Entropy-Based Anomaly Detection for Gaussian Mixture Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Aim and Organization of the Paper
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gaussian Mixtures in Model-Based Clustering and Density Estimation
2.2. Model Selection
2.3. Including a Noise Component in Gaussian Mixtures
- The volume of the convex hull, i.e., the smallest convex polygon that contains all the data points;
- The volume of the ellipsoid hull, i.e., the ellipsoid of minimal volume such that all observed points lie either inside or on the boundary of the ellipsoid;
- The volume computed as the minimum between the hyper-rectangle containing the observed data and the box obtained from principal components.
2.4. Initial Noise Detection Using Entropy Contribution of Data Points
| Algorithm 1: Anomaly detection algorithm |
Input:
|
3. Results
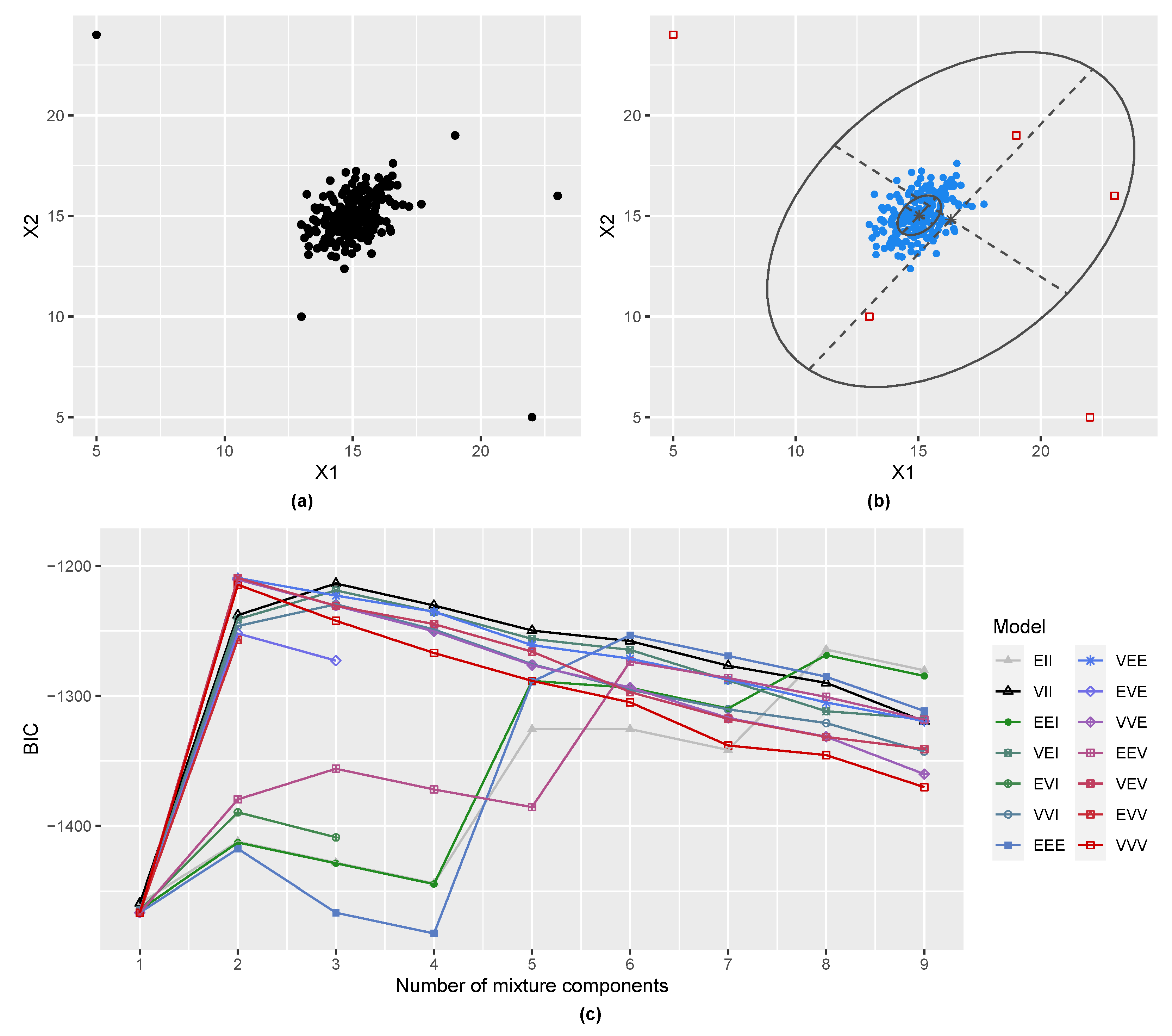
3.1. Gaussian Distribution with Outliers
3.2. Three-Component Gaussian Mixture with Uniform Random Noise
3.3. Wisconsin Diagnostic Breast Cancer Data
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLachlan, G.J.; Peel, D. Finite Mixture Models; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, K.Y.; Fraley, C.; Murua, A.; Raftery, A.E.; Ruzzo, W.L. Model-based clustering and data transformations for gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLachlan, G.; Bean, R.; Peel, D. A mixture model-based approach to the clustering of microarray expression data. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najarian, K.; Zaheri, M.; Rad, A.A.; Najarian, S.; Dargahi, J. A novel mixture model method for identification of differentially expressed genes from DNA microarray data. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.; Zhai, C.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L. Inference of gene pathways using Gaussian mixture models. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM 2007), Fremont, CA, USA, 2–4 November 2007; pp. 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, M.; Habeck, M. Mixture models for protein structure ensembles. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Raftery, A.E. Detecting features in spatial point processes with clutter via model-based clustering. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1998, 93, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, C.; Raftery, A.E. How many clusters? Which clustering method? Answers via model-based cluster analysis. Comput. J. 1998, 41, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coretto, P.; Hennig, C. Robust improper maximum likelihood: Tuning, computation, and a comparison with other methods for robust Gaussian clustering. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, U.J.; Browne, R.P.; McNicholas, P.D. Mixtures of multivariate power exponential distributions. Biometrics 2015, 71, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punzo, A.; McNicholas, P.D. Parsimonious mixtures of multivariate contaminated normal distributions. Biom. J. 2016, 58, 1506–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Escudero, L.A.; Gordaliza, A.; Matràn, C.; Mayo-Iscar, A. A general trimming approach to robust cluster analysis. Ann. Stat. 2008, 36, 1324–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, F.; Farcomeni, A. Robust inference for parsimonious model-based clustering. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2019, 89, 414–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcomeni, A.; Punzo, A. Robust model-based clustering with mild and gross outliers. TEST 2020, 29, 989–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, C.; Raftery, A.E. Model-based clustering, discriminant analysis, and density estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 611–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfield, J.; Raftery, A.E. Model-based Gaussian and non-Gaussian clustering. Biometrics 1993, 49, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeux, G.; Govaert, G. Gaussian parsimonious clustering models. Pattern Recognit. 1995, 28, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fraley, C.; Raftery, A.E.; Scrucca, L. mclust: Gaussian Mixture Modelling for Model-Based Clustering, Classification, and Density Estimation; R Package Version 6.0.