Magnetic Graphene Oxide: Effect of Preparation Route on Reactive Black 5 Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation Routes of Adsorbents
2.2.1. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide (GO)
2.2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4-GO Nanocomposites by co-Precipitation (mGOp)
2.2.4. Synthesis of Fe3O4-GO Nanocomposites by Impregnation (mGOi)
2.3. Dye (Reactive Black 5)

2.4. Characterization
2.5. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization




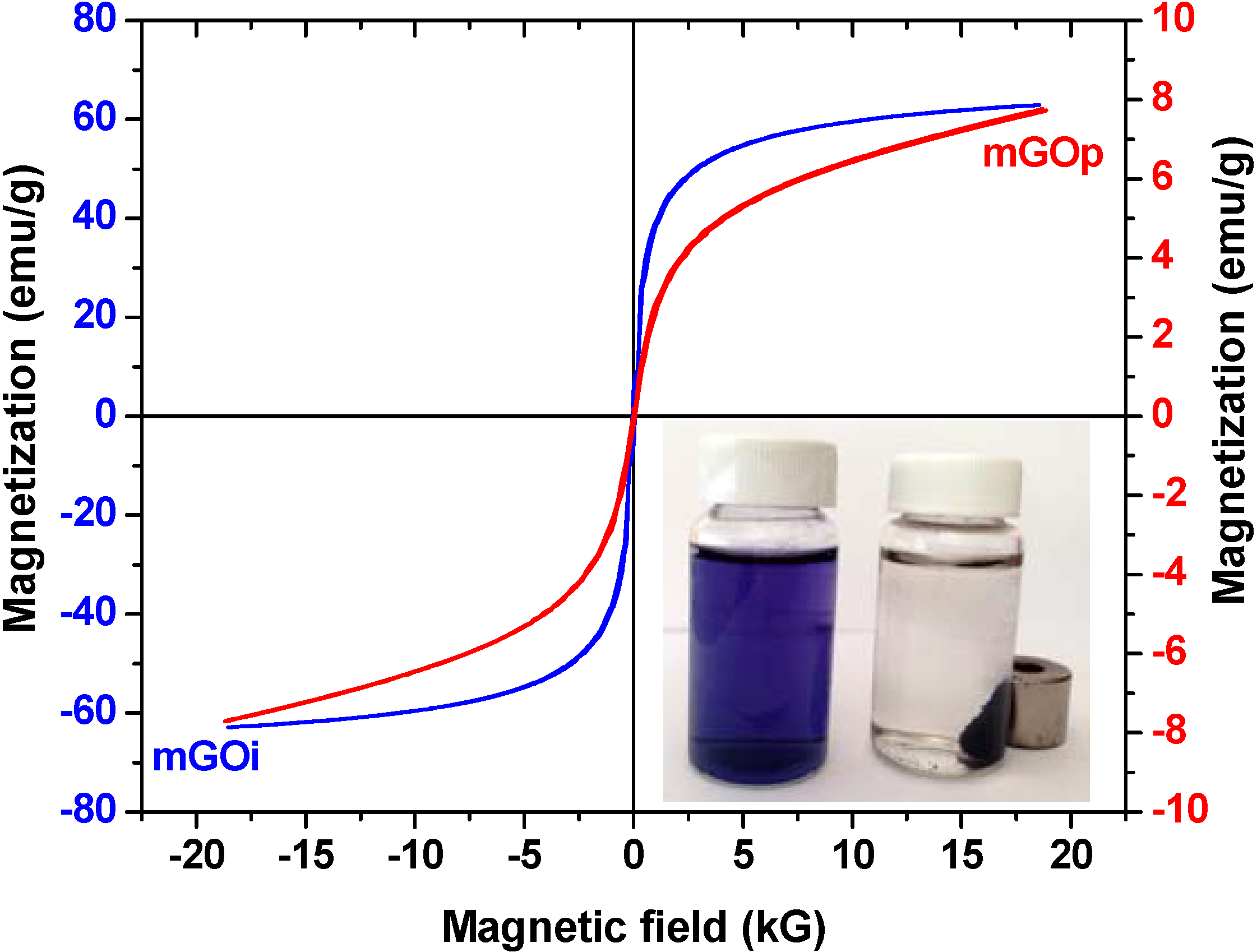

3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. Kinetics
| Adsorbent | Pseudo–first order | Pseudo–second order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | R2 | k2 (min−1) | R2 | |
| mGOi | 0.072 | 0.915 | 0.143 | 0.990 |
| mGOp | 0.029 | 0.954 | 0.064 | 0.991 |

