Effect of Degradation on Wood Hygroscopicity: The Case of a 400-Year-Old Coffin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
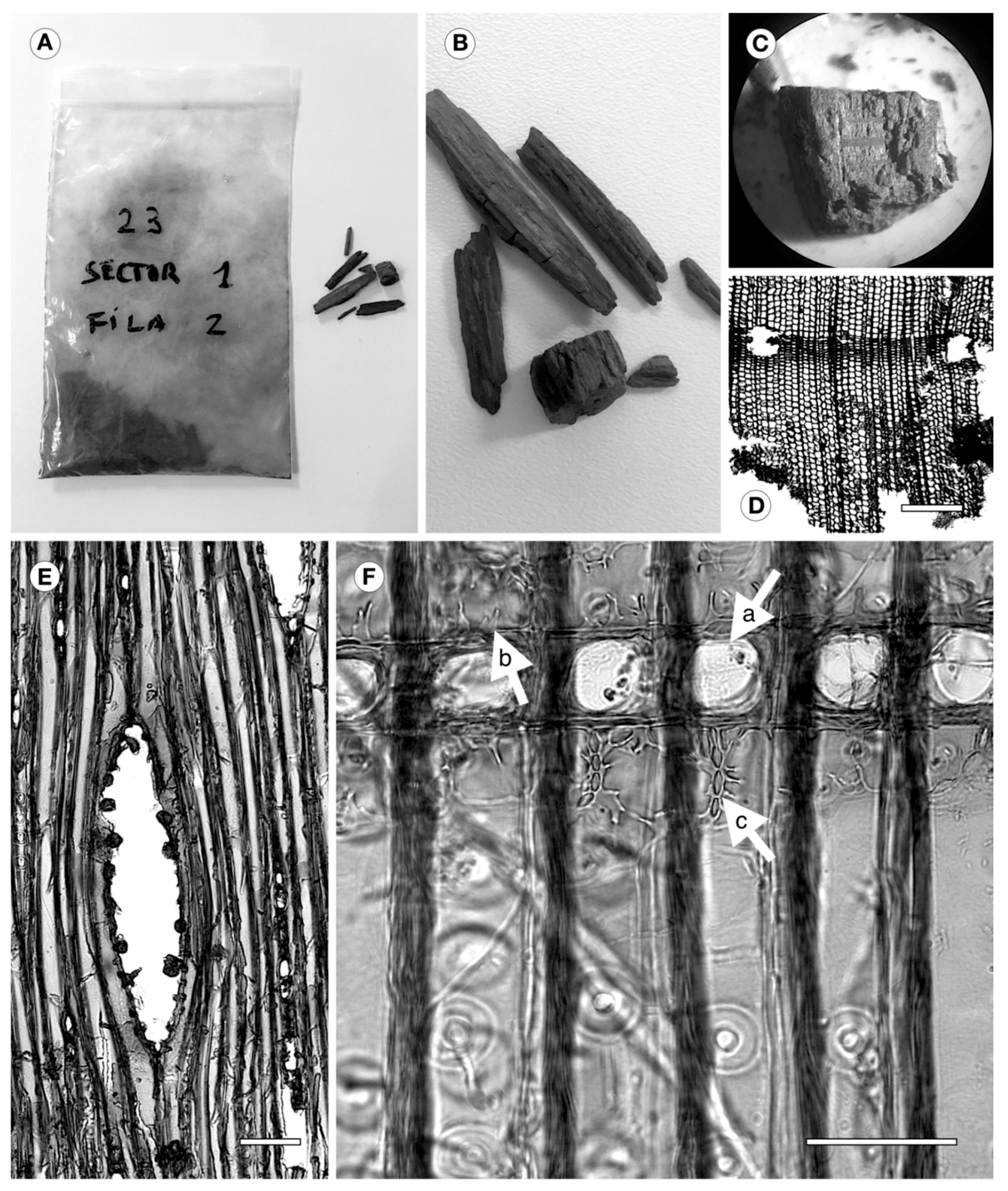
2.1. Archaeological Wood
2.2. Wood Identification
2.3. Reference Material
2.4. Sorption Isotherms
2.5. Functional Groups. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
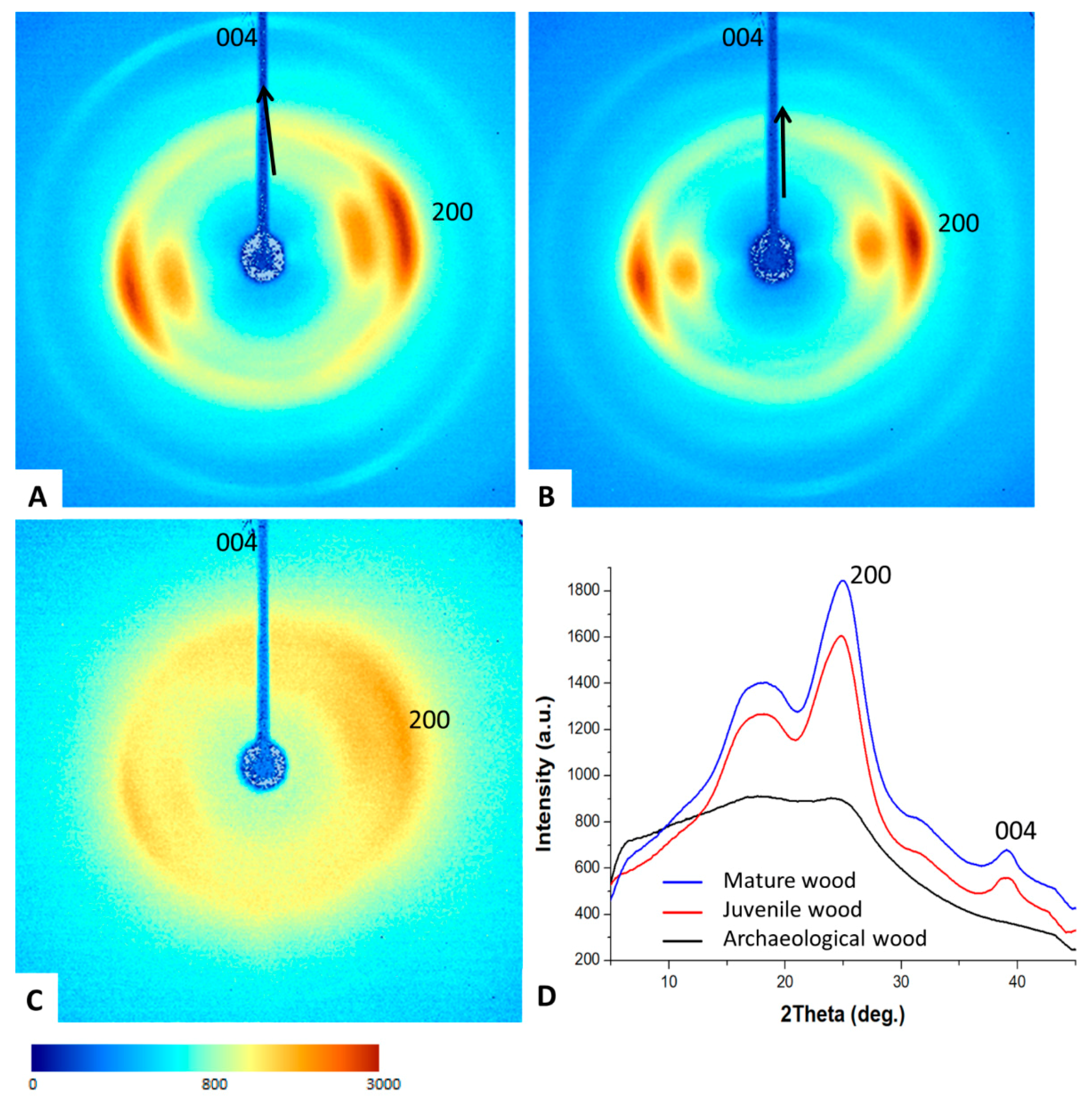
2.6. Two-Dimensional (2D) X-Ray Diffraction
2.7. Thermodynamic Properties
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sorption Isotherms
3.2. Functional Groups
3.3. Two-Dimensional (2D) X-ray Diffraction
3.4. Thermodynamic Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Zhou, H.; Stevanic, J.S.; Dong, M.; Yu, M.; Salmén, L.; Yin, Y. Effects of ageing on the cell wall and its hygroscopicity of wood in ancient timber construction. Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebotnik, E.; Messner, K. Immunoelectron microscopical study of the porosity of brown-rot degraded pine wood. Holzforschung 1991, 45, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, R.A. A review of microbial deterioration found in archaeological wood. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2000, 46, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.B.; Schmitt, U.; Koch, G.; Felby, C.; Thygesen, L.G. Lignin distribution in waterlogged archaeological Picea abies (L.) Karst degraded by erosion bacteria. Holzforschung 2014, 68, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.B.; Gierlinger, N.; Thygesen, L.G. Bacterial and abiotic decay in waterlogged archaeological Picea abies (L.) Karst studied by Confocal Raman imaging and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintner, J.; Smidt, E.; Tieben, J.; Reschreiter, H.; Kowarik, K.; Grabner, M. Aging of wood under long-term storage in a salt environment. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Iruela, A.; Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Garcia Fernandez, F.; Martin-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M. Changes in Cell Wall Components of Pinus sylvestris L. Wood after 300 Years in Contact with Salt (NaCl). BioResources 2019, 14, 3069–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Fernandez, F.G.; Guindeo, A.; de Palacios, P.; Gril, J. Comparison of the hygroscopic behaviour of 205-year-old and recently cut juvenile wood from Pinus sylvestris L. Ann. For. Sci. 2006, 63, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Fernandez, F.G.; Guindeo, A.; Conde, M.; Baonza, V. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood after 103 years of submersion. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; García Fernandez, F.; Martin, J.A.; Genova, M.; Fernandez-Golfin, J.I. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of buried juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood aged 1,170 ± 40 BP. Wood Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; García Fernandez, F.; García-Amorena, I. Effects of burial of Quercus spp. wood aged 5910 ± 250 BP on sorption and thermodynamic properties. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2010, 64, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, C.; Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Fernandez, F.G.; García-Iruela, A.; Martín-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of wood of Pinus canariensis C. Sm. ex DC. buried in volcanic ash during eruption. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchette, R.A.; Cease, K.R.; Abad, A.R.; Koestler, R.J.; Simpson, E.; Sams, G.K. An Evaluation of Different Forms of Deterioration Found in Archaeological Wood. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 1991, 28, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAWA Committee. IAWA list of microscopic features for softwood identification. IAWA J. 2004, 25, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Guindeo, A. Anatomía e Identificación de Maderas de Coníferas Españolas; AiTiM: Madrid, Spain, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Guindeo, A.; García, L.; Lázaro, I.; González, L.; Rodríguez, Y.; García, F.; Bobadilla, I.; Camacho, A. Anatomía e Identificación de Maderas de Coníferas a Nivel de Especie/Anatomy and Identification of Conifers Wood as a Species; Fundación Conde del Valle de Salazar-Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Troncoso, O.; Greslebin, A. Trabeculae in Patagonian mountain cypress (Austrocedrus chilensis) associated with Phytophthora austrocedri infection. IAWA J. 2018, 39, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, E.C. The Anatomy of Woody Plants; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, J.D. The structure of wood. In Canadian Woods: Their Properties and Uses; Forest Service Department of Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Catalán, G.; Gil, P.; Galera, R.M.; Martín, S.; Agúndez, D.; Alía, R. Las Regiones de Procedencia de Pinus Sylvestris L. y Pinus Nigra Arn. subsp. Salzmannii (Dunal) Franco en España; Instituto Nacional para la Conservación de la Naturaleza: Madrid, Spain, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, J.A.; Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; García Fernández, F. Variation in wood anatomical traits of Pinus sylvestris L. between Spanish regions of provenance. Trees 2010, 24, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Martín, J.A.; de Palacios, P.; García-Fernández, F. Influence of region of provenance and climate factors on wood anatomical traits of Pinus nigra Arn. subsp. salzmannii. Eur. J. Forest Res. 2012, 131, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Simón, C.; Fernández, F.G.; de Palacios, P.; Martín-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E.; Hosseinpourpia, R. Juvenile and mature wood of Abies pinsapo Boissier: Sorption and thermodynamic properties. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, M.; Thybring, E.E. Scanning or desorption isotherms? Characterising sorption hysteresis of wood. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4477–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arevalo-Pinedo, A.; Giraldo-Zuñiga, A.D.; Dos Santos, F.L.; Arevalo, R.P. Sorption isotherms experimental data and mathematical models for murici pulp (Byrsonima sericea). In Proceedings of the 14th International Drying Symposium, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 22–25 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jannot, Y.; Kanmogne, A.; Talla, A.; Monkam, L. Experimental determination and modelling of water desorption isotherms of tropical woods: Afzelia, Ebony, Iroko, Moabi and Obeche. Holz. Roh. Werkst. 2006, 64, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollaz, P.E.; Rovedo, C.O. Equilibrium sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of starch and gluten. J. Food Eng. 1999, 40, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Iruela, A.; Esteban, L.G.; García Fernández, F.; de Palacios, P.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; Martí-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E. Effect of vacuum/pressure cycles on cell wall composition and structure of poplar wood. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8543–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, W. Sorption theories applied to wood. Wood Fiber Sci. 1980, 12, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zelinka, S.L.; Glass, S.V.; Thybring, E.E. Myth versus reality: Do parabolic sorption isotherm models reflect actual wood–water thermodynamics? Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramidis, S. The basics of sorption. In Proceedings of the International Conference of COST Action E8: Mechanical Performance of Wood and Wood Products, Copenhagen, Denmark, 16–17 June 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, P.N.; Bangi, A.P.; Lee, A.W.C. Thermodynamics of moisture sorption by the giant-timber bamboo. Holzforschung 1997, 51, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siau, J.F. Wood: Influence of Moisture on Physical Properties; Department of Wood Science and Forest Products, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette, R.A. Biodeterioration of archaeological wood. CAB Biodeterior. Abstr. 1995, 9, 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bjordal, C.G.; Nilsson, T.; Daniel, G. Microbial decay of waterlogged wood found in Sweden applicable to archaeology and conservation. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 1999, 43, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilgör, N.; Köse, C.; Kartal, S.N. Effect of 300 year water-logging on chemical properties and natural decay and termite resistance of wood Abies bornmuleriana M. Wood Res. Slovak. 2005, 50, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gelbrich, J.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Chemical changes in wood degraded by bacteria. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2008, 61, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S. Chemical characteristics of waterlogged archaeological wood. Holzforschung 1990, 44, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fengel, D. Aging and fossilization of wood and its components. Wood Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardet, M.; Foray, M.F.; Maron, S.; Goncalves, P.; Trân, Q.K. Characterization of wood components of Portuguese medieval dugout canoes with high-resolution solid-state-NMR. Carbohyd. Polym. 2004, 57, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D.; Kim, H.J. Cotton fiber structure. In Cotton Fiber, Physics and Biology; Fang, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 13–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Z.; Wang, T.; Makarem, M.; Santiago-Cintrón, M.; Cheng, H.N.; Kang, X.; Bacher, M.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T.; King, H.; et al. Effects of ball milling on the structure of cotton cellulose. Cellulose 2019, 26, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| 15 °C Isotherm | 35 °C Isotherm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juvenile Wood | Mature Wood | Archaeological Wood | Juvenile Wood | Mature Wood | Archaeological Wood | ||
| Adsorption | Xm | A5.89 ± 0.29 | B7.01 ± 0.32 | B7.37 ± 0.29 | A5.64 ± 0.06 | B6.48 ± 0.06 | C6.69 ± 0.12 |
| K | 0.79 ± 0.32 | 0.77 ± 0.30 | 0.77 ± 0.29 | 0.78 ± 0.07 | 0.77 ± 0.06 | 0.76 ± 0.13 | |
| Cg | 5.04 ± 0.09 | 4.54 ± 0.10 | 5.40 ± 0.08 | 4.93 ± 0.02 | 4.50 ± 0.02 | 5.28 ± 0.03 | |
| R | 0.996 | 0.996 | 0.993 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.998 | |
| RMSE (%) | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.22 | |
| RH (%) | 29.60 | 29.2 | 31.0 | 29.8 | 29.1 | 31.0 | |
| EMCa (%) | 4.66 | 5.17 | 6.07 | 4.39 | 4.74 | 5.45 | |
| EMCf (%) | 1.23 | 1.84 | 1.30 | 1.25 | 1.74 | 1.24 | |
| Desorption | Xm | A8.51 ± 0.07 | B10.19 ± 0.03 | C10.40 ± 0.07 | A7.46 ± 0.08 | B8.25 ± 0.07 | C8.92 ± 0.07 |
| K | 0.71 ± 0.06 | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.68 ± 0.06 | 0.69 ± 0.07 | 0.70 ± 0.07 | 0.69 ± 0.07 | |
| Cg | 5.56 ± 0.02 | 5.13 ± 0.01 | 6.61 ± 0.01 | 5.29 ± 0.02 | 5.20 ± 0.02 | 6.05 ± 0.02 | |
| R | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| RMSE (%) | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |
| RH (%) | 33.9 | 35.0 | 36.4 | 34.0 | 33.6 | 35.5 | |
| EMCd (%) | 7.12 | 8.17 | 9.43 | 6.08 | 6.64 | 7.79 | |
