TaMoNbTiZr Multielement Alloy for Medical Instruments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
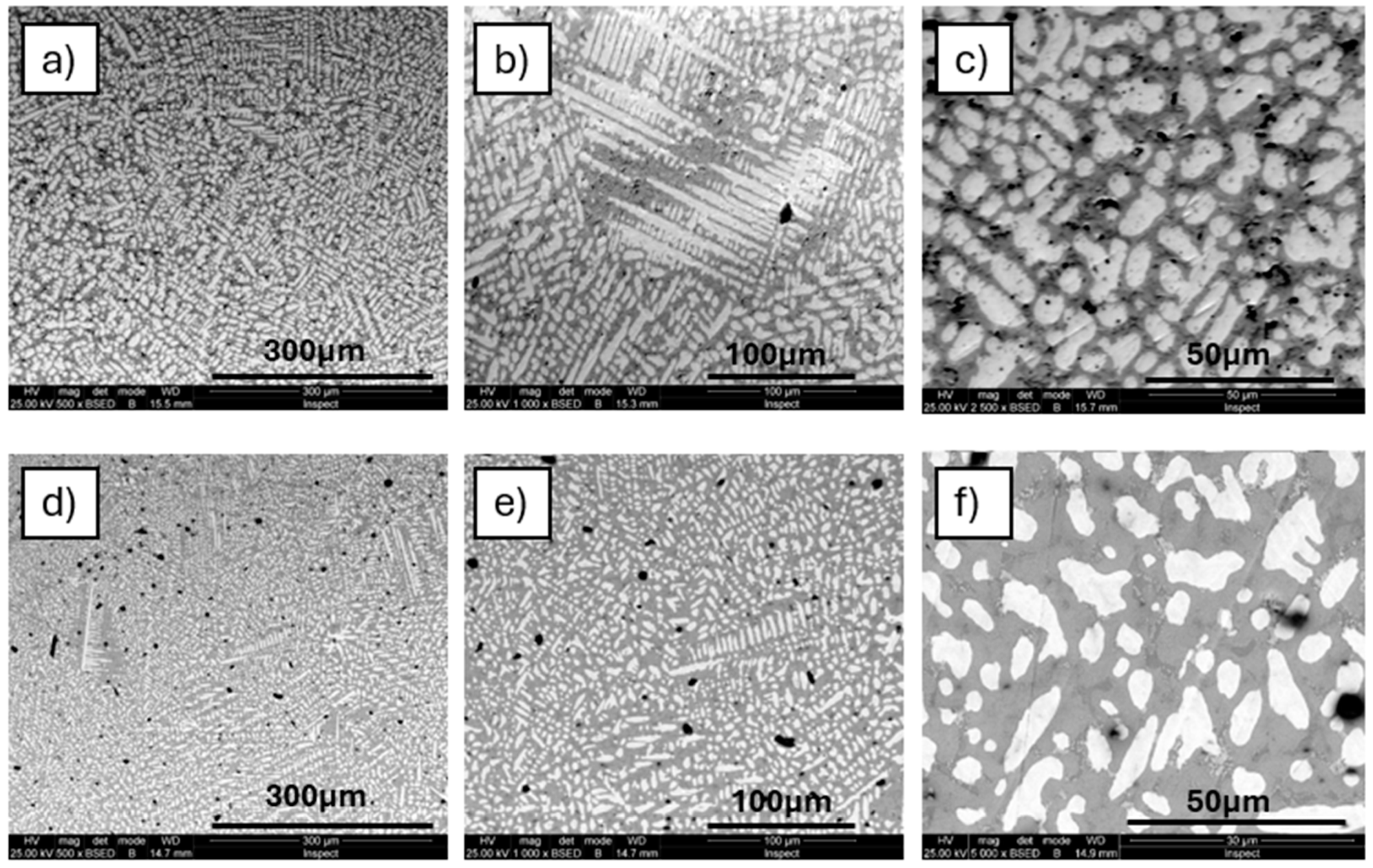
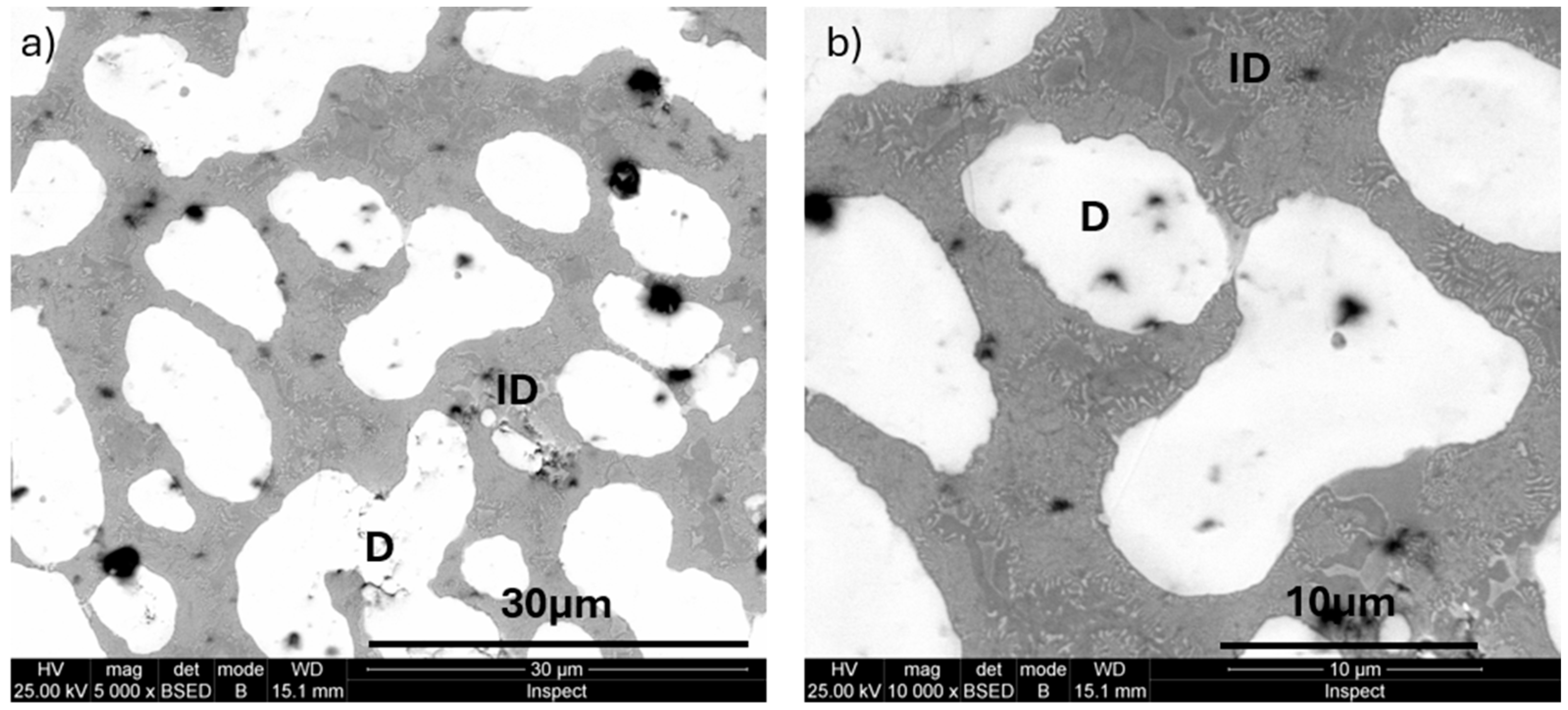
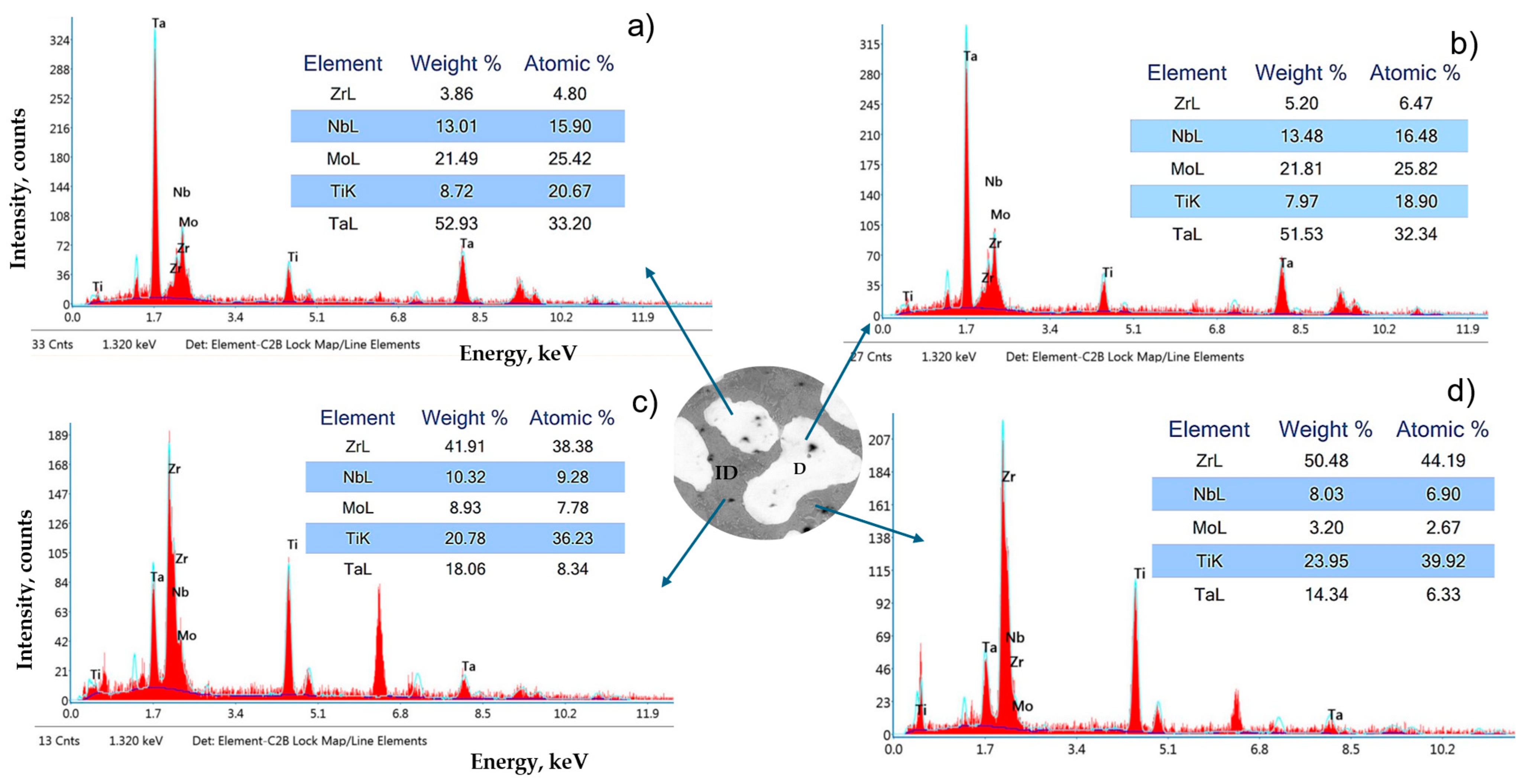
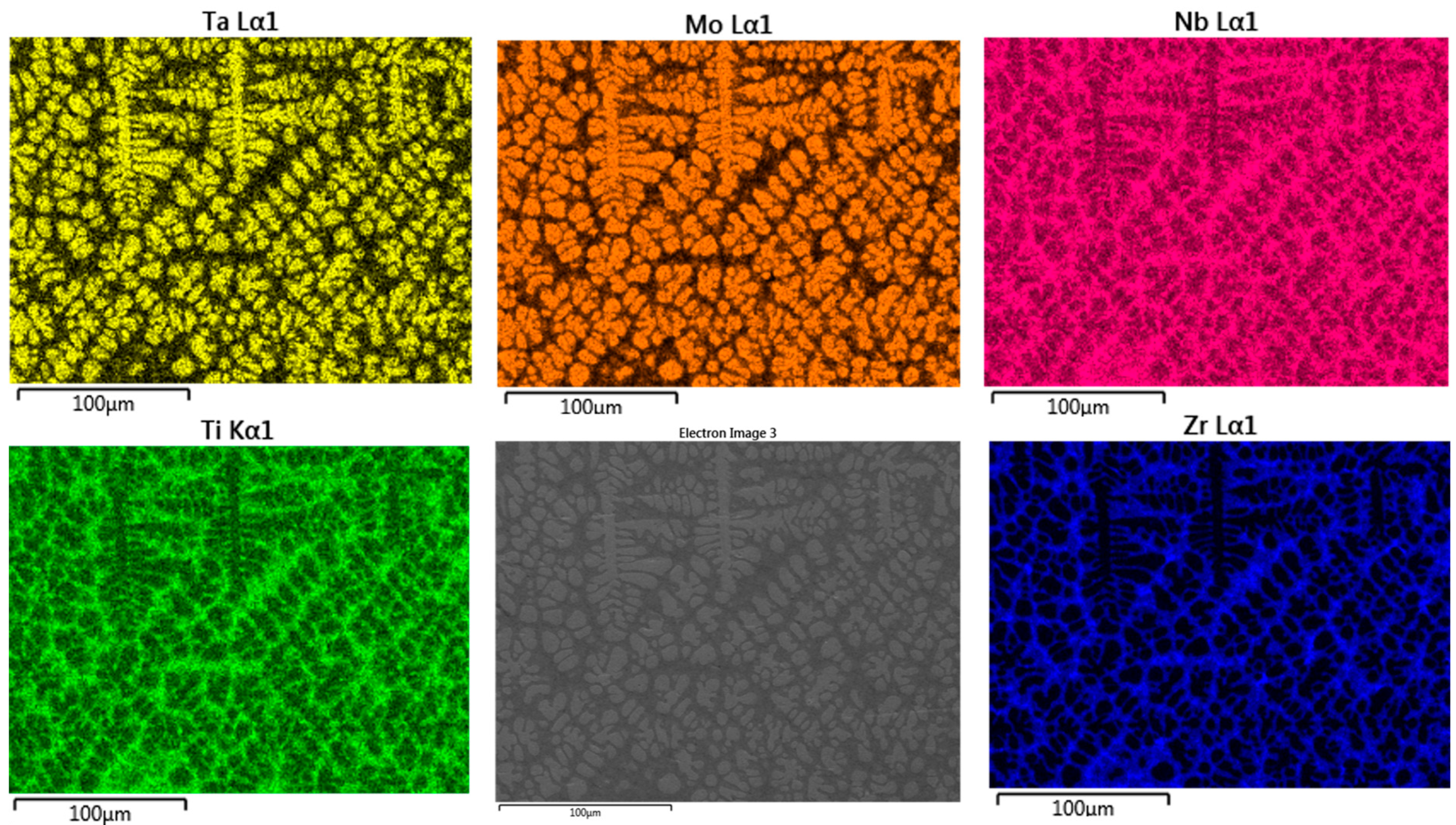
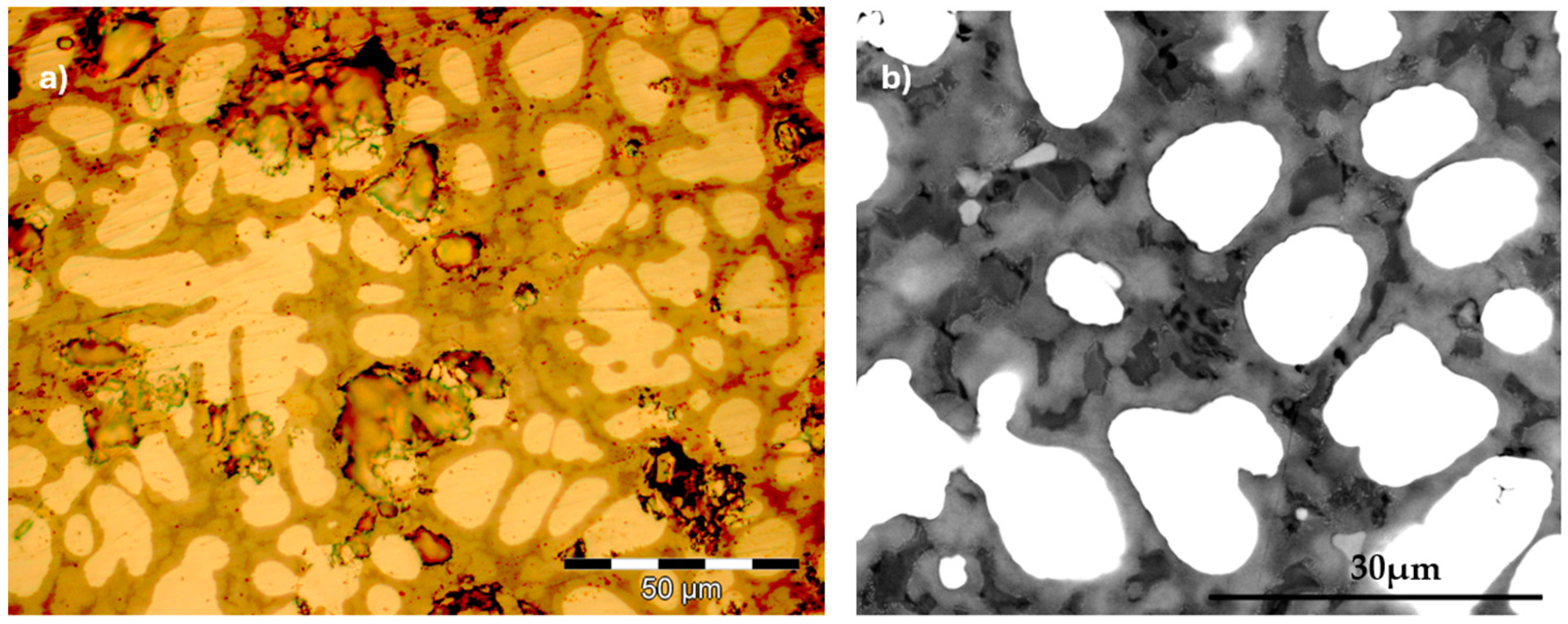
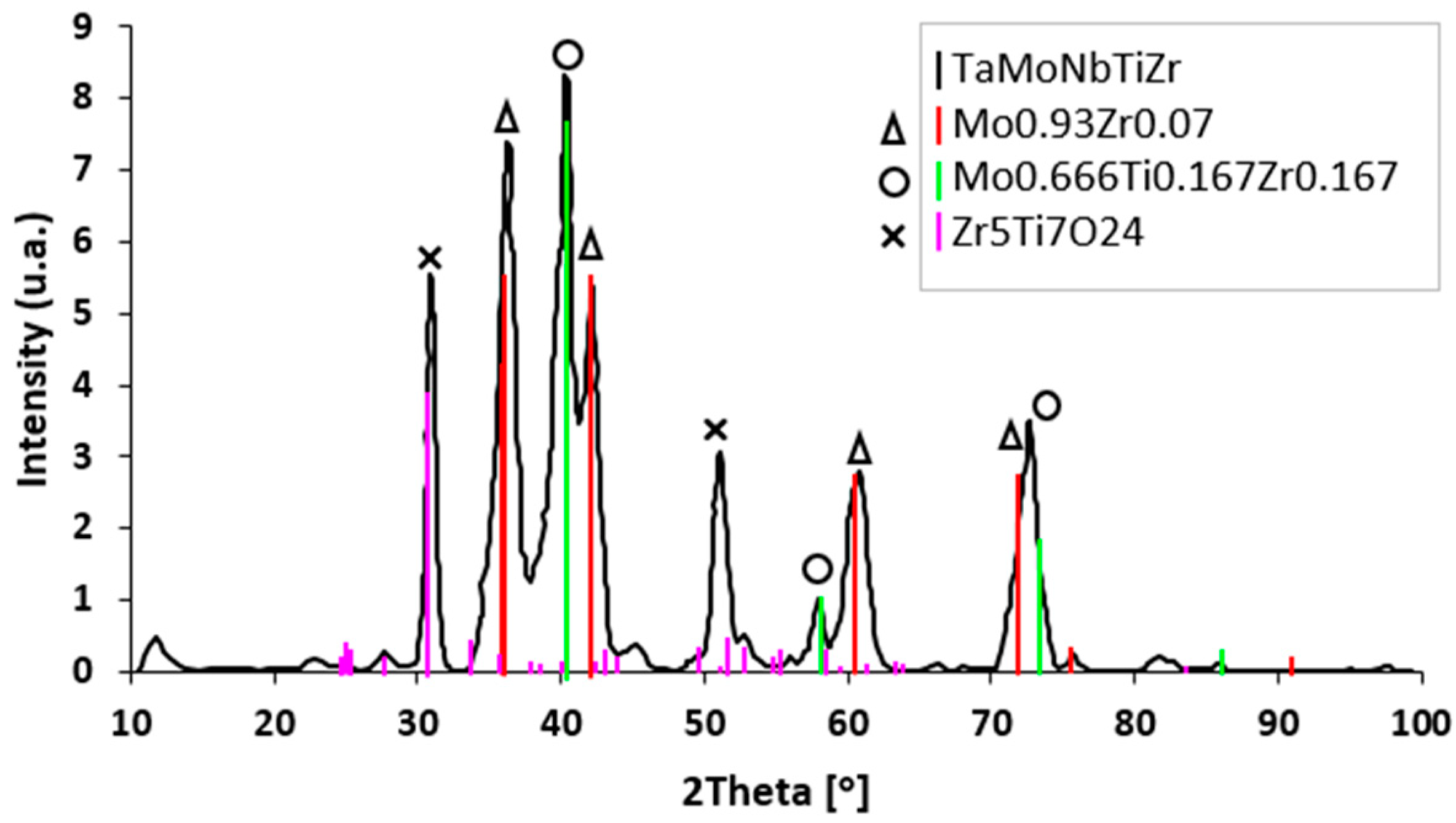
3.1. Microstructure
3.2. Microhardness
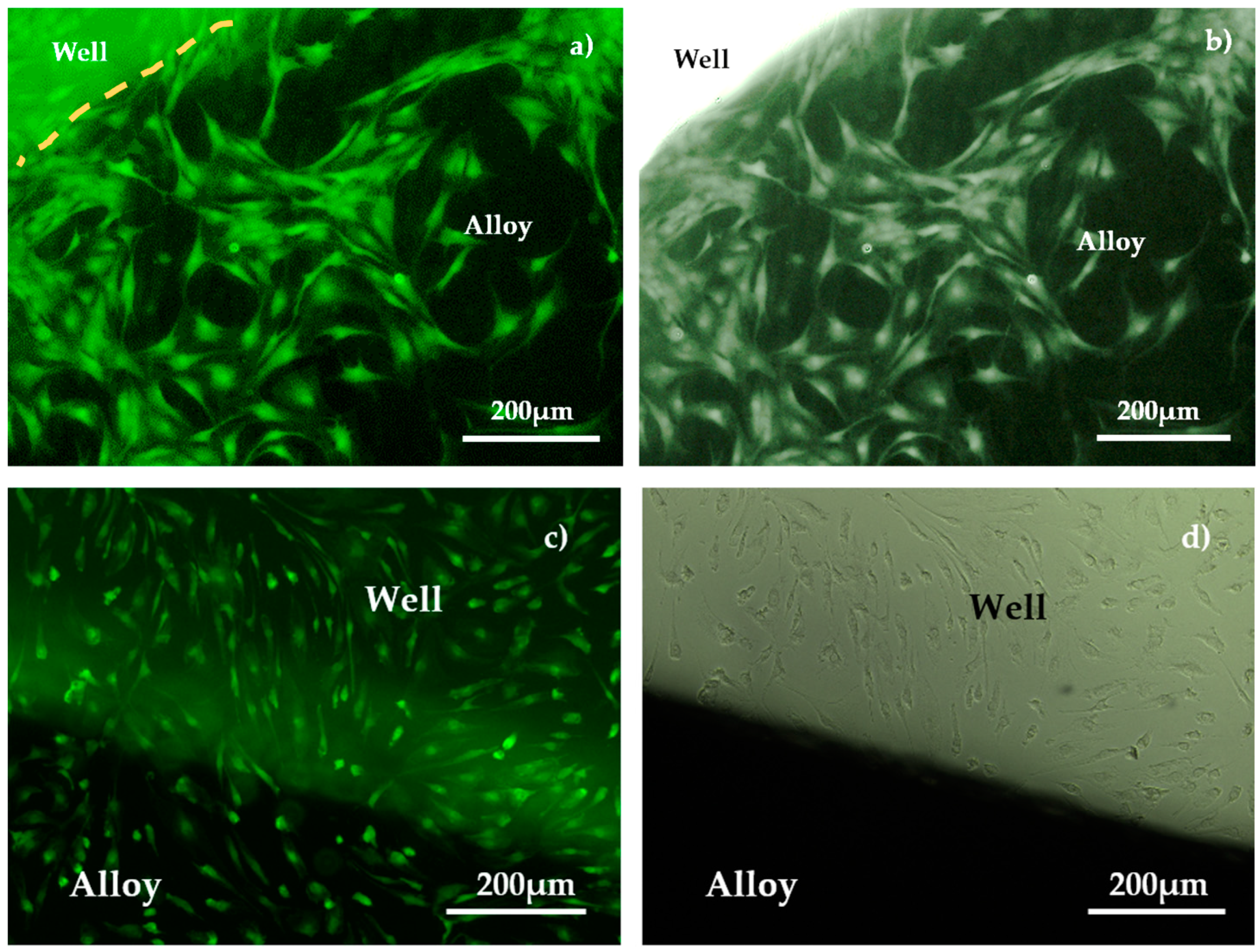
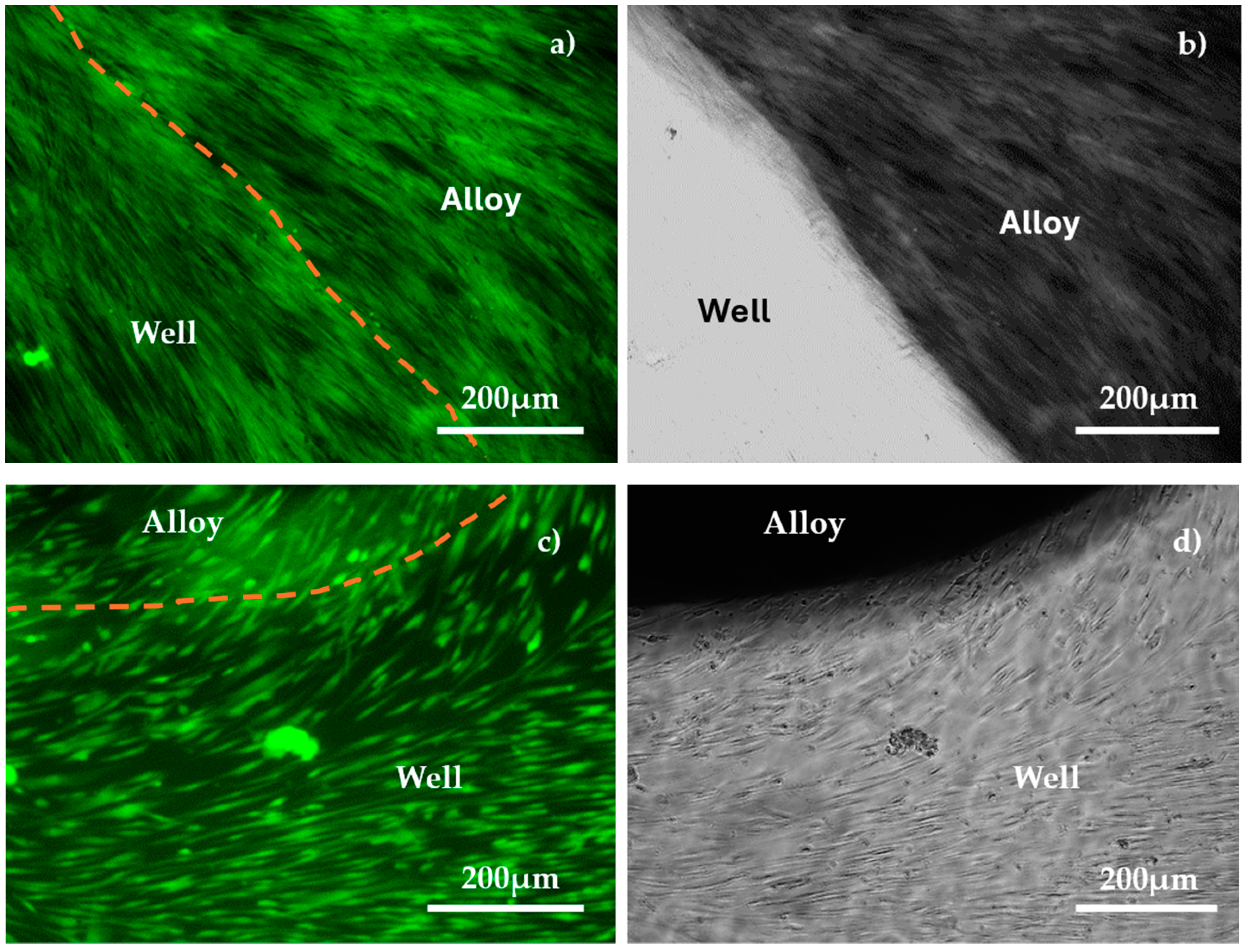
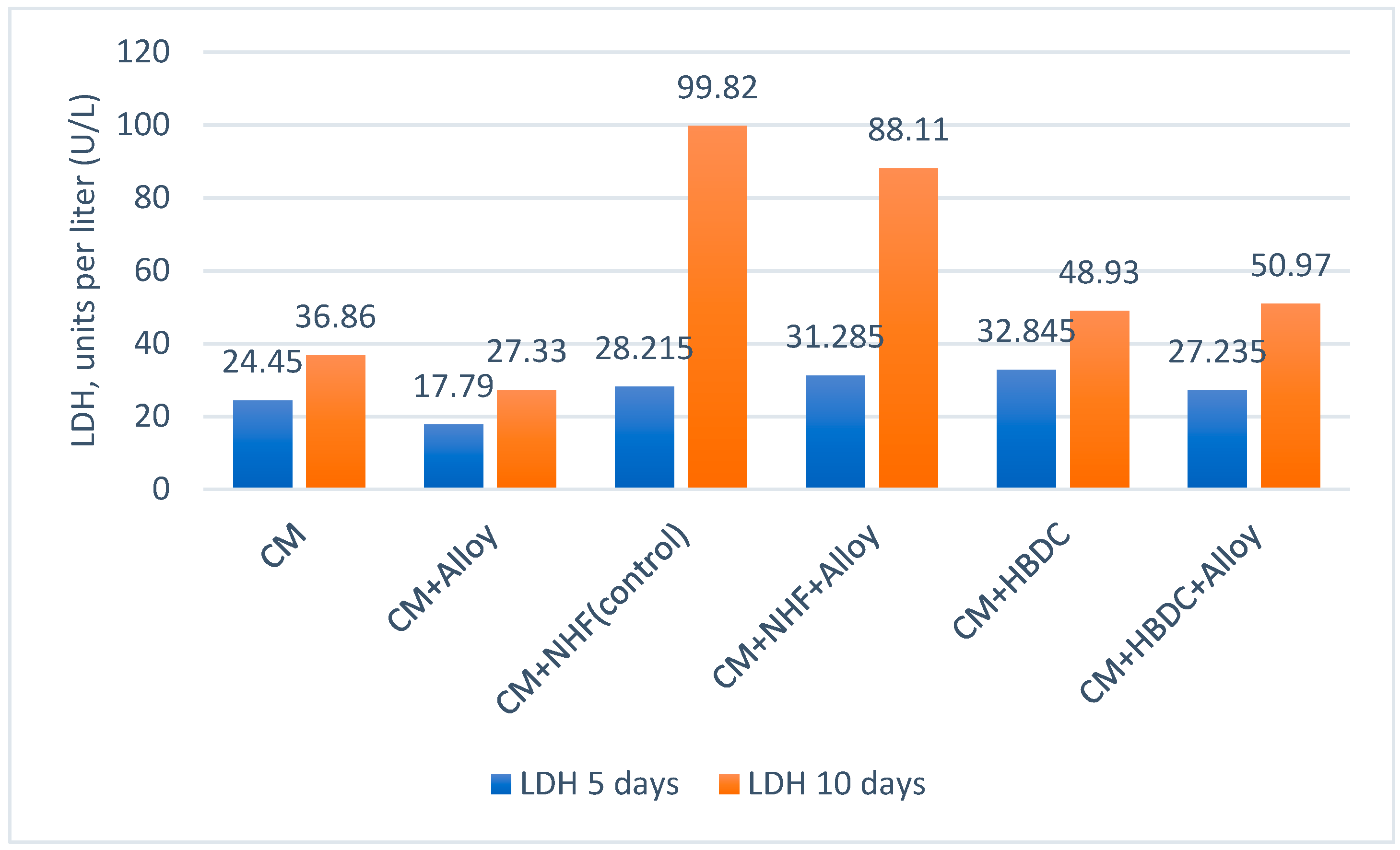
3.3. Biological Tests
3.3.1. Biocompatibility Test
3.3.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstructure Analysis
4.2. Microhardness Evolution
4.3. Biocompatibility Analysis
4.3.1. Biological Evaluation
4.3.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MEA | Multielement alloys |
| b.c.c. | Body-centered cubic |
| f.c.c. | Face-centered cubic |
| HBDC | Bone mesenchymal stem cells |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| NHF | Normal human fibroblast |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified minimal essential medium |
| HBMSC | Human bone mesenchymal stem cells |
| CM | Culture media |
| FOV | Field of view |
| HV | Vickers hardness |
References
- Liu, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, L.; Liang, H.; Lu, W.; Wang, L. Medical high-entropy alloy: Outstanding mechanical properties and superb biological compatibility. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 952536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.-W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrisna; Prasetiyo, A.B.; Kartikasari, R.; Aziz, I. Effect of milling time variation on TiTaVWCr HEA powder as nuclear material on microstructure and mechanical properties by a mechanical alloying method. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1151, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Gan, G.; Tang, B. The mechanical properties of high entropy (-like) alloy Wx (TaTiVCr)1-x via first-principles calculations. Fusion Eng. Des. 2018, 137, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Mahajan, C.; Muskeri, S.; Mukherjee, S. Corrosion Behavior of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys in FLiNaK Molten Salts. Metals 2023, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Garcia, S.J.; Mirza-Rosca, J.C.; Jimenez-Marcos, C.; Voiculescu, I. EIS Study of doped high-entropy alloy. Metals 2023, 13, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltatu, M.S.; Spataru, M.C.; Verestiuc, L.; Balan, V.; Solcan, C.; Sandu, A.V.; Geanta, V.; Voiculescu, I.; Vizureanu, P. Design, Synthesis, and Preliminary Evaluation for Ti-Mo-Zr-Ta-Si Alloys for Potential Implant Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, Y.; Pang, S.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, T. Bio-corrosion behaviour and in vitro biocompatibility of equimolar TiZrHfNbTa high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2020, 124, 106845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, O.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.M.; Ryu, H.J. The effect of Ti on the sintering and mechanical properties of refractory high-entropy alloy TixWTaVCr fabricated via spark plasma sintering for fusion plasma-facing materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codescu, M.M.; Vladescu, A.; Geanta, V.; Voiculescu, I.; Pana, I.; Dinu, M.; Kiss, A.E.; Braic, V.; Patroi, D.; Marinescu, V.E.; et al. Zn-based hydroxyapatite-based coatings deposited on a novel FeMoTaTiZr biocompatible high entropy alloy used for bone implants. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelwal, S. Biomaterials and Its Applications; CSIR-CSIR: Chandigarh, India, 2013; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, G.A. The importance of metallic materials as biomaterials. Adv. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 3, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambic, H.E. Changing strategies for biomaterials and biotechnology. In Biomaterials Mechanical Properties; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1994; pp. 293–301. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, M.; Singh, Y.; Arora, P.; Arora, V.; Jain, K. Implant biomaterials: A comprehensive review. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, N.; Jiang, Q.; Li, N.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Z. Phase stability of a ductile single-phase BCC Hf0.5Nb0.5Ta0.5Ti1.5Zr refractory high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2018, 98, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, B.; Shen, T. Ultrahard bulk nanocrystalline VNbMoTaW high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 69, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todai, M.; Nagase, T.; Hori, T.; Matsugaki, A.; Sekita, A.; Nakano, T. Novel TiNbTaZrMo high-entropy alloys for metallic biomaterials. Scripta. Mater. 2017, 129, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Tong, Y.; Tseng, K.-K.; Yeh, J.-W.; Poplawsky, J.; Wen, J.; Gao, M.; Kim, G.; Chen, W.; Ren, Y.; et al. Phase transformations of HfNbTaTiZr high-entropy alloy at intermediate temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2019, 158, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-P.; Xu, J. TiZrNbTaMo high-entropy alloy designed for orthopaedic implants: As-cast microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 73, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.; Scott, J.; Senkova, S.; Miracle, D.; Woodward, C. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6043–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Meisenkothen, F.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and elevated temperature properties of a refractory TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4062–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Tseng, K.; Hsu, W.; Tsai, M.; Tsai, C.; Lin, C.; Chen, S.; Lin, S.; Yeh, J.W. Solution strengthening of ductile refractory HfMoxNbTaTiZr high-entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2016, 175, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.; Li, X.; Su, Y.; Guo, J.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory MoNbHfZrTi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 81, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of Zr content on microstructure and mechanical properties of MoNbTaTiZrx refractory high-entropy alloy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2783, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Fu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z. Strategies for optimizing mechanical properties of refractory high entropy alloys induced by solid solution strengthening mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 923, 147696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.-K.; Juan, C.-C.; Tso, S.; Chen, H.-C.; Tsai, C.-W.; Yeh, J.-W. Effects of Mo, Nb, Ta, Ti, and Zr on Mechanical Properties of Equiatomic Hf-Mo-Nb-Ta-Ti-Zr Alloys. Entropy 2019, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzinié, J.-P.; Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Dirras, G. Comprehensive data compilation on the mechanical properties of refractory high-entropy alloys. Data Brief 2018, 21, 1622–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, J. Development of Refractory High Entropy Alloys with Tensile Ductility at Room Temperature. Metals 2023, 13, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geantă, V.; Voiculescu, I.; Miloșan, I.; Istrate, B.; Mateș, I.M. Chemical Composition Influence on Microhardness, Microstructure and Phase Morphology of AlxCrFeCoNi High Entropy Alloys. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Wu, W.; Hu, L.; Chen, Z. Structure and mechanical properties of ambient ductile TiZrNbHf refractory high-entropy alloy: A first principles and experimental study. Vacuum 2024, 233, 113910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roco Parra, F.R.; Deluigi, O.; Opazo, M.; Amigo, N.; Rojas-Nunez, J.; Valencia, F.; Tramontina, D.; Bringa, E.M. Temperature effects on the strength of a nanocrystalline refractory high entropy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 128, 107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Tsai, C.-W.; Lin, C.-M.; Wang, W.-R.; Yang, C.-C.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W. Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2015, 62, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. Definitions in Biomaterials. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 1987, 4, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Verestiuc, L.; Spataru, M.