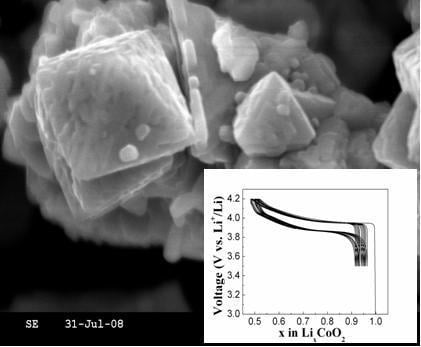
Nitrate-Melt Synthesized HT-LiCoO2 as a Superior Cathode-Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
Share and Cite
Sathiya, M.; Prakash, A.S.; Ramesha, K.; Shukla, A.K. Nitrate-Melt Synthesized HT-LiCoO2 as a Superior Cathode-Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials 2009, 2, 857-868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2030857
Sathiya M, Prakash AS, Ramesha K, Shukla AK. Nitrate-Melt Synthesized HT-LiCoO2 as a Superior Cathode-Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials. 2009; 2(3):857-868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2030857
Chicago/Turabian StyleSathiya, Mariyappan, Annigere S. Prakash, Kannadka Ramesha, and Ashok K. Shukla. 2009. "Nitrate-Melt Synthesized HT-LiCoO2 as a Superior Cathode-Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries" Materials 2, no. 3: 857-868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2030857
APA StyleSathiya, M., Prakash, A. S., Ramesha, K., & Shukla, A. K. (2009). Nitrate-Melt Synthesized HT-LiCoO2 as a Superior Cathode-Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials, 2(3), 857-868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2030857