Current and Emerging Detoxification Therapies for Critical Care
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Motivation for Detoxification
3. Treatment Methods
3.1. Colloids and Particles

3.1.1. Important Design Parameters
3.1.2. Current and Emerging Colloid/Particle Therapies
 ) and unilamellar (
) and unilamellar (  ) liposomes and spherulites (
) liposomes and spherulites (  ) in the presence and absence of 50% fetal bovine serum (FBS), adapted from Dhanikula et al. [31] with permission.
) in the presence and absence of 50% fetal bovine serum (FBS), adapted from Dhanikula et al. [31] with permission.
 ) and unilamellar (
) and unilamellar (  ) liposomes and spherulites (
) liposomes and spherulites (  ) in the presence and absence of 50% fetal bovine serum (FBS), adapted from Dhanikula et al. [31] with permission.
) in the presence and absence of 50% fetal bovine serum (FBS), adapted from Dhanikula et al. [31] with permission.
 ) and 0.72 (
) and 0.72 (  ) mg lipid/mL, and 50:50 DMPC:DOPG liposomes (
) mg lipid/mL, and 50:50 DMPC:DOPG liposomes (  ) at 0.72 mg lipid/mL. Free drug reductions were calculated based on the differences between free drug concentrations in human serum samples and free drug concentrations in human serum samples mixed with liposomes. Figure adapted from [50].
) at 0.72 mg lipid/mL. Free drug reductions were calculated based on the differences between free drug concentrations in human serum samples and free drug concentrations in human serum samples mixed with liposomes. Figure adapted from [50].
 ) and 0.72 (
) and 0.72 (  ) mg lipid/mL, and 50:50 DMPC:DOPG liposomes (
) mg lipid/mL, and 50:50 DMPC:DOPG liposomes (  ) at 0.72 mg lipid/mL. Free drug reductions were calculated based on the differences between free drug concentrations in human serum samples and free drug concentrations in human serum samples mixed with liposomes. Figure adapted from [50].
) at 0.72 mg lipid/mL. Free drug reductions were calculated based on the differences between free drug concentrations in human serum samples and free drug concentrations in human serum samples mixed with liposomes. Figure adapted from [50].
 ) and by a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 1.44 mg lipid/mL (▲) and a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-5000 liposomes at 1.68 mg lipid/mL (
) and by a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 1.44 mg lipid/mL (▲) and a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-5000 liposomes at 1.68 mg lipid/mL (  ) versus final imipramine concentration. Figure adapted from [44].
) versus final imipramine concentration. Figure adapted from [44].
 ) and by a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 1.44 mg lipid/mL (▲) and a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-5000 liposomes at 1.68 mg lipid/mL (
) and by a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 1.44 mg lipid/mL (▲) and a mixture of human serum and 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-5000 liposomes at 1.68 mg lipid/mL (  ) versus final imipramine concentration. Figure adapted from [44].
) versus final imipramine concentration. Figure adapted from [44].
 ) and presence (
) and presence (  ) of unilamellar, 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 2.9 mg lipid/mL. Differences were significant at all concentrations tested (P = 0.037, 0.022, 0.042 and 0.018 for 5, 20, 35, and 50 µM, respectively). Figure adapted from [51].
) of unilamellar, 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 2.9 mg lipid/mL. Differences were significant at all concentrations tested (P = 0.037, 0.022, 0.042 and 0.018 for 5, 20, 35, and 50 µM, respectively). Figure adapted from [51].
 ) and presence (
) and presence (  ) of unilamellar, 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 2.9 mg lipid/mL. Differences were significant at all concentrations tested (P = 0.037, 0.022, 0.042 and 0.018 for 5, 20, 35, and 50 µM, respectively). Figure adapted from [51].
) of unilamellar, 95:5 DOPG:DPPE-mPEG-2000 liposomes at 2.9 mg lipid/mL. Differences were significant at all concentrations tested (P = 0.037, 0.022, 0.042 and 0.018 for 5, 20, 35, and 50 µM, respectively). Figure adapted from [51].
