnetic behavior of the (Co77Si13.5B9.5)90Fe7Nb3 amorphous alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 034911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, M.; Herzer, G.; Kozikowski, P.; Polak, C.; Budinsky, V.; Koppoju, S. Structural anisotropy of amorphous alloys with creep-induced magnetic anisotropy. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, M.; Hono, K.; Yanai, T.; Nakano, M.; Fukunaga, H.; Yoshizawa, Y. Origin of the magnetic anisotropy induced by stress annealing in Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 152513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shuai, S.; Lu, S.; Xiang, Z.; Xu, H.; Lu, W. Impact of stress and magnetic field in annealing process on gmi and gsi effect of CoFeSiB amorphous material. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 588, 171466. [Google Scholar]
- Herzer, G. Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 157/158, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Herzer, G.; Marsilius, M.; Polak, C. Temperature Dependence of Creep Induced Anisotropy in Nanocrystalline Fe-Cu-Nb-Si-B Alloys. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2013, 62, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, B.; Kronmüller, H. Stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in nano-crystalline FeCuNbSiB alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 152, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Modern soft magnets: Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 718–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idzikowski, B.; Svec, P.; Miglierini, M. Properties and Applications of Nanocrystalline Alloys from Amorphous Precursors. In Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Properties and Applications of Nanocrystalline Alloys from Amorphous Precursors, Budmerice, Slovakia, 9–15 June 2003; pp. 389–392. [Google Scholar]
- Herzer, G. Creep induced magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline Fe-Cu-Nb-Si-B alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1994, 30, 4800–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.F.; Tang, P.H.; Chen, H.A.; Lan, S.; Wang, J.G.; Luan, J.H.; Du, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.T.; Pao, C.W.; et al. Understanding chemical short-range ordering/demixing coupled with lattice distortion in solidsolution high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2021, 216, 117140. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Jiang, S.S.; Ye, L.X.; Zhu, C.; Gao, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.G. Nanoscale structural heterogeneity perspective on the ameliorated magnetic properties of a Fe-based amorphous alloy with decreasing cooling rate. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 2022, 581, 121433. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhu, F.; Yuan, Y.K.; Chang, D.J.; Kim, D.S.; Pham, M.; Rana, A.; Tian, X.Z.; Ya, Y.G.; et al. Determining the three-dimensional atomic structure of an amorphous solid. Nature 2021, 592, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohnuma, M.; Yanai, T.; Hono, K.; Nakano, M.; Fukunaga, H.