Theoretical Study of the Wear of a Reduced-Diameter Wheel for Freight Wagons, Based on Its Diameter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Wheel factors: geometry (diameter, conicity, tread width, contact angle), machining (roughness), material (properties), load, and previous wear.
- Wagon factors: configuration (bogies or axles distribution and type of bogies), type of suspension, braking system, running speed, and load distribution (axle load).
- Railway superstructure factors: track gauge, line layout (curve radii, windiness, sagitta, gradient, etc.), layout quality (excess or deficiency in cant, transition curves, etc.), type of rail (welded or with joints), track materials (properties) and track previous degradation (previous rail wear, specially).
- External factors: Temperature, humidity, wind, rain, snow, and weather in general. The presence of moisture, leaves, and pollutants (saltpeter, oil, etc.) is important here too.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Abbreviations List
2.2. Hypotheses
- (a)
- (b)
- The method relies on global calculations for the contact patch without dividing it into finite elements.
- (c)
- It is stationary, meaning it does not account for changes in variables over time. In transition curves, where these variations are more significant, average values are calculated.
- (d)
- It ignores any rail wear and the prior wear of the wheels, meaning it does not update the contact parameters as the profile changes, since this profile is consistently renewed.
- (e)
- It is applied to all the bogie wheels. For each wheel, the parameters and wear calculations are stored separately, as the wear varies among the different bogie wheels [18].
- (f)
- It is applied to a single bogie of a wagon. Typically, a wagon comprises two bogies, which can generally rotate independently of one another.
- (g)
- It overlooks the tractive and compressive forces that certain wagons transfer to one another through couplings while navigating curves, due to the inherent coupling slacks [19].
- (h)
- (i)
- (j)
- It can account for up to two contact patches on the same wheel: one on the tread and the other on the flange [17].
- (k)
- In Kalker’s and Polach’s equations, the spin is assumed to be positive when it is clockwise, as it must comply with the sign convention applied for creepage. This spin is later passed on to the energy transfer model employed.
- (l)
- Creepage is derived from the kinematic analyses of the wheelset rather than from the non-dimensional slips, which involve partial derivatives typically not used in global calculations.
- (m)
- Throughout this study, the radial deformation is considered negligible compared to the wheel radius (). Additionally, since (specifically, , based on the values obtained in Ref. [17]), the influence of on can also be disregarded.
- (n)
- However, the influence of on the wear occurring at transition curves is taken into account, as it contributes to a slight increase in wear.
- (o)
- The displacements from the bogie suspensions and anti-yaw mechanisms are not considered in the kinematic analysis.
- (p)
- The variation in wheel and rail curvatures at transition curves is ignored because although the location of the rail–wheel contact shifts across the widths of the wheel and rail (affecting their curvatures), these changes are typically minimal. When the variations are significant, the most unfavorable values are used directly (for example, the curvatures at the flange–rail contact when such contact is expected to occur at a specific transition curve).
- (q)
- (r)
- RCF is only anticipated without calculating the extent of the damage caused, often involving subsurface cracks [20].
- (s)
- The bogie wheels are assumed to be non-powered, which means at the contact patches.
- (t)
- The bogie wheels are assumed to have disk brakes that do not cause wear on the wheels [17].
- (u)
- The railway vehicle is expected to navigate curves (both circular and transitional) at a constant speed, applying brakes (if necessary) before entering the curve, resulting in during the curve. An exception to this occurs when the vehicle is traveling downhill, as outlined in the next hypothesis.
- (v)
- It is assumed that the railway vehicle brakes slightly when descending, and reducing or cutting off traction is insufficient to maintain a constant speed while navigating curves: when the slope is less than 10‰, the vehicle brakes will be off; when the slope is between 10 and 15‰, the brakes will brake 5% of the accelerating force at each wheelset; and when the slope is greater than 15‰, the brakes will brake 10% of the accelerating force.
- (w)
- The infrastructure parameters or conditions modifying the wear conditions, such as warp, rail deflection, joints, running on turnouts/switches and other track devices, and track irregularities are not observed [22].
- (x)
- No manufacturing or assembly tolerances for any component are considered.
- (y)
- By neglecting rail deflection and manufacturing or assembly tolerances, it can be assumed that the longitudinal rail curve radius () approaches infinity, causing the associated curvature () to approach zero (which is treated as such).
- (z)
- It is assumed that the bogie wheels do not derail or become blocked (this was numerically verified in Ref. [17]). Furthermore, they are expected not to displace laterally under conditions of cant deficiency or excess, as well as low static friction, and to remain free from hunting oscillations within the considered speed ranges (this was numerically demonstrated in Ref. [17]).
2.3. Calculation Process
- At the top of the algorithm, the input data (represented by green blocks) was entered to the calculation blocks. The data is arranged in blocks that are added before going down to the main branches. These blocks gather information on the wheelset and bogie geometry, vehicle speed, railway line geometry, wheel geometry, load characteristics, rail geometry and contact materials properties.
- On the left, in the 3 central blocks (in light blue), the kinematic parameters for the wheelsets are obtained through relations dependent on the line geometry after inputting information on the wheelset and bogie geometry, vehicle speed, railway line geometry and wheel geometry. After that, the uncentering of each wheelset is saturated through equations dependent on the line geometry and finally, creepages are obtained through kinematics equations.
- On the right, in the 6 central blocks (in dark blue), the normal force on each wheel is computed by means of dynamics equations after entering data on the vehicle speed, line geometry, load characteristics, and some results coming from the left main branch after the saturation of uncentering. Afterwards, the geometric and normal contact problems are solved by means of Hertz’s solution, for which data on the wheel and rail geometries and the contact materials properties is needed. The results of Hertz’s solution and the creepages computed in the left main branch allows for the application of Polach’s method. This solution can be applied either with constant or variable friction. At the end of this branch, the flange–rail contact is characterized by equilibrium equations.