 ), 8.6 (
), 8.6 (  ), 38 (
), 38 (  ), and 150 (
), and 150 (  ) μM. Means are shown with n = 2-4. Marker denotes p < 0.05 (*). Figure adapted from [52].
) μM. Means are shown with n = 2-4. Marker denotes p < 0.05 (*). Figure adapted from [52].
 ), 8.6 (
), 8.6 (  ), 38 (
), 38 (  ), and 150 (
), and 150 (  ) μM. Means are shown with n = 2-4. Marker denotes p < 0.05 (*). Figure adapted from [52].
) μM. Means are shown with n = 2-4. Marker denotes p < 0.05 (*). Figure adapted from [52].

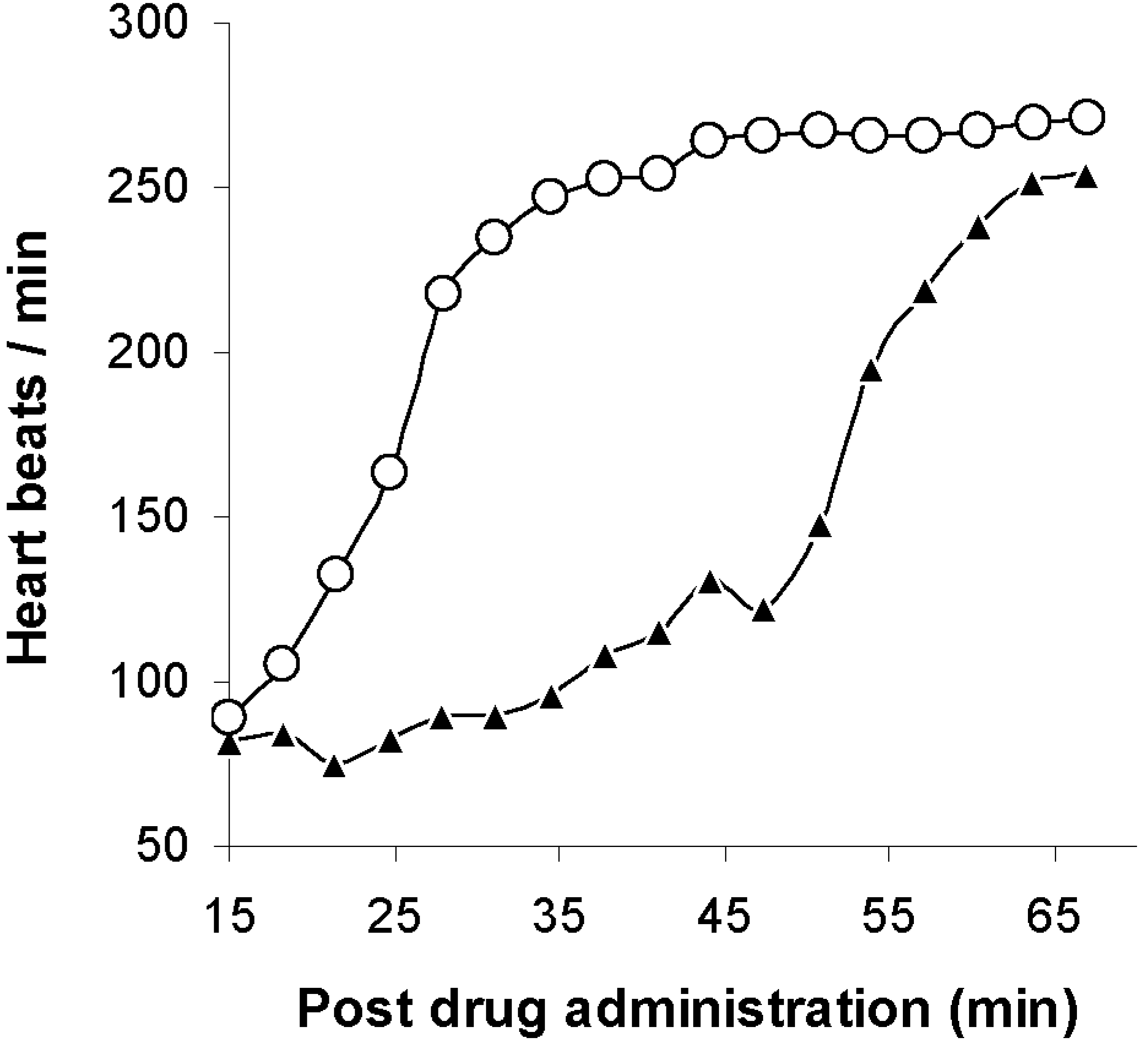
 ) and with sterically stabilized liposomes (
) and with sterically stabilized liposomes (  ) in mice. The potency ratio is the LD50 of the organophosphate diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) with the antagonist divided by the LD50 of DFP without the antagonists. Adapted from Petrikovics et al. with permission [58].
