Two Novel C3N4 Phases: Structural, Mechanical and Electronic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational Method
3. Results and Discussion
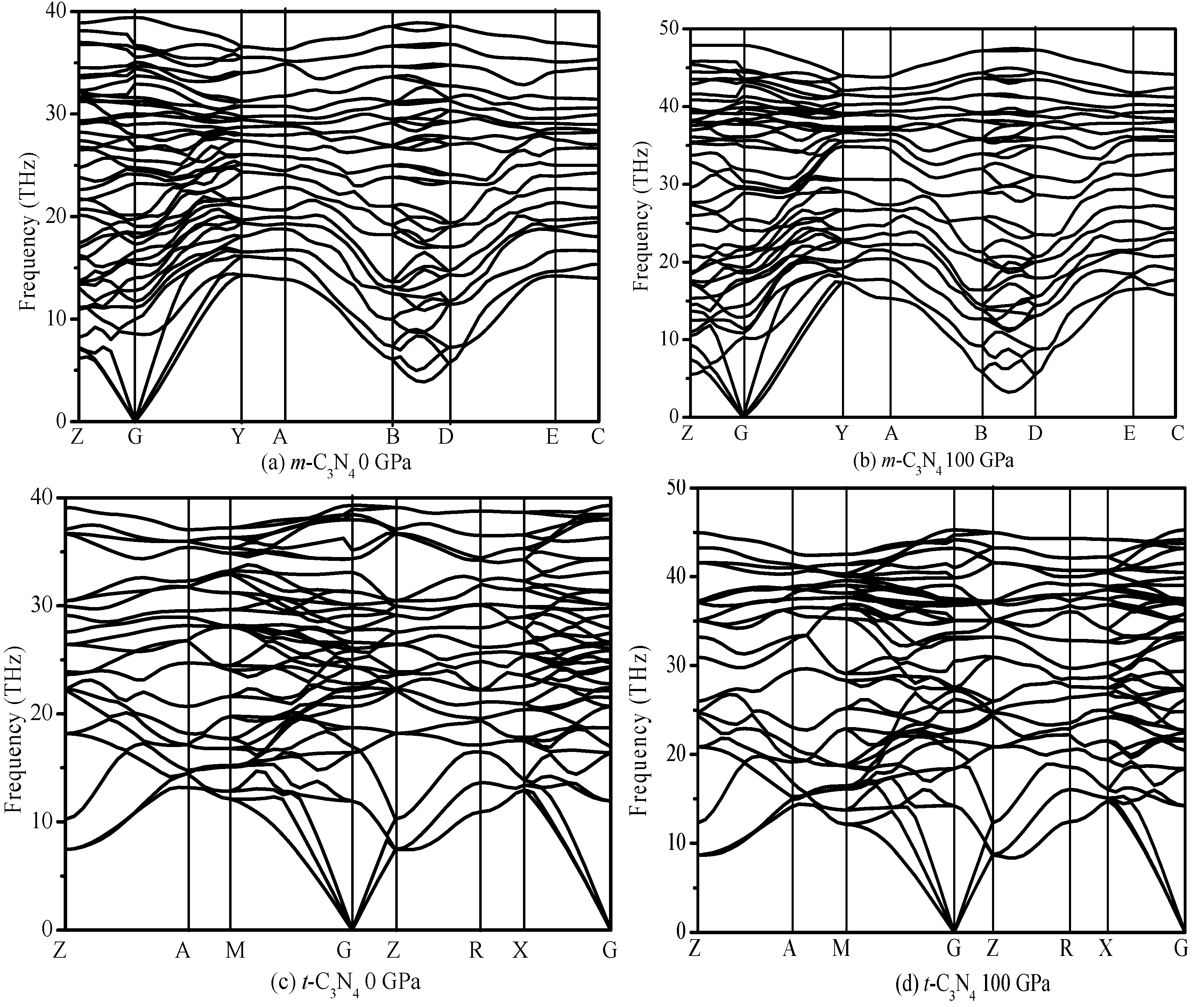
3.1. Structural Properties
3.2. Elastic Properties and Hardness
3.3. Electronic Structures
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannay, J.B. Artificial Diamonds. Nature 1880, 22, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgman, P.W. An experimental contribution to the problem of diamond synthesis. J. Chem. Phys. 1947, 15, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, M.; Cohen, M.L. Carbon nitride compounds with 1:1 stoichiometry. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 5684–5688. [Google Scholar]
- Betranhandy, E.; Matar, S.F. A model study for the breaking of cyanogen out of CNx within DFT. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Chen, C.F.; Kawazoe, Y. Orthorhombic carbon allotrope of compressed graphite: Ab initio calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 033410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Chen, C.F.; Kawazoe, Y. Low-temperature phase transformation from graphite to sp3 orthorhombic carbon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 075501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemoto, K.; Wentzcovitch, R.M.; Saito, S.; Miyake, T. Body-centered tetragonal C4: A viable sp3 carbon allotrope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 125504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Bao, K.; Tian, F.B.; Zeng, Z.W.; He, Z.; Liu, B.B.; Cui, T. Lowest enthalpy polymorph of cold-compressed graphite phase. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 4347–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.K.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y. Lonsdaleite—A material stronger and stiffer than diamond. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.L.; Zeng, X.C. Polymorphic phases of sp3-hybridized carbon under cold compression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7530–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.Y.; Du, Y.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, Q. Orthorhombic C32: A novel superhard sp3 carbon allotrope. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 14120–14125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.Y.; Sun, L.Z.; Zhang, C.X.; Peng, X.Y.; Zhang, K.W.; Zhong, J.X. New superhard carbon phases between graphite and diamond. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.L.; Yan, Q.B.; Ye, F.; Zheng, Q.R.; Su, G. T-carbon: A novel carbon allotrope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 155703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, M.G.; Yan, H.Y.; Lin, Z.Z.; Zhu, X.M. Structural, electronic and mechanical properties of Imma-carbon. EPL 2014, 107, 27007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Lv, Z.L.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.R.; Cai, L.C. A possible superhard orthorhombic carbon. Diam. Relat. Mat. 2014, 43, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentorf, R.H., Jr. Cubic form of boron nitride. J. Chem. Phys. 1957, 26, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueorguiev, G.K.; Neidhardt, J.; Stafstrom, S.; Hultman, L. First-principles calculations on the role of CN precursors for the formation of fullerene-like carbon nitride. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 401, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueorguiev, G.K.; Neidhardt, J.; Stafstrom, S.; Hultman, L. First-principles calculations on the curvature evolution and cross-linkage in carbon nitride. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 410, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Y.; Cohen, M.L. Prediction of new low compressibility solids. Science 1989, 245, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Wei, Q.; Chai, C.C.; Yan, H.Y.; Zhang, M.G.; Lin, Z.Z.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.Y. Structural, mechanical, and electronic properties of P3m1-BCN. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2015, 79, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeuseler, H. X-ray investigations in the system CdIn2S4-CdIn2Se4. J. Solid State Chem. 1979, 29, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Y.; Wentzcovitch, R.M. Stability of carbon nitride solids. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 10362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teter, D.M.; Hemley, R.J. Low-compressibility carbon nitrides. Science 1996, 271, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.D.; Ouyang, L.; Ching, W.Y.; Tanaka, I.; Koyama, Y.; Riedel, R. Interesting physical properties of the new spinel phase of Si3N4 and C3N4. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 5046–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, P. Pathways to metastable nitride structures. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 176, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyali, G.S.; Warmbier, R.; Quandt, A.; Lowther, J.E. Ab initio study of elastic properties of super hard and graphitic structures of C3N4. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 69, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Hu, M.; Wang, Q.Q.; Xu, B.; Yu, D.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; He, J.L. Prediction of novel hard phases of Si3N4: First-principles calculations. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 228, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.J.; Segall, M.D.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Probert, M.I.J.; Refson, K.; Payne, M.C. First principles methods using CASTEP. Z. Kristallogr. 2005, 220, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrommer, B.G.; Côté, M.; Louie, S.G.; Cohen, M.L. Relaxation of crystals with the quasi-newton method. J. Comput. Phys. 1997, 131, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krukau, A.V.; Vydrov, O.A.; Izmaylov, A.F.; Scuseria, G.E. Influence of the exchange screening parameter on the performance of screened hybrid functionals. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 224106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Chai, C.C.; Wei, Q.; Yang, Y.T. Two novel silicon phases with direct band gaps. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 12905–12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.W.; Xu, G.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Yuan, Y.P.; Jiang, X.; Lu, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.J. The elastic behavior of dense C3N4 under high pressure: First-principles calculations. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2014, 75, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.W.; Zhang, F.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Qin, Z.C.; Zhang, M.; Liu, R.P.; Xu, Y.F.; Wang, W.K. Synthesis of carbon nitride crystals at high pressures and temperatures. J. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 3458–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, B.; Sansores, L.E. Eelectronic structure of six phases of C3N4: A theoretical approach. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 1999, 13, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gil, J.; Martin-Gil, F.J.; Sarikaya, M.; Qian, M.; Jose-Yacaman, M.; Rubio, A. Evidence of a low compressibility carbon nitride with defect-zincblende structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hao, J.; Lia, Y.W. A first-principles study of orthorhombic CN as a potential superhard material. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 27821–27825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goglio, G.; Foy, D.; Demazeau, G. State of Art and recent trends in bulk carbon nitrides synthesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2008, 58, 195–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, S.P. Band gap of C3N4 in the GW approximation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11072–11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.J.; Zhao, E.J.; Xiang, H.P.; Hao, X.F.; Liu, X.J.; Meng, J. Crystal structures and elastic properties of superhard IrN2 and IrN3 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 054115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Wei, Q.; Yan, H.Y.; Zhang, M.G.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. A New Potential Superhard Phase of OsN2. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 126, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, W. Lehrburch der Kristallphysik; Teubner, B.G., Ed.; Johnson Reprint Corp: Leipzig, Germany, 1928. [Google Scholar]
