Ultrafast Rechargeable Aluminum-Chlorine Batteries Enabled by a Confined Chlorine Conversion Chemistry in Molten Salts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
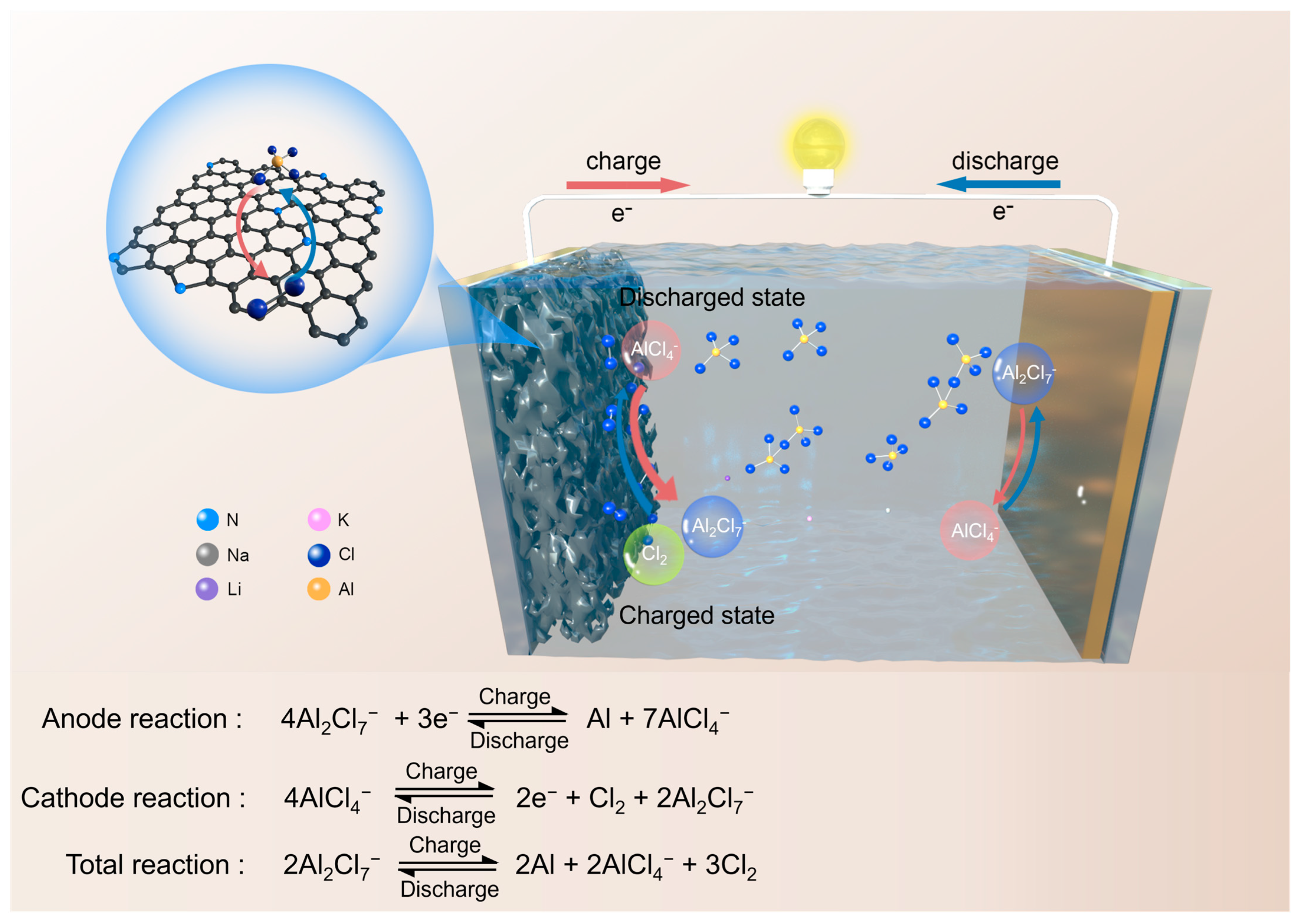
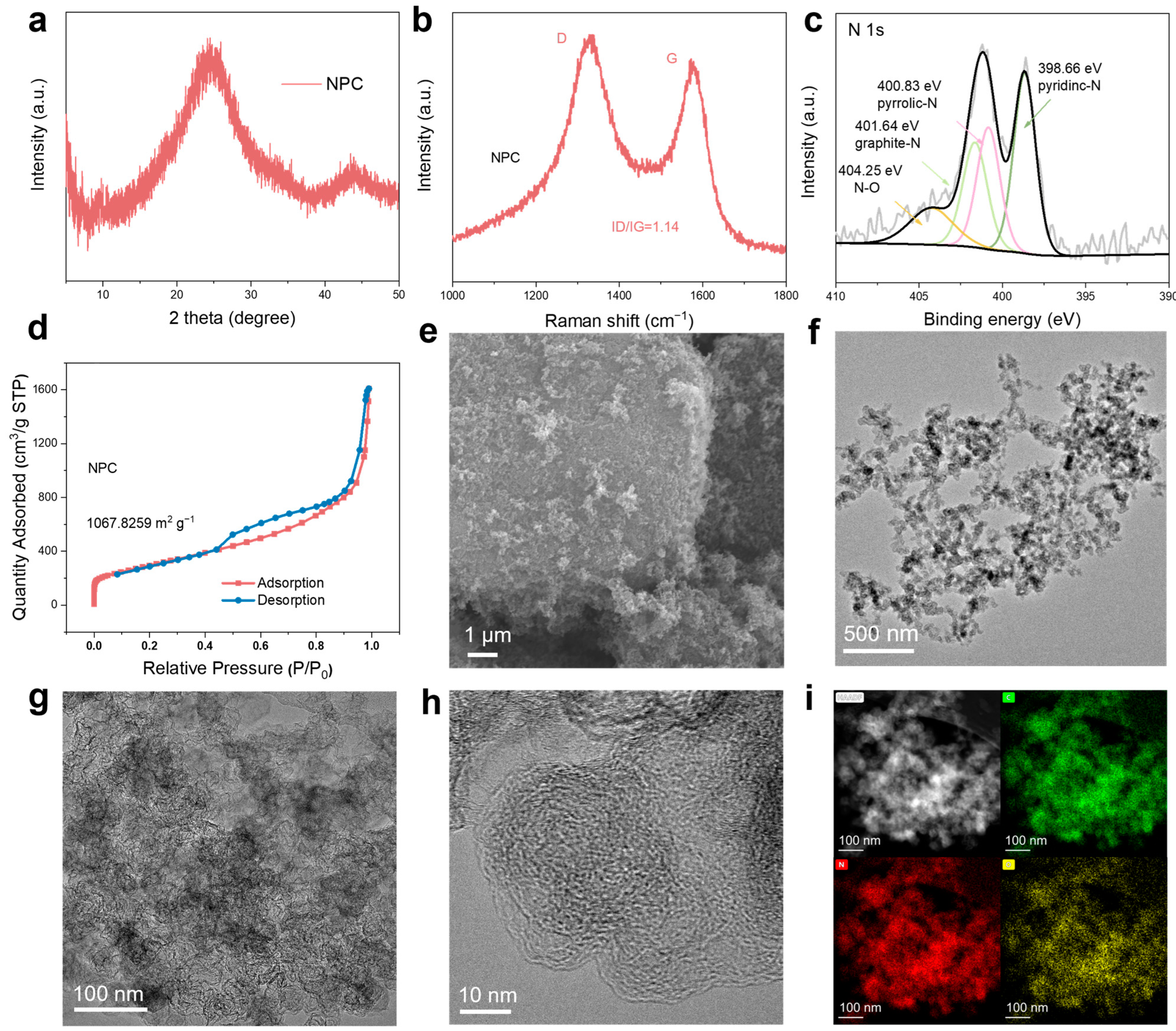
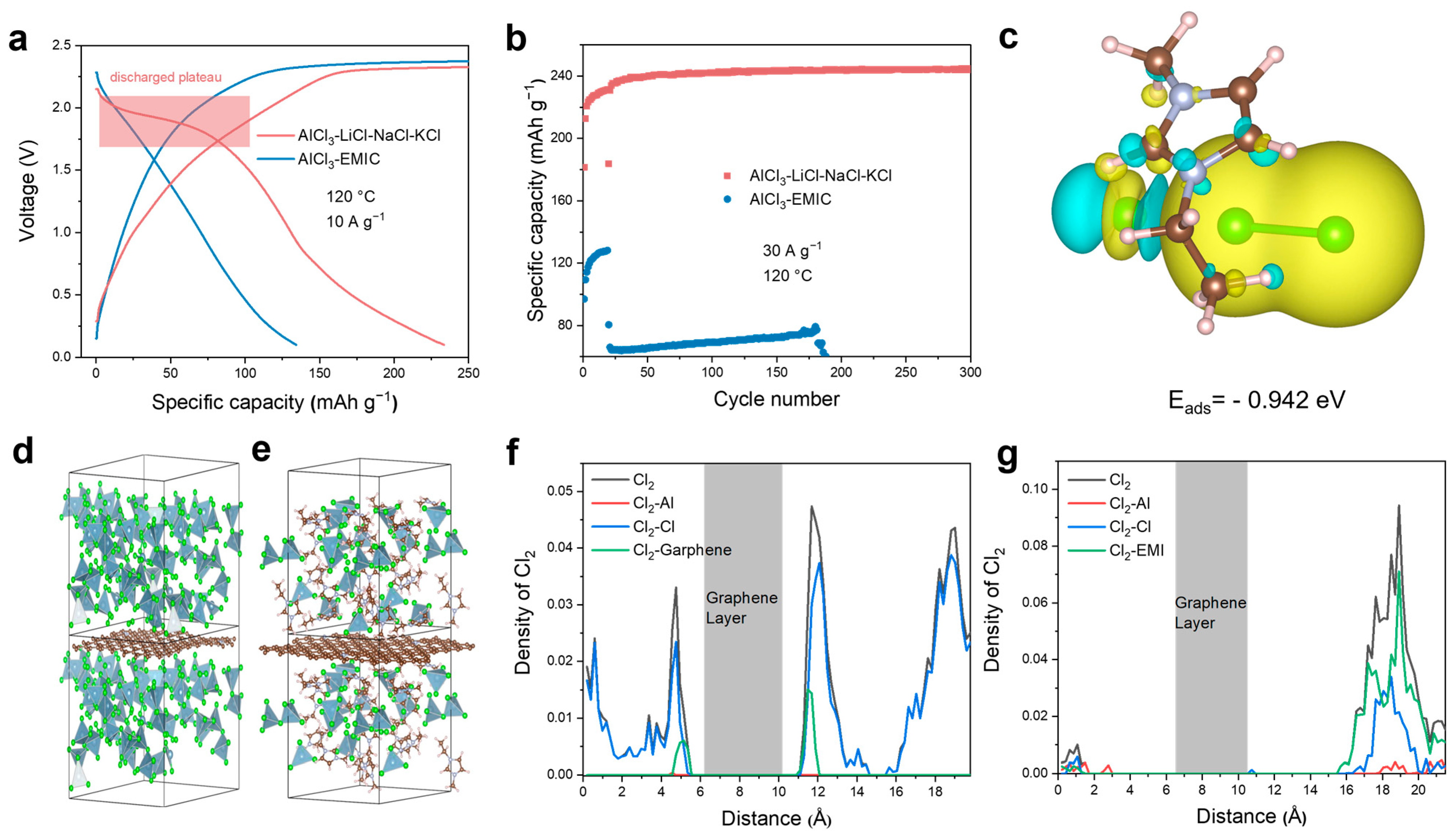
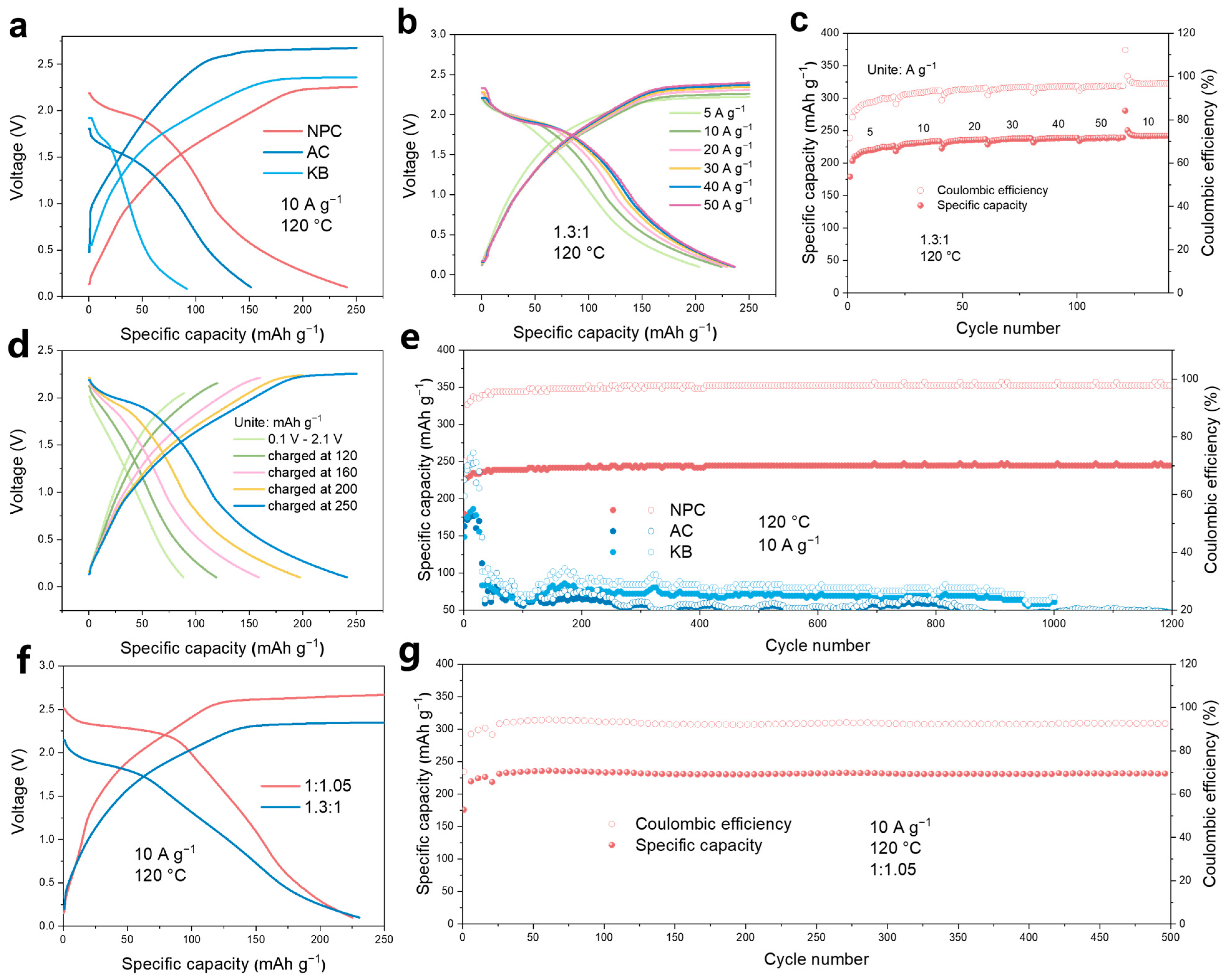
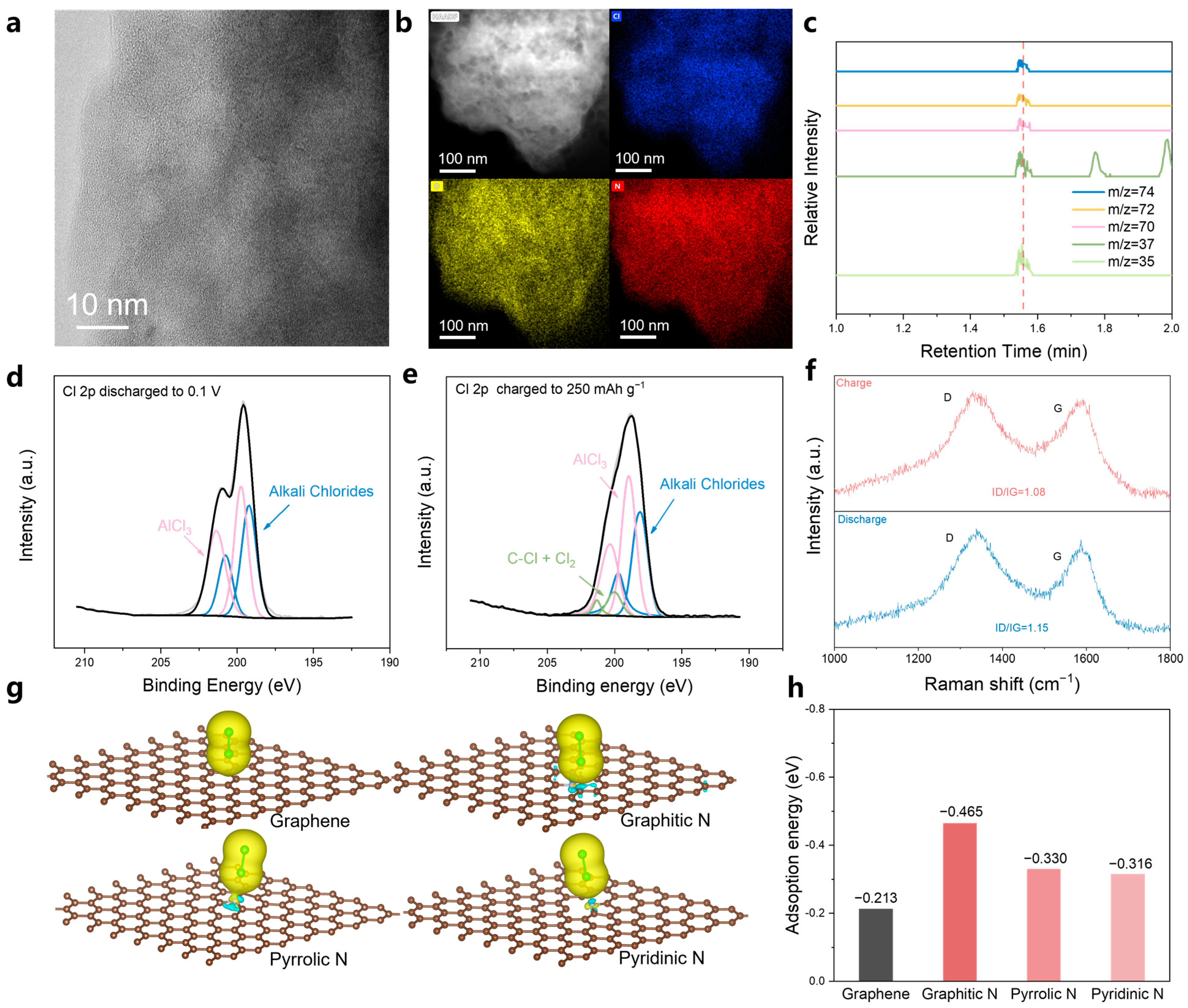
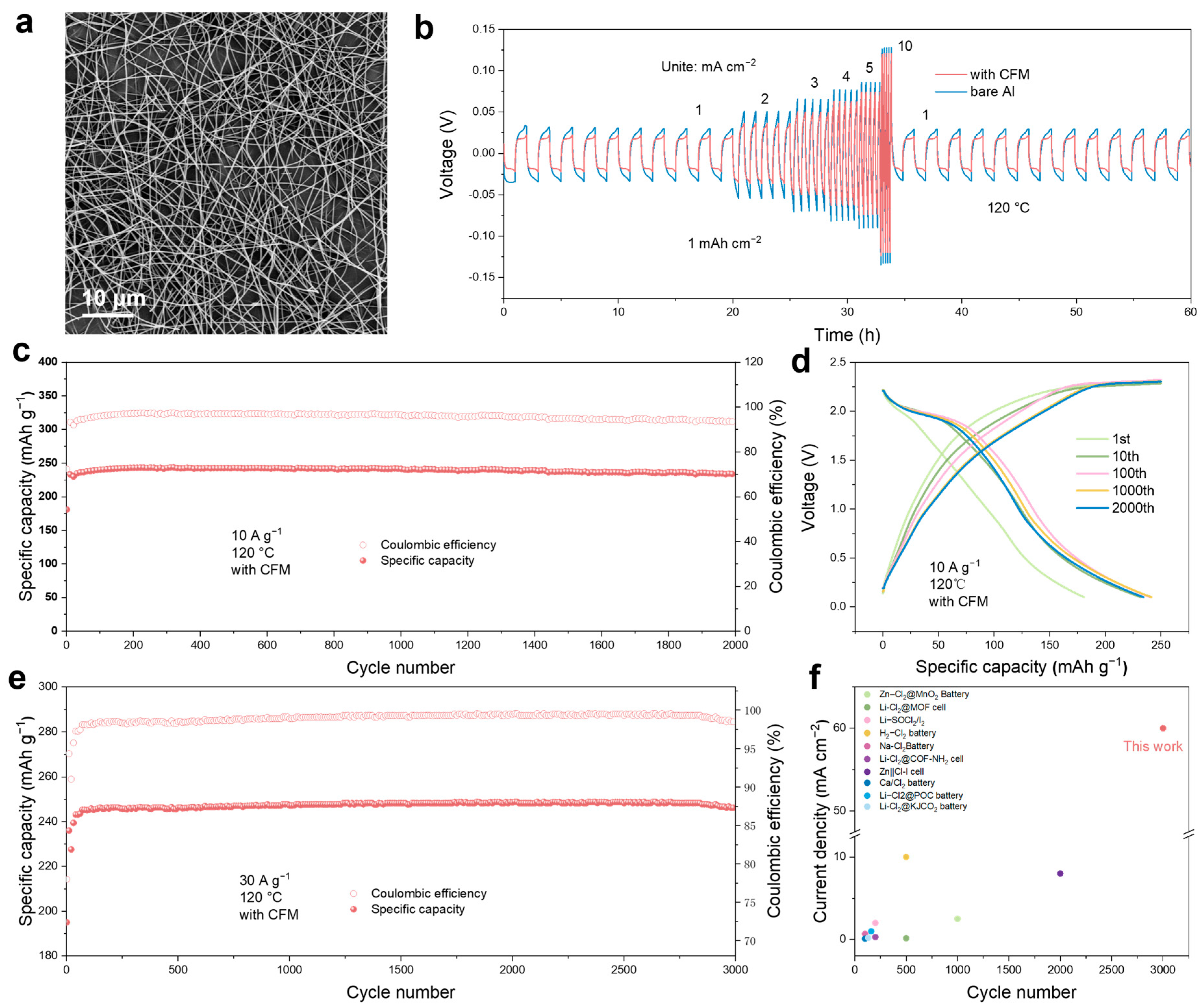
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, B.; Kamath, H.; Tarascon, J.-M. Electrical Energy Storage for the Grid: A Battery of Choices. Science 2011, 334, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Kintner-Meyer, M.C.W.; Lu, X.; Choi, D.; Lemmon, J.P.; Liu, J. Electrochemical Energy Storage for Green Grid. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3577–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, M.; Tarascon, J.M. Building better batteries. Nature 2008, 451, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lu, Y.-C. A retrospective on lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffner, F.; Kronemeyer, N.; Tübke, J.; Leker, J.; Winter, M.; Schmuch, R. Post-lithium-ion battery cell production and its compatibility with lithium-ion cell production infrastructure. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubi, G.; Dufo-López, R.; Carvalho, M.; Pasaoglu, G. The lithium-ion battery: State of the art and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.K.; Yang, L.; Brehm, W.; Adelhelm, P. From Lithium-Ion to Sodium-Ion Batteries: Advantages, Challenges, and Surprises. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 102–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-C.; Gong, M.; Lu, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.-Y.; Guan, M.; Angell, M.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Hwang, B.