Atomistic Simulation and Micro-Pillar Compression Studies on the Influence of Glass–Glass Interfaces on Plastic Deformation in Co-P Metallic Nano-Glasses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Computational Methods
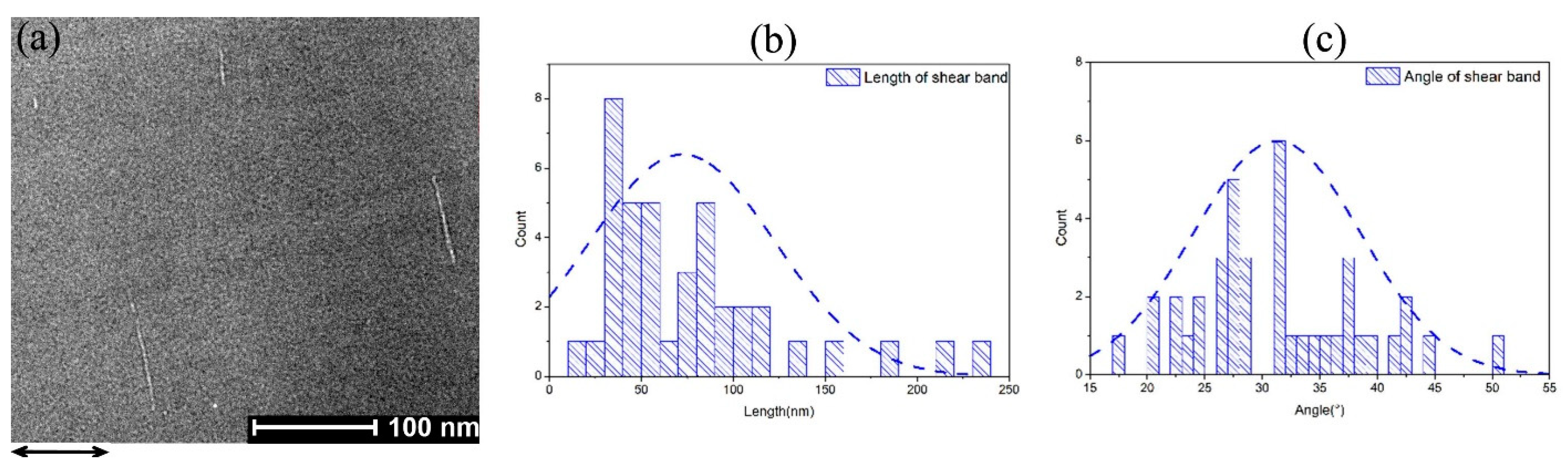
2.1. Experimental Methods
2.2. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effects of a GGI with an Inclining Angle ax on the Mechanical Properties of NGs
3.2. Micro-Pillar Compression on Co-P Nano-Glasses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klement, W.; Willens, R.H.; Duwez, P. Non-crystalline structure in solidified gold-silicon alloys. Nature 1960, 187, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L. Metallic glasses on the threshold. Mater. Today 2009, 12, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Rector, D.; Conner, R.; Schroers, J. Embrittlement of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3572–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudino, S.; Jerliu, B.; Pauly, S.; Surreddi, K.; Kühn, U.; Eckert, J. Ductile bulk metallic glasses produced through designed heterogeneities. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, M.D.; Launey, M.E.; Garrett, G.; Schramm, J.P.; Hofmann, D.C.; Johnson, W.L.; Ritchie, R.O. A damage-tolerant glass. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Shang, J.K.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. Crack-resistance curve of a Zr-Ti-Cu-Al bulk metallic glass with extraordinary fracture toughness. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4940–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Yim, H.; Johnson, W.L. Bulk metallic glass matrix composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 3808–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, R.D.; Dandliker, R.B.; Johnson, W.L. Mechanical properties of tungsten and steel fiber reinforced Zr41.25Ti13.75Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 metallic glass matrix composites. