Long-Term Soft Denture Lining Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Compositions of LTSDLs
3. Clinical Effects of Long-Term Soft Denture Linings

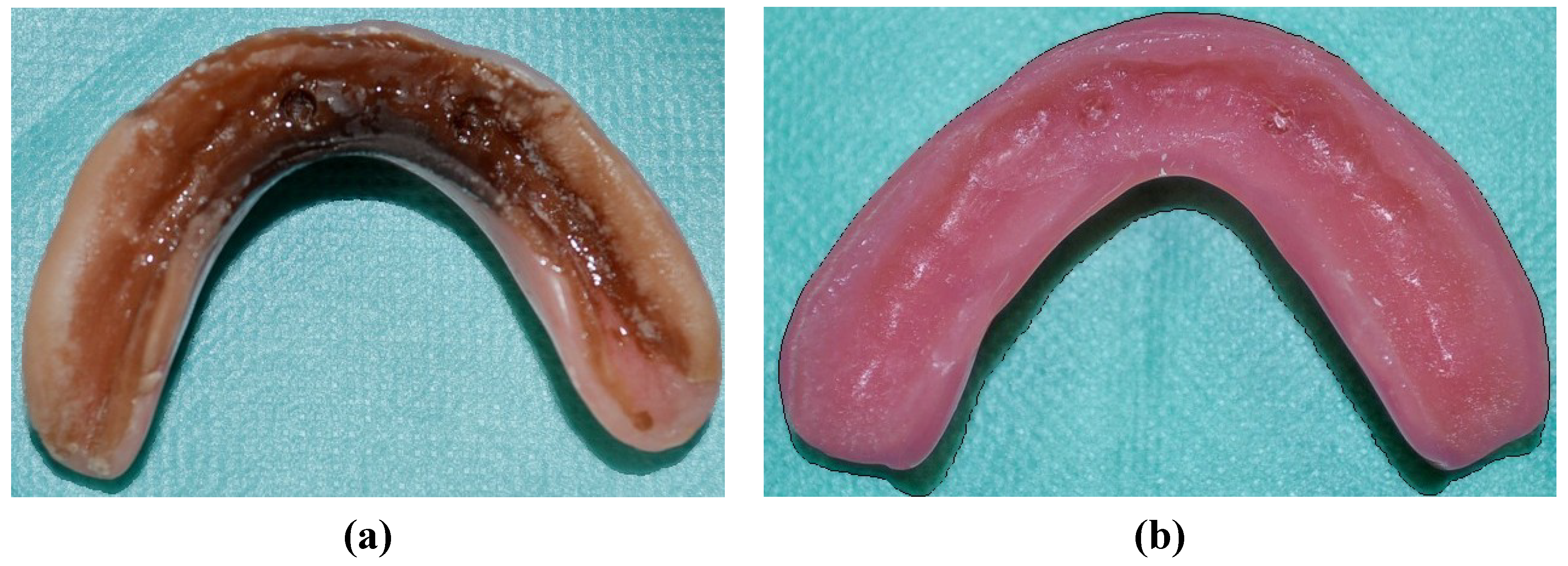
4. Colonization of Soft Denture Lining Materials by Microorganisms
5. The Hardness of LTSDLs
| Source | Material/type | Samples thickness, mm | Hardness, Shore A units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yoeli, Z. et al. [58] | Molloplast B/heat-cured silicone | 8 | 46 |
| Permaflex/heat-cured silicone | 45 | ||
| Permasoft/autopolymerized acrylic | 28 | ||
| Flexacryl/autopolymerized acrylic | 56 | ||
| Canay, S. et al. [59] | Molloplast B/heat-cured silicone | 2 | 44 |
| Flexor/heat-cured silicone | 39 | ||
| Mese, A. et al. [60] | Mollosil Plus, autopolymerized silicone | 12 | 29 |
| Molloplast B/heat-cured silicone | 42 | ||
| Polyzois, G.L. et al. [61] | EverSoft/heat-cured acrylic | 10 | 27 |
| Super-Soft/heat-cured acrylic | 78 | ||
| Parr, G.R. et al. [62] | Luci-Soft/heat-cured silicone | 10 | 42 |
| Tokuyama Soft/autopolymerized silicone | 19 | ||
| Kiat-Amnuay, S. et al. [9] | Novus/heat-cured polyphosphazene | 11 | 33 |
| Luci-Soft/heat-cured silicone | 38 | ||
| Molloplast B/heat-cured silicone | 36 | ||
| Tokuyama Soft/autopolymerized silicone | 22 | ||
| Permasoft/autopolymerized acrylic | 18 | ||
| Pavan, S. et al. [65] | Molloplast B/heat-cured silicone | 6 | 35 |
| UfiGel P/autopolymerized silicone | 19 | ||
| EverSoft, heat-cured acrylic | 18 | ||
| Mucopren soft/autopolymerized silicone | 27 | ||
| Mancuso, D.N. et al. [67] | Dentusil/autopolymerized silicone | 3 | 37 |
| UfiGel P/autopolymerized silicone | 30 | ||
| UfiGel SC/autopolymerized silicone | 32 | ||
| Mante, F.K. et al. [14] | Permasoft/autopolymerized acrylic | 4 | 29 |
| Tokuyama Soft/autopolymerized silicone | 27 | ||
| Chladek, G. et al. [52] | UfiGel SC/autopolymerized silicone | 6 | 31 |
| Kim, B-J. et al. [63] | Durabase/autopolymerized acrylic | 6 | 29 |
| Dentusil/autopolymerized silicone | 29 | ||
| GC Reline Soft/autopolymerized silicone | 50 | ||
| GC Reline Ultrasoft/autopolymerized silicone | 21 | ||
| Mucopren Soft/autopolymerized silicone | 33 | ||
| Mucosoft/autopolymerized silicone | 38 | ||
| Sofreliner Tough/autopolymerized silicone | 35 |
6. The Bond Strength to Denture Base Polymers


7. Sorption and Solubility
8. Viscoelastic Properties
9. Color Stability
10. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bulad, K.; Taylor, R.L.; Verran, J.; McCord, J.F. Colonization and penetration of denture soft lining materials by Candida albicans. Dent. Mater. 2004, 20, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, P.J. Denture soft linings: Clinical indications. Aust. Dent. J. 1989, 34, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hadary, A.; Drummond, J.L. Comparative study of water sorption, solubility, and tensile bond strength of two soft lining materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2000, 83, 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Saber-Sheikh, K.; Clarke, R.L.; Braden, M. Viscoelastic properties of some soft lining materials. II-Ageing characteristics. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Braden, M.; Wright, P.S.; Parker, S. Soft lining materials—A review. Eur. J Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 1995, 3, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawano, F.; Dootz, E.R.; Koran, A., III; Craig, R.G. Comparison of bond strength of six soft denture liners to denture base resin. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 62, 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, S.; Riggs, P.D.; Braden, M.; Kalachandra, S.; Taylor, D.F. Water uptake of soft lining materials from osmotic solutions. J. Dent. 1997, 25, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colas, A.; Curtis, J. Silicone biomaterials: History and chemistry. In Biomaterial Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine, 2nd ed.; Ratner, B.D., Hoffman, A.S., Schoen, F.J., Lemmons, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kiat-Amnuay, S.; Gettleman, L.; Mekayarajjananonth, T.; Khan, Z.; Goldsmith, L.J. The influence of water storage on durometer hardness of 5 soft denture liners over time. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 14, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Santawisuk, W.; Kanchanavasita, W.; Sirisinha, C.; Harnirattisai, C. Mechanical properties of experimental silicone soft lining materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoenix, R.D. Denture base resins. In Phillips’ Science of Dental Materials, 11th ed.; Anusavice, K., Ed.; Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2003; pp. 750–752. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, S.; Shenoy, V.; Shetty, T. Resilient liners: A review. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2013, 13, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brożek, R.; Rogalewicz, R.; Koczorowski, R.; Voelkel, A. The influence of denture cleansers on the release of organic compounds from soft lining materials. J. Environ. Monit. 2008, 10, 770–774. [Google Scholar]
- Mante, F.K.; Mante, M.O.; Petropolous, V.C. In vitro changes in hardness of sealed resilient lining materials on immersion in various fluids. J. Prosthodont. 2008, 17, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, S.; Martin, D.; Braden, M. Soft acrylic resin materials containing a polymerisable plasticiser I: Mechanical properties. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, S.; Martin, D.; Braden, M. Soft acrylic resin materials containing a polymerisable plasticiser II: Water absorption characteristics. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brożek, R.; Koczorowski, R.; Rogalewicz, R.; Voelkel, A.; Czarnecka, B.; Nicholson, J.W. Effect of denture cleansers on chemical and mechanical behavior of selected soft lining materials. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Sofou, A.; Tsoupi, I.; Karayannis, M.; Owall, B. Determination of residual monomers released from soft lining materials with the use of HPLC. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2007, 8, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, J. Soft lining materials: Composition and structure. J. Oral Rehabil. 1976, 3, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, W.F.; Smith, D.E. A six-year retrospective study of Molloplast-B-lined dentures. Part II: Liner service ability. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, W.F.; Smith, D.E. A six-year retrospective study of Molloplast-B-lined dentures. Part I: Patient response. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, S.; Kimoto, K.; Gunji, A.; Kawai, Y.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, K.; Syu, K.; Aoki, H.; Toyoda, M.; Kobayashi, K. Clinical effects of acrylic resilient denture liners applied to mandibular complete dentures on the alveolar ridge. J. Oral Rehabil. 2007, 34, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimoto, S.; Kimoto, K.; Gunji, A.; Kawai, Y.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, K.; Syu, K.; Aoki, H.; Tani, M.; Toyoda, M.; et al. Effects of resilient denture liner in mandibular complete denture on the satisfaction ratings of patients at the first appointment following denture delivery. Nihon Hotetsu Shika Gakkai Zasshi 2008, 52, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, M.X.; de Luna Malheiros-Segundo, A.; Balbino, K.L.; de Freitas Souza, R.; de Freitas Oliveira Paranhos, H.; da Silva, C.H.L. Oral health related quality of life of edentulous patients after denture relining with a silicone-based soft liner. Gerodontology 2011, 29, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, H.; Taguchi, N.; Hamada, T.; Kawamura, M.; McCabe, J.F. Dynamic viscoelasticity of soft liners and masticatory function. J. Dent. Res. 2002, 81, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, I.; Hirano, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Keh, E.S. Changes in the masticatory function of complete denture wearers after relining the mandibular denture with a soft denture liner. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2000, 13, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shinomiya, M. In-vivo and in vitro studies for analysis of mastication in complete denture wearers with resilient denture liners. Int. J. Oral-Med. Sci. 2006, 2, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, S.; So, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Ohno, Y.; Shinomiya, M.; Ogura, K.; Kobayashi, K. Randomized controlled clinical trial for verifying the effect of silicone-based resilient denture liner on the masticatory function of complete denture wearers. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2006, 19, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomasi, C.; Idmyr, B.O.; Wennström, J.L. Patient satisfaction with mini-implant stabilised full dentures. A 1-year prospective study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2013, 40, 526–534. [Google Scholar]