-J.; et al. An ultrafast rechargeable aluminium-ion battery. Nature 2015, 520, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, S.; Wheeler, S.; Capone, I.; Pasta, M. Outlook on K-Ion Batteries. Chem 2020, 6, 2442–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Du, A.; Sun, M.; Cui, G. Progress and perspective on rechargeable magnesium-ion batteries. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 214–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liang, G.; Cui, X.; Liu, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhi, C.; Yang, Y. Engineering hosts for Zn anodes in aqueous Zn-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Myung, S.-T.; Sun, Y.-K. Sodium-ion batteries: Present and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3529–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Xiao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Li, W.; et al. A family of dual-anion-based sodium superionic conductors for all-solid-state sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Mater. 2025, 24, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Xia, D.; Gabriel, E.; Russell, J.A.; Graff, K.; Ren, Y.; Sun, C.-J.; Lin, F.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, H. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Sodium-Ion Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 4023–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, S.; Cattermull, J.; Jagger, B.; Schart, M.; Olbrich, L.F.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sada, K.; Goodwin, A.; Pasta, M. Characterisation and modelling of potassium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jian, Z.; Yang, J.; Ji, X.; Liu, J. The Quest for Stable Potassium-Ion Battery Chemistry. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Fu, H.; Gao, C.; Fan, L.; Xie, E.; Lyu, W.; Zhou, J.; Lu, B. Tailoring Interface to Boost the High-Performance Aqueous Al Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.-E.; Thang, A.Q.; Yan, C.; Liu, C.; Lv, C.