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Herzer, G. Stress-induced magnetic and structural anisotropy of nanocrystalline Fe-based alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 093927. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, L.K.; Gercsi, Z.; Kovács, G.; Kákay, A.; Mazaleyrat, F. Stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 254–255, 477–479. [Google Scholar]
- Herzer, G.; Flohrer, S.; Polak, C. Effect of Stress Annealing on the Saturation Magnetostriction of Nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si9B13.5. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukshina, V.A.; Dmitrieva, N.V.; Cerdeira, M.A.; Potapov, A.P. Stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy withaddition of 1–5 at.% Cr. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 536, 374–376. [Google Scholar]
- Leary, A.M.; Keylin, V.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; McHenry, M.E. Stress induced anisotropy in CoFeMn soft magnetic nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 17A338. [Google Scholar]
- Lukshina, V.A.; Serikov, V.V.; Kleinerman, N.M.; Dmitrieva, N.V.; Volkova, E.G.; Potapov, A.P. Induced magnetic anisotropy and structure of Fe-based nanocrystalline material with different Si and Co content. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 316, e816–e819. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.; Grahl, H.; Mattem, N.; Kuhn, U.; Schnell, B. The influence of Co on the structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline FeSiBCuNb and FeZrBCu-based alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 160, 284–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Lukshina, V.A.; Larrañaga, A.; Orue, I.; Zaharova, A.A.; Shishkin, D.A. Induced magnetic anisotropy features in FeCrSiBNbCu nanocrystalline alloy: Role of stress distribution proven by direct X-ray measurements. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 566, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, B.; Kronmiiller, H. Creep induced magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9. Nano-Struc. Mater. 1995, 6, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.Z.; Zheng, J.J.; Wu, F.M.; Xu, Q.M.; Zhang, J.Q.; Ye, H.Q.; Zheng, J.L.; Li, T.Y. Mesostructural origin of stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in Fe-based nanocrystalline ribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 092508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, L. Anisotropie magnétique superficielle et surstructures d’ orientation. J. Phys. 1954, 4, 225–378. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Chen, H.R.; Shi, Q.; He, J.Y.; Nie, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.F.; Tian, M.Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. Interdiffusion mechanism of hybrid interfacial layers for enhanced electrical resistivity and ultralow loss in Fe-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 670, 160662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.T.; Liu, Y.; Yin, T.F.; Li, D.H.; Sun, Z.W.; Xue, C.X.; Yip, W.S.; To, S. Magnetic and ultrasonic vibration dual-field assisted ultra-precision diamond cutting of high-entropy alloys. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2024, 202, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, D.; Marsilius, M.; Bednarcik, J. Structural aspects of stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 171011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Su, F.C.; Zhou, J.; Mao, Y.C.; Yang, J.M.; Xue, Z.Y.; Ke, H.B.; Sun, B.A.; Wang, W.H.; Bai, H.Y. Ductile Fe-based amorphous alloy with excellent soft magnetic properties induced by low-temperature stress annealing. Intermetallics 2024, 166, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematov, M.G.; Baraban, I.; Yudanov, N.A.; Rodionova, V.; Qin, F.X.; Peng, H.X.; Panina, L.V. Evolution of the magnetic anisotropy and magnetostriction in Co-based amorphous alloys microwires due to current annealing and stress-sensory applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 837, 155584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G.; Budinsky, V.; Polak, C. Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline FeCuNbSiB with huge creep induced anisotropy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 266, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csizmadia, E.; Varga, L.K.; Palánki, Z.; Zámborszky, F. Creep or tensile stress induced anisotropy in FINEMET-type ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.J.; Fan, X.Z.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, J.G.; Ye, H.Q.; Zheng, J.J.; Fang, Y.Z. Unraveling the origin of stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in Fe-based nanocrystalline alloys using in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction and first-principles calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1013, 178612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
