Iodine Fractions in Soil and Their Determination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
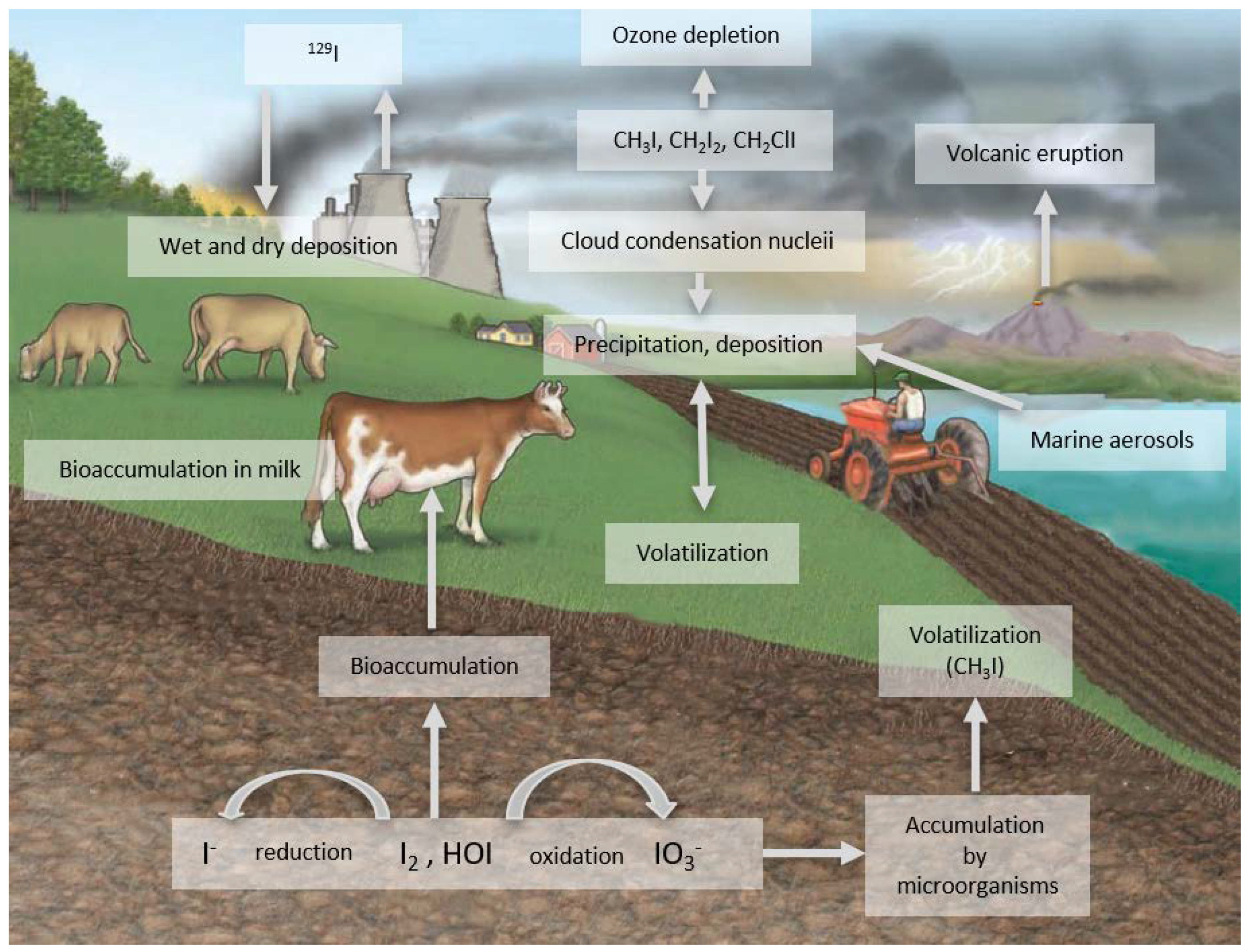
2. Biogeochemical Cycling of Iodine
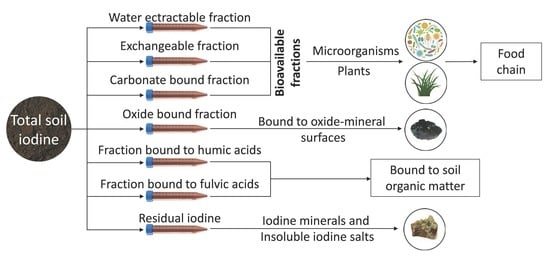
3. Iodine in Soils and Their Fractions
3.1. Water-Extractable Fraction
3.2. Exchangeable Fraction
3.3. Carbonate-Bound Fraction
3.4. Metal Oxides-Bound Fraction
3.5. Organic Matter-Bound Fraction
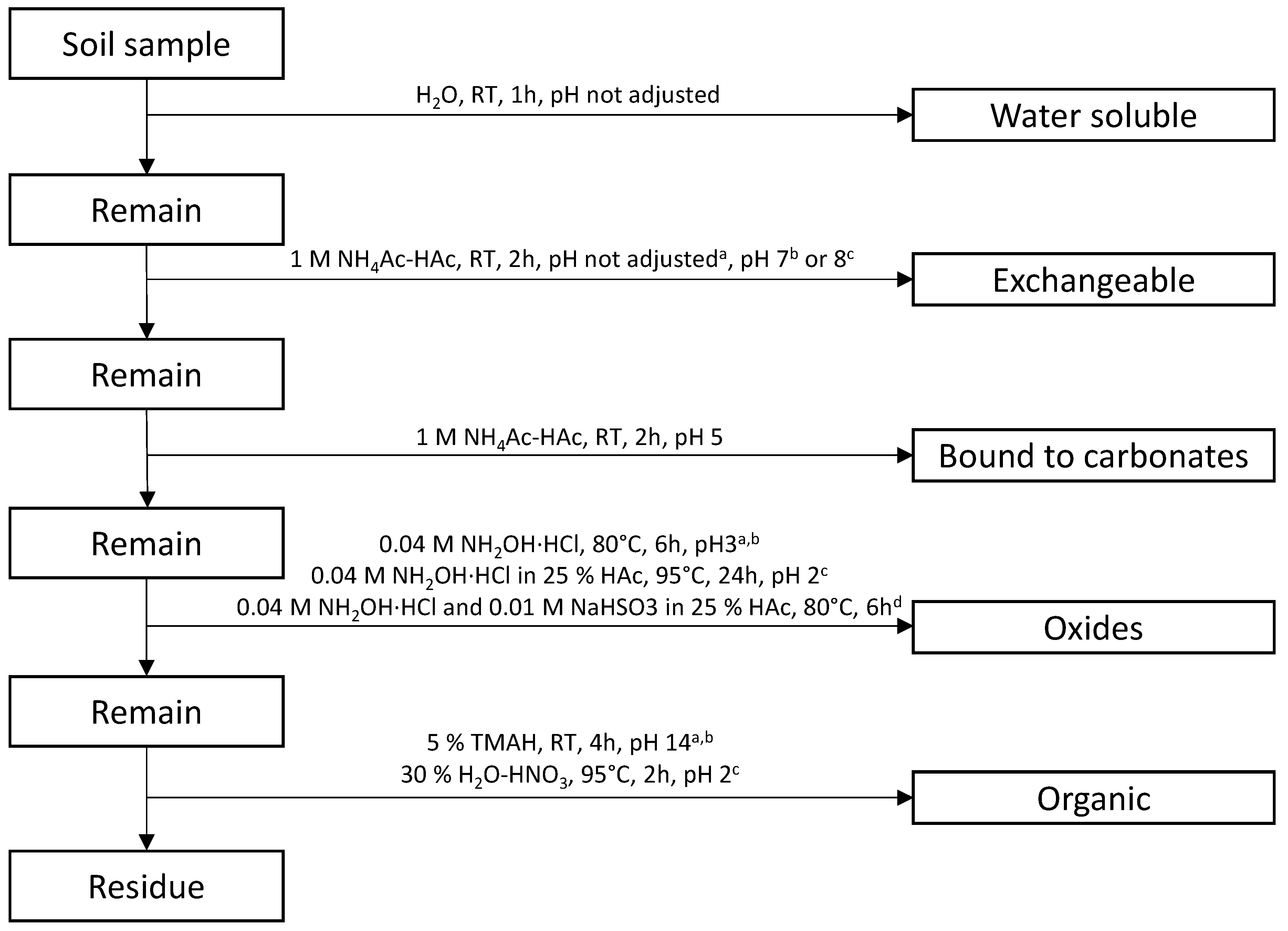
4. Methods for Iodine Fractionation
5. Recent Studies on Iodine Soil Fractionation and Extraction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Assessment of Iodine Deficiency Disorders and Monitoring Their Elimination: A Guide for Programme Managers, 3rd ed.; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C. Database of the Iodine Content of Soils Populated with Data from Published Literature; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2003; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Šeda, M.; Švehla, J.; Trávniček, J.; Kroupová, V.; Konecny, R.; Fiala, K.; Svozilová, M.; Krhovjaková, J. The effect of volcanic activity of the Eyjafjallajökul volcano on iodine concentration in precipitation in the Czech Republic. Geochemistry 2012, 72, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowley, H.E.; Young, S.; Ander, E.; Crout, N.; Watts, M.; Bailey, E. Iodine bioavailability in acidic soils of Northern Ireland. Geoderma 2019, 348, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, Y.; Yoshida, S. Effects of microorganisms on the fate of iodine in the soil environment. Geomicrobiol. J. 1999, 16, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Roulier, M.; Coppin, F.; Bueno, M.; Nicolas, M.; Thiry, Y.; Della Vedova, C.; Février, L.; Pannier, F.; Le Hécho, I. Iodine budget in forest soils: Influence of environmental conditions and soil physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roulier, M.; Bueno, M.; Thiry, Y.; Coppin, F.; Redon, P.-O.; Le Hécho, I.; Pannier, F. Iodine distribution and cycling in a beech (Fagus sylvatica) temperate forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Hou, X.; Zhou, W.; He, C.; Chen, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L. Speciation and migration of 129I in soil profiles. J. Environ. Radioact. 2013, 118, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, F.; Riebe, B.; Weller, A.; Walther, C. Determination of iodine mobility in the soil vadose zone using long-term column experiments. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2019, 322, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.; Bailey, E.; Crout, N.; Field, L.; Freeman, S.; Gaschak, S.; Hou, X.; Izquierdo, M.; Wells, C.; Xu, S.; et al. Analysis of 129I and 127I in soils of the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, 29 years after the deposition of 129I. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuge, R.; Johnson, C.C. The geochemistry of iodine—A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 1986, 8, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuge, R.; Johnson, C.C. Iodine and human health, the role of environmental geochemistry and diet, a review. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Hansen, V.; Aldahan, A.; Possnert, G.; Lind, O.C.; Lujaniene, G. A review on speciation of iodine-129 in the environmental and biological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, X. Iodine Speciation in Foodstuffs, Tissues, and Environmental Samples: Iodine Species and Analytical Method. In Comprehensive Handbook of Iodine: Nutritional, Biochemical, Pathological and Therapeutic Aspect; Preedy, V.R., Burrow, G.N., Watson, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.; Crawford, J.; Liu, S.; McKeen, S.; Bandy, A.; Thornton, D.; Rowland, F.; Blake, D. Potential impact of iodine on tropospheric levels of ozone and other critical oxidants. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.C. The Geochemistry of Iodine and Its Application to Environmental Strategies for Reducing the Risks from Iodine Deficiency Disorders (IDD); British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2003; p. 54, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu, Y.; Wedepohl, K.H. The distribution of iodine in the earth’s crust. Chem. Geol. 1998, 147, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulier, M.; Bueno, M.; Coppin, F.; Nicolas, M.; Thiry, Y.; Rigal, F.; Le Hécho, I.; Pannier, F. Atmospheric iodine, selenium and caesium depositions in France: I. Spatial and seasonal variations. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, M.; Virkanen, J.; Aromaa, H.; Gracheva, N.; Lehto, J. Sorption and speciation of iodine in boreal forest soil. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2017, 311, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Lopez, A.; Plane, J.M.C.; McFiggans, G.; Williams, P.I.; Ball, S.M.; Bitter, M.; Jones, R.L.; Hongwei, C.; Hoffmann, T. Modelling molecular iodine emissions in a coastal marine environment: The link to new particle formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ban-Nai, T.; Muramatsu, Y.; Amachi, S. Rate of iodine volatilization and accumulation by filamentous fungi through laboratory cultures. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redeker, K.R.; Treseder, K.; Allen, M.F. Ectomycorrhizal fungi: A new source of atmospheric methyl halides? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagwell, C.E.; Zhong, L.; Wells, J.R.; Mitroshkov, A.V.; Qafoku, N.P. Microbial methylation of iodide in unconfined aquifer sediments at the Hanford Site, USA. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redeker, K.R.; Manley, S.L.; Walser, M.; Cicerone, R.J. Physiological and biochemical controls over methyl halide emissions from rice plants. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redeker, K.R.; Cicerone, R.J. Environmental controls over methyl halide emissions from rice paddies. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, D.B. Halomethane from halide ion—A highly efficient fungal conversion of environmental significance. Nature 1985, 315, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, Y.; Yoshida, S. Volatilization of methyl iodide from the soil-plant system. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Wassmann, R.; Rennenberg, H. Methane emissions from rice fields—Quantification, mechanisms, role of man-agement, and mitigation options. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; Volume 70, pp. 193–260. [Google Scholar]
