Material Removal Modeling for Free-Form Rubber Materials
Abstract
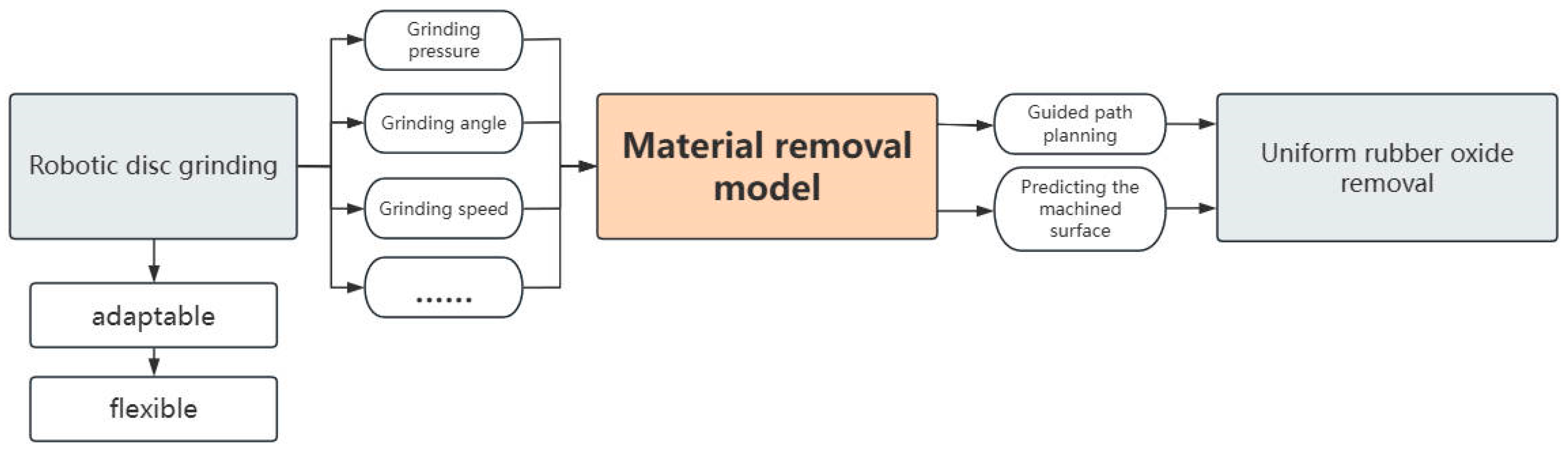
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling of Rubber Material Removal
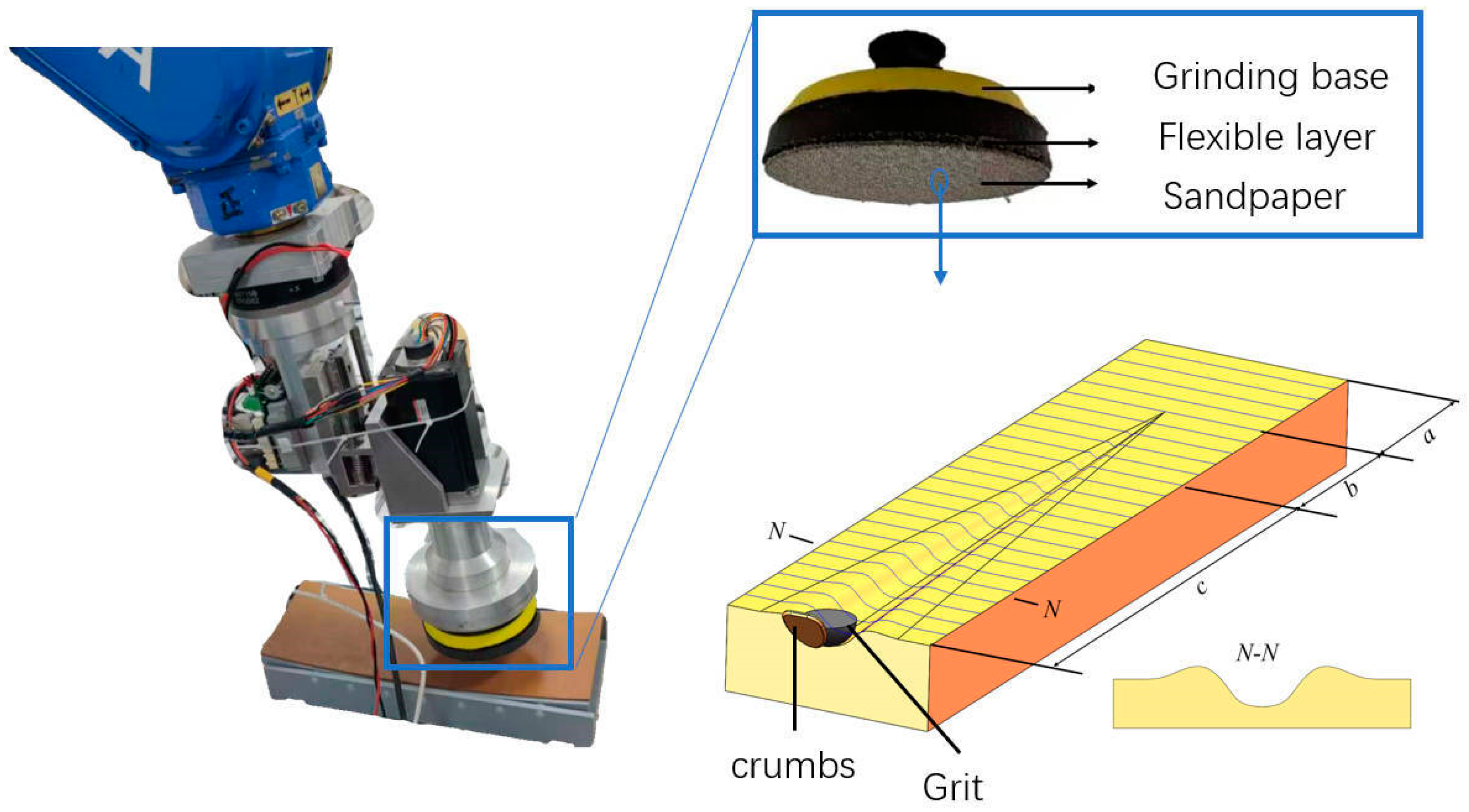
2.1. Analysis of Grinding Mechanisms
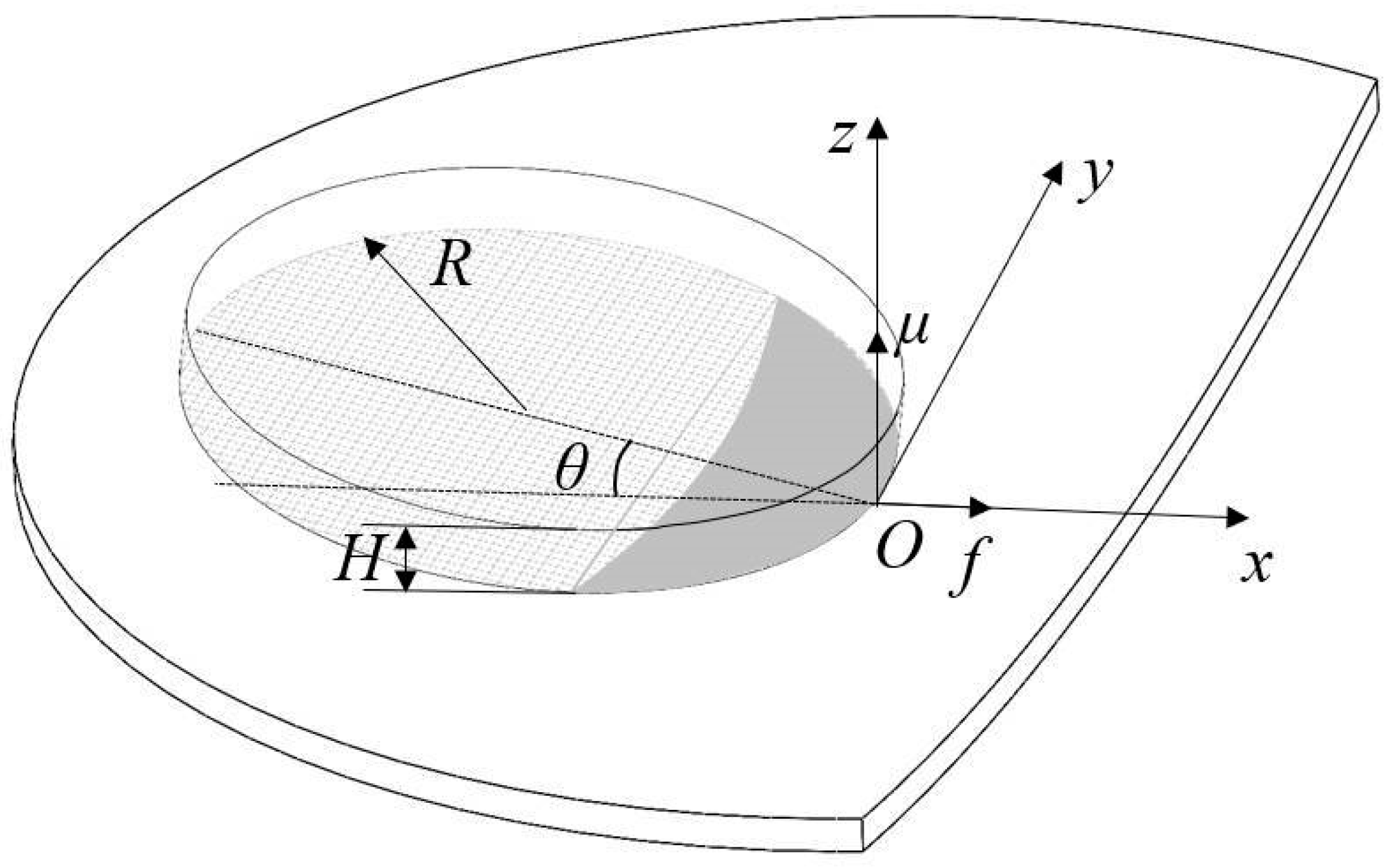
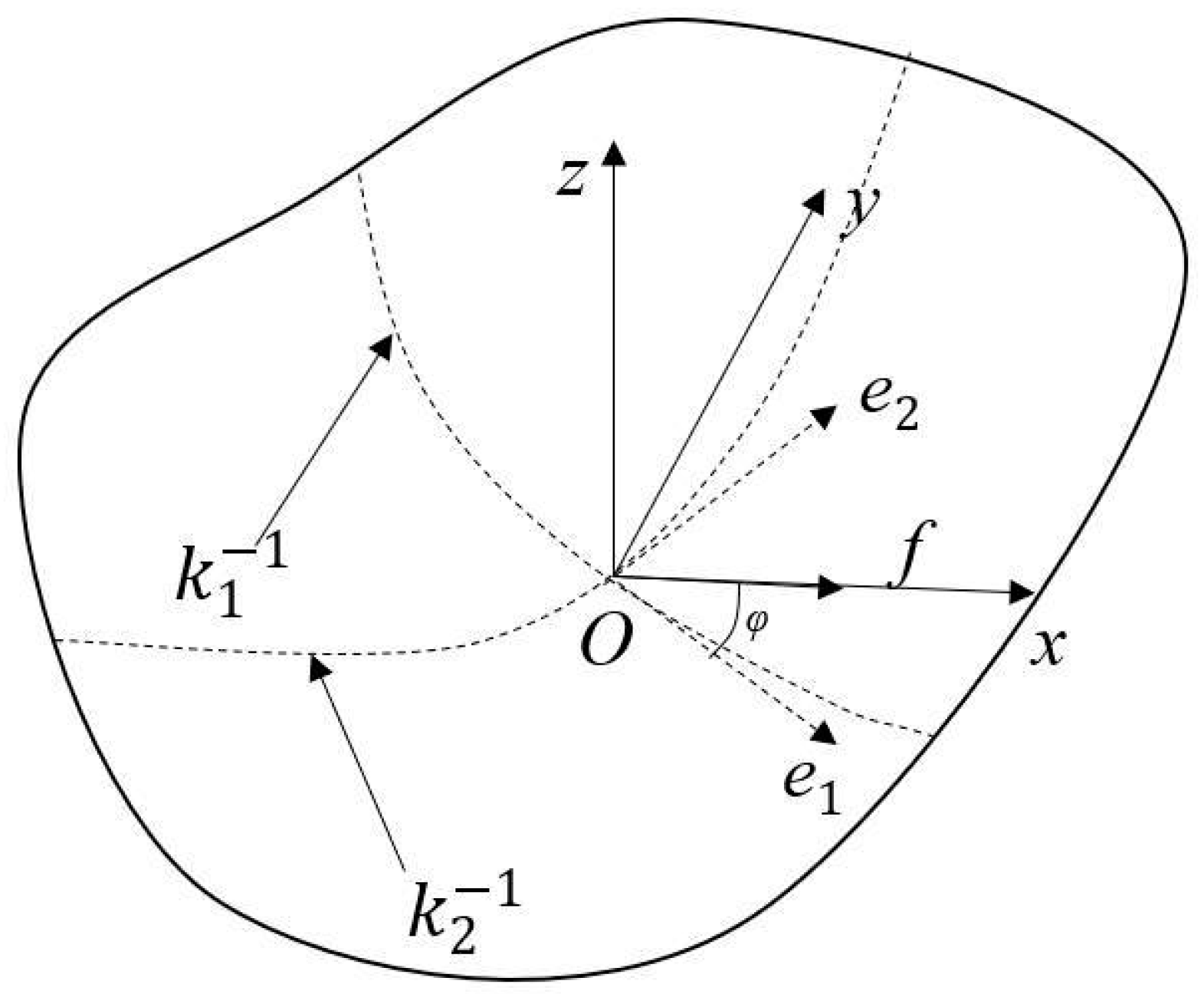
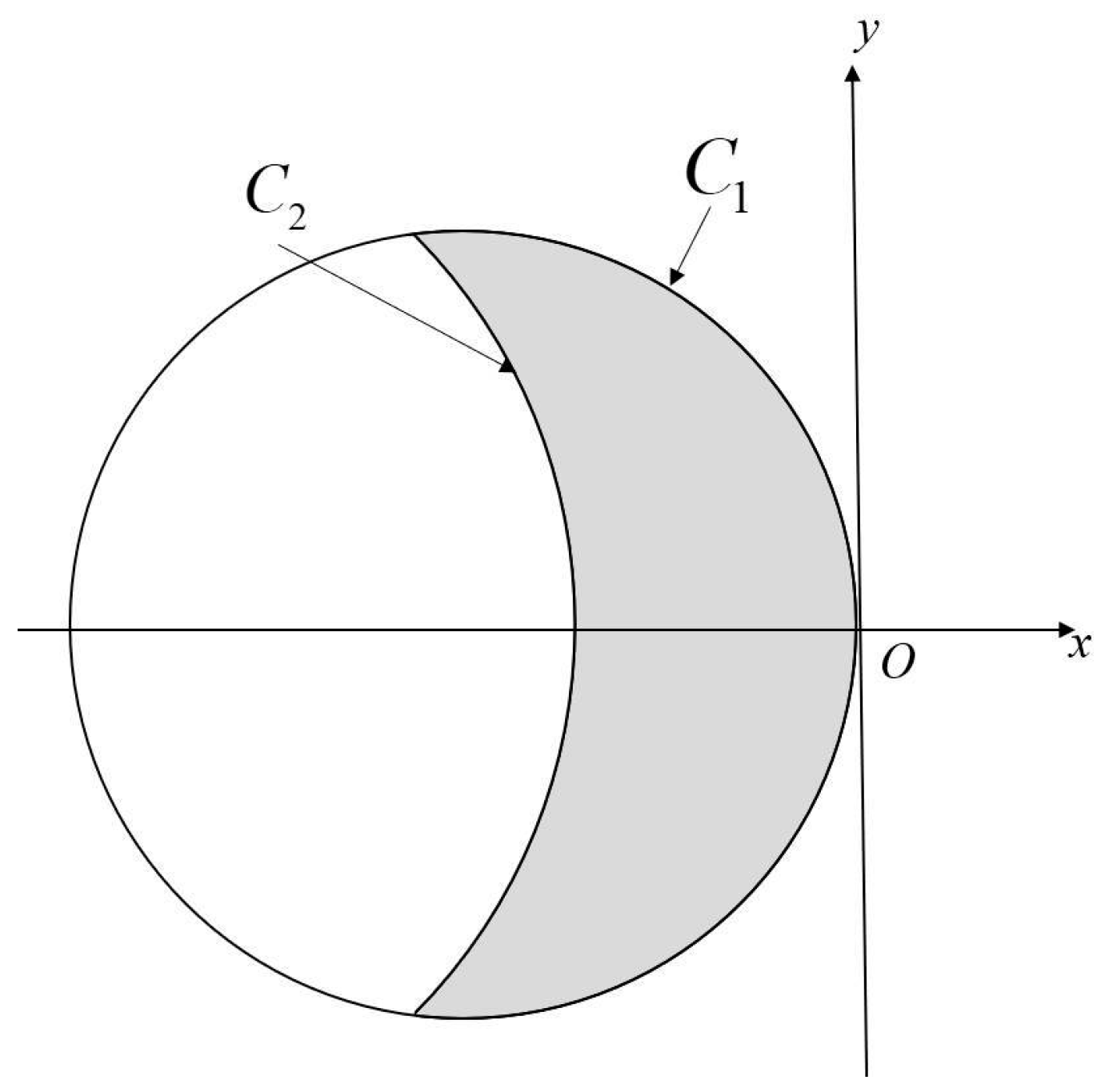