) in mice. The potency ratio is the LD50 of the organophosphate diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) with the antagonist divided by the LD50 of DFP without the antagonists. Adapted from Petrikovics et al. with permission [58].
 ) and with sterically stabilized liposomes (
) and with sterically stabilized liposomes (  ) in mice. The potency ratio is the LD50 of the organophosphate diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) with the antagonist divided by the LD50 of DFP without the antagonists. Adapted from Petrikovics et al. with permission [58].
) in mice. The potency ratio is the LD50 of the organophosphate diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) with the antagonist divided by the LD50 of DFP without the antagonists. Adapted from Petrikovics et al. with permission [58].
3.2. Antibody Fragments (Fab)
3.2.1. Important Design Parameters
3.2.2. Current and Emerging Fab Therapies
 ) and after a third dose of drug specific antibody fragments (
) and after a third dose of drug specific antibody fragments (  ) [76].
) [76].
 ) and after a third dose of drug specific antibody fragments (
) and after a third dose of drug specific antibody fragments (  ) [76].
) [76].
3.3. Indirect Treatment Methods
3.3.1. Important Design Parameters
3.3.2. Current and Emerging Indirect Treatment Methods
4. Conclusions
References and Notes
- Wysowski, D.K. Surveillance of prescription drug-related mortality using death certificate data. Drug Safety 2007, 30, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.A.; Alexander, C.A.; Sener, E.K. Relative mortality from overdose of antidepressants. Brit. Med. J. 1995, 310, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, G.W.; McGuffie, A.C.; Wilkie, S. Tricyclic antidepressant overdose: A review. Emerg. Med. J. 2001, 18, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyan, S.; Aksay, E.; Yanturali, S.; Atilla, R.; Ersel, M. Acute myocardial infarction associated with amitriptyline overdose. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 98, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebelt, E.L.; Francis, P.D. Cyclic Antidepressants. In Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 7th ed.; Goldfrank, L.R., Flomenbaum, N.E., Lewin, N.A., Howland, M.A., Hoffman, R.S., Nelson, L.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA; pp. 847–864.
- Morgan, O.; Griffiths, C.; Baker, A.; Majeed, A. Fatal toxicity of antidepressants in England and Wales, 1993–2002. Health Stat. Quart. 2004, 23, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Prahlow, J.A.; Landrum, J.E. Amitriptyline abuse and misuse. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2005, 26, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nau, C.; Seaver, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.K. Block of human heart hH1 sodium channels by amitriptyline. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zima, A.V.; Qin, J.; Fill, M.; Blatter, L.A. Tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline alters sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium handling in ventricular myocytes. Am. J. Physiol-Heart 2008, 295, H2008–H2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, K.; Cain, B.S.; Dart, R.C.; Cairns, C.B. Tricyclic antidepressants directly depress human myocardial mechanical function independent of effects on the conduction system. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unverir, P.; Atilla, R.; Karcioglu, O.; Topacoglu, H.; Demiral, Y.; Tuncok, Y. A retrospective analysis of antidepressant poisonings in the emergency department: 11-year experience. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludot, H.; Tharin, J.Y.; Belooudah, M.; Mazoit, J.X.; Malinovsky, J.M. Successful resuscitation after ropivacaine and lidocaine-induced ventricular arrhythmia following posterior lumbar plexus block in a child. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, J.; Brian, T.; Georgescu, A.; Shah, S. Intravenous lipid infusion in the successful resuscitation of local anesthetic-induced cardiovascular collapse after supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1578–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litz, R.J.; Roessel, T.; Heller, A.R.; Stehr, S.N. Reversal of central nervous system and cardiac toxicity after local anesthetic intoxication by lipid emulsion injection. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, J. Reversal of local anaesthetic induced CNS toxicity with lipid emulsion. Anaesthesia 2008, 63, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, B.; Wahlander, S. Local Anesthetics. In Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 7th ed.; Goldfrank, L.R., Flomenbaum, N.E., Lewin, N.A., Howland, M.A., Hoffman, R.S., Nelson, L.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 824–834. [Google Scholar]