-C.; Baltatu, M.S.; Butnaru, M.; Solcan, C.; Sandu, A.V.; Voiculescu, I.; Geanta, V.; Vizureanu, P. New Ti–Mo–Si materials for bone prosthesis applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 113, 104198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spataru, C.M.; Butnaru, M.; Sandu, A.V.; Vulpe, V.; Vlad, M.D.; Baltatu, M.S.; Geanta, V.; Voiculescu, I.; Vizureanu, P.; Solcan, C. In-depth Assessment of New Ti-based Biocompatible Materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rios, M.; Brito-Garcia, S.; Mirza-Rosca, J.C.; Voiculescu, I. Comparative Study of (Fe,Nb)MoTaTiZr High Entropy Alloys in Ringer Grifols Solution. Metals 2024, 14, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, B.; Souza, N.D.; Mason, C.; Dong, H.B. Influence of Al and Nb on castability of a Ni-base superalloy IN713LC. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2009, 22, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.; James, P.F.; Akbarzadeh, R.; Subramanian, A.; Flavin, C.; Oudadesse, H. Prospect of stem cells in bone tissue engineering: A review. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Hellwarth, P.B.; Bao, X. Biomaterials for stem cell engineering and biomanufacturing. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Peng, S.; Feng, P.; Shuai, C. Bone biomaterials and interactions with stem cells. Bone Res. 2017, 5, 17059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselme, K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dito, W.R. Lactate dehydrogenase: A brief review. Clin. Enzymol. 1979, 1, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.F. On the nature of biomaterials. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5897–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 17639:2022; Destructive Tests on Welds in Metallic Materials—Macroscopic and Microscopic Examination of Welds. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- SR EN ISO 6507-1:2006; Metallic Materials—Vickers Hardness Test—Part 1: Test Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Gartland, A.; Rumney, R.M.H.; Dillon, J.P.; Gallagher, J.A. Isolation and culture of Human Osteoblasts. Hum. Cell Cult. Protoc. 2012, 806, 337–355. [Google Scholar]
