Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Chemical Spray Technique, Starting from Zinc Acetylacetonate and Indium Chloride
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure


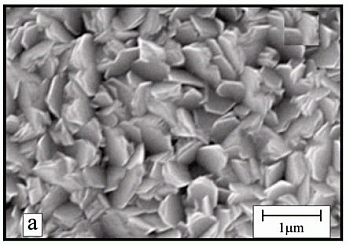
3.2. Morphology

3.3. Electrical Characteristics
| [In]/[In+Zn] | Electrical Resistivity (Ω·cm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 °C | 425 °C | 450 °C | |
| 1.5 | 1.2 × 10−2 | 4.5 × 10−3 | 4.2 × 10−3 |
| 3 | 8.4 × 10−3 | 3.6 × 10−3 | 3.42 × 10−3 |
| 4 | 2.9 × 10−2 | 1.8 × 10 −2 | 5.6 × 10−3 |
3.4. Optical Characteristics

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janotti, A.; van de Walle, C.G. Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Lee, J.; Chung, J.; Lim, S. Improvement of ZnO nanorod-based dye-sensitized solar cell efficiency by Al-doping. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, K.L.; Major, S.; Pandya, D.K. Transparent conductors-A status review. Thin Solid Films 1983, 102, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, G.; Bashir, A.; Thomas, S.; Gillin, W.P.; Georgakopoulos, S.; Shkunov, M.; Baklar, M.A.; Stingelin, N.; Maher, R.C.; Cohen, L.F.; et al. Spray-deposited Li-doped transistors with electron mobility exceeding 50 cm2/Vs. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4764–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, A. Transparent conducting oxides—An up-to-date overview. Materials 2012, 5, 661–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratheesh Kumar, P.M.; Sudha Kartha, C.; Vijayakumar, K.P.; Abe, T.; Kashiwaba, Y.; Singh, F.; Avasthi, D.K. On the properties of indium doped ZnO thin films. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K. Resistivity of polycrystalline zinc oxide films: Current status and physical limit. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.S. Versatility of chemical spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1999, 59, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.C.; Zhang, X.D.; Wei, C.C.; Sun, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Effect of acetic acid on ZnO:In transparent conductive oxide prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 2011, 520, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandenet, G.; Court, M.; Lagarde, Y. Thin layers deposited by the pyrosol process. Thin Solid Films 1981, 77, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, M.G.; Hamilton, J.A.; O’Brien, S.; Bruno, G.; Pereira, L.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Povey, I.M.; Pemble, M.E. The characterisation of aerosol assisted CVD conducting, photocatalytic indium doped zinc oxide films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2011, 219, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Leinen, D.; Dalchiele, E.A.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R.; Martín, F. The effects of zinc acetate and zinc chloride precursors on the preferred crystalline orientation of ZnO and Al-doped ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 2006, 515, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Rodriguez-Clemente, R. Morphological differences in ZnO films deposited by the pyrosol technique: Effect of HCl. Thin Solid Films 1999, 345, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, R.R.; Maldonado, A.; de la Luz Olvera, M. Electrical and optical properties of in-doped ZnO thin films via ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), Mexico City, Mexico, 30 September–4 October 2013.
- Ilican, S.; Caglar, Y.; Caglar, M.; Demirci, B. Polycrystalline indium-doped ZnO thin films: Preparation and characterization. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2008, 10, 2592–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Xua, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Jiang, M.; Wei, S.; Zhang, T. Low temperature growth of highly crystallized ZnO:Al films by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis from acetylacetone salt. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 167, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.S.; Huang, J.L.; Li, D.F. The effects of R.F. power and substrate temperature on the properties of ZnO thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 176, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, E. Anomalous optical absorption limit in InSb. Phys. Rev. 1954, 93, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswal, R.; Maldonado, A.; Vega-Pérez, J.; Acosta, D.R.; De La Luz Olvera, M. Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Chemical Spray Technique, Starting from Zinc Acetylacetonate and Indium Chloride. Materials 2014, 7, 5038-5046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7075038
Biswal R, Maldonado A, Vega-Pérez J, Acosta DR, De La Luz Olvera M. Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Chemical Spray Technique, Starting from Zinc Acetylacetonate and Indium Chloride. Materials. 2014; 7(7):5038-5046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7075038
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswal, Rajesh, Arturo Maldonado, Jaime Vega-Pérez, Dwight Roberto Acosta, and María De La Luz Olvera. 2014. "Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Chemical Spray Technique, Starting from Zinc Acetylacetonate and Indium Chloride" Materials 7, no. 7: 5038-5046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7075038
APA StyleBiswal, R., Maldonado, A., Vega-Pérez, J., Acosta, D. R., & De La Luz Olvera, M. (2014). Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Chemical Spray Technique, Starting from Zinc Acetylacetonate and Indium Chloride. Materials, 7(7), 5038-5046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7075038