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, H.; Yan, Q. Rechargeable Aqueous Aluminum-Ion Battery: Progress and Outlook. Small 2022, 18, 2107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Jun, S.C.; Poznyak, S.; Guo, N.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Dai, L.; et al. Stabilizing Zinc Anode through Ion Selection Sieving for Aqueous Zn-Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 9137–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, B.D.; Mathieson, A.; Wen, B.; Feldmann, S.; Dose, W.M.; De Volder, M. Photo-rechargeable zinc-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ji, Y.; Ma, J.; Yu, H. Emerging Nonaqueous Aluminum-Ion Batteries: Challenges, Status, and Perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; He, K.; Cheng, H.-M.; Li, F. The Rechargeable Aluminum Battery: Opportunities and Challenges. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11978–11996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiku, M.; Takeda, H.; Matsumura, S.; Higuchi, E.; Inoue, H. Amorphous Vanadium Oxide/Carbon Composite Positive Electrode for Rechargeable Aluminum Battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24385–24389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Luo, B.; Ye, D.; Zhu, X.; Lyu, M.; Wang, L. An Innovative Freeze-Dried Reduced Graphene Oxide Supported SnS2 Cathode Active Material for Aluminum-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Han, F.; Fan, X.; Suo, L.; Pearse, A.J.; Lee, S.B.; Rubloff, G.W.; et al. A Rechargeable Al/S Battery with an Ionic-Liquid Electrolyte. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9898–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, S.; Meng, Z.; He, W.; Han, W.-Q. Rechargeable Aluminum/Iodine Battery Redox Chemistry in Ionic Liquid Electrolyte. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiao, S.; Tu, J.; Song, W.-L.