Fuzzy Q-Learning Agent for Online Tuning of PID Controller for DC Motor Speed Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
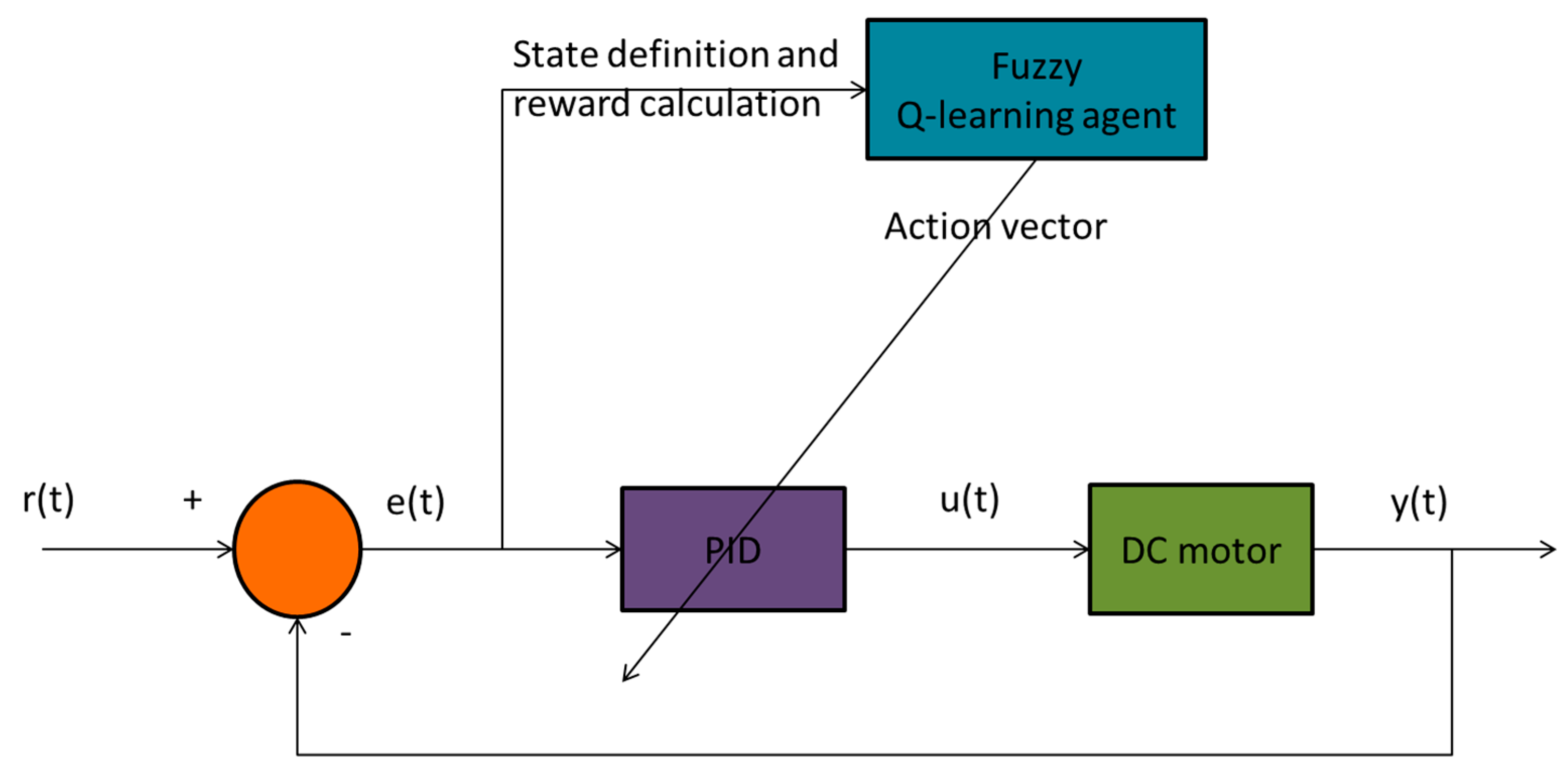
- We deploy a Q-Learning algorithm for adapting online the gains of a PID controller with the initial values that arise by the Z-N method. This PID controller is dedicated to control the speed of a DC motor. This supervision scheme is independent of prior knowledge and is not based on the expert knowledge.