- At the bottom of the algorithm (purple blocks), the wheel wear is computed through the energy transfer model, and the appearance of RCF is predicted with the fatigue index model.
- Regarding the symbology, the orange symbol with a diagonal cross indicates the addition of values, the orange symbol with a Greek cross represents a disjunction, the gray symbol signifies that only one flow is input, and the yellow symbol denotes a bifurcation:
2.4. Calculation Model
2.4.1. Reference Frames Definition
- Absolute reference frame , clockwise, fixed, with its origin located on the rolling plane, anchored at the start of the track and centered between the rails.
- Track reference frame , clockwise, moving at the vehicle’s speed, with its origin located on the rolling plane along the centerline of the track, maintaining the axis always tangent to that line.
- Axle reference frame , clockwise, moving at the axle speed, with its origin located at the center of gravity of the wheelset.
- Contact area reference frame , clockwise, moving at the speed of the contact area, with its origin positioned at the center of that area.
2.4.2. Obtention of the Kinematic Parameters
- Uncentering and its change rate.
- Average uncentering and its change rate.
- Yaw angle and its change rate.
- Average sinus of yaw angle and of yaw angle change rate.
- Average yaw angle.
- Combination of the uncentering and yaw angle effects.
- Angle of longitudinal displacement of the contact area.
- Tilt and its change rate.
2.4.3. Saturation of Uncentering
- SC—Rolling radius ().
- SC—Track gauge ( for Iberian gauge).
- SC—Rail inclination ( for Iberian gauge).
- SC—Track play/slack (.
- C—Curve radius ().
- C—Gauge widening ().
- C—Curve sagitta ().
- C—Total uncentering () and uncentering limit ( or ).
- C—Outer | inner wheel rolling radius ().
- C—Yaw () and tilt angles ().
- C—Angle of longitudinal displacement of the contact area ().
2.4.4. Obtention of the Creepages
- Difference between the nominal wheel radius and the real rolling one (generating ).
- Application of tractive or braking torques to the wheel (generating ).
- Variation of yaw angle (generating ).
- Not null yaw angle (generating ).
- Adoption of a new equilibrium position by the wheelset (generating ).
- Not null tilt angle (generating ).
- Conicity (generating , alternatively known as the camber effect [20]).
- Variation of yaw angle (generating ).
2.4.5. Obtention of the Normal Force on Each Wheel
- Axle load (), which is obtained from the payload, tare and number of axles.
- Center of gravity of the axle load (), considering the contribution of each load.
- Gradient angle (), which is directly inferred from the inclination ().
- Cant angle (), which depends on the cant and the distance between contact areas.
- Lateral acceleration (), which considers the effect of cant excess or deficiency.
- Wheel contact angle () and longitudinal displacement angle of the contact patch ().
2.4.6. Solution of the Geometric and Normal Contact Problems
- Hertzian contact theory. This theory was the first satisfactory analysis for the stresses appearing at the contact zone between 2 elastic solid bodies and solves the geometric problem at the same time if a series of hypotheses are fulfilled. According to this theory, the contact area is the intersection of two perfect paraboloids: a perfect ellipse.
- Kik–Piotrowski theory. This is a quasi-Hertzian theory and is also based on the virtual interpenetration between surfaces. It assumes the same pressure distribution in the longitudinal direction as Hertz, but not in the lateral direction as the curvature is not always constant in that direction. It is interesting to point out that this theory disregards the real shape of the bodies and replaces them by elastic half-spaces, which allows employing Boussinesq’s influence functions.
- Ayasse–Chollet. This is also a quasi-Hertzian theory, a variant of the previous one.
- Stiff approach. This theory is based on a stiff contact in which there is a theoretical contact point for which a series of constraints is imposed.
- The bodies in contact are homogeneous, isotropic, and linearly elastic.
- Displacements are assumed to be infinitesimal, significantly smaller than the characteristic dimensions of the bodies.
- The surfaces of the bodies are smooth in the contact zone, meaning they have no roughness.
- Each body can be modeled as an elastic half-space, necessitating non-conformal contact.
- The surfaces of the bodies can be approximated by quadratic functions near the point of maximum interpenetration, indicating that the curvatures (the second derivatives of the functions) are constant.
- The distance between the undeformed profiles of both bodies at the maximum interpenetration point can be modeled as a paraboloid.
- The contact between the bodies occurs without friction, allowing only normal pressure to be transmitted.
2.4.7. Solution of the Tangential Contact Problem
- Analytical. The values are calculated for the entire contact patch as a whole. A series of analytical equations are employed, allowing the tangential problem to be decoupled from the geometric and normal problems due to the satisfaction of non-conformity and quasi-identity conditions.
- Finite element. The values of the variables are calculated locally and then summed to obtain the global values. To achieve this, the contact patch is divided into a mesh.
- Carter’s theory. This was the first theory ever. Carter coined the term “creepage” as “the ratio of the distance gained by a surface with respect to the other divided by the distance run“. He stated that the longitudinal dimension of Hertz’s ellipse in the unworn profiles was, in general, greater than the lateral one, but as a consequence of wear, the profiles flattened, giving rise to a uniform-width strip. He assumed that the wheel and rail profiles could be approximated by two parallel-axis cylinders, so the problem was reduced to a plane stress problem, i.e., bi-dimensional.
- Johnson’s theory. Johnson published the first contact theory for circular contacts. In this theory, the stick region is circle-shaped, and it touches the leading edge at a single point, although he later showed that this hypothesis leads to a contradiction: tangential stress does not oppose slip at the slip region adjacent to the leading edge. He also derived relations between creepages that were decreasingly small and tangential forces. Finally, he showed that the spin effect also contributes to lateral force.
- Johnson–Vermeulen’s theory. Johnson worked later with Vermeulen and both extended the theory of circular contacts under pure creepage (no spin) conditions to cases of elliptical contact. They used the solution for slipping contacts with microslip derived by Deresiewick for elliptical contact, with the only difference being that the stick region touches the leading edge at a single point with the purpose of reducing the erroneous area for a rolling contact case. However, in this theory, there was still a region where the friction law was not fulfilled.