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Scrucca, L.; Fop, M.; Murphy, T.B.; Raftery, A.E. mclust 5: Clustering, classification and density estimation using Gaussian finite mixture models. R J. 2016, 8, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1977, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan, G.; Krishnan, T. The EM Algorithm and Extensions, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, C.; Celeux, G.; Govaert, G. Assessing a mixture model for clustering with the integrated completed likelihood. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, D.; Fraley, C. Nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation of features in spatial point processes using Voronoï tessellation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1997, 92, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, S.; Raftery, A.E. Nearest-neighbor clutter removal for estimating features in spatial point processes. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1998, 93, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Raftery, A.E. Nearest neighbor variance estimation (NNVE): Robust covariance estimation via nearest neighbor cleaning (with discussion). J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 994–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Michalowicz, J.V.; Nichols, J.M.; Bucholtz, F. Handbook of Differential Entropy; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, S.; Scrucca, L. Mixture-based estimation of entropy. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2023, 177, 107582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, C. Algorithms for model-based Gaussian hierarchical clustering. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1998, 20, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, D.; Graff, C. UCI Machine Learning Repository. 2019. Available online: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Mangasarian, O.L.; Street, W.N.; Wolberg, W.H. Breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis via linear programming. Oper. Res. 1995, 43, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| ---------------------------------------------------- | |||||||||
| Gaussian finite mixture model fitted by EM algorithm | |||||||||
| ---------------------------------------------------- | |||||||||
| Mclust VVE (ellipsoidal, equal orientation) model with 2 components: | |||||||||
| log-likelihood | n | df | BIC | ICL | Entropy | ||||
| −4449.632 | 569 | 16 | −9000.766 | −9099.815 | 7.820091 | ||||
| Clustering table: | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | ||||||||
| 240 | 329 | ||||||||
| Confusion matrix: | |||||||||
| Cluster | |||||||||
| Diagnosis | 1 | 2 | |||||||
| B | 40 | 317 | |||||||
| M | 200 | 12 | |||||||
| ---------------------------------------------------- | ||||||||
| Gaussian finite mixture model fitted by EM algorithm | ||||||||
| ---------------------------------------------------- | ||||||||
| Mclust EVI (diagonal, equal volume, varying shape) model with 2 components and a noise term: | ||||||||
| log-likelihood | n | df | BIC | ICL | Entropy | |||
| −4457.913 | 569 | 14 | −9004.64 | −9077.593 | 7.834645 | |||
| Clustering table: | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||
| 142 | 412 | 15 | ||||||
| Confusion matrix: | ||||||||
| Cluster | ||||||||
| Diagnosis noise | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| B | 1 | 0 | 356 | |||||
| M | 14 | 142 | 56 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scrucca, L. Entropy-Based Anomaly Detection for Gaussian Mixture Modeling. Algorithms 2023, 16, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16040195
Scrucca L. Entropy-Based Anomaly Detection for Gaussian Mixture Modeling. Algorithms. 2023; 16(4):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16040195
Chicago/Turabian StyleScrucca, Luca. 2023. "Entropy-Based Anomaly Detection for Gaussian Mixture Modeling" Algorithms 16, no. 4: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16040195
APA StyleScrucca, L. (2023). Entropy-Based Anomaly Detection for Gaussian Mixture Modeling. Algorithms, 16(4), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16040195