| EMCf (%) | 1.39 | 2.02 | 0.97 | 1.38 | 1.61 | 1.13 | |
| Functional Group | Wave Number (cm−1) | Juvenile Wood | Mature Wood | Archaeological Wood |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl (–OH) | 3400–3500 | 3349.75 | 3363.97 | 3350.95 |
| C-H bond | 2890–2930 | 2888.36 | 2889.09 | 2938.26 |
| Carbonyl (C=O) a | 1730–1750 | 1721.88 | 1731.04 | - |
| Lignin b | 1510 | 1507.34 | 1507.82 | 1508.06 |
| Deformation strains CH3. CH2 c | 1370 | 1368.01 | 1370.18 | 1373.79 |
| Carboxyl (C-O) | 1200 | 1233.98 | 1263.87 | 1220.96 |
| FWHM_200 (°) | FWHM_004 (°) | AS_200 (°) | Oriented Fraction | Cellulose Ibeta (%) | Crystallite Size (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juvenile wood | 4.18 ± 0.1 | 2.19 ± 0.1 | 35.8 ± 0.48 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 17.5 | 15.7 |
| Mature wood | 3.96 ± 0.1 | 2.25 ± 0.2 | 29.9 ± 6.1 | 0.46 ± 0.08 | 14.6 | 14.2 |
| Archaeological wood | 10.31 ± 0.4 | - | 74.6 ± 53 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 9.6 | 7 |
| Adsorption | Desorption | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSP (%) | qs (KJ/mol) | W0 (KJ/mol Dry) Wood) | FSP (%) | qs (KJ/mol) | W0 (KJ/mol Dry Wood) | |||
| Max | Min | Max | Min | |||||
| Juvenile wood | 26.59 | 3.05 | 0.88 | 0.45 | 25.66 | 7.90 | 1.65 | 1.23 |
| Mature wood | 29.20 | 3.78 | 0.81 | 0.59 | 28.46 | 8.05 | 1.44 | 1.37 |
| Archaeological wood | 30.02 | 5.27 | 1.15 | 0.85 | 29.95 | 9.43 | 1.76 | 1.64 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Iruela, A.; García Esteban, L.; García Fernández, F.; de Palacios, P.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.B.; Sánchez, L.G.; Hosseinpourpia, R. Effect of Degradation on Wood Hygroscopicity: The Case of a 400-Year-Old Coffin. Forests 2020, 11, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11070712
García-Iruela A, García Esteban L, García Fernández F, de Palacios P, Rodriguez-Navarro AB, Sánchez LG, Hosseinpourpia R. Effect of Degradation on Wood Hygroscopicity: The Case of a 400-Year-Old Coffin. Forests. 2020; 11(7):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11070712
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Iruela, Alberto, Luis García Esteban, Francisco García Fernández, Paloma de Palacios, Alejandro B. Rodriguez-Navarro, Luis Gil Sánchez, and Reza Hosseinpourpia. 2020. "Effect of Degradation on Wood Hygroscopicity: The Case of a 400-Year-Old Coffin" Forests 11, no. 7: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11070712
APA StyleGarcía-Iruela, A., García Esteban, L., García Fernández, F., de Palacios, P., Rodriguez-Navarro, A. B., Sánchez, L. G., & Hosseinpourpia, R. (2020). Effect of Degradation on Wood Hygroscopicity: The Case of a 400-Year-Old Coffin. Forests, 11(7), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11070712