- In order to cope with the continuous state-action space, a fuzzy logic system is used as fuzzy function approximator.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. DC Motor
2.2. PID
2.3. Fuzzy Logic Systems (FLS)
2.4. Reinforcement Learning
2.4.1. Q-Learning
2.4.2. Fuzzy Q-Learning
- Observe state
- Take an action for each rule according to exploration/exploitation algorithm
- Calculate the global output according to Equation (10)
- Calculate the corresponding value according to Equation (11)
- Capture the new state information
- Calculate reward
- Update q-values according to Equation (12)
- (1)
- Observation of the state
- (2)
- For each fired rule, one action is selected according to the exploration/exploitation strategy.
- (3)
- Calculation of the global outputwhere is as specified in Section 2.4.2 (consequents of the rule ) and corresponds to the selected action of rule .
- (4)
- Calculation of the corresponding value .where is the corresponding q-value of the fired rule for the selection of the action by the exploration algorithm.
- (5)
- Application of the action and observation of the new state .
- (6)
- Calculation of the reward .
- (7)
- Updating the q values according to:where , and is the selection of the action that has the maximum Q value for the fired rule .
3. Control Strategy
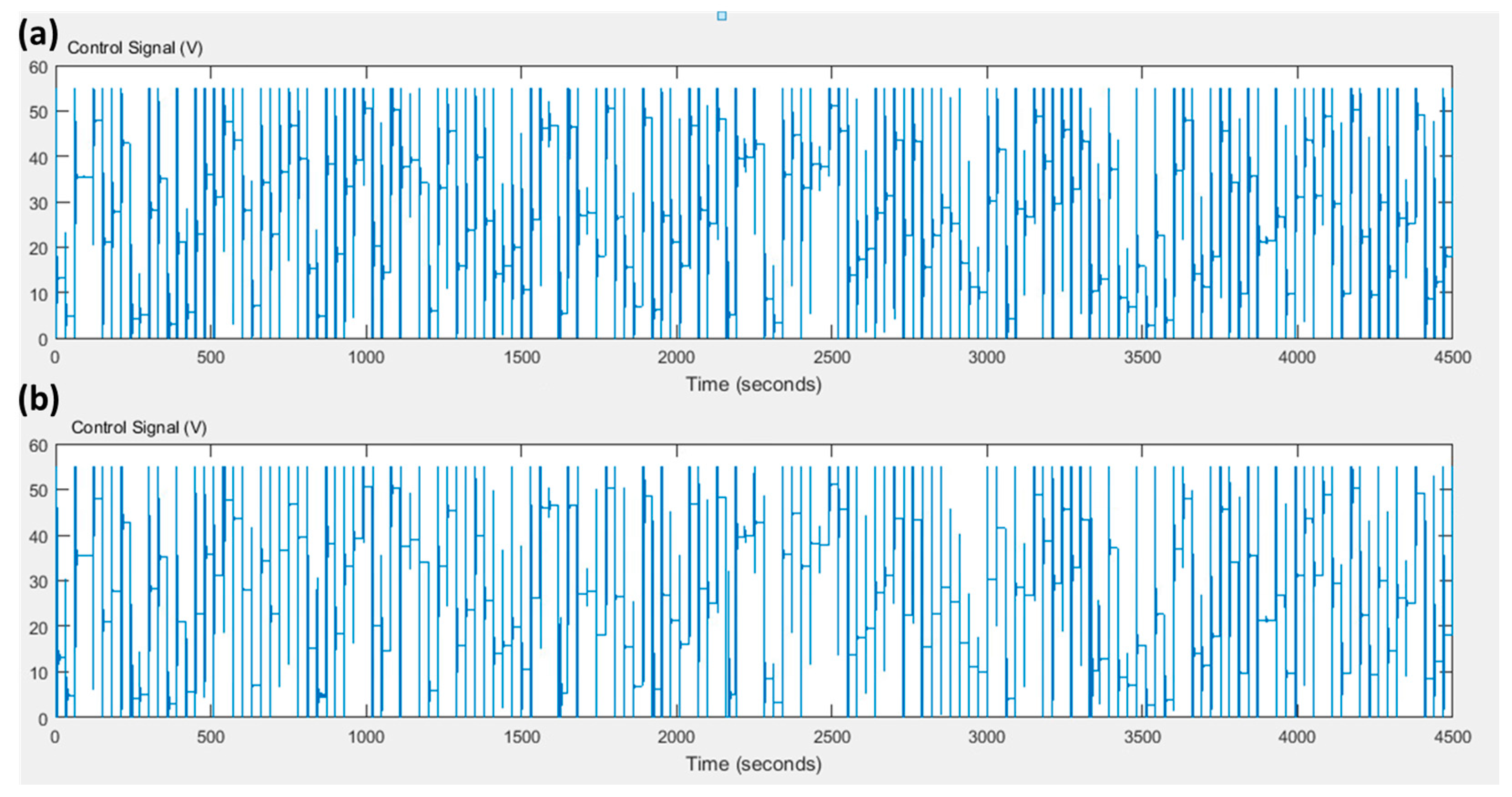
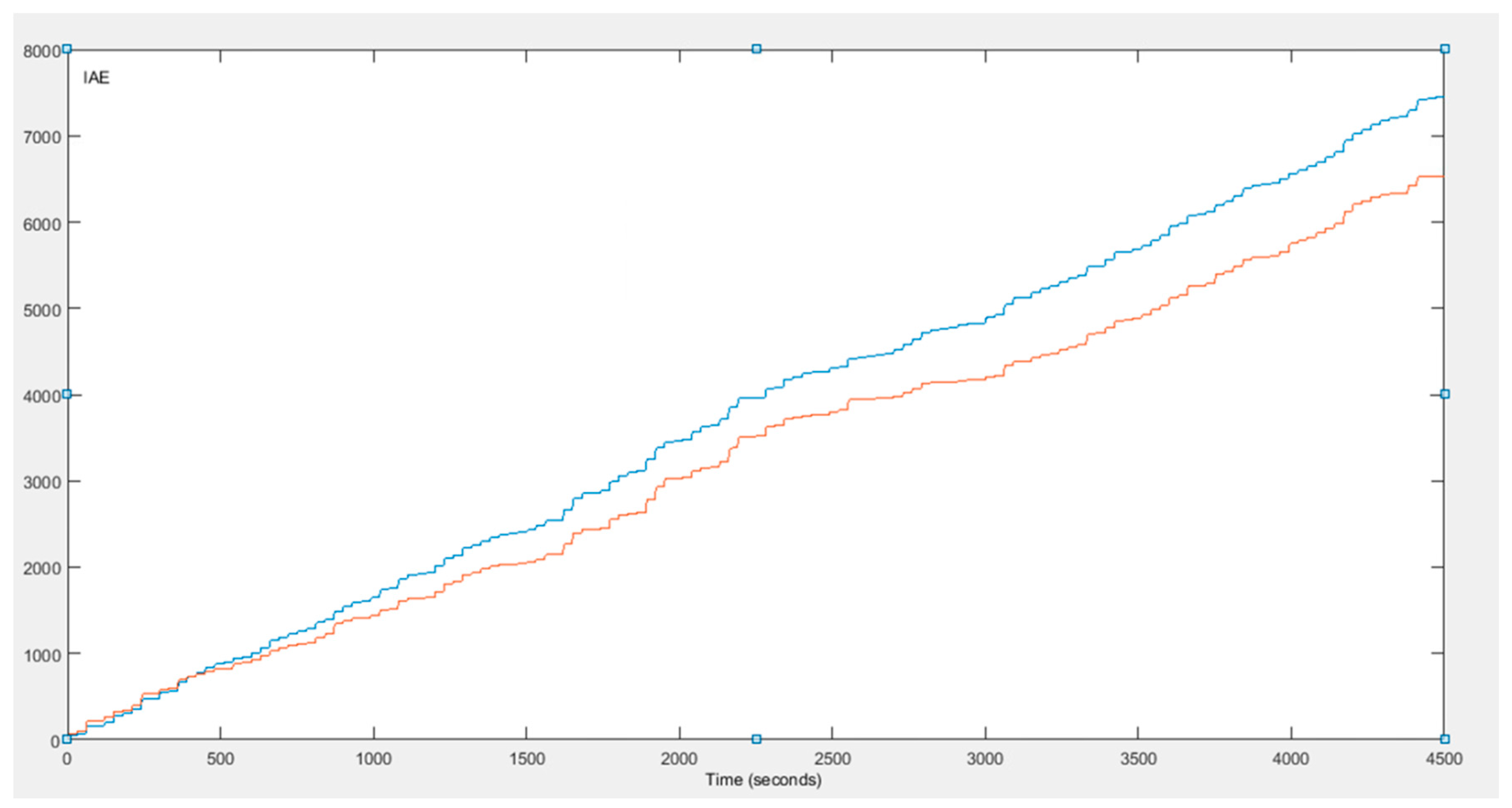
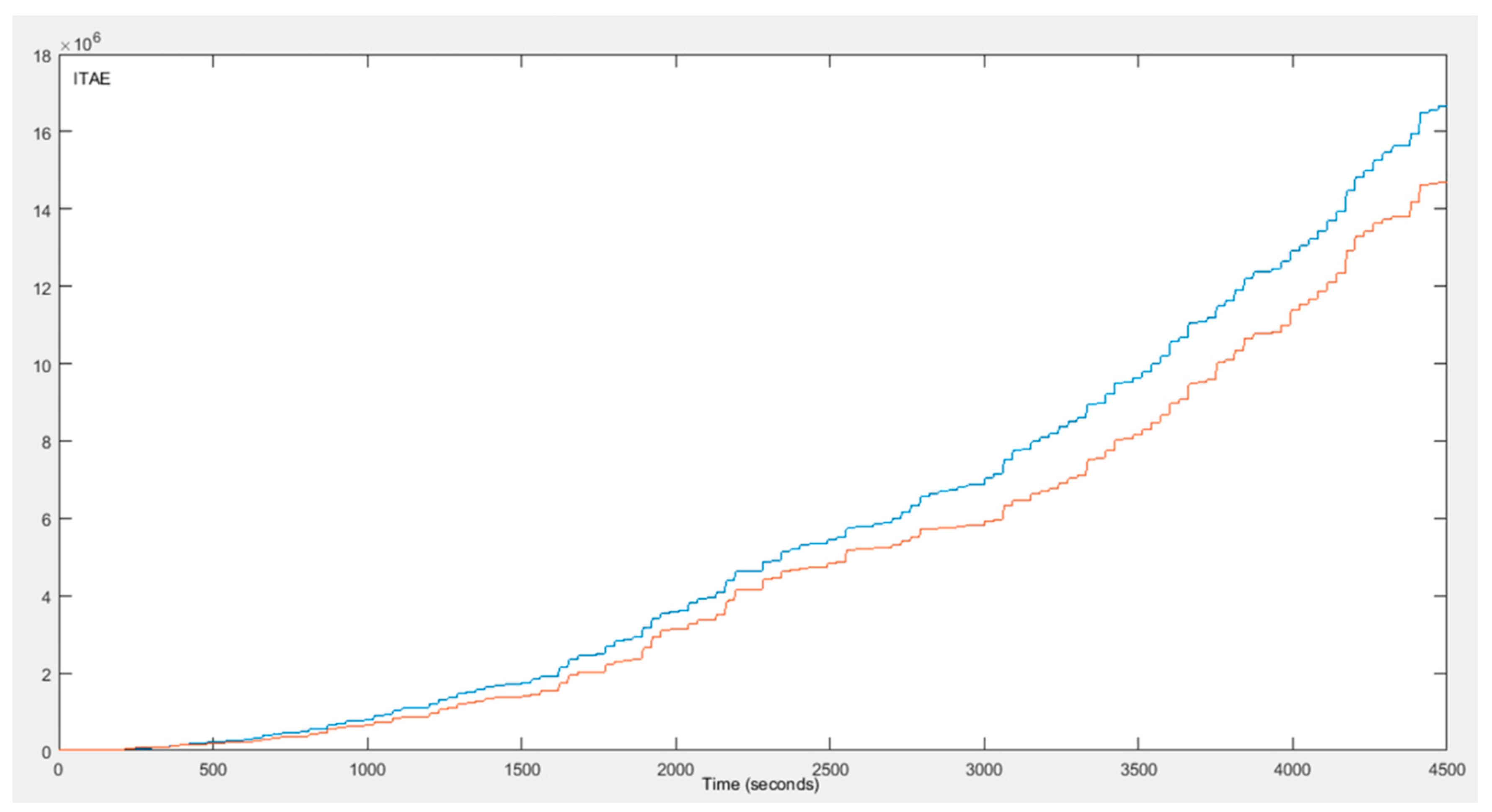
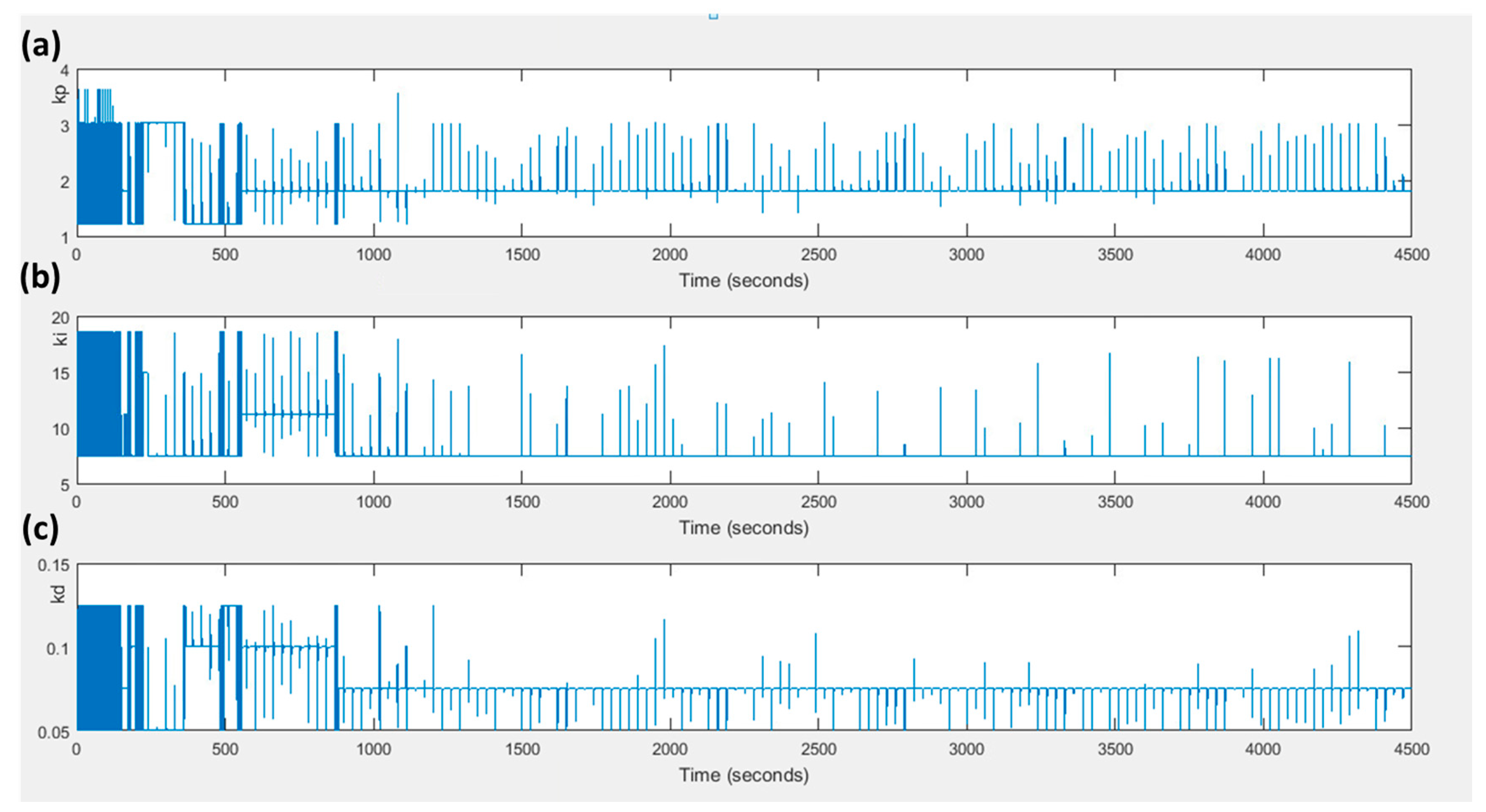
4. Simulation Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akbari-Hasanjani, R.; Javadi, S.; Sabbaghi-Nadooshan, R. DC motor speed control by self-tuning fuzzy PID algorithm. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2015, 37, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.M.; Kanojiya, R.G. Tuning of PID Controller using Ziegler-Nichols Method for Speed Control of DC Motor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advances in Engineering, Science and Management (ICAESM-2012), Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India, 30–31 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-X. A Course in Fuzzy Systems and Control; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Luo, J. Research of PID Control Algorithm Based on Neural Network. Energy Procedia 2011, 13, 6988–6993. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, A.Z. Neural Network Based Adaptive PID Controller. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1997, 30, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.B.; Bui, T.W.; Li, V.; Wong, Y.K. A new on-line PID tuning method using neural networks. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2000, 33, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, J.; Jegatheesan, V.; Shi, G. Dissolved Oxygen Control in Activated Sludge Process Using a Neural Network-Based Adaptive PID Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Z.; Yusoff, Z.M.; Kasuan, N.; Nordin, M.N.N.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Taib, M.N. Online Tuning PID using Fuzzy Logic Controller with Self-Tuning Method. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on System Engineering and Technology, Shah Alam, Malaysia, 19–20 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dounis, A.I.; Kofinas, P.; Alafodimos, C.; Tseles, D. Adaptive fuzzy gain scheduling PID controller for maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic system. Renew. Energy 2013, 60, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Sun, L.; Hua, Q.; Liu, P. A Fuzzy Adaptive PID Controller Design for Fuel Cell Power Plant. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.F.M.; Tanscheit, R.; Pacheco, M.A.C. Tuning PID Controllers through Genetic Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2001 WSES International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Puerto De La, Spain, 11–15 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jayachitra, A.; Vinodha, R. Genetic Algorithm Based PID Controller Tuning Approach for Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2014, 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Li, W. Optimization Design by Genetic Algorithm Controller for Trajectory Control of a 3-RRR Parallel Robot. Algorithms 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jigang, H.; Jie, W.; Hui, F. An anti-windup self-tuning fuzzy PID controller for speed control of brushless DC motor. J. Control Meas. Electron. Comput. Commun. 2017, 58, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.M.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L. Adaptive PID regulator based on neural network for DC motor speed control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering, Yichang, China, 16–18 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Li, Z. Design of Neural Network PID Controller Based on Brushless DC Motor. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Changsha, China, 10–11 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Elsrogy, W.M.; Fkirin, M.A.; Hassan, M.A.M. Speed Control of DC Motor Using PID Controller Based on Artificial Intelligence Techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies, Hammamet, Tunisia, 6–8 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, B.J.; Noel, M.M. Control of a bioreactor using a new partially supervised reinforcement learning algorithm. J. Process Control 2018, 69, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Roman, R.-C. Data-driven model reference control of MIMO vertical tank systems with model-free VRFT and Q-Learning. ISA Trans. 2018, 73, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulameer, A.; Sulaiman, M.; Aras, M.S.M.; Saleem, D. Tuning Methods of PID Controller for DC Motor Speed Control. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2016, 3, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, N.A.; Bhaganagare, M.; Pandey, P.C. DC Motor Speed Control Using PID Controllers; EE 616 Electronic System Design Course Project; EE Dept., IIT Bombay: Mumbai, India, November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukalas, L.H.; Uhring, R.E. Fuzzy and Neural Approaches in Engineering, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mamdani, E.H.; Assilian, S. An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 1975, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M. Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1985, 15, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, S.; Norving, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, C.J.C.H. Learning from Delayed Reinforcement Signals. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.; Barto, A. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- François-Lavet, V.; Fonteneau, R.; Ernst, D. How to Discount Deep Reinforcement Learning: Towards New Dynamic Strategies. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1512.02011. [Google Scholar]
- Glorennec, P.Y.; Jouffe, L. Fuzzy Q-Learning. In Proceedings of the 6th International Fuzzy Systems Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 5 July 1997; pp. 659–662. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.X. Fuzzy Systems are Universal approximators. In Proceedings of the First IEEE Conference on Fuzzy System, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 March 1992; pp. 1163–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hasselt, H. Reinforcement Learning in Continuous State and Action Spaces. In Reinforcement Learning: State of the Art; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; pp. 207–251. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, J.L. Fuzzy logic controllers are universal approximators. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1995, 25, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Step Response at 60 s | Step Response at 4260 s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID Z-N | Fuzzy Q-Learning PID | PID Z-N | Fuzzy Q-Learning PID | |
| Settling time (s) | 3.30 | 4.05 | 3.67 | 1.72 |
| Rising time (s) | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| Overshoot (%) | 54.2 | 58.3 | 71.0 | 67.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kofinas, P.; Dounis, A.I. Fuzzy Q-Learning Agent for Online Tuning of PID Controller for DC Motor Speed Control. Algorithms 2018, 11, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100148
Kofinas P, Dounis AI. Fuzzy Q-Learning Agent for Online Tuning of PID Controller for DC Motor Speed Control. Algorithms. 2018; 11(10):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100148
Chicago/Turabian StyleKofinas, Panagiotis, and Anastasios I. Dounis. 2018. "Fuzzy Q-Learning Agent for Online Tuning of PID Controller for DC Motor Speed Control" Algorithms 11, no. 10: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100148
APA StyleKofinas, P., & Dounis, A. I. (2018). Fuzzy Q-Learning Agent for Online Tuning of PID Controller for DC Motor Speed Control. Algorithms, 11(10), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100148