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Lei, H.; Tian, D.; Chen, H.; et al. Rechargeable ultrahigh-capacity tellurium–aluminum batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yin, L.; Liang, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; He, K.; Ma, L.; Peng, Z.; Qiu, S.; et al. An Aluminum–Sulfur Battery with a Fast Kinetic Response. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Sun, L.; Sajid, M.; Feng, Y.; Lv, Z.; Chen, W. Rechargeable alkali metal–chlorine batteries: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 8424–8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Lei, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, M.; Scida, A.M.; Sandstrom, S.K.; Stickle, W.; O’Larey, T.D.; Jiang, D.-e.; et al. Li2MnO3: A Catalyst for a Liquid Cl2 Electrode in Low-Temperature Aqueous Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2302595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Zhi, C. Halogen-powered static conversion chemistry. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Chuai, M.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, K.; et al. Aqueous Zinc–Chlorine Battery Modulated by a MnO2 Redox Adsorbent. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2201553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Geng, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, C.; Sun, H. Revitalizing Chlorine–Based Batteries for Low–Cost and High–Performance Energy Storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, P.; Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Ding, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.; et al. Metal-organic frameworks for nanoconfinement of chlorine in rechargeable lithium-chlorine batteries. Joule 2023, 7, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Sajid, M.; Meng, Y.; Xie, Z.; Sun, L.; Jin, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, S. Organocatalytic Lithium Chloride Oxidation by Covalent Organic Frameworks for Rechargeable Lithium-Chlorine Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202315931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Deng, W.; Chen, R.; Cao, T.; Chai, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Metal Halides for High-Capacity Energy Storage. Small 2023, 19, 2205071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Liang, B.; Chen, A.