- Nau, C.; Wang, S.; Strichartz, G.R.; Wang, G.K. Block of human heart hh1 sodium channels by the enantiomers of bupivacaine. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hack, J.B.; Lewin, N.A. Cardioactive Steroids. In Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies, 8th ed.; Flomenbaum, N.E., Goldfrank, L.R., Hoffman, R.S., Howland, M.A., Lewin, N.A., Nelson, L., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, USA, 2006; pp. 971–988. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, M.J.; Juhascik, M.; Mazur, F.; Flomenbaum, M.A.; Behonick, G.S. Fatalities associated with fentanyl and co-administered cocaine or opiates. J. Forensic Sci. 2007, 52, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.L.; Woodall, K.L.; McLellan, B.A. Fentanyl-Related Deaths in Ontario, Canada: Toxicological findings and circumstances of death in 112 cases (2002–2004). J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, K.T.; Bucciarelli, A.; Piper, T.M.; Gross, C.; Tardiff, K.; Galea, S. Cocaine- and opiate-related fatal overdose in New York City, 1990–2000. BMC Public Health 2007, 7, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, L.S. Opioids. In Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies, 8th ed.; Flomenbaum, N.E., Goldfrank, L.R., Hoffman, R.S., Howland, M.A., Lewin, N.A., Nelson, L., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 590–619. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, L. Ethanol. In Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 7th ed.; Goldfrank, L.R., Flomenbaum, N.E., Lewin, N.A., Howland, M.A., Hoffman, R.S., Nelson, L.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 952–970. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, P. Cocaethylene toxicity. J. Addict. Dis. 1997, 16, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, J.E.; Hoffman, R.S. Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 7th ed.; Goldfrank, L.R., Flomenbaum, N.E., Lewin, N.A., Howland, M.A., Hoffman, R.S., Nelson, L.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1004–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, N.A.; Roberts, D.; Eddleston, M. Overcoming apathy in research on organophosphate poisoning. Br. Med. J. 2004, 329, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.; Ho, R.J.Y. Trends and developments in liposome drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szoka, F.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Comparative properties and methods of preparation of lipid vesicles (liposomes). Ann. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 1980, 9, 467–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.C.; MacDonald, R.I.; Menco, B.P.; Takeshita, K.; Subbarao, N.K.; Hu, L.R. Small-volume extrusion apparatus for preparation of large, unilamellar vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1061, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, Y.; Howell, B.A.; Chauhan, A. Liposome assay for evaluating ocular toxicity of surfactants. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanikula, A.B.; Lafleur, M.; Leroux, J. Characterization and in vitro evaluation of spherulites as sequestering vesicles with potential application in drug detoxification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchford, K.; Burt, H. A review of the formation and classification of amphiphilic block copolymer nanoparticulate structures: Micelles, nanospheres, nanocapsules and polymersomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, M.; Morey, T.E.; Shah, D.O.; Flint, J.A.; Moudgil, B.M.; Seubert, C.N.; Dennis, D.M. Pluronic microemulsions as nanoreservoirs for extraction of bupivacaine from normal saline. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5108–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.I. Human Physiology, 9th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 383–494. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, T.; Harashima, H.; Kiwada, H. Liposome Clearance. Bioscience Rep. 2002, 22, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, E.T.M.; Laverman, P.