Disentangling the Effects of Tree and Soil Properties on the Water Uptake of a Waterlogging Tolerant Tree in the Yangtze River Delta, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
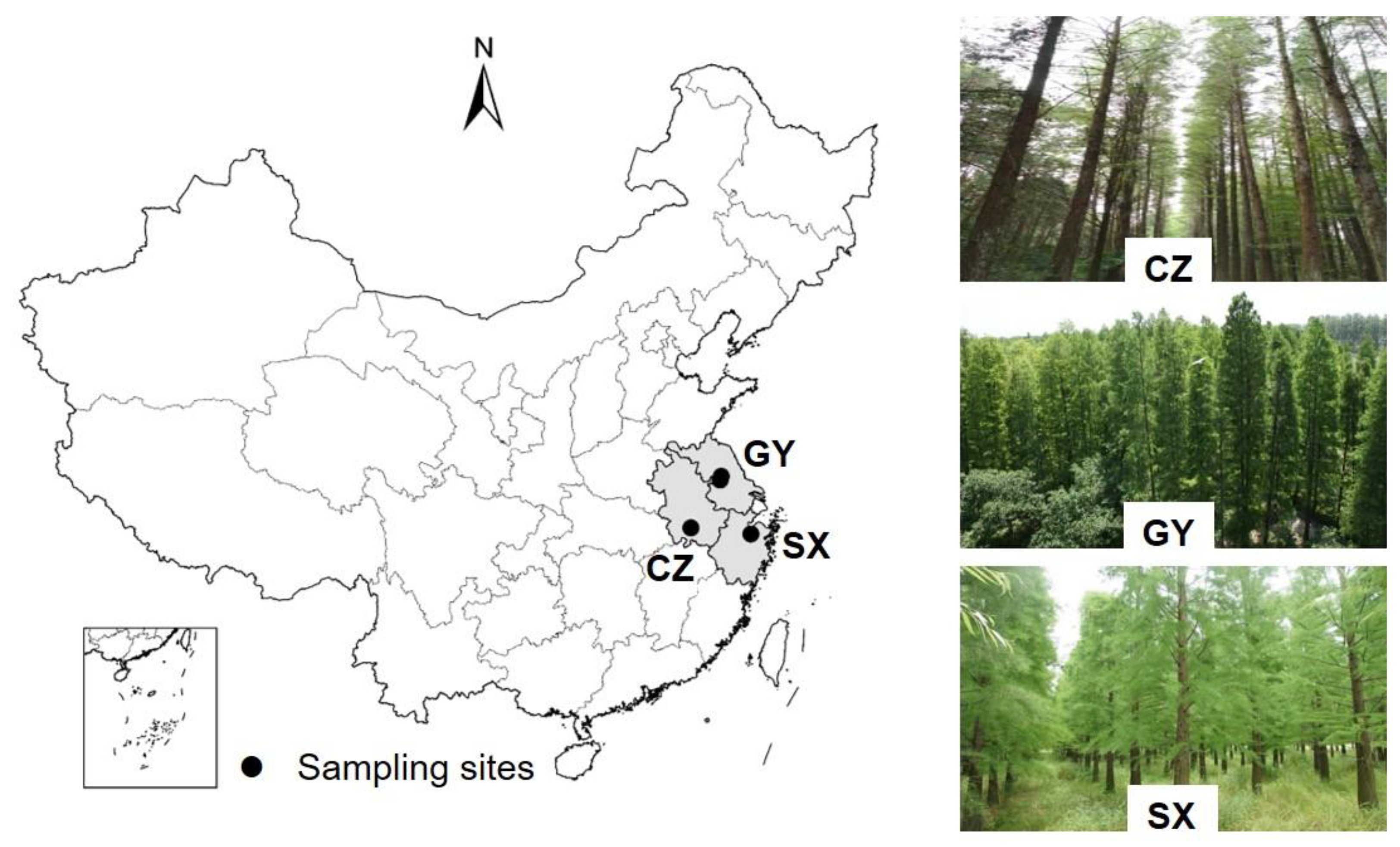
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Determining Water Isotopes and Calculating Water Uptake Pattern of T. distichum
2.4. Determination of Tree Traits and Soil Properties
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
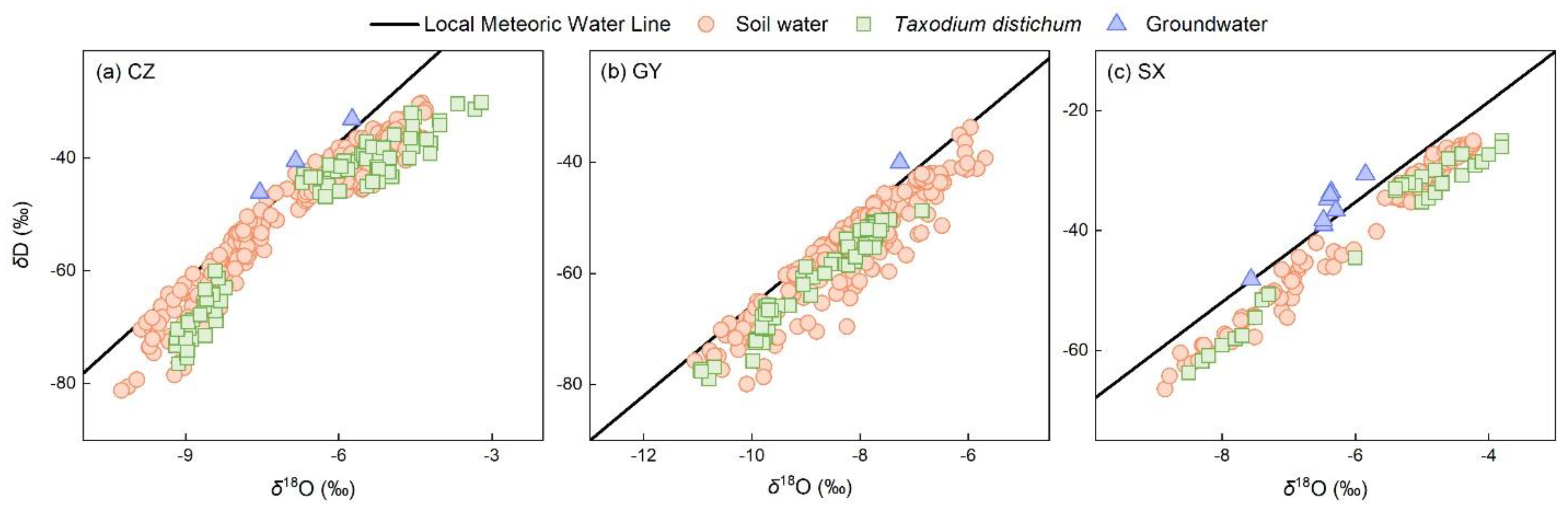
3.1. Characteristics of δD and δ18O in Soil Water, Xylem Water, and Groundwater
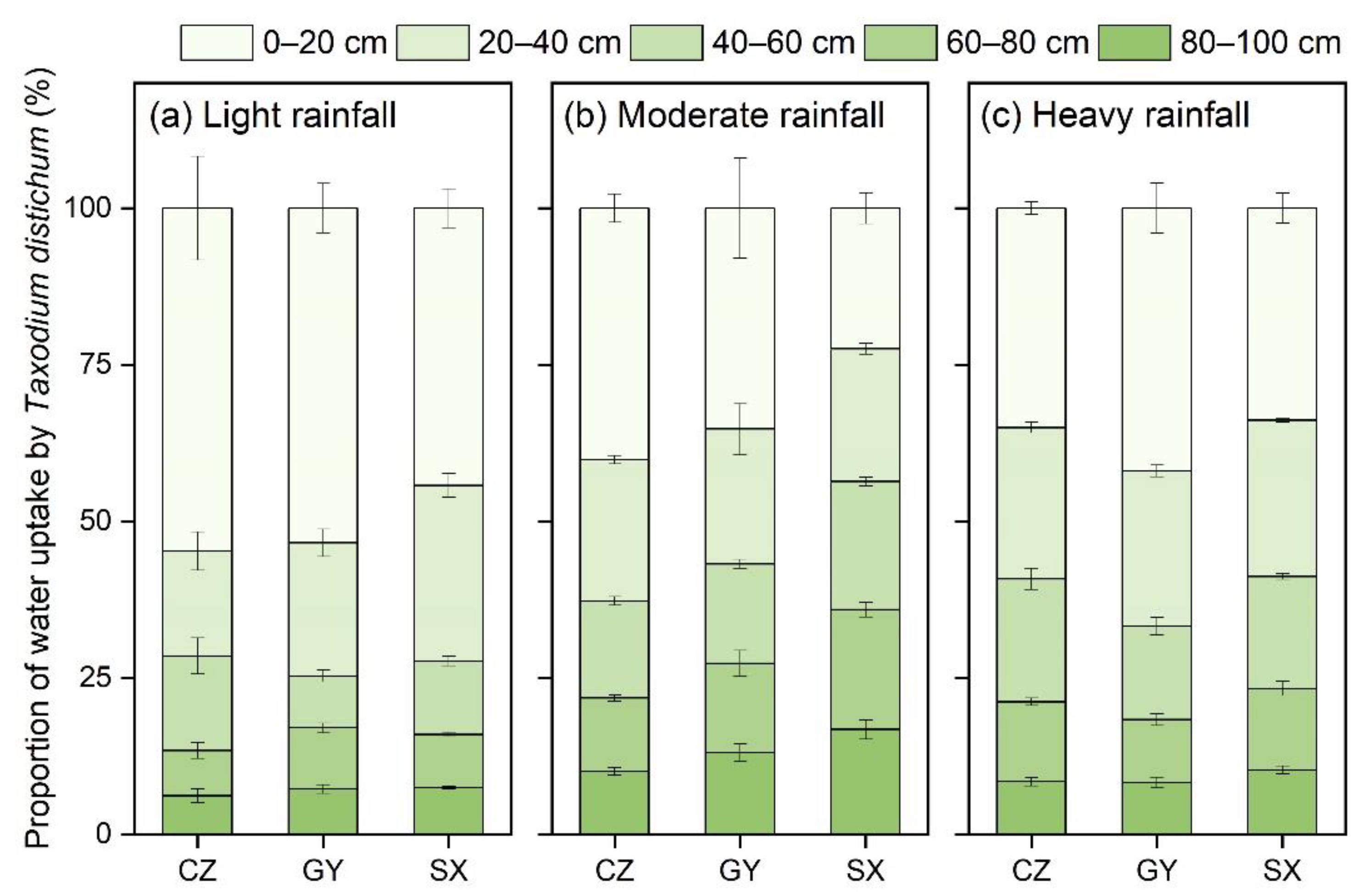
3.2. Water Uptake Patterns of T. distichum under Light, Moderate, and Heavy Rainfalls
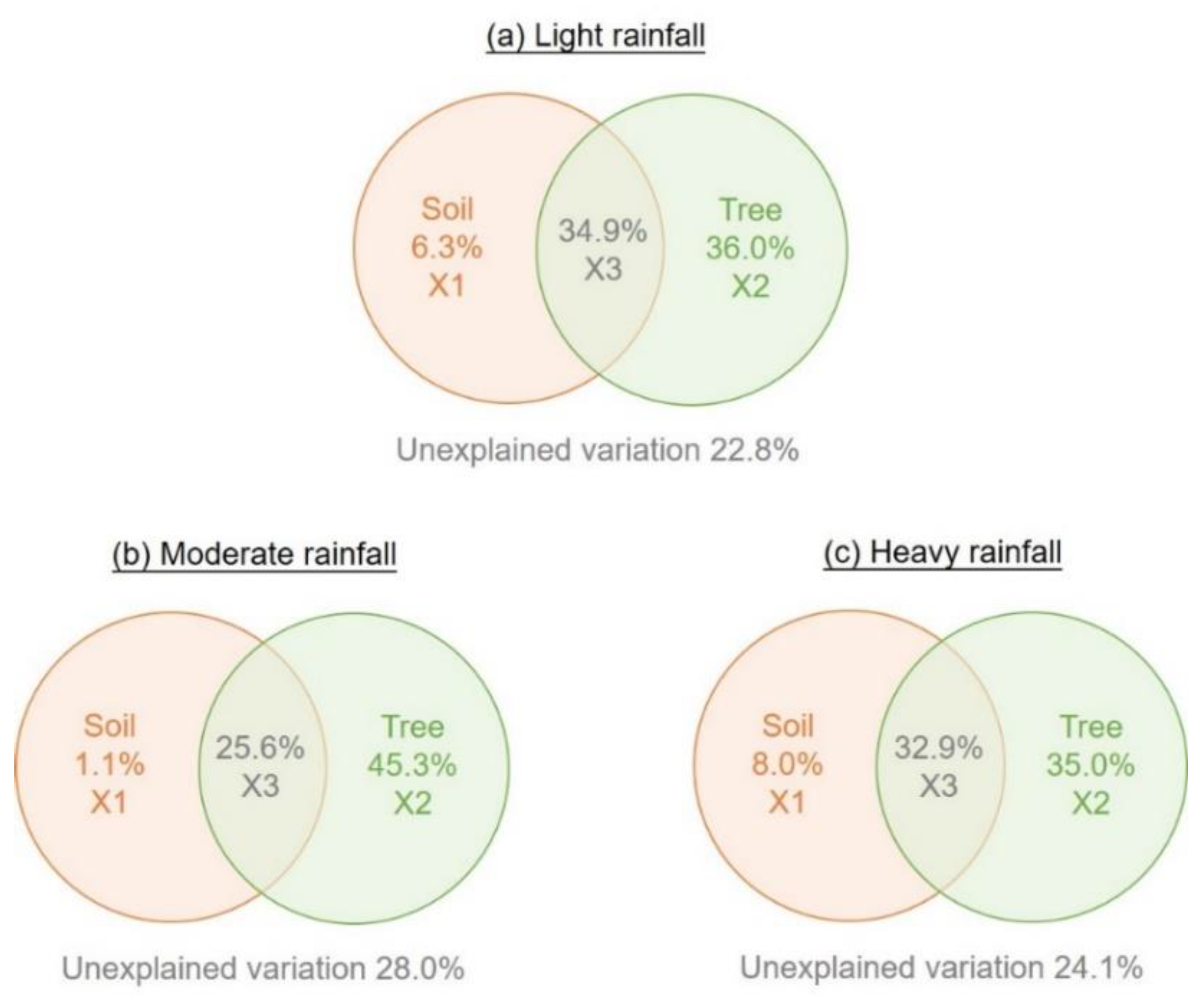
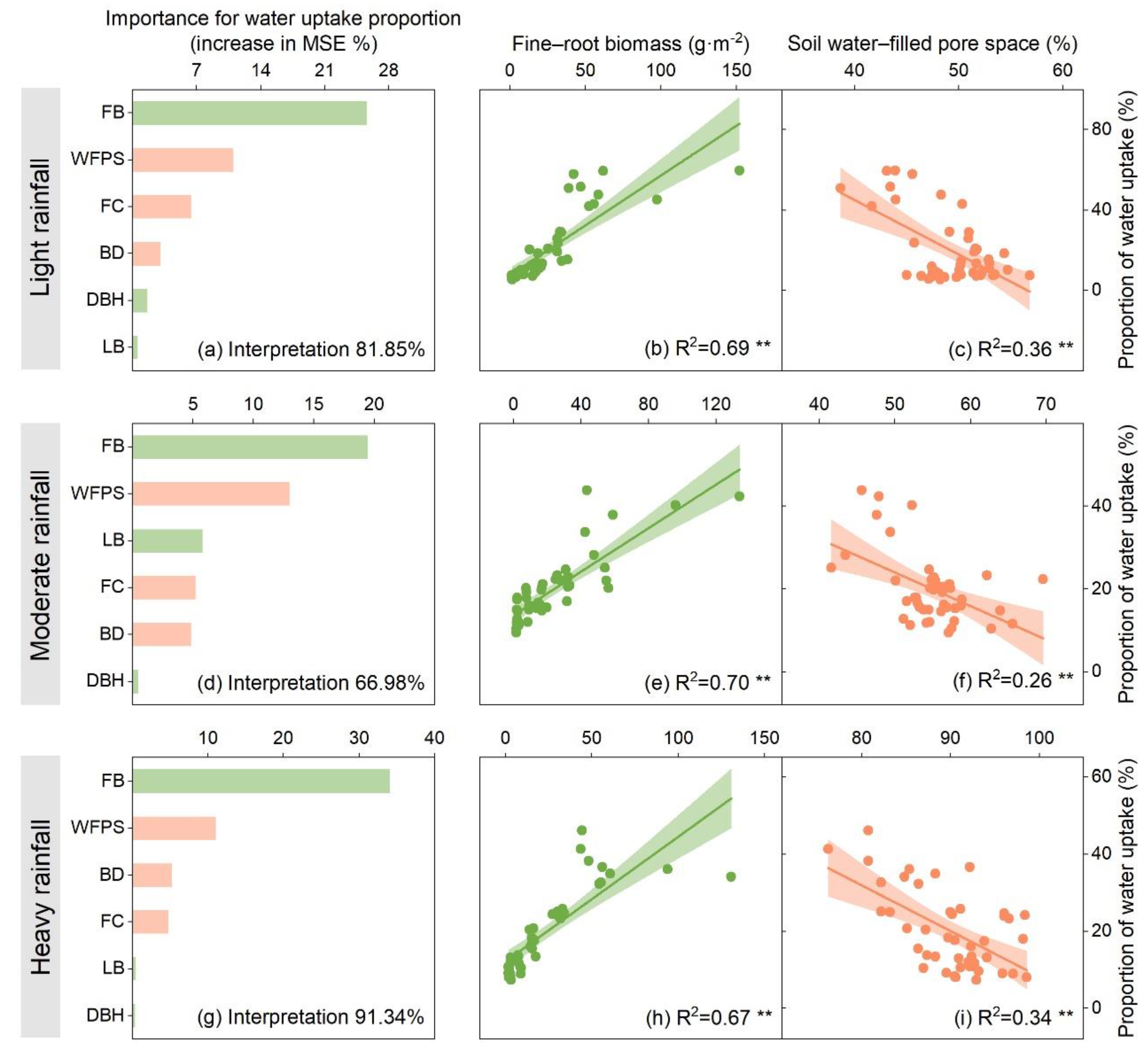
3.3. Dominant Drivers Influencing T. distichum Water Uptake
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Water Was the Dominant Water Source of T. distichum
4.2. Tree Traits Primarily Regulated the Water Uptake of T. distichum
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bao, J.; Sherwood, S.C.; Alexander, L.V.; Evans, J.P. Future increases in extreme precipitation exceed observed scaling rates. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Pendergrass, A.G. What precipitation is extreme? Science 2018, 360, 1072–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, G.Q.; Marino, N.A.C.; MacDonald, A.A.M.; Céréghino, R.; Trzcinski, M.K.; Mercado, D.A.; Leroy, C.; Corbara, B.; Farjalla, V.F.; Barberis, I.M.; et al. Extreme rainfall events alter the trophic structure in bromeliad tanks across the Neotropics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoire, L.P.; Isabelle, L.; Celine, L.; Corinne, S.; Karine, L.; Jean, A.; Jean-Charles, L.; Christophe, P. Implication of the suberin pathway in adaptation to waterlogging and hypertrophied lenticels formation in pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.). Tree Physiol. 2016, 36, tpw056. [Google Scholar]