- Amachi, S.; Kasahara, M.; Hanada, S.; Kamagata, Y.; Shinoyama, H.; Fujii, T.; Muramatsu, Y. Microbial Participation in Iodine Volatilization from Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3885–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attieh, J.M.; Hanson, A.D.; Saini, H.S. Purification and characterization of a novel methyltransferase responsible for biosynthesis of halomethanes and methanethiol in Brassica oleracea. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 9250–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saini, H.S.; Attieh, J.M.; Hanson, A.D. Biosynthesis of halomethanes and methanethiol by higher plants via a novel methyltransferase reaction. Plant Cell Environ. 1995, 18, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Chorover, J. Chemical processes affecting contaminant transport and fate. In Environmental and Pollution Science, 2nd ed.; Pepper, I.L., Gerba, P.C., Brusseau, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier Science Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, V.; Roos, P.; Aldahan, A.; Hou, X.; Possnert, G. Partition of iodine (129I and 127I) isotopes in soils and marine sediments. J. Environ. Radioact. 2011, 102, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duborská, E.; Bujdoš, M.; Urík, M.; Matúš, P. Iodine fractionation in agricultural and forest soils using extraction methods. CATENA 2020, 195, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Tsukada, H.; Takaku, Y.; Hisamatsu, S. Effect of aging on availability of iodine in grassland soil collected in Rokkasho, Japan. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 303, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuita, K.; Kihou, N. Behavior of iodine in a forest plot, an upland field, and a paddy field in the upland area of Tsukuba, Japan: Vertical distribution of iodine in soil horizons and layers to a depth of 50 m. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2005, 51, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otosaka, S.; Schwehr, K.A.; Kaplan, D.I.; Roberts, K.A.; Zhang, S.; Xu, C.; Li, H.-P.; Ho, Y.-F.; Brinkmeyer, R.; Yeager, C.M.; et al. Factors controlling mobility of 127I and 129I species in an acidic groundwater plume at the Savannah River Site. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3857–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuita, K.; Tanaka, T.; Abe, C.; Aso, S. Dynamics of iodine, bromine, and chlorine in soil: I. Effect of moisture, temperature, and pH on the dissolution of the triad from soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1991, 37, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Wachi, T.; Yoshihira, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Takagi, D.; Tezuka, A.; Yoshida, H.; Yoshida, S.; Sekimoto, H.; et al. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots have iodate reduction activity in response to iodine. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zelazny, L.W.; He, L.; Vanwormhoudt, A. Charge Analysis of Soils and Anion Exchange. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Sumner, M.E., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 1231–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; p. 993. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.L.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhang, M.; Song, J.L. Availability of iodide and iodate to spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) in relation to total iodine in soil solution. Plant Soil 2006, 289, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, D.I.; Serne, R.J.; Parker, A.K.E.; Kutnyakov, I.V. Iodide sorption to subsurface sediments and illitic minerals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 34, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, W.; Serne, R.; Krupka, K.M. Linearity and reversibility of iodide adsorption on sediments from Hanford, Washington under water saturated conditions. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, H.P.; Xu, C.; Ho, Y.