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Storm, G.; Scherphof, G.L.; Van Der Meer, J.W.M.; Corstens, F.H.M.; Boerman, O.C. Accelerated blood clearance and altered biodistribution of repeated injections of sterically stabilized liposomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gregoriadis, G.; Senior, J. The phospholipid component of small unilamellar liposomes controls the rate of clearance of entrapped solutes from the circulation. FEBS Lett. 1980, 119, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, S.C.; Chonn, A.; Cullis, P.R. Interactions of liposomes and lipid-based carrier systems with blood proteins: Relation to clearance behavior in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 1998, 32, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, V.D.; Garcia, D.; Goins, B.A.; Phillips, W.T. Circulation and biodistribution profiles of long-circulating PEG-liposomes of various sizes in rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 253, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodle, M.C. Controlling liposome blood clearance by surface-grafted polymers. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 1998, 32, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, V.D.; Garcia, D.; Klipper, R.; Goins, B.A.; Phillips, W.T. Neutral and anionic liposome-encapsulated hemoglobin: Effect of postinserted poly(ethylene glycol)-distearoylphosphatidyl-ethanolamine on distribution and circulation kinetics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 309, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoarau, D.; Delmas, P.; David, S.; Roux, E.; Leroux, J.C. Novel long-circulating lipid nanocapsules. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Choi, Y.; Huh, E.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Song, H.C.; Sun, M.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Cho, C.S.; Bom, H.S. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) modified 99mTcHMPAO Liposome for improving blood circulation and biodistribution: the Effect of the extent of PEGylation. Cancer Biother. Radio. 2005, 20, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.A.; Chauhan, A. Binding of imipramine, dosulepin, and opipramol to liposomes for overdose treatment. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 3718–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasic, D.D. Novel applications of liposomes. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanikula, A.B.; Lamontagne, D.; Leroux, J.C. Rescue of amitriptyline-intoxicated hearts with nanosized vesicles. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 74, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanikula, A.B.; Khalid, N.M.; Lee, S.D.; Yeung, R.; Risovic, V.; Wasan, K.M.; Leroux, J. Long circulating lipid nanocapsules for drug detoxification. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, M.S.; Chauhan, A. Sequestration of amitriptyline by liposomes. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 300, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.; Chauhan, A. Uptake of amitriptyline and nortriptyline with liposomes, proteins, and serum: Implications for drug detoxification. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2008, 319, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.; Chauhan, A. Amitriptyline overdose treatment by pegylated anionic liposomes. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2008, 324, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.A.; Chauhan, A. Bupivacaine binding to pegylated liposomes. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, B.A.; Chauhan, A. Interaction of cationic drugs with liposomes. Langmuir 2006, 25, 12056–12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.A.; Chauhan, A. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic (pbpk) model for predicting the efficacy of drug overdose treatment with liposomes in man. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, T.; Leahy, D.; Rowland, M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling 1: Predicting the tissue distribution of moderate-to-strong bases. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1259–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrikovics, I.; Budai, M.; Baskin, S.I.; Rockwood, G.A.; Childress, J.; Budai, L.; Grof, P.; Klebovich, I.; Szilasi, M. Characterization of liposomal vesicles encapsulating rhodanese for cyanide antagonism. Drug Deliv. 2009, 16, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budai, M.; Chapela, P.; Grof, P.; Zimmer, A.; Wales, M.E.; Wild, J.R.; Klebovich, I.; Petrikovics, I.; Szilasi, M. Physicochemical characterization of stealth liposomes encapsulating an organophosphate hydrolyzing enzyme. J. Liposome Res. 2009, 19, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrikovics, I.; Papahadjopoulos, D.; Hong, K.; Cheng, T.C.; Baskin, S.I.; Jiang, J.; Jaszberenyi, J.C.; Logue, B.A.; Szilasi, M.; McGuinn, W.D.; Way, J.L. Comparing therapeutic and prophylactic protection against the lethal effect of paraoxon. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 77, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrikovics, I.; Cheng, T.C.; Papahadjopoulos, D.; Hong, K.; Yin, R.; DeFrank, J.J.; Jaing, J.; Song, Z.H.; McGuinn, W.D.; Sylvester, D.; Pei, L.; Madec, J.; Tamulinas, C.; Jaszberenyi, J.C.; Barcza, T.; Way, J.L. Long circulating liposomes encapsulating organophosphorus acid anhydrolase in diisopropylfluorophosphate antagonism. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 57, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrikovics, I.; McGuinn, W.D.; Sylvester, D.; Yuzapavik, P.; Jiang, J.; Way, J.L.; Papahadjopoulos, D.; Hong, K.; Yin, R.; Cheng, T.C.; DeFrank, J.J. Health statistics quarterly studies on sterically stabilized liposomes (SL) as enzyme carriers in organophosphorus (OP) antagonism. Drug Deliv. 2000, 7, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrikovics, I.; Hong, K.; Omburo, G.; Hu, Q.Z.; Pei, L.; McGuinn, W.D.; Sylvester, D.; Tamulinas, C.; Papahadjopoulos, D.; Jaszberenyi, J.C.; Way, J.L. Antagonism of paraoxon intoxication by recombinant phosphotriesterase encapsulated within sterically stabilized liposomes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1999, 156, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, T.E.; Varshney, M.; Flint, J.A.; Rajasekaran, S.; Shah, D.O.; Dennis, D.M. Treatment of local anesthetic-induced cardiotoxicity using drug scavenging nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James-Smith, M.A.; Shekhawat, D.; Moudgil, B.M.; Shah, D.O. Determination of drug and fatty acid binding capacity to pluronic F127 in microemulsions. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underhill, R.S.; Jovanovic, A.V.; Carino, S.R.; Varshney, M.; Shah, D.O.; Dennis, D.M.; Morey, T.E.; Duran, R.S. Oil-Filled silica nanocapsules for lipophilic drug uptake: Implications for drug detoxification therapy. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4919–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Somasundaran, P. Sequestration of drugs using poly(acrylic acid) and alkyl modified poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Baney, R. Detoxification of amitriptyline by oligochitosan derivatives. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Flint, J.; Morey, T.; Dennis, D.; Partch, R.; Baney, R. Aromatic-Aromatic interaction of amitriptyline: Implication of overdosed drug detoxification. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curd, J.; Smith, T.W.; Jaton, J.C.; Haber, E. The isolation of digoxin-specific antibody and its use in reversing the effects of digoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, V.P., Jr.; Schmidt, D.H.; Smith, T.W.; Haber, E.; Raynor, B.D.; Demartini, P. Effects of sheep digoxin specific antibodies and their Fab fragments on digoxin pharmacokinetics in dogs. J. Clin. Invest. 1977, 59, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, B.L.; Smith, T.W. Contrasting rates of reversal of digoxin toxicity by digoxin-specific IgG and Fab fragments. Circulation 1978, 58, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapostolle, F.; Borron, S.W.; Verdier, C.; Taboulet, P.; Guerrier, G.; Adnet, F.; Clemessy, J.L.; Bismuth, C.; Baud, F.J. Digoxin-specific Fab fragments as single first-line therapy in digitalis poisoning. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapostolle, F.; Borron, S.W.; Verdier, C.; Arnaud, F.; Couvreur, J.; Megarbane, B.; Baud, F.; Adnet, F. Assessment of digoxin antibody use in patients with elevated serum digoxin following chronic or acute exposure. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 34, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentel, P.R.; Scarlett, W.; Ross, C.A.; Landon, J.; Sidki, A.; Keyler, D.E. Reduction of desipramine cardiotoxicity and prolongation of survival in rats with the use of polyclonal drug-specific antibody Fab fragments. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1995, 26, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelver, W.L.; Keyler, D.E.; Lin, G.; Murtaugh, M.P.; Flickinger, M.C.; Ross, C.A.; Pentel, P.R. Effects of recombinant drug-specific single chain antibody Fv fragment on [3H]-desipramine distribution in rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusi, C.; Boschi, G.; Risede, P.; Rips, R.; Harrison, K.; Scherrmann, J.M. Influence of various combinations of specific antibody dose and affinity on tissue imipramine redistribution. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusi, C.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Harrison, K.; Smith, D.S.; Rips, R.; Boschi, G. Redistribution of imipramine from regions of the brain under the influence of circulating specific antibodies. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heard, K.; Dart, R.C.; Bogdan, G.; O’Malley, G.F.; Burkhart, K.K.; Donovan, J.W.; Ward, S.B. A preliminary study of tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) ovine FAB for TCA toxicity. Clin. Toxciol. 2006, 44, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dart, R.; Seifert, S.; Carroll, L.; Clark, R.; Hall, E.; Boyer-Hassen, L.; Curry, S.; Kitchens, C.; Garcia, R. Affinity-purified, mixed monospecific crotalid antivenom ovine Fab for the treatment of crotalid venom poisoning. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1997, 30, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dart, R.C.; Seifert, S.A.; Boyer, L.V.; Clark, R.F.; Hall, E.; McKinney, P.; McNally, J.; Kitchens, C.S.; Curry, S.C.; Bogdan, G.M.; Ward, S.B.; Porter, R.S. A randomized multicenter trial of crotalinae polyvalent immune Fab (Ovine) antivenom for the treatment for crotaline snakebite in the united states. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, G.L.; VadeBoncouer, T.; Ramaraju, G.A.; Garcia-Amaro, M.F.; Cwik, M.J. Pretreatment or resuscitation with a lipid infusion shifts the dose response to bupivacaine-induced asystole in rats. Anesthesiology 1998, 88, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wat, C.Y.; Yuen, M.K.; Li, R.W.S.; Leung, G.P.H.; NG, K.F.J. Lipid Emulsion Infusion vs. Standard Cardiac Resuscitation in Management of Ropivacaine Cardiac Toxicity in Pigs. In Presented at the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists Annual Scientific Meeting, Cairns, Queensland, Australia, May 2009.
- Zausig, Y.A; Zink, W.; Keil, M.; Sinner, B.; Barwing, J.; Wiese, C.H.R.; Graf, B.M. Lipid emulsion improves recovery from bupivacaine-induced cardiac arrest, but not from ropivacaine- or mepivacaine-induced cardiac arrest. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, G.; Ripper, R.; Feinstein, D.L.; Hoffman, W. Lipid emulsion infusion rescues dogs from bupivacaine-induced cardiac toxicity. Region. Anesth. Pain M. 2003, 28, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litz, R.J.; Popp, M.; Stehr, S.N.; Koch, T. Successful resuscitation of a patient with ropivacaine-induced asystole after axillary plexus block using lipid emulsion. Anaesthesia 2006, 61, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, M.A.; Abel, M.; Fischer, G.W.; Itzkovich, C.J.; Eisenkraft, J.B. Successful use of a 20% lipid emulsion to resuscitate a patient after a presumed bupivacaine-related cardiac arrest. Anesthesiology 2006, 105, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, S.D.H.; Uncles, D.R.; Willers, J.; Sable, N. Early treatment of a quetiapine and sertraline overdose with Intralipid®. Anaesthesia 2009, 64, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cave, G.; Harvey, M. Intravenous lipid emulsion as antidote beyond local anesthetic toxicity: A Systematic review. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2009, 16, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.F. Insectisides: Organic Phosphorous Compounds and Carbamates. In Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies, 8th ed.; Flomenbaum, N.E., Goldfrank, L.R., Hoffman, R.S., Howland, M.A., Lewin, N.A., Nelson, L., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1497–1522. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Howell, B.A.; Chauhan, A. Current and Emerging Detoxification Therapies for Critical Care. Materials 2010, 3, 2483-2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042483
Howell BA, Chauhan A. Current and Emerging Detoxification Therapies for Critical Care. Materials. 2010; 3(4):2483-2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042483
Chicago/Turabian StyleHowell, Brett A., and Anuj Chauhan. 2010. "Current and Emerging Detoxification Therapies for Critical Care" Materials 3, no. 4: 2483-2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042483
APA StyleHowell, B. A., & Chauhan, A. (2010). Current and Emerging Detoxification Therapies for Critical Care. Materials, 3(4), 2483-2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042483