- Kalker’s theory. At first, Kalker established a linear relation between the tangential forces and decreasingly small creepages. At such a restrictive situation, it is possible to assume that the whole contact area is in adhesion (there is no slip region). This first linear theory was also known as “non-slip theory” in which the friction law and the friction coefficient were discarded. Due to the lack of saturation of this theory (Coulomb–Amonton’s law would be the only saturation), this theory was improved with linear and cubic saturation approaches (CONTACT and SHE methods, respectively).
- Polach’s theory. Even with the improvements, Kalker’s theory was not enough for computing the lateral tangential force accurately when the spin grows beyond a certain threshold. Polach proposed a method to tackle this problem: (1) Tangential forces computation considering null spin. (2) Tangential forces computation considering pure spin. (3) Addition of the forces computed in steps (1) and (2) and saturation according to the traction limit. For this method, Polach assumed that the ellipse semi-axis in the rolling direction () tends to zero, so the position of the spin center tends to the ellipse center. He extended this assumption to higher semi-axes ratios ().
2.4.8. Characterization of Flange–Rail Contact
2.4.9. Calculation of Wear
- The equations are parameterized for abrasive wear rather than adhesive wear for several reasons: (1) Plastic deformation occurs, but modeling it accurately is challenging without finite-element methods, which are computationally intensive. (2) It is reasonable to assume that abrasive wear is the primary contributor. (3) When the mathematical tools are calibrated with experimental data, both wear phenomena are inherently included in the resulting wear law.
- The various mathematical tools analyze the wear on the wheel profile, where the wear calculated at each moment is cumulative.
- Wear is considered to be uniform, i.e., the focus is on the variation of the transverse profile rather than on pattern formation in the longitudinal (circumferential) direction. Therefore, the wear measured at a specific position and time is extrapolated to the entire circumference.
- There are no pollutants present at the contact interface. The impact of pollutants is accounted for by adjusting the friction coefficient or by introducing new wear laws.
- Energy transfer models. These models compute the energy dissipated at the wheel–rail interface and associate it with the wear rate, which can be ultimately associated with the wear depth. There are various models, each with its own wear law: Zoroby’s model, which is based on the energy flow; the model developed by the British Railway Research (BRR), which is based on a non-continuous wear law depending on the wear regime (mild, transition, severe); and the model developed by the University of Sheffield (USFD), which is based on a continuous wear law divided into several regimes (mild, severe, catastrophic).
- Reye–Archand–Khruschchov (RAK) model. This is the simplest model and characterizes the abrasive wear appearing at the slip zone of the contact area. In this model, the volume of material lost is expressed as a function of the slip speed, normal force, hardness of the wheel material (steel), and a coefficient coming from a wear chart divided in wear zones depending on the normal pressure and the slip speed.
2.4.10. Prediction of RCF
- If , RCF alone is insufficient to initiate cracks because the tangential force is controlled by moderated (utilized) friction.
- If , this represents the limiting condition. Cracks do not form because the shear stress at yield () has not yet been exceeded.
- If , RCF triggers surface cracks due to the increased tangential force resulting from higher (utilized) friction.
2.5. Choice of the Calculation Software
2.6. Calculation Scenarios
- Y—25. This bogie has four wheels (two wheelsets) and supports a total load of 45 tons (22.5 tons per axle) at a maximum speed of 120 km/h. The total wheelbase () is variable, and the wheels are typically braked by brake shoes. The nominal wheel diameter () ranges from 920 mm (original maximum) to 840 mm (operational minimum).
- Saas-z 703. This bogie also features four wheels (two wheelsets) and supports a total load of 32 tons (16 tons per axle) at a maximum speed of 100 km/h. The wheelbase () is variable, and the wheels are braked by brake disks. The nominal wheel diameter () ranges from 680 mm to 630 mm.
- Graz Pauker 702. This bogie has eight wheels (four wheelsets) and supports a total load of 20 tons (5 tons per axle) at a maximum speed of 100 km/h. The wheelbase () is variable, and the nominal wheel diameter () ranges from 355 mm to 335 mm.
- Axle load (). Maintaining a constant axle load across all scenarios would result in some wheels being overloaded and others underloaded. For instance, axle loads of 22.5 tons would be unrealistic for 680 mm and 355 mm wheels, whereas loads as low as 5 tons would be feasible but would place extreme stress on the smallest wheels. To ensure comparable conditions, the axle load that generates a normal pressure of 1235 MPa is chosen. This value is common since maximum axle loads usually induce between 1100 and 1300 MPa on the wheel, with 1235 MPa being a mean value, even if it exceeds the manufacturer’s limit for the smallest wheels.
- Flange radius (). This is the sum of the nominal rolling radius (, which is half of ) and a constant. Therefore, decreases in proportion to .
2.7. Input Data
- Initial and final metric points ( and , respectively).
- Stretch type: RECTA (straight), CIR (circular curve), CLO (clothoid), PARACUAD (quadratic parabola), or PARACUB (cubic parabola).
- Curve direction: NING (the stretch is straight), IZDA (curve to the left), or DCHA (curve to the right).
- Bogie position on the curve: NING (the stretch is straight), ENT (the bogie is entering the curve), or SAL (the bogie is exiting the curve).
- Curve radius (), cant (), and inclination ().
- Initial and final maximum allowed speeds ( and , respectively).
3. Results
- The 920-mm wheels can travel up to 124,275 km before their diameter reduces to 840 mm. These wheels lose 2 mm in diameter with each reprofiling cycle, at which point they are replaced for safety and operational reasons.