-F.; Zhang, S.; Schwehr, K.A.; Lilley, M.; Kaplan, D.I.; Santschi, P.H.; Powell, B.A. Geochemical controls of iodine uptake and transport in Savannah River Site subsurface sediments. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 45, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamoto, Y.S.; Itai, T.; Takahashi, Y. Soil column experiments for iodate and iodide using K-edge XANES and HPLC–ICP-MS. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Muramatsu, Y.; Uchida, S. Studies on the sorption of I-(iodide) and IO3-(iodate) onto Andosols. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1992, 63, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobova, E. Soil and landscape geochemical factors which contribute to iodine spatial distribution in the main environmental components and food chain in the central Russian plain. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyohara, M.; Kaneko, M.; Mitsutsuka, N.; Fujihara, H.; Saito, N.; Murase, T. Contribution to understanding iodine sorption mechanism onto mixed solid alumina cement and calcium compounds. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2002, 39, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, D.C. The sorption of iodide by soil components. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1974, 25, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, M.; Bajt, S.; Schoonen, M.A. Sorption of iodine on minerals investigated by X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and 125I tracer sorption experiments. Appl. Geochem. 1998, 13, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.; Davis, J.A.; Luther, G. The kinetics of iodide oxidation by the manganese oxide mineral birnessite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 2850–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qafoku, N.P.; Szecsody, J.E.; Strickland, C.E.; Brown, C.F.; Freedman, V.L. Time-dependent iodate and iodide adsorption to Fe oxides. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldahan, A.; Englund, E.; Possnert, G.; Cato, I.; Hou, X. Iodine-129 enrichment in sediment of the Baltic Sea. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, M.G.; Schnabel, C.; Suter, M.; Synal, H.; Szidat, S.; Garciatenorio, R. Relative influence of 129I sources in a sediment core from the Kattegat area. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 323, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.; Pedersen, K.M.; Iversen, F.; Terpling, S.; Gustenhoff, P.; Petersen, S.B.; Laurberg, P. Naturally occurring iodine in humic substances in drinking water in Denmark is bioavailable and determines population iodine intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shetaya, W.; Young, S.; Watts, M.; Ander, E.; Bailey, E. Iodine dynamics in soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 77, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seki, M.; Oikawa, J.-I.; Taguchi, T.; Ohnuki, T.; Muramatsu, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Amachi, S. Laccase-Catalyzed Oxidation of Iodide and Formation of Organically Bound Iodine in Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihei, R.; Usami, M.; Taguchi, T.; Amachi, S. Role of fungal laccase in iodide oxidation in soils. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 189, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, M.I.; Thibault, D.H. Chemical behaviour of iodine in organic and mineral soils. Appl. Geochem. 