Error Investigation on Wi-Fi RTT in Commercial Consumer Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- This paper fully investigates, analyzes, and summarises four categories of errors in Wi-Fi RTT distance measurements, including hardware-dependent bias, blocker-dependent bias, fluctuations, and outliers.
- Two cases of keeping the smartphone static or varying its position during continuous measurement of the Wi-Fi RTT distance are stipulated to analyze the errors against user movements.
- Different materials are used to block the signal path to evaluate the errors against complex NLOS conditions.
2. Related Works
2.1. Fine Time Measurement Protocol

2.2. Ranging with Wi-Fi RTT in Android
3. Wi-Fi RTT Distance Error Measurements
3.1. Experiment Devices and Software
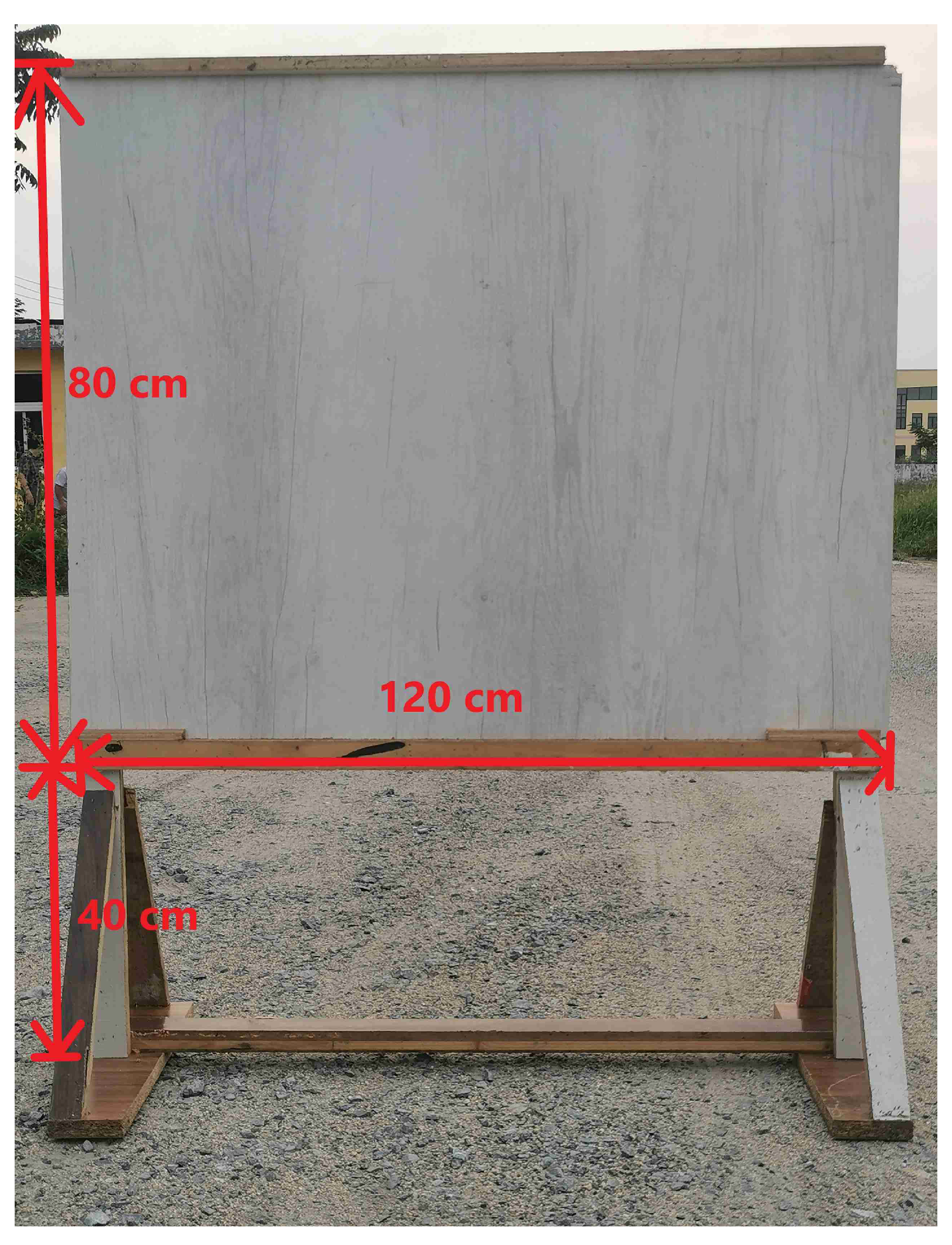
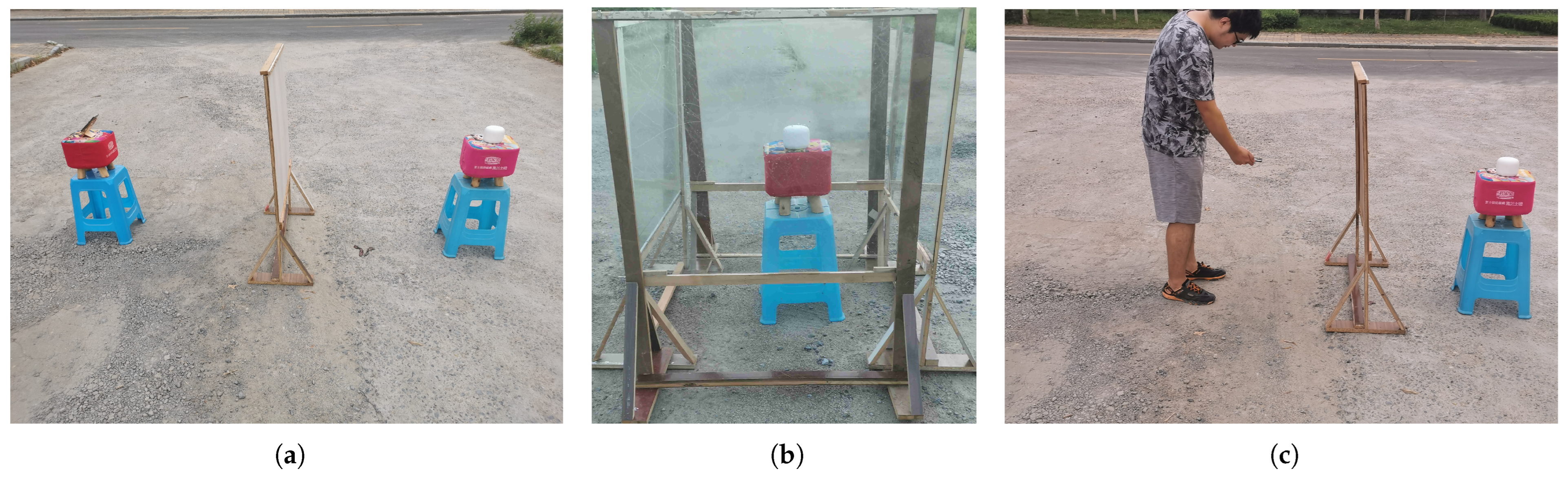
3.2. Experimental Sites
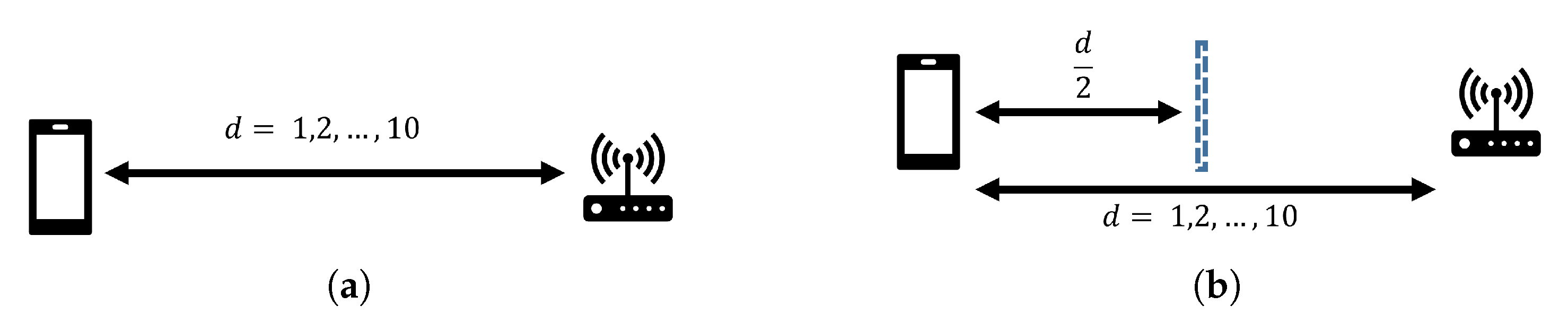
- Range and position-fixed environment (RFPF): considering a sampling period of t s, the smartphone was fixed at a certain position at a distance d m to the AP.
