A Review on Computer Vision Technology for Physical Exercise Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Sources
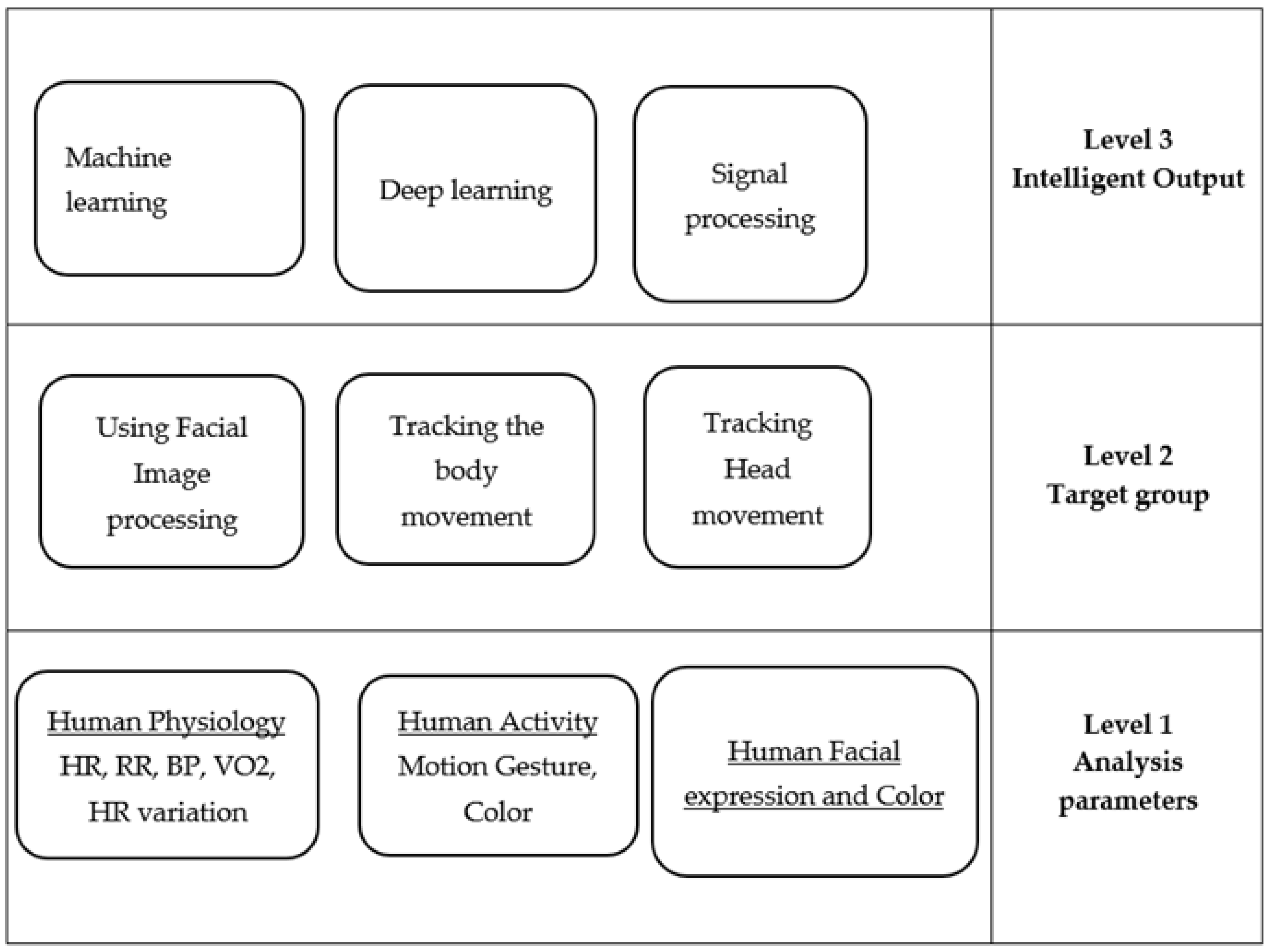
Taxonomy
3. Discussion about Articles
3.1. Heart Rate Extraction
3.1.1. Doppler-Based System
3.1.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1.3. Photoplethysmography
3.1.4. Video-Based Image Processing
3.1.5. Facial Expression
3.2. Heart Rate Variability
3.3. Blood Pressure
3.3.1. Photoplethysmography and Pulse Arrival Time
3.3.2. Photoplethysmography and Pulse Transmit Time
3.4. Body Temperature
3.5. Energy Expenditure
3.5.1. Thermal Imaging
3.5.2. RGB Depth
3.6. Respiratory Rate
3.6.1. Video-Based Image Processing
3.6.2. RGB Depth
3.7. Muscle Fatigue
3.8. Other Approaches
3.8.1. Muscle Oxygenation
3.8.2. Facial Expression
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paterson, D.H.; Warburton, D.E.R. Physical activity and functional limitations in older adults: A systematic review related to Canada’s Physical Activity Guidelines. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borg, R.L. Music In the Education of Children. J. Res. Music. Educ. 1962, 10, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, J.; Eston, R.G. Percieved exertion research in the 21st century: Developments, reflections and questions for the future. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2008, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Huanga, D.H.; Chioua, W.K.; Chenb, B.H. Judgment of perceived exertion by static and dynamic facial expression. In Proceedings of the 19th Triennial Congress of the IEA, Melbourne, Australia, 9–14 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, M.; Leat, S.J. Quantitative assessment of perceived visibility enhancement with image processing for single face images: A preliminary study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4502–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, B.T.; Hashmi, M.F.; Bokde, N.D. A Comprehensive Review of Computer Vision in Sports: Open Issues, Future Trends and Research Directions. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, M.A.R.; Antar, A.D.; Shahid, O. Vision-based Action Understanding for Assistive Healthcare: A Short Review. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hõrak, H. Computer Vision-Based Unobtrusive Physical Activity Monitoring in School by Room-Level Physical Activity Estimation: A Method Proposition. Information 2019, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knobloch, K.; Hoeltke, V.; Jakob, E.; Vogt, P.M.; Phillips, R. Non-invasive ultrasonic cardiac output monitoring in exercise testing. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 126, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour Ebrahim, M.; Sarvi, M.; Yuce, M.R. A Doppler Radar System for Sensing Physiological Parameters in Walking and Standing Positions. Sensors 2017, 17, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jöbsis, F.F. Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science 1977, 198, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Mao, Z.; Wang, B. Noninvasive detection of gas exchange rate by near infrared spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Photonics and Imaging in Biology and Medicine, Wuhan, China, 8–10 August 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astaras, A.; Kokonozi, A.; Michail, E.; Filos, D.; Chouvarda, I.; Grossenbacher, O.; Koller, J.M.; Leopoldo, R.; Porchet, J.A.; Correvon, M.; et al. Pre-clinical physiological data acquisition and testing of the IMAGE sensing device for exercise guidance and real-time monitoring of cardiovascular disease patients. In XII Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capraro, G.; Kobayashi, L.; Etebari, C.; Luchette, K.; Mercurio, L.; Merck, D.; Kirenko, I.; van Zon, K.; Bartula, M.; Rocque, M. ‘No Touch’ Vitals: A Pilot Study of Non-contact Vital Signs Acquisition in Exercising Volunteers. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Cleveland, OH, USA, 17–19 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.H.C.; White, F.A.; Tipoe, T.; Liu, T.; Wong, M.C.; Jesuthasan, A.; Baranchuk, A.; Tse, G.; Yan, B.P. The Current State of Mobile Phone Apps for Monitoring Heart Rate, Heart Rate Variability, and Atrial Fibrillation: Narrative Review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019, 7, 11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Sabharwal, A. DistancePPG: Robust non-contact vital signs monitoring using a camera. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 1565–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gambi, E.; Agostinelli, A.; Belli, A.; Burattini, L.; Cippitelli, E.; Fioretti, S.; Pierleoni, P.; Ricciuti, M.; Sbrollini, A.; Spinsante, S. Heart Rate Detection Using Microsoft Kinect: Validation and Comparison to Wearable Devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Xu, J.; Hu, D.; Wang, J. Combination of Denoising Algorithms for Video-Based Non-contact Heart Rate Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd Information Communication Technologies Conference (ICTC), Nanjing, China, 6–8 May 2022; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Li, H.; Lin, I.-S.; Yu, T.-H. A new class of nonlinear filters for image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Toronto, ON, Canada, 14–17 April 1991; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 2525–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Flury, B. Common Principal Components & Related Multivariate Models; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.E. A User’s Guide to Principal Components; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolean, Y.; Marwade, A.; Tomen, N.; Alkemade, P.; Eijsvogels, T.; van Gemert, J. Heart rate estimation in intense exercise videos. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.02509. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y. Step Count and Pulse Rate Detection Based on the Contactless Image Measurement Method. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fu, C.-H.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, F. Non-contact time varying heart rate monitoring in exercise by video camera. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 15–17 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, S.; Azorin-Peris, V.; Zheng, J.; Greenwald, S.; Chambers, J.; Zhu, Y. Detection of physiological changes after exercise via a remote opto-physiological imaging system. In Proceedings of the Design and Quality for Biomedical Technologies IV, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28–29 January 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Papin, C.; Azorin-Peris, V.; Kalawsky, R.; Greenwald, S.; Hu, S. Use of ambient light in remote photoplethysmographic systems: Comparison between a high-performance camera and a low-cost webcam. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.K.; Moradi, P.; Malihi, M.; Karimi, S.; Shamsollahi, M.B. Heart Rate monitoring during physical exercise using wrist-type photoplethysmographic (PPG) signals. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 6166–6169. [Google Scholar]
- Fallet, S.; Vesin, J.-M. Robust heart rate estimation using wrist-type photoplethysmographic signals during physical exercise: An approach based on adaptive filtering. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriani, N.S.; Jumain, N.A.; Ali, A.A.; Mohd, N.H. Facial Video based Heart Rate Estimation for Physical Exercise. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium on Industrial Electronics & Applications (ISIEA), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 10–11 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Heart rate monitoring from wrist-type photoplethysmographic (PPG) signals during intensive physical exercise. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–5 December 2014; pp. 698–702. [Google Scholar]
- Bosi, I.; Cogerino, C.; Bazzani, M. Real-time monitoring of heart rate by processing of Microsoft KinectTM 2.0 generated streams. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Multidisciplinary Conference on Computer and Energy Science (SpliTech), Split, Croatia, 13–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Durand, F.; Guttag, J. Detecting pulse from head motions in video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3430–3438. [Google Scholar]
- Spinsante, S.; Ricciuti, M.; Scalise, L. Contactless Measurement of Heart Rate for Exergames Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Rome, Italy, 11–13 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; den Brinker, A.C.; Stuijk, S.; de Haan, G. Robust heart rate from fitness videos. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, 1023–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poh, M.-Z.; McDuff, D.J.; Picard, R.W. Non-contact, automated cardiac pulse measurements using video imaging and blind source separation. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 10762–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, M.Z.; McDuff, D.J.; Picard, R.W. Advancements in noncontact, multiparameter physiological measurements using webcam. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- More, A.V.; Wakankar, A.; Gawande, J.P. Automated heart rate measurement using wavelet analysis of face video sequences. In Innovations in Electronics and Communication Engineering; Saini, H.S., Sing, R.K., Patel, V.M., Santhi, K., Ranganayakulu, S.V., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Fu, C.; Liang, H.; Hong, H.; Zhu, X.; Yang, J. Non-contact Heart Rate Monitoring for Intensive Exercise Based on Singular Spectrum Analysis. Int. J. Distrib. Syst. Technol. 2021, 12, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Jin, J.; Wu, X. Motion-resistant heart rate measurement from face videos using patch-based fusion. Signal Image Video Process. 2019, 13, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.P.; Kwan, B.H.; Lim, C.L.; Wong, S.L.; Raveendran, P. Video-Based Heart Rate Measurement Using Short-time Fourier Transform. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communications Systems (Ispacs), Naha, Japan, 12–15 November 2013; pp. 704–707. [Google Scholar]
- Monkaresi, H.; Calvo, R.A.; Yan, H. A Machine Learning Approach to Improve Contactless Heart Rate Monitoring Using a Webcam. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-F.; Lin, C.-H.; Huang, P.-W.; Lin, T.-M.; Chung, M.-L. A contactless sport training monitor based on facial expression and remote PPG. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Banff, AB, Canada, 5–8 October 2017; pp. 846–852. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, S.R.; Sampaio, J.; Barroso, J.; Filipe, V. Classification of Physical Exercise Intensity Based on Facial Expression Using Deep Neural Network; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11573 LNCS. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.R.; Fonseca, A.; Marques, A.; Barroso, J.; Filipe, V. Physical exercise intensity monitoring through eye-blink and mouth’s shape analysis. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Technology and Innovation in Sports, Health and Wellbeing (TISHW), Thessaloniki, Greece, 20–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fumoto, K.; Nakahara, K.; Teraoka, M. Basic Study on Non-contact Respiration Measurement during Exercise Tolerance Test by Using Kinect Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (Sii), Nagoya, Japan, 11–13 December 2015; pp. 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.-F.; Chan, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.-T. Contactless and Cuffless Monitoring of Blood Pressure on a Chair Using E-Textile Materials. In Proceedings of the 2006 3rd IEEE/EMBS International Summer School on Medical Devices and Biosensors, Cambridge, MA, USA, 4–6 September 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.J.; Fankhauser, S.E. Heart rate control during treadmill exercise using input-sensitivity shaping for disturbance rejection of very-low-frequency heart rate variability. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 30, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stricker, R.; Muller, S.; Gross, H.-M. Non-contact video-based pulse rate measurement on a mobile service robot. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, IEEE RO-MAN 2014, Edinburgh, Scotland, 25–29 August 2014; pp. 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, D. WiFit: A Bodyweight Exercise Monitoring System with Commodity Wi-Fi. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM International Joint Conference and 2018 International Symposium on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Wearable Computers, Singapore, 8–12 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shirbani, F.; Blackmore, C.; Kazzi, C.; Tan, I.; Butlin, M.; Avolio, A.P. Sensitivity of Video-Based Pulse Arrival Time to Dynamic Blood Pressure Changes. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirbani, F.; Moriarty, A.; Hui, N.; Cox, J.; Tan, I.; Avolio, A.P.; Butlin, M. Contactless video-based photoplethysmography technique comparison investigating pulse transit time estimation of arterial blood pressure. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Jalisco, Mexico, 26–30 July 2021; pp. 5650–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.C.; Finkelstein, J. Introducing Contactless Blood Pressure Assessment Using a High Speed Video Camera. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Formenti, D.; Gargano, M.; Alberti, G. Skin temperature evaluation by infrared thermography: Comparison of image analysis methods. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2014, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.A.; Richardson, A.J.; Watt, P.W.; Maxwell, N.S. Reliability and validity of skin temperature measurement by telemetry thermistors and a thermal camera during exercise in the heat. J. Therm. Biol. 2014, 45, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McFarlin, B.; Venable, A.; Williams, R.; Jackson, A. Comparison of techniques for the measurement of skin temperature during exercise in a hot, humid environment. Biol. Sport 2015, 32, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Fernandes, A.; dos Santos Amorim, P.R.; Brito, C.J.; Sillero-Quintana, M.; Marins, J.C.B. Regional Skin Temperature Response to Moderate Aerobic Exercise Measured by Infrared Thermography. Asian J. Sport. Med. 2016, 7, e29243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korman, P.; Straburzynska-Lupa, A.; Kusy, K.; Kantanista, A.; Zielinski, J. Changes in body surface temperature during speed endurance work-out in highly-trained male sprinters. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 78, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardasca, R. Infrared Thermography in Water Sports, in Application of Infrared Thermography in Sports Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sawka, M.N.; Wenger, C.B.; Young, A.J.; Pandolf, K.B. Physiological Responses to Exercise in the Heat. In Nutritional Needs in Hot Environments: Applications for Military Personnel in Field Operations; Marriott, B.M., Ed.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Lükens, J.; Boström, K.J.; Puta, C.; Schulte, T.L.; Wagner, H. Using ultrasound to assess the thickness of the transversus abdominis in a sling exercise. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manullang, M.C.T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lai, S.-J.; Chou, N.-K. Implementation of Thermal Camera for Non-Contact Physiological Measurement: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.M.; Poulsen, M.K.; Alldieck, T.; Larsen, R.G.; Gade, R.; Moeslund, T.B.; Franch, J. Estimation of Energy Expenditure during Treadmill Exercise via Thermal Imaging. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gade, R.; Larsen, R.G.; Moeslund, T.B. Measuring energy expenditure in sports by thermal video analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndahimana, D.; Kim, E. Measurement methods for physical activity and energy expenditure: A review. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2017, 6, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koehler, K.; Drenowatz, C. Monitoring Energy Expenditure Using a Multi-Sensor Device—Applications and Limitations of the SenseWear Armband in Athletic Populations. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koporec, G.; Vučković, G.; Milić, R.; Perš, J. Quantitative Contact-Less Estimation of Energy Expenditure from Video and 3D Imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, L. SPHERE-Calorie; University of Bristol: Bristol, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Burghardt, T.; Mirmehdi, M.; Damen, D.; Cooper, A.; Hannuna, S.; Camplani, M.; Paiement, A.; Craddock, I. Calorie Counter: RGB-Depth Visual Estimation of Energy Expenditure at Home. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ACCV 2016 Workshops, Proceedings of ACCV 2016 International Workshops, Revised Selected Papers, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ellwein, L.; Samyn, M.M.; Danduran, M.; Schindler-Ivens, S.; Liebham, S.; LaDisa, J.F. Toward translating near-infrared spectroscopy oxygen saturation data for the non-invasive prediction of spatial and temporal hemodynamics during exercise. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucero, A.A.; Addae, G.; Lawrence, W.; Neway, B.; Credeur, D.P.; Faulkner, J.; Rowlands, D.; Stoner, L. Reliability of muscle blood flow and oxygen consumption response from exercise using near-infrared spectroscopy. Exp. Physiol. 2017, 103, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, H.; Nakamura, H. Non-Contact Respiration Measurement during Exercise Tolerance Test by Using Kinect Sensor. Sports 2018, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, H.; Ichimura, S.; Kiyooka, S.; Koshiji, K. Non-contact measurement method of respiratory movement under pedal stroke motion. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Fujimoto, H.; Tsuzuki, K.; Nakamura, H. Noncontact Respiration Measurement under Pedaling Motion with Upright Bicycle Ergometer Using Dot-matrix Pattern Light Projection. In Proceedings of the Tencon 2010 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 21–24 November 2010; pp. 