Harvesting and Local Knowledge of a Cultural Non-Timber Forest Product (NTFP): Gum-Resin from Boswellia serrata Roxb. in Three Protected Areas of the Western Ghats, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
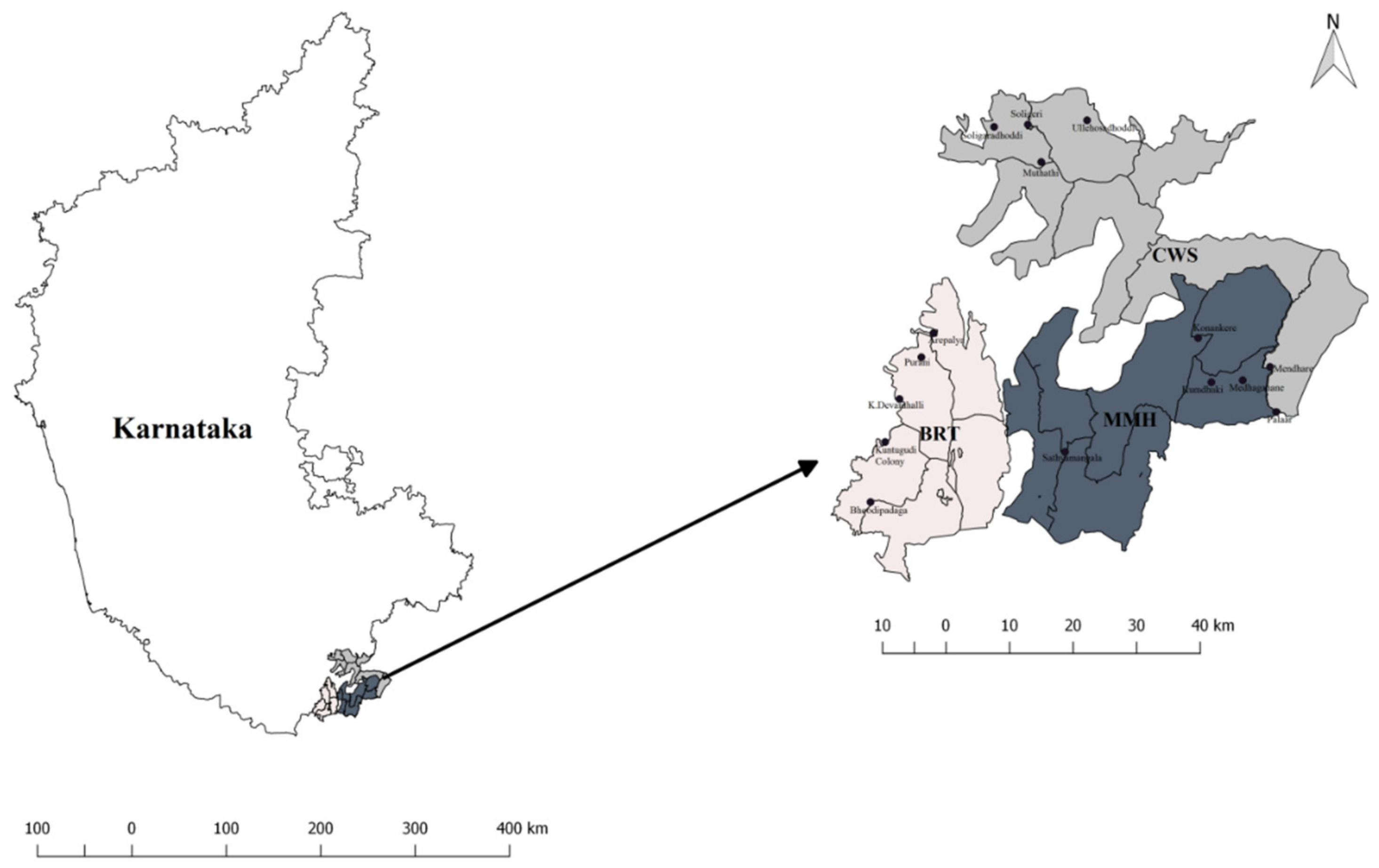
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Methods
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Profile of Harvesters and Non-Harvesters
3.2. Harvesting Practices
3.3. Findings from the Harvest Trips
3.4. Knowledge of Gum-Resin Use and Tree Distribution and Damage Agents
3.5. Non-Harvesters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angelsen, A.; Jagger, P.; Babigumira, R.; Belcher, B.; Hogarth, N.J.; Bauch, S.; Börner, J.; Smith-Hall, C.; Wunder, S. Environmental Income and Rural Livelihoods: A Global-Comparative Analysis. World Dev. 2014, 64, S12–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dash, M.; Behera, B. Determinants of Household Collection of Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs) and Alternative Livelihood Activities in Similipal Tiger Reserve, India. For. Policy Econ. 2016, 73, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, C.M.; Pullanikkatil, D. Considering the Links between Non-Timber Forest Products and Poverty Alleviation. In Poverty Reduction through Non-Timber Forest Products; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wunder, S.; Angelsen, A.; Belcher, B. Forests, Livelihoods, and Conservation: Broadening the Empirical Base. World Dev. 2014, 64, S1–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wunder, S.; Noack, F.; Angelsen, A. Climate, Crops, and Forests: A Pan-Tropical Analysis of Household Income Generation. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2018, 23, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Rahut, D.B. Forest-Based Livelihoods, Income, and Poverty: Empirical Evidence from the Himalayan Region of Rural Pakistan. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 57, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, B.; Günter, S.; Acevedo-Cabra, R.; Knoke, T. Livelihood Strategies, Ethnicity and Rural Income: The Case of Migrant Settlers and Indigenous Populations in the Ecuadorian Amazon. For. Policy Econ. 2018, 86, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santika, T.; Wilson, K.A.; Budiharta, S.; Kusworo, A.; Meijaard, E.; Law, E.A.; Friedman, R.; Hutabarat, J.A.; Indrawan, T.P.; St John, F.A. Heterogeneous Impacts of Community Forestry on Forest Conservation and Poverty Alleviation: Evidence from Indonesia. People Nat. 2019, 1, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, M.; Nakama, E.; Satriadi, T.; Fauzi, H.; Aryadi, M.; Morikawa, Y. An Approach to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals Through Participatory Land and Forest Conservation: A Case Study in South Kalimantan Province, Indonesia. J. Sustain. For. 2019, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, M.; López, C.; Dold, T. Cultural Importance of Non-Timber Forest Products: Opportunities They Pose for Bio-Cultural Diversity in Dynamic Societies. In Non-Timber Forest Products in the Global Context; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 107–128. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, D.; Voeks, R.; Short, L. Is Non-Timber Forest Product Harvest Sustainable in the Less Developed World? A Systematic Review of the Recent Economic and Ecological Literature. Ethnobiol. Conserv. 2012, 1, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, C.M.; Pandey, A.K.; Ticktin, T. Ecological Sustainability for Non-Timber Forest Products: Dynamics and Case Studies of Harvesting; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cosiaux, A.; Gardiner, L.M.; Stauffer, F.W.; Bachman, S.P.; Sonké, B.; Baker, W.J.; Couvreur, T.L. Low Extinction Risk for an Important Plant Resource: Conservation Assessments of Continental African Palms (Arecaceae/Palmae). Biol. Conserv. 2018, 221, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, S.; Cadena, A.J.; Hartman, P. Adaptation Planning in the Lower Mekong Basin: Merging Scientific Data with Local Perspective to Improve Community Resilience to Climate Change. Clim. Dev. 2018, 10, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticktin, T.; Shackleton, C. Harvesting Non-Timber Forest Products Sustainably: Opportunities and Challenges. In Non-Timber Forest Products in the Global Context; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Barrios, J.C.; Anten, N.P.; Martínez-Ramos, M. Sustainable Harvesting of Non-timber Forest Products Based on Ecological and Economic Criteria. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Toledo, L.; Perez-Decelis, A.; Macedo-Santana, F.; Cuevas, E.; Endress, B.A. Chronic Leaf Harvesting Reduces Reproductive Success of a Tropical Dry Forest Palm in Northern Mexico. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemenih, M.; Abebe, T.; Olsson, M. Gum and Resin Resources from Some Acacia, Boswellia and Commiphora Species and Their Economic Contributions in Liban, South-East Ethiopia. J. Arid Environ. 2003, 55, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachathi, F.N.; Eriksen, S. Gums and Resins: The Potential for Supporting Sustainable Adaptation in Kenya’s Drylands. Clim. Dev. 2011, 3, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellema, W.; Mujawamariy, G.; D’Haese, M.; Burger, K. An Economic Approach to Household Collection of Gum Arabic from the Wild. Int. For. Rev. 2013, 15, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, A.K.; Tewari, D. Importance of Non-Timber Forest Products in the Economic Valuation of Dry Deciduous Forests of India. For. Policy Econ. 2005, 7, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejene, T.; Lemenih, M.; Bongers, F. Manage or Convert Boswellia Woodlands? Can Frankincense Production Payoff? J. Arid Environ. 