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiong, B.; et al. Development of rechargeable high-energy hybrid zinc-iodine aqueous batteries exploiting reversible chlorine-based redox reaction. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, J.N.; Schlögl, R.; Menezes, P.W.; Driess, M. Is direct seawater splitting economically meaningful? Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3679–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Jorné, J. The Kinetics of a Chlorine Graphite Electrode in the Zinc-Chlorine Battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1977, 124, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralik, D.; Jorne, J. Hydrogen Evolution and Zinc Nodular Growth in the Zinc Chloride Battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1980, 127, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Tian, X.; Tai, H.-C.; Li, Y.-Y.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Liang, P.; Angell, M.; Huang, C.-L.; Ku, C.-S.; et al. Rechargeable Na/Cl2 and Li/Cl2 batteries. Nature 2021, 596, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Geng, S.; Cui, R.; Xiao, T.; Chen, P.; Wu, L.; Yu, W.; Peng, H.; et al. Ultrahigh-Rate Na/Cl2 Batteries Through Improved Electron and Ion Transport by Heteroatom-Doped Bicontinuous-Structured Carbon. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202312001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, W.; Du, X.; Wang, C.; Qu, X.; Gao, X.; Dong, S.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. Transforming a Primary Li-SOCl2 Battery into a High-Power Rechargeable System via Molecular Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 22158–22167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Nohira, T. Non-conventional electrolytes for electrochemical applications. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Chollier Brym, M.J.; Dubé, G.; Lasia, A.; Brisard, G.M. Electrodeposition of aluminium from ionic liquids: Part I—Electrodeposition and surface morphology of aluminium from aluminium chloride (AlCl3)–1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([EMIm]Cl) ionic liquids. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gu, S.; Bai, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhu, N.; Wu, C.; Wu, F. Anion-effects on electrochemical properties of ionic liquid electrolytes for rechargeable aluminum batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22677–22686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleck, G.L. The Reduction of Chlorine on Carbon in AlCl3-KCl-NaCl Melts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1972, 119, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jiao, S.; Tu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, H.; Mao, X.; Guo, Z.; Fray, D.J. A long-life rechargeable Al ion battery based on molten salts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Meng, J.; Gupta, S.; Hong, X.; Kwok, C.Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Xu, L.; Karahan, O.; Wang, Z.; et al. Fast-charging aluminium–chalcogen batteries resistant to dendritic shorting. Nature 2022, 608, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Sajid, M.; Chen, N.; Wang, M.; Meng, Y.; Peng, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; et al. Rechargeable Hydrogen–Chlorine Battery Operates in a Wide Temperature Range. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 25422–25430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.-A.; Wu, M.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X. Ionothermal Synthesis of Covalent Triazine Frameworks in a NaCl-KCl-ZnCl2 Eutectic Salt for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Hong, X.