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 6089–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.P.; Busch, R.; Masuhr, A.; Choi-Yim, H.; Johnson, W.L. Processing of carbon-fiber-reinforced Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5 bulk metallic glass composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.C.; Suh, J.-Y.; Wiest, A.; Duan, G.; Lind, M.-L.; Demetriou, M.D.; Johnson, W.L. Designing metallic glass matrix composites with high toughness and tensile ductility. Nature 2008, 451, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, C.C.; Kim, C.P.; Johnson, W.L. Microstructure Controlled Shear Band Pattern Formation and Enhanced Plasticity of Bulk Metallic Glasses Containing in situ Formed Ductile Phase Dendrite Dispersions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 2901–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, A.; Fu, H.; Ding, B.; Hu, Z. Synthesis and characteristics of 80vol.% tungsten (W) fibre/Zr based metallic glass composite. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Tang, M.B.; Kim, K.B.; Theissmann, R.; Baier, F.; Wang, W.H.; Eckert, J. “Work-hardenable” ductile bulk metallic glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 205501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, D.C. Bulk Metallic Glasses and Their Composites: A Brief History of Diverging Fields. J. Mater. 2013, 2013, 517904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Wei, B.C.; Wang, Y.R.; Li, W.H.; Cheung, T.L.; Shek, C.H. Plasticity-improved Zr-Cu-Al bulk metallic glass matrix composites containing martensite phase. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 051905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, S.; Das, J.; Bednarcik, J.; Mattern, N.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, D.H.; Eckert, J. Deformation-induced martensitic transformation in Cu-Zr-(Al, Ti) bulk metallic glass composites. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, D.Q.; Song, W.