- Reuss, A. Berechnung der Fließgrenze von Mischkristallen auf Grund der Plastizitätsbedingung für Einkristalle. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1929, 9, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R. The elastic behaviour of a crystalline aggregate. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. Sect. A 1952, 65, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Chai, C.C.; Wei, Q.; Yang, Y.T.; Qiao, L.P.; Zhao, Y.B.; Zhou, P.K.; Xing, M.J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yao, R.H. Mechanical and electronic properties of Ca1-xMgxO alloys. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 40, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsditch, M.; Zouboulis, E.S.; Polian, A. Elastic constants of boron nitride. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.B.; Nguyen, S.L.; Rasool, H.I.; Wright, J.A.; Brown, S.E.; Kaner, R.B. Preparation and properties of metallic, superhard rhenium diboride crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16953–16958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Fan, C. First-principles study on hardness of five polymorphs of C3N4. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2008, 403, 1956–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.L.; Guo, L.C.; Guo, X.J.; Liu, R.P.; Tian, Y.J.; Wang, H.T.; Gao, C.X. Predicting hardness of dense C3N4 polymorphs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Wei, Q.; Yan, H.Y.; Zhang, M.G.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.Y. Elastic and electronic properties of Pbca-BN: First-principles calculations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 85, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, S.; Xiong, M.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Luo, K.; He, J.L.; Tian, Y.J. First-principles study of O-BN: A sp3-bonding boron nitride allotrope. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 053518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, S.F. XCII. Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. Ser. 7 1954, 45, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.H.; Sun, Y.; Peng, M.J.; Zhou, S.G. Anisotropic elastic properties of the Ca–Pb compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 595, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.I.; Ostoja-Starzewski, M. Universal elastic anisotropy index. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 055504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmier, A.; Lethbridge, Z.A.D.; Walton, R.I.; Smith, C.W.; Parker, S.C.; Evans, K.E. ElAM: A computer program for the analysis and representation of anisotropic elastic properties. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2010, 181, 2102–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.C.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.J.; Zeng, X.Q.; Xu, C.S. First-principles study of structural and electronic properties of C14-type Laves phase Al2Zr and Al2Hf. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 83, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, J. Band Theory and Electronic Properties of Solids; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]









| Materials | This Work | Other Works | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | a, b, c | |
| α-C3N4 | 6.512 | – | 4.742 | a = 6.489, c = 4.729 a; a = 6.425, c = 4.715 b; a = 6.467, c = 4.710 c; a = 6.453, c = 4.699 d; a = 6.47, c = 4.71 e |
| β-C3N4 | 6.449 | – | 2.422 | a = 6.426, c = 2.418 a; a = 6.419, c = 2.425 b; a = 6.402, c = 2.404 c; a = 6.394, c = 2.397 d; a = 6.40, c = 2.40 e |
| d-ZB-C3N4 | 3.456 | – | – | a = 3.455 f; a = 3.52 e; a = 3.43 g |