- The 680-mm wheels are able to travel for 75,648 km before reaching their minimum allowed diameter of 630 mm. In practice, this is the point at which the wheels are retired. However, if the wear and reprofiling cycles are extended as though the minimum diameter could be 600 mm (similar to the difference between 680 and 600 being analogous to the difference between 920 and 840), the wheels would theoretically last 118,683 km.
- The 355-mm wheels are capable of traveling 26,983 km before their diameter reaches the minimum allowed size of 335 mm. This is the practical end of their service life. If wear and reprofiling cycles were extended as if the final diameter could be 275 mm (with the difference being similar to that of the 920 to 840 scenario), the wheels would theoretically travel 101,433 km.
4. Discussion
- Comparing the real life ends (124,275; 75,648; and 26,985 km) in percentual terms with respect to the first value, it is obtained that the 680-mm wheels’ life is 30.13% shorter and the 355-mm wheels’ life is 78.29% shorter.
- Due to the elevated life shortening of 355-mm wheels, operators prefer using bigger wheels. For example, in Ref. [17], 380-mm wheels, which are mounted on the Saadkms690 bogie, are presented, which can be reprofiled until reaching 335 mm and the difference between both values (45 mm) is 25 mm higher than for 355-mm wheels (20 mm). Escalating the life of 355-mm wheels heuristically with the ratio 45/20, the result is 43,176 km, only 65.26% shorter than 920-mm wheels’ life. This is very advantageous despite the elevation in 25 mm of the loading plane height, so replacing 355-mm wheels by 380-mm wheels will ultimately depend on the application (semi-trailers’ heights and tunnels and bridges’ loading gauges).
- The distance difference between reprofiling (the reprofiling span) is very variable when reprofiling a same wheel and, obviously, when moving across wheels, so adopting arithmetic mean values is required. The mean value is 4,603 km for 920-mm wheels, 4,396 km for 680-mm ones, and 3,757 km for 355-mm ones.
- Should the wagons perform routes Albarque–Zacarín–Albarque (75.272 km) a week, then reprofiling the periodicity should be . Using the average value of 4250 km, the approximate result obtained is .
- If all of the wheels were reprofiled the same number of cycles (always eliminating 80 mm in diameter), then the wheels’ life (fictional, as eliminating 80 mm would be against the manufacturers and operators’ regulations) would be: 118,683 km for 680-mm wheels and 101,433 km for 355-mm wheels. The former value is 4.50% lower than that of 920-mm wheels (124,275 km), while the latter value is 18.38% lower.
- These trends are summarized in Figure 17, where it can be seen that neither the behavior of the real life end nor that of the fictional life end are linear:
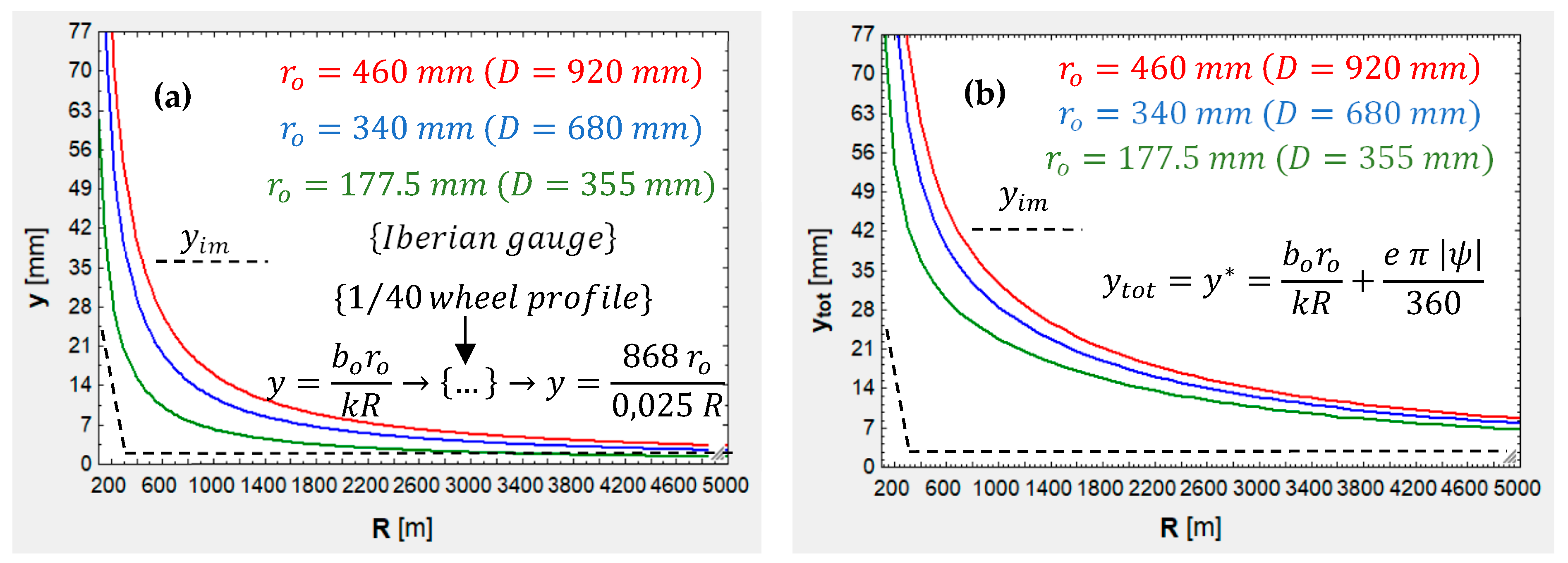
- This non-linear behavior responds to the different kinematic response of reduced-diameter wheels when negotiating curves. As demonstrated by Redtenbacher’s formula, uncentering is proportional to wheel radius (to wheel diameter in turn, as the radius is half), so not only do reduced-diameter wheels uncenter less than ordinary-diameter ones, but also their flanges will push against the rails less intensely. Moreover, the bogies where reduced-diameter wheels are mounted are less loaded, which will further reduce the force exerted by the rail on the flange (coming from force and torque balances). Figure 18a illustrates the partial uncentering (differential effect) for the three scenarios and shows how saturation () is reached at a lower radius threshold for reduced-diameter wheels, while Figure 18b shows the total uncentering (adding bogie rotation) in the worst case (leading wheelset, outer wheel), but even in this case, flange–rail contact is less aggressive owing to dynamics:
- The results for the three scenarios were obtained for a 1235-MPa normal pressure at the tread contact area with the rail when the wheels run on straight tracks, attaining such a value by adjusting the axle load for each scenario. Pressures existing at the flanges were not equated due to the variability of the force exerted by the rail on the flange on the curve radius, which would make it very difficult to obtain unique axle load values.
