Radial Growth Responses to Climate of Pinus yunnanensis at Low Elevations of the Hengduan Mountains, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
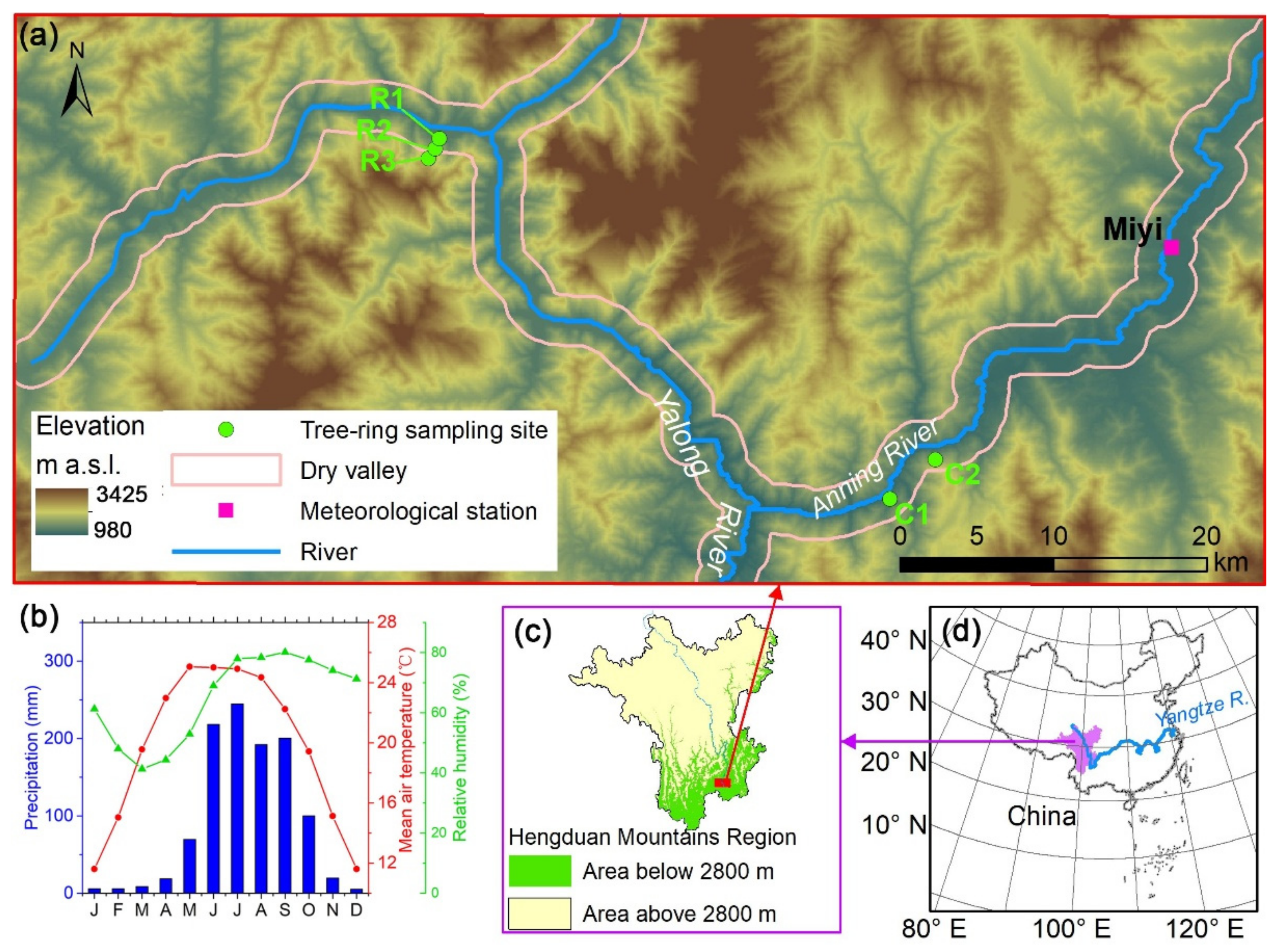
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling Sites, Tree Rings, and Meteorological Data
2.3. Methods of Growth—Climate Relationship Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Tree Ring Chronologies
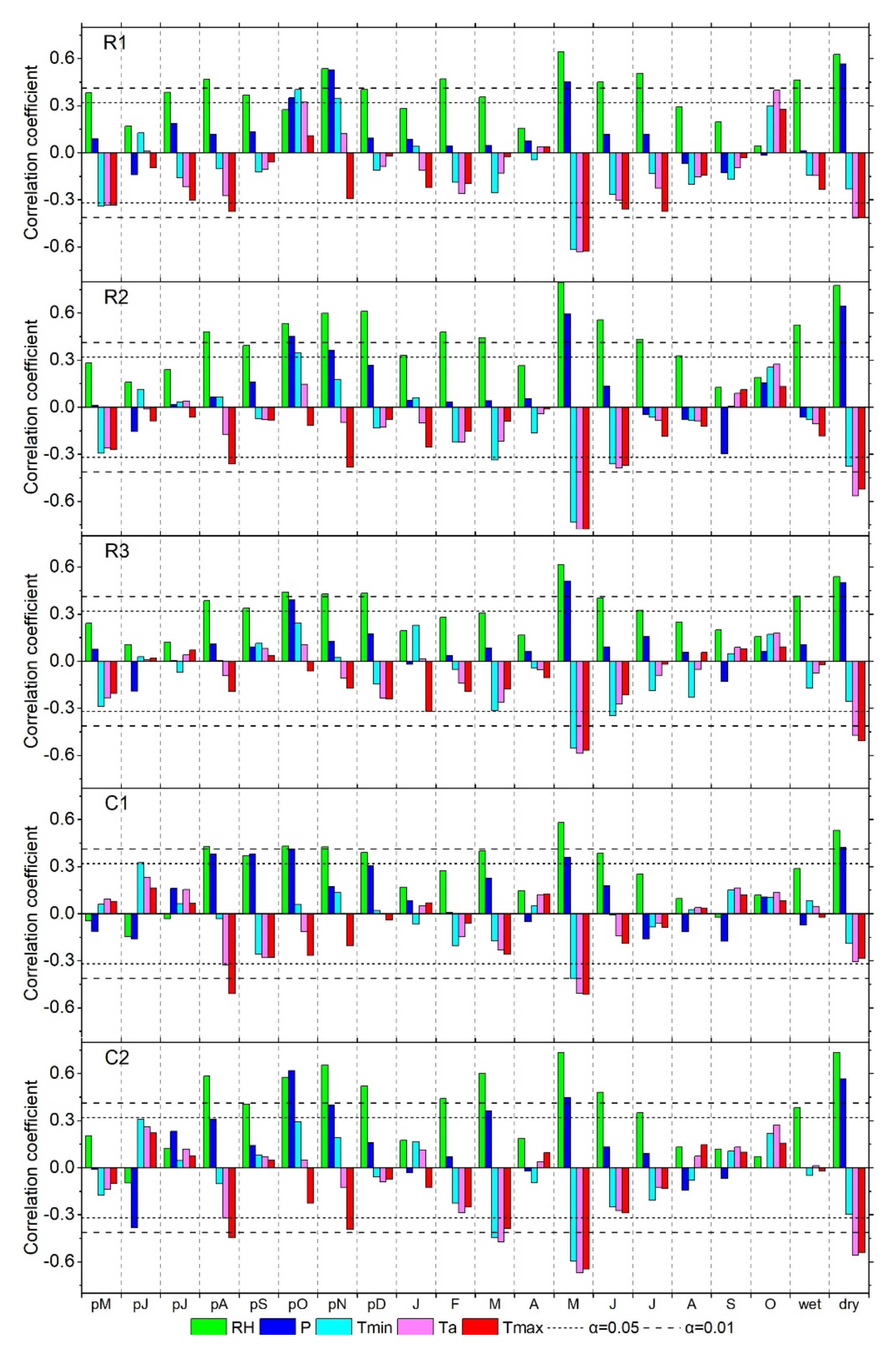
3.2. Tree Growth—Climate Relationship
3.3. Tree Growth—Elevation Relationship
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. The IPCC and the Sixth Assessment Cycle; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Madani, N.; Kimball, J.S.; Ballantyne, A.P.; Affleck, D.L.R.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Reich, P.B.; Kattge, J.; Sala, A.; Nazeri, M.; Jones, M.O.; et al. Future global productivity will be affected by plant trait response to climate. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirschbaum, M.U.F. Direct and indirect climate change effects on photosynthesis and transpiration. Plant Biol. 2004, 6, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shestakova, T.A.; Gutierrez, E.; Kirdyanov, A.V.; Camarero, J.J.; Genova, M.; Knorre, A.A.; Linares, J.C.; Resco de Dios, V.; Sanchez-Salguero, R.; Voltas, J. Forests synchronize their growth in contrasting Eurasian regions in response to climate warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, Y.W.; Ree, R.H. Uplift-driven diversification in the Hengduan Mountains, a temperate biodiversity hotspot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3444–E3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Trouet, V. Century-scale temperature variability and onset of industrial-era warming in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.N.; Zhou, T.; Wei, L.Y.; Shu, Y. The spatial distribution of forest carbon sinks and sources in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Composition and spatio-temporal variation of soil microarthropods in the biodiversity hotspot of northern Hengduan Mountains, China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 62, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, R.; Mullen, R.; Haomin, L.; Zhengong, F.; Yi, W. Spatial patterns of plant diversity and communities in Alpine ecosystems of the Hengduan Mountains, Northwest Yunnan, China. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Yi, G.; Chen, T.; Bie, X.; He, Y. Tempo-spatial variations and driving factors analysis of net primary productivity in the Hengduan mountain area from 2004 to 2014. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Peng, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q. Spatio-temporal pattern of net primary productivity in Hengduan Mountains area, China: Impacts of climate change and human activities. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 948–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, B.; Zang, W.; Yang, F.; Han, B.