- Range-fixed and position-varied environment (RFPV): considering a sampling period of t s, the smartphone was held by a pedestrian (volunteer) while the distance between the pedestrian and the AP remained at d m to the AP.
- Range and position-varied environment (RVPV): considering a sampling period of t s, the smartphone was held by a pedestrian (volunteer) while the distance between the pedestrian and the AP varied between d m to m.
3.2.1. Range and Position-Fixed Environment
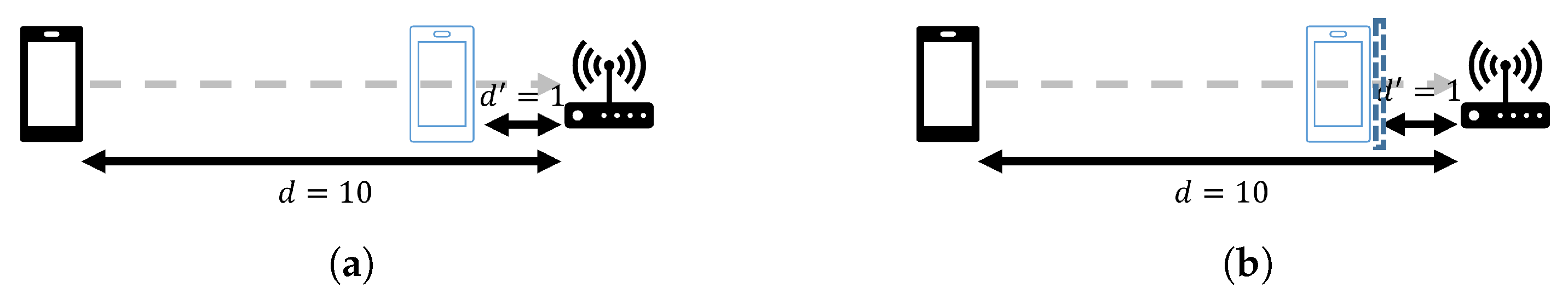
3.2.2. Range-Fixed and Position-Varied Environment
3.2.3. Range and Position-Varied Environment
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
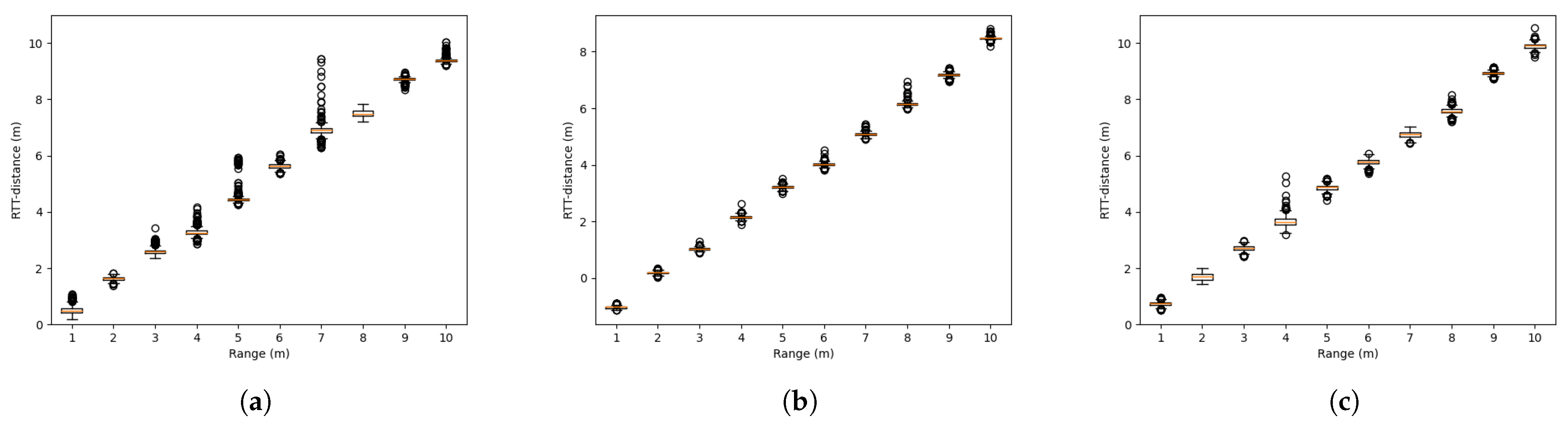
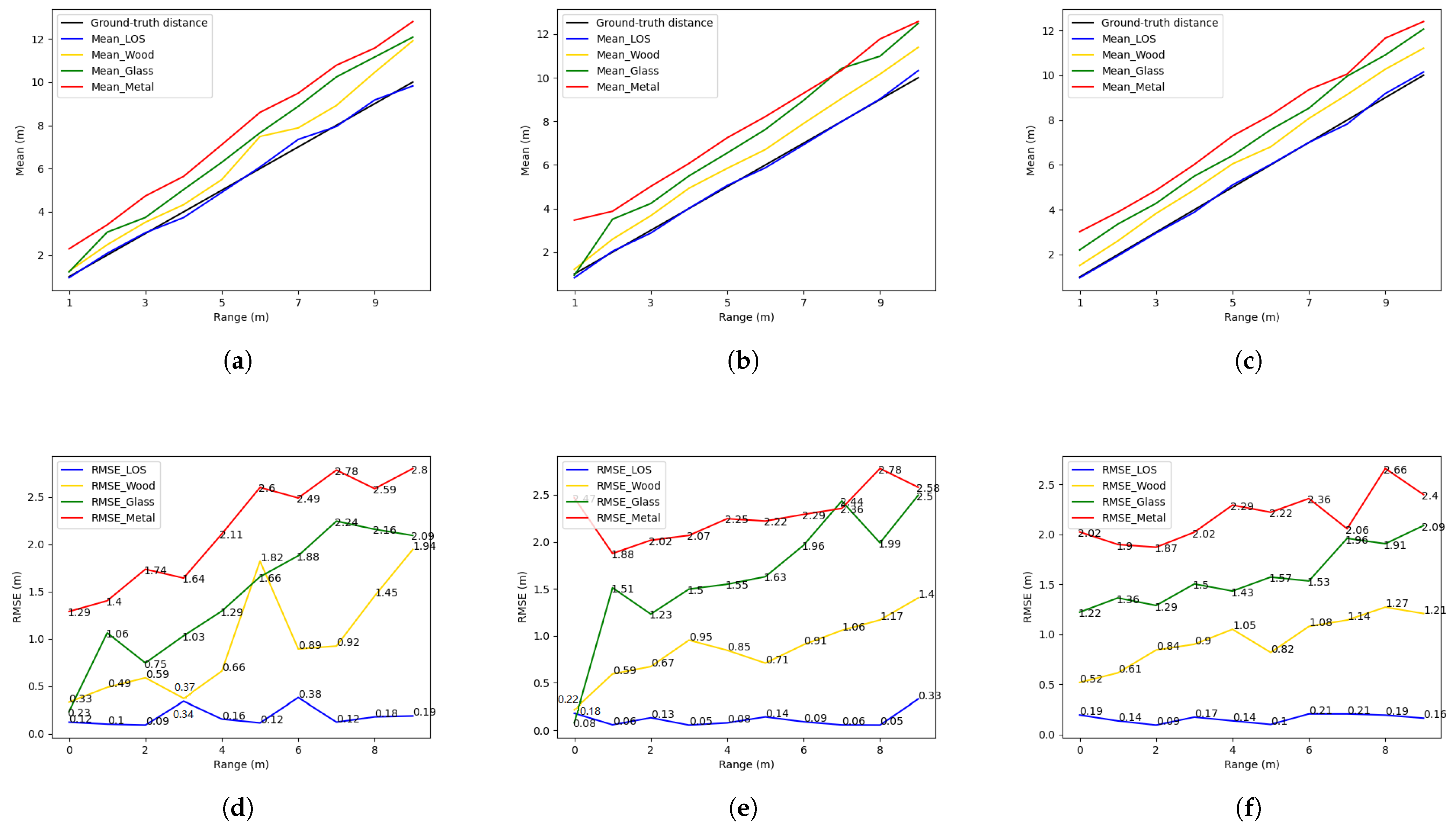
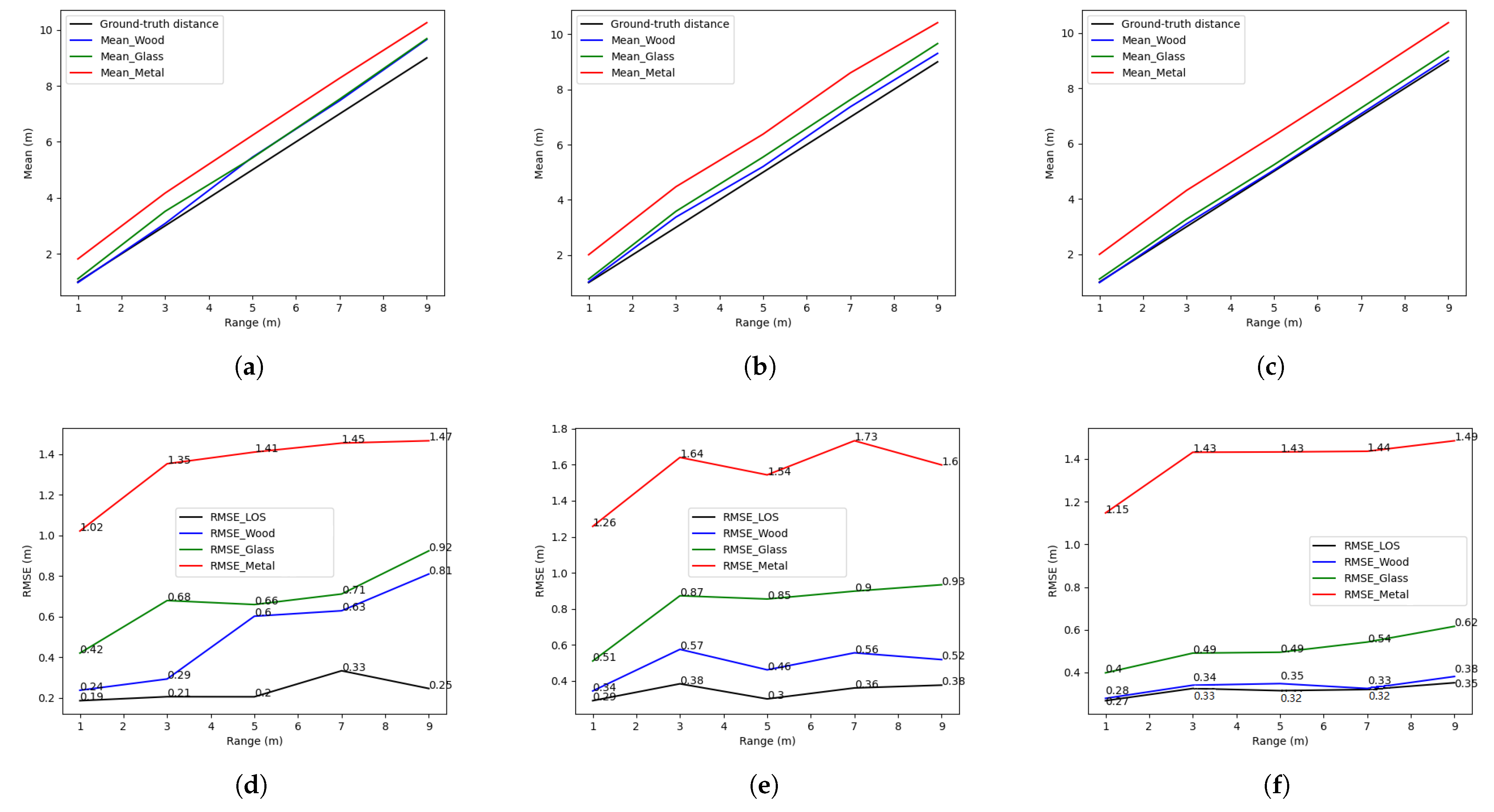
4.1. Verification of the Effectiveness of the Blockers
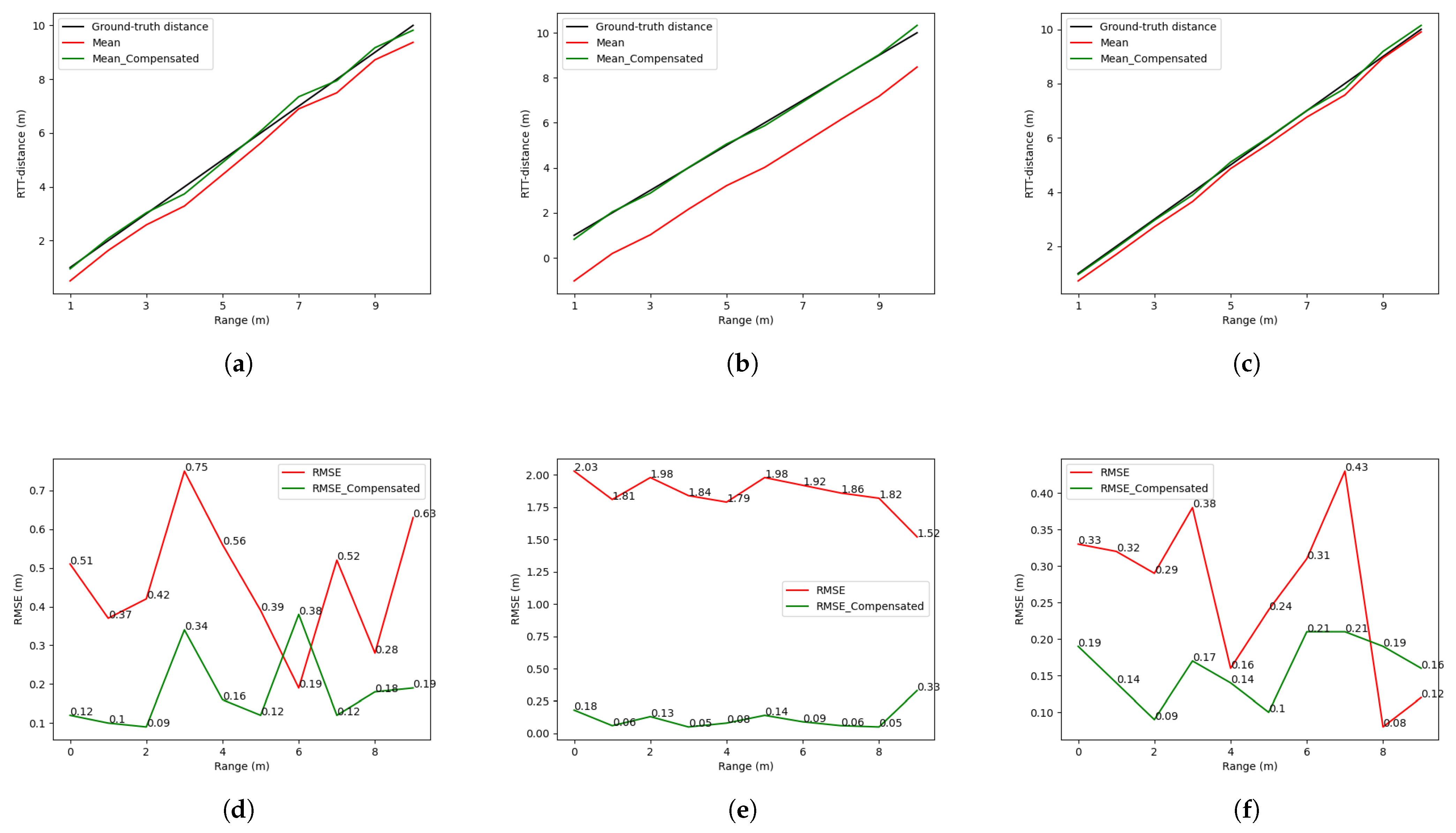
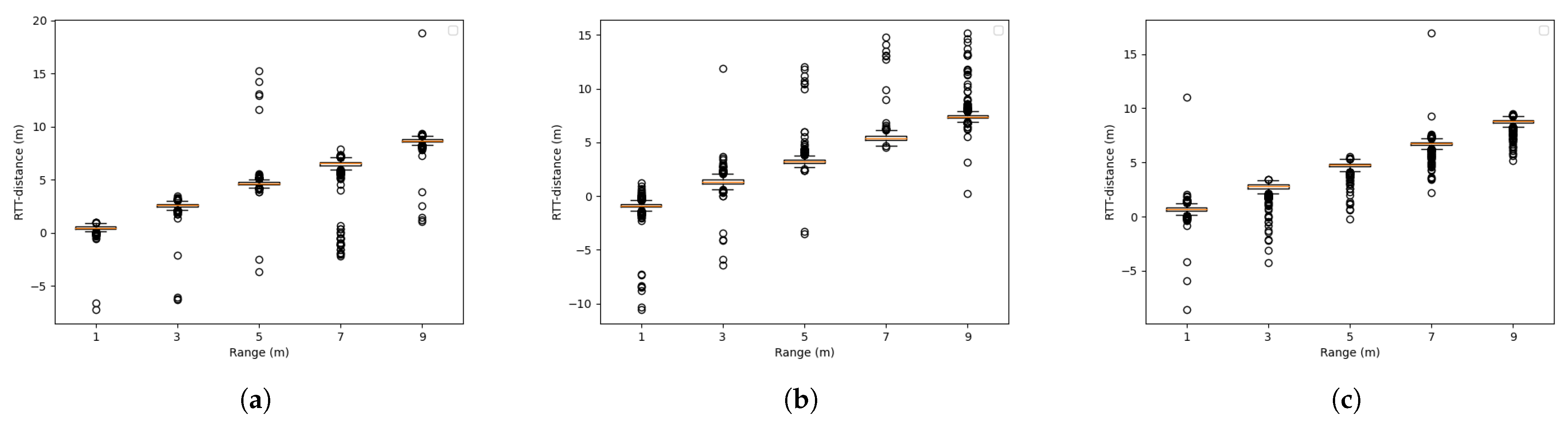
4.2. Range and Position-Fixed Environment
4.3. Range-Fixed and Position-Varied Environment
4.4. Range and Position-Varied Environment
4.5. Summary
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheikhrouhou, O.; MBhatti, G.; Alroobaea, R. A hybrid DV-hop algorithm using RSSI for localization in large-scale wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Park, J. An