- It is necessary to limit axle load on reduced-diameter wheels, as their contact area with the rail is reduced as well, and the normal pressure is proportional to the load–area ratio. This reduction in the contact area responds to the decrease in the longitudinal radius , which is proportional to the wheel diameter. With a lower value, a greater longitudinal relative curvature () is obtained, which diminishes the intersection between the theoretical paraboloids and, as a result, the contact patch size (as diminishes, the longitudinal semi-axis (a) does as well).
- Flange wear is between 10 and 1000 times more intense than tread wear, so the former was taken for elaborating the curves. This is due to the fact that lateral radii are very reduced for flange–rail contact ( mm, mm), opposing tread–rail contact radii ( mm, ), increasing in turn the relative lateral curvature (), which diminishes the intersection between the theoretical paraboloids and, as a result, the contact patch size (as diminishes, the longitudinal semi-axis (b) does as well). This size is smaller than that of the tread contact patch.
- Wheel diameter is more influential on tread wear than on flange wear. This owes to the fact that the radius (proportional to wheel diameter) is dominating, along with the radius (which is in the same order of magnitude), at the tread ( and ). In contrast, at the flange, is not the dominating radius, being dominated by and values, which are in a lower order of magnitude ( and ), and and hold constant independently of the wheel diameter.
- RCF is predicted for every flange–rail contact (except for isolated cases where the 355-mm wheel is negotiating a curve with a radius closely below 1850 m, this value being the threshold radius in this case) as a consequence of the high normal pressure (5–7 GPa) at the flange contact area with the rail. Although the contact patch size is smaller than that of the tread contact patch, such a high pressure is withstandable by the material since indentation is elevated (0.2–0.3 mm) and pressure can stack in many layers (isobaric surfaces), as in hydrostatics.
- RCF effects can be mitigated by setting a reduced wear depth limit and in the current work, it was due to the hypothesis established. In the real operation, it is the economical factor the one prioritized, which forces to find the trade-off between the crack growth and wear depth limit.
- As a consequence of RCF and the fatigue induced during reprofiling (which leaves residual stresses) and also for operational safety reasons, operators’ internal regulations forbid eliminating more than 80 mm in diameter for a 920-mm wheel, more than 60 for a 680-mm one, and more than 20 for a 355-mm one.
- Last, Table A4 (Appendix C) gathers the RCF and wear results for the three different wheels when negotiating the tightest curve, the one with the 265-m radius. As it can be seen, even though the forces and RCF are less aggressive for reduced-diameter wheels, the wear depth increases as the wheel diameter decreases because the reduced-diameter wheels must revolve more times around its diameter so as to cover the same linear distance. However, the increase in wear depth is not simply inversely proportional to diameter (Figure 17 shows the same non-linear trend).
5. Conclusions
- Contemplating kinematics, reduced-diameter wheels navigate curves more smoothly than standard-diameter wheels due to their lower uncentering, which results in less frequent flange contact with the rails and a lower threshold radius.
- Contemplating dynamics, the contact between the flange and the rail is gentler with reduced-diameter wheels. When the flanges of these wheels make contact with the rails, the interaction is less forceful due to the reduced uncentering forces. Additionally, because bogies using reduced-diameter wheels carry less load, the force exerted by the rails on the flange is lower. As a result, the balance of forces and torques leads to reduced rail–flange forces.
- Repetition of the results for other track gauges present around the world.
- Computation of the speed effects through finite elements, proving more accurate results by obtaining the elastic distortions for every different speed.
- Computation of the exact load distribution between the tread and the flange in the event of simultaneous contacts. Finite elements would allow for knowing the real deformations, strains, stresses, and forces at both areas.
- Inclusion of more superstructure factors modifying wheel (and rail) wear, such as warp, rail deflection, joints, irregularities and cant excess and deficiency under low static friction conditions.
- Inclusion of dynamic loads, especially those appearing as the wheels traverse a turnout/switch.
- Inclusion of impacts between the wheels and the superstructure, especially those of the wheels with the switch frogs and track devices.
- Inclusion of other types of wheel damage shortening wheel life, such as cracks, flats and spalling.