2013, 89, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.B.; Yang, Q.; Osban, J.; Azzarello, J.T.; Saban, M.R.; Saban, R.; Ashley, R.A.; Welter, J.C.; Fung, K.-M.; Lin, H.-K. Frankincense Oil Derived from Boswellia carteri Induces Tumor Cell Specific Cytotoxicity. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepper, F.N. Arabian and African Frankincense Trees. J. Egypt. Archaeol. 1969, 55, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, T.K.; Shiva, M. Salai Guggul from Boswellia serrata Roxb.-Its Exploitation and Utilization. Indian For. 1977, 103, 466–474. [Google Scholar]
- Bongers, F.; Groenendijk, P.; Bekele, T.; Birhane, E.; Damtew, A.; Decuyper, M.; Eshete, A.; Gezahgne, A.; Girma, A.; Khamis, M.A. Frankincense in Peril. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, M.; Dold, A. The Informal Trade of Cassipourea flanaganii as a Cosmetic in South Africa. In Ethnobiology and Biocultural Diversity: Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Ethnobiology; University of Georgia Press: Athens, GA, USA, 2004; pp. 412–431. [Google Scholar]
- Rijkers, T.; Ogbazghi, W.; Wessel, M.; Bongers, F. The Effect of Tapping for Frankincense on Sexual Reproduction in Boswellia papyrifera. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendijk, P.; Eshete, A.; Sterck, F.J.; Zuidema, P.A.; Bongers, F. Limitations to Sustainable Frankincense Production: Blocked Regeneration, High Adult Mortality and Declining Populations. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaamri, M.M.H. Distribution Boswellia sacra in Dhofar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman: Economic Value And. J. Life Sci. 2012, 6, 632. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, B.A.; Glover, E.K.; Luukkanen, O.; Kanninen, M.; Jamnadass, R. Boswellia and Commiphora Species as a Resource Base for Rural Livelihood Security in the Horn of Africa: A Systematic Review. Forests 2019, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harrasi, A.; Khan, A.L.; Asaf, S.; Al-Rawahi, A. Taxonomy, Distribution and Ecology of Boswellia. In Biology of Genus Boswellia; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 11–34. [Google Scholar]
- MOE. The National Red List 2012 of Sri Lanka: Conservation Status of the Fauna and Flora; Ministry of Environment: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2012.