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ma, D.; Wang, X.L.; Lu, Z.P. Ductilizing Bulk Metallic Glass Composite by Tailoring Stacking Fault Energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 245506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.C. Shape memory bulk metallic glass composites. Science 2010, 329, 1294–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, J. Toughen and harden metallic glass through designing statistical heterogeneity. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, J. Mechanical properties of spinodal decomposed metallic glass composites. Scr. Mater. 2017, 135, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, J. Free volume gradient effect on mechanical properties of metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2017, 130, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gleiter, H.; Li, M. From patterning heterogeneity to nanoglass: A new approach to harden and toughen metallic glasses. MRS Bull. 2023, 48, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Jiang, F.; Hahn, H.; Li, J.; Gleiter, H.; Sun, J.; Fang, J.X. Plasticity of a scandium-based nanoglass. Scr. Mater. 2015, 98, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, G.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J. Nanostructural metallic materials: Structures and mechanical properties. Mater. Today 2020, 38, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, H. Nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1989, 33, 223–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Kramer, A.; Birringer, R.; Gleiter, H.; Gonser, U. Modified atomic structure in a Pd-Fe-Si nanoglass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1989, 113, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjaoud, O.; Albe, K. Microstructure formation of metallic nanoglasses: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.X.; Vainio, U.; Puff, W.; Wurschum, R.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, D.; Ghafari, M.; Jiang, F.; Sun, J.; Hahn, H.; et al. Atomic structure and structural stability of Sc75Fe25 nanoglasses. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Frank, R.; Asao, N.