1992, 7, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallard, H.; Allard, S.; Nicolau, R.; von Gunten, U.; Croué, J.P. Formation of iodinated organic compounds by oxidation of iodide-containing waters with manganese dioxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7003–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiller, P.; Mercier-Bion, F.; Gimenez, N.; Barré, N.; Miserque, F. Iodination of humic acid samples from different origins. Radiochim. Acta 2006, 94, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Xu, C.; Yeager, C.M.; Lin, P.; Xing, W.; Schwehr, K.A.; Chen, N.; Arthur, Z.; Kaplan, D.I.; Santschi, P. Molecular interaction of aqueous iodine species with humic acid studied by I and C K-Edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12416–12424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujdoš, M.; Kubová, J.; Streško, V. Problems of selenium fractionation in soils rich in organic matter. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 408, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englund, E.; Aldahan, A.; Hou, X.; Petersen, R.; Possnert, G. Speciation of iodine (127I and 129I) in lake sediments. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 2010, 268, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujdoš, M.; Muľová, A.; Kubová, J.; Medveď, J. Selenium fractionation and speciation in rocks, soils, waters and plants in polluted surface mine environment. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagarova, I.; Zemberyova, M.; Bajcan, D. Sequential and single step extraction procedures used for fractionation of selenium in soil samples. Chem. Pap. 2005, 59, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Fogh, C.; Kucera, J.; Andersson, K.; Dahlgaard, H.; Nielsen, S. Iodine-129 and Caesium-137 in Chernobyl contaminated soil and their chemical fractionation. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 308, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, K.; Genčurová, V.; Trávníček, J.; Švehla, J.; Krhovjáková, J. Jod v Půde; Agrovýzkum Rapotín: Rapotín, Czech Republic, 2010; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, S.; Forsman, U. Determination of total iodine in biological material by alkaline ashing and column-switching ion-pair liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1997, 692, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, Y. Determination of ultra-low level 129I in vegetation using pyrolysis for iodine separation and accelerator mass spectrometry measurements. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stärk, H.-J.; Mattusch, J.; Wennrich, R.; Mroczek, A. Investigation of the IC-ICP-MS determination of iodine species with reference to sample digestion procedures. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 359, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, G.; Maichin, B.; Fecher, P.; Hasse, S.; Schramel, P. Iodine determination in biological materials options for sample preparation and final determination. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1998, 362, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Kiriyama, T.; Onagawa, Y.; Hisamori, I.; Miyazaki, C.; Yonebayashi, K. Speciation of iodine in soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1999, 45, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Kiriyama, T.; Yonebayashi, K. Determination of Total iodine in soils by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1996, 42, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagami, K.; Uchida, S.; Hirai, I.; Tsukada, H.; Takeda, H. Determination of chlorine, bromine and iodine in plant samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry after leaching with tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide under a mild temperature condition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 570, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecher, P.A.; Goldmann, I.; Nagengast, A. Determination of iodine in food samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after alkaline extraction. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1998, 13, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecher, P.A.; Nagengast, A. Trace analysis in high matrix aqueous solutions using helium microwave induced plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1994, 9, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duborská, E.; Urik, M.; Bujdoš, M.; Kubová, J. Aging and substrate type effects on iodide and iodate accumulation by Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duborská, E.; Urík, M.; Bujdoš, M. Comparison of Iodide and Iodate Accumulation and Volatilization by Filamentous Fungi during Static Cultivation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.J.; Pickford, C.J.; Thompson, M. Determination of iodine-129 in vegetable samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1992, 7, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, H. Rapid and sensitive determination of iodine in fresh milk and milk powder by inductively coupled plasma? Mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1990, 338, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramel, P.; Hasse, S. Iodine determination in biological materials by ICP-MS. Microchim. Acta 1994, 116, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šeda, M.; Švehla, J.; Trávníček, J.; Kroupová, V.; Fiala, K.; Svozilová, M. Optimalizace stanovení stopových koncentrací jodu v povrchových vodách metodou ICP-MS. Chem. Listy 2011, 105, 538–541. [Google Scholar]
- Rädlinger, G.; Heumann, K.G. Iodine Determination in Food Samples Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2221–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrubá, L.; Kaňa, A.; Mestek, O. Kvantitativní analýza specií jodu v biologických vzorcích spojením vylučovací chromatografie a hmotnostní spektrometrie s indukčně vázaným plazmatem. Chem. Listy 2015, 109, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, M.J.; Mitchell, C.J. A pilot study on iodine in soils of Greater Kabul and Nangarhar provinces of Afghanistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaku, Y.; Shimamura, T.; Masuda, K.; Igarashi, Y. Iodine determination in natural and tap water using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 1995, 11, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kučera, J. Assay of iodine in foodstuffs: Methods and applications. In Comprehensive Handbook of Iodine: Nutritional, Biochemical, Pathological and Therapeutic Aspects; Preedy, V.R., Burrow, G.N., Watson, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Niedobová, E.; Machát, J.; Kanický, V.; Otruba, V. Determination of iodine in enriched chlorella by ICP-OES in the VUV Region. Microchim. Acta 2005, 150, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Yamasaki, S.