2.2. Geometry of Contact Area
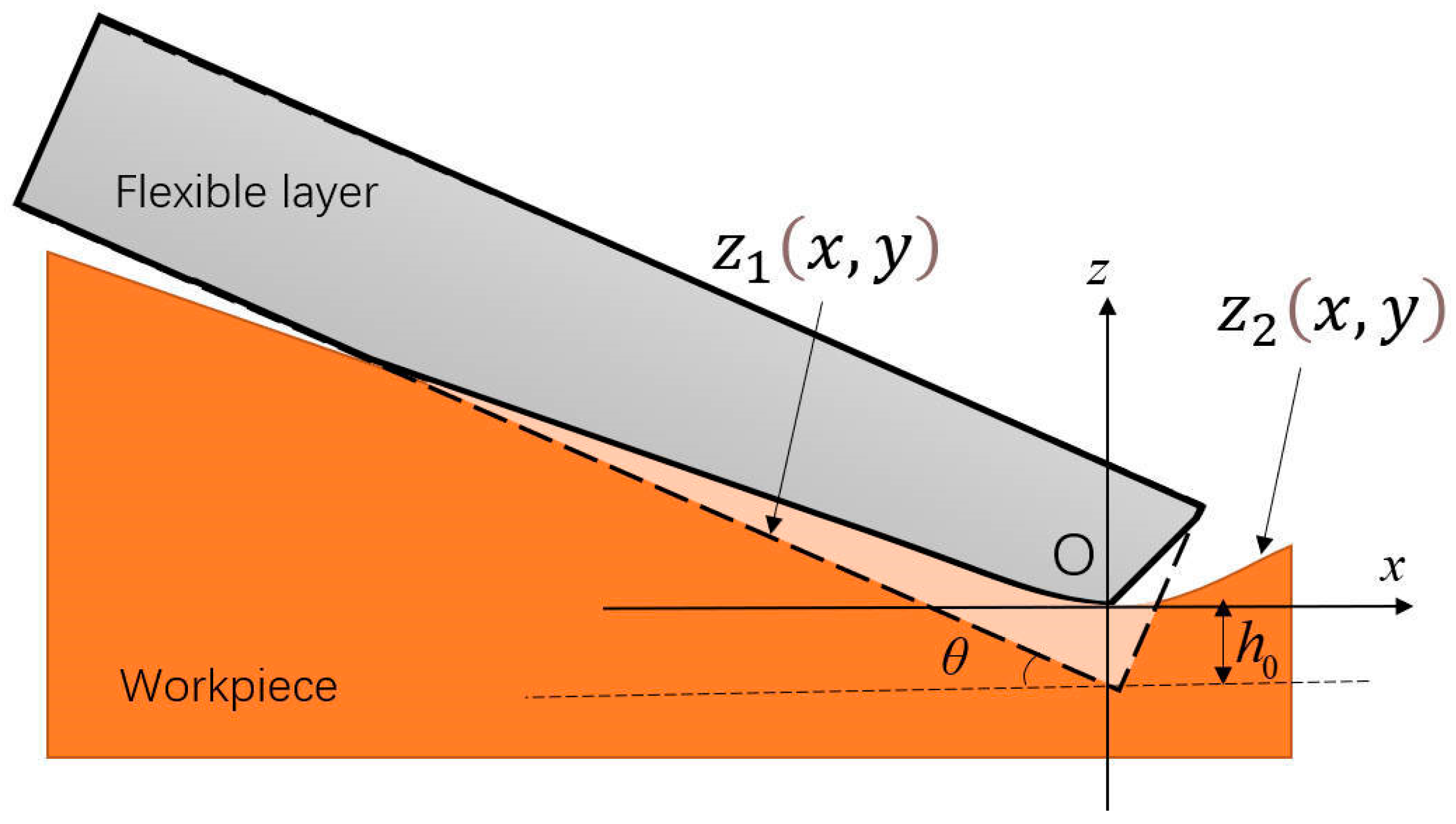
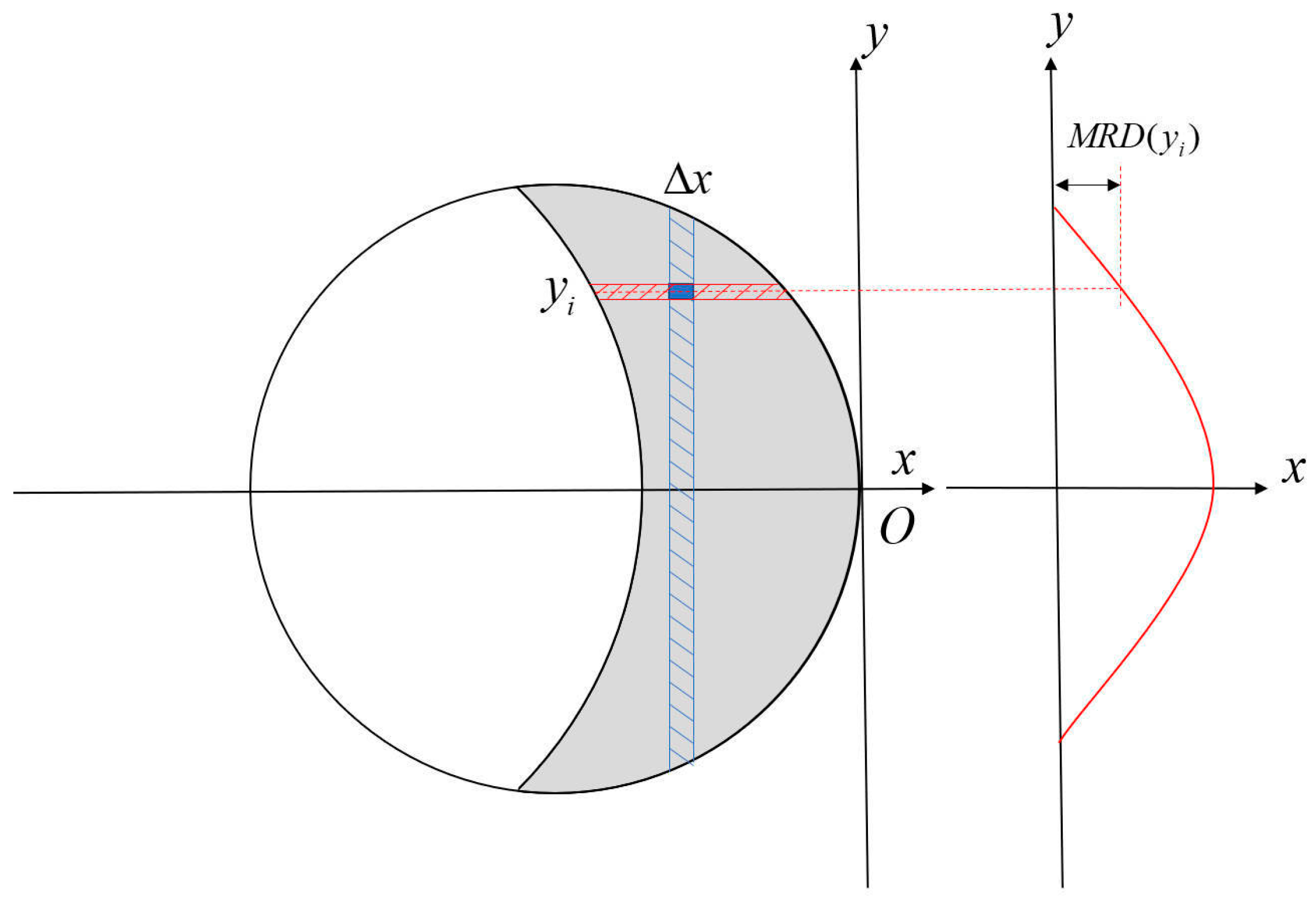
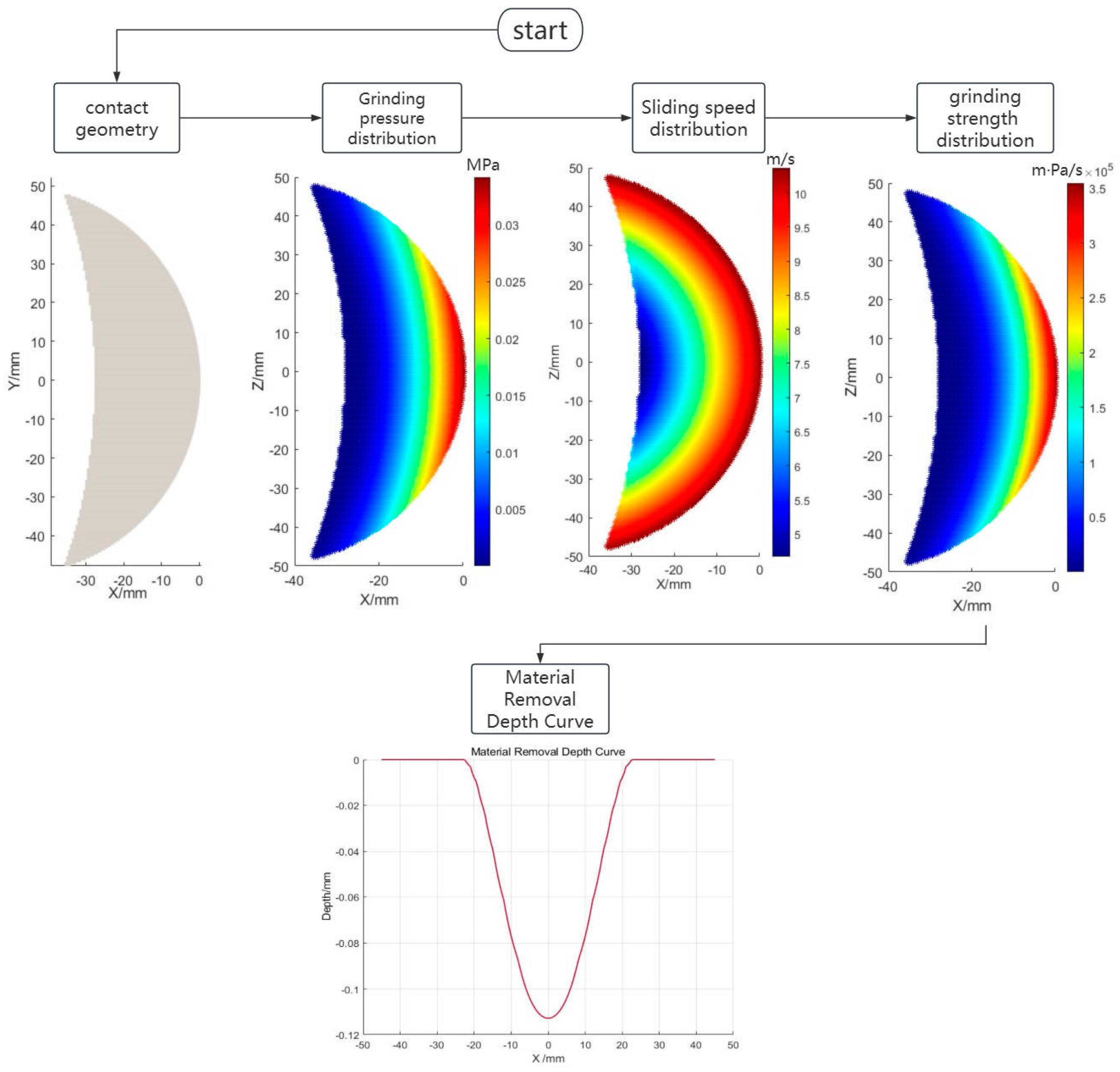
2.3. Modeling of Material Removal
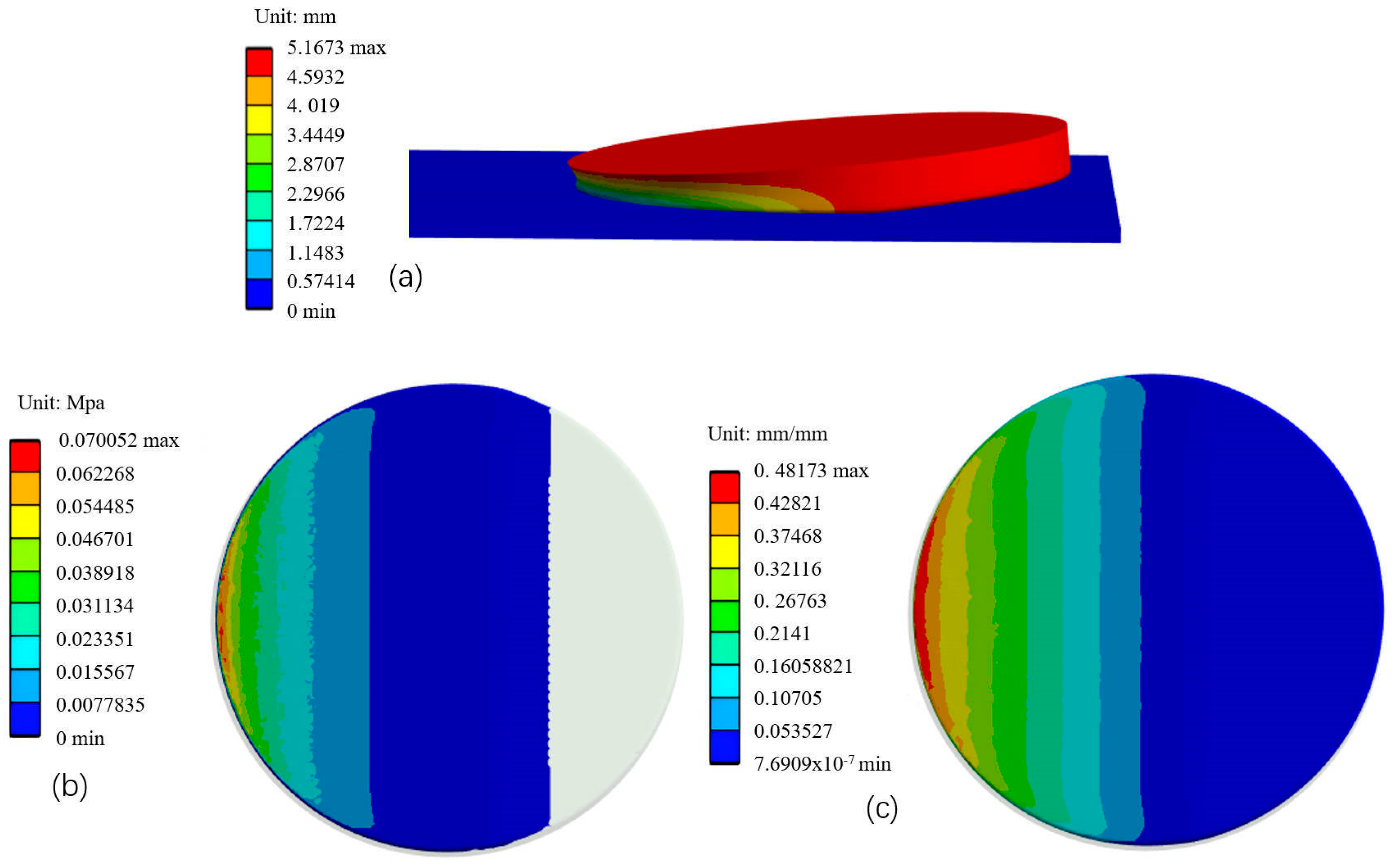
2.4. Model Discretization
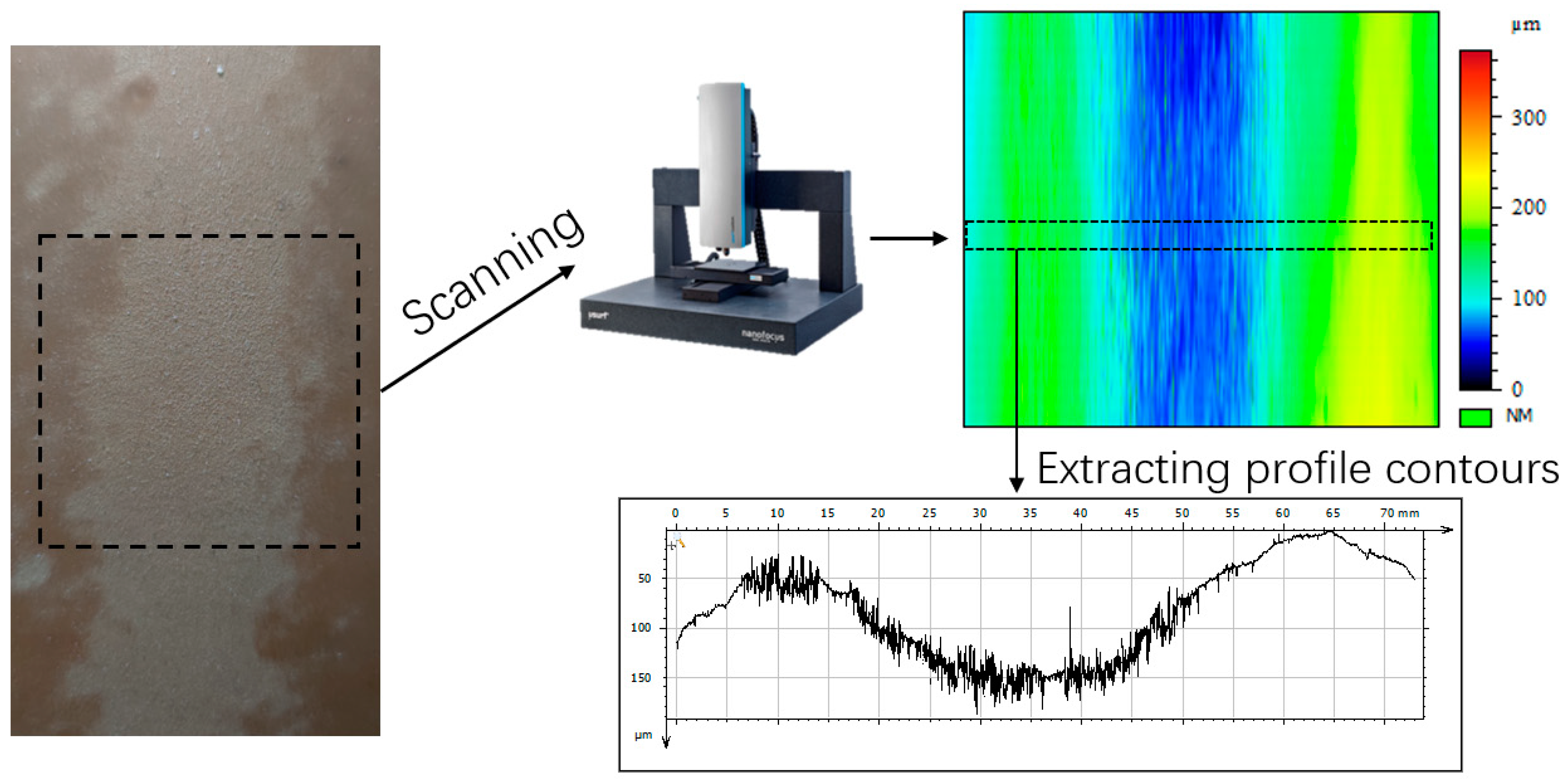
3. Experimental Verification and Analysis
3.1. Parametric Identification
