Charged Triazole Cross-Linkers for Hyaluronan-Based Hybrid Hydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
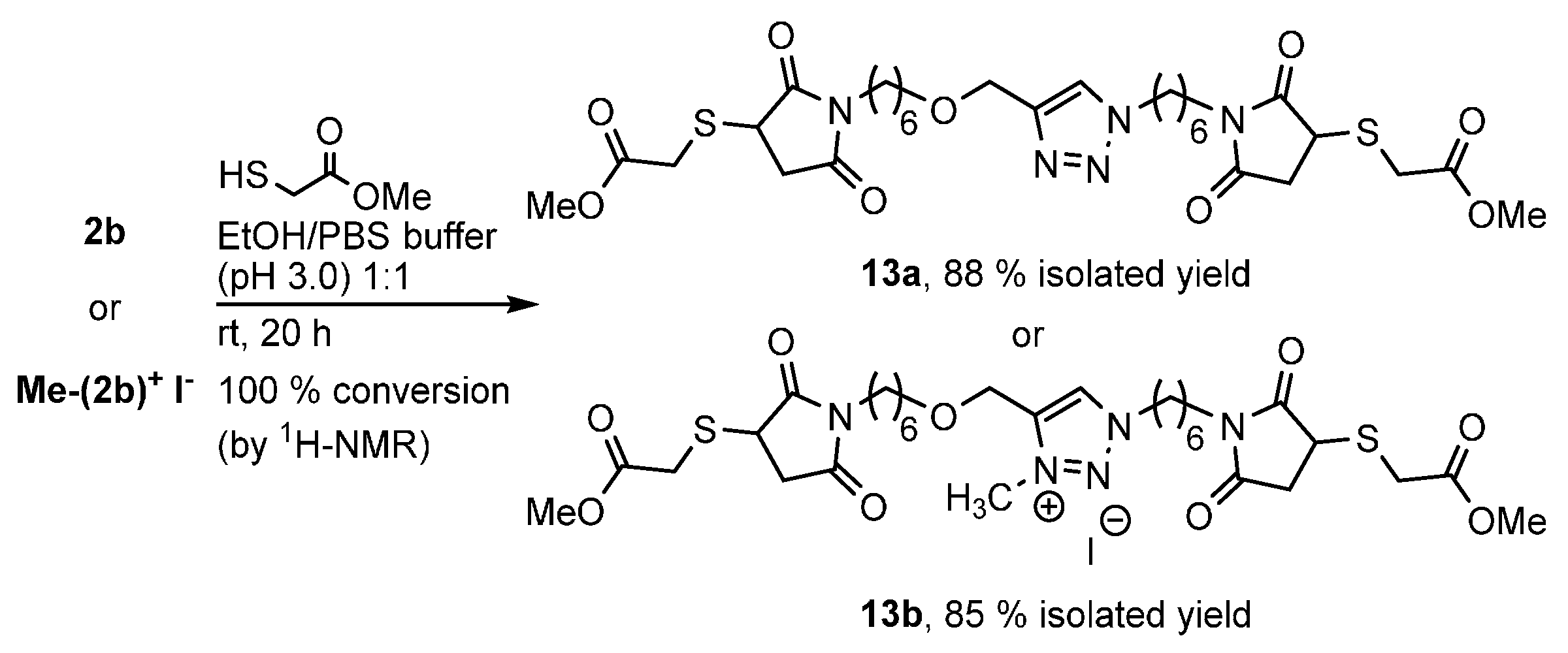
2.1. Synthesis of Cross-Linkers 2 and Me-(2)+ I−
2.2. Formation of Hydrogels with Thiolated Hyaluronan
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Maleimide Cross-Linkers 2 and Me-(2)+ I−
3.2. Thiolation of HA and Ellman’s Assay
3.3. HA-Hydrogel Formation
3.4. Mechanical Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HA | hyaluronan, hyaluronic acid |
| HA-SH | thiolated hyaluronan |
| HA125-SH40 | hyaluronan with an average molecular weight of 125 kDa and a thiolation degree of 40% |
| CuAAC | Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition |
| NPhth | N-phthalimido |
| rt | room temperature |
| Me | methyl |
| Et | ethyl |
| Ac | acetyl |
| equiv | equivalents |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| Ts | tosyl (protecting group) |
| TBAI | tetrabutylammonium iodide |
| ddH2O | double-distilled water |
References
- Marcellin, E.; Steen, J.A.; Nielsen, L.K. Insight into hyaluronic acid molecular weight control. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6947–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic acid—A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato Endrocrinol. 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.K.; Mishra, P.; Agrawal, G.P. An insight on hyaluronic acid in drug targeting and drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2008, 16, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliktar, D. Designing Cell-Compatible Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Science 2012, 336, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdick, J.A.; Prestwich, G.D. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H41–H56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.N.; Birkinshaw, C. Hyaluronic acid based scaffolds for tissue engineering—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.Z.; Ahmad, S.; Liu, Y.; Prestwich, G.D. Synthesis and evaluation of injectable, in situ crosslinkable synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Res. A 2006, 79, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.Z.; Liu, Y.; Palumbo, F.S.; Luo, Y.; Prestwich, G.D. In situ crosslinkable hyaluronan hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.; Moreira Teixeira, L.S.; Krouwels, A.; Dijkstra, P.J.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M.; Feijen, J. Synthesis and characterization of hyaluronic acid-poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels via Michael addition: An injectable biomaterial for cartilage repair. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, C.B.; Barnett, S.M. Swelling Behavior of Hyaluronic Acid Gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 45, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadsetan, M.; Pumberger, M.; Casper, M.E.; Shogren, K.; Giuliani, M.; Ruesink, T.; Hefferan, T.E.; Currier, B.L.; Yaszemski, M.J. The effects of fixed electrical charge on chondrocyte behavior. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Gatta, A.; Schiraldi, C.; Esposito, A.; D’Agostino, A.; De Rosa, A. Novel poly(HEMA-co-METAC)/alginate semi-interpenetrating hydrogels for biomedical applications: Synthesis and characterization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 90, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Tian, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, J. Robust and Flexible Free-Standing Films for Unidirectional Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8328–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.D.; Bruening, M.L. Correlation of the Swelling and Permeability of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Films. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5375–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.G.; Li, H.; Chow, J.K.; Geissler, S.A.; McElroy, A.B.; Nguy, L.; Hernandez, D.S.; Schmidt, C.E. Conducting polymer-based multilayer films for instructive biomaterial coatings. Future Sci. OA 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Ratiometric Fluorescent Biosensor for Hyaluronidase with Hyaluronan as Both Nanoparticle Scaffold and Substrate for Enzymatic Reaction. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Cunningham, C.; Pandit, A.; Wall, J.G. Improved Gene Transfection Efficacy and Cytocompatibility of Multifunctional Polyamidoamine-Cross-Linked Hyaluronan Particles. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.-Q.; Wu, J.; Chu, C.-C. A novel family of biodegradable hybrid hydrogels from arginine-based poly(ester amide) and hyaluronic acid precursors. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3965–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavila, S.; Eivgi, O.; Berkovich, I.; Lemcoff, N.G. Intramolecular Cross-Linking Methodologies for the Synthesis of Polymer Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 878–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagel, V.; Mateescu, M.; Southan, A.; Wegner, S.V.; Nuss, I.; Haraszti, T.; Kleinhans, C.; Schuh, C.; Spatz, J.P.; Kluger, P.J.; et al. Desmosine-Inspired Cross-Linkers for Hyaluronan Hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateescu, M.; Nuss, I.; Southan, A.; Messenger, H.; Wegner, S.V.; Kupka, J.; Bach, M.; Tovar, G.E.M.; Boehm, H.; Laschat, S. Synthesis of Pyridine Acrylates and Acrylamides and Their Corresponding Pyridinium Ions as Versatile Cross-Linkers for Tunable Hydrogels. Synthesis 2014, 46, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Southan, A.; Mateescu, M.; Hagel, V.; Bach, M.; Schuh, C.; Kleinhans, C.; Kluger, P.J.; Tussetschläger, S.; Nuss, I.; Haraszti, T.; et al. Toward Controlling the Formation, Degradation Behavior, and Properties of Hydrogels Synthesized by Aza-Michael Reactions. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juríček, M.; Kouwer, P.H.J.; Rowan, A.E. Triazole: A unique building block for the construction of functional materials. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8740–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obadia, M.M.; Drockenmuller, E. Poly(1,2,3-triazolium)s: A new class of functional polymer electrolytes. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2433–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzi, V.; Cornelio, L.; Di Meo, C.; Nardecchia, S.; Lamanna, R. Novel Hydrogels via Click Chemistry: Synthesis and Potential Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, G.; Di Meo, C.; Nardecchia, S.; Capitani, D.; Mannina, L.; Lamanna, R.; Barbetta, A.; Dentini, M. Influence of dialkyne structure on the properties of new click-gels based on hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 378, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Suhara, T.; Omichi, K.; Shimizu, A.; Hasegawa, K.; Kokudo, N.; Ohta, S.; Ito, T. In Situ Cross-Linkable Hydrogel of Hyaluronan Produced via Copper-Free Click Chemistry. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3581–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, K.C.; Kaller, M.; Axenov, K.V.; Tussetschläger, S.; Laschat, S. Synthesis and mesomorphic properties of calamitic malonates and cyanoacetates tethered to 4-cyanobiphenyls. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsden, D.M.; Nicholson, R.L.; Ladlow, M.; Spring, D.R. 3D small-molecule microarrays. Chem. Commun. 2009, 7107–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; Shi, J.; Gao, S.; Li, S.; Niu, C.; Xi, Z. Sulfonium alkylation followed by ‘click’ chemistry for facile surface modification of proteins and tobacco mosaic virus. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, F.; Odell, A.V.; Ward, G.E.; Westwood, N.J. A Modular Approach to Triazole-Containing Chemical Inducers of Dimerisation for Yeast Three-Hybrid Screening. Molecules 2013, 18, 11639–11657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, B.; Jing, X.; Cammidge, A.N. A Mesogenic Triphenylene-Perylene-Triphenylene Triad. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakanen, J.R.; Coward, J.K.; Pegg, A.E. α-Methyl Polyamines: Metabolically Stable Spermidine and Spermine Mimics Capable of Supporting Growth in Cells Depleted of Polyamines. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himo, F.; Lovell, T.; Hilgraf, R.; Rostovtsev, V.V.; Noodleman, L.; Sharpless, K.B.; Fokin, V.V. Copper(I)-Catalyzed Synthesis of Azoles. DFT Study Predicts Unprecedented Reactivity and Intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casnati, A.; Della Ca’, N.; Fontanella, M.; Sansone, F.; Ugozzoli, F.; Ungaro, R.; Liger, K.; Dozol, J.-F. Calixarene-Based Picolinamide Extractants for Selective An/Ln Separation from Radioactive Waste. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ni, A.S.Y.; Lim, Y.; Mohanram, H.; Bhattacharjya, S.; Xing, B. Lipopolysaccharide Neutralizing Peptide-Porphyrin Conjugates for Effective Photoinactivation and Intracellular Imaging of Gram-Negative Bacteria Strains. Bioconj. Chem. 2012, 23, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.E.M.N.; Holzwarth, M.S.; Hohloch, S.; Sarkar, B.; Plietker, B. Redox-Active Triazolium-Derived Ligands in Nucleophilic Fe-Catalysis—Reactivity Profile and Development of a Regioselective O-Allylation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 6310–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.P.; Podgórski, M.; Chatani, S.; Gong, T.; Xi, W.; Fenoli, C.R.; Bowman, C.N. The Thiol-Michael Addition Click Reaction: A Powerful and Widely Used Tool in Materials Chemistry. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 724–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Modeling the effects of pH and ionic strength on swelling of anionic polyelectrolyte gels. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 055005:01–055005:38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košovan, P.; Richter, T.; Holm, C. Modeling of Polyelectrolyte Gels in Equilibrium with Salt Solutions. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7698–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesalski, M.; Rühe, J. Tailoring the Charge Density of Surface-Attached Polyelectrolyte Brushes. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Roberts, M.C.; Prestwich, G.D. Disulfide Cross-Linked Hyaluronan Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruysse, K.P.; Marecak, D.M.; Marecek, J.F.; Prestwich, G.D. Synthesis and in vitro Degradation of New Polyvalent Hydrazide Cross-Linked Hydrogels of Hyaluronic Acid. Bioconj. Chem. 1997, 8, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellmann, G.L. Tissue Sulfhydryl Groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Hydrogel | Spacer Length n | E-Modulus (kPa) | Reacted Thiols (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA125-SH40-2a | 4 | 14.60 ± 3.60 | 85 ± 3 |
| HA125-SH40-2b | 6 | 14.53 ± 7.07 | 84 ± 2 |
| HA125-SH40-2c | 8 | 1.16 ± 0.85 | 83 ± 4 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2a)+ I− | 4 | 25.32 ± 10.06 | 87 ± 4 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2b)+ I− | 6 | 12.15 ± 3.41 | 85 ± 3 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2c)+ I− | 8 | 17.41 ± 8.60 | 84 ± 3 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2d)+ I− | 10 | 16.99 ± 8.99 | 85 ± 4 |
| Hydrogel | Spacer Length n | Swelling Ratio (PBS) | Swelling Ratio (ddH2O) | Mesh Size (PBS) (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA125-SH40-2a | 4 | 79.63 ± 1.16 | 162.37 ± 45.16 | 51.82 ± 26.31 |
| HA125-SH40-2b | 6 | 30.22 ± 17.83 | 68.89 ± 44.36 | 61.52 ± 10.02 |
| HA125-SH40-2c | 8 | 100.58 ± 49.91 | 208.85 ± 134.57 | 55.81 ± 27.77 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2a)+ I− | 4 | 67.70 ± 5.79 | 139.79 ± 28.15 | 83.93 ± 9.64 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2b)+ I− | 6 | 49.47 ± 8.63 | 98.05 ± 9.90 | 157.84 ± 44.00 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2c)+ I− | 8 | 33.75 ± 5.75 | 59.30 ± 13.14 | 55.94 ± 8.59 |
| HA125-SH40-Me-(2d)+ I− | 10 | 18.79 ± 4.14 | 31.22 ± 9.13 | 27.16 ± 6.77 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martini, M.; Hegger, P.S.; Schädel, N.; Minsky, B.B.; Kirchhof, M.; Scholl, S.; Southan, A.; Tovar, G.E.M.; Boehm, H.; Laschat, S. Charged Triazole Cross-Linkers for Hyaluronan-Based Hybrid Hydrogels. Materials 2016, 9, 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9100810
Martini M, Hegger PS, Schädel N, Minsky BB, Kirchhof M, Scholl S, Southan A, Tovar GEM, Boehm H, Laschat S. Charged Triazole Cross-Linkers for Hyaluronan-Based Hybrid Hydrogels. Materials. 2016; 9(10):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9100810
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartini, Maike, Patricia S. Hegger, Nicole Schädel, Burcu B. Minsky, Manuel Kirchhof, Sebastian Scholl, Alexander Southan, Günter E. M. Tovar, Heike Boehm, and Sabine Laschat. 2016. "Charged Triazole Cross-Linkers for Hyaluronan-Based Hybrid Hydrogels" Materials 9, no. 10: 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9100810
APA StyleMartini, M., Hegger, P. S., Schädel, N., Minsky, B. B., Kirchhof, M., Scholl, S., Southan, A., Tovar, G. E. M., Boehm, H., & Laschat, S. (2016). Charged Triazole Cross-Linkers for Hyaluronan-Based Hybrid Hydrogels. Materials, 9(10), 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9100810