| cubic-C3N4 | 5.398 | – | – | a = 5.395–5.444 h; a = 5.40 e |
| pseudocubic-C3N4 | 3.456 | – | – | a = 3.41–3.44 h |
| g-C3N4 | 4.791 | – | 6.769 | a = 4.74, 6.72 e |
| m-C3N4 | 8.032 | 2.418 | 6.246 | – |
| t-C3N4 | 3.483 | – | 6.933 | – |
| Materials | C11 | C22 | C33 | C44 | C55 | C66 | C12 | C13 | C23 | C15 | C25 | C35 | C46 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-C3N4 | 848 | – | 906 | 319 | – | 335 | 179 | 131 | – | −27 | – | – | 27 |
| Reference [37] | 851 | – | 906 | 326 | – | 334 | 183 | 129 | – | – | – | – | – |
| β-C3N4 | 852 | – | 1150 | 286 | – | 312 | 228 | 111 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Reference [37] | 833 | – | 1049 | 289 | – | 287 | 259 | 110 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Reference [22] | 834 | – | 1120 | 305 | – | – | 279 | 138 | – | – | – | – | – |
| d-ZB-C3N4 | 791 | – | – | 443 | – | – | 184 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Reference [41] | 794 | – | – | 431 | – | – | 184 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cubic-C3N4 | 889 | – | – | 518 | – | – | 309 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Reference [26] | 861 | – | 469 | – | – | 300 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Pseudocubic-C3N4 | 790 | – | 792 | 445 | – | 444 | 188 | 187 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Reference [37] | 804 | – | 805 | 439 | – | 439 | 183 | 183 | – | – | – | – | – |
| m-C3N4 | 564 | 1002 | 859 | 209 | 331 | 213 | 51 | 195 | 36 | −57 | 6 | 60 | 48 |
| t-C3N4 | 702 | – | 767 | 428 | – | 424 | 212 | 195 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cubic-BN | 823 | – | – | 479 | – | – | 185 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Reference [50]-Exp. | 820 | – | – | 480 | – | – | 190 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Materials | BV | BR | GV | GR | BH | GH | B/G | E | v | Hv | AU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-C3N4 | 386.83 | 386.82 | 338.65 | 335.09 | 387 | 337 | 1.15 | 784 | 0.16 | 78 | 0.053 |
| Reference [48] | 387.60 | 387.60 | 341.85 | 338.96 | 388 | 340 | 1.14 | 790 | 0.16 | 82 | 0.043 |
| β-C3N4 | 406.11 | 405.57 | 330.77 | 320.96 | 406 | 326 | 1.25 | 772 | 0.18 | 78 | 0.154 |
| Reference [48] | 408.21 | 407.84 | 322.09 | 311.12 | 408 | 317 | 1.29 | 755 | 0.19 | 63, 85 a | 0.176 |
| d-ZB-C3N4 | 386.59 | 386.59 | 387.23 | 374.16 | 387 | 381 | 1.02 | 861 | 0.13 | 81 | 0.175 |
| Reference [51] | – | – | – | – | 387 | 375 | 1.03 | 850 | 0.13 | 63 | – |
| Cubic-C3N4 | 502.48 | 502.48 | 426.82 | 394.18 | 502 | 411 | 1.22 | 969 | 0.18 | 88 | 0.414 |
| Reference [48] | – | – | – | – | 496 | 401 | 1.24 | 948 | 0.18 | 90, 87 b | – |
| Pseudocubic-C3N4 | 388.21 | 388.21 | 387.66 | 373.98 | 388 | 381 | 1.02 | 861 | 0.13 | 81 | 0.183 |
| Reference [48] | 390.02 | 390.02 | 387.76 | 376.88 | 390 | 382 | 1.02 | 864 | 0.13 | 70, 80 c | 0.144 |
| m-C3N4 | 332.22 | 320.80 | 293.26 | 254.44 | 327 | 274 | 1.19 | 643 | 0.17 | 37 | 0.798 |
| t-C3N4 | 374.81 | 374.47 | 360.75 | 340.05 | 375 | 350 | 1.07 | 801 | 0.14 | 80 | 0.305 |
| c-BN | 397.43 | 397.43 | 414.90 | 398.88 | 397 | 407 | 0.98 | 910 | 0.12 | 63 | 0.201 |
| - | – | – | – | – | 400 d | – | – | – | – | 66 e, 64 f | – |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Q.; Chai, C.; Wei, Q.; Yang, Y. Two Novel C3N4 Phases: Structural, Mechanical and Electronic Properties. Materials 2016, 9, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060427
Fan Q, Chai C, Wei Q, Yang Y. Two Novel C3N4 Phases: Structural, Mechanical and Electronic Properties. Materials. 2016; 9(6):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060427
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Qingyang, Changchun Chai, Qun Wei, and Yintang Yang. 2016. "Two Novel C3N4 Phases: Structural, Mechanical and Electronic Properties" Materials 9, no. 6: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060427
APA StyleFan, Q., Chai, C., Wei, Q., & Yang, Y. (2016). Two Novel C3N4 Phases: Structural, Mechanical and Electronic Properties. Materials, 9(6), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060427