- Chladek, G.; Wrzuś-Wieliński, M. The evaluation of selected attachment systems for implant-retained overdenture based on retention characteristics analysis. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2010, 12, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wright, P.S. Observations on long-term use of a soft-lining material for mandibular complete dentures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1994, 72, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutluay, M.M.; Oguz, S.; Fløystrand, F.; Saxegaard, E.; Dogan, A.; Bek, B.; Ruyter, I.E. A prospective study on the clinical performance of polysiloxane soft liners: One-year results. Dent. Mater. J. 2008, 27, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglass, C.W.; Watson, A.J. Future needs for fixed and removable partial dentures in the United States. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 87, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikawa, H.; Chen, J.; Hamada, T. Interactions between thermal cycled resilient denture lining materials, salivary and serum pellicles and Candida albicans in vitro. Part I. Effects on fungal growth. J. Oral Rehabil. 2000, 27, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nikawa, H.; Jin, C.; Makihira, S.; Egusa, H.; Hamada, T.; Kumagai, H. Biofilm formation of Candida albicans on the surface of denture lining materials caused by denture cleansers in vitro. J. Oral Rehabil. 2003, 30, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, S.; dos Santos, P.H.; Filho, J.N.; Spolidorio, D.M. Colonisation of soft lining materials by micro-organisms. Gerodontology 2010, 27, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikawa, H.; Hamada, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kumagai, H. Effects of salivary or serum pellicles on the Candida albicans growth and biofilm formation on soft lining materials in vitro. J. Oral Rehabil. 1997, 24, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikawa, H.; Hayashi, S.; Nikawa, Y.; Hamada, T.; Samaranayake, L.P. Interactions between denture lining material, protein pellicles and Candida albicans. Arch. Oral Biol. 1993, 38, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikawa, H.; Jin, C.; Hamada, T.; Makihira, S.; Kumagai, H.; Murata, H. Interactions between thermal cycled resilient denture lining materials, salivary and serum pellicles and Candida albicans in vitro. Part II. Effects on fungal colonization. J. Oral Rehabil. 2000, 27, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Verran, J.; Maryan, C.J. Retention of Candida albicans on acrylic resin and silicone of different surface topography. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1997, 77, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.G.; Williams, D.W.; Jagger, R.G.; Lewis, M.A. Adherence of Candida albicans to experimental denture soft lining materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1997, 77, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevzatoğlu, E.U.; Ozcan, M.; Kulak-Ozkan, Y.; Kadir, T. Adherence of Candida albicans to denture base acrylics and silicone-based resilient liner materials with different surface finishes. Clin. Oral Investig. 2007, 11, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.S.; Jones, D.W.; Burke, J.; Thompson, J.P. In vivo fungal presence and growth on two resilient denture liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 65, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, T.Y. Influence of surface characteristics on the adhesion of Candida albicans to various denture lining materials. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2013, 71, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tari, B.F.; Nalbant, D.; Dogruman Al, F.; Kustimur, S. Surface roughness and adherence of Candida albicans on soft lining materials as influenced by accelerated aging. J Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2007, 8, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.L.; Bulad, K.; Verran, J.; McCord, J.F. Colonization and deterioration of soft denture lining materials in vivo. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2008, 16, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boscato, N.; Radavelli, A.; Faccio, D.; Loguercio, A.D. Biofilm formation of Candida albicans on the surface of a soft denture-lining material. Gerodontology 2009, 26, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.-B.; Lim, Y.; Youn, H.-I.; Chang, B.M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shin, S.-W. Effect of denture cleansers on Candida albicans biofilm formation over resilient liners. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2014, 6, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccio, D.R.; Pereira-Cenci, T.; Cenci, M.S.; Demarco, F.F.; Moraes, R.R.; Boscato, N. In vivo biofilm formation on a soft denture liner in elderly patients with controlled diabetes. Gerodontology 2012, 29, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skupien, J.A.; Valentini, F.; Boscato, N.; Pereira-Cenci, T. Prevention and treatment of Candida colonization on denture liners: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 110, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chladek, G.; Mertas, A.; Barszczewska-Rybarek, I.; Nalewajek, T.; Żmudzki, J.; Król, W.; Łukaszczyk, J. Antifungal Activity of Denture Soft Lining Material Modified by Silver Nanoparticles—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4735–4744. [Google Scholar]
- Chladek, G.; Kasperski, J.; Barszczewska-Rybarek, I.; Żmudzki, J. Sorption, Solubility, Bond Strength and Hardness of Denture Soft Lining Incorporated with Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 563–574. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowski, J.; Szynkowska, M.I.; Kleczewska, J.; Kowalski, Z.; Sobczak-Kupiec, A.; Pawlaczyk, A.; Sokołowski, K.; Łukomska-Szymańska, M. Evaluation of resin composites modified with nanogold and nanosilver. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2014, 16, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, J.R.; Mesquita, M.F.; Henriques, G.E.; de Arruda Nóbilo, M.A. Effect of thermocycling on bond strength and elasticity of 4 long-term soft denture liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 88, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO International Organization for Standardization. ISO 10139-2:2009 Dentistry—Soft Lining Materials for Removable Dentures—Part 2: Materials for Long-Term Use; ISO International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness; D2240-05; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, A.; Braden, M.; Patel, M.P.; Parker, S. An experimental and theoretical study of the effect of sample thickness on the Shore hardness of elastomers. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoeli, Z.; Miller, V.; Zeltser, C. Consistency and softness of soft liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 75, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canay, S.; Hersek, N.; Tulunoğlu, I.; Uzun, G. Evaluation of colour and hardness changes of soft lining materials in food colorant solutions. J. Oral Rehabil. 1999, 26, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mese, A.; Guzel, K.G. Effect of storage duration on the hardness and tensile bond strength of silicone- and acrylic resin-based resilient denture liners to a processed denture base acrylic resin. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 99, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzois, G.L.; Frangou, M.J. Influence of curing method, sealer, and water storage on the hardness of a soft lining material over time. J. Prosthodont. 2001, 10, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, G.R.; Rueggeberg, F.A. In vitro hardness, water sorption, and resin solubility of laboratory-processed and autopolymerized long-term resilient denture liners over one year of water storage. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 88, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Yang, H.S.; Chun, M.G.; Park, Y.J. Shore hardness and tensile bond strength of long-term soft denture lining materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, M.; Akiba, N.; Minakuchi, S.; Takahashi, H. Influence of methyl mercaptan at early setting stages on the properties of self curing addition silicone resilient denture lining materials. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2009, 53, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, S.; Arioli Filho, J.N.; dos Santos, P.H.; Nogueira, S.S.; Batista, A.U. Effect of disinfection treatments on the hardness of soft denture liner materials. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 16, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, D.L.; Breeding, L.C.; Faler, T.A. Microwave disinfection of denture base materials colonized with Candida albicans. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, D.N.; Goiato, M.C.; Zuccolotti, B.C.; Moreno, A.; dos Santos, D.M.; Pesqueira, A.A. Effect of thermocycling on hardness, absorption, solubility and colour change of soft liners. Gerodontology 2012, 29, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainieri, V.C.; Beck, J.; Oshima, H.M.; Hirakata, L.M.; Shinkai, R.S. Surface changes in denture soft liners with and without sealer coating following abrasion with mechanical brushing. Gerodontology 2011, 28, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Athel, M.S.; Jagger, R.G. Effect of test method on the bond strength of a silicone resilient denture lining material. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 76, 535–540. [Google Scholar]
- Mutluay, M.M.; Ruyter, I.E. Evaluation of bond strength of soft relining materials to denture base polymers. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, J.F.; Carrick, T.E.; Kamohara, H. Adhesive bond strength and compliance for denture soft lining materials. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertgöz, A.; Kulak, Y.; Gedik, H.; Taskonak, B. The effect of thermocycling on peel strength of six soft lining materials. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 583–587. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard Test Methods for Rubber Property—Adhesion to Rigid Substrates; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, M.; Amarnath, G.S.; Muddugangadhar, B.C.; Swetha, M.U.; Das, K.A. Tensile and shear bond strength of hard and soft denture relining materials to the conventional heat cured acrylic denture base resin: An in-vitro study. J. Int. Oral Health 2014, 6, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elias, C.N.; Henriques, F.Q. Effect of thermocycling on the tensile and shear bond strengths of three soft liners to a denture base resin. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2007, 15, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulak-Ozkan, Y.; Sertgoz, A.; Gedik, H. Effect of thermocycling on tensile bond strength of six silicone-based, resilient denture liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 89, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Kutay, O. Comparison of tensile and peel bond strength of resilient liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1994, 71, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, A.K.; Terzioğlu, H.; Akinay, A.E.; Ulubayram, K.; Hasirci, N. Bond strength and failure analysis of lining materials to denture resin. Dent. Mater. 1999, 15, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meşe, A.; Güzel, K.G.; Uysal, E. Effect of storage duration on tensile bond strength of acrylic or silicone-based soft denture liners to a processed denture base polymer. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2005, 63, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yanikoglu, N.; Denizoglu, S. The effect of different solutions on the bond strength of soft lining materials to acrylic resin. Dent. Mater. J. 2006, 25, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, J.R.; Mesquita, M.F.; Nóbilo, M.A.; Henriques, G.E. Evaluation of varying amounts of thermal cycling on bond strength and permanent deformation of two resilient denture liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.S.; Parkhedkar, R. The effect of denture base surface pretreatments on bond strengths of two long term resilient liners. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2011, 3, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraç, Y.S.; Başoğlu, T.; Ceylan, G.K.; Saraç, D.; Yapici, O. Effect of denture base surface pretreatment on microleakage of a silicone-based resilient liner. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Lassila, L.V.; Mutluay, M.M.; Tezvergil-Mutluay, A.; Vallittu, P.K. Bond strength of soft liners to fiber-reinforced denture-base resin. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 19, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimoto, Y.; Saeki, H.; Kimoto, S.; Nishiwaki, T.; Nishiyama, N. Evaluation of adhesive properties of three resilient denture liners by the modified peel test method. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.L.; Breeding, L.C.; Puckett, A.D. Effect of microwave disinfection on the hardness and adhesion of two resilient liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 94, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagger, R.G.; Al-Athel, M.S.; Jagger, D.C.; Vowles, R.W. Some variables influencing the bond strength between PMMA and a silicone denture lining material. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 15, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Athel, M.; Jagger, R.; Jagger, D. Effect of ageing on the bond strength of a permanent denture soft lining material. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 992–996. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, I.; Keh, E.S.; Morizawa, M.; Muraoka, G.; Hirano, S. A new polyisoprene-based light-curing denture soft lining material. J. Dent. 2003, 31, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, P.S. Characterization of the rupture properties of denture soft lining materials. J. Dent. Res. 1980, 59, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinçkal Yanikoğlu, N.; Denizoğlu, S. An investigation of the tear energy of five soft lining materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2003, 22, 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Baysan, A.; Parker, S.; Wright, P.S. Adhesion and tear energy of a long-term soft lining material activated by rapid microwave energy. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1998, 79, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landayan, J.; Manaloto, A.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, S.W. Effect of aging on tear strength and cytotoxicity of soft denture lining materials; in vitro. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2014, 6, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, F.; Dootz, E.R.; Koran, A., 3rd; Craig, R.G. Sorption and solubility of 12 soft denture liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1994, 72, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, S.; Braden, M. Water absorption of methacrylate soft lining materials. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazhat, S.N.; Parker, S.; Braden, M. Silica-filled elastomer/methacrylate systems as soft liners. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2004, 15, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.G.; Jagger, R.G.; Winter, R.W. Effect of surface modified fillers on the water absorption of a (RTV) silicone denture soft lining material. J. Dent. 1996, 24, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.C.; Pearson, G.J.; Braden, M.; Wright, P.S. The interaction of various liquids with long-term denture soft lining materials. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, G.; Takahashi, H.; Hayakawa, I. Effects of cyclic loading on viscoelastic properties of soft lining materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2003, 22, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinçkal Yanikoglu, N.; Yeşil Duymuş, Z. Comparative study of water sorption and solubility of soft lining materials in the different solutions. Dent. Mater. J. 2004, 23, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, H.; Taguchi, N.; Hamada, T.; McCabe, J.F. Dynamic viscoelastic properties and the age changes of long-term soft denture liners. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, F.; Suzuki, S.; Mukai, Y. An evaluation of the viscoelastic characteristics of soft denture liners. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 11, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santawisuk, W.; Kanchanavasita, W.; Sirisinha, C.; Harnirattisai, C. Dynamic viscoelastic properties of experimental silicone soft lining materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2010, 29, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, R.W. Denture lining materials. In Science of Dental Materials, 2nd ed.; Skinner, E.W., Ed.; Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1991; p. 211. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, I.; Hirano, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Nagao, M.; Masuhara, E. The creep behavior of denture-supporting tissues and soft lining materials. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1994, 7, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braden, M.; Clarke, R.L. Viscoelastic properties of soft lining materials. J. Dent. Res. 1972, 51, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.; Jagger, R.; Williams, K.; Jerolimov, V. Dynamic mechanical thermal analysis of denture soft lining materials. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 1627–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber-Sheikh, K.; Clarke, R.L.; Braden, M. Viscoelastic properties of some soft lining materials: I—Effect of temperature. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 817–822. [Google Scholar]