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.; Sharma, P.; Wang, J.; Xie, G.; Ishikawa, Y.; Hatakeyama, N.; Lin, Y.; et al. Formation and properties of Au-based nanograined metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6433–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, F.; Hahn, H.; Li, J.; Gleiter, H.; Sun, J.; Fang, J. Sample size effects on strength and deformation mechanism of Sc75Fe25 nanoglass and metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2016, 116, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, O.; Leisen, D.; Gleiter, H.; Hahn, H. Thermal and plastic behaviour of nanoglasses. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.; Zhao, R.; Fang, Y.; Wu, S.; Cui, Z.; Sun, B.; Lan, S.; Luo, P.; Wang, W.; Feng, T. The structural and dynamic heterogeneities of Ni-P nanoglass characterized by stress-relaxation. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 836, 155506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, S.; Fu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, F.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.H. Manufacturing of metallic glass components: Processes, structures and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 144, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comp. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, H.; Doyama, M. The calculation of a vacancy and divacancies in α-iron. J. Fac. Eng. Univ. Tokyo B 1969, 30, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, V.V.; Hung, N.H.; Anh, N.H.T. Computer simulation of the effects of B, P concentration on the pore distribution in the amorphous Co-B, Co-P alloys. J. Meta. Nanocryst. Mater. 2002, 18, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, N.; Yu, T.; Zheng, G. The Modulation of Compositional Heterogeneity for Controlling Shear Banding in Co-P Metallic Nanoglasses. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsari, M.H.; Alavi, S.; Ashrafizaadeh, M.; Najafi, B. Molecular dynamics simulation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. I. Dynamics and diffusion coefficient. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 224508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, A.; Ma, E. Correlation between the elastic modulus and the intrinsic plastic behavior of metallic glasses: The roles of atomic configuration and alloy composition. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3253–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, M.L.; Langer, J.S. Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 57, 7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, F.; Ogata, S.; Li, J. Theory of shear banding in metallic glasses and molecular dynamics calculations. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 2923–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Q.-M.; Zhang, J.-C.; Zheng, G.-P.; Wang, X.-Y. The prominent combination of ultrahigh strength and superior tensile plasticity in Cu–Zr nanoglass connected by oxide interfaces: A molecular dynamics study. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 801, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, Y.; Şopu, D.; Gleiter, H.; Albe, K. Structure, stability and mechanical properties of internal interfaces in Cu64Zr36 nanoglasses studied by MD simulations. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6588–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şopu, D.; Able, K. Influence of grain size and composition, topology and excess free volume on the deformation behavior of Cu–Zr nanoglasses. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Abraham, A.; Chawla, N.; Jiang, H. Evaluation of micro-pillar compression tests for accurate determination of elastic-plastic constitutive relations. Appl. Mech. 2012, 79, 061011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
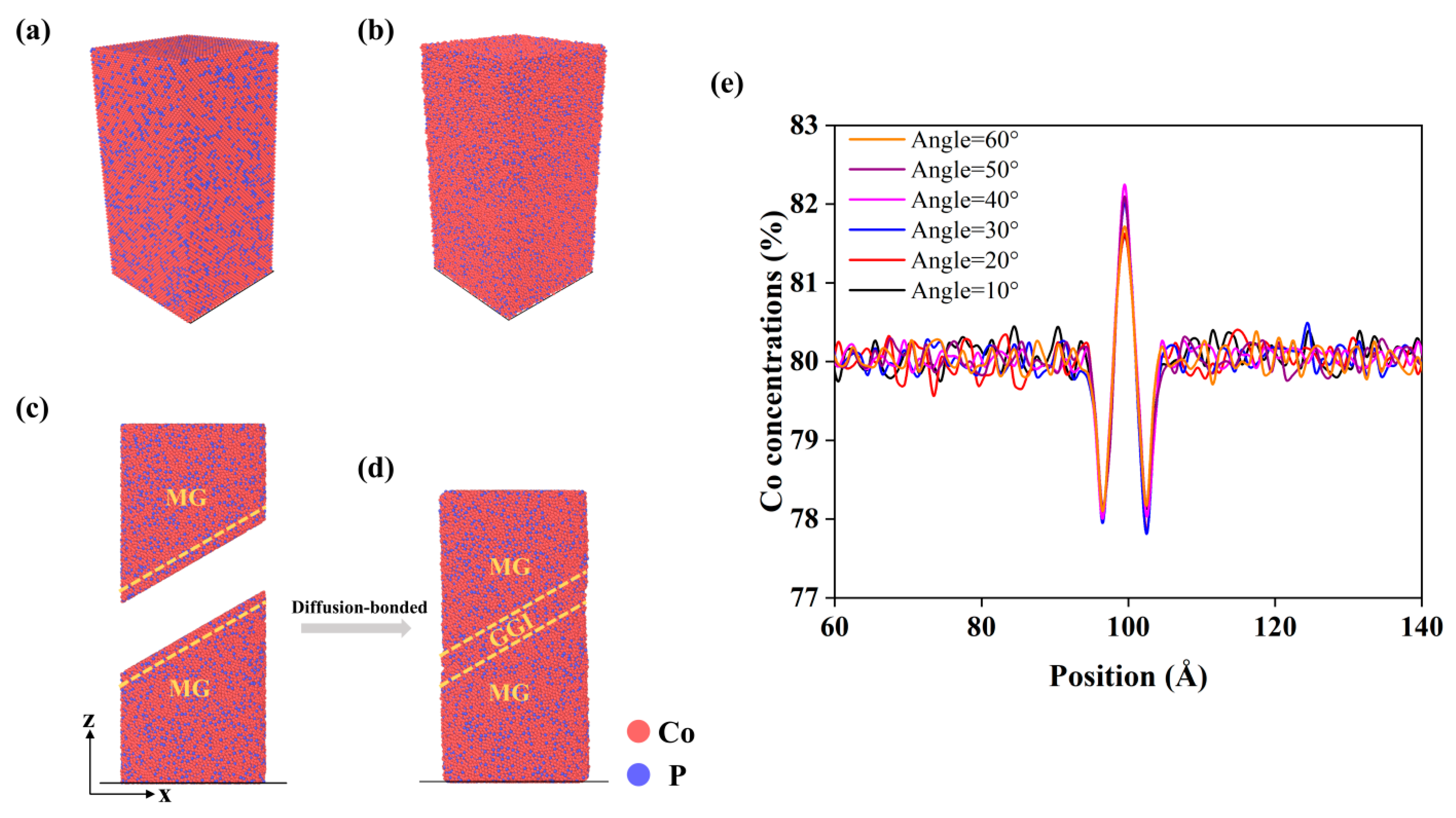
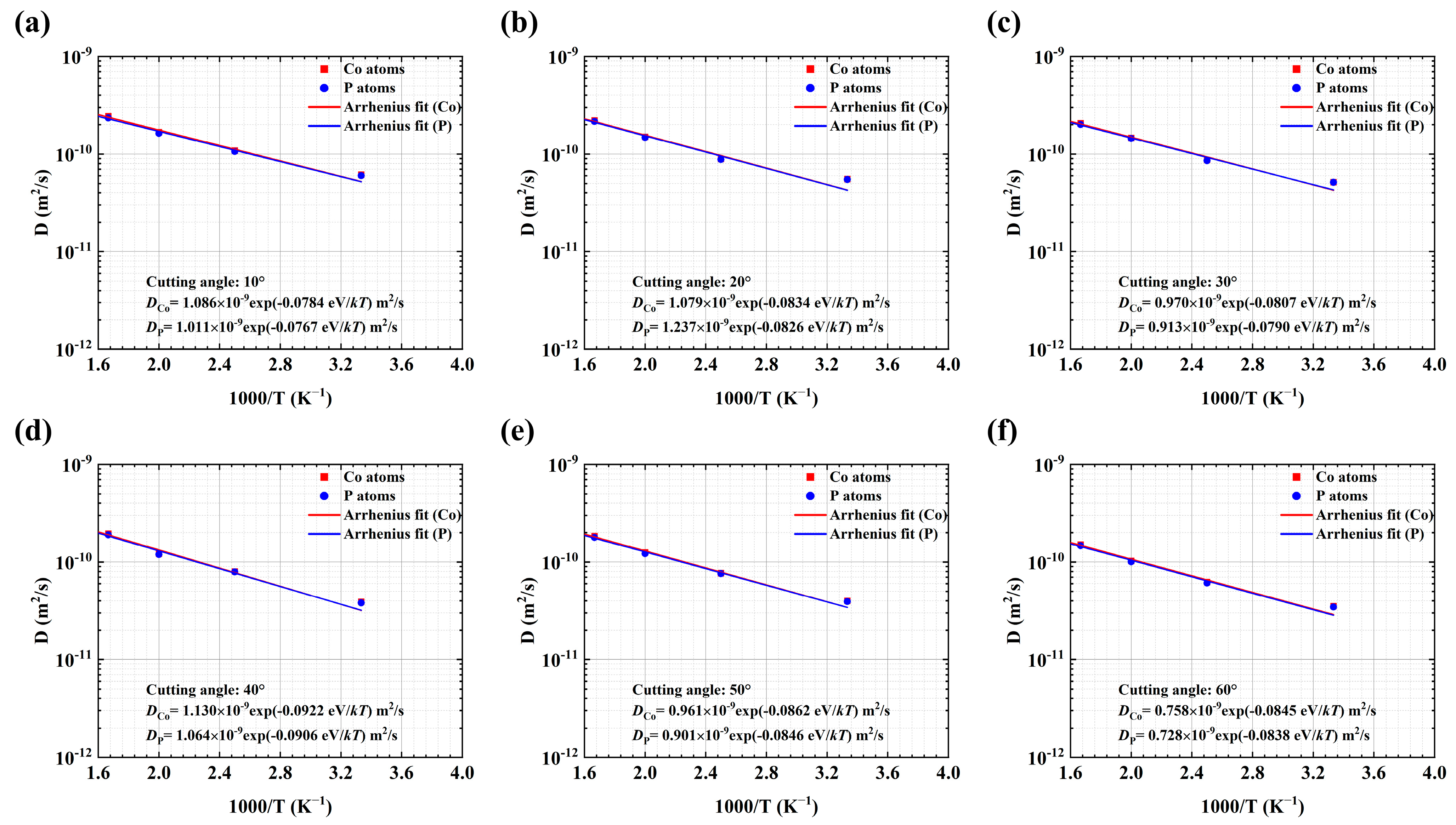


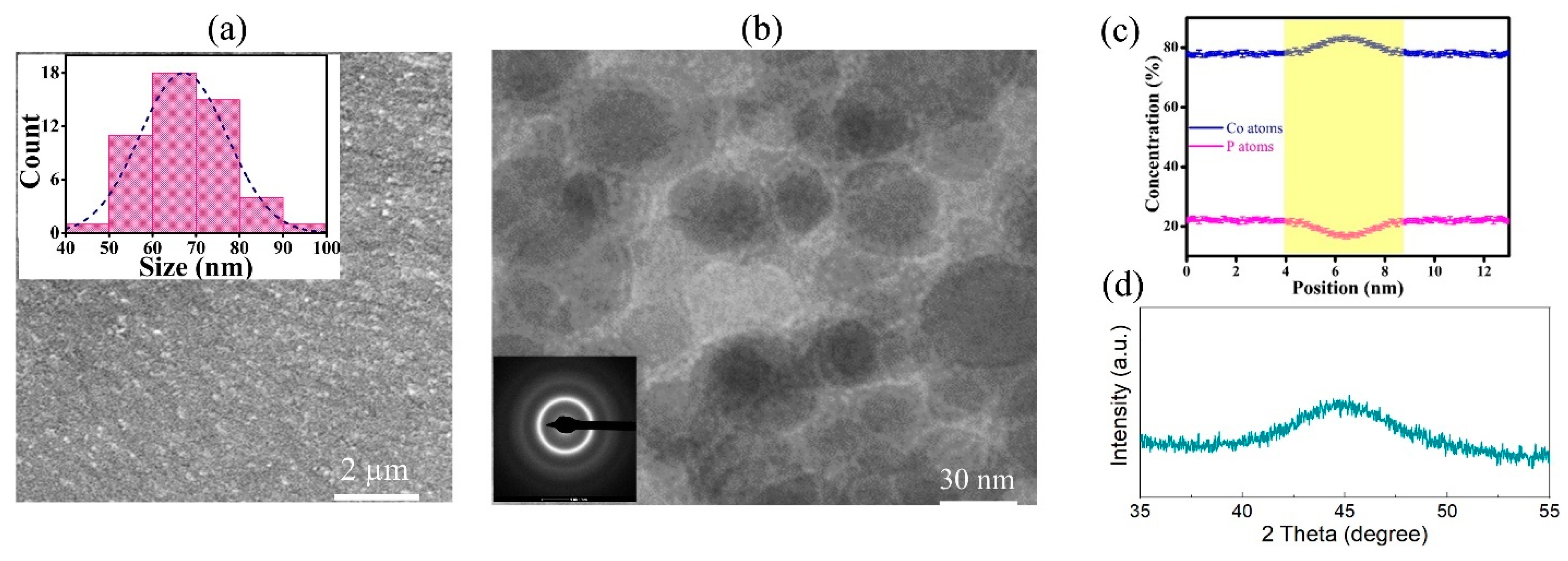
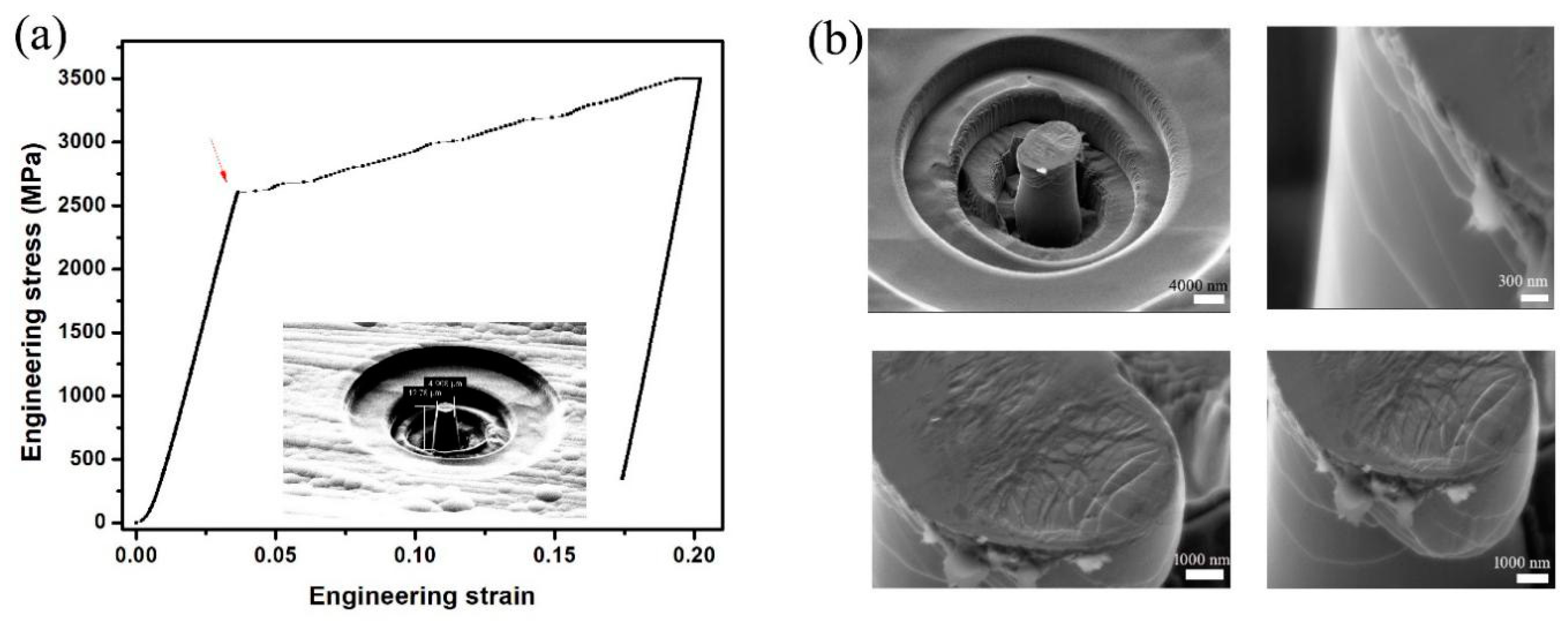
| GGI Incline Angle (°) | Region | D0 (10−9 m2/s) | Ea (eV) | D (10−11 m2/s) at T = 300 K | BCC-like VPs (%) | Icosahedron <0,0,12,0> (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | P | Co | P | Co | P | ||||