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, A.; Selvakumar, K. Non-contact breath cycle analysis for different breathing patterns using RGB-D videos. Smart Health 2022, 25, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persinger, R.; Foster, C.; Gibson, M.; Fater, D.C.W.; Porcari, J.P. Consistency of the Talk Test for exercise prescription. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 1632–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Matsui, T.; Watai, Y.; Kim, S.; Kirimoto, T.; Suzuki, S.; Hakozaki, Y. Vital-SCOPE: Design and Evaluation of a Smart Vital Sign Monitor for Simultaneous Measurement of Pulse Rate, Respiratory Rate, and Body Temperature for Patient Monitoring. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 4371872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilar, J.G. Respiration Tracking Using the Wii Remote Game-Controller. In User Centred Networked Health Care; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 169, pp. 455–459. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, M.; Wilks, D. Fatigue. BMJ 2002, 325, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupp, L.B. Fatigue in multiple sclerosis: Definition, pathophysiology and treatment. CNS Drugs 1972, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, K.; Safari, R.; Thomas, S.; Mercer, T.; White, C.; Van der Linden, M.; Moss-Morris, R. Fatigue interventions in long term, physical health conditions: A scoping review of systematic reviews. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 203367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, K.; Larsen, J.P.; Tandberg, E.; Jørgensen, K. Fatigue in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 1999, 14, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Irani, R.; Nasrollahi, K.; Thomas, M.B. Facial video based detection of physical fatigue for maximal muscle activity. IET Comput. Vis. 2016, 10, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irani, R.; Nasrollahi, K.; Moeslund, T.B. Contactless measurement of muscle fatigue by tracking facial feature points in video. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 4181–5186. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, M.C.; Carvalho, R.; Tessutti, V.D.; Pereira Bacurau, R.F.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Portas Capelo, L.; Prando Ramos, H.; dos Santos, M.C.; Teixeira, L.F.M.; Marchetti, P.H. Identification of muscle fatigue by tracking facial expressions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 208834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.B.; Del-Blanco, C.R.; Garcia, N. Detecting exercise-induced fatigue using thermal imaging and deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 Seventh International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 28 November–1 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, B.; Marzorati, M.; Lanfranconi, F.; Ferri, A.; Longaretti, M.; Stucchi, A.; Vago, P.; Marconi, C.; Morandi, L. Impaired oxygen extraction in metabolic myopathies: Detection and quantification by near-infrared spectroscopy. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.R.; Barroso, J.; Sampaio, J.; Filipe, V. Classification of physical exercise intensity by using facial expression analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 15–16 February 2018; pp. 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.R.; Sampaio, J.; Exel, J.; Barroso, J.; Filipe, V. Using Computer Vision to Track Facial Color Changes and Predict Heart Rate. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawiro, E.A.P.J.; Hu, C.C.; Chan, Y.S.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, Y.H. A heart rate detection method for low power exercise intensity monitoring device. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Bioelectronics and Bioinformatics (IEEE ISBB 2014), Chung Li, Taiwan, 11–14 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wiles, J.D.A.; Allum, S.R.; Coleman, D.A.; Swaine, I.L. The relationships between exercise intensity, heart rate, and blood pressure during an incremental isometric exercise test. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comon, P. Independent component analysis, A new concept? Signal Process. 1994, 36, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Roy, R.; Basu, J.; Bepari, M.S. Blind source separation: A review and analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference Oriental COCOSDA held jointly with 2013 Conference on Asian Spoken Language Research and Evaluation (O-COCOSDA/CASLRE), Gurgaon, India, 25–27 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vojciechowski, A.S.; Natal, J.Z.; Gomes, A.R.S.; Rodrigues, E.V.; Villegas, I.L.P.; Korelo, R.I.G. Effects of exergame training on the health promotion of young adults. Fisioter. Mov. 2017, 30, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.; Zhang, Y. Preliminary investigation of pupil size variability: Toward non-contact assessment of cardiovascular variability. In Proceedings of the 2006 3rd IEEE/EMBS International Summer School on Medical Devices and Biosensors, Cambridge, MA, USA, 4–6 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Inder, J.D.; Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; McFarlane, J.R.; Hess, N.C.