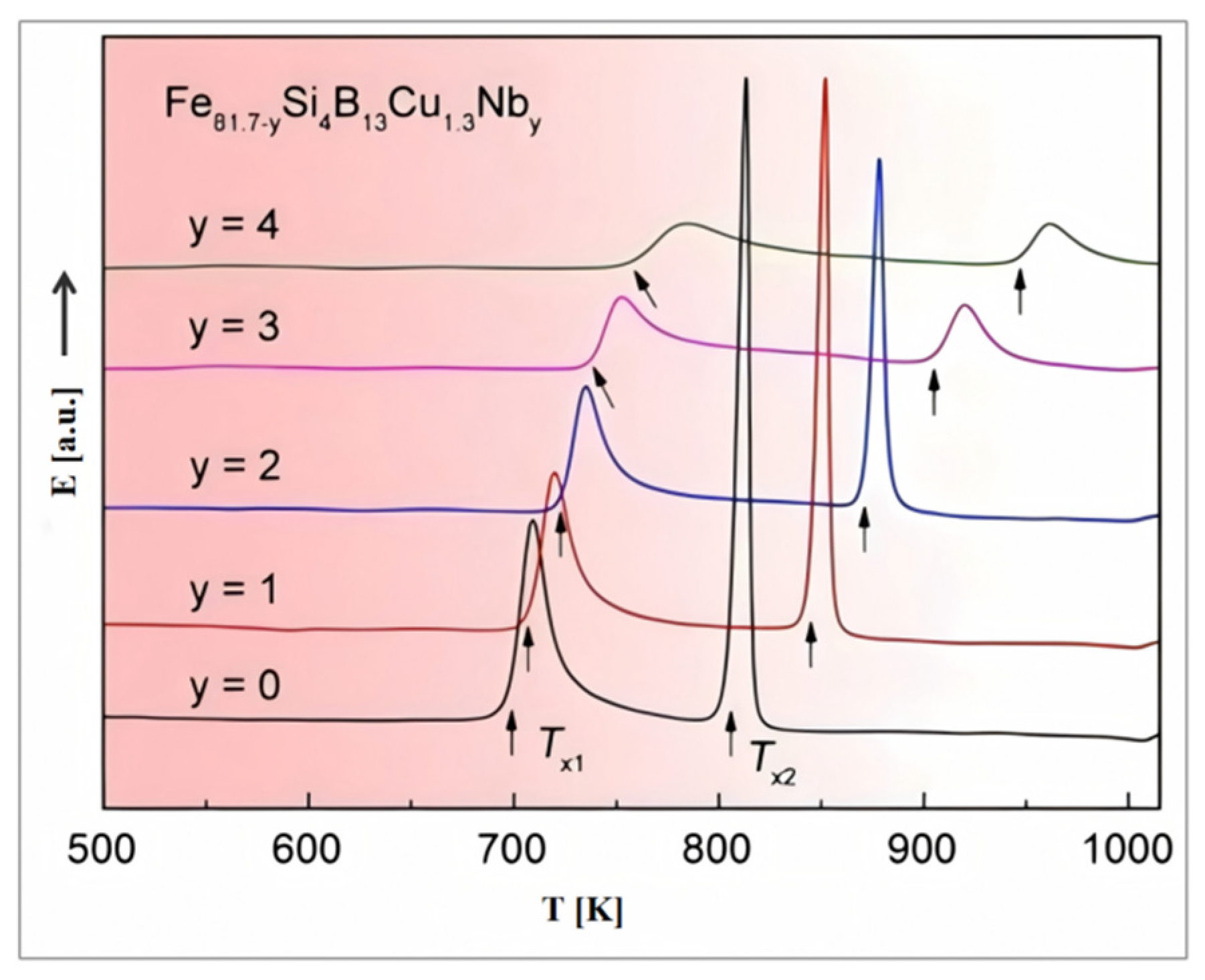
- Xu, X.J.; Fang, Z.; Lu, X.A.; Ye, H.Q.; Fan, X.Z.; Zheng, J.J.; He, X.W.; Guo, C.Y.; Li, W.Z.; Fang, Y.Z. The characteristics of multiple isothermal tempered Fe-based alloy ribbons. Acta Phys. Sin. 2019, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


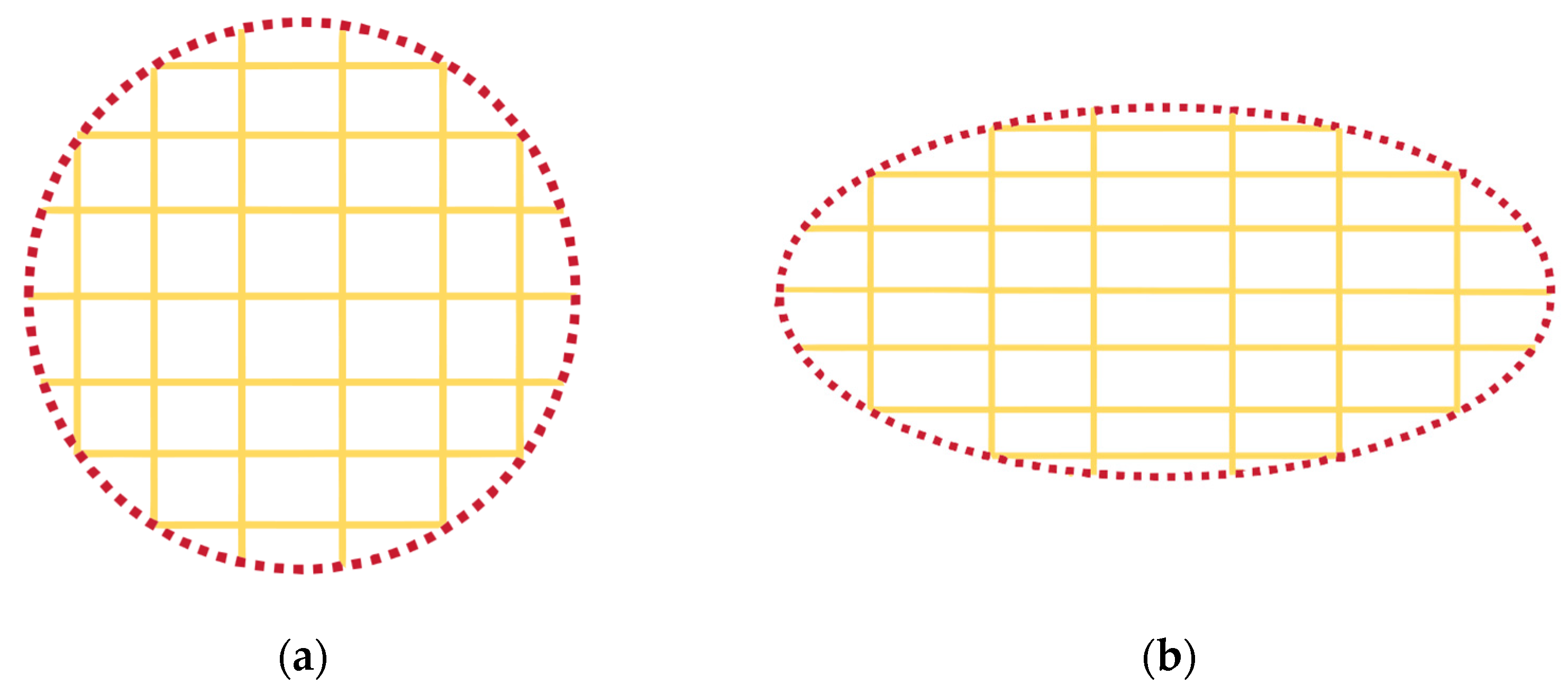
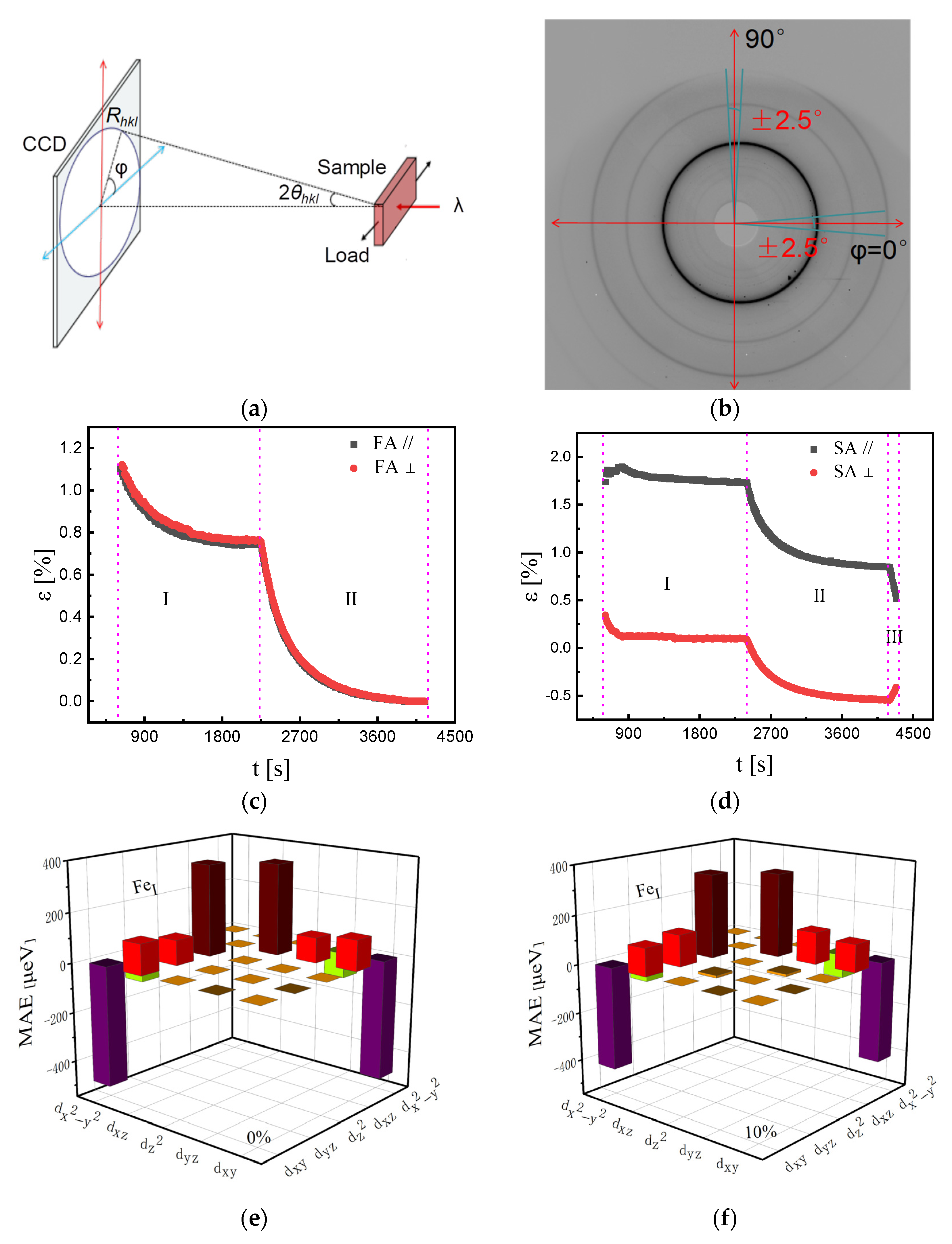
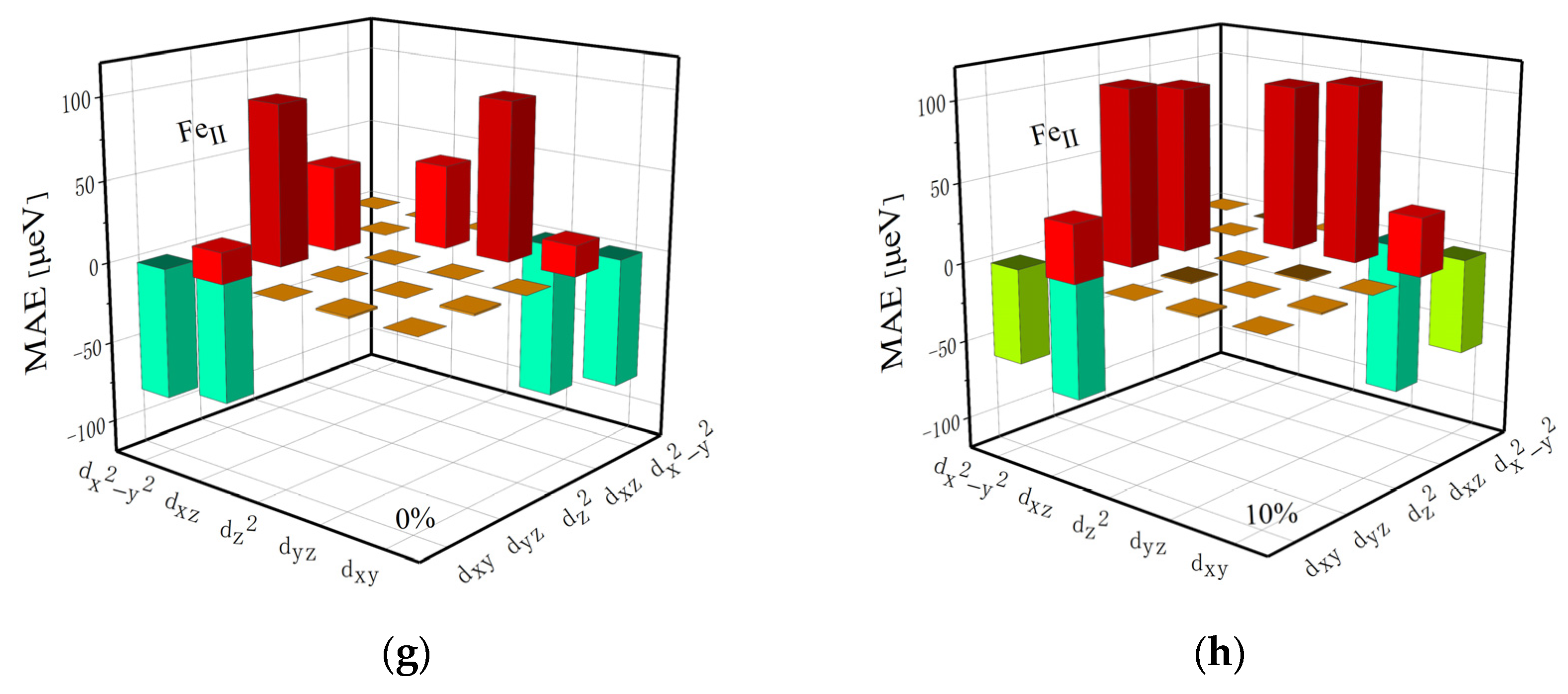
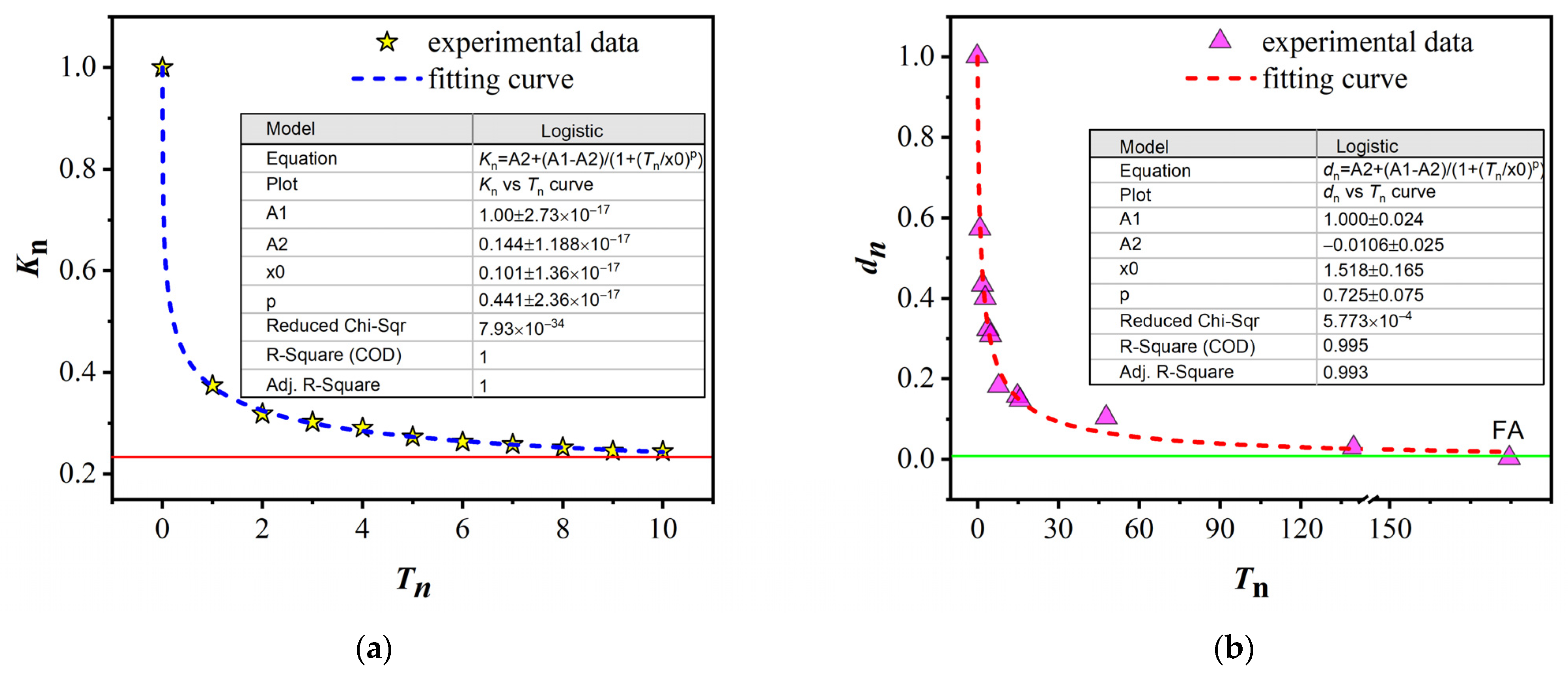
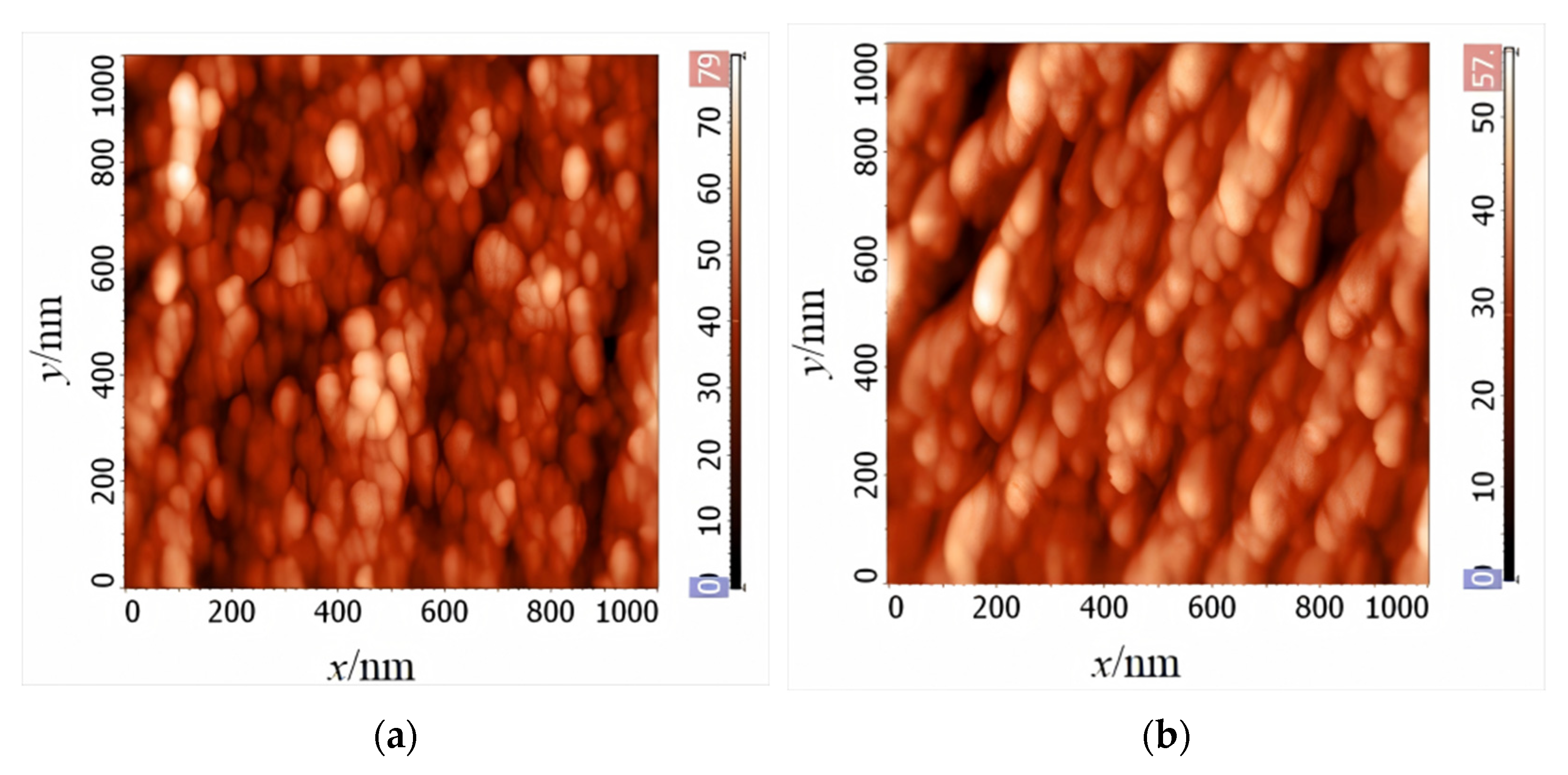
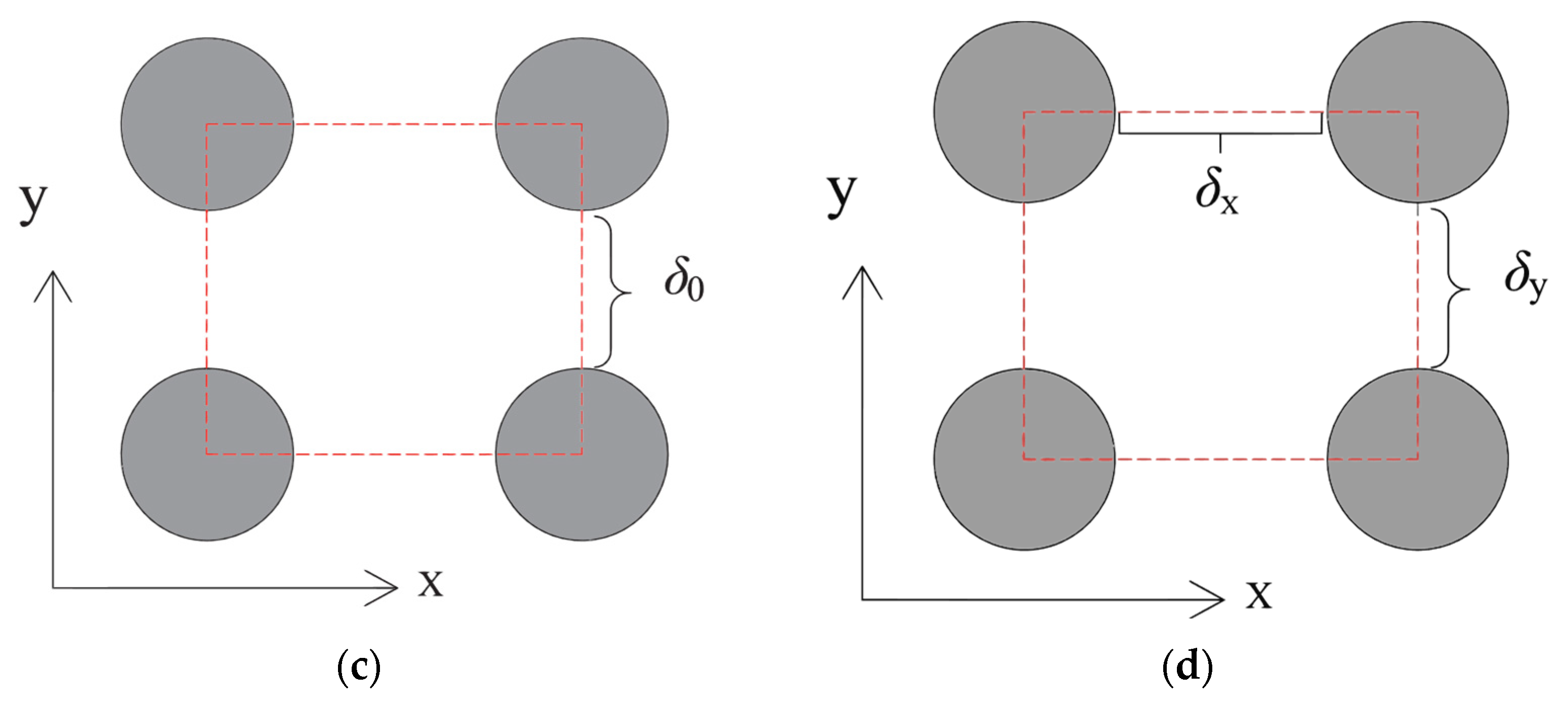
| Alloys | Composition [at %] | Bs [T] | Hc [Am−1] | μ (1 kHz) | Tc [K] | D [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FINEMET | Fe73.5Si13.5B9Nb3Cu1 | 1.24 | 0.53 | 100,000 | 573 | 10~12 |
| NANOPERM | Fe91Zr7B2 | 1.70 | 7.2 | 14,000 | ~750 | 10~20 |
| HITPERM | Fe44Co44Zr7B4Cu1 | 1.61 | 10 | 1800 | 980 | 10~17 |
| NANOMET | Fe85Si2B8P4Cu1 | 1.85 | 5.8 | 27,000 | 728 | ~20 |
| States | Types | Alloy Compositions | Annealing Conditions | Magnetostriction | MA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta [°C] | t [min] | [MPa] | λs [ppm] | K [kJ/m3] | |||
| NA | FINEMET [58,70,71,72] | Fe77.5Cu1Nb3B15.5 | 450 | 20 | 433 | −0.60 | - |
| Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si9B13.5 | 550 | 20 | 469 | −3.30 | 2.000 | ||
| Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si15.5B7 | 550 | 20 | 600 | −7.70 | 7.000 | ||
| 700 | 5 | 54 | 0.5963 | ||||
| 700 | 5 | 200 | 2.313 | ||||
| 700 | 5 | 342 | 4.356 | ||||
| 675 | 5 | 19.2 | 0.1913 | ||||
| 675 | 5 | 204 | 2.294 | ||||
| 675 | 5 | 339 | 4.188 | ||||