- Brendler, T.; Brinckmann, J.; Schippmann, U. Sustainable Supply, a Foundation for Natural Product Development: The Case of Indian Frankincense (Boswellia serrata Roxb. Ex Colebr.). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ali, R.; Parveen, R.; Najmi, A.K.; Ahmad, S. Pharmacological Evidences for Cytotoxic and Antitumor Properties of Boswellic Acids from Boswellia serrata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, C.P.; Dubey, Y. Anthropogenic Disturbances and Status of Forest and Wildlife in the Dry Deciduous Forests of Chhattisgarh State in India. J. For. Res. 2012, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunnichan, V.; Mohan Ram, H.; Shivanna, K. Reproductive Biology of Boswellia serrata, the Source of Salai Guggul, an Important Gum-Resin. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2005, 147, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, K.S.; Ganesh, T. Faunal Mortality on Roads Due to Religious Tourism across Time and Space in Protected Areas: A Case Study from South India. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumya, K.V.; Shackleton, C.M.; Setty, S.R. Impacts of Gum-Resin Harvest and Lantana Camara Invasion on the Population Structure and Dynamics of Boswellia serrata in the Western Ghats, India. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 453, 117618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, A.; Veena, N. Mobility Patterns and Gendered Practices among Soliga People in Karnataka, India. In Gender, Mobilities, and Livelihood Transformations; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2013; pp. 132–147. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple Comparisons Using Rank Sums. Technometrics 1964, 6, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, A.; Camill, P.; Brown, J. Conservation as If People Also Mattered: Policy and Practice of Community-Based Conservation. Conserv. Soc. 2013, 11, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, A.; Nusrat, R.; Vungthianmuang, M.; Donnemching, G. Block-1 Tribals of South India; IGNOU: New Delhi, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mandle, L.; Ticktin, T.; Nath, S.; Setty, S.; Varghese, A. A Framework for Considering Ecological Interactions for Common Non-Timber Forest Product Species: A Case Study of Mountain Date Palm (Phoenix loureiroi Kunth) Leaf Harvest in South India. Ecol. Process. 2013, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, A.; Kusakabe, K.; Veena, N. Indigenous People’s Response to the Ban on Use of Forest Resources in South India: A Gender Analysis of Governmobility. In Environment Development and Sustainability; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland, T.; Achdiawan, R.; Angelsen, A.; Babigumira, R.; Ickowitz, A.; Paumgarten, F.; Reyes-García, V.; Shively, G. Challenging Perceptions about Men, Women, and Forest Product Use: A Global Comparative Study. World Dev. 2014, 64, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aravind, N.; Rao, D.; Ganeshaiah, K.; Shaanker, R.U.; Poulsen, J.G. Impact of the Invasive Plant, Lantana camara, on Bird Assemblages at Male Mahadeshwara Reserve Forest, South India. Trop. Ecol. 2010, 51, 325–338. [Google Scholar]
- Si, A. The Traditional Ecological Knowledge of the Solega: A Linguistic Perspective; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, A.; Ticktin, T.; Mandle, L.; Nath, S. Assessing the Effects of Multiple Stressors on the Recruitment of Fruit Harvested Trees in a Tropical Dry Forest, Western Ghats, India. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, D.R. Agricultural Transformation and Indigenous Communities: A Case Study of the Soliga Communities in the Montane Forests, Southern India; Universitäts-und Landesbibliothek Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Pérez, M.; Belcher, B.; Achdiawan, R.; Alexiades, M.; Aubertin, C.; Caballero, J.; Campbell, B.; Clement, C.; Cunningham, T.; Fantini, A. Markets Drive the Specialization Strategies of Forest Peoples. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, S.; Shanley, P.; Ndoye, O. Invisible but Viable: Recognising Local Markets for Non-Timber Forest Products. Int. For. Rev. 2007, 9, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhwezi, O.; Cunningham, A.; Bukenya-Ziraba, R. Lianas and Livelihoods: The Role of Fibrous Forest Plants in Food Security and Society around Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda. Econ. Bot. 2009, 63, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, H.L.; Huntsinger, L. Salal Harvester Local Ecological Knowledge, Harvest Practices and Understory Management on the Olympic Peninsula, Washington. Hum. Ecol. 2006, 34, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.; Cunningham, A.; Campbell, B.M.; Luckert, M.K. Bark: Use, Management and Commerce in Africa; New York Botanical Garden Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Botha, J.; Witkowski, E.; Shackleton, C. The Impact of Commercial Harvesting on Warburgia salutaris (‘Pepper-Bark Tree’) in Mpumalanga, South Africa. Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 1675–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCarlo, A.; Ali, S.H. Sustainable Sourcing of Phytochemicals as a Development Tool: The Case of Somaliland’s Frankincense Industry; Institute for Environmental Diplomacy and Security, University of Vermont: Burlington, VT, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eshete, A.; Teketay, D.; Lemenih, M.; Bongers, F. Effects of Resin Tapping and Tree Size on the Purity, Germination and Storage Behavior of Boswellia papyrifera (Del.) Hochst. Seeds from Metema District, Northwestern Ethiopia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 269, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.; Ticktin, T. Regional Variation in Non-Timber Forest Product Harvest Strategies, Trade, and Ecological Impacts: The Case of Black Dammar (Canarium strictum Roxb.) Use and Conservation in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, India. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandle, L.; Ticktin, T.; Zuidema, P.A. Resilience of Palm Populations to Disturbance Is Determined by Interactive Effects of Fire, Herbivory and Harvest. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negussie, A.; Gebrehiwot, K.; Yohannes, M.; Aynekulu, E.; Manjur, B.; Norgrove, L. An Exploratory Survey of Long Horn Beetle Damage on the Dryland Flagship Tree Species Boswellia papyrifera (Del.) Hochst. J. Arid Environ. 2018, 152, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.; Mamocha Singh, K.; Ramamurthy, V. A Checklist of the Long-Horned Beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) of Arunachal Pradesh, Northeastern India with Several New Reports. J. Threat. Taxa 2015, 7, 7879–7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, M.K.; Punekar, S.A.; Ranade, R.V.; Paknikar, K.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Stingless Bee (Trigona Sp.) Propolis Used in the Folk Medicine of Western Maharashtra, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mìshra, S.; Behera, N.; Paramanik, T. Comparative Assessment of Gum Yielding Capacities of Boswellia serrata Roxb. and Sterculia urens Roxb. in Relation to Their Girth Sizes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Anthropogenic Impact on Environment & Conservation Strategy, Ranchi, India, 2–4 November 2012; pp. 327–330. [Google Scholar]
- Tolera, M.; Menger, D.; Sass-Klaassen, U.; Sterck, F.J.; Copini, P.; Bongers, F. Resin Secretory Structures of Boswellia papyrifera and Implications for Frankincense Yield. Ann. Bot. 2012, 111, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, N.C.; Mills, M.; Tam, J.; Hicks, C.C.; Klain, S.; Stoeckl, N.; Bottrill, M.C.; Levine, J.; Pressey, R.L.; Satterfield, T. A Social–Ecological Approach to Conservation Planning: Embedding Social Considerations. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Gardner, T.A.; Bennett, E.M.; Balvanera, P.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.; Daw, T.; Folke, C.; Hill, R.; Hughes, T.P. Advancing Sustainability through Mainstreaming a Social–Ecological Systems Perspective. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunhabunyatip, P.; Sasaki, N.; Grünbühel, C.; Kuwornu, J.; Tsusaka, T. Influence of Indigenous Spiritual Beliefs on Natural Resource Management and Ecological Conservation in Thailand. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, J.N.; Mandal, K. Scientific Analysis of Indigenous Techniques for Guggal (Commiphora wightii) Tapping in India. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasishth, A.; Guleria, V. Standardized Gum Tapping Techniques to Maximize Yield from High-Value Indian Tree, Sterculia urens. J. For. Res. 2017, 28, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Study Site | BRT | CWS | MMH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total area (km2) | 655 | 1097 | 984 |
| Elevation (m a.s.l.) | 600–1800 | 250–1500 | 700–1500 |
| Annual rainfall (mm) | 900–1800 | 750–800 | 600–900 |
| Temperature range (°C) | 8–38 | 15–38 | 15–45 |
| Forest types | Scrub, ever-green, woodland savanna and deciduous forests | Thorn scrub, dry deciduous forest, dry mixed deciduous, tropical moist deciduous and bamboo forests | Scrub, dry deciduous, evergreen and bamboo forests |
| Human population (approx.) | 12,500 | 450 | 12,000 |
| No. of Soliga villages | 61 | 5 | 30 |
| Type of Gum-Resin | Study Site | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BRT | CWS | MMH | |
| Pure form (Figure 4a) | 49 ± 57 | 55 ± 33 | 20 ± 7 |
| Pure + bark mixed (Figure 4a,b) | 50 ± 51 | 105 ± 95 | 41 ± 24 |
| Soil mixed (Figure 4c) | 145 ± 106 | 226 ± 274 | 0 |
| Soil + pure mixed (Figure 4c,4a) | 119 ± 85 | 167 ± 126 | 0 |
| Soil + bark mixed (Figure 4c,b) | 150 ± 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Longhorn beetle (Figure 4d) | 95 ± 35 | 285 ± 477 | 0 |
| Scaly bark (Figure 4e) | 0 | 0 | 150 ± 48 |
| Scaly bark + deadwood (Figure 4e,f) | 0 | 0 | 140 ± 85 |
| Deadwood (Figure 4f) | 0 | 0 | 204 ± 189 |
| Type of Damage | Age (Months) | Extent of Damage (cm3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRT | CWS | MMH | BRT | CWS | MMH | |
| Elephant | 7.3 ± 7.6 | 8.3 ± 9.6 | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 5285 ± 11,580 | 6483 ± 7924 | 3408 ± 4618 |
| Manual | 11.8 ± 15.3 | 9 ± 2.6 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 4823 ± 10,637 | 658 ± 269 | 3337 ± 1633 |
| Wind | 15.9 ± 22.8 | 17 ± 5.2 | 8 ± 0 | 29,406 ± 86,297 | 5930 ± 12,490 | 100 ± 0 |
| Trigona honey harvest | 52.5 ± 33.7 | - | - | 25,388 ± 11,178 | - | - |
| Deer horn/body rubbed | 18 ± 16.9 | - | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 344 ± 148 | - | 398 ± 223 |
| Longhorn beetle | 9 ± 4.2 | 12.7 ± 8.3 | - | 2384 ± 1629 | 23,548 ± 32,873 | - |
| Ceased Harvesting | BRT | CWS | MMH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Never harvested | 15 | 15 | 24 |
| 1–3 years ago | 36 | 52 | 21 |
| 4–10 years ago | 33 | 19 | 32 |
| >10 years ago | 15 | 15 | 21 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soumya, K.V.; M. Shackleton, C.; R. Setty, S. Harvesting and Local Knowledge of a Cultural Non-Timber Forest Product (NTFP): Gum-Resin from Boswellia serrata Roxb. in Three Protected Areas of the Western Ghats, India. Forests 2019, 10, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100907
Soumya KV, M. Shackleton C, R. Setty S. Harvesting and Local Knowledge of a Cultural Non-Timber Forest Product (NTFP): Gum-Resin from Boswellia serrata Roxb. in Three Protected Areas of the Western Ghats, India. Forests. 2019; 10(10):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100907
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoumya, Kori Veeranna, Charlie M. Shackleton, and Siddappa R. Setty. 2019. "Harvesting and Local Knowledge of a Cultural Non-Timber Forest Product (NTFP): Gum-Resin from Boswellia serrata Roxb. in Three Protected Areas of the Western Ghats, India" Forests 10, no. 10: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100907
APA StyleSoumya, K. V., M. Shackleton, C., & R. Setty, S. (2019). Harvesting and Local Knowledge of a Cultural Non-Timber Forest Product (NTFP): Gum-Resin from Boswellia serrata Roxb. in Three Protected Areas of the Western Ghats, India. Forests, 10(10), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100907