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; He, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Spatial and temporal change patterns of net primary productivity and its response to climate change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China from 2000 to 2015. J. Arid. Land 2019, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Guo, L.; Li, J. Impacts of climate change on ecosystem in priority areas of biodiversity conservation in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4668–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wu, S.; Dai, E.; Zhao, N.; Ren, P.; Zhang, X. NPP vulnerability of the potential vegetation of China to climate change in the past and future. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, E.R. The decomposition of tree-ring series for environmental studies. Tree Ring Bull. 1987, 47, 37–59. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Esper, J.; Büntgen, U.; Li, L.; Xoplaki, E.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Luterbacher, J. Weakening of annual temperature cycle over the Tibetan Plateau since the 1870s. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babst, F.; Poulter, B.; Trouet, V.; Tan, K.; Neuwirth, B.; Wilson, R.; Carrer, M.; Grabner, M.; Tegel, W.; Levanič, T.; et al. Site- and species-specific responses of forest growth to climate across the European continent. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-X.; Bräuning, A.; Cao, K.-F. Tree-ring based drought reconstruction in the central Hengduan Mountains region (China) since A.D. 1655. Int. J. Clim. 2008, 28, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Li, Z.-S.; Zhang, Q.B.; Ma, K.-P.; Mu, C. Dendroclimatological studies of Picea likiangensis and Tsuga dumosa in Lijiang, china. IAWA J. 2009, 30, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, K.; Gou, X.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; D’Arrigo, R.; Cook, E.; Yang, T.; Davi, N. Reconstructed droughts for the southeastern Tibetan Plateau over the past 568 years and its linkages to the Pacific and Atlantic Ocean climate variability. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 35, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Li, J.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, G. Three centuries of winter temperature change on the southeastern Tibetan Plateau and its relationship with the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.-X.; Bräuning, A.; Cao, K.-F. Annual temperature reconstruction in the central Hengduan Mountains, China, as deduced from tree rings. Dendrochronologia 2008, 26, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-X.; Bräuning, A.; Tian, Q.-H.; Yang, B.; Cao, K.-F. Tree ring recorded May–August temperature variations since A.D. 1585 in the Gaoligong Mountains, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2010, 296, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, J. A 564-year annual minimum temperature reconstruction for the east central Tibetan Plateau from tree rings. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 157, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-X.; Bräuning, A.; Yang, B.; Cao, K.