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Jia, Y.; Liu, F.; Mai, L.; Pang, Q. Rapid-charging aluminium-sulfur batteries operated at 85 °C with a quaternary molten salt electrolyte. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-W.; Wang, Z.-X.; Qu, F.; Chu, T.-W.; Wang, X.-Y. Reaction Mechanism of Cl2 and 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 13452–13466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, D.; Chiappe, C. What is the Nature of the First-Formed Intermediates in the Electrophilic Halogenation of Alkenes, Alkynes, and Allenes? Chem.—A Eur. J. 2003, 9, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, T.; Nishikawa, K. Syntheses and crystal structures of two ionic liquids with halogen-bonding groups: 4,5-dibromo- and 4,5-diiodo-1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonates. Solid State Sci. 2010, 12, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Wu, C. Electrolytes for rechargeable aluminum batteries. Prog. Mater Sci. 2022, 128, 100960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trémillon, B.; Letisse, G. Proprietes en solution dans le tetrachloroaluminate de sodium fondu I. systemes “acide-base”. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1968, 17, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Liang, P.; Huang, C.-L.; Wu, S.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Li, Y.-Y.; Jiang, S.-K.; Huang, W.-H.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; et al. Shedding light on rechargeable Na/Cl2 battery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2310903120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhu, G.; Huang, C.-L.; Li, Y.-Y.; Sun, H.; Yuan, B.; Wu, S.-C.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Hwang, B.-J.; et al. Rechargeable Li/Cl2 Battery Down to −80 °C. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2307192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, B.; Wang, Y.; Liao, M.; Ye, L.