3.2. Experimental Verification
- (1)
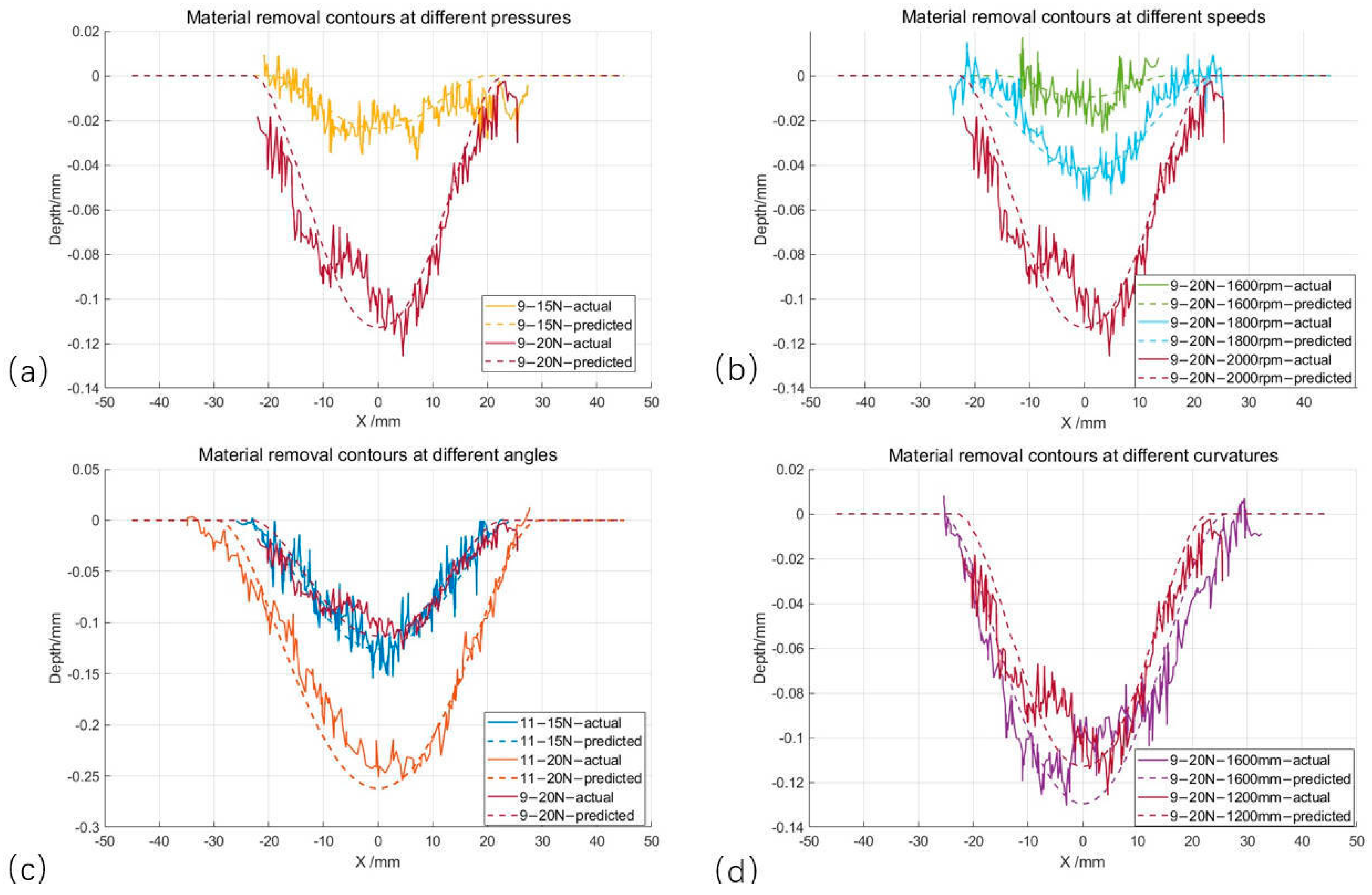
- Influence of downward pressure: Comparison of material removal contours with different pressures at the same angle in Figure 13a,c; when a larger amount of downward pressure is used, the deformation of the grinding disk is larger, and the contact width increases, but the