-F. Tree ring density-based summer temperature reconstruction for the central Hengduan Mountains in southern China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-M.; Li, Z.-S.; Fan, Z.-X. Tree-ring based February–April relative humidity reconstruction since A.D. 1695 in the Gaoligong Mountains, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Asian Geogr. 2017, 34, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Xu, D.; Tian, K.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, W.; Sun, D.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y. Radial Growth Response of Abies georgei to Climate at the Upper Timberlines in Central Hengduan Mountains, Southwestern China. Forests 2018, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Au, T.F. Tree growth divergence from winter temperature in the Gongga Mountains, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Asian Geogr. 2019, 37, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuning, A. Summer temperature and summer monsoon history on the Tibetan plateau during the last 400 years recorded by tree rings. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, Q.B. A 449 year warm season temperature reconstruction in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau and its relation to solar activity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Liu, G.H.; Gong, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.C. Tree ring-based temperature reconstruction over the past 186 years for the Miyaluo Natural Reserve, western Sichuan Province of China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 120, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, X. Tree-ring-based temperature reconstruction for the Wolong Natural Reserve, western Sichuan Plateau of China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3296–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-X.; Bräuning, A.; Cao, K.-F.; Zhu, S.-D. Growth—Climate responses of high-elevation conifers in the central Hengduan Mountains, southwestern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, D.; Tian, K.; Zhang, W.; He, R.; He, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z. Radial growth responses of Picea likiangensis to climate variabilities at different altitudes in Yulong Snow Mountain, southwest China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2018, 42, 629–639. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.-M.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Wang, X.-C.; Liu, S.-R. Difference in responses of major tree species growth to climate in the Miyaluo Mountains, western Sichuan, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar]