Enhanced Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on Fingerprint Using Fine-Grained CSI and RSSI Measurements of IEEE 802.11n WLAN. Sensors 2021, 21, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Peng, A.; Tang, B.; Ou, G.; Lu, X. The Time-of-Arrival Offset Estimation in Neural Network Atomic Denoising in Wireless Location. Sensors 2022, 22, 5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfared, S.; Copa, E.I.P.; Doncker, P.D.; Horlin, F. AoA-Based Iterative Positioning of IoT Sensors With Anchor Selection in NLOS Environments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 6211–6216. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE 802.11 Working Group. IEEE Std 802.11-2016 (Revision of IEEE Std 802.11-2012); IEEE Standard for Information Technology-Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems Local and Metropolitan Area Networks–Specific Requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–3534.
- Huang, L.; Yu, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhu, R.; Li, Y. HPIPS: A High-Precision Indoor Pedestrian Positioning System Fusing WiFi-RTT, MEMS, and Map Information. Sensors 2020, 20, 6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, W.-Y.; Seo, D.-H. High-Precision RTT-Based Indoor Positioning System Using RCDN and RPN. Sensors 2021, 21, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, B.K.P. Indoor Localization Using Uncooperative Wi-Fi Access Points. Sensors 2022, 22, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmann, M.; Fetzer, T.; Ebner, F.; Ebner, M.; Deinzer, F.; Grzegorzek, M. Comparison of 2.4 GHz WiFi FTM- and RSSI-Based Indoor Positioning Methods in Realistic Scenarios. Sensors 2020, 20, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, B.K.P. Observation Model for Indoor Positioning. Sensors 2020, 20, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Luo, H.; Zhao, F.; Crivello, A. Wi-Fi RTT based indoor positioning with dynamic weighted multidimensional scaling. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Pisa, Italy, 30 September–3 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Bi, J.; Xu, S.; Si, M.; Qi, H. Indoor Positioning Method Using WiFi RTT Based on LOS Identification and Range Calibration. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Cao, H. A Wi-Fi FTM-Based Indoor Positioning Method with LOS/NLOS Identification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 956. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Fernandez, M.; Hoyas-Ester, I.; Lopez-Cruces, A.; Siutkowska, M.; Banqué-Casanovas, X. Accuracy in WiFi Access Point Position Estimation Using Round Trip Time. Sensors 2021, 21, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Merino, C.S.; Luo-Chen, H.Q.; Khatib, E.J.; Barco, R. WiFi FTM, UWB and Cellular-Based Radio Fusion for Indoor Positioning. Sensors 2021, 21, 7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Escalona, I.; Zola, E. Passive Round-Trip-Time Positioning in Dense IEEE 802.11 Networks. Electronics 2020, 9, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google. Wi-Fi Location: Ranging with RTT. 2022. Available online: https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/wifi-rtt (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Horn, B.K.P. Doubling the Accuracy of Indoor Positioning: Frequency Diversity. Sensors 2020, 5, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, Z.; Guo, G.; Chen, L. Wi-Fi fine time measurement: Data analysis and processing for indoor localisation. J. Navig. 2020, 73, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Arslan, T.; Yang, Y. Real-time NLOS/LOS Identification for Smartphone-based Indoor Positioning Systems using WiFi RTT and RSS. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 5199–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google. Wi-Fi Aware Overview. 2022. Available online: https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/wifi-aware (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Compulab. WiFi Indoor Location Device. 2022. Available online: https://fit-iot.com/web/products/wild/ (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Google Play. WifiRttScan App. 2022. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.location.rtt.wifirttscan (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Google. Android WifiRttScan Sample. Available online: https://github.com/googlearchive/android-WifiRttScan (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Martin-Escalona, I.; Zola, E. Ranging Estimation Error in WiFi Devices Running IEEE 802.11mc. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2020–2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Compulab. WILD Minimal. Available online: https://github.com/Compulab-WILD/WILD-minimal (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Google. WifiRttLocator. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.location.rtt.wifirttlocator (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Google Play FTMRTT App. 2022. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.welwitschia.ftmrtt (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- FTMRTT. 2022. Available online: https://people.csail.mit.edu/bkph/FTMRTT_app (accessed on 15 November 2022).