- Tapani, R.; Timo, D.; Jouni, K.; Sirpa, P.; Raimo, S.; Tarja, L. Dynamics of fine root production and mortality of Scots pine in waterlogged peat soil during the growing season. Can. J. Forest Res. 2020, 50, 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Peng, C.; Harrison, S.; Wei, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, M. Allocation Mechanisms of Non-Structural Carbohydrates of Robinia pseudoacacia L. Seedlings in Response to Drought and Waterlogging. Forests 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar]
- Asaeda, T.; Gomes, P.I.A.; Takeda, E. Spatial and temporal tree colonization in a midstream sediment bar and the mechanisms governing tree mortality during a flood event. River Res. Applic. 2010, 26, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assahira, C.; Piedade, M.T.F.; Trumbore, S.E.; Wittmann, F.; Cintra, B.B.L.; Batista, E.S.; Faria de Resende, A.; Schöngart, J. Tree mortality of a flood-adapted species in response of hydrographic changes caused by an Amazonian river dam. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2017, 396, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Faria de Resende, A.; Schöngart, J.; Streher, A.S.; Ferreira-Ferreira, J.; Piedade, M.T.F.; Silva, T.S.F. Massive tree mortality from flood pulse disturbances in Amazonian floodplain forests: The collateral effects of hydropower production. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.M.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, F.D.; Guan, Z.Y.; Fang, W.M. Morpho-anatomical and physiological responses of two Dendranthema species to waterlogging. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 68, 122–130. [Google Scholar]