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Wu, L.; et al. A rechargeable Ca/Cl2 battery. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Meng, Y.; Xie, Z.; Sun, L.; Huang, C.; Chen, W. Enrichment of Chlorine in Porous Organic Nanocages for High-Performance Rechargeable Lithium–Chlorine Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 27877–27885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeweyher, E.; Ehlert, S.; Hansen, A.; Neugebauer, H.; Spicher, S.; Bannwarth, C.; Grimme, S. A generally applicable atomic-charge dependent London dispersion correction. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 154122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Tong, X.; Guo, C.; Han, K.; Li, J.; et al. Ultrafast Rechargeable Aluminum-Chlorine Batteries Enabled by a Confined Chlorine Conversion Chemistry in Molten Salts. Materials 2025, 18, 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081868
Huang J, Xu L, Wang Y, Wu X, Zhang M, Zhang H, Tong X, Guo C, Han K, Li J, et al. Ultrafast Rechargeable Aluminum-Chlorine Batteries Enabled by a Confined Chlorine Conversion Chemistry in Molten Salts. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081868
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Junling, Linhan Xu, Yu Wang, Xiaolin Wu, Meng Zhang, Hao Zhang, Xin Tong, Changyuan Guo, Kang Han, Jianwei Li, and et al. 2025. "Ultrafast Rechargeable Aluminum-Chlorine Batteries Enabled by a Confined Chlorine Conversion Chemistry in Molten Salts" Materials 18, no. 8: 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081868
APA StyleHuang, J., Xu, L., Wang, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, M., Zhang, H., Tong, X., Guo, C., Han, K., Li, J., Meng, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Ultrafast Rechargeable Aluminum-Chlorine Batteries Enabled by a Confined Chlorine Conversion Chemistry in Molten Salts. Materials, 18(8), 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081868