- Roche Lactate Dehydrogenase Acc. to IFCC Ver.2. Available online: https://diagnostics.roche.com/global/en/products/lab/ldhi2-cps-000156.html (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Lei, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, S.; Hui, X.; Wu, Y.; Gault, B.; Kontis, P.; et al. Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes. Nature 2018, 563, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.-C.; Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Hsu, W.L.; Lin, C.M.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W. Simultaneously increasing the strength and ductility of a refractory highentropy alloy via grain refining. Mater. Lett. 2016, 184, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Zhao, X.; Yi, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, G.; You, D.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Effect of phase decomposition on the mechanical properties of Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Mo multi-principal element alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 199, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lai, W.; He, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, Q.; You, D.; Cao, S.; Li, W.; Wang, X. Correlations between local chemical fluctuations and grain boundary strength in Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Mo refractory multi-principal element alloys. Scr. Mater. 2025, 256, 116438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Zou, Y. Enhanced elasticity, fracture toughness and hardness in refractory TiZrHfNb high-entropy alloys by N-and O-doping engineering. Intermetallics 2025, 181, 108714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, S.; Guo, Y.; Di, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, C. Dynamic mechanical response of TaMoNbZrTi refractory high entropy alloy via multi-wire arc additive manufacturing. Philos. Mag. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Alloy | Individual Values | Average Value | Coefficient of Variation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast state | |||||||
| TaMoNbTiZr | 515 | 535 | 565 | 564 | 546 | 545 | 3.85 |
| Annealed and quenched | |||||||
| TaMoNbTiZr | 986 | 941 | 999 | 998 | 994 | 984 | 2.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mates, I.M.; Geanta, V.; Manu, D.; Kelemen, H.; Onici, A.E.; Mirza-Rosca, J.C.; Voiculescu, I. TaMoNbTiZr Multielement Alloy for Medical Instruments. Materials 2025, 18, 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081876
Mates IM, Geanta V, Manu D, Kelemen H, Onici AE, Mirza-Rosca JC, Voiculescu I. TaMoNbTiZr Multielement Alloy for Medical Instruments. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081876
Chicago/Turabian StyleMates, Ileana Mariana, Victor Geanta, Doina Manu, Hajnal Kelemen, Adrian Emanuel Onici, Julia Claudia Mirza-Rosca, and Ionelia Voiculescu. 2025. "TaMoNbTiZr Multielement Alloy for Medical Instruments" Materials 18, no. 8: 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081876
APA StyleMates, I. M., Geanta, V., Manu, D., Kelemen, H., Onici, A. E., Mirza-Rosca, J. C., & Voiculescu, I. (2025). TaMoNbTiZr Multielement Alloy for Medical Instruments. Materials, 18(8), 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081876