- Colón-Rivera, R.J.; Feagin, R.A.; West, J.B.; López, N.B.; Benítez-Joubert, R.J. Hydrological modification, saltwater intrusion, and tree water use of a Pterocarpus officinalis swamp in Puerto Rico. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 147, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.H.; Chambers, J.L.; Krauss, K.W.; Allen, S.T.; Keim, R.F. Hydrologic exchanges and baldcypress water use on deltaic hummocks, Louisiana, USA. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duberstein, J.; Krauss, K.; Baldwin, M.; Allen, S.; Conner, W.; Salter, J.; Miloshis, M. Small gradients in salinity have large effects on stand water use in freshwater wetland forests. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2020, 473, 118308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meißner, M.; Köhler, M.; Schwendenmann, L.; Hölscher, D.; Dyckmans, J. Soil water uptake by trees using water stable isotopes (δ2H and δ18O)-a method test regarding soil moisture, texture and carbonate. Plant Soil 2014, 376, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voltas, J.; Lucabaugh, D.; Chambel, M.R.; Ferrio, J.P. Intraspecific variation in the use of water sources by the circum-Mediterranean conifer Pinus halepensis. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, W.; He, Z.; Yan, J.; Zhang, G. Variation in depth of water uptake for Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica along a precipitation gradient in sandy regions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Dawson, T.E. Water uptake by plants: Perspectives from stable isotope composition. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, M.F.; Nippert, J.B.; Holdo, R.M.; Staver, A.C. Root-niche separation between savanna trees and grasses is greater on sandier soils. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Meng, P.; Zhang, J.S.; Wan, X.C. Variation in soil water uptake and its effect on plant water status in Juglans regia L. during dry and wet seasons. Tree Physiol. 