deformation of the grinding disk increases, and the grinding pressure increases from 15 N to 20 N, increasing the contact pressure and increasing the depth and width of the material removal.
- (2)
- The effect of grinding speed: (b) shows the use of different speeds under the material removal trajectory; the two grinding angles and grinding pressure are the same, the grinding speed from 1600 m increased to 2000 rpm, and the grinding depth from 0.0096 mm increased to 0.112 mm; the increase is more obvious. In the actual grinding, the fluctuation of the grinding rotational speed is greatly influenced by the grinding rotational speed, and it should be ensured that the grinding rotational speed is unchanged.
- (3)
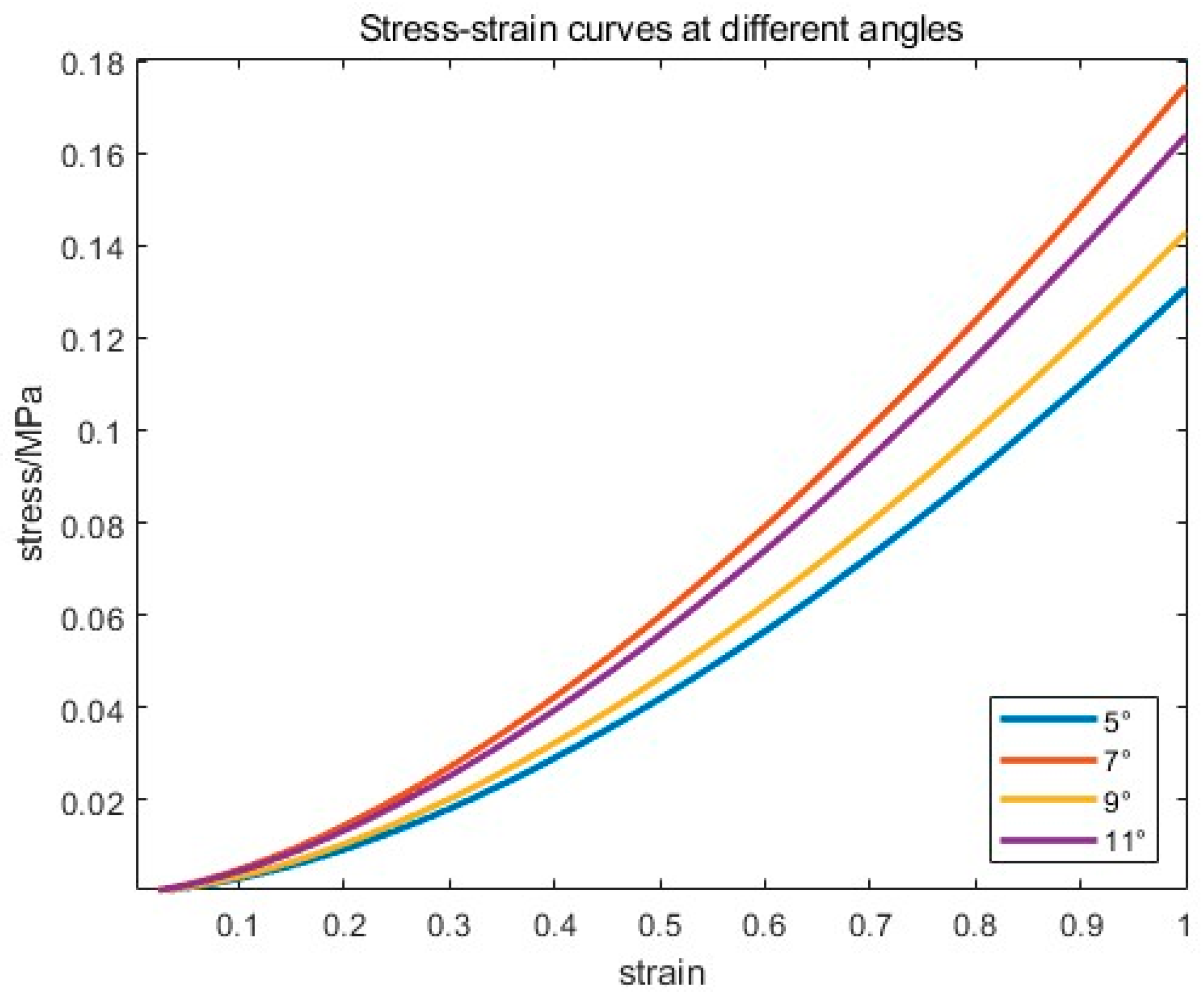
- Influence of inclination angle: Comparison of trajectories with different grinding angles under the same grinding pressure in (c); when the inclination angle increases, the contact area decreases, the pressure in the contact area increases, the amount of material removed increases, and the depth of material removed and the width of material removed increase.