| Model | * Chipset | OS |
|---|---|---|
| Google Pixel 2 | Snapdragon 835 | Android 10 (upgradable to Android 11) |
| Xiaomi Redmi K20 | Snapdragon 730 | Android 10 |
| LG V50 | Snapdragon 855 | Android 10 (upgradable to Android 12) |
| LOS | Wood Blocker | Glass Blocker | Metal Blocker | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Pixel 2 | −74.3364 | −80.2417 | −79.5688 | −84.3012 |
| Xiaomi Redmi K20 | −68.2389 | −72.9978 | −71.9982 | −79.3582 |
| LG V50 | −73.0837 | −82.3104 | −77.9049 | −83.4068 |
| 1 m | 3 m | 5 m | 7 m | 9 m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP2 static | 0.115 m | 0.086 m | 0.121 m | 0.155 m | 0.056 m |
| GP2 dynamic | m | m | m | m | m |
| XM static | 0.038 m | 0.038 m | 0.052 m | 0.051 m | 0.047 m |
| XM dynamic | m | m | m | m | m |
| LG static | 0.191 m | 0.084 m | 0.087 m | 0.205 m | 0.059 m |
| LG dynamic | m | m | m | m | m |
| LOS | NLOS (Metal) | NLOS (Glass) | NLOS (Wood) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP2 | 0.822 m | m | 0.899 m | 0.668 m |
| XM | 0.717 m | m | 0.593 m | 0.543 m |
| LG | 0.318 m | m | 0.499 m | 1.247 m |
| LOS | NLOS (Metal) | NLOS (Glass) | NLOS (Wood) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP2 | 2.724 m | m | 2.778 m | 2.549 m |
| XM | 2.852 m | m | 2.821 m | 2.703 m |
| LG | 2.541 m | m | 2.831 m | 2.937 m |
| Hardware-Dependent Bias † | Blocker-Dependent Bias | Fluctuations | Outliers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range-fixed, position-fixed, LOS | ✓ | - | ✓ | - |
| Range-fixed, position-varied, LOS | ✓ | - | ✓✓ | ✓ |
| Range-varied, position-varied, LOS | ✓ | - | ✓✓ | ✓ |
| Range-fixed, position-fixed, NLOS * | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Range-fixed, dynamic, NLOS * | ✓ | ✓ | ✓✓ | ✓✓ |
| Range-varied, position-varied, NLOS * | ✓ | ✓ | ✓✓ | ✓✓✓ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Shi, D.; Arslan, T.; Yang, Y. Error Investigation on Wi-Fi RTT in Commercial Consumer Devices. Algorithms 2022, 15, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120464
Dong Y, Shi D, Arslan T, Yang Y. Error Investigation on Wi-Fi RTT in Commercial Consumer Devices. Algorithms. 2022; 15(12):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120464
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yinhuan, Duanxu Shi, Tughrul Arslan, and Yunjie Yang. 2022. "Error Investigation on Wi-Fi RTT in Commercial Consumer Devices" Algorithms 15, no. 12: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120464
APA StyleDong, Y., Shi, D., Arslan, T., & Yang, Y. (2022). Error Investigation on Wi-Fi RTT in Commercial Consumer Devices. Algorithms, 15(12), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15120464