2011, 31, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Sun, G.; Mitra, B.; Noormets, A.; Gavazzi, M.J.; Domec, J.C.; Hallema, D.W.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; King, J.S.; et al. Drought and thinning have limited impacts on evapotranspiration in a managed pine plantation on the southeastern United States coastal plain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 262, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coners, H.; Leuschner, C. In situ measurement of fine-root water absorption in three temperate tree species-temporal variability and control by soil and atmospheric factors. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2005, 6, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Knighton, J.; Evaristo, J.; Wassen, M. Contrasting adaptive strategies by Caragana korshinskii and Salix psammophila in a semiarid revegetated ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 300, 108323. [Google Scholar]
- Pezeshki, S.R. Wetland plant responses to soil flooding. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2001, 46, 299–312. [Google Scholar]
- Dwire, K.A.; Kauffman, J.B.; Baham, J.E. Plant species distribution in relation to water-table depth and soil redox potential in montane riparian meadows. Wetlands 2006, 26, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Lu, N.; Zhang, L. Seasonal variation inwater uptake patterns of three lant species based on stable isotopes in the semi-arid loess plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.B.; Xu, Q.; Gao, D.Q.; Jiang, C.W.; Liu, F.T.; Jiang, J.; Wang, T. Altered water uptake patterns of Populus deltoides in mixed riparian forest stands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Roden, J.; Dawson, T.E. Assessing ecosystem-level water relations through stable isotope ratio analyses. In Methods in Ecosystem Science; Sala, O.E., Jackson, R.B., Mooney, H.A., Howarth, R.