- Huan-Cheng, M.; McConchie, J.A. The dry-hot valleys and forestation in southwest China. J. For. Res. 2001, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integrated Scientific Expeditional Team to Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Dry Valleys of the Hengduan Mountains Region; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Q.; Shi, Z. New discussion on dry valley formation in the Three Parallel Rivers Region. J. Desert Res. 2007, 27, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, T.; Chen, F.; Xu, W.; Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, Z. Spatial-temporal variations of methane emissions from the Ertan hydroelectric reservoir in southwest China. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.D.; Osborn, T.J.; Lister, D.H. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations—The CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, G.; Qi, C. Dedrochronology (South China Version), 3rd ed.; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Cai, Y.; Yang, W.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z. Climatic variations within the dry valleys in southwestern China and the influences of artificial reservoirs. Clim. Chang. 2019, 155, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cai, Y.; Jaramillo, F.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Exploring the influence of reservoir impoundment on growth of surrounding vegetation. Adv. Water Res. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.R.; Kairiukstis, L.A. Methods of Dendrochronology: Applications in the Environmental Sciences; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, E.; Wang, Y.; Piao, S.; Lu, X.; Camarero, J.J.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, L.; Ellison, A.M.; Ciais, P.; Peñuelas, J. Species interactions slow warming-induced upward shifts of treelines on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 113, 4380–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stroke, M.A.; Smiley, T.L. Introduction to Tree-Ring Dating; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, R.L. Computer-assisted quality control in tree-ring dating and measurement. Tree Ring Bull. 1983, 43, 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Grissino-Mayer, H.D. Evaluating crossdating accuracy: A manual and tutorial for the computer program COFECHA. Tree Ring Res. 2001, 57, 31621719. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.R.; Peters, K. Calculating unbiased tree-ring indices for the study of climatic and environmental change. Holocene 1997, 7, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, T.J.; Biffa, K.; Jones, P. Adjusting variance for sample-size in tree-ring chronologies and other regional-mean timeseries. Dendrochronologia 1997, 15, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allan, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO irrigation and drainage paper No. 56; FAO: Quebec, BC, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Xu, J.; Gebrekirstos, A.; Guo, L.; Zhao, M.; Liang, E.; Yang, X. Assessing drought variability since 1650 AD from tree-rings on the Jade Dragon Snow Mountain, southwest China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 4057–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.; Bugmann, H.; Rigling, A. Radial growth responses to drought of Pinus sylvestris and Quercus pubescens in an inner-Alpine dry valley. J. Veg. Sci. 2007, 18, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, D.; Tian, K.; He, R.