- Extension of the algorithm to cover any other bogies belonging to the wagon (wagons have at least one more bogie).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Abbreviation | Definition | Unit (SI) | Abbreviation | Definition | Unit (SI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longitudinal semi-axis of Hertz’s ellipse | Degree of the function deceleration-time | ||||
| Lateral acceleration experienced by the vehicle | Number of axles on the vehicle | ||||
| Relative longitudinal curvature | Number of axles on the bogie | ||||
| Hertz’s ellipse area | Lateral Hertz’s coefficient | ||||
| Ratio between the minimum friction coefficient (infinite slip speed) and the maximum (null slip) | Reaction force of the rail on the wheel on the normal contact direction (normal force) | ||||
| Lateral semi-axis of Hertz’s ellipse | Reaction force of the rail on the wheel in the normal direction to the contact area at the (tread flange) at a wheel experiencing flange–rail contact | ||||
| Distance from track center to the rolling radius of the (inner | outer) wheel in relation to the curve | Normal force acting on the (outer| inner) wheel in relation to the curve | ||||
| Distance from track center to rolling radius | Normal force component in the radial |tangential direction (the tangential one is perpendicular to the radial one) | ||||
| Relative lateral curvature | Normal force component acting on the wheel (perpendicularly|tangentially) to contact area | ||||
| Exponential constant at friction law | Existing offset between the track gauge minus the flange—rail play and the distance between the nominal radius center of the wheelset wheels | ||||
| Effective size of contact patch | Horizontal distance between the center of the flange contact area center and the center of the wheel | ||||
| Contact tangential stiffness | Maximum contact normal pressure | ||||
| Contact tangential stiffness for the pure spin case | Initial | final metric point | ||||
| Longitudinal| lateral | vertical Kalker’s coefficient | Theorical rolling radius of the (outer| inner) wheel in relation to the curve | ||||
| Kalker’s coefficient (longitudinal |lateral) corrected according to non-dimensional slip components | Rolling radius of the (outer | inner) wheel in relation to the curve including the displacement due to the yaw angle | ||||
| plane | Nominal rolling radius | ||||
| Nominal wheel diameter | Wheel radius measured until the flange contact patch | ||||
| Total bogie wheelbase (measured from its leading to trailing wheelset) | Real rolling radius | ||||
| Partial bogie wheelbase (measured between 2 next wheelsets) | Vertical Hertz’s coefficient | ||||
| Equivalent Young’s modulus of the materials in contact | Curve radius (measured from its center to the track axis) | ||||
| Young’s modulus of the rail | wheel | Rail lateral radius | ||||
| Sagitta of the inner rail in relation to the curve | Wheel lateral radius | ||||
| Magnitude of tangential force vector | Rail longitudinal radius | ||||
| Braking force | Longitudinal wheel radius | ||||
| Traction force | Magnitude of non-dimensional slip vector | ||||
| Longitudinal | lateral tangential force | Longitudinal | lateral non-dimensional slip | ||||
| Magnitude of non-dimensional slip corrected with the spin contribution | |||||
| Lateral tangential force (lateral force) corrected with the spin contribution | Lateral non-dimensional slip corrected with the spin contribution | ||||
| Increase in lateral force due to spin | Wear index for the USFD law | ||||
| Maximum tangential force before rolling contact fatigue appears | |||||
| Fatigue index | |||||
| Gravity acceleration | |||||
| Equivalent shear modulus of the materials in contact | |||||
| Shear module of the rail | wheel | Longitudinal| lateral creepage | ||||
| Real cant of the railway line | Vehicle speed | ||||
| height over the rolling plane | Final | initial vehicle speed | ||||
| height over the rolling plane | Longitudinal| lateral slip speed | ||||
| height over the rolling plane | Wheel width | ||||
| Total wheel wear depth (USFD law) | Wear rate (USFD law) | ||||
| Railway line gradient/slope | Wheelset uncentering | ||||
| Track gauge | Total wheelset uncentering | ||||
| Wheel semi-conicity or inclination | Available play for the bogie leading wheelset when it uncenters towards the outside of a curve | ||||
| Reduction coefficient for the initial slope of the traction curve at the stick | slip region | Available play for the bogie trailing wheelset when it uncenters towards the inside of a curve | ||||
| Wheelset uncentering rate | |||||
| Length really rolled by a wheel | Total wheelset uncentering rate | ||||
| Longitudinal Hertz’s coefficient | Number of wheels on the bogie | ||||
| Spin torque |
| Abbreviation | Definition | Unit (SI) | Abbreviation | Definition | Unit (SI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fraction of the force normal to the wheel falling on the flange contact patch | Initial friction coefficient or maximum (null slip speed) | ||||
| Gradient angle | Equivalent Poisson’s ratio of the materials in contact | ||||
| Wheel contact angle | Poisson’s ratio of the rail | wheel | ||||
| Maximum indentation between the two bodies in contact | Gauge widening (at tight curves) | ||||
| Density of the wheel material | |||||
| Tangential stress gradient at the stick region | Longitudinal displacement angle of the contact patch | rad | |||
| Tangential stress gradient at the stick region for the pure spin case | Maximum tangential stress transmitted | ||||
| Load (horizontal | vertical) on the flange contact patch | Tangential yield stress of the wheel material | ||||
| Play between the flange and the rail | Tilt angle | ||||
| Hertz’s angle | rad | Variation angle of tilt angle | |||
| Real cant angle | rad | Spin (rotational creepage) | |||
| Axle load | Yaw angle | ||||
| Vehicle tare | Variation rate of yaw angle | ||||
| Payload transported by the vehicle | Angular slip speed when braking per unit length | ||||
| Dynamic friction coefficient (or adhesion coefficient) |
Appendix B
| Variable | Value | Variable | Value | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ) | 0.400 | ) | 1.235–2.747 | (◦) | 1.432 |
| (s/m) | 0.600 | ) | 1 | (◦) | 1.432 |
| (m) | 1.800 | ) | 0.400 | (◦) | 51–70 |
| (Pa) | (m) | (m) | |||
| (Pa) | (m) | (kg) | 20,000 | ||
| (m·s−2) | (m) | ) | 0.400 | ||
| (Pa) | (m) | ) | 0.550 | ||
| (Pa) | (m) | ) | |||
| (m) | 0.512 | (m) | ) | ||
| (m) | 1.573 | ) | 0 | (kg·m−3) | |
| (m) | (m) | (Pa) | |||
| ) | 0.025 | (m) | 0.140 | ||
| ) | 0.025 | ) | 0.750 |
Appendix C
| Variable | 920-mm Wheel | 680-mm Wheel | 355-mm Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | 0.920 | 0.680 | 0.355 |
| (m) | 265 | 265 | 265 |
| ) | 0.433 | 0.426 | 0.409 |
| ) | 109 | 109 | 109 |
| 468.088 | 367.463 | 367.887 | |
| 10.030 | 8.249 | 6.276 | |
| 0.636 | 0.611 | 0.881 | |