- Saber-Sheikh, K. The Viscoelastic Properties of Some Dental Soft Lining Materials. In Ph.D. Thesis; University of London: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, J.F.; Basker, R.M.; Murata, H.; Wollwage, P.G. The development of a simple test method to characterise the compliance and viscoelasticity of long-term soft lining materials. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 1996, 4, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jepson, N.J.; McCabe, J.F.; Storer, R. Age changes in the viscoelasticity of permanent soft lining materials. J. Dent. 1993, 21, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, J.F. A polyvinylsiloxane denture soft lining material. J. Dent. 1998, 26, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, Y.; Taji, T.; Hiasa, K.; Tsuga, K.; Akagawa, Y. Dynamic viscoelastic properties of vinyl polysiloxane denture soft lining materials. J. Oral Rehabil. 2009, 36, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Ogimoto, T.; Koyano, K.; Ogawa, T. Denture wearing and strong bite force reduce pressure pain threshold of edentulous oral mucosa. J. Oral Rehabil. 2004, 31, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ogimoto, T.; Okushi, N.; Koyano, K.; Takeuchi, K. Mapping, profiling and clustering of pressure pain threshold (PPT) in edentulous oral mucosa. J. Dent. 2004, 32, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmudzki, J.; Chladek, G.; Kasperski, J. The influence of a complete lower denture destabilization on the pressure of the mucous membrane foundation. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2012, 14, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, L.C. Movement of maxillary complete dentures—A kinesiographic study. J. Dent. 1983, 11, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, K.; Sekita, T.; Minakuchi, S.; Hirano, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Nagao, M. Denture mobility with six degrees of freedom during function. J. Oral Rehabil. 1998, 25, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żmudzki, J.; Chladek, G.; Kasperski, J.; Dobrzański, L.A. One versus two implant-retained dentures: Comparing biomechanics under oblique mastication forces. J. Biomech. Eng. 2013, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmudzki, J.; Chladek, G.; Kasperski, J. Single implant–retained dentures: loading of various attachment types under oblique occlusal forces. J Mech. Med. Biol. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.; Braden, M. New soft lining materials. J. Dent. 1982, 10, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, F.; Asaoka, K.; Nagao, K.; Matsumoto, N. Effect of viscoelastic deformation of soft tissue on stresses in the structures under complete denture. Dent. Mater. J. 1990, 9, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, F.; Koran, A., 3rd; Asaoka, K.; Matsumoto, N. Effect of soft denture liner on stress distribution in supporting structures under a denture. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1993, 6, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kasperski, J.; Żmudzki, J.; Chladek, G. Denture foundation tissues loading criteria in evaluation of dentures wearing characteristics. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2010, 43, 324–332. [Google Scholar]