| 675 | 15 | 0 | 0.0063 | ||||
| 675 | 15 | 105.4 | 1.138 | ||||
| 675 | 15 | 132.5 | 1.45 | ||||
| Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 | 550 | 60 | 0 | 0.0227 | |||
| 550 | 60 | 20 | 0.2168 | ||||
| 550 | 60 | 41 | 0.4534 | ||||
| 550 | 60 | 62 | 0.622 | ||||
| 550 | 60 | 82 | 0.8929 | ||||
| 550 | 60 | 102 | 1.152 | ||||
| 540 | 60 | 850 | - | 8.000 | |||
| Co-FINEMET [46] | Fe68.5Co5Cu1Nb3Si15.5B7 | 580 | 4 | 250 | −10.0 | 2.900 | |
| Cr-FINEMET [68] | Fe72.5Cr1Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 | 520 | 120 | 150 | - | 2.500 | |
| Fe71.5Cr2Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 | 520 | 120 | 150 | - | 2.380 | ||
| Fe70.5Cr3Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 | 520 | 120 | 150 | - | 2.250 | ||
| Fe69.5Cr4Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 | 520 | 120 | 150 | - | 2.120 | ||
| Co-based [41,73] | Co89Zr7B4 | 550 | 4 | 300/250 | −27.0/−26.0 | 9.000/8.000 | |
| (Co97.5Fe2.5)89Zr7B4 | 550 | 4 | 300/250 | −30.0/−28.0 | 11.000/8.000 | ||
| (Co90Fe10)89Zr7B4 | 550 | 4 | 300/250 | −32.0/−30.0 | 12.000/9.000 | ||
| (Co97.5Fe2.5)89Zr7B4 | 550 | 4 | 450 | −34.2 | 18.900 | ||
| Co72Fe4Mn4Nb4Si2B14 | 520 | 30 | 200/600 | 1.62/- | 16.700/50.000 | ||
| AM [54] | Co-based | Co69.5Fe3.5Mo3Nb1Si16B7 | 350 | 0.5 | 249 | −0.06 | 0.209 |
| Co72Fe1Mn4Mo1Si13B9 | 350 | 0.5 | 254 | −0.12 | 0.324 | ||
| Co72.5Fe5Si5.5B17 | 350 | 0.5 | 353 | −0.25 | 0.616 | ||
| Co72.5Fe1.5Mn4Si5B17 | 350 | 0.5 | 332 | −0.41 | 0.424 | ||
| Co56.5Fe6Mn1Ni16Si4B16.5 | 350 | 0.5 | 364 | −0.90 | 1.406 | ||
| FeNi-based | Fe24Ni58Mo2B16 | 350 | 0.5 | 308 | 7.50 | 2.666 | |