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, W. Relationship between radial growth of Abies georgei and climate factors at different altitudes on the eastern slope of Yulong Snow Mountain, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Kang, D.; Guo, W.; Zhao, L.; Cui, L.; Li, J. Climate sensitivity of purple cone spruce (Picea purpurea) across an altitudinal gradient on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Dendrochronologia 2019, 56, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Fan, Z.; Li, Z.; Wen, Q. Radial growth of Pinus yunnanensis at different elevations and their responses to climatic factors in the Yulong Snow Mountain, Northwest Yunnan. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8983–8991. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Seasonal variations in depth of water uptake for a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to drought in an East Asian monsoon region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| R1 | R2 | R3 | C1 | C2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation (m a.s.l.) | 1256 | 1502 | 1725 | 1170 | 1359 |
| Slope | 34% | 42% | 46% | 45% | 38% |
| Aspect | N | N | NE | NE | N |
| Numbers (tree/core) | 14/23 | 15/27 | 12/21 | 19/39 | 16/37 |
| Time span | 1956–2016 | 1976–2016 | 1942–2017 | 1974–2017 | 1967–2017 |
| Time span of EPS > 0.85 | 1972–2016 | 1976–2016 | 1968–2017 | 1977–2017 | 1979–2017 |
| Average autocorrelation | 0.678 | 0.580 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.517 |
| Average sensitivity | 0.288 | 0.324 | 0.258 | 0.411 | 0.365 |
| Master correlation | 0.481 | 0.659 | 0.630 | 0.739 | 0.738 |
| R2 | R3 | C1 | C2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronology | R1 | 0.80 * | 0.51 * | 0.41 * | 0.63 * |
| R2 | 0.66 * | 0.61 * | 0.69 * | ||
| R3 | 0.30 | 0.60 * | |||
| C1 | 0.69 * | ||||
| First difference chronology | R1 | 0.78 * | 0.71 * | 0.41 * | 0.62 * |
| R2 | 0.66 * | 0.62 * | 0.62 * | ||
| R3 | 0.31 | 0.54 * | |||
| C1 | 0.77* |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gunnarson, B.E.; Jaramillo, F. Radial Growth Responses to Climate of Pinus yunnanensis at Low Elevations of the Hengduan Mountains, China. Forests 2020, 11, 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101066
Sun L, Cai Y, Zhou Y, Shi S, Zhao Y, Gunnarson BE, Jaramillo F. Radial Growth Responses to Climate of Pinus yunnanensis at Low Elevations of the Hengduan Mountains, China. Forests. 2020; 11(10):1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lian, Yanpeng Cai, Yang Zhou, Shiyuan Shi, Yesi Zhao, Björn E. Gunnarson, and Fernando Jaramillo. 2020. "Radial Growth Responses to Climate of Pinus yunnanensis at Low Elevations of the Hengduan Mountains, China" Forests 11, no. 10: 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101066
APA StyleSun, L., Cai, Y., Zhou, Y., Shi, S., Zhao, Y., Gunnarson, B. E., & Jaramillo, F. (2020). Radial Growth Responses to Climate of Pinus yunnanensis at Low Elevations of the Hengduan Mountains, China. Forests, 11(10), 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101066