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis to optimize benefit. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatini, P. Blood Pressure Behaviour During Physical Activity. Sport. Med. 1988, 5, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.A.; Gomes Moreira, D.; Brito, C.J.; da Silva, C.D.; Sillero-Quintana, M.; Mendonca Pimenta, E.; Bach, A.J.E.; Silami Garcia, E.; Bouzas Marins, J.C. Validity of inner canthus temperature recorded by infrared thermography as a non-invasive surrogate measure for core temperature at rest, during exercise and recovery. J. Therm. Biol. 2016, 62, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliverti, A. The respiratory muscles during exercise. Breathe 2016, 12, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, A.T.; Aguiar, E.; Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Facial expression recognition with Convolutional Neural Networks: Coping with few data and the training sample order. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 610–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, K.H.; Clark, B.; Périard, J.D.; Goecke, R.; Thompson, K.G. Facial feature tracking: A psychophysiological measure to assess exercise intensity? J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Robust Real-time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Statistical and Computational Theories of Vision, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 13 July 2001; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]

| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
|
|
| Parameters | Technology Used | Articles |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | Doppler-based system | [10,11,12] |
| Near-Infrared spectroscopy | [13,14,15] | |
| Photoplethysmography | [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32] | |
| Video-based Image processing | [25,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] | |
| Facial expression based | [43,44,45] | |
| Heart Rate Variability | Various Technologies | [46,47,48,49,50] |
| Blood pressure | Photoplethysmography (PAT) | [51,52] |
| Pulse Transmit time (PPT) | [53] | |
| Body temperature | Thermal Imaging | [54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62] |
| Telemetry Thermistor | [55] | |
| Energy expenditure | Thermal Imaging | [63,64,65,66,67,68] |
| RGB-Depth | [67,69] | |
| Near-infrared spectroscopy | [70,71] | |
| Respiratory rate | Near-Infrared spectroscopy | [13,14,15] |
| Video Based | [72,73,74,75,76,77] | |
| Doppler-based system | [11] | |
| Infrared Camera | [78] | |
| RGB-Depth | [46,72] | |
| Muscle fatigue | Video Based (RGB) | [79,80,81,82,83,84,85] |
| Infrared Camera | [86] | |
| Thermal Camera | [86] | |
| Oxygen Uptake (VO2) | Doppler-based system | [13,35] |
| Others (muscle oxygenation) | Near-Infrared spectroscopy | [70] |
| Kee Load estimation | Camera Based | [87] |
| Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS) | Infrared Technology | [35] |
| Exercise intensity analysis (Facial expression) | Camera Based | [44,85,88,89] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khanal, S.R.; Paulino, D.; Sampaio, J.; Barroso, J.; Reis, A.; Filipe, V. A Review on Computer Vision Technology for Physical Exercise Monitoring. Algorithms 2022, 15, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120444
Khanal SR, Paulino D, Sampaio J, Barroso J, Reis A, Filipe V. A Review on Computer Vision Technology for Physical Exercise Monitoring. Algorithms. 2022; 15(12):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120444
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhanal, Salik Ram, Dennis Paulino, Jaime Sampaio, Joao Barroso, Arsénio Reis, and Vitor Filipe. 2022. "A Review on Computer Vision Technology for Physical Exercise Monitoring" Algorithms 15, no. 12: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120444
APA StyleKhanal, S. R., Paulino, D., Sampaio, J., Barroso, J., Reis, A., & Filipe, V. (2022). A Review on Computer Vision Technology for Physical Exercise Monitoring. Algorithms, 15(12), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120444