| 10 | GGI | 1.0861 | 1.0112 | 0.0784 | 0.0767 | 6.1490 | 6.0229 | 18.2 | 3.7 |
| MG | 1.2952 | 1.2371 | 0.0871 | 0.0857 | 5.5274 | 5.5119 | |||
| 20 | GGI | 1.0793 | 1.2374 | 0.0834 | 0.0829 | 5.5524 | 5.4942 | 18.0 | 3.8 |
| MG | 1.1391 | 1.0928 | 0.0870 | 0.0858 | 4.8682 | 4.8477 | |||
| 30 | GGI | 0.9701 | 0.9126 | 0.0807 | 0.0790 | 5.1572 | 5.1374 | 18.2 | 3.6 |
| MG | 1.1057 | 1.0255 | 0.0877 | 0.0853 | 4.6282 | 4.5856 | |||
| 40 | GGI | 1.1301 | 1.0642 | 0.0922 | 0.0906 | 3.9001 | 3.8102 | 18.4 | 3.5 |
| MG | 0.9453 | 0.8948 | 0.0874 | 0.0858 | 4.1331 | 4.0989 | |||
| 50 | GGI | 0.9606 | 0.9012 | 0.0862 | 0.0846 | 3.9960 | 3.9357 | 18.6 | 3.3 |
| MG | 0.9720 | 0.9161 | 0.0876 | 0.0857 | 4.1142 | 4.0908 | |||
| 60 | GGI | 0.7579 | 0.7276 | 0.0845 | 0.0838 | 3.5312 | 3.4485 | 18.3 | 3.5 |
| MG | 0.8489 | 0.7922 | 0.0884 | 0.0862 | 3.4833 | 3.4529 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Zheng, G. Atomistic Simulation and Micro-Pillar Compression Studies on the Influence of Glass–Glass Interfaces on Plastic Deformation in Co-P Metallic Nano-Glasses. Materials 2025, 18, 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081853
Wang Y, Chen J, Li M, Zheng G. Atomistic Simulation and Micro-Pillar Compression Studies on the Influence of Glass–Glass Interfaces on Plastic Deformation in Co-P Metallic Nano-Glasses. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081853
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yongwei, Jiashu Chen, Mo Li, and Guangping Zheng. 2025. "Atomistic Simulation and Micro-Pillar Compression Studies on the Influence of Glass–Glass Interfaces on Plastic Deformation in Co-P Metallic Nano-Glasses" Materials 18, no. 8: 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081853
APA StyleWang, Y., Chen, J., Li, M., & Zheng, G. (2025). Atomistic Simulation and Micro-Pillar Compression Studies on the Influence of Glass–Glass Interfaces on Plastic Deformation in Co-P Metallic Nano-Glasses. Materials, 18(8), 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081853