| 20.031 | 15.834 | 17.360 | |
| ) | 23.368 | 23.207 | 21.192 |
| 55 | 55 | 55 | |
| 2.295 | 2.427 | 3.538 | |
| (N) | 1274 | 1034 | 1009 |
| (N) | 41,159 | 32,931 | 34,760 |
| (N·m) | 197.200 | 112.100 | 55.280 |
| ) | 10−3 | 10−3 | 10−3 |
| ) | 10−3 | 10−3 | 10−3 |
| 1.152 | −1.559 | −2.986 | |
| (N) | 85,465 | 69,622 | 76,224 |
References
- Pellicer, D.S.; Larrodé, E. Sensitivity Analysis of Bogie Wheelbase and Axle Load for Low-Floor Freight Wagons, Based on Wheel Wear. Machines 2024, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Fomento. Orden FOM/1630/2015, de 14 de julio, por la que se aprueba la “Instrucción ferroviaria de gálibos”. Boletín Of. Del Estado 2015, 185, 68208–68650. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Fomento; Ministère de l’Environnement, de l’Énergie et de la Mer. Servicios de Autopista Ferroviaria (AF) en los ejes Atlántico y Mediterráneo. Convocatoria de Manifestaciones de Interés. Consulta a Los Fabricantes y Diseñadores de Material Móvil. Report. 2018. Available online: https://www.ecologie.gouv.fr/sites/default/files/180410_AMI_Constructeurs_rapport_ES-min.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish)
- Cai, W.; Chi, M.; Wu, X.; Li, F.; Wen, Z.; Liang, S.; Jin, X. Experimental and numerical analysis of the polygonal wear of high-speed trains. Wear 2019, 440–441, 203079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunyan, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Naeimi, M.; Dollevoet, R.; Li, Z. A finite element thermomechanical analysis of the development of wheel polygonal wear. Tribol. Int. 2024, 195, 109577. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Gao, L.; Cui, R.; Xin, T. The initiation mechanism and distribution rule of wheel high-order polygonal wear on high-speed railway. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 119, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Wen, Z.; Jin, X.; Yang, X. Polygonisation of railway wheels: A critical review. Railw. Eng. Sci. 2020, 28, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Vicente, S.; Pascual-Guillamón, M. Use of the fatigue index to study rolling contact wear. Wear 2019, 436–437, 203036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C.; Mu, J.; Qi, Y.; Kang, W.; Liang, Y. Theoretical study on wheel wear mechanism of high-speed train under different braking modes. Wear 2024, 540–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; Wang, K.; Ling, L.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhai, W. Influence of wheel diameter difference on surface damage for heavy-haul locomotive wheels: Measurements and simulations. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 132, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Wang, K.; Ling, L.; Chen, Z. Effect of wheel diameter difference on tread wear of freight wagons. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 127, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.; Pacheco, L.; Dalvi, I.; Endlich, C.; Queiroz, J.; Antoniolli, F.; Santos, G. The effect of railway wheel wear on reprofiling and service life. Wear 2021, 477, 203799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Song, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, B.; Xie, M.; Tang, X. An Optimal Life Cycle Reprofiling Strategy of Train Wheels Based on Markov Decision Process of Wheel Degradation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, P.A.; Calçada, R. Wheel–rail contact model for railway vehicle–structure interaction applications: Development and validation. Railw. Eng. Sci. 2023, 31, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosso, N.; Magelli, M.; Zampieri, N. Simulation of wheel and rail profile wear: A review of numerical models. Railw. Eng. Sci. 2022, 30, 403–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, P.A.d.P.; Magelli, M.; Lopes, M.V.; Correa, P.H.A.; Zampieri, N.; Bosso, N.; dos Santos, A.A. The effectiveness of different wear indicators in quantifying wear on railway wheels of freight wagons. Railw. Eng. Sci. 2024, 32, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer, D.S.; Larrodé, E. Analysis of the Rolling Phenomenon of a Reduced-Diameter Railway Wheel for Freight Wagons, as a Function of Operating Factors. Master’s Thesis, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain, 2021. Available online: https://deposita.unizar.es/record/64448 (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Rovira, A. Modelado del Contacto Rueda-Carril Para Aplicaciones de Simulación de Vehículos Ferroviarios y Estimación del Desgaste en eL Rango de BAJA frecuencia. Ph.D. Thesis, Polytechnical University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2012. Available online: https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/14671 (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Moody, J.C. Critical Speed Analysis of Railcars and Wheelsets on Curved and Straight Track. Bachelor’s Thesis, Bates College, Lewison, ME, USA, 2014. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/230689735.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Ortega, E. Simulación Del Contacto Rueda—Carril Con Pro/ENGINEER. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Carlos III, Madrid, España, 2012. Available online: https://e-archivo.uc3m.es/entities/publication/1ad42047-7a29-4236-a081-52f4c2ec2646 (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- RENFE. Temario Específico Para Las Pruebas Presenciales de la Especialidad Máquinas—Herramientas. Material de Studio. 2020. Available online: https://www.renfe.com/content/dam/renfe/es/Grupo-Empresa/Talento-y-personas/Empleo/2024/ingenier%C3%ADa-y-mantenimiento/04.%20IYM%20Manual_%20Especialidad_Maquinas_Herramientasv2.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Larrodé, E. Ferrocarriles Y Tracción Eléctrica, 1st ed.; Editorial Copy Center: Zaragoza, España, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sichani, M.S. On Efficient Modelling of Wheel—Rail Contact in Vehicle Dynamics Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. Available online: https://kth.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?dswid=6030 (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Fissette, P. Railway Vehicle Dynamics. Teaching Content. Catholic University of Louvain, Louvain. 2016. Available online: https://es.scribd.com/document/559372304/RailVehicles (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Oldknow, K. Wheel—Rail Interaction Fundamentals. Course Content. 2015. Available online: https://www.coursehero.com/file/185769149/PC-1-3-Wheel-Rail-Interaction-Fundamentals-WRI-2017-20170604pdf/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- ADIF. Calificación, Geometría, Montaje y Diseño de la vía; ADIF: Madrid, Spain, 1983–2021. [Google Scholar]