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, M.; Gökbulak, F.; Hizal, A. Exclosure effects on recovery of selected soil properties in a mixed broadleaf forest recreation site. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 24, 266–276. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Peng, Y.; Olefeldt, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; et al. Changes in Methane Flux along a Permafrost Thaw Sequence on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Steven, M.H.H.; Wagner, H.; Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 1.15-1. 2008. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, J.R.; Barnard, H.R.; Coulombe, R.; Mcdonnell, J.J. Ecohydrologic separation of water between trees and streams in a Mediterranean climate. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, J.; Jasechko, S.; Mcdonnell, J.J. Global separation of plant transpiration from groundwater and streamflow. Nature 2015, 525, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, G.R.; Muñoz-Villers, L.E.; Holwerda, F.; Mcdonnell, J.J.; Asbjornsen, H.; Dawson, T.E. Stable isotopes reveal linkages among ecohydrological processes in a seasonally dry tropical montane cloud forest. Ecohydrology 2012, 78, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeta, A.; Mejia-Chang, M.; Ogaya, R.; Voltas, J.; Dawson, T.E.; Peñuelas, J. The combined effects of a long-term experimental drought and an extreme drought on the use of plant-water sources in a Mediterranean forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magh, R.K.; Eiferle, C.; Burzlaff, T.; Dannenmann, M.; Rennenberg, H.; Dubbert, M. Competition for water rather than facilitation in mixed beech-fir forests after drying-wetting cycle. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Fu, X. Deep soil water extraction helps to drought avoidance but shallow soil water uptake during dry season controls the inter-annual variation in tree growth in four subtropical plantations. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2017, 234–235, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González de Andrés, E.; Camarero, J.J.; Blanco, J.A.; Imbert, J.B.; Lo, Y.H.; Sangüesa-Barreda, G.; Castillo, F.J. Tree-to-tree competition in mixed european beech-scots pine forests has different impacts on growth and water-use efficiency depending on site conditions. J. Ecol. 2017, 106, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossiord, C.; Sevanto, S.; Dawson, T.E.; Adams, H.D.; Collins, A.D.; Dickman, L.T.; Newman, B.D.; Stockton, E.A.; McDowell, N.G. Warming combined with more extreme precipitation regimes modifies the water sources used by trees. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 584–596. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.B.; Xu, Q.; Gao, D.Q.; Jiang, C.W.; Liu, F.T.; Jiang, J.; Ma, Y.B. Higher soil capacity of intercepting heavy rainfall in mixed stands than in pure stands in riparian forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; He, B.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Sun, W. Identifying water sources used by alpine riparian plants in a restoration zone on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Evidence from stable isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, A.; Miyaura, T.; Torii, H. Relationships of tree height and diameter at breast height revisited: Analyses of stem growth using 20-year data of an even-aged Chamaecyparis obtusa stand. Tree Physiol. 2013, 33, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Feng, Q.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Variations of deep soil moisture under different vegetation types and influencing factors in a watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3309–3323. [Google Scholar]