| Ni-based | Fe24Co12Ni46Si2B16 | 350 | 0.5 | 293 | 10.9 | 1.626 | |
| FeNi-based | Fe40Ni40Mo4B16 | 350 | 0.5 | 328 | 14.5 | 2.865 | |
| Fe-based | Fe65Co18Si1B16 | 350 | 0.5 | 336 | 42.9 | −1.053 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dang, W.; Fan, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Gao, S.; et al. Stress-Induced Magnetic Anisotropy in Fe-Based Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Alloys: Mechanisms, Advances and Challenges. Materials 2025, 18, 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071499
Zhang J, Qin Y, Liu X, Zhao Y, Dang W, Fan X, Chen X, Yu Y, Yang Z, Gao S, et al. Stress-Induced Magnetic Anisotropy in Fe-Based Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Alloys: Mechanisms, Advances and Challenges. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071499
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jianqiang, Yanjun Qin, Xiaobin Liu, Yuxiang Zhao, Wenqiang Dang, Xiaozhen Fan, Xinyi Chen, Yuanrong Yu, Zixuan Yang, Shipeng Gao, and et al. 2025. "Stress-Induced Magnetic Anisotropy in Fe-Based Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Alloys: Mechanisms, Advances and Challenges" Materials 18, no. 7: 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071499
APA StyleZhang, J., Qin, Y., Liu, X., Zhao, Y., Dang, W., Fan, X., Chen, X., Yu, Y., Yang, Z., Gao, S., Wu, D., & Fang, Y. (2025). Stress-Induced Magnetic Anisotropy in Fe-Based Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Alloys: Mechanisms, Advances and Challenges. Materials, 18(7), 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071499