- ADIF. Declaración Sobre la Red. Annual Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.adif.es/sobre-adif/conoce-adif/declaracion-sobre-la-red (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Andrews, H.I. Railway Traction. The Principles of Mechanical and Electrical Railway Traction, 1st ed.; ElSevier Science: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Tipler, P.A.; Mosca, G. Physics for Scientists and Engineers Vol. I, 6th ed.; Macmillan Education: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, P. Ferrocarriles. Teaching Content. Polythecnical University of Cartagena, Murcia, Spain, 2016. Available online: https://ocw.bib.upct.es/course/view.php?id=162&topic=al (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Rincón, L.A. Circulación En Curva, Esfuerzos y Solicitaciones Verticales en el Ferrocarril Convencional. Master’s Thesis, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain, 2018. Available online: https://eupla.unizar.es/sites/eupla/files/archivos/AsuntosAcademicos/TFG/2013-2014/Civil/convocatoria_3/5rincongarcia.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Santamaría, J.; Vadillo, E.G.; Gómez, J. Influence of creep forces on the risk of derailment of railway vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2009, 47, 721–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, H.R. Über die Berührung fester elastische Körper. J. Für Die Reine Und Angew. Math. 1882, 92, 156–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, D.H. Tables of Hertzian Contact—Stress Coefficients. Report No. 387 from the Coordinated Science Laboratory. 1968. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/158319603.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Greenwood, J.A. Hertz theory and Carlson elliptic integrals. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2018, 119, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polach, O. A Fast Wheel—Rail Forces Calculation Computer Code. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2000, 33, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polach, O. Creep forces in simulations of traction vehicles running on adhesion limit. Wear 2005, 258, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalker, J.J. Rolling Contact Phenomena—Linear Elasticity, CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences, 411th ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2000; Volume 411. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski, J.; Chollet, H. Wheel—Rail contact models for vehicle system dynamics including multi-point contact. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2005, 43, 455–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cachón, S. Tribological Behavior of Micro-Alloyed Steels and Conventional C–Mn in Pure Sliding Condition. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain, 2017. Available online: https://digibuo.uniovi.es/dspace/handle/10651/44961 (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Kalker, J.J.; Chudzikiewicz, A. Calculation of the Evolution of the Form of a Railway Wheel Profile through Wear. In International Series of Numerical Mathematics; Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 1991; Volume 101. [Google Scholar]
- Kisilowski, J.; Kowalik, R. Mechanical Wear Contact between the Wheel and Rail on a Turnout with Variable Stiffness. Energies 2021, 14, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Iwnicki, S.; Shackleton, P.; Crosbee, D. Comparison of wear models for simulation of railway wheel polygonization. Wear 2019, 436–437, 203010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, M.V. Optimización de la Política de Reperfilado de Ruedas para el Citadis 302, en la explotación de Metro Ligero Oeste. Rev. Vía Libre Técnica 2015, 9, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dirks, B.; Enblom, R.; Ekberg, A.; Berg, M. The development of a crack propagation model for railway wheels and rails. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2015, 18, 1478–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.A. Development and integration of an equation-solving program for engineering thermodynamics courses. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 1993, 1, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AENOR. Aplicaciones Ferroviarias. Ruedas Y Carriles; AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar]
- de San Dámaso, R. La vía de tres carriles. Situación actual y perspectivas. Informe de la Dirección General de Operaciones e Ingeniería–Dirección Ejecutiva de Operaciones e Ingeniería de Red de Alta Velocidad. 2017. Available online: https://cip.org.pt/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Ref-33.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Vera, C. Proyecto Constructivo de una Línea Ferroviaria de Transporte de Mercancías y su Conexión a la Red Principal. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Seville, Seville, Spain, 2015. Available online: https://idus.us.es/handle/11441/44482 (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Yassine, B. Los Trabajos Topográficos en la Ejecución de Una vía de Ferrocarril de Alta Velocidad. Bachelor’s Thesis, Polytechnical University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2015. Available online: https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/54675 (accessed on 25 September 2024). (In Spanish).
- Pellicer, D.S.; Larrodé, E. Supplementary Material of “Analysis of the Rolling Phenomenon of a Reduced-Diameter Railway Wheel for Freight Wagons, as a Function of OPERATING factors”. Mendeley Data, 3rd version, 2024. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17632/xw3hxy5xcx.3 (accessed on 25 September 2024).
















| Variable | Value for 920-mm Wheels Scenario | Value for 680-mm Wheels Scenario | Value for 355-mm Wheels Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | 0.920 | 0.680 | 0.355 |
| ) | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| (m) | 0.467–0.475 | 0.347–0.355 | 0.185–0.193 |
| (kg) | 18,784 | 15,325 | 6996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellicer, D.S.; Larrodé, E. Theoretical Study of the Wear of a Reduced-Diameter Wheel for Freight Wagons, Based on Its Diameter. Algorithms 2024, 17, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17100437
Pellicer DS, Larrodé E. Theoretical Study of the Wear of a Reduced-Diameter Wheel for Freight Wagons, Based on Its Diameter. Algorithms. 2024; 17(10):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17100437
Chicago/Turabian StylePellicer, David S., and Emilio Larrodé. 2024. "Theoretical Study of the Wear of a Reduced-Diameter Wheel for Freight Wagons, Based on Its Diameter" Algorithms 17, no. 10: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17100437
APA StylePellicer, D. S., & Larrodé, E. (2024). Theoretical Study of the Wear of a Reduced-Diameter Wheel for Freight Wagons, Based on Its Diameter. Algorithms, 17(10), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17100437