- (4)
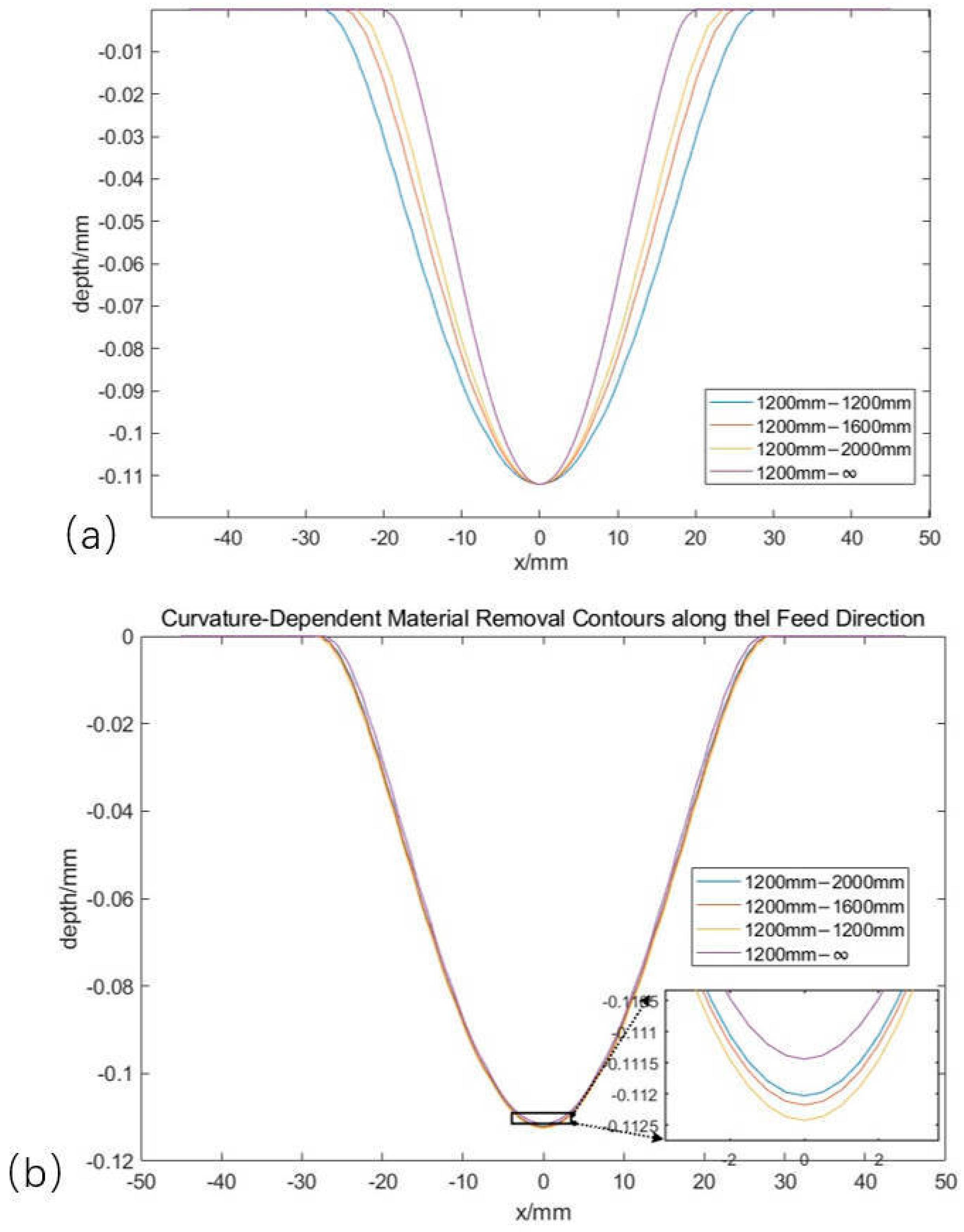
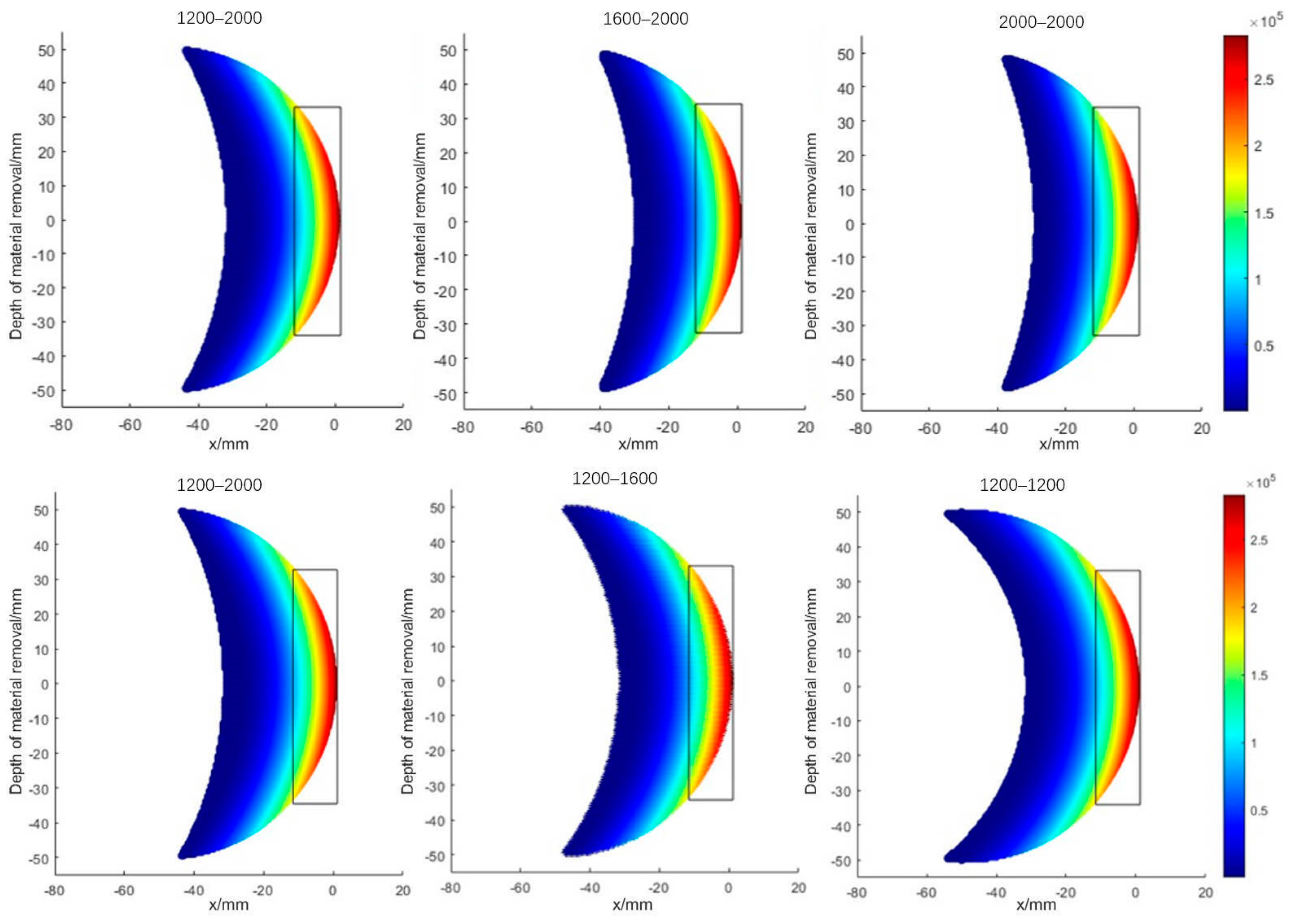
- The effect of the shape of the Rubber insulation layer: In (d), two curvature radii are shown in the material removal contour; as the curvature radius decreases, the area of the grinding contact area decreases, the contact stress increases, and the actual grinding depth and grinding width both increase.