3.2.2. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration and Temperature (Isotherms)
| Adsorbents | Langmuir equation | Freundlich equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg(n−1)/n L1/n g−1) | n | R2 | |
| mGOi | 25 | 164 | 0.007 | 0.989 | 4.55 | 0.58 | 0.960 |
| 45 | 124 | 0.008 | 0.993 | 4.13 | 0.55 | 0.970 | |
| 65 | 118 | 0.004 | 0.990 | 1.24 | 0.71 | 0.973 | |
| mGOp | 25 | 188 | 0.007 | 0.991 | 4.24 | 0.63 | 0.966 |
| 45 | 186 | 0.004 | 0.995 | 2.17 | 0.69 | 0.988 | |
| 65 | 178 | 0.002 | 0.999 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.995 | |

3.3. Thermodynamics
| Adsorbent | C0 (mg/L) | T (K) | Qe (mg/g) | Kc | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (kJ/mol K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mGOi | 40 | 298 | 18.02 | 0.82 | -0.50 | -24.83 | -0.085 |
| 318 | 12.01 | 0.43 | -2.24 | ||||
| 338 | 8.09 | 0.25 | -3.90 | ||||
| 100 | 298 | 48.56 | 0.92 | -0.20 | -23.54 | -0.071 | |
| 318 | 40.75 | 0.67 | -1.07 | ||||
| 338 | 25.41 | 0.33 | -3.09 | ||||
| 300 | 298 | 130.02 | 0.76 | -0.66 | -21.13 | -0.082 | |
| 318 | 79.99 | 0.36 | -2.67 | ||||
| 338 | 60.01 | 0.25 | -3.90 | ||||
| mGOp | 20 | 298 | 22.02 | 1.22 | -0.50 | -27.04 | -0.089 |
| 318 | 17.09 | 0.74 | -0.80 | ||||
| 338 | 10.08 | 0.33 | -3.09 | ||||
| 80 | 298 | 52.10 | 1.08 | -0.20 | -20.32 | -0.067 | |
| 318 | 42.12 | 0.72 | -0.85 | ||||
| 338 | 29.03 | 0.41 | -2.52 | ||||
| 300 | 298 | 145.62 | 0.94 | -0.17 | -19.31 | -0.068 | |
| 318 | 95.58 | 0.46 | -2.03 | ||||
| 338 | 81.04 | 0.37 | -2.80 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Forgacs, E.; Cserháti, T.; Oros, G. Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzas, G.Z. A decolorization technique with spent “Greek coffee” grounds as zero-cost adsorbents for industrial textile wastewaters. Materials 2012, 5, 2069–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z. Commercial coffee wastes as materials for adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Materials 2012, 5, 1826–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Removal of dyes from aqueous solutions with untreated coffee residues as potential low-cost adsorbents: Equilibrium, reuse and thermodynamic approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezohegyi, G.; van der Zee, F.P.; Font, J.; Fortuny, A.; Fabregat, A. Towards advanced aqueous dye removal processes: A short review on the versatile role of activated carbon. J. Environ. Manage. 2012, 102, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, J.N.; Mahesh, K.; Le, N.H.; Kemp, K.C.; Timilsina, R.; Tiwari, R.N.; Kim, K.S. Reduced graphene oxide-based hydrogels for the efficient capture of dye pollutants from aqueous solutions. Carbon 2013, 56, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wei, T.; Qiao, W.; Shao, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Z. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of graphene nanosheet/Co3O4 composite for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6973–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z. Controlled assembly of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles on graphene oxide. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, Y.; Yuan, P.X.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.Q.; Hong, C.L. Bienzyme functionalized three-layer composite magnetic nanoparticles for electrochemical immunosensors. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Q.; Ai, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L. Electrocatalytic oxidation behavior of guanosine at graphene, chitosan and Fe3O4 nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode and its determination. Talanta 2010, 82, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Pallavkar, S.; Chen, M.; Yerra, N.; Luo, Z.; Colorado, H.A.; Lin, H.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Khasanov, A.; Ho, T.C.; et al. Magnetic carbon nanostructures: Microwave energy-assisted pyrolysis vs. conventional pyrolysis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhua, J.; Sadua, R.; Weib, S.; Chena, D.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Luo, Z.; Gomesa, J.A.; Young, D.P.; Guo, Z. Magnetic graphene nanoplatelet composites toward arsenic removal. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, M1–M5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Gu, H.; Rapole, S.B.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Young, D.P.; Guo, Z. One-pot synthesis of magnetic graphene nanocomposites decorated with core@double-shell nanoparticles for fast chromium removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wei, S.; Kaila, C.; Su, X.; Wu, J.; Karki, A.B.; Young, D.P.; Guo, Z. Carbon-stabilized iron nanoparticles for environmental remediation. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Rapole, S.B.; Sharma, J.; Huang, Y.; Cao, D.; Colorado, H.A.; Luo, Z.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Young, D.P.; Walters, B.; et al. Magnetic polyaniline nanocomposites toward toxic hexavalent chromium removal. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 11007–11018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Gu, H.; Rapole, S.B.; Luo, Z.; Pallavkar, S.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Benson, T.J.; Ho, T.C.; Hopper, J.; Young, D.P.; et al. Looped carbon capturing and environmental remediation: Case study of magnetic polypropylene nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 4844–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Deliyanni, E.A. Functionalization of graphite oxide with magnetic chitosan for the preparation of a nanocomposite dye adsorbent. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, V.; Park, J.; Chun, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Hwang, I.C.; Kim, K.S. Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3979–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Fan, J.; Ma, D.; Zhang, L.; Leung, C.; Chan, H.L. The attachment of Fe3O4 nanoparticles to graphene oxide by covalent bonding. Carbon 2010, 48, 3139–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Otyepka, M.