- Gwak, Y.; Kim, S. Factors affecting soil moisture spatial variability for a humid forest hillslope. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 431–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth, P.Z.; Sternberg, L.S. Seasonal water use by deciduous and evergreen woody species in a scrub community is based on water availability and root distribution. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Site | Rainfall Event Ⅰ | Rainfall Event Ⅱ | Rainfall Event Ⅲ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Precipitation (mm) | Time | Precipitation (mm) | Time | Precipitation (mm) | |
| CZ | 11 July 2018 | 8.7 | 14 December 2017 | 14.5 | 4 September 2018 | 27.0 |
| GY | 27 November 2017 | 9.3 | 8 November 2016 | 19.5 | 8 October 2016 | 29.2 |
| SX | 10 July 2017 | 7.5 | 22 May 2017 | 14.5 | 16 September 2016 | 35.5 |
| Trait | Site | Rainfall Event | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 40–60 cm | 60–80 cm | 80–100 cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB | CZ | Light | 103.7 ± 26.2 b | 28.3 ± 7.8 a | 19.3 ± 1.1 a | 3.7 ± 0.4 a | 1.3 ± 0.2 a |
| Moderate | 96.4 ± 21.7 b | 26.1 ± 0.8 a | 17.5 ± 1.2 a | 3.1 ± 0.2 a | 1.7 ± 0.1 a | ||
| Heavy | 95.0 ± 20.2 b | 30.5 ± 0.6 a | 15.5 ± 0.9 a | 2.9 ± 0.1 a | 1.8 ± 0.1 a | ||
| GY | Light | 42.6 ± 2.3 e | 29.5 ± 2.2 d | 15.9 ± 0.6 c | 8.3 ± 0.7 b | 2.9 ± 0.5 a | |
| Moderate | 44.6 ± 1.6 e | 31.7 ± 0.4 d | 14.2 ± 0.3 c | 9.0 ± 0.3 b | 2.1 ± 0.2 a | ||
| Heavy | 45.3 ± 1.4 e | 30.3 ± 1.7 d | 15.7 ± 0.9 c | 8.7 ± 0.2 b | 2.8 ± 0.1 a | ||
| SX | Light | 55.5 ± 1.7 e | 32.8 ± 0.8 d | 18.0 ± 1.9 c | 8.3 ± 0.3 b | 2.4 ± 0.3 a | |
| Moderate | 55.2 ± 0.6 e | 32.2 ± 0.6 d | 16.9 ± 0.3 c | 7.6 ± 0.1 b | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | ||
| Heavy | 55.2 ± 0.6 e | 32.5 ± 1.1 d | 15.3 ± 0.1c | 7.4 ± 0.1 b | 1.9 ± 0.2 a | ||
| WFPS | CZ | Light | 43.6 ± 0.3 a | 51.6 ± 0.8 b | 53.0 ± 0.8 b | 49.9 ± 0.8 b | 50.7 ± 3.1 b |
| Moderate | 49.2 ± 1.5 a | 62.4 ± 4.1 b | 59.1 ± 2.4 ab | 58.5 ± 3.9 ab | 59.1 ± 1.8 ab | ||