- Oomens, C.W.J.; Bressers, O.F.J.T.; Bosboom, E.M.H.; Bouten, C.V.C.; Bader, D.L. Can loaded interface characteristics influence strain distributions in muscle adjacent to bony prominences? Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 6, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ragan, R.; Kernozek, T.W.; Bidar, M.; Matheson, J.W. Seat interface pressures on various thicknesses of foam wheelchair cushions: A finite modeling approach. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder-Ganz, E.; Shabshin, N.; Itzchak, Y.; Gefen, A. Assessment of mechanical conditions in sub-dermal tissues during sitting: A combined experimental-MRI and finite element approach. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Kivovics, P.; Jáhn, M.; Borbély, J.; Márton, K. Frequency and location of traumatic ulcerations following placement of complete dentures. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 20, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okuma, K.; Hirano, S.; Hayakawa, I. Occlusal pressure pattern analysis of complete dentures for evaluation of occlusal adjustment. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2004, 51, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cha, H.S.; Yu, B.; Lee, Y.K. Changes in stress relaxation property and softness of soft denture lining materials after cyclic loading. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, H.; Sakurai, K. Changes of blood flow in the mucosa underlying a mandibular denture following pressure assumed as a result of light clenching. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruo, Y.; Nishigawa, G.; Irie, M.; Oka, M.; Hara, T.; Suzuki, K.; Minagi, S. Stress distribution prevents ischaemia and bone resorption in residual ridge. Arch. Oral Biol. 2010, 55, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, J.B.; Kydd, W.L.; Daly, C. The thickness measurement of masticatory mucosa in vivo. Int. Dent. J. 1971, 21, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okada, C.; Ueda, T.; Sakurai, K. Blood flow in denture-supporting maxillary mucosa in response to simulated mastication by loading. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2010, 54, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shotwell, J.L.; Razzoog, M.E.; Koran, A. Color stability of long-term soft denture liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 68, 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imirzalioglu, P.; Karacaer, O.; Yilmaz, B.; Ozmen, I. Color stability of denture acrylic resins and a soft lining material against tea, coffee, and nicotine. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 19, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Akiba, N.; Minakuchi, S.; Matsushita, N.; Hishimoto, M. Basic evaluation on physical properties of experimental fluorinated soft lining materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oğuz, S.; Mutluay, M.M.; Doğan, O.M.; Bek, B. Color change evaluation of denture soft lining materials in coffee and tea. Dent. Mater. J. 2007, 26, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Anil, N.; Hekimoglu, C.; Sahin, S. Color stability of heat-polymerized and autopolymerized soft denture liners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Nikawa, H.; Makihira, S.; Hamada, T.; Furukawa, M.; Murata, H. Changes in surface roughness and colour stability of soft denture lining materials caused by denture cleansers. J. Oral Rehabil. 2003, 30, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraç, D.; Saraç, Y.S.; Kurt, M.; Yüzbaşioğlu, E. The effectiveness of denture cleansers on soft denture liners colored by food colorant solutions. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 16, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Handa, R.K.; Jagger, D.C.; Vowles, R.W. Denture cleansers, soft lining materials and water temperature: What is the effect? Prim. Dent. Care 2008, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Goiato, M.C.; Falcón-Antenucci, R.M.; Santos, D.M.; Pellizzer, E.P. Evaluation of hardness and color stability in the soft lining materials after thermocycling and chemical polishing. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2009, 22, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chladek, G.; Żmudzki, J.; Kasperski, J. Long-Term Soft Denture Lining Materials. Materials 2014, 7, 5816-5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085816
Chladek G, Żmudzki J, Kasperski J. Long-Term Soft Denture Lining Materials. Materials. 2014; 7(8):5816-5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085816
Chicago/Turabian StyleChladek, Grzegorz, Jarosław Żmudzki, and Jacek Kasperski. 2014. "Long-Term Soft Denture Lining Materials" Materials 7, no. 8: 5816-5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085816
APA StyleChladek, G., Żmudzki, J., & Kasperski, J. (2014). Long-Term Soft Denture Lining Materials. Materials, 7(8), 5816-5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085816