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Chandra, V.; Kim, N.; Kemp, K.C.; Hobza, P.; Zboril, R.; Kim, K.S. Functionalization of graphene: Covalent and non-covalent approaches, derivatives and applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6156–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Miao, S.; Yu, S.; Ping Ma, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Fabrication of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles attached to graphene oxide and its use as an adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 379, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Zhao, Y.; Jang, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, K.S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, P.; Choi, J.-Y.; Hong, B.H. Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 2009, 457, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummers, W.S., Jr.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R. Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1981, 17, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Ding, M. Facile and tunable fabrication of Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposites and their application in the magnetic solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. Talanta 2012, 101, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.M.; van Ness, H.C. Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Joint Committee on Power Diffraction Standards in International Centre for Diffraction Data: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2005;Card No. 19–0629
- Seung, H.H. Thermal Reduction of Graphene Oxide. In Physics and Applications of Graphene—Experiments; Mikhailov, S., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Deliyanni, E.; Bandosz, T.J. Importance of carbon surface chemistry in development of iron-carbon composite adsorbents for arsenate removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanel, S.R.; Greneche, J.M.; Choi, H. Arsenic(V) removal from groundwater using nano scale zero-valent iron as a colloidal reactive barrier material. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanel, S.R.; Manning, B.; Charlet, L.; Choi, H. Removal of arsenic(III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, E.E.; Calvin, S.; Stroud, R.M.; Harris, V.G. Passivated iron as core-shell nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3245–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Yuan, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, T.; Yuan, A.; He, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, D. Core-shell structured iron nanoparticles well dispersed on montmorillonite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 3515–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattana; Chaiyakun, S.; Witit-anun, N.; Nuntawong, N.; Chindaudom, P.; Oaew, S.; Kedkeaw, C.; Limsuwan, P. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide nanosheets. Procedia Eng. 2012, 32, 759–764. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.-Z.; Zhao, D.-L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.-M.; Gao, Y.-L.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Tang, J.-T. Inductive heating property of graphene oxide–Fe3O4 nanoparticles hybrid in an AC magnetic field for localized hyperthermia. Mater. Lett. 2012, 68, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Li, H.S.; Chen, C.H. Effect of surface acidic oxides of activated carbon on adsorption of ammonia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 159, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travlou, N.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Deliyanni, E.A. Graphite oxide/chitosan composite for reactive dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, A. Adsorption properties of congo red from aqueous solution onto N,O-carboxymethyl-chitosan. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G. Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto a cyclodextrin polymer. Dyes Pigm. 2008, 77, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, B.P.; Das, A.R.; Guha, A.K. Adsorption of a model anionic dye, eosin Y, from aqueous solution by chitosan hydrobeads. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 288, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunauer, S.; Deming, L.S.; Deming, W.E.; Teller, E. On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M.; Lazaridis, N.K. Copper and chromium(VI) removal by chitosan derivatives-Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnithan, M.R.; Anirudhan, T.S. The kinetics and thermodynamics of sorption of chromium(VI) onto the iron(III) complex of a carboxylated polyacrylamide-grafted sawdust. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M.; Vassiliou, A.A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Treatment of real effluents from dyeing reactor: Experimental and modeling approach by adsorption onto chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, A.; Yazdanipour, A.; Ghasemi, J.; Kubista, M. Spectrophotometric and thermodynamic study on the dimerization equilibrium of ionic dyes in water by chemometrics method. Spectrochim. Acta A 2006, 65, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyzas, G.Z.; Travlou, N.A.; Kalogirou, O.; Deliyanni, E.A. Magnetic Graphene Oxide: Effect of Preparation Route on Reactive Black 5 Adsorption. Materials 2013, 6, 1360-1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041360
Kyzas GZ, Travlou NA, Kalogirou O, Deliyanni EA. Magnetic Graphene Oxide: Effect of Preparation Route on Reactive Black 5 Adsorption. Materials. 2013; 6(4):1360-1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041360
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyzas, George Z., Nikolina A. Travlou, Orestis Kalogirou, and Eleni A. Deliyanni. 2013. "Magnetic Graphene Oxide: Effect of Preparation Route on Reactive Black 5 Adsorption" Materials 6, no. 4: 1360-1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041360
APA StyleKyzas, G. Z., Travlou, N. A., Kalogirou, O., & Deliyanni, E. A. (2013). Magnetic Graphene Oxide: Effect of Preparation Route on Reactive Black 5 Adsorption. Materials, 6(4), 1360-1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041360







