Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Transmission through a Small Rectangular Aperture: A Solution Based on the Cagniard–DeHoop Method of Moments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
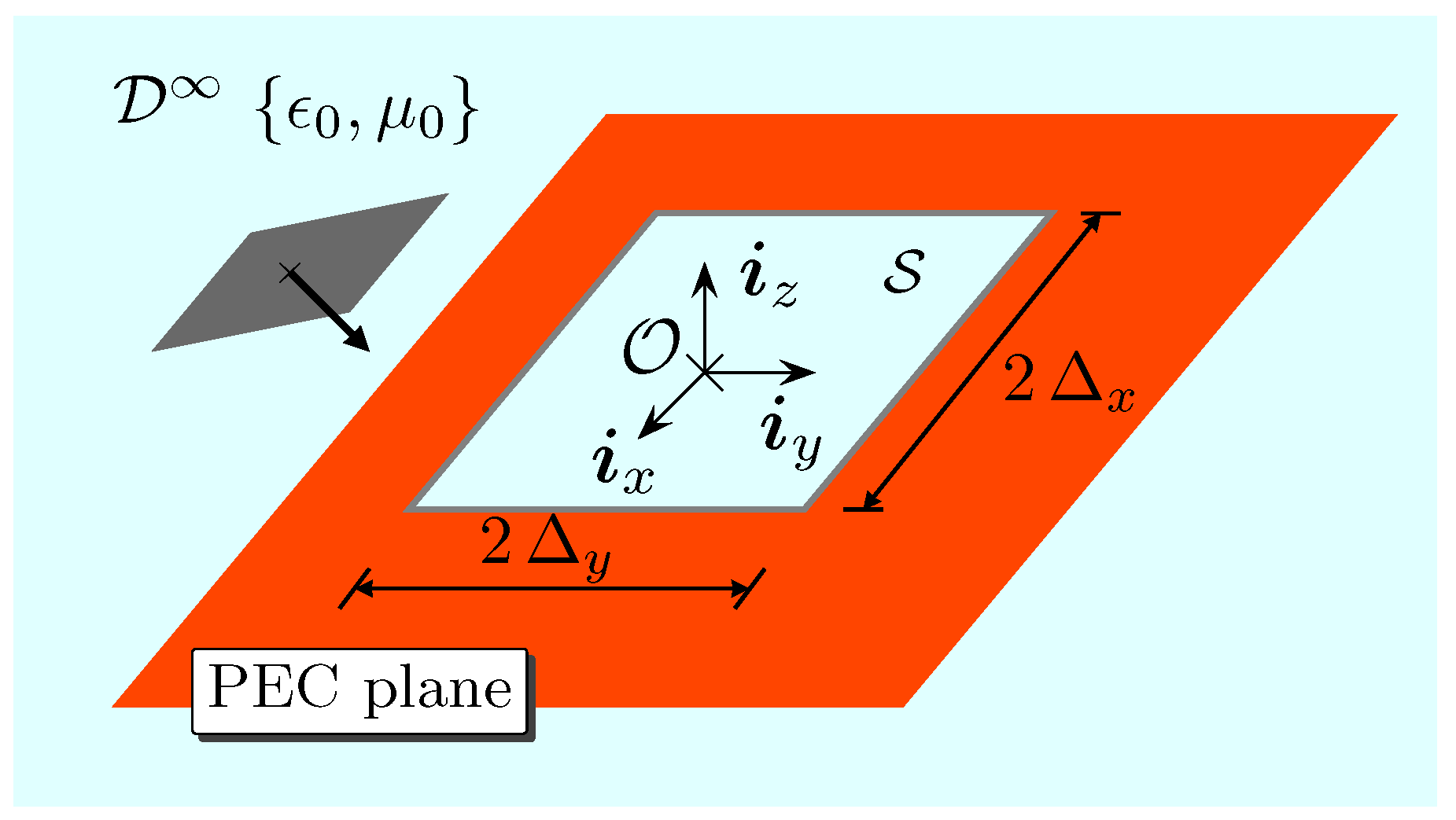
2. Problem Definition
3. Time Domain Problem Formulation
4. Problem Solution
5. Illustrative Examples
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| CdH | Cagniard–deHoop |
| CdH-MoM | Cagniard–deHoop method of moments |
| PEC | Perfectly electrically conducting |
| TD | Time domain |
Appendix A. Time Domain Admittance Array
References
- Van Bladel, J.G. Singular Electromagnetic Fields and Sources; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rayleigh, L. On the passage of waves through apertures in plane screens, and allied problems. Phil. Mag. 1897, 43, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, B.B.; Copson, E.T. The Mathematical Theory of Huygens’ Principle, 3rd ed.; AMS Chelsea Publishing: Providence, RI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwkamp, C.J. Diffraction theory. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1954, 17, 35–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bladel, J.G. Low frequency scattering through an aperture in a rigid screen. J. Sound Vib. 1967, 6, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bladel, J.G. Low-frequency scattering through an aperture in a soft screen. J. Sound Vib. 1968, 8, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethe, H.A. Theory of diffraction by small holes. Phys. Rev. 1944, 66, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meulenaere, F.; Van Bladel, J.G. Polarizability of some small apertures. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1977, 25, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chremmos, I. Tutorial view of electromagnetic wave diffraction through small apertures based on energy considerations. Electromagnetics 2011, 31, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, H.; Schwinger, J. On the theory of diffraction by an aperture in an infinite plane screen. I. Phys. Rev. 1948, 74, 958–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, H.; Schwinger, J. On the theory of electromagnetic wave diffraction by an aperture in an infinite plane conducting screen. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1950, 3, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.M.; Rahmat-Samii, Y.; Mittra, R. Electromagnetic penetration through apertures in conducting surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1978, 26, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Dudley, D.G. Transient current propagation along a wire penetrating a circular aperture in an infinite planar conducting screen. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1990, 32, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, D.; Young, J.L. Far-field time domain calculation from aperture radiators using the FDTD method. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2001, 49, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Gao, C.; Chen, B.; Duan, Y.T.; Yin, Q. Uniform Two-Step Method for the FDTD Analysis of Aperture Coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Mag. 2014, 56, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.D. Electromagnetic pulse penetration through small apertures. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1973, 15, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, F.M.; Ianoz, M.V.; Karlsson, T. EMC Analysis Methods and Computational Models; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- De Hoop, A.T. A modification of Cagniard’s method for solving seismic pulse problems. Appl. Sci. Res. 1960, B, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoop, A.T. Pulsed electromagnetic radiation from a line source in a two-media configuration. Radio Sci. 1979, 14, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, B.J. The electromagnetic field emitted by a pulsed current point source above the interface of a nonperfectly conducting Earth. Radio Sci. 1996, 31, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štumpf, M.; de Hoop, A.T.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E. Generalized ray theory for time domain electromagnetic fields in horizontally layered media. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lager, I.E.; Voogt, V.; Kooij, B.J. Pulsed EM field, close-range signal transfer in layered configurations–a time domain analysis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar]
- De Hoop, A.T. Handbook of Radiation and Scattering of Waves; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fokkema, J.T.; Van den Berg, P.M. Seismic Applications of Acoustic Reciprocity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Štumpf, M. Electromagnetic Reciprocity in Antenna Theory; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wapenaar, C.P.A. Reciprocity theorems for two-way and one-way wave vectors: A comparison. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 3508–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štumpf, M. Time-Domain Electromagnetic Reciprocity in Antenna Modeling; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Štumpf, M. Transient response of a transmission line above a thin conducting sheet—A numerical model based on the Cagniard-DeHoop method of moments. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2021, 20, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štumpf, M. Pulsed electromagnetic scattering by metasurfaces—A numerical solution based on the Cagniard-DeHoop method of moments. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7761–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štumpf, M. Metasurface Electromagnetics: The Cagniard-DeHoop Time-Domain Approach; IET: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wilton, D.; Govind, S. Incorporation of edge conditions in moment method solutions. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1977, 25, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Štumpf, M. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Transmission through a Small Rectangular Aperture: A Solution Based on the Cagniard–DeHoop Method of Moments. Algorithms 2022, 15, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15060216
Štumpf M. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Transmission through a Small Rectangular Aperture: A Solution Based on the Cagniard–DeHoop Method of Moments. Algorithms. 2022; 15(6):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15060216
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtumpf, Martin. 2022. "Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Transmission through a Small Rectangular Aperture: A Solution Based on the Cagniard–DeHoop Method of Moments" Algorithms 15, no. 6: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15060216
APA StyleŠtumpf, M. (2022). Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Transmission through a Small Rectangular Aperture: A Solution Based on the Cagniard–DeHoop Method of Moments. Algorithms, 15(6), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/a15060216