3.3. Influence of Shape Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xin, C.B.; Gu, Y.Z.; Li, M.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.G. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Effect of Rubber Mold Configuration on the Compaction of Composite Angle Laminates during Autoclave Processing. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Ding, H. Grain Shape-Protrusion-Based Modeling and Analysis of Material Removal in Robotic Belt Grinding. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 110, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, D.; Chen, L.; Tan, C.; Ding, H. Robotic Grinding of a Blisk with Two Degrees of Freedom Contact Force Control. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, G. Research on Polishing Parameters Optimization for Free Curved Surface. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Wuhan, China, 31 May–2 June 2018; pp. 2339–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; He, C.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Ren, C. Material Removal Mechanism and Corresponding Models in the Grinding Process: A Critical Review. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 103, 354–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.-X.; Dong, F.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Meng, X.-K.; Peng, X.-D. Effect of Abrasive Size on Friction and Wear Characteristics of Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) in Two-Body Abrasion. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Ding, H. Dual Flexible Contact Material Removal Model for Robotic Disk Grinding. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 124, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Wang, L. Industrial Robotic Machining: A Review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Cripps, A.C. The Hertzian Contact Surface. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Nasri, H.; Bolmsjo, G. A Process Model for Robotic Disc Grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1995, 35, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.R. Contact Mechanics; Solid Mechanics and Its Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 250, pp. 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, B.J.; Srivastava, A.K.; Elbestawi, M.A. Analysis of the Robotic Disc Grinding Process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 1992, 7, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Sun, Y.; Du, H. Investigations on the Automatic Precision Polishing of Curved Surfaces Using a Five-Axis Machining Centre. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, A.P.S.; Idapalapati, S. Material Removal Analysis for Compliant Polishing Tool Using Adaptive Meshing Technique and Archard Wear Model. Wear 2019, 418–419, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ji, P.; Jin, Y.; Li, D.; Walker, D.; Yu, G.; Li, H.; Wang, B. Simulation and Experimental Study on Form-Preserving Capability of Bonnet Polishing for Complex Freeform Surfaces. Precis. Eng. 2019, 60, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, X.; Feng, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. A Novel Material Removal Rate Model Based on Single Grain Force for Robotic Belt Grinding. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhu, D.; Yan, S.; Ding, H. Prediction and Analysis of Material Removal Characteristics for Robotic Belt Grinding Based on Single Spherical Abrasive Grain Model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 190, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Z.; Li, S.; Su, S. A Material Removal Model for Nonconstant-Contact Flexible Grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 6163–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Ding, H. Accurate Modeling of Material Removal Depth in Convolutional Process Grinding for Complex Surfaces. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 267, 109005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Peng, Z.; Qu, C.; Zhu, D. An Adaptive Trajectory Planning Algorithm for Robotic Belt Grinding of Blade Leading and Trailing Edges Based on Material Removal Profile Model. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 66, 101987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyan, V.; Caesarendra, W.; Tjahjowidodo, T.; Praveen, G. Predictive Modelling and Analysis of Process Parameters on Material Removal Characteristics in Abrasive Belt Grinding Process. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Yang, Z.S. Model of an Abrasive Belt Grinding Surface Removal Contour and Its Application. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Ding, Y.; Fang, Z.; Yang, G. Contact Force Modeling and Analysis for Robotic Tilted-Disc Polishing of Freeform Workpieces. Precis. Eng. 2020, 66, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-H.; Liang, Y.-J.; Xu, C.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Zhou, X.-F. Generation of Material Removal Map for Freeform Surface Polishing with Tilted Polishing Disk. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 4213–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ge, P.; Bi, W.; Jiang, J. Grain Trajectory and Grain Workpiece Contact Analyses for Modeling of Grinding Force and Energy Partition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 70, 2111–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yang, Q.; Yang, W.; Hu, Y.; He, Q.; Yang, X. Impact of Friction Speeds on the Wear Mechanisms of X-Shaped Nitrile Rubber Seals in Oil-Rich Lubrication Condition. Wear 2025, 205933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoran, M.; Azarhoushang, B.; Daneshi, A. Investigation of the Effects of Reinforcement Particles in Polymers on Their Grindability in Single Grit Scratch Test. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2024, 238, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-W. Tribology of Elastomers; Tribology and Interface Engineering Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 85–110. [Google Scholar]


| Parametric Type | Parametric |
|---|---|
| Grinding disk type | 100 mm diameter round grinding discs |
| Flexible layer thickness | 12 mm |
| Grinding angle | 9°, 11° |
| Grinding pressure | 15 N, 20 N |
| RPM | 1600 mm, 1800 rpm, 2000 rpm |
| Speed of movement | 10 mm/s |
| Grit | 80 |
| Material type | EPDM |
| Workpiece curvature |
| C10 (MPa) | C01 (MPa) |
|---|---|
| 0.446 | 1.7849 |
| C10 (MPa) | C20 (MPa) | C30 (MPa) | D (Pa-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.007 | 0.0044 | 0.465 |
| Angle (°) | Pressure (N) | Speed (RPM) | Radius of Curvature (mm) | Width Relative Error | Depth Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 15 | 2000 | 1200–2000 | −5.915% | −2.315% |
| 9 | 20 | 2000 | 1200–2000 | −10.263% | −3.991% |
| 9 | 20 | 2000 | 1600–2000 | 8.296% | −4.041% |
| 9 | 20 | 1600 | 1200–2000 | −11.070% | 15.171% |
| 9 | 20 | 1800 | 1200–2000 | −8.150% | −9.186% |
| 11 | 15 | 2000 | 1200–2000 | −1.666% | −2.699% |
| 11 | 20 | 2000 | 1200–2000 | 6.113% | 1.827% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Fu, W.; Ma, Y.; Chai, X.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Z. Material Removal Modeling for Free-Form Rubber Materials. Materials 2025, 18, 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071584
Zhang Y, Fu W, Ma Y, Chai X, Bai J, Zhang Z. Material Removal Modeling for Free-Form Rubber Materials. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071584
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yaodong, Weiqi Fu, Yanzhao Ma, Xiang Chai, Jiong Bai, and Zhiqiang Zhang. 2025. "Material Removal Modeling for Free-Form Rubber Materials" Materials 18, no. 7: 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071584
APA StyleZhang, Y., Fu, W., Ma, Y., Chai, X., Bai, J., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Material Removal Modeling for Free-Form Rubber Materials. Materials, 18(7), 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071584