| Heavy | 86.2 ± 1.1 a | 95.0 ± 2.6 c | 87.6 ± 1.6 ab | 92.4 ± 0.9 abc | 92.9 ± 2.9 bc | ||
| GY | Light | 42.5 ± 2.0 a | 49.6 ± 1.9 b | 49.2 ± 1.3 b | 50.7 ± 2.1 b | 49.1 ± 2.2 b | |
| Moderate | 46.1 ± 1.8 a | 53.7 ± 1.1 b | 54.7 ± 1.6 b | 55.9 ± 1.4 b | 53.8 ± 1.5 b | ||
| Heavy | 79.2 ± 1.5 a | 92.5 ± 1.8 b | 90.3 ± 2.0 b | 92.2 ± 2.9 b | 93.1 ± 1.5 b | ||
| SX | Light | 46.8 ± 2.6 a | 50.3 ± 0.6 a | 50.2 ± 1.6 a | 50.8 ± 0.7 a | 50.1 ± 2.6 a | |
| Moderate | 48.8 ± 3.8 a | 55.5 ± 0.5 ab | 56.2 ± 0.6 a | 55.4 ± 1.4 a | 55.2 ± 1.8 a | ||
| Heavy | 86.9 ± 2.9 a | 87.1 ± 4.5 a | 93.9 ± 2.4 ab | 89.5 ± 1.7 b | 92.2 ± 0.6 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Q.; Gao, D.; Zuo, H.; Ren, R. Disentangling the Effects of Tree and Soil Properties on the Water Uptake of a Waterlogging Tolerant Tree in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Forests 2021, 12, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111547
Zhang B, Jiang J, Xu Q, Gao D, Zuo H, Ren R. Disentangling the Effects of Tree and Soil Properties on the Water Uptake of a Waterlogging Tolerant Tree in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Forests. 2021; 12(11):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111547
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Beibei, Jing Jiang, Qing Xu, Deqiang Gao, Haijun Zuo, and Ranran Ren. 2021. "Disentangling the Effects of Tree and Soil Properties on the Water Uptake of a Waterlogging Tolerant Tree in the Yangtze River Delta, China" Forests 12, no. 11: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111547
APA StyleZhang, B., Jiang, J., Xu, Q., Gao, D., Zuo, H., & Ren, R. (2021). Disentangling the Effects of Tree and Soil Properties on the Water Uptake of a Waterlogging Tolerant Tree in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Forests, 12(11), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111547