-I.; Tsukada, H.; Takaku, Y.; Hisamatsu, S.; Tsuchiya, N. Determination of total contents of bromine, iodine and several trace elements in soil by polarizing energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, O.S.; Young, S.D.; Bailey, E.; Crout, N.M.J.; Ander, E.L.; Watts, M.J. Iodine soil dynamics and methods of measurement: A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 288–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Okumura, K.; Uruga, T. Speciation of iodine in solid environmental samples by iodine K-edge XANES: Application to soils and ferromanganese oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 363, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Bailey, E.H.; Arshad, M.; Ahmed, S.; Watts, M.J.; Young, S.D. Multiple geochemical factors may cause iodine and selenium deficiency in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4493–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bailey, E.; Sanders, H.; Izquierdo, M.; Crout, N.; Shaw, G.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wei, B.; Young, S. Using chemical fractionation and speciation to describe uptake of technetium, iodine and selenium by Agrostis capillaris and Lolium perenne. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 212, 106131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, O.S.; Young, S.D.; Crout, N.M.J.; Bailey, E.H.; Ander, E.L.; Watts, M.J. Short-term iodine dynamics in soil solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Unno, Y.; Tsukada, H.; Takaku, Y.; Hisamatsu, S. Speciation of iodine in soil solution in fores and grassland soils in Rokkasho, Japan. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2019, 184, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.; Orth, B.; Reiser, R.; Bürge, D.; Lehto, N.J.; Almond, P.; Gaw, S.; Thomson, B.; Lilburne, L.; Robinson, B. Environmental parameters affecting the concentration of iodine in New Zealand pasture. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, F.; Riebe, B.; Scheinost, A.; König, C.; Hölzer, A.; Walther, C. Sorption of iodine in soils: Insight from selective sequential extractions and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23850–23860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, L.; Schulz, K.; Birkel, C.; Biester, H. Iron oxides control sorption and mobilisation of iodine in a tropical rainforest catchment. SOIL Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Fraction | Hou et al. [68] | Hansen et al. [33] | Duborská et al. [34] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water soluble | 13% | 5–7% | 2–7% |
| Exchangeable | 8% | 4–17% | 0–4% |
| Bound to carbonates | 4% | 4–5% | 1–8% |
| Bound to oxides | 31% | 16–18% | 24–85% |
| Bound to humic acids | 39% | 38–40% | 1–39% |
| Bound to fulvic acids | 11–17% | 1–12% | |
| Residual | 7% | not determined | 2–26% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duborská, E.; Matulová, M.; Vaculovič, T.; Matúš, P.; Urík, M. Iodine Fractions in Soil and Their Determination. Forests 2021, 12, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111512
Duborská E, Matulová M, Vaculovič T, Matúš P, Urík M. Iodine Fractions in Soil and Their Determination. Forests. 2021; 12(11):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111512
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuborská, Eva, Michaela Matulová, Tomáš Vaculovič, Peter Matúš, and Martin Urík. 2021. "Iodine Fractions in Soil and Their Determination" Forests 12, no. 11: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111512
APA StyleDuborská, E., Matulová, M., Vaculovič, T., Matúš, P., & Urík, M. (2021). Iodine Fractions in Soil